অ্যান্ড্রয়েড ডিবাগ ব্রিজ ( adb ) একটি বহুমুখী কমান্ড-লাইন টুল যা আপনাকে একটি ডিভাইসের সাথে যোগাযোগ করতে দেয়। adb কমান্ডটি বিভিন্ন ধরণের ডিভাইস ক্রিয়াকে সহজতর করে, যেমন অ্যাপ ইনস্টল এবং ডিবাগ করা। adb একটি ইউনিক্স শেল অ্যাক্সেস প্রদান করে যা আপনি একটি ডিভাইসে বিভিন্ন কমান্ড চালানোর জন্য ব্যবহার করতে পারেন। এটি একটি ক্লায়েন্ট-সার্ভার প্রোগ্রাম যার মধ্যে তিনটি উপাদান রয়েছে:
- একটি client , যা কমান্ড পাঠায়। ক্লায়েন্টটি আপনার ডেভেলপমেন্ট মেশিনে চলে। আপনি একটি কমান্ড-লাইন টার্মিনাল থেকে একটি
adbকমান্ড জারি করে একটি ক্লায়েন্টকে আহ্বান করতে পারেন। - একটি ডেমন (adbd) , যা একটি ডিভাইসে কমান্ড চালায়। প্রতিটি ডিভাইসে ডেমনটি একটি ব্যাকগ্রাউন্ড প্রক্রিয়া হিসেবে চলে।
- একটি সার্ভার , যা ক্লায়েন্ট এবং ডেমনের মধ্যে যোগাযোগ পরিচালনা করে। সার্ভারটি আপনার ডেভেলপমেন্ট মেশিনে একটি ব্যাকগ্রাউন্ড প্রক্রিয়া হিসেবে চলে।
adb অ্যান্ড্রয়েড SDK প্ল্যাটফর্ম টুলস প্যাকেজের অন্তর্ভুক্ত। SDK ম্যানেজার দিয়ে এই প্যাকেজটি ডাউনলোড করুন, যা এটি android_sdk /platform-tools/ ওয়েবসাইটে ইনস্টল করে। আপনি যদি স্বতন্ত্র অ্যান্ড্রয়েড SDK প্ল্যাটফর্ম টুলস প্যাকেজ চান, তাহলে এখান থেকে ডাউনলোড করুন ।
adb এর মাধ্যমে ব্যবহারের জন্য একটি ডিভাইস সংযোগ করার তথ্যের জন্য, সাধারণ সমস্যা সমাধানের জন্য সংযোগ সহকারী কীভাবে ব্যবহার করবেন তা সহ, হার্ডওয়্যার ডিভাইসে অ্যাপ চালান দেখুন।
adb কিভাবে কাজ করে
যখন আপনি একটি adb ক্লায়েন্ট শুরু করেন, তখন ক্লায়েন্ট প্রথমে পরীক্ষা করে যে কোনও adb সার্ভার প্রক্রিয়া ইতিমধ্যেই চলছে কিনা। যদি না থাকে, তবে এটি সার্ভার প্রক্রিয়া শুরু করে। সার্ভার শুরু হলে, এটি স্থানীয় TCP পোর্ট 5037 এর সাথে আবদ্ধ হয় এবং adb ক্লায়েন্টদের কাছ থেকে প্রেরিত কমান্ডগুলি শোনে।
দ্রষ্টব্য: সমস্ত adb ক্লায়েন্ট adb সার্ভারের সাথে যোগাযোগের জন্য পোর্ট 5037 ব্যবহার করে।
এরপর সার্ভারটি সমস্ত চলমান ডিভাইসের সাথে সংযোগ স্থাপন করে। এটি ৫৫৫৫ থেকে ৫৫৮৫ রেঞ্জের মধ্যে বিজোড়-সংখ্যাযুক্ত পোর্ট স্ক্যান করে এমুলেটরগুলি সনাক্ত করে, যা প্রথম ১৬টি এমুলেটর দ্বারা ব্যবহৃত পরিসর। যেখানে সার্ভার একটি adb ডেমন (adbd) খুঁজে পায়, সেখানে এটি সেই পোর্টের সাথে একটি সংযোগ স্থাপন করে।
প্রতিটি এমুলেটর একজোড়া ক্রমিক পোর্ট ব্যবহার করে — কনসোল সংযোগের জন্য একটি জোড়-সংখ্যাযুক্ত পোর্ট এবং adb সংযোগের জন্য একটি বিজোড়-সংখ্যাযুক্ত পোর্ট। উদাহরণস্বরূপ:
এমুলেটর ১, কনসোল: ৫৫৫৪
এমুলেটর ১, adb : ৫৫৫৫
এমুলেটর ২, কনসোল: ৫৫৫৬
এমুলেটর 2, adb : 5557
ইত্যাদি।
যেমন দেখানো হয়েছে, 5555 পোর্টে adb এর সাথে সংযুক্ত এমুলেটরটি এবং 5554 পোর্টে যে এমুলেটরটির কনসোল শোনে তার একই এমুলেটর।
সার্ভারটি একবার সমস্ত ডিভাইসের সাথে সংযোগ স্থাপন করে ফেললে, আপনি সেই ডিভাইসগুলি অ্যাক্সেস করতে adb কমান্ড ব্যবহার করতে পারেন। যেহেতু সার্ভার ডিভাইসের সাথে সংযোগ পরিচালনা করে এবং একাধিক adb ক্লায়েন্টের কমান্ড পরিচালনা করে, আপনি যেকোনো ক্লায়েন্ট বা স্ক্রিপ্ট থেকে যেকোনো ডিভাইস নিয়ন্ত্রণ করতে পারেন।
আপনার ডিভাইসে adb ডিবাগিং সক্ষম করুন
USB এর মাধ্যমে সংযুক্ত ডিভাইসের সাথে adb ব্যবহার করতে, আপনাকে ডিভাইস সিস্টেম সেটিংসে, Developer options এর অধীনে USB ডিবাগিং সক্ষম করতে হবে। Android 4.2 (API লেভেল 17) এবং উচ্চতর সংস্করণে, Developer options স্ক্রিনটি ডিফল্টরূপে লুকানো থাকে। এটি দৃশ্যমান করতে, Developer options সক্ষম করুন।
এখন আপনি আপনার ডিভাইসটি USB দিয়ে সংযুক্ত করতে পারেন। android_sdk /platform-tools/ ডিরেক্টরি থেকে adb devices ব্যবহার করে আপনার ডিভাইসটি সংযুক্ত কিনা তা যাচাই করতে পারেন। সংযুক্ত থাকলে, আপনি ডিভাইসের নামটি "ডিভাইস" হিসাবে তালিকাভুক্ত দেখতে পাবেন।
দ্রষ্টব্য: যখন আপনি Android 4.2.2 (API লেভেল 17) বা তার বেশি চলমান একটি ডিভাইস সংযোগ করেন, তখন সিস্টেমটি একটি ডায়ালগ দেখায় যেখানে জিজ্ঞাসা করা হয় যে এই কম্পিউটারের মাধ্যমে ডিবাগিং করার অনুমতি দেয় এমন একটি RSA কী গ্রহণ করা উচিত কিনা। এই সুরক্ষা ব্যবস্থা ব্যবহারকারীর ডিভাইসগুলিকে সুরক্ষিত করে কারণ এটি নিশ্চিত করে যে USB ডিবাগিং এবং অন্যান্য adb কমান্ডগুলি কার্যকর করা যাবে না যদি না আপনি ডিভাইসটি আনলক করতে এবং ডায়ালগটি স্বীকার করতে সক্ষম হন।
USB এর মাধ্যমে ডিভাইসের সাথে সংযোগ স্থাপন সম্পর্কে আরও তথ্যের জন্য, হার্ডওয়্যার ডিভাইসে অ্যাপ চালান পড়ুন।
Wi-Fi এর মাধ্যমে একটি ডিভাইসের সাথে সংযোগ করুন
দ্রষ্টব্য: নীচের নির্দেশাবলী Android 11 (API লেভেল 30) চালিত Wear ডিভাইসের ক্ষেত্রে প্রযোজ্য নয়। আরও তথ্যের জন্য Wear OS অ্যাপ ডিবাগ করার নির্দেশিকাটি দেখুন।
