Android 14 כולל תכונות וממשקי API מצוינים למפתחים. המאמרים הבאים יעזרו לכם להבין את התכונות של האפליקציות ולהתחיל להשתמש בממשקי ה-API שקשורים אליהן.
רשימה מפורטת של ממשקי API שנוספו, שונו או הוסרו מופיעה בדוח ההבדלים בין ממשקי ה-API. פרטים על ממשקי API שנוספו זמינים בהפניה ל-Android API. ב-Android 14, אפשר לחפש ממשקי API שנוספו ברמת API 34. כדי לקבל מידע על תחומים שבהם שינויים בפלטפורמה עשויים להשפיע על האפליקציות שלכם, כדאי לעיין בשינויים בהתנהגות ב-Android 14 באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 14 ובכל האפליקציות.
אינטרנציונליזציה
העדפות שפה לכל אפליקציה
Android 14 expands on the per-app language features that were introduced in Android 13 (API level 33) with these additional capabilities:
Automatically generate an app's
localeConfig: Starting with Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 and AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, you can configure your app to support per-app language preferences automatically. Based on your project resources, the Android Gradle plugin generates theLocaleConfigfile and adds a reference to it in the final manifest file, so you no longer have to create or update the file manually. AGP uses the resources in theresfolders of your app modules and any library module dependencies to determine the locales to include in theLocaleConfigfile.Dynamic updates for an app's
localeConfig: Use thesetOverrideLocaleConfig()andgetOverrideLocaleConfig()methods inLocaleManagerto dynamically update your app's list of supported languages in the device's system settings. Use this flexibility to customize the list of supported languages per region, run A/B experiments, or provide an updated list of locales if your app utilizes server-side pushes for localization.App language visibility for input method editors (IMEs): IMEs can utilize the
getApplicationLocales()method to check the language of the current app and match the IME language to that language.
Grammatical Inflection API
3 billion people speak gendered languages: languages where grammatical categories—such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and prepositions—inflect according to the gender of people and objects you talk to or about. Traditionally, many gendered languages use masculine grammatical gender as the default or generic gender.
Addressing users in the wrong grammatical gender, such as addressing women in masculine grammatical gender, can negatively impact their performance and attitude. In contrast, a UI with language that correctly reflects the user's grammatical gender can improve user engagement and provide a more personalized and natural-sounding user experience.
To help you build a user-centric UI for gendered languages, Android 14 introduces the Grammatical Inflection API, which lets you add support for grammatical gender without refactoring your app.
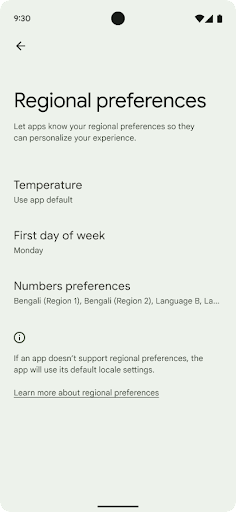
העדפות הפורמט והמידות
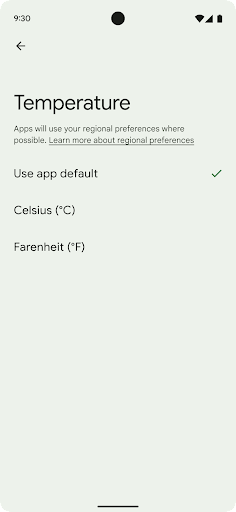
Regional preferences enable users to personalize temperature units, the first day of the week, and numbering systems. A European living in the United States might prefer temperature units to be in Celsius rather than Fahrenheit and for apps to treat Monday as the beginning of the week instead of the US default of Sunday.
New Android Settings menus for these preferences provide users with a
discoverable and centralized location to change app preferences. These
preferences also persist through backup and restore. Several APIs and
intents—such as
getTemperatureUnit
and
getFirstDayOfWeek—
grant your app read access to user preferences, so your app can adjust how it
displays information. You can also register a
BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
to handle locale configuration changes when regional preferences change.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & input > Regional preferences.
