Android 14 では、デベロッパー向けに優れた機能と API が導入されました。以下では、アプリの機能を確認し、関連する API を試すことができます。
追加、変更、削除された API の詳細な一覧については、API 差分レポートをご覧ください。追加された API について詳しくは、Android API リファレンスをご覧ください。Android 14 の場合は、API レベル 34 で追加された API をご確認ください。プラットフォームの変更がアプリに影響する可能性がある領域については、Android 14 の動作変更(Android 14 をターゲットとするアプリの場合とすべてのアプリの場合)をご確認ください。
多言語対応
アプリ別の言語設定
Android 14 expands on the per-app language features that were introduced in Android 13 (API level 33) with these additional capabilities:
Automatically generate an app's
localeConfig: Starting with Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 and AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, you can configure your app to support per-app language preferences automatically. Based on your project resources, the Android Gradle plugin generates theLocaleConfigfile and adds a reference to it in the final manifest file, so you no longer have to create or update the file manually. AGP uses the resources in theresfolders of your app modules and any library module dependencies to determine the locales to include in theLocaleConfigfile.Dynamic updates for an app's
localeConfig: Use thesetOverrideLocaleConfig()andgetOverrideLocaleConfig()methods inLocaleManagerto dynamically update your app's list of supported languages in the device's system settings. Use this flexibility to customize the list of supported languages per region, run A/B experiments, or provide an updated list of locales if your app utilizes server-side pushes for localization.App language visibility for input method editors (IMEs): IMEs can utilize the
getApplicationLocales()method to check the language of the current app and match the IME language to that language.
Grammatical Inflection API
