Seiring pertumbuhan aplikasi, akan lebih mudah jika Anda menempatkan beberapa komponen aplikasi dalam proses yang berbeda dari proses utama aplikasi Anda. Untuk menguji komponen aplikasi dalam proses non-default ini, Anda dapat menggunakan fungsionalitas Multiprocess Espresso. Fitur yang tersedia di Android 8.0 (level API 26) dan yang lebih tinggi ini memungkinkan Anda menguji interaksi UI aplikasi yang melintasi batas proses aplikasi dengan lancar sambil mempertahankan jaminan sinkronisasi Espresso.
Saat menggunakan Multiprocess Espresso, perhatikan cakupan pembuatan versi dan pertimbangan berikut:
- Aplikasi Anda harus menargetkan Android 8.0 (API level 26) atau yang lebih tinggi.
- Alat ini hanya dapat menguji komponen aplikasi yang Anda sertakan dalam proses di dalam paket aplikasi Anda. Fitur tersebut tidak dapat menguji proses eksternal.
Menggunakan fitur
Untuk menguji suatu proses dalam aplikasi Anda menggunakan Multiprocess Espresso, tambahkan referensi
ke artefak espresso-remote dalam file build.gradle aplikasi Anda:
app/build.gradle
Groovy
dependencies { ... androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-remote:3.6.1' }
Kotlin
dependencies { ... androidTestImplementation('androidx.test.espresso:espresso-remote:3.6.1') }
Anda juga perlu menambahkan elemen berikut ke manifes androidTest aplikasi:
- Elemen
<instrumentation>yang menentukan proses. - Elemen
<meta-data>yang menunjukkan bahwa Anda ingin menggunakan Multiprocess Espresso.
Cuplikan kode berikut menunjukkan cara menambahkan elemen ini:
src/androidTest/AndroidManifest.xml
<manifest ... package="androidx.test.mytestapp.tests"> <uses-sdk android:targetSdkVersion="27" android:minSdkVersion="14" /> <instrumentation android:name="androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner" android:targetPackage="androidx.test.mytestapp" android:targetProcesses="*"> <meta-data android:name="remoteMethod" android:value="androidx.test.espresso.remote.EspressoRemote#remoteInit" /> </instrumentation> </manifest>
Cuplikan sebelumnya menunjukkan framework Android yang Anda inginkan untuk menguji setiap proses dalam paket aplikasi Anda. Jika Anda ingin menguji hanya sebagian proses aplikasi, Anda dapat menentukan daftar yang dipisahkan koma dalam elemen targetProcesses sebagai gantinya:
<instrumentation
...
android:targetProcesses=
"androidx.test.mytestapp:myFirstAppProcessToTest,
androidx.test.mytestapp:mySecondAppProcessToTest" ... />
Memahami arsitektur fitur
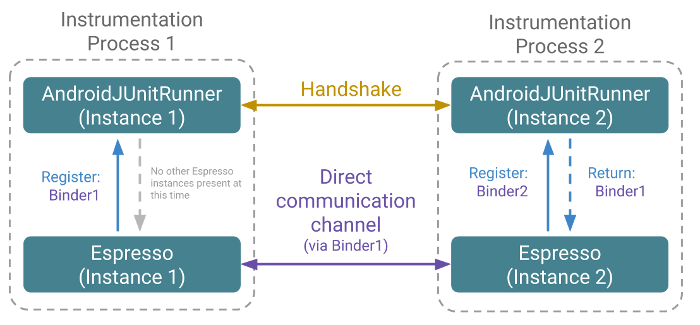
Saat menguji aplikasi dan meluncurkan proses defaultnya, Anda dapat melakukan interaksi UI (misalnya menekan tombol) yang memulai aktivitas dalam proses sekunder. Sistem kemudian menyelesaikan langkah-langkah berikut untuk mengaktifkan pengujian lintas proses menggunakan Espresso:
- Framework Android membuat dan memulai proses baru untuk mengikuti struktur navigasi aplikasi Anda. Setiap proses
Instrumentationmenyertakan instanceAndroidJUnitRunnerbaru. Pada tahap ini, 2 proses instrumentasi tidak dapat berkomunikasi satu sama lain. - Setiap instance
AndroidJUnitRunnermendaftarkan Espresso sebagai framework pengujiannya. - 2 instance
AndroidJUnitRunnermelakukan handshake untuk terhubung antara satu sama lain. Pada saat yang sama, setiap instanceAndroidJUnitRunnermenghubungkan semua klien terdaftar seperti Espresso dengan kliennya masing-masing di dalam proses lain sehingga klien tersebut dapat membentuk saluran komunikasi langsung satu sama lain. - Setiap instance
AndroidJUnitRunnerakan terus mencari instance instrumen yang baru ditambahkan dan menguji framework klien sehingga membangun saluran komunikasi tambahan sesuai kebutuhan.
Gambar 1 menggambarkan hasil dari proses ini:
Referensi lainnya
Untuk informasi selengkapnya tentang topik ini, lihat referensi berikut.
- Video sesi Pengembangan yang Didorong Pengujian di Android dengan Support Library Pengujian Android dari Google I/O 2017, dimulai pada 36.41.