נגישות
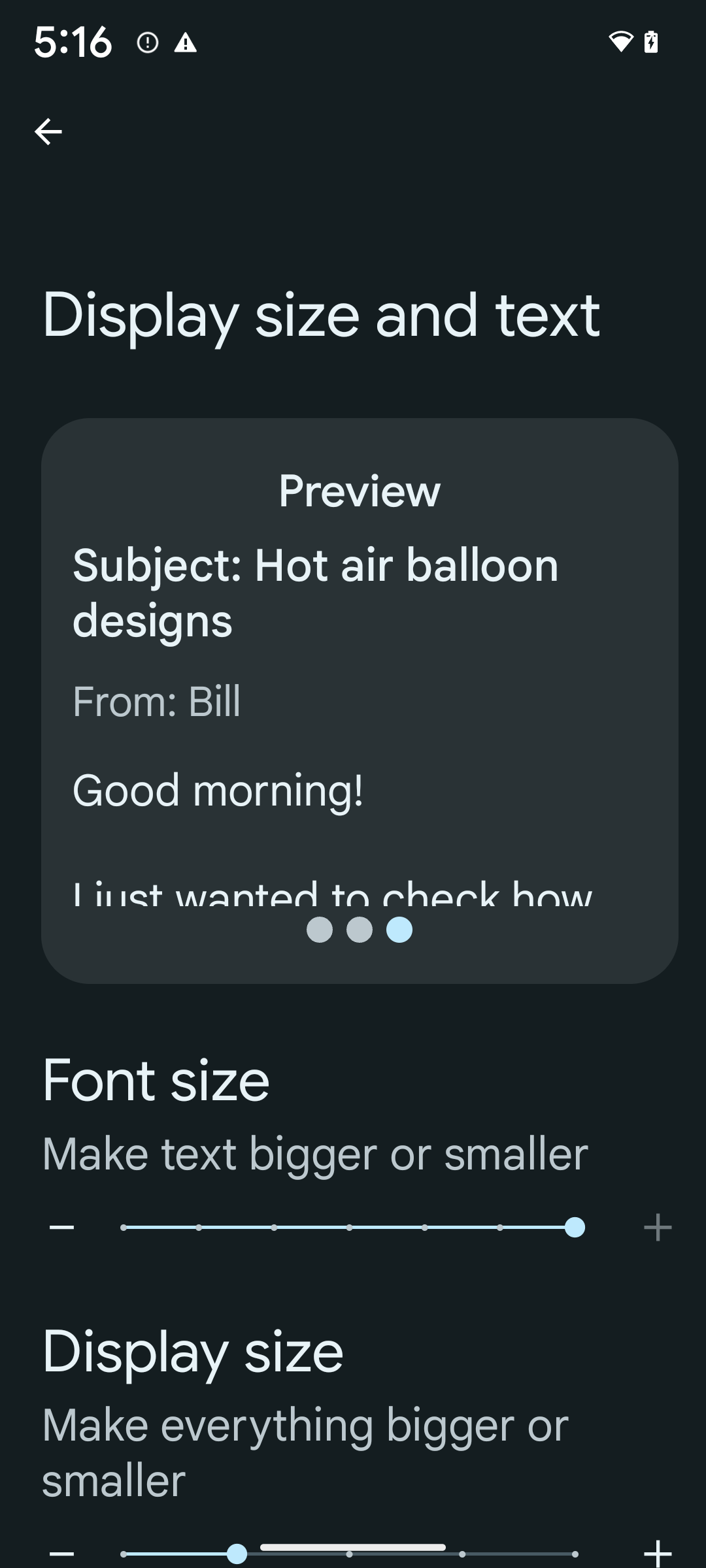
הגדלת הגופן עד 200% באופן לא לינארי
החל מגרסה 14 של Android, המערכת תומכת בהגדלת גופן עד 200%, ומספקת למשתמשים עם לקות ראייה אפשרויות נוספות של נגישות בהתאם להנחיות הנגישות לתוכן אינטרנט (WCAG).