অ্যান্ড্রয়েড ১১ (এপিআই লেভেল ৩০) এবং উচ্চতর সংস্করণগুলি অ্যান্ড্রয়েড ডিবাগ ব্রিজ (এডিবি) ব্যবহার করে আপনার ওয়ার্কস্টেশন থেকে ওয়্যারলেসভাবে আপনার অ্যাপ স্থাপন এবং ডিবাগিং সমর্থন করে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, আপনি আপনার ডিবাগযোগ্য অ্যাপটি একাধিক দূরবর্তী ডিভাইসে স্থাপন করতে পারেন, USB এর মাধ্যমে আপনার ডিভাইসটি শারীরিকভাবে সংযুক্ত না করেই। এটি ড্রাইভার ইনস্টলেশনের মতো সাধারণ USB সংযোগ সমস্যাগুলি মোকাবেলা করার প্রয়োজন দূর করে।
ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং ব্যবহার শুরু করার আগে, নিম্নলিখিতগুলি করুন:
নিশ্চিত করুন যে আপনার ওয়ার্কস্টেশন এবং ডিভাইস একই ওয়্যারলেস নেটওয়ার্কের সাথে সংযুক্ত।
নিশ্চিত করুন যে আপনার ডিভাইসটি ফোনের জন্য Android 11 (API লেভেল 30) বা তার উচ্চতর সংস্করণ অথবা TV এবং WearOS এর জন্য Android 13 (API লেভেল 33) বা তার উচ্চতর সংস্করণে চলছে। আরও তথ্যের জন্য, আপনার Android সংস্করণটি পরীক্ষা করুন এবং আপডেট করুন দেখুন।
যদি আপনি IDE ব্যবহার করেন, তাহলে নিশ্চিত করুন যে আপনার কাছে Android Studio এর সর্বশেষ সংস্করণ ইনস্টল করা আছে। আপনি এটি এখান থেকে ডাউনলোড করতে পারেন।
আপনার ওয়ার্কস্টেশনে, SDK প্ল্যাটফর্ম টুলস এর সর্বশেষ সংস্করণে আপডেট করুন।
ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং ব্যবহার করার জন্য, আপনাকে একটি QR কোড অথবা একটি পেয়ারিং কোড ব্যবহার করে আপনার ডিভাইসটিকে আপনার ওয়ার্কস্টেশনের সাথে পেয়ার করতে হবে। আপনার ওয়ার্কস্টেশন এবং ডিভাইসটি একই ওয়্যারলেস নেটওয়ার্কের সাথে সংযুক্ত থাকতে হবে। আপনার ডিভাইসের সাথে সংযোগ স্থাপন করতে, এই পদক্ষেপগুলি অনুসরণ করুন:
আপনার ডিভাইসে ডেভেলপার বিকল্পগুলি সক্ষম করুন ।
অ্যান্ড্রয়েড স্টুডিও খুলুন এবং রান কনফিগারেশন মেনু থেকে "ওয়াই-ফাই ব্যবহার করে জোড়া ডিভাইস" নির্বাচন করুন।
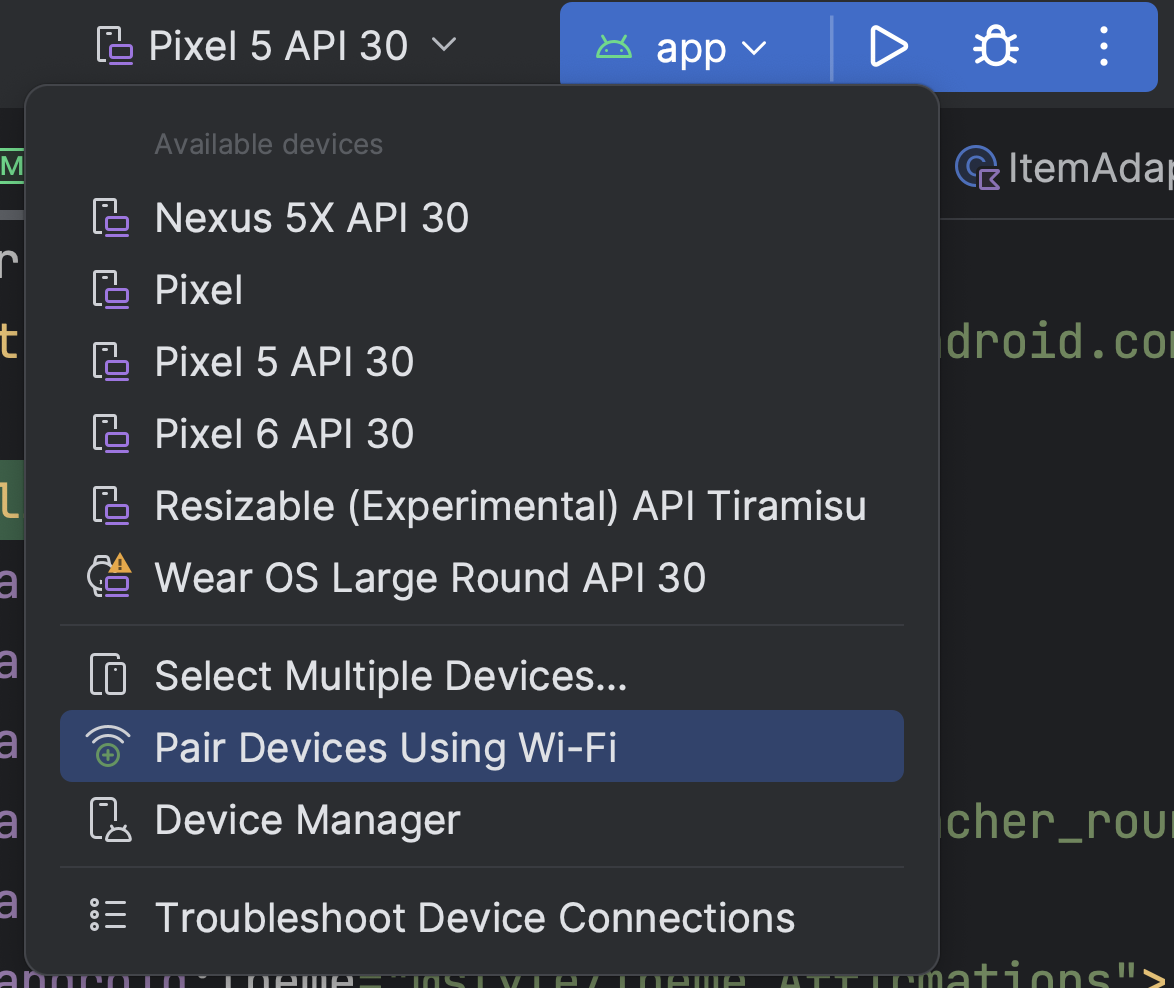 চিত্র ১. রান কনফিগারেশন মেনু।
চিত্র ১. রান কনফিগারেশন মেনু।চিত্র ২-এ দেখানো হয়েছে, "ওয়াই-ফাই ওভার পেয়ার ডিভাইস" উইন্ডোটি পপ আপ হবে।
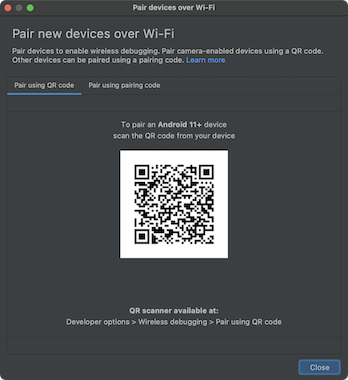 চিত্র ২. QR কোড বা পেয়ারিং কোড ব্যবহার করে ডিভাইস জোড়া লাগানোর জন্য পপআপ উইন্ডো।
চিত্র ২. QR কোড বা পেয়ারিং কোড ব্যবহার করে ডিভাইস জোড়া লাগানোর জন্য পপআপ উইন্ডো।আপনার ডিভাইসে, ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং-এ ট্যাপ করুন এবং আপনার ডিভাইসটি পেয়ার করুন:
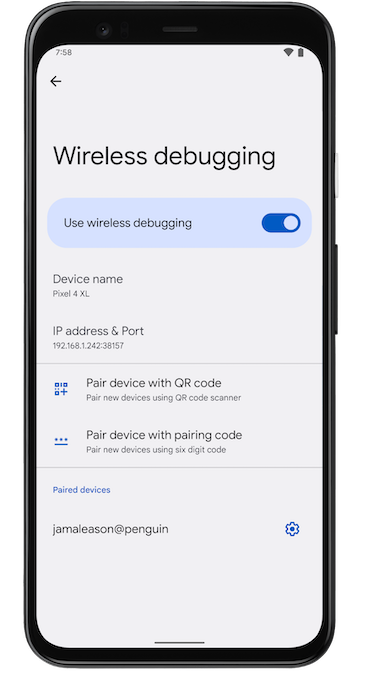 চিত্র ৩। গুগল পিক্সেল ফোনে ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং সেটিং এর স্ক্রিনশট।
চিত্র ৩। গুগল পিক্সেল ফোনে ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং সেটিং এর স্ক্রিনশট।আপনার ডিভাইসটিকে QR কোডের সাথে পেয়ার করতে, "QR কোডের সাথে ডিভাইস পেয়ার করুন" নির্বাচন করুন এবং চিত্র 2-এ দেখানো Wi-Fi পপআপের মাধ্যমে ডিভাইস পেয়ার করুন থেকে প্রাপ্ত QR কোডটি স্ক্যান করুন।
আপনার ডিভাইসটিকে একটি পেয়ারিং কোডের সাথে পেয়ার করতে, "Pair devices over Wi-Fi" পপআপ থেকে "Pair device with pairing code" নির্বাচন করুন। আপনার ডিভাইসে, "Pairing code" ব্যবহার করে "Pair" নির্বাচন করুন এবং প্রদত্ত ছয়-সংখ্যার কোডটি নোট করুন। "Pair devices over Wi-Fi" উইন্ডোতে আপনার ডিভাইসটি প্রদর্শিত হলে, আপনি "Pair" নির্বাচন করতে পারেন এবং আপনার ডিভাইসে প্রদর্শিত ছয়-সংখ্যার কোডটি লিখতে পারেন।
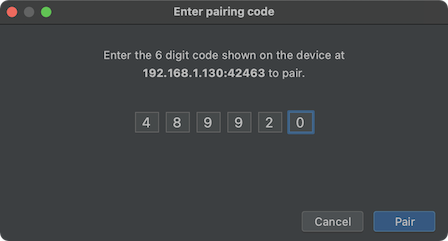 চিত্র ৪। ছয়-সংখ্যার কোড এন্ট্রির উদাহরণ।
চিত্র ৪। ছয়-সংখ্যার কোড এন্ট্রির উদাহরণ।
আপনার ডিভাইসটি পেয়ার করার পরে, আপনি আপনার ডিভাইসে আপনার অ্যাপটি স্থাপন করার চেষ্টা করতে পারেন।
অন্য কোনও ডিভাইস পেয়ার করতে অথবা আপনার ওয়ার্কস্টেশনে বর্তমান ডিভাইসটি ভুলে যেতে, আপনার ডিভাইসে ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং -এ নেভিগেট করুন। পেয়ারড ডিভাইসের অধীনে আপনার ওয়ার্কস্টেশনের নাম ট্যাপ করুন এবং Forget নির্বাচন করুন।
আপনি যদি দ্রুত ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং চালু এবং বন্ধ করতে চান, তাহলে আপনি ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিংয়ের জন্য কুইক সেটিংস ডেভেলপার টাইল ব্যবহার করতে পারেন, যা ডেভেলপার অপশন > কুইক সেটিংস ডেভেলপার টাইলসে পাওয়া যায়।
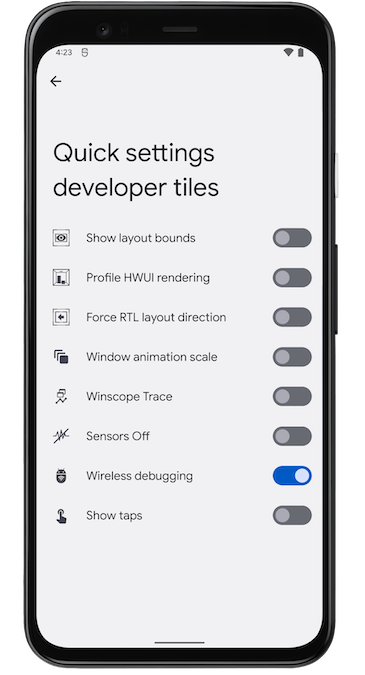 চিত্র ৫. কুইক সেটিংস ডেভেলপার টাইলস সেটিং আপনাকে দ্রুত ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং চালু এবং বন্ধ করতে দেয়।
চিত্র ৫. কুইক সেটিংস ডেভেলপার টাইলস সেটিং আপনাকে দ্রুত ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং চালু এবং বন্ধ করতে দেয়।
কমান্ড লাইন ব্যবহার করে ওয়াই-ফাই সংযোগ
বিকল্পভাবে, অ্যান্ড্রয়েড স্টুডিও ছাড়াই কমান্ড লাইন ব্যবহার করে আপনার ডিভাইসের সাথে সংযোগ করতে, এই পদক্ষেপগুলি অনুসরণ করুন:
আপনার ডিভাইসে ডেভেলপার অপশন সক্রিয় করুন, যেমনটি আগে বর্ণনা করা হয়েছে।
আপনার ডিভাইসে ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং সক্ষম করুন, যেমনটি আগে বর্ণিত হয়েছে।
আপনার ওয়ার্কস্টেশনে, একটি টার্মিনাল উইন্ডো খুলুন এবং
