Android 14, geliştiriciler için muhteşem özellikler ve API'ler sunar. Aşağıdaki yardım uygulamalarınızın özellikleri hakkında bilgi edinir ve ilgili API'leri kullanmaya başlarsınız.
Eklenen, değiştirilen ve kaldırılan API'lerin ayrıntılı listesi için API karşılaştırma raporunu okuyun. Eklenen API'ler hakkında ayrıntılı bilgi için Android API referansı sayfasını ziyaret edin. Android 14 için API düzeyi 34'te eklenen API'leri arayın. Bölgeler hakkında bilgi edinmek için Uygulamalarınızı etkileyebilecek platform değişiklikleri hakkında daha fazla bilgi edinmek için Android 14'e göz atmayı unutmayın. Android 14'ü hedefleyen uygulamalarda ve tüm uygulamalarda davranış değişiklikleri.
Uluslararası hale getirme
Uygulamaya özgü dil tercihleri
Android 14 expands on the per-app language features that were introduced in Android 13 (API level 33) with these additional capabilities:
Automatically generate an app's
localeConfig: Starting with Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 and AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, you can configure your app to support per-app language preferences automatically. Based on your project resources, the Android Gradle plugin generates theLocaleConfigfile and adds a reference to it in the final manifest file, so you no longer have to create or update the file manually. AGP uses the resources in theresfolders of your app modules and any library module dependencies to determine the locales to include in theLocaleConfigfile.Dynamic updates for an app's
localeConfig: Use thesetOverrideLocaleConfig()andgetOverrideLocaleConfig()methods inLocaleManagerto dynamically update your app's list of supported languages in the device's system settings. Use this flexibility to customize the list of supported languages per region, run A/B experiments, or provide an updated list of locales if your app utilizes server-side pushes for localization.App language visibility for input method editors (IMEs): IMEs can utilize the
getApplicationLocales()method to check the language of the current app and match the IME language to that language.
Grammatal Inflection API'si
3 milyar insan cinsiyete dayalı diller konuşuyor: İsim, fiil, sıfat ve edat gibi dil bilgisi kategorilerinin, konuştuğunuz veya bahsettiğiniz kişilerin ve nesnelerin cinsiyetine göre değiştiği diller. Cinsiyetli dillerin çoğunda, geleneksel olarak varsayılan veya genel cinsiyet olarak eril dil bilgisi cinsiyeti kullanılır.
Kullanıcılara yanlış dil bilgisi cinsiyetiyle hitap etmek (ör. kadınları eril dil bilgisi cinsiyetiyle hitap etmek) performanslarını ve tutumlarını olumsuz yönde etkileyebilir. Buna karşılık, kullanıcının dil bilgisi açısından cinsiyetini doğru yansıtan bir kullanıcı arayüzü, kullanıcı etkileşimini artırabilir ve daha kişiselleştirilmiş ve doğal bir kullanıcı deneyimi sunabilir.
To help you build a user-centric UI for gendered languages, Android 14 introduces the Grammatical Inflection API, which lets you add support for grammatical gender without refactoring your app.
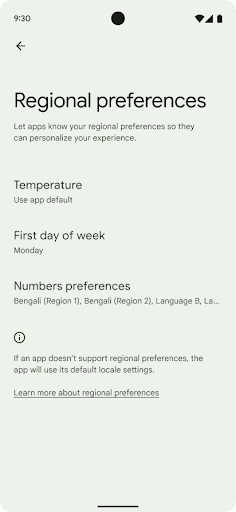
Bölgeye özgü tercihler
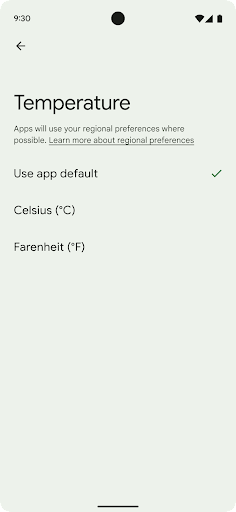
Regional preferences enable users to personalize temperature units, the first day of the week, and numbering systems. A European living in the United States might prefer temperature units to be in Celsius rather than Fahrenheit and for apps to treat Monday as the beginning of the week instead of the US default of Sunday.