כדי למנוע הגדלה גדולה מדי של אלמנטים גדולים של טקסט במסך, המערכת מחילה עקומת שינוי לא לינארית. באמצעות אסטרטגיה זו של הגדלה באחוזים לא משתנה באותו קצב של טקסט קטן. שינוי גודל גופנים לא לינארי עוזר לשמר את ההיררכיה הפרופורציונלית בין רכיבים בגדלים שונים, צמצום בעיות עם שינוי גודל טקסט ליניארי במעלות גבוהות (למשל נחתך או טקסט שקשה יותר לקרוא עקב תצוגה גדולה מאוד גדלים).
בדיקת האפליקציה עם שינוי גודל גופן לא לינארי
אם אתם כבר משתמשים ביחידות פיקסלים (sp) מותאמות כדי להגדיר את גודל הטקסט, אפשרויות נוספות ושיפורים בהתאמה לעומס (scaling) מיושמים באופן אוטומטי טקסט באפליקציה. עם זאת, עדיין צריך לבצע בדיקת ממשק משתמש עם גודל הגופן הופעל (200%) כדי לוודא שהאפליקציה מחילה את גודלי הגופנים בצורה נכונה ויכולה להתאים לגופנים גדולים יותר בלי להשפיע על נוחות השימוש.
כדי להגדיל את גודל הגופן ל-200%:
- פותחים את אפליקציית ההגדרות ועוברים אל נגישות > גודל התצוגה ו text.
- באפשרות גודל הגופן, מקישים על סמל הפלוס (+) עד לגופן המקסימלי. הגדרת הגודל מופעלת, כפי שמוצג בתמונה הנלווית .
שימוש ביחידות של פיקסלים משוקללים (sp) לגודל הטקסט
חשוב לזכור תמיד לציין את גדלי הטקסט ביחידות sp. מתי באפליקציה שלך נעשה שימוש ביחידות sp, מערכת Android יכולה להחיל את גודל הטקסט המועדף על המשתמש וגם להתאים אותו לעומס.
לא להשתמש ביחידות sp למרווחים פנימיים או להגדיר גובה תצוגה בהנחה שיש מרווח פנימי משתמע: כשמשתמשים בהתאמת גודל גופן לא לינארית, יכול להיות שהמידות ב-sp לא יהיו פרופורציונליות, כך ש-4sp + 20sp לא יהיה שווה ל-24sp.
המרת יחידות פיקסלים (sp) מותאמות
כדי להמיר מיחידות sp, צריך להשתמש ב-TypedValue.applyDimension()
לפיקסלים, ומשתמשים ב-TypedValue.deriveDimension() כדי
להמיר פיקסלים ל-sp. בשיטות האלה המערכת מיישמת את ההתאמה לעומס (scaling) המתאים
עקומה באופן אוטומטי.
מומלץ להימנע מכתיבת משוואות בתוך הקוד באמצעות
Configuration.fontScale או
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. מפני ששינוי גודל הגופן
שאינו לינארי, השדה scaledDensity כבר לא מדויק. fontScale
יש להשתמש בשדה למטרות מידע בלבד, מאחר שהגופנים כבר לא קיימים
עם ערך סקלר יחיד.
שימוש ביחידות sp עבור lineHeight
תמיד צריך להגדיר android:lineHeight באמצעות יחידות sp
של dp, כך שגובה השורה ישתנה בהתאם לטקסט. אחרת, אם הטקסט
הוא sp אבל הערך של lineHeight הוא ב-dp או ב-px, הוא לא גדל ונראה דחוס.
TextView מתקן באופן אוטומטי את lineHeight כדי לשמור על הפרופורציות הרצויות, אבל רק אם גם textSize וגם lineHeight מוגדרים ביחידות sp.
מצלמה ומדיה
תמונות ב-Ultra HDR

Android 14 adds support for High Dynamic Range (HDR) images that retain more of the information from the sensor when taking a photo, which enables vibrant colors and greater contrast. Android uses the Ultra HDR format, which is fully backward compatible with JPEG images, allowing apps to seamlessly interoperate with HDR images, displaying them in Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) as needed.