android_sdk/platform-toolsএ নেভিগেট করুন।"পেয়ারিং কোড সহ ডিভাইস পেয়ার করুন" নির্বাচন করে আপনার আইপি ঠিকানা, পোর্ট নম্বর এবং পেয়ারিং কোড খুঁজুন। ডিভাইসে প্রদর্শিত আইপি ঠিকানা, পোর্ট নম্বর এবং পেয়ারিং কোডটি নোট করুন।
আপনার ওয়ার্কস্টেশনের টার্মিনালে,
adb pair ipaddr:portচালান। উপরে থেকে IP ঠিকানা এবং পোর্ট নম্বর ব্যবহার করুন।অনুরোধ করা হলে, নীচে দেখানো পেয়ারিং কোডটি লিখুন।
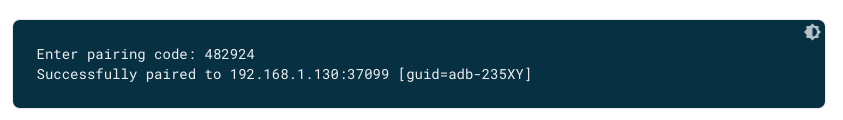 চিত্র ৬। একটি বার্তা নির্দেশ করে যে আপনার ডিভাইসটি সফলভাবে জোড়া হয়েছে।
চিত্র ৬। একটি বার্তা নির্দেশ করে যে আপনার ডিভাইসটি সফলভাবে জোড়া হয়েছে।
ওয়্যারলেস সংযোগের সমস্যা সমাধান করুন
যদি আপনার ডিভাইসের সাথে ওয়্যারলেসভাবে সংযোগ করতে সমস্যা হয়, তাহলে সমস্যা সমাধানের জন্য নিম্নলিখিত সমস্যা সমাধানের ধাপগুলি চেষ্টা করে দেখুন।
আপনার ওয়ার্কস্টেশন এবং ডিভাইস পূর্বশর্ত পূরণ করে কিনা তা পরীক্ষা করুন।
এই বিভাগের শুরুতে তালিকাভুক্ত পূর্বশর্তগুলি পূরণ করে কিনা তা পরীক্ষা করুন।
অন্যান্য পরিচিত সমস্যাগুলির জন্য পরীক্ষা করুন
ওয়্যারলেস ডিবাগিং (adb অথবা Android Studio সহ) সম্পর্কিত বর্তমান পরিচিত সমস্যাগুলির একটি তালিকা এবং সেগুলি কীভাবে সমাধান করবেন তা নীচে দেওয়া হল:
ওয়াই-ফাই সংযোগ হচ্ছে না : কর্পোরেট ওয়াই-ফাই নেটওয়ার্কের মতো নিরাপদ ওয়াই-ফাই নেটওয়ার্কগুলি p2p সংযোগগুলিকে ব্লক করে দিতে পারে এবং আপনাকে ওয়াই-ফাইয়ের মাধ্যমে সংযোগ করতে দেয় না। কেবল বা অন্য কোনও (নন-কর্প) ওয়াই-ফাই নেটওয়ার্ক দিয়ে সংযোগ করার চেষ্টা করুন।
adb connect ip : portআরেকটি বিকল্প, যদি কোনও নন-কর্প নেটওয়ার্ক ব্যবহার করা একটি বিকল্প হয়।Wi-Fi-এর মাধ্যমে
adbকখনও কখনও স্বয়ংক্রিয়ভাবে বন্ধ হয়ে যায় : ডিভাইসটি যদি Wi-Fi নেটওয়ার্ক পরিবর্তন করে অথবা নেটওয়ার্ক থেকে সংযোগ বিচ্ছিন্ন করে তবে এটি ঘটতে পারে। সমাধানের জন্য, নেটওয়ার্কে পুনরায় সংযোগ করুন।সফলভাবে পেয়ার করার পর ডিভাইসটি সংযোগ করছে না :
adbপেয়ার করা ডিভাইসগুলি আবিষ্কার করতে এবং স্বয়ংক্রিয়ভাবে সংযোগ করতে mDNS এর উপর নির্ভর করে। যদি আপনার নেটওয়ার্ক বা ডিভাইস কনফিগারেশন mDNS সমর্থন না করে বা এটি অক্ষম করে থাকে, তাহলে আপনাকেadb connect ip : portব্যবহার করে ম্যানুয়ালি ডিভাইসের সাথে সংযোগ করতে হবে।
প্রাথমিক USB সংযোগের পরে একটি ডিভাইসের সাথে ওয়্যারলেসভাবে সংযোগ করুন (শুধুমাত্র Android 10 এবং তার নিচের সংস্করণগুলিতে উপলব্ধ বিকল্প)
দ্রষ্টব্য: এই ওয়ার্কফ্লোটি অ্যান্ড্রয়েড ১১ (এবং উচ্চতর) এর ক্ষেত্রেও প্রযোজ্য, সতর্কতা হল এতে ফিজিক্যাল ইউএসবি-র মাধ্যমে একটি *প্রাথমিক* সংযোগও অন্তর্ভুক্ত।
দ্রষ্টব্য: নিম্নলিখিত নির্দেশাবলী Android 10 (API লেভেল 29) বা তার নিচের ভার্সনে চলমান Wear ডিভাইসের ক্ষেত্রে প্রযোজ্য নয়। আরও তথ্যের জন্য Wear OS অ্যাপ ডিবাগ করার নির্দেশিকাটি দেখুন।
adb সাধারণত USB এর মাধ্যমে ডিভাইসের সাথে যোগাযোগ করে, তবে আপনি Wi-Fi এর মাধ্যমেও adb ব্যবহার করতে পারেন। Android 10 (API লেভেল 29) বা তার নিচের ভার্সন চলমান একটি ডিভাইস সংযোগ করতে, USB এর মাধ্যমে এই প্রাথমিক পদক্ষেপগুলি অনুসরণ করুন:
- আপনার অ্যান্ড্রয়েড ডিভাইস এবং
adbহোস্ট কম্পিউটারকে একটি সাধারণ ওয়াই-ফাই নেটওয়ার্কের সাথে সংযুক্ত করুন। - একটি USB কেবল ব্যবহার করে ডিভাইসটিকে হোস্ট কম্পিউটারের সাথে সংযুক্ত করুন।
- ৫৫৫৫ পোর্টে একটি TCP/IP সংযোগ শোনার জন্য টার্গেট ডিভাইসটি সেট করুন:
adb tcpip 5555
- লক্ষ্য ডিভাইস থেকে USB কেবলটি সংযোগ বিচ্ছিন্ন করুন।
- অ্যান্ড্রয়েড ডিভাইসের আইপি ঠিকানাটি খুঁজুন। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, একটি নেক্সাস ডিভাইসে, আপনি সেটিংস > ট্যাবলেট সম্পর্কে (অথবা ফোন সম্পর্কে ) > স্থিতি > আইপি ঠিকানা এ আইপি ঠিকানাটি খুঁজে পেতে পারেন।
- ডিভাইসটির আইপি ঠিকানা দিয়ে সংযোগ করুন:
adb connect device_ip_address:5555
- নিশ্চিত করুন যে আপনার হোস্ট কম্পিউটারটি লক্ষ্য ডিভাইসের সাথে সংযুক্ত আছে:
$ adb devices List of devices attached device_ip_address:5555 device
দ্রষ্টব্য: সাবধান থাকুন যে সমস্ত অ্যাক্সেস পয়েন্ট উপযুক্ত নয়। আপনাকে এমন একটি অ্যাক্সেস পয়েন্ট ব্যবহার করতে হতে পারে যার ফায়ারওয়াল adb সমর্থন করার জন্য সঠিকভাবে কনফিগার করা আছে।
আপনার ডিভাইসটি এখন adb এর সাথে সংযুক্ত।
যদি আপনার ডিভাইসের সাথে adb সংযোগ বিচ্ছিন্ন হয়ে যায়:
- নিশ্চিত করুন যে আপনার হোস্টটি এখনও আপনার অ্যান্ড্রয়েড ডিভাইসের মতো একই Wi-Fi নেটওয়ার্কের সাথে সংযুক্ত আছে।
- আবার
adb connectধাপটি সম্পাদন করে পুনরায় সংযোগ করুন। - যদি এটি কাজ না করে, তাহলে আপনার
adbহোস্ট রিসেট করুন:adb kill-server
তারপর শুরু থেকে আবার শুরু করো।
ডিভাইসের জন্য কোয়েরি
adb কমান্ড দেওয়ার আগে, adb সার্ভারের সাথে কোন ডিভাইসের ইন্সট্যান্স সংযুক্ত আছে তা জেনে রাখা সহায়ক। devices কমান্ড ব্যবহার করে সংযুক্ত ডিভাইসের একটি তালিকা তৈরি করুন:
adb devices -l