New Android Settings menus for these preferences provide users with a
discoverable and centralized location to change app preferences. These
preferences also persist through backup and restore. Several APIs and
intents—such as
getTemperatureUnit
and
getFirstDayOfWeek—
grant your app read access to user preferences, so your app can adjust how it
displays information. You can also register a
BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
to handle locale configuration changes when regional preferences change.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & input > Regional preferences.
Erişilebilirlik
%200'e kadar doğrusal olmayan yazı tipi ölçeklendirme
Starting in Android 14, the system supports font scaling up to 200%, providing low-vision users with additional accessibility options that align with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
To prevent large text elements on screen from scaling too large, the system applies a nonlinear scaling curve. This scaling strategy means that large text doesn't scale at the same rate as smaller text. Nonlinear font scaling helps preserve the proportional hierarchy between elements of different sizes while mitigating issues with linear text scaling at high degrees (such as text being cut off or text that becomes harder to read due to an extremely large display sizes).
Test your app with nonlinear font scaling
If you already use scaled pixels (sp) units to define text sizing, then these additional options and scaling improvements are applied automatically to the text in your app. However, you should still perform UI testing with the maximum font size enabled (200%) to ensure that your app applies the font sizes correctly and can accommodate larger font sizes without impacting usability.
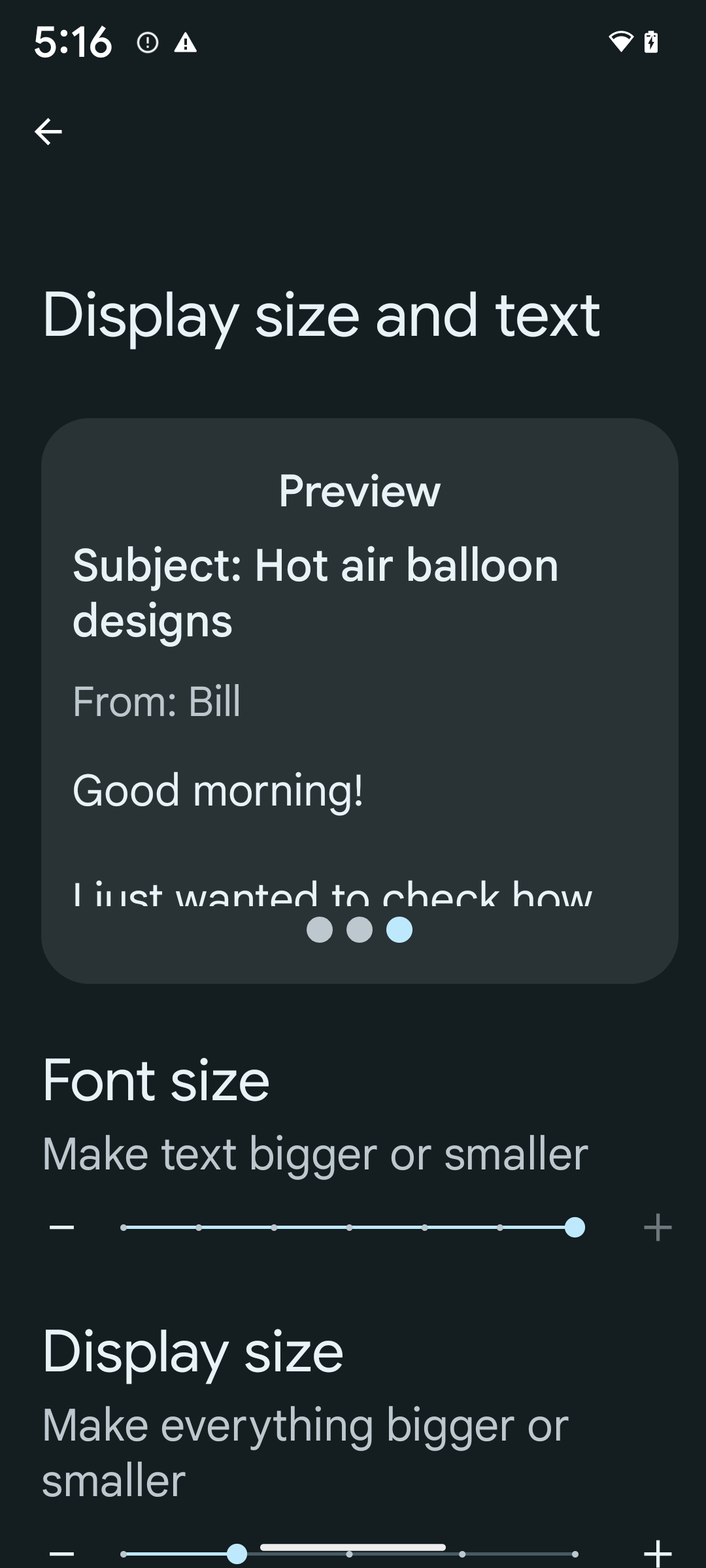
To enable 200% font size, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Accessibility > Display size and text.