Rendering these images in the UI in HDR is done automatically by the framework
when your app opts in to using HDR UI for its Activity Window, either through a
manifest entry or at runtime by calling
Window.setColorMode(). You can also capture compressed Ultra
HDR still images on supported devices. With more colors recovered
from the sensor, editing in post can be more flexible. The
Gainmap associated with Ultra HDR images can be used to render
them using OpenGL or Vulkan.
זום, מיקוד, תצוגה מקדימה ועוד בתוספים למצלמה
ב-Android 14 יש שיפורים בתוספים למצלמה, שמאפשרים לאפליקציות להתמודד עם זמני עיבוד ארוכים יותר. כך אפשר לצלם תמונות טובות יותר באמצעות אלגוריתמים שמבוססים על חישובים כבדים, כמו צילום בתאורה חלשה במכשירים נתמכים. התכונות האלה מספקות למשתמשים חוויה חזקה עוד יותר כשהם משתמשים ביכולות של התוספים למצלמה. דוגמאות לשיפורים האלה:
- אומדן זמן האחזור הדינמי של עיבוד התמונות הסטטיות מספק אומדנים מדויקים הרבה יותר של זמן האחזור של התמונות הסטטיות, על סמך תנאי הסביבה והסצנה הנוכחיים. קוראים ל-
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()כדי לקבל אובייקטStillCaptureLatencyעם שתי שיטות להערכת זמן האחזור. השיטהgetCaptureLatency()מחזירה את זמן האחזור המשוער ביןonCaptureStartedל-onCaptureProcessStarted(), והשיטהgetProcessingLatency()מחזירה את זמן האחזור המשוער ביןonCaptureProcessStarted()לבין זמינות המסגרת הסופית שעברה עיבוד. - תמיכה בקריאות חזרה (callbacks) של התקדמות הצילום, כדי שאפליקציות יוכלו להציג את ההתקדמות הנוכחית של פעולות עיבוד ממושכות של צילומי סטילס. אפשר לבדוק אם התכונה הזו זמינה באמצעות
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable. אם כן, מטמיעים את פונקציית הקריאה החוזרתonCaptureProcessProgressed(), שבה מועבר הפרמטר של ההתקדמות (מ-0 עד 100). מטא-נתונים ספציפיים לתוסף, כמו
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHכדי להזין את מידת האפקט של התוסף, למשל מידת הטשטוש של הרקע באמצעותEXTENSION_BOKEH.התכונה 'תצוגה לאחר הצילום' לצילום סטילס בתוספים למצלמה, שמספקת תמונה שעברה עיבוד פחות מאשר התמונה הסופית, במהירות גבוהה יותר. אם תוסף מאריך את זמן האחזור לעיבוד, אפשר לספק תמונה שלאחר הצפייה כתמונה זמנית כדי לשפר את חוויית המשתמש, ולאחר מכן להחליף אותה בתמונה הסופית. אפשר לבדוק אם התכונה הזו זמינה באמצעות
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. לאחר מכן תוכלו להעבירOutputConfigurationאלExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.תמיכה ב-
SurfaceViewשמאפשרת נתיב עיבוד נתונים יעיל יותר וחסכוני יותר באנרגיה לתצוגה מקדימה.תמיכה בהקשה כדי להתמקד ובשינוי מרחק התצוגה במהלך השימוש בתוסף.
זום בחיישן
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
אודיו ב-USB ללא אובדן נתונים
ב-Android 14 יש תמיכה בפורמטים של אודיו ללא אובדן נתונים, כדי שתוכלו ליהנות מחוויית אודיו ברמה גבוהה באמצעות אוזניות קוויות עם חיבור USB. אפשר לשלוח שאילתה למכשיר USB כדי לקבל את מאפייני המיקסר המועדפים שלו, לרשום מאזין לשינויים במאפייני המיקסר המועדפים ולהגדיר את מאפייני המיקסר באמצעות הכיתה AudioMixerAttributes. המחלקה הזו מייצגת את הפורמט, כמו מסכת הערוץ, קצב הדגימה וההתנהגות של מיקסר האודיו. הסוג הזה מאפשר לשלוח אודיו ישירות, בלי ערבוב, שינוי עוצמת קול או עיבוד אפקטים.