30 億人もの人々が、性別で文法が変わる言語を話します。こうした言語では、話す相手、または言及する人や物の性別に応じて、各文法範疇(名詞、動詞、形容詞、前置詞など)の語形が変化します。伝統的に、性別で文法が変わる多くの言語では、男性形をデフォルトまたは汎用の性別として使用しています。
女性を男性形で呼ぶなど、ユーザーに対して不適切な文法的性を使用すると、そのユーザーのパフォーマンスと態度に悪影響を及ぼす可能性があります。一方、ユーザーの文法的性を適切に反映した言語を使用して UI を作成すると、ユーザー エンゲージメントが向上し、より自然でパーソナライズされたユーザー エクスペリエンスを提供できます。
Android 14 では、性別で文法が変わる言語に合わせてユーザー中心の UI を構築するため、アプリをリファクタリングせずに文法上の性別への対応を追加できる Grammatical Inflection API が導入されています。
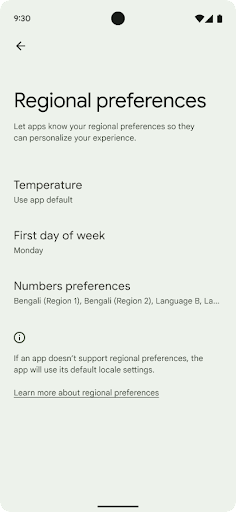
地域の設定
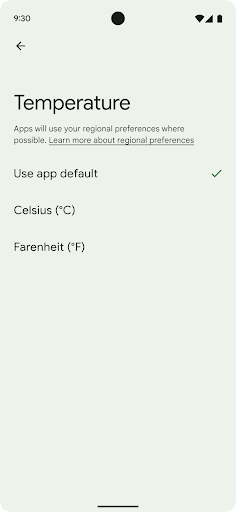
地域の設定を使用すると、ユーザーは温度単位、週の最初の曜日、番号体系をカスタマイズできます。米国に住んでいる欧州のユーザーの場合、温度の単位は華氏ではなく摂氏で表示し、アプリで週の始まりを米国のデフォルトの日曜日ではなく月曜日に指定することを好む可能性があります。
Android の新しい設定メニューは見つけやすく、ユーザーはここでアプリのそうした設定を一元的に変更できます。これらの設定は、バックアップや復元を行った場合も保持されます。複数の API とインテント(getTemperatureUnit や getFirstDayOfWeek など)により、アプリにそうしたユーザー設定への読み取りアクセス権を付与することで、アプリでの情報の表示方法を調整できます。また、ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED に BroadcastReceiver を登録して、地域の設定が変更されたときに言語 / 地域の構成の変更を処理することも可能です。
これらの設定を確認するには、設定アプリを開いて [システム] > [言語と入力] > [地域の設定] に移動します。
ユーザー補助
非線形フォント スケーリングを 200% にする
Android 14 以降では、フォント スケーリングが 200% までサポートされます。これにより、ロービジョンのユーザーは、Web Content Accessibility Guidelines(WCAG)に準拠した追加のユーザー補助オプションを利用できます。
画面上の大きいテキスト要素が拡大しすぎないように、システムでは非線形のスケーリング曲線が適用されます。このスケーリング戦略では、大きいテキストが小さいテキストとは異なる率でスケーリングされます。非線形フォント スケーリングにより、さまざまなサイズの要素間の比例階層を維持しながら、線形テキスト スケーリングの高度な問題(テキストが途切れる、表示サイズが大きすぎて文字が読みづらくなるなど)を軽減できます。
非線形フォント スケーリングでアプリをテストする
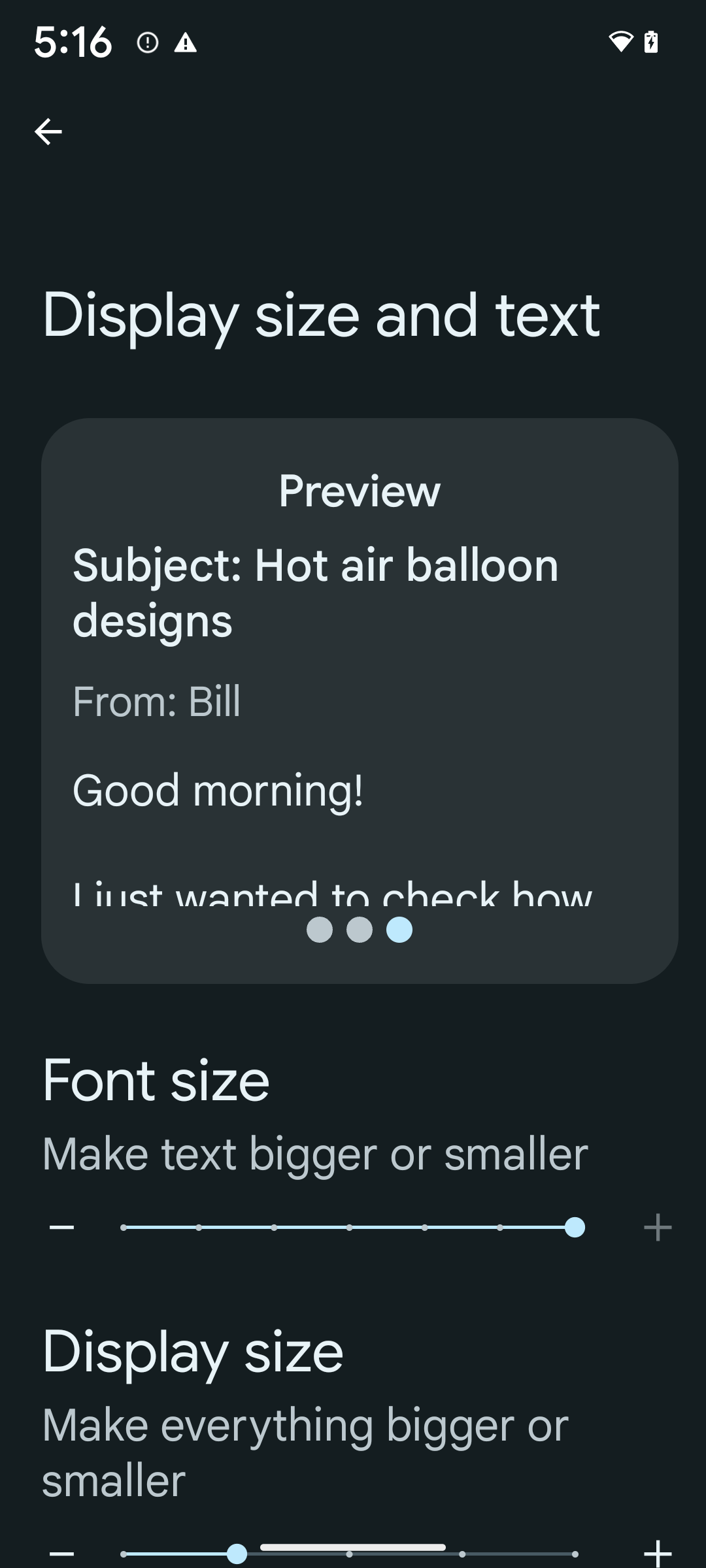
すでにスケール非依存ピクセル(sp)単位を使用してテキストのサイズを定義している場合は、これらの追加オプションとスケーリングの改善がアプリ内のテキストに自動的に適用されます。ただし、最大フォントサイズを有効にして(200%)、UI テストを実施し、アプリがフォントサイズを正しく適用し、ユーザビリティに影響を与えることなく大きなフォントサイズに対応できることを確認する必要があります。
200% のフォントサイズを有効にする手順は次のとおりです。
- 設定アプリを開き、[ユーザー補助] > [表示サイズとテキスト] に移動します。
- [フォントサイズ] オプションでは、最大フォントサイズの設定が有効になるまで、プラス(+)アイコンをタップします(このセクションに表示される画像で確認できます)。
テキストサイズにはスケール非依存ピクセル(sp)単位を使用する