- For the Font size option, tap the plus (+) icon until the maximum font size setting is enabled, as shown in the image that accompanies this section.
Use scaled pixel (sp) units for text-sizes
Remember to always specify text sizes in sp units. When your app uses sp units, Android can apply the user's preferred text size and scale it appropriately.
Don't use sp units for padding or define view heights assuming implicit padding: with nonlinear font scaling sp dimensions might not be proportional, so 4sp + 20sp might not equal 24sp.
Convert scaled pixel (sp) units
Use TypedValue.applyDimension() to convert from sp units
to pixels, and use TypedValue.deriveDimension() to
convert pixels to sp. These methods apply the appropriate nonlinear scaling
curve automatically.
Avoid hardcoding equations using
Configuration.fontScale or
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Because font scaling is
nonlinear, the scaledDensity field is no longer accurate. The fontScale
field should be used for informational purposes only because fonts are no longer
scaled with a single scalar value.
Use sp units for lineHeight
Always define android:lineHeight using sp units instead
of dp, so the line height scales along with your text. Otherwise, if your text
is sp but your lineHeight is in dp or px, it doesn't scale and looks cramped.
TextView automatically corrects the lineHeight so that your intended
proportions are preserved, but only if both textSize and lineHeight are
defined in sp units.
Kamera ve medya içerikleri
Resimler için ultra HDR

Android 14 adds support for High Dynamic Range (HDR) images that retain more of the information from the sensor when taking a photo, which enables vibrant colors and greater contrast. Android uses the Ultra HDR format, which is fully backward compatible with JPEG images, allowing apps to seamlessly interoperate with HDR images, displaying them in Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) as needed.
Rendering these images in the UI in HDR is done automatically by the framework
when your app opts in to using HDR UI for its Activity Window, either through a
manifest entry or at runtime by calling
Window.setColorMode(). You can also capture compressed Ultra
HDR still images on supported devices. With more colors recovered
from the sensor, editing in post can be more flexible. The
Gainmap associated with Ultra HDR images can be used to render
them using OpenGL or Vulkan.
Kamera uzantılarında yakınlaştırma, odaklama, son görüntüleme ve daha fazlası
Android 14 upgrades and improves camera extensions, allowing apps to handle longer processing times, which enables improved images using compute-intensive algorithms like low-light photography on supported devices. These features give users an even more robust experience when using camera extension capabilities. Examples of these improvements include:
- Dynamic still capture processing latency estimation provides much more
accurate still capture latency estimates based on the current scene and
environment conditions. Call
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()to get aStillCaptureLatencyobject that has two latency estimation methods. ThegetCaptureLatency()method returns the estimated latency betweenonCaptureStartedandonCaptureProcessStarted(), and thegetProcessingLatency()method returns the estimated latency betweenonCaptureProcessStarted()and the final processed frame being available. - Support for capture progress callbacks so that apps can display the current
progress of long-running, still-capture processing operations. You can check
if this feature is available with
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable, and if it is, you implement theonCaptureProcessProgressed()callback, which has the progress (from 0 to 100) passed in as a parameter. Extension specific metadata, such as
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHfor dialing in the amount of an extension effect, such as the amount of background blur withEXTENSION_BOKEH.Postview Feature for Still Capture in camera extensions, which provides a less-processed image more quickly than the final image. If an extension has increased processing latency, a postview image could be provided as a placeholder to improve UX and switched out later for the final image. You can check if this feature is available with
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. Then you can pass anOutputConfigurationtoExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Support for
SurfaceViewallowing for a more optimized and power-efficient preview render path.Support for tap to focus and zoom during extension usage.