פרודוקטיביות וכלים למפתחים
מנהל פרטי הכניסה
ב-Android 14 נוספה התמיכה ב-Credential Manager כ-API בפלטפורמה, עם תמיכה נוספת במכשירי Android 4.4 (רמת API 19) דרך ספריית Jetpack באמצעות Google Play Services. המטרה של Credential Manager היא להקל על המשתמשים להיכנס באמצעות ממשקי API שמאחזרים ומאחסנים את פרטי הכניסה באמצעות ספקי פרטי כניסה שהמשתמשים מגדירים. Credential Manager תומך במספר שיטות כניסה, כולל שם משתמש וסיסמה, מפתחות גישה ופתרונות כניסה מאוחדת (כמו 'כניסה באמצעות חשבון Google') בממשק API אחד.
למפתחות הגישה יש יתרונות רבים. לדוגמה, מפתחות הגישה מבוססים על תקנים מקובלים בתחום, יכולים לפעול במגוון מערכות הפעלה וסביבות עסקיות בדפדפנים, ואפשר להשתמש בהם גם באתרים וגם באפליקציות.
למידע נוסף, עיינו במסמכי העזרה בנושא Credential Manager ומפתחות גישה ובפוסט בבלוג בנושא Credential Manager ומפתחות גישה.
Health Connect
Health Connect is an on-device repository for user health and fitness data. It allows users to share data between their favorite apps, with a single place to control what data they want to share with these apps.
On devices running Android versions prior to Android 14, Health Connect is available to download as an app on the Google Play store. Starting with Android 14, Health Connect is part of the platform and receives updates through Google Play system updates without requiring a separate download. With this, Health Connect can be updated frequently, and your apps can rely on Health Connect being available on devices running Android 14 or higher. Users can access Health Connect from the Settings in their device, with privacy controls integrated into the system settings.
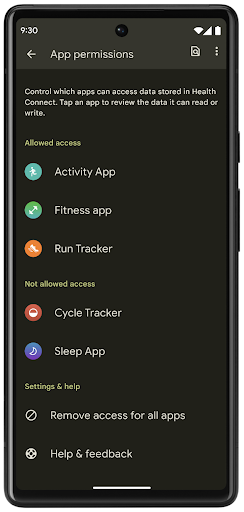
Health Connect includes several new features in Android 14, such as exercise routes, allowing users to share a route of their workout which can be visualized on a map. A route is defined as a list of locations saved within a window of time, and your app can insert routes into exercise sessions, tying them together. To ensure that users have complete control over this sensitive data, users must allow sharing individual routes with other apps.
For more information, see the Health Connection documentation and the blogpost on What's new in Android Health.
עדכונים ל-OpenJDK 17
Android 14 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases, including both library updates and Java 17 language support for app and platform developers.
The following features and improvements are included:
- Updated approximately 300
java.baseclasses to Java 17 support. - Text Blocks, which introduce multi-line string literals to the Java programming language.
- Pattern Matching for instanceof, which allows an object to
be treated as having a specific type in an
instanceofwithout any additional variables. - Sealed classes, which allow you restrict which classes and interfaces can extend or implement them.
Thanks to Google Play system updates (Project Mainline), over 600 million devices are enabled to receive the latest Android Runtime (ART) updates that include these changes. This is part of our commitment to give apps a more consistent, secure environment across devices, and to deliver new features and capabilities to users independent of platform releases.
Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
שיפורים בחנויות אפליקציות
ב-Android 14 נוספו כמה ממשקי API של PackageInstaller שמאפשרים לחנויות האפליקציות לשפר את חוויית המשתמש שלהן.