テキストサイズは必ず sp 単位で指定してください。日時 アプリが sp 単位を使用している場合、Android はユーザーが指定したテキストサイズと 適切にスケーリングする必要があります。
パディングに sp 単位を使用したり、暗黙的なパディングを前提としてビューの高さを定義したりしないでください。 非線形フォント スケーリングの場合、sp の寸法は比例しない場合があるため、4sp + 20sp と 24sp は異なる場合があります。
スケール非依存ピクセル(sp)単位を変換する
sp 単位からピクセルに変換するには TypedValue.applyDimension() を、ピクセルを sp に変換するには TypedValue.deriveDimension() を使用します。これらのメソッドでは、適切な非線形スケーリング曲線が自動的に適用されます。
Configuration.fontScale または DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity を使用して方程式をハードコードしないでください。フォントのスケーリングが非線形であるため、scaledDensity フィールドは正確ではありません。fontScale
フォントは廃止されたため、情報提供のみを目的として使用してください。
単一のスカラー値でスケーリングされます。
lineHeight には sp 単位を使用する
行の高さがテキストに合わせてスケーリングされるように、android:lineHeight は常に dp ではなく sp 単位で定義してください。テキスト メッセージに
sp は sp ですが、lineHeight は dp または px で表示されます。拡大縮小されず、表示がきれいに見えます。
TextView は、textSize と lineHeight の両方が sp 単位で定義されている場合にのみ、意図した比率が維持されるように lineHeight を自動的に修正します。
カメラとメディア
画像のウルトラ HDR

Android 14 adds support for High Dynamic Range (HDR) images that retain more of the information from the sensor when taking a photo, which enables vibrant colors and greater contrast. Android uses the Ultra HDR format, which is fully backward compatible with JPEG images, allowing apps to seamlessly interoperate with HDR images, displaying them in Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) as needed.
Rendering these images in the UI in HDR is done automatically by the framework
when your app opts in to using HDR UI for its Activity Window, either through a
manifest entry or at runtime by calling
Window.setColorMode(). You can also capture compressed Ultra
HDR still images on supported devices. With more colors recovered
from the sensor, editing in post can be more flexible. The
Gainmap associated with Ultra HDR images can be used to render
them using OpenGL or Vulkan.