প্রতিক্রিয়ায়, adb প্রতিটি ডিভাইসের জন্য এই স্থিতির তথ্য প্রিন্ট করে:
- সিরিয়াল নম্বর:
adbএকটি স্ট্রিং তৈরি করে যা ডিভাইসটিকে তার পোর্ট নম্বর দ্বারা অনন্যভাবে সনাক্ত করে। এখানে একটি উদাহরণ সিরিয়াল নম্বর দেওয়া হল:emulator-5554 - অবস্থা: ডিভাইসের সংযোগ অবস্থা নিম্নলিখিতগুলির মধ্যে একটি হতে পারে:
-
offline: ডিভাইসটিadbএর সাথে সংযুক্ত নেই অথবা সাড়া দিচ্ছে না। -
device: ডিভাইসটিadbসার্ভারের সাথে সংযুক্ত। মনে রাখবেন যে এই অবস্থাটি বোঝায় না যে অ্যান্ড্রয়েড সিস্টেম সম্পূর্ণরূপে বুট এবং কার্যকরী, কারণ সিস্টেমটি বুট করার সময় ডিভাইসটিadbএর সাথে সংযুক্ত হয়। বুট-আপের পরে, এটি একটি ডিভাইসের স্বাভাবিক কার্যকরী অবস্থা। -
no device: কোনও ডিভাইস সংযুক্ত নেই।
-
- বর্ণনা: যদি আপনি
-lবিকল্পটি অন্তর্ভুক্ত করেন, তাহলেdevicesকমান্ড আপনাকে ডিভাইসটি কী তা বলে দেবে। এই তথ্যটি সহায়ক যখন আপনার একাধিক ডিভাইস সংযুক্ত থাকে যাতে আপনি তাদের মধ্যে পার্থক্য করতে পারেন।
নিচের উদাহরণে devices কমান্ড এবং এর আউটপুট দেখানো হয়েছে। তিনটি ডিভাইস চলমান রয়েছে। তালিকার প্রথম দুটি লাইন হল এমুলেটর, এবং তৃতীয় লাইন হল একটি হার্ডওয়্যার ডিভাইস যা কম্পিউটারের সাথে সংযুক্ত।
$ adb devices List of devices attached emulator-5556 device product:sdk_google_phone_x86_64 model:Android_SDK_built_for_x86_64 device:generic_x86_64 emulator-5554 device product:sdk_google_phone_x86 model:Android_SDK_built_for_x86 device:generic_x86 0a388e93 device usb:1-1 product:razor model:Nexus_7 device:flo
এমুলেটর তালিকাভুক্ত নয়
adb devices কমান্ডের একটি কর্নার-কেস কমান্ড সিকোয়েন্স থাকে যার ফলে চলমান এমুলেটরগুলি adb devices আউটপুটে প্রদর্শিত হয় না যদিও এমুলেটরগুলি আপনার ডেস্কটপে দৃশ্যমান থাকে। এটি তখন ঘটে যখন নিম্নলিখিত সমস্ত শর্ত সত্য হয়:
-
adbসার্ভারটি চলছে না। - আপনি
-portঅথবা-portsবিকল্পের সাথেemulatorকমান্ড ব্যবহার করেন যার পোর্ট মান ৫৫৫৪ এবং ৫৫৮৪ এর মধ্যে বিজোড় সংখ্যাযুক্ত। - আপনার বেছে নেওয়া বিজোড় সংখ্যার পোর্টটি ব্যস্ত নয়, তাই নির্দিষ্ট পোর্ট নম্বরে পোর্ট সংযোগ করা যেতে পারে — অথবা, যদি এটি ব্যস্ত থাকে, তাহলে এমুলেটরটি অন্য পোর্টে স্যুইচ করে যা 2-এর প্রয়োজনীয়তা পূরণ করে।
- এমুলেটর শুরু করার পর আপনি
adbসার্ভার শুরু করবেন।
এই পরিস্থিতি এড়ানোর একটি উপায় হল এমুলেটরকে নিজস্ব পোর্ট বেছে নিতে দেওয়া এবং একসাথে ১৬টির বেশি এমুলেটর চালানো যাবে না। আরেকটি উপায় হল emulator কমান্ড ব্যবহার করার আগে সর্বদা adb সার্ভার চালু করা, যেমনটি নিম্নলিখিত উদাহরণগুলিতে ব্যাখ্যা করা হয়েছে।
উদাহরণ ১: নিম্নলিখিত কমান্ড ক্রমানুসারে, adb devices কমান্ড adb সার্ভার শুরু করে, কিন্তু ডিভাইসের তালিকা প্রদর্শিত হয় না।
adb সার্ভার বন্ধ করুন এবং প্রদর্শিত ক্রমে নিম্নলিখিত কমান্ডগুলি লিখুন। AVD নামের জন্য, আপনার সিস্টেম থেকে একটি বৈধ AVD নাম দিন। AVD নামের তালিকা পেতে, emulator -list-avds টাইপ করুন। emulator কমান্ডটি android_sdk /tools ডিরেক্টরিতে রয়েছে।
$ adb kill-server $ emulator -avd Nexus_6_API_25 -port 5555 $ adb devices List of devices attached * daemon not running. starting it now on port 5037 * * daemon started successfully *
উদাহরণ ২: নিম্নলিখিত কমান্ড ক্রমানুসারে, adb devices ডিভাইসগুলির তালিকা প্রদর্শন করে কারণ adb সার্ভারটি প্রথমে শুরু হয়েছিল।
adb devices আউটপুটে এমুলেটরটি দেখতে, adb সার্ভারটি বন্ধ করুন, এবং তারপর emulator কমান্ড ব্যবহার করার পরে এবং adb devices কমান্ড ব্যবহার করার আগে এটি আবার শুরু করুন, নিম্নরূপ:
$ adb kill-server $ emulator -avd Nexus_6_API_25 -port 5557 $ adb start-server $ adb devices List of devices attached emulator-5557 device
এমুলেটর কমান্ড-লাইন বিকল্পগুলি সম্পর্কে আরও তথ্যের জন্য, কমান্ড-লাইন স্টার্টআপ বিকল্পগুলি দেখুন।
একটি নির্দিষ্ট ডিভাইসে কমান্ড পাঠান
যদি একাধিক ডিভাইস চলমান থাকে, তাহলে adb কমান্ড দেওয়ার সময় আপনাকে অবশ্যই লক্ষ্য ডিভাইসটি নির্দিষ্ট করতে হবে। লক্ষ্য নির্দিষ্ট করতে, এই পদক্ষেপগুলি অনুসরণ করুন:
- টার্গেটের সিরিয়াল নম্বর পেতে
devicesকমান্ড ব্যবহার করুন। - একবার আপনার সিরিয়াল নম্বর হয়ে গেলে, সিরিয়াল নম্বর নির্দিষ্ট করতে
adbকমান্ডের সাথে-sবিকল্পটি ব্যবহার করুন।- যদি আপনি অনেক
adbকমান্ড ইস্যু করতে চান, তাহলে আপনি$ANDROID_SERIALএনভায়রনমেন্ট ভেরিয়েবলটি সিরিয়াল নম্বর ধারণ করার জন্য সেট করতে পারেন। - যদি আপনি
-sএবং$ANDROID_SERIALউভয়ই ব্যবহার করেন,-s$ANDROID_SERIALকে ওভাররাইড করে।
- যদি আপনি অনেক
নিম্নলিখিত উদাহরণে, সংযুক্ত ডিভাইসের তালিকা পাওয়া যায়, এবং তারপর ডিভাইসগুলির একটির সিরিয়াল নম্বর ব্যবহার করে সেই ডিভাইসে helloWorld.apk ইনস্টল করা হয়:
$ adb devices List of devices attached emulator-5554 device emulator-5555 device 0.0.0.0:6520 device # To install on emulator-5555 $ adb -s emulator-5555 install helloWorld.apk # To install on 0.0.0.0:6520 $ adb -s 0.0.0.0:6520 install helloWorld.apk