בקשה לאישור התקנה לפני ההורדה
יכול להיות שתצטרכו אישור משתמש כדי להתקין או לעדכן אפליקציה.
לדוגמה, כשתוכנית התקנה שמשתמשת בהרשאה REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES מנסה להתקין אפליקציה חדשה. בגרסאות קודמות של Android, חנויות אפליקציות יכולות לבקש אישור מהמשתמש רק אחרי שקבצי ה-APK נכתבים בסשן ההתקנה והסשן מוגדר.
החל מ-Android 14, השיטה requestUserPreapproval() מאפשרת למתקינים לבקש אישור מהמשתמשים לפני ביצוע סשן ההתקנה. השיפור הזה מאפשר לחנות אפליקציות לדחות את הורדת חבילות ה-APK עד שהמשתמש יאשר את ההתקנה. בנוסף, אחרי שהמשתמש מאשר את ההתקנה, חנות האפליקציות יכולה להוריד ולהתקין את האפליקציה ברקע בלי להפריע למשתמש.
לטעון לבעלות על עדכונים עתידיים
השיטה setRequestUpdateOwnership() מאפשרת למתקין להציין למערכת שהוא מתכוון להיות אחראי על עדכונים עתידיים לאפליקציה שהוא מתקין. היכולת הזו מאפשרת לאכוף את הבעלות על העדכון, כלומר רק בעל העדכון רשאי להתקין עדכונים אוטומטיים לאפליקציה. אכיפת הבעלות על העדכון עוזרת לוודא שהמשתמשים מקבלים עדכונים רק מחנות האפליקציות הצפויה.
כל מתקין אחר, כולל אלה שמשתמשים בהרשאה INSTALL_PACKAGES, צריך לקבל אישור מפורש מהמשתמש כדי להתקין עדכון. אם משתמש מחליט להמשיך עם עדכון ממקור אחר, הבעלות על העדכון אבודה.
עדכון אפליקציות בזמנים פחות מפריעים
בדרך כלל, בחנויות האפליקציות לא רוצים לעדכן אפליקציה שבשימוש פעיל, כי זה מוביל לסגירת התהליכים שפועלים באפליקציה, ויכול להפריע למה שהמשתמש עושה.
החל מ-Android 14, ממשק ה-API של InstallConstraints מאפשר למתקינים לוודא שהעדכונים של האפליקציות שלהם מתבצעים בזמן המתאים. לדוגמה, חנות אפליקציות יכולה להפעיל את השיטה commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() כדי לוודא שהעדכון יאושר רק כשהמשתמש כבר לא יוצר אינטראקציה עם האפליקציה הרלוונטית.
התקנה חלקה של חלוקות אופציונליות
כשמשתמשים ב-APKs מפוצלים, אפשר לספק את התכונות של האפליקציה בקובצי APK נפרדים, במקום כ-APK מונוליתי. קובצי APK מפוצלים מאפשרים לחנויות אפליקציות לבצע אופטימיזציה של העברת הרכיבים השונים של האפליקציה. לדוגמה, חנויות אפליקציות עשויות לבצע אופטימיזציה על סמך המאפיינים של מכשיר היעד. ה-API של PackageInstaller תומך בחלוקות מאז ההשקה שלו ברמת API 22.
ב-Android 14, השיטה setDontKillApp() מאפשרת למנהל ההתקנה לציין שלא צריך להרוג את התהליכים שפועלים באפליקציה כשמתקינים פלחים חדשים. חנויות האפליקציות יכולות להשתמש בתכונה הזו כדי להתקין בצורה חלקה תכונות חדשות של אפליקציה בזמן שהמשתמש משתמש באפליקציה.
חבילות של מטא-נתונים של אפליקציות
Starting in Android 14, the Android package installer lets you specify app metadata, such as data safety practices, to include on app store pages such as Google Play.