カメラ拡張機能のズーム、フォーカス、ポストビューなど
Android 14 upgrades and improves camera extensions, allowing apps to handle longer processing times, which enables improved images using compute-intensive algorithms like low-light photography on supported devices. These features give users an even more robust experience when using camera extension capabilities. Examples of these improvements include:
- Dynamic still capture processing latency estimation provides much more
accurate still capture latency estimates based on the current scene and
environment conditions. Call
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()to get aStillCaptureLatencyobject that has two latency estimation methods. ThegetCaptureLatency()method returns the estimated latency betweenonCaptureStartedandonCaptureProcessStarted(), and thegetProcessingLatency()method returns the estimated latency betweenonCaptureProcessStarted()and the final processed frame being available. - Support for capture progress callbacks so that apps can display the current
progress of long-running, still-capture processing operations. You can check
if this feature is available with
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable, and if it is, you implement theonCaptureProcessProgressed()callback, which has the progress (from 0 to 100) passed in as a parameter. Extension specific metadata, such as
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHfor dialing in the amount of an extension effect, such as the amount of background blur withEXTENSION_BOKEH.Postview Feature for Still Capture in camera extensions, which provides a less-processed image more quickly than the final image. If an extension has increased processing latency, a postview image could be provided as a placeholder to improve UX and switched out later for the final image. You can check if this feature is available with
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. Then you can pass anOutputConfigurationtoExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Support for
SurfaceViewallowing for a more optimized and power-efficient preview render path.Support for tap to focus and zoom during extension usage.
センサー内ズーム
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
ロスレス USB オーディオ
Android 14 gains support for lossless audio formats for audiophile-level
experiences over USB wired headsets. You can query a USB device for its
preferred mixer attributes, register a listener for changes in preferred mixer
attributes, and configure mixer attributes using the
AudioMixerAttributes class. This class represents the
format, such as channel mask, sample rate, and behavior of the audio mixer. The
class allows for audio to be sent directly, without mixing,
volume adjustment, or processing effects.
デベロッパーの生産性とツール
認証情報マネージャー
Android 14 では、プラットフォーム API として 認証情報マネージャーが追加され、Google Play 開発者サービスを使用する Jetpack ライブラリを介して Android 4.4(API レベル 19)デバイスまでサポートが拡張されています。認証情報マネージャーは、ユーザーが構成した認証情報プロバイダを使用して認証情報を取得して保存する API を使用して、ユーザーのログインを容易にすることを目的としています。認証情報マネージャーは、ユーザー名とパスワード、パスキー、フェデレーション ログイン ソリューション(Google でログインなど)といった複数のログイン方法を単一の API でサポートしています。
パスキーには多くのメリットがあります。たとえば、パスキーは業界標準に基づいて構築されており、さまざまなオペレーティング システムやブラウザのエコシステムで動作し、ウェブサイトとアプリの両方で使用できます。
詳細については、認証情報マネージャーとパスキーのドキュメントと、認証情報マネージャーとパスキーに関するブログ投稿をご覧ください。
ヘルスコネクト
Health Connect is an on-device repository for user health and fitness data. It allows users to share data between their favorite apps, with a single place to control what data they want to share with these apps.
On devices running Android versions prior to Android 14, Health Connect is available to download as an app on the Google Play store. Starting with Android 14, Health Connect is part of the platform and receives updates through Google Play system updates without requiring a separate download. With this, Health Connect can be updated frequently, and your apps can rely on Health Connect being available on devices running Android 14 or higher. Users can access Health Connect from the Settings in their device, with privacy controls integrated into the system settings.
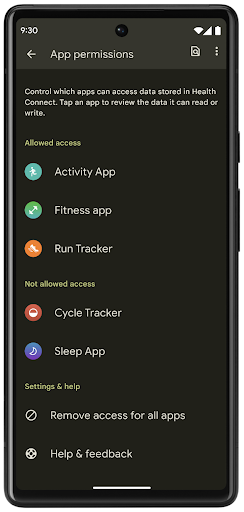
Health Connect includes several new features in Android 14, such as exercise routes, allowing users to share a route of their workout which can be visualized on a map. A route is defined as a list of locations saved within a window of time, and your app can insert routes into exercise sessions, tying them together. To ensure that users have complete control over this sensitive data, users must allow sharing individual routes with other apps.
For more information, see the Health Connection documentation and the blogpost on What's new in Android Health.