দ্রষ্টব্য: একাধিক ডিভাইস উপলব্ধ থাকাকালীন যদি আপনি একটি টার্গেট ডিভাইস নির্দিষ্ট না করে একটি কমান্ড জারি করেন, তাহলে adb "adb: একাধিক ডিভাইস/এমুলেটর" একটি ত্রুটি প্রদর্শন করে।
যদি আপনার একাধিক ডিভাইস থাকে কিন্তু শুধুমাত্র একটি এমুলেটর থাকে, তাহলে এমুলেটরে কমান্ড পাঠাতে -e বিকল্পটি ব্যবহার করুন। যদি একাধিক ডিভাইস থাকে কিন্তু শুধুমাত্র একটি হার্ডওয়্যার ডিভাইস সংযুক্ত থাকে, তাহলে হার্ডওয়্যার ডিভাইসে কমান্ড পাঠাতে -d বিকল্পটি ব্যবহার করুন।
একটি অ্যাপ ইনস্টল করুন
আপনি install কমান্ডের সাহায্যে একটি এমুলেটর বা সংযুক্ত ডিভাইসে একটি APK ইনস্টল করতে adb ব্যবহার করতে পারেন:
adb install path_to_apk
একটি পরীক্ষামূলক APK ইনস্টল করার সময় আপনাকে install কমান্ডের সাথে -t বিকল্পটি ব্যবহার করতে হবে। আরও তথ্যের জন্য, -t দেখুন।
একাধিক APK ইনস্টল করতে install-multiple ব্যবহার করুন। আপনি যদি Play Console থেকে আপনার অ্যাপের জন্য একটি নির্দিষ্ট ডিভাইসের জন্য সমস্ত APK ডাউনলোড করেন এবং সেগুলি একটি এমুলেটর বা ফিজিক্যাল ডিভাইসে ইনস্টল করতে চান তবে এটি কার্যকর।
একটি এমুলেটর/ডিভাইস ইনস্ট্যান্সে ইনস্টল করতে পারেন এমন একটি APK ফাইল কীভাবে তৈরি করবেন সে সম্পর্কে আরও তথ্যের জন্য, "আপনার অ্যাপ তৈরি করুন এবং চালান" দেখুন।
দ্রষ্টব্য: আপনি যদি অ্যান্ড্রয়েড স্টুডিও ব্যবহার করেন, তাহলে এমুলেটর বা ডিভাইসে আপনার অ্যাপ ইনস্টল করার জন্য সরাসরি adb ব্যবহার করার প্রয়োজন নেই। পরিবর্তে, অ্যান্ড্রয়েড স্টুডিও আপনার জন্য অ্যাপটির প্যাকেজিং এবং ইনস্টলেশন পরিচালনা করে।
পোর্ট ফরওয়ার্ডিং সেট আপ করুন
forward কমান্ড ব্যবহার করে ইচ্ছামত পোর্ট ফরওয়ার্ডিং সেট আপ করা যা একটি নির্দিষ্ট হোস্ট পোর্টের অনুরোধগুলিকে একটি ডিভাইসের অন্য পোর্টে ফরোয়ার্ড করে। নিম্নলিখিত উদাহরণটি হোস্ট পোর্ট 6100 কে ডিভাইস পোর্ট 7100 এ ফরোয়ার্ডিং সেট আপ করে:
adb forward tcp:6100 tcp:7100
নিম্নলিখিত উদাহরণটি হোস্ট পোর্ট 6100 কে local:logd এ ফরোয়ার্ড করার পদ্ধতি সেট করে:
adb forward tcp:6100 local:logd
ডিভাইসের কোন নির্দিষ্ট পোর্টে কী পাঠানো হচ্ছে তা নির্ধারণ করার চেষ্টা করলে এটি কার্যকর হতে পারে। সমস্ত প্রাপ্ত ডেটা সিস্টেম-লগিং ডেমনে লেখা হবে এবং ডিভাইস লগে প্রদর্শিত হবে।
একটি ডিভাইসে এবং থেকে ফাইলগুলি অনুলিপি করুন
ডিভাইসে এবং ডিভাইস থেকে ফাইল কপি করার জন্য pull এবং push কমান্ড ব্যবহার করুন। install কমান্ডের বিপরীতে, যা শুধুমাত্র একটি নির্দিষ্ট স্থানে একটি APK ফাইল কপি করে, pull এবং push কমান্ড আপনাকে ডিভাইসের যেকোনো স্থানে ইচ্ছামত ডিরেক্টরি এবং ফাইল কপি করতে দেয়।
ডিভাইস থেকে একটি ফাইল বা ডিরেক্টরি এবং এর সাব-ডিরেক্টরি কপি করতে, নিম্নলিখিতগুলি করুন:
adb pull remote local
ডিভাইসে একটি ফাইল বা ডিরেক্টরি এবং এর সাব-ডিরেক্টরি কপি করতে, নিম্নলিখিতগুলি করুন:
adb push local remote
আপনার ডেভেলপমেন্ট মেশিনে (স্থানীয়) এবং ডিভাইসে (দূরবর্তী) টার্গেট ফাইল/ডিরেক্টরির পাথ দিয়ে local এবং remote প্রতিস্থাপন করুন। উদাহরণস্বরূপ:
adb push myfile.txt /sdcard/myfile.txt
adb সার্ভার বন্ধ করুন
কিছু ক্ষেত্রে, সমস্যা সমাধানের জন্য আপনাকে adb সার্ভার প্রক্রিয়াটি বন্ধ করে পুনরায় চালু করতে হতে পারে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, যদি adb কোনও কমান্ডে সাড়া না দেয় তবে এটি হতে পারে।
adb সার্ভার বন্ধ করতে, adb kill-server কমান্ডটি ব্যবহার করুন। এরপর আপনি অন্য যেকোনো adb কমান্ড জারি করে সার্ভারটি পুনরায় চালু করতে পারেন।
adb কমান্ড ইস্যু করুন
আপনার ডেভেলপমেন্ট মেশিনের কমান্ড লাইন থেকে অথবা নিম্নলিখিত ব্যবহার করে একটি স্ক্রিপ্ট থেকে adb কমান্ড ইস্যু করুন:
adb [-d | -e | -s serial_number] command
যদি শুধুমাত্র একটি এমুলেটর চলমান থাকে অথবা শুধুমাত্র একটি ডিভাইস সংযুক্ত থাকে, তাহলে ডিফল্টরূপে adb কমান্ডটি সেই ডিভাইসে পাঠানো হয়। যদি একাধিক এমুলেটর চলমান থাকে এবং/অথবা একাধিক ডিভাইস সংযুক্ত থাকে, তাহলে আপনাকে -d , -e , অথবা -s বিকল্পটি ব্যবহার করে লক্ষ্য ডিভাইসটি নির্দিষ্ট করতে হবে যেখানে কমান্ডটি নির্দেশিত হবে।
নিম্নলিখিত কমান্ড ব্যবহার করে আপনি সমস্ত সমর্থিত adb কমান্ডের একটি বিস্তারিত তালিকা দেখতে পাবেন:
adb --help
শেল কমান্ড ইস্যু করুন
আপনি adb এর মাধ্যমে ডিভাইস কমান্ড ইস্যু করতে অথবা একটি ইন্টারেক্টিভ শেল শুরু করতে shell কমান্ড ব্যবহার করতে পারেন। একটি একক কমান্ড ইস্যু করতে, shell কমান্ডটি এভাবে ব্যবহার করুন:
adb [-d |-e | -s serial_number] shell shell_command
একটি ডিভাইসে একটি ইন্টারেক্টিভ শেল শুরু করতে, shell কমান্ডটি এভাবে ব্যবহার করুন:
adb [-d | -e | -s serial_number] shell
একটি ইন্টারেক্টিভ শেল থেকে বেরিয়ে আসতে, Control+D টিপুন অথবা exit টাইপ করুন।