Sensör içi yakınlaştırma
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
USB'de kayıpsız ses
Android 14 gains support for lossless audio formats for audiophile-level
experiences over USB wired headsets. You can query a USB device for its
preferred mixer attributes, register a listener for changes in preferred mixer
attributes, and configure mixer attributes using the
AudioMixerAttributes class. This class represents the
format, such as channel mask, sample rate, and behavior of the audio mixer. The
class allows for audio to be sent directly, without mixing,
volume adjustment, or processing effects.
Geliştirici verimliliği ve araçları
Kimlik Bilgisi Yöneticisi
Android 14 adds Credential Manager as a platform API, with additional support back to Android 4.4 (API level 19) devices through a Jetpack Library using Google Play services. Credential Manager aims to make sign-in easier for users with APIs that retrieve and store credentials with user-configured credential providers. Credential Manager supports multiple sign-in methods, including username and password, passkeys, and federated sign-in solutions (such as Sign-in with Google) in a single API.
Passkeys provide many advantages. For example, passkeys are built on industry standards, can work across different operating systems and browser ecosystems, and can be used with both websites and apps.
For more information, see the Credential Manager and passkeys documentation and the blogpost about Credential Manager and passkeys.
Health Connect
Health Connect is an on-device repository for user health and fitness data. It allows users to share data between their favorite apps, with a single place to control what data they want to share with these apps.
On devices running Android versions prior to Android 14, Health Connect is available to download as an app on the Google Play store. Starting with Android 14, Health Connect is part of the platform and receives updates through Google Play system updates without requiring a separate download. With this, Health Connect can be updated frequently, and your apps can rely on Health Connect being available on devices running Android 14 or higher. Users can access Health Connect from the Settings in their device, with privacy controls integrated into the system settings.
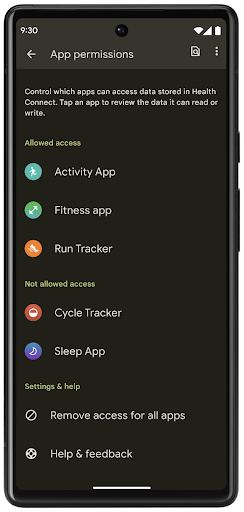
Health Connect includes several new features in Android 14, such as exercise routes, allowing users to share a route of their workout which can be visualized on a map. A route is defined as a list of locations saved within a window of time, and your app can insert routes into exercise sessions, tying them together. To ensure that users have complete control over this sensitive data, users must allow sharing individual routes with other apps.
For more information, see the Health Connection documentation and the blogpost on What's new in Android Health.
OpenJDK 17 güncellemeleri
Android 14 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases, including both library updates and Java 17 language support for app and platform developers.
The following features and improvements are included:
- Updated approximately 300
java.baseclasses to Java 17 support. - Text Blocks, which introduce multi-line string literals to the Java programming language.
- Pattern Matching for instanceof, which allows an object to
be treated as having a specific type in an
instanceofwithout any additional variables. - Sealed classes, which allow you restrict which classes and interfaces can extend or implement them.
Thanks to Google Play system updates (Project Mainline), over 600 million devices are enabled to receive the latest Android Runtime (ART) updates that include these changes. This is part of our commitment to give apps a more consistent, secure environment across devices, and to deliver new features and capabilities to users independent of platform releases.
Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Uygulama mağazalarında yapılan iyileştirmeler
Android 14, uygulama mağazalarının kullanıcı deneyimini iyileştirmesine olanak tanıyan çeşitli PackageInstaller API'leri sunar.
İndirmeden önce yükleme onayı isteme
Uygulama yüklemek veya güncellemek için kullanıcı onayı gerekebilir.
Örneğin, REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES iznini kullanan bir yükleyici yeni bir uygulama yüklemeye çalıştığında. Önceki Android sürümlerinde uygulama mağazaları, yalnızca APK'lar yükleme oturumuna yazıldıktan ve oturum taahhüt edildikten sonra kullanıcı onayı isteyebilir.