OpenJDK 17 の更新
Android 14 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases, including both library updates and Java 17 language support for app and platform developers.
The following features and improvements are included:
- Updated approximately 300
java.baseclasses to Java 17 support. - Text Blocks, which introduce multi-line string literals to the Java programming language.
- Pattern Matching for instanceof, which allows an object to
be treated as having a specific type in an
instanceofwithout any additional variables. - Sealed classes, which allow you restrict which classes and interfaces can extend or implement them.
Thanks to Google Play system updates (Project Mainline), over 600 million devices are enabled to receive the latest Android Runtime (ART) updates that include these changes. This is part of our commitment to give apps a more consistent, secure environment across devices, and to deliver new features and capabilities to users independent of platform releases.
Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
アプリストアの改善
Android 14 introduces several PackageInstaller APIs that
allow app stores to improve their user experience.
Request install approval before downloading
Installing or updating an app might require user approval.
For example, when an installer making use of the
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES permission attempts to install a
new app. In prior Android versions, app stores can only request user approval
after APKs are written to the install session and the
session is committed.
Starting with Android 14, the requestUserPreapproval()
method lets installers request user approval before committing the install
session. This improvement lets an app store defer downloading any APKs until
after the installation has been approved by the user. Furthermore, once a user
has approved installation, the app store can download and install the app in the
background without interrupting the user.
Claim responsibility for future updates
The setRequestUpdateOwnership() method allows an installer
to indicate to the system that it intends to be responsible for future updates
to an app it is installing. This capability enables update ownership
enforcement, meaning that only the update owner is permitted
to install automatic updates to the app. Update ownership enforcement helps to
ensure that users receive updates only from the expected app store.
Any other installer, including those making use of the
INSTALL_PACKAGES permission, must receive explicit user
approval in order to install an update. If a user decides to proceed with an
update from another source, update ownership is lost.
Update apps at less-disruptive times
App stores typically want to avoid updating an app that is actively in use because this leads to the app's running processes being killed, which potentially interrupts what the user was doing.
Starting with Android 14, the InstallConstraints API
gives installers a way to ensure that their app updates happen at an opportune
moment. For example, an app store can call the
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() method to
make sure that an update is only committed when the user is no longer
interacting with the app in question.
Seamlessly install optional splits
With split APKs, features of an app can be delivered in separate APK files,
rather than as a monolithic APK. Split APKs allow app stores to optimize the
delivery of different app components. For example, app stores might optimize
based on the properties of the target device. The
PackageInstaller API has supported splits since its
introduction in API level 22.
In Android 14, the setDontKillApp() method allows an
installer to indicate that the app's running processes shouldn't be killed when
new splits are installed. App stores can use this feature to seamlessly install
new features of an app while the user is using the app.
アプリのメタデータ バンドル
Android 14 以降では、Android パッケージ インストーラを使用して、Google Play などのアプリストア ページにデータ セーフティ方針などのアプリのメタデータを指定できます。
ユーザーがデバイスのスクリーンショットを撮影したときに検出する
To create a more standardized experience for detecting screenshots, Android 14 introduces a privacy-preserving screenshot detection API. This API lets apps register callbacks on a per-activity basis. These callbacks are invoked, and the user is notified, when the user takes a screenshot while that activity is visible.