অ্যান্ড্রয়েড বেশিরভাগ সাধারণ ইউনিক্স কমান্ড-লাইন টুল সরবরাহ করে। উপলব্ধ টুলের তালিকার জন্য, নিম্নলিখিত কমান্ডটি ব্যবহার করুন:
adb shell ls /system/bin
--help আর্গুমেন্টের মাধ্যমে বেশিরভাগ কমান্ডের জন্য সাহায্য পাওয়া যায়। অনেক শেল কমান্ড toybox দ্বারা সরবরাহ করা হয়। সমস্ত toybox কমান্ডের জন্য প্রযোজ্য সাধারণ সাহায্য toybox --help এর মাধ্যমে পাওয়া যায়।
অ্যান্ড্রয়েড প্ল্যাটফর্ম টুলস ২৩ এবং উচ্চতর সংস্করণের সাথে, adb আর্গুমেন্টগুলিকে ssh(1) কমান্ডের মতোই পরিচালনা করে। এই পরিবর্তনটি কমান্ড ইনজেকশনের সাথে অনেক সমস্যার সমাধান করেছে এবং শেল মেটাচ্যারেক্টার ধারণকারী কমান্ডগুলিকে নিরাপদে কার্যকর করা সম্ভব করেছে, যেমন adb install Let\'sGo.apk । এই পরিবর্তনের অর্থ হল শেল মেটাচ্যারেক্টার ধারণকারী যেকোনো কমান্ডের ব্যাখ্যাও পরিবর্তিত হয়েছে।
উদাহরণস্বরূপ, adb shell setprop key ' two words ' এখন একটি ত্রুটি, কারণ উদ্ধৃতিগুলি স্থানীয় শেল দ্বারা গ্রাস করা হয় এবং ডিভাইসটি adb shell setprop key two words দেখতে পায়। কমান্ডটি কাজ করার জন্য, দুবার উদ্ধৃতি করুন, একবার স্থানীয় শেলের জন্য এবং একবার রিমোট শেলের জন্য, যেমনটি আপনি ssh(1) এর সাথে করেন। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, adb shell setprop key "' two words '" কাজ করে কারণ স্থানীয় শেল উদ্ধৃতিটির বাইরের স্তর নেয় এবং ডিভাইসটি এখনও উদ্ধৃতিটির ভিতরের স্তর দেখতে পায়: setprop key 'two words' । এস্কেপিংও একটি বিকল্প, তবে দুবার উদ্ধৃতি করা সাধারণত সহজ।
লগক্যাট কমান্ড-লাইন টুলটিও দেখুন, যা সিস্টেম লগ পর্যবেক্ষণের জন্য কার্যকর।
অ্যাক্টিভিটি ম্যানেজারকে কল করুন
একটি adb শেলের মধ্যে, আপনি অ্যাক্টিভিটি ম্যানেজার ( am ) টুল দিয়ে বিভিন্ন সিস্টেম অ্যাকশন সম্পাদনের জন্য কমান্ড জারি করতে পারেন, যেমন একটি অ্যাক্টিভিটি শুরু করা, একটি প্রক্রিয়া জোর করে বন্ধ করা, একটি ইনটেন্ট সম্প্রচার করা, ডিভাইসের স্ক্রিন বৈশিষ্ট্য পরিবর্তন করা এবং আরও অনেক কিছু।
শেলের মধ্যে থাকাকালীন, am সিনট্যাক্সটি হল:
am command
আপনি রিমোট শেল প্রবেশ না করেই সরাসরি adb থেকে একটি অ্যাক্টিভিটি ম্যানেজার কমান্ড ইস্যু করতে পারেন। উদাহরণস্বরূপ:
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW
সারণি ১. উপলব্ধ কার্যকলাপ ব্যবস্থাপক কমান্ড
| কমান্ড | বিবরণ |
|---|---|
start [ options ] intent | intent দ্বারা নির্দিষ্ট একটি Activity শুরু করুন।উদ্দেশ্য আর্গুমেন্টের জন্য স্পেসিফিকেশন দেখুন। বিকল্পগুলি হল:
|
startservice [ options ] intent | intent দ্বারা নির্দিষ্ট Service শুরু করুন।উদ্দেশ্য আর্গুমেন্টের জন্য স্পেসিফিকেশন দেখুন। বিকল্পগুলি হল:
|
force-stop package | package সাথে সম্পর্কিত সবকিছু জোর করে বন্ধ করুন। |
kill [ options ] package | package সাথে সম্পর্কিত সকল প্রক্রিয়া বন্ধ করে দেয়। এই কমান্ডটি কেবলমাত্র সেই প্রক্রিয়াগুলি বন্ধ করে দেয় যেগুলি বন্ধ করা নিরাপদ এবং ব্যবহারকারীর অভিজ্ঞতাকে প্রভাবিত করবে না।বিকল্পগুলি হল:
|
kill-all | সমস্ত ব্যাকগ্রাউন্ড প্রসেস বন্ধ করুন। |
broadcast [ options ] intent | একটি সম্প্রচারের উদ্দেশ্য ইস্যু করুন। উদ্দেশ্য আর্গুমেন্টের জন্য স্পেসিফিকেশন দেখুন। বিকল্পগুলি হল:
|
instrument [ options ] component | একটি Instrumentation ইনস্ট্যান্স দিয়ে পর্যবেক্ষণ শুরু করুন। সাধারণত লক্ষ্য component হল test_package / runner_class ফর্ম।বিকল্পগুলি হল:
|
profile start process file | process প্রোফাইলার শুরু করুন, file ফলাফল লিখুন। |
profile stop process | process চলাকালীন প্রোফাইলার বন্ধ করুন। |
dumpheap [ options ] process file | process স্তূপ ফেলে দিন, file লিখুন।বিকল্পগুলি হল:
|
dumpbitmaps [ options ] [-p process ] | process থেকে বিটম্যাপ তথ্য ডাম্প করুন (API স্তর 36 এবং তার উপরে)।বিকল্পগুলি হল:
process নির্দিষ্ট না করা থাকে, তাহলে সমস্ত প্রক্রিয়া থেকে বিটম্যাপ ডাম্প করা হবে। |
set-debug-app [ options ] package | অ্যাপ package ডিবাগে সেট করুন।বিকল্পগুলি হল:
|
clear-debug-app | set-debug-app দিয়ে ডিবাগিংয়ের জন্য পূর্ববর্তী সেট প্যাকেজটি সাফ করুন। |
monitor [ options ] | ক্র্যাশ বা ANR-এর জন্য পর্যবেক্ষণ শুরু করুন। বিকল্পগুলি হল:
|
screen-compat {on | off} package | package স্ক্রিন সামঞ্জস্য মোড নিয়ন্ত্রণ করুন। |
display-size [reset | width x height ] | ডিভাইসের ডিসপ্লে সাইজ ওভাররাইড করুন। এই কমান্ডটি আপনার অ্যাপটিকে বিভিন্ন স্ক্রিন সাইজ জুড়ে পরীক্ষা করার জন্য সহায়ক, একটি বড় স্ক্রিনযুক্ত ডিভাইস ব্যবহার করে একটি ছোট স্ক্রিন রেজোলিউশন অনুকরণ করে, এবং বিপরীতভাবে। উদাহরণ: |
display-density dpi | ডিভাইসের ডিসপ্লে ঘনত্ব ওভাররাইড করুন। এই কমান্ডটি আপনার অ্যাপটিকে বিভিন্ন স্ক্রিন ঘনত্বে পরীক্ষা করার জন্য সহায়ক, কম ঘনত্বের স্ক্রিন ব্যবহার করে উচ্চ-ঘনত্বের স্ক্রিন পরিবেশ অনুকরণ করে, এবং বিপরীতভাবে। উদাহরণ: |