Android 14'ten itibaren requestUserPreapproval() yöntemi, yükleyicilerin yükleme oturumunu önce kullanıcı onayı istemesine olanak tanır. Bu iyileştirme, uygulama mağazalarının APK'ları yüklemeyi, yükleme işlemi kullanıcı tarafından onaylanana kadar ertelemelerine olanak tanır. Ayrıca, kullanıcı yüklemeyi onayladıktan sonra uygulama mağazası, kullanıcıyı rahatsız etmeden uygulamayı arka planda indirip yükleyebilir.
Gelecekteki güncellemeler için sorumluluk alma
setRequestUpdateOwnership() yöntemi, yükleyicinin yüklediği bir uygulamanın gelecekteki güncellemelerinden sorumlu olmayı amaçladığını sisteme belirtmesine olanak tanır. Bu özellik, güncelleme sahipliği yaptırımını etkinleştirir. Bu sayede, uygulamaya otomatik güncelleme yüklenmesine yalnızca güncelleme sahibinin izin verilir. Güncelleme sahipliği yaptırımı, kullanıcıların yalnızca beklenen uygulama mağazasından güncelleme almasını sağlar.
INSTALL_PACKAGES iznini kullananlar da dahil olmak üzere diğer tüm yükleyicilerin, güncelleme yüklemek için açık kullanıcı onayı alması gerekir. Kullanıcı başka bir kaynaktan güncelleme yapmaya karar verirse güncelleme sahipliği kaybedilir.
Uygulamaları kullanıcıların günlük rutinini etkilemeyecek zamanlarda güncelleme
Uygulama mağazaları, etkin olarak kullanılan bir uygulamanın güncellenmesini genellikle istemez. Bunun nedeni, uygulamanın çalışan işlemlerinin sonlandırılmasıdır. Bu da kullanıcının yaptığı işlemi kesintiye uğratabilir.
Android 14'ten itibaren InstallConstraints API, yükleyicilere uygulama güncellemelerinin uygun bir zamanda yapılmasını sağlamanın bir yolunu sunar. Örneğin, bir uygulama mağazası, bir güncellemenin yalnızca kullanıcı söz konusu uygulamayla etkileşimde bulunmadığında kaydolmasını sağlamak için commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() yöntemini çağırabilir.
İsteğe bağlı bölmelerin sorunsuz şekilde yüklenmesi
Bölünmüş APK'lar sayesinde, bir uygulamanın özellikleri tek bir APK yerine ayrı APK dosyalarında yayınlanabilir. Bölünmüş APK'lar, uygulama mağazalarının farklı uygulama bileşenlerinin dağıtımını optimize etmesine olanak tanır. Örneğin, uygulama mağazaları hedef cihazın özelliklerine göre optimizasyon yapabilir. PackageInstaller API, API düzeyi 22'de kullanıma sunulmasından bu yana bölünmeleri desteklemektedir.
Android 14'te setDontKillApp() yöntemi, yükleyicinin yeni bölümler yüklenirken uygulamanın çalışan işlemlerinin sonlandırılmaması gerektiğini belirtmesine olanak tanır. Uygulama mağazaları, kullanıcı uygulamayı kullanırken uygulamanın yeni özelliklerini sorunsuz bir şekilde yüklemek için bu özelliği kullanabilir.
Uygulama meta veri paketleri
Starting in Android 14, the Android package installer lets you specify app metadata, such as data safety practices, to include on app store pages such as Google Play.
Kullanıcılar cihaz ekran görüntüsü aldığında bunu algılar
To create a more standardized experience for detecting screenshots, Android 14 introduces a privacy-preserving screenshot detection API. This API lets apps register callbacks on a per-activity basis. These callbacks are invoked, and the user is notified, when the user takes a screenshot while that activity is visible.
Kullanıcı deneyimi
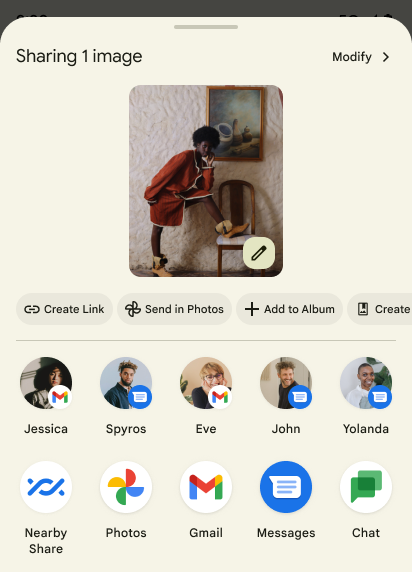
Sharesheet'te özel işlemler ve iyileştirilmiş sıralama
Android 14 updates the system sharesheet to support custom app actions and more informative preview results for users.