ユーザー エクスペリエンス
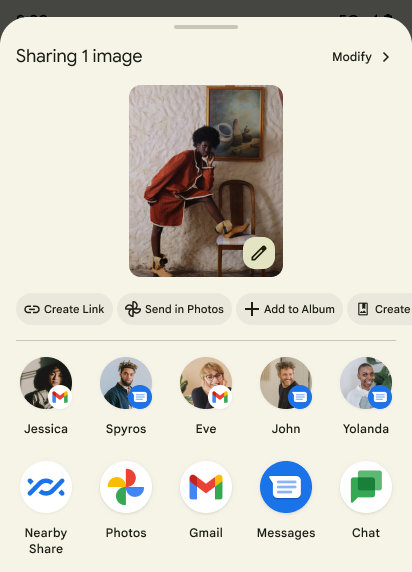
共有シートのカスタム アクションとランキングの改善
Android 14 では、システム共有シートが更新され、カスタムのアプリ アクションと有益なプレビュー結果をユーザーに提供できるようになりました。
カスタム アクションを追加する
Android 14 では、アプリで呼び出すシステム共有シートにカスタム アクションを追加できます。
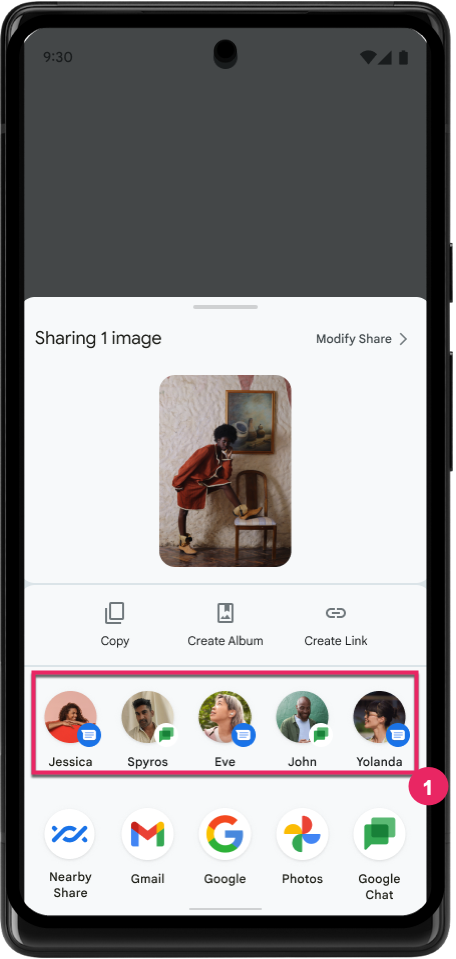
直接共有ターゲットのランキングを改善する
Android 14 では、アプリからの多数のシグナルを使用して、直接共有ターゲットのランキングを決定し、より有用な結果をユーザーに提供しています。ランキングに最も有用なシグナルを提供するには、直接共有ターゲットのランキングを改善するためのガイダンスに沿って対応してください。通信アプリは、送受信メッセージのショートカットの使用状況を報告することもできます。
予測型「戻る」の組み込みアニメーションとカスタム アニメーションのサポート
Android 13 introduced the predictive back-to-home animation behind a developer option. When used in a supported app with the developer option enabled, swiping back shows an animation indicating that the back gesture exits the app back to the home screen.
Android 14 includes multiple improvements and new guidance for Predictive Back:
- You can set
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueto opt in to predictive back system animations per-Activity instead of for the entire app. - We've added new system animations to accompany the back-to-home animation from Android 13. The new system animations are cross-activity and cross-task, which you get automatically after migrating to Predictive Back.
- We've added new Material Component animations for Bottom sheets, Side sheets, and Search.
- We've created design guidance for creating custom in-app animations and transitions.
- We've added new APIs to support custom in-app transition animations:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Use
overrideActivityTransitioninstead ofoverridePendingTransitionfor transitions that respond as the user swipes back.
With this Android 14 preview release, all features of Predictive Back remain behind a developer option. See the developer guide to migrate your app to predictive back, as well as the developer guide to creating custom in-app transitions.
大画面デバイスのメーカーによるアプリごとのオーバーライド
Per-app overrides enable device manufacturers to change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the FORCE_RESIZE_APP override instructs the system to resize the app to fit display dimensions (avoiding size compatibility mode) even if resizeableActivity="false" is set in the app manifest.
Overrides are intended to improve the user experience on large screens.
New manifest properties enable you to disable some device manufacturer overrides for your app.