to-uri intent | প্রদত্ত ইন্টেন্ট স্পেসিফিকেশনটি URI হিসেবে প্রিন্ট করুন। |
to-intent-uri intent | প্রদত্ত ইন্টেন্ট স্পেসিফিকেশনটি একটি intent: URI। |
উদ্দেশ্য আর্গুমেন্টের জন্য স্পেসিফিকেশন
যেসব অ্যাক্টিভিটি ম্যানেজার কমান্ড একটি intent আর্গুমেন্ট গ্রহণ করে, আপনি নিম্নলিখিত বিকল্পগুলি ব্যবহার করে ইনটেন্ট নির্দিষ্ট করতে পারেন:
প্যাকেজ ম্যানেজারকে কল করুন ( pm )
একটি adb শেলের মধ্যে, আপনি ডিভাইসে ইনস্টল করা অ্যাপ প্যাকেজগুলিতে ক্রিয়া এবং প্রশ্ন সম্পাদনের জন্য প্যাকেজ ম্যানেজার ( pm ) টুল দিয়ে কমান্ড জারি করতে পারেন।
শেলের মধ্যে থাকাকালীন, pm সিনট্যাক্সটি হল:
pm command
আপনি রিমোট শেল প্রবেশ না করেই সরাসরি adb থেকে একটি প্যাকেজ ম্যানেজার কমান্ড ইস্যু করতে পারেন। উদাহরণস্বরূপ:
adb shell pm uninstall com.example.MyApp
সারণি ২। উপলব্ধ প্যাকেজ ম্যানেজার কমান্ড
| কমান্ড | বিবরণ |
|---|---|
list packages [ options ] filter | সমস্ত প্যাকেজ প্রিন্ট করুন, ঐচ্ছিকভাবে শুধুমাত্র সেইসব প্যাকেজ প্রিন্ট করুন যাদের প্যাকেজের নামে filter লেখা আছে।বিকল্প:
|
list permission-groups | সমস্ত পরিচিত অনুমতি গ্রুপ প্রিন্ট করুন। |
list permissions [ options ] group | সমস্ত পরিচিত অনুমতি প্রিন্ট করুন, ঐচ্ছিকভাবে শুধুমাত্র group এ থাকা অনুমতিগুলি।বিকল্প:
|
list instrumentation [ options ] | সমস্ত পরীক্ষার প্যাকেজ তালিকাভুক্ত করুন। বিকল্প:
|
list features | সিস্টেমের সমস্ত বৈশিষ্ট্য মুদ্রণ করুন। |
list libraries | বর্তমান ডিভাইস দ্বারা সমর্থিত সমস্ত লাইব্রেরি প্রিন্ট করুন। |
list users | সিস্টেমের সকল ব্যবহারকারী প্রিন্ট করুন। |
path package | প্রদত্ত package APK-এর পথটি প্রিন্ট করুন। |
install [ options ] path | সিস্টেমে path দ্বারা নির্দিষ্ট একটি প্যাকেজ ইনস্টল করুন।বিকল্প:
|
uninstall [ options ] package | সিস্টেম থেকে একটি প্যাকেজ সরিয়ে দেয়। বিকল্প:
|
clear package | প্যাকেজের সাথে সম্পর্কিত সমস্ত ডেটা মুছে ফেলুন। |
enable package_or_component | প্রদত্ত প্যাকেজ বা উপাদানটি সক্রিয় করুন ("প্যাকেজ/শ্রেণী" হিসাবে লেখা)। |
disable package_or_component | প্রদত্ত প্যাকেজ বা উপাদানটি ("প্যাকেজ/শ্রেণী" হিসাবে লেখা) অক্ষম করুন। |
disable-user [ options ] package_or_component | বিকল্প:
|
grant package_name permission | একটি অ্যাপকে অনুমতি দিন। Android 6.0 (API লেভেল 23) এবং তার উপরের ভার্সনে চলমান ডিভাইসগুলিতে, অনুমতিটি অ্যাপ ম্যানিফেস্টে ঘোষিত যেকোনো অনুমতি হতে পারে। Android 5.1 (API লেভেল 22) এবং তার নিচের ভার্সনে চলমান ডিভাইসগুলিতে, অ্যাপ দ্বারা সংজ্ঞায়িত একটি ঐচ্ছিক অনুমতি থাকতে হবে। |
revoke package_name permission | কোনও অ্যাপ থেকে অনুমতি প্রত্যাহার করুন। Android 6.0 (API লেভেল 23) এবং তার চেয়ে উচ্চতর সংস্করণে চলমান ডিভাইসগুলিতে, অনুমতিটি অ্যাপ ম্যানিফেস্টে ঘোষিত যেকোনো অনুমতি হতে পারে। Android 5.1 (API লেভেল 22) এবং তার চেয়ে কম সংস্করণে চলমান ডিভাইসগুলিতে, অ্যাপ দ্বারা সংজ্ঞায়িত একটি ঐচ্ছিক অনুমতি থাকতে হবে। |
set-install-location location | ডিফল্ট ইনস্টলেশনের অবস্থান পরিবর্তন করুন। অবস্থানের মান:
দ্রষ্টব্য: এটি শুধুমাত্র ডিবাগিংয়ের জন্য তৈরি। এটি ব্যবহার করলে অ্যাপগুলি ভেঙে যেতে পারে এবং অন্যান্য অবাঞ্ছিত আচরণ হতে পারে। |
get-install-location | বর্তমান ইনস্টলেশন অবস্থান ফেরত পাঠায়। মান ফেরত পাঠায়:
|
set-permission-enforced permission [true | false] | প্রদত্ত অনুমতি কার্যকর করা উচিত কিনা তা উল্লেখ করুন। |
trim-caches desired_free_space | প্রদত্ত খালি জায়গায় পৌঁছানোর জন্য ক্যাশে ফাইলগুলি ছাঁটাই করুন। |
create-user user_name | প্রদত্ত user_name দিয়ে একটি নতুন ব্যবহারকারী তৈরি করুন, ব্যবহারকারীর নতুন ব্যবহারকারী শনাক্তকারী মুদ্রণ করুন। |
remove-user user_id | প্রদত্ত user_id সহ ব্যবহারকারীকে সরিয়ে ফেলুন, সেই ব্যবহারকারীর সাথে সম্পর্কিত সমস্ত ডেটা মুছে ফেলুন। |
get-max-users | ডিভাইসটি দ্বারা সমর্থিত সর্বাধিক সংখ্যক ব্যবহারকারী প্রিন্ট করুন। |
get-app-links [ options ] [ package ] | প্রদত্ত package জন্য ডোমেন যাচাইকরণের অবস্থা প্রিন্ট করুন, অথবা যদি কোনও প্যাকেজ নির্দিষ্ট না থাকে তবে সমস্ত প্যাকেজের জন্য। রাজ্য কোডগুলি নিম্নরূপ সংজ্ঞায়িত করা হয়েছে:
Options are:
|
reset-app-links [ options ] [ package ] | Reset domain verification state for the given package, or for all packages if none is specified.
Options are:
|
verify-app-links [ --re-verify ] [ package ] | Broadcast a verification request for the given package , or for all packages if none is specified. Only sends if the package has previously not recorded a response.
|
set-app-links [--package package ] state domains | Manually set the state of a domain for a package. The domain must be declared by the package as autoVerify for this to work. This command will not report a failure for domains that could not be applied.