זיהוי מתי משתמשים מצלמים צילומי מסך במכשיר
To create a more standardized experience for detecting screenshots, Android 14 introduces a privacy-preserving screenshot detection API. This API lets apps register callbacks on a per-activity basis. These callbacks are invoked, and the user is notified, when the user takes a screenshot while that activity is visible.
חוויית משתמש
פעולות מותאמות אישית בגיליון השיתוף ודירוג משופר
ב-Android 14 מתבצע עדכון של גיליון השיתוף של המערכת כדי לתמוך בפעולות מותאמות אישית באפליקציות ובתצוגות מקדימות מפורטות יותר של תוצאות למשתמשים.
הוספת פעולות בהתאמה אישית
ב-Android 14, האפליקציה יכולה להוסיף פעולות בהתאמה אישית לגיליון השיתוף של המערכת שהיא מפעילה.
שיפור הדירוג של יעדים לשיתוף ישיר
ב-Android 14 נעשה שימוש באותות רבים יותר מאפליקציות כדי לקבוע את הדירוג של יעדי השיתוף הישיר, וכך לספק תוצאות מועילות יותר למשתמש. כדי לספק את האות הכי שימושי לדירוג, פועלים לפי ההנחיות לשיפור הדירוג של היעדים של שיתוף ישיר. אפליקציות תקשורת יכולות גם לדווח על שימוש במקשי קיצור להודעות יוצאות ונכנסות.
תמיכה באנימציות מובנות ומותאמות אישית לחיזוי של תנועת החזרה
ב-Android 13 הוספנו את האפשרות להפעיל אנימציה חזרה למסך הבית באופן יזום, כאפשרות לפיתוח. כשמשתמשים בתנועת החלקה לאחור באפליקציה נתמכת עם אפשרות הפיתוח מופעלת, מוצגת אנימציה שמציינת שתנועת ההחלקה לאחור יוצאת מהאפליקציה ומחזירה למסך הבית.
Android 14 כולל כמה שיפורים והנחיות חדשות לגבי 'חזרה חזותית':
- אפשר להגדיר את
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueכדי להביע הסכמה לשימוש באנימציות מערכת לחיזוי תנועת החזרה לכל פעילות בנפרד, במקום לכל האפליקציה. - הוספנו אנימציות מערכת חדשות שיתלוו לאנימציה של החזרה למסך הבית מ-Android 13. אנימציות המערכת החדשות הן פעילות בכל פעילות ומשימות שונות, והן מופיעות באופן אוטומטי אחרי העברה ל'חזרה חזוי'.
- הוספנו אנימציות חדשות של רכיבי Material לגיליונות בתחתית המסך, לגיליונות צדדיים ולחיפוש.
- יצרנו הנחיות לעיצוב ליצירת אנימציות ומעברים מותאמים אישית באפליקציה.
- הוספנו ממשקי API חדשים שתומכים באנימציות מעבר בהתאמה אישית באפליקציה:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- משתמשים ב-
overrideActivityTransitionבמקום ב-overridePendingTransitionכדי ליצור מעברים שתגובה כשהמשתמש מחליק חזרה.
בגרסה הזו של Android 14 בתצוגה מקדימה, כל התכונות של 'חזרה חזותית חזרה' נותרו מאחורי אפשרות למפתחים. כדאי לעיין במדריך למפתחים בנושא העברת האפליקציה לחזרה חזותית חזוי, וגם במדריך למפתחים בנושא יצירת מעברים מותאמים אישית באפליקציה.
שינויים בהגדרות של אפליקציות ספציפיות במכשירים עם מסך גדול
שינוי הגדרות ברמת האפליקציה מאפשר ליצרני המכשירים לשנות את ההתנהגות של האפליקציות במכשירים עם מסך גדול. לדוגמה, ההחרגה FORCE_RESIZE_APP מורה למערכת לשנות את גודל האפליקציה כך שיתאים למימדי המסך (מבלי להשתמש במצב תאימות לגודל) גם אם הערך resizeableActivity="false" מוגדר בקובץ המניפסט של האפליקציה.
השינויים מברירת המחדל נועדו לשפר את חוויית המשתמש במסכים גדולים.