Add custom actions
With Android 14, your app can add custom actions to the system sharesheet it invokes.
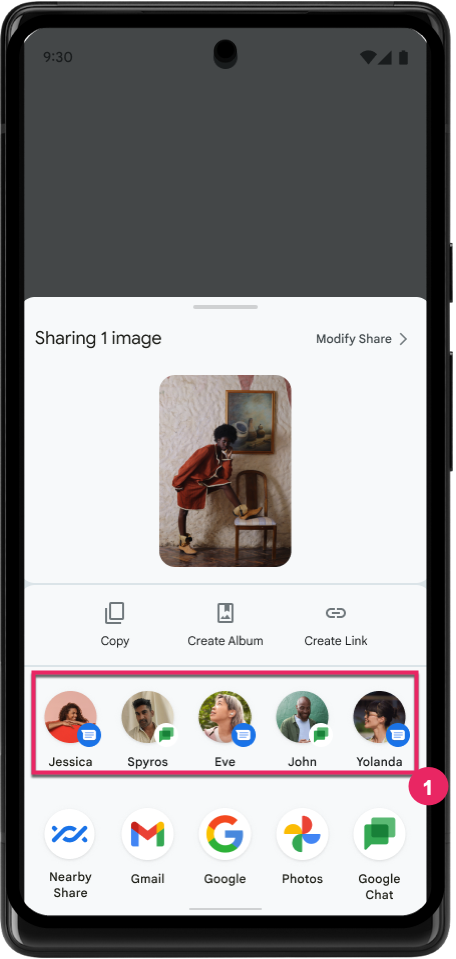
Improve ranking of Direct Share targets
Android 14 uses more signals from apps to determine the ranking of the direct share targets to provide more helpful results for the user. To provide the most useful signal for ranking, follow the guidance for improving rankings of your Direct Share targets. Communication apps can also report shortcut usage for outgoing and incoming messages.
Tahmine Dayalı Geri Dönme özelliği için yerleşik ve özel animasyonlar için destek
Android 13 introduced the predictive back-to-home animation behind a developer option. When used in a supported app with the developer option enabled, swiping back shows an animation indicating that the back gesture exits the app back to the home screen.
Android 14 includes multiple improvements and new guidance for Predictive Back:
- You can set
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueto opt in to predictive back system animations per-Activity instead of for the entire app. - We've added new system animations to accompany the back-to-home animation from Android 13. The new system animations are cross-activity and cross-task, which you get automatically after migrating to Predictive Back.
- We've added new Material Component animations for Bottom sheets, Side sheets, and Search.
- We've created design guidance for creating custom in-app animations and transitions.
- We've added new APIs to support custom in-app transition animations:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Use
overrideActivityTransitioninstead ofoverridePendingTransitionfor transitions that respond as the user swipes back.
With this Android 14 preview release, all features of Predictive Back remain behind a developer option. See the developer guide to migrate your app to predictive back, as well as the developer guide to creating custom in-app transitions.
Büyük ekranlı cihaz üreticisinin uygulama bazında geçersiz kılmaları
Per-app overrides enable device manufacturers to change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the FORCE_RESIZE_APP override instructs the system to resize the app to fit display dimensions (avoiding size compatibility mode) even if resizeableActivity="false" is set in the app manifest.
Overrides are intended to improve the user experience on large screens.
New manifest properties enable you to disable some device manufacturer overrides for your app.
Büyük ekran kullanıcı başına uygulama başına geçersiz kılmalar
Per-app overrides change the behavior of apps on large screen devices. For example, the OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE device manufacturer override sets the app aspect ratio to 16:9 regardless of the app's configuration.
Android 14 QPR1 enables users to apply per‑app overrides by means of a new settings menu on large screen devices.
Uygulama ekran paylaşımı
App screen sharing enables users to share an app window instead of the entire device screen during screen content recording.
With app screen sharing, the status bar, navigation bar, notifications, and other system UI elements are excluded from the shared display. Only the content of the selected app is shared.