大画面ユーザーのアプリごとのオーバーライド
アプリごとのオーバーライドを使用すると、大画面デバイスでのアプリの動作を変更できます。たとえば、デバイス メーカーのオーバーライド OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE は、アプリの構成に関係なく、アプリのアスペクト比を 16:9 に設定します。
Android 14 QPR1 では、大画面デバイスの新しい設定メニューを使用して、アプリごとのオーバーライドを適用できるようになりました。
アプリの画面共有
アプリ画面共有を使用すると、画面コンテンツの録画中にデバイスの画面全体ではなく、アプリ ウィンドウを共有できます。
アプリの画面共有では、ステータスバー、ナビゲーション バー、通知などのシステム UI 要素は共有ディスプレイから除外されます。選択したアプリのコンテンツのみが共有されます。
アプリの画面共有では、ユーザーが複数のアプリを実行しながら、コンテンツの共有を 1 つのアプリに制限できるため、生産性とプライバシーが向上します。
Google Pixel 8 Pro の Gboard で LLM を活用したスマート リプライを使用する
On Pixel 8 Pro devices with the December Feature Drop, developers can try out higher-quality smart replies in Gboard powered by on-device Large Language Models (LLMs) running on Google Tensor.
This feature is available as a limited preview for US English in WhatsApp, Line, and KakaoTalk. It requires using a Pixel 8 Pro device with Gboard as your keyboard.
To try it out, first enable the feature in Settings > Developer Options > AiCore Settings > Enable Aicore Persistent.
Next, open a conversation in a supported app to see LLM-powered Smart Reply in Gboard's suggestion strip in response to incoming messages.
グラフィック
パスのクエリと補間に対応
Android's Path API is a powerful and flexible mechanism for
creating and rendering vector graphics, with the ability to stroke or fill a
path, construct a path from line segments or quadratic or cubic curves, perform
boolean operations to get even more complex shapes, or all of these
simultaneously. One limitation is the ability to find out what is actually in a
Path object; the internals of the object are opaque to callers after creation.
To create a Path, you call methods such as
moveTo(), lineTo(), and
cubicTo() to add path segments. But there has been no way to
ask that path what the segments are, so you must retain that information at
creation time.
Starting in Android 14, you can query paths to find out what's inside of them.
First, you need to get a PathIterator object using the
Path.getPathIterator API:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Next, you can call PathIterator to iterate through the segments
one by one, retrieving all of the necessary data for each segment. This example
uses PathIterator.Segment objects, which packages up the data
for you:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator also has a non-allocating version of next() where you can pass
in a buffer to hold the point data.
One of the important use cases of querying Path data is interpolation. For
example, you might want to animate (or morph) between two different paths. To
further simplify that use case, Android 14 also includes the
interpolate() method on Path. Assuming the two paths have
the same internal structure, the interpolate() method creates a new Path
with that interpolated result. This example returns a path whose shape is
halfway (a linear interpolation of .5) between path and otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
The Jetpack graphics-path library enables similar APIs for earlier versions of Android as well.
頂点シェーダーとフラグメント シェーダーを使用したカスタム メッシュ
Android では長い間、カスタム シェーディングによる三角形メッシュの描画をサポートしてきましたが、入力メッシュ形式は、事前定義された属性の組み合わせに限定されていました。Android 14 では、カスタムメッシュのサポートが追加されました。これは、三角形または三角形ストリップとして定義でき、必要に応じてインデックスを付けることができます。これらのメッシュは、カスタム属性、頂点ストライド、変化、AGSL で記述された頂点シェーダーとフラグメント シェーダーで指定されます。
頂点シェーダーは位置や色などの変化を定義しますが、フラグメント シェーダーは、通常は頂点シェーダーによって作成された変化を使用して、ピクセルの色を定義することもできます。フラグメント シェーダーによって色が指定されている場合は、メッシュの描画時に選択されたブレンドモードを使用して、現在の Paint 色とブレンドされます。ユニフォームをフラグメント シェーダーと頂点シェーダーに渡して柔軟性を高めることができます。
Canvas のハードウェア バッファ レンダラ
Android の Canvas API を使った描画をサポートする
HardwareBuffer へのハードウェア アクセラレーション(Android 14)
HardwareBufferRenderer が導入されました。この API は、低レイテンシの描画のために SurfaceControl を介してシステム コンポーザとの通信が必要なユースケースに特に便利です。