מאפייני מניפסט חדשים מאפשרים להשבית חלק מהשינויים של יצרן המכשירים באפליקציה שלכם.
הגדרות שונות לכל אפליקציה למשתמשים במסכים גדולים
Per-app overrides change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE device manufacturer override sets the app aspect ratio to 16:9 regardless of the app's configuration.
Android 14 QPR1 enables users to apply per‑app overrides by means of a new settings menu on large screen devices.
שיתוף מסך של אפליקציה
App screen sharing enables users to share an app window instead of the entire device screen during screen content recording.
With app screen sharing, the status bar, navigation bar, notifications, and other system UI elements are excluded from the shared display. Only the content of the selected app is shared.
App screen sharing improves productivity and privacy by enabling users to run multiple apps but limit content sharing to a single app.
תשובה מהירה מבוססת-LLM ב-Gboard ב-Pixel 8 Pro
On Pixel 8 Pro devices with the December Feature Drop, developers can try out higher-quality smart replies in Gboard powered by on-device Large Language Models (LLMs) running on Google Tensor.
This feature is available as a limited preview for US English in WhatsApp, Line, and KakaoTalk. It requires using a Pixel 8 Pro device with Gboard as your keyboard.
To try it out, first enable the feature in Settings > Developer Options > AiCore Settings > Enable Aicore Persistent.
Next, open a conversation in a supported app to see LLM-powered Smart Reply in Gboard's suggestion strip in response to incoming messages.
גרפיקה
אפשר להריץ שאילתות על נתיבים ולבצע אינטרפולציה שלהם
Android's Path API is a powerful and flexible mechanism for
creating and rendering vector graphics, with the ability to stroke or fill a
path, construct a path from line segments or quadratic or cubic curves, perform
boolean operations to get even more complex shapes, or all of these
simultaneously. One limitation is the ability to find out what is actually in a
Path object; the internals of the object are opaque to callers after creation.
To create a Path, you call methods such as
moveTo(), lineTo(), and
cubicTo() to add path segments. But there has been no way to
ask that path what the segments are, so you must retain that information at
creation time.
Starting in Android 14, you can query paths to find out what's inside of them.
First, you need to get a PathIterator object using the
Path.getPathIterator API:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Next, you can call PathIterator to iterate through the segments
one by one, retrieving all of the necessary data for each segment. This example
uses PathIterator.Segment objects, which packages up the data
for you:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator also has a non-allocating version of next() where you can pass
in a buffer to hold the point data.
One of the important use cases of querying Path data is interpolation. For
example, you might want to animate (or morph) between two different paths. To
further simplify that use case, Android 14 also includes the
interpolate() method on Path. Assuming the two paths have
the same internal structure, the interpolate() method creates a new Path
with that interpolated result. This example returns a path whose shape is
halfway (a linear interpolation of .5) between path and otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
The Jetpack graphics-path library enables similar APIs for earlier versions of Android as well.
רשתות מותאמות אישית עם הצללות של קודקודים ושל פרגמנטים
Android has long supported drawing triangle meshes with custom shading, but the input mesh format has been limited to a few predefined attribute combinations. Android 14 adds support for custom meshes, which can be defined as triangles or triangle strips, and can, optionally, be indexed. These meshes are specified with custom attributes, vertex strides, varying, and vertex and fragment shaders written in AGSL.
The vertex shader defines the varyings, such as position and color, while the
fragment shader can optionally define the color for the pixel, typically by
using the varyings created by the vertex shader. If color is provided by the
fragment shader, it is then blended with the current Paint
color using the blend mode selected when
drawing the mesh. Uniforms can be passed
into the fragment and vertex shaders for additional flexibility.
מעבד מאגר נתונים זמני של חומרה ל-Canvas
To assist in using Android's Canvas API to draw with
hardware acceleration into a HardwareBuffer, Android 14
introduces HardwareBufferRenderer. This API is
particularly useful when your use case involves communication with the system
compositor through SurfaceControl for low-latency
drawing.