App screen sharing improves productivity and privacy by enabling users to run multiple apps but limit content sharing to a single app.
Pixel 8 Pro'daki Gboard'da LLM destekli Akıllı Yanıt
On Pixel 8 Pro devices with the December Feature Drop, developers can try out higher-quality smart replies in Gboard powered by on-device Large Language Models (LLMs) running on Google Tensor.
This feature is available as a limited preview for US English in WhatsApp, Line, and KakaoTalk. It requires using a Pixel 8 Pro device with Gboard as your keyboard.
To try it out, first enable the feature in Settings > Developer Options > AiCore Settings > Enable Aicore Persistent.
Next, open a conversation in a supported app to see LLM-powered Smart Reply in Gboard's suggestion strip in response to incoming messages.
Grafik
Yollar sorgulanabilir ve birlikte kullanılabilir
Android'in Path API'si, vektör grafikleri oluşturmaya ve oluşturmaya yönelik güçlü ve esnek bir mekanizmadır. Bir yolu çizme veya doldurma, çizgi segmentlerinden veya ikinci dereceden ya da kübik eğrilerden yol oluşturma, daha da karmaşık şekiller elde etmek için boole işlemleri veya bunların tümünü eş zamanlı olarak gerçekleştirme yeteneğine sahip. Bunun bir sınırlaması, Yol nesnesinde gerçekte neyin olduğunu bulma yeteneğidir. Nesnenin iç kısımları, oluşturulduktan sonra arayanlar için opak olur.
Path oluşturmak için moveTo(), lineTo() ve cubicTo() gibi yöntemleri çağırarak yol segmentleri ekleyebilirsiniz. Ancak bu yolda segmentlerin ne olduğunu sormanın bir yolu olmadığından, bu bilgileri oluşturma sırasında saklamanız gerekir.
Android 14'ten itibaren, içinde ne olduğunu öğrenmek için yolları sorgulayabilirsiniz.
Öncelikle, Path.getPathIterator API'yi kullanarak bir PathIterator nesnesi almanız gerekir:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Daha sonra, segmentleri tek tek güncellemek ve her bir segment için gerekli tüm verileri almak üzere PathIterator öğesini çağırabilirsiniz. Bu örnekte, verileri sizin için paketleyen PathIterator.Segment nesneleri kullanılmaktadır:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator, nokta verilerini tutmak için bir arabellek iletebileceğiniz, next()'un ayırt etmeyen bir sürümüne de sahiptir.
Path verilerini sorgulamanın önemli kullanım alanlarından biri de kesme noktasıdır. Örneğin, iki farklı yol arasında animasyon (veya morph) oluşturmak isteyebilirsiniz. Bu kullanım alanını daha da basitleştirmek için Android 14, Path üzerinde interpolate() yöntemini de içerir. İki yolun aynı dahili yapıya sahip olduğu varsayıldığında interpolate() yöntemi, ara değer alınan bu sonuçla yeni bir Path oluşturur. Bu örnek, şekli path ile otherPath arasında yarı yolda olan (0,5 değerinin doğrusal bir kesişimi) bir yol döndürür:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Jetpack graphics-path kitaplığı, Android'in önceki sürümleri için de benzer API'leri etkinleştirir.
Köşe ve parça gölgelendiricileri olan özel örgüler
Android has long supported drawing triangle meshes with custom shading, but the input mesh format has been limited to a few predefined attribute combinations. Android 14 adds support for custom meshes, which can be defined as triangles or triangle strips, and can, optionally, be indexed. These meshes are specified with custom attributes, vertex strides, varying, and vertex and fragment shaders written in AGSL.
The vertex shader defines the varyings, such as position and color, while the
fragment shader can optionally define the color for the pixel, typically by
using the varyings created by the vertex shader. If color is provided by the
fragment shader, it is then blended with the current Paint
color using the blend mode selected when
drawing the mesh. Uniforms can be passed
into the fragment and vertex shaders for additional flexibility.
Tuval için donanım arabelleği oluşturma aracı
To assist in using Android's Canvas API to draw with
hardware acceleration into a HardwareBuffer, Android 14
introduces HardwareBufferRenderer. This API is
particularly useful when your use case involves communication with the system
compositor through SurfaceControl for low-latency
drawing.