|
set-app-links-user-selection --user user_id [--package package ] enabled domains | Manually set the state of a host user selection for a package. The domain must be declared by the package for this to work. This command will not report a failure for domains that could not be applied.
|
set-app-links-allowed --user user_id [--package package ] allowed | Toggle the auto-verified link-handling setting for a package.
|
get-app-link-owners --user user_id [--package package ] domains | Print the owners for a specific domain for a given user in low- to high-priority order.
|
Call device policy manager ( dpm )
To help you develop and test your device management apps, issue commands to the device policy manager ( dpm ) tool. Use the tool to control the active admin app or change a policy's status data on the device.
While in a shell, the dpm syntax is:
dpm command
You can also issue a device policy manager command directly from adb without entering a remote shell:
adb shell dpm command
Table 3. Available device policy manager commands
| Command | বিবরণ |
|---|---|
set-active-admin [ options ] component | Sets component as active admin. Options are:
|
set-profile-owner [ options ] component | Set component as active admin and its package as profile owner for an existing user. Options are:
|
set-device-owner [ options ] component | Set component as active admin and its package as device owner. Options are:
|
remove-active-admin [ options ] component | Disable an active admin. The app must declare android:testOnly in the manifest. This command also removes device and profile owners.Options are:
|
clear-freeze-period-record | Clear the device's record of previously set freeze periods for system OTA updates. This is useful to avoid the device scheduling restrictions when developing apps that manage freeze periods. See Manage system updates . Supported on devices running Android 9.0 (API level 28) and higher. |
force-network-logs | Force the system to make any existing network logs ready for retrieval by a DPC. If there are connection or DNS logs available, the DPC receives the onNetworkLogsAvailable() callback. See Network activity logging .This command is rate-limited. Supported on devices running Android 9.0 (API level 28) and higher. |
force-security-logs | Force the system to make any existing security logs available to the DPC. If there are logs available, the DPC receives the onSecurityLogsAvailable() callback. See Log enterprise device activity .This command is rate-limited. Supported on devices running Android 9.0 (API level 28) and higher. |
একটি স্ক্রিনশট নিন
The screencap command is a shell utility for taking a screenshot of a device display.
While in a shell, the screencap syntax is:
screencap filename
To use screencap from the command line, enter the following:
adb shell screencap /sdcard/screen.png
Here's an example screenshot session, using the adb shell to capture the screenshot and the pull command to download the file from the device:
$ adb shell shell@ $ screencap /sdcard/screen.png shell@ $ exit $ adb pull /sdcard/screen.png
Alternatively, if you omit the filename, screencap writes the image to standard output. When combined with the -p option to specify PNG format, you can stream the device screenshot directly to a file on your local machine.
Here's an example of capturing a screenshot and saving it locally in a single command:
# use 'exec-out' instead of 'shell' to get raw data $ adb exec-out screencap -p > screen.png
Record a video
The screenrecord command is a shell utility for recording the display of devices running Android 4.4 (API level 19) and higher. The utility records screen activity to an MPEG-4 file. You can use this file to create promotional or training videos or for debugging and testing.
In a shell, use the following syntax:
screenrecord [options] filename
To use screenrecord from the command line, enter the following:
adb shell screenrecord /sdcard/demo.mp4
Stop the screen recording by pressing Control+C. Otherwise, the recording stops automatically at three minutes or the time limit set by --time-limit .
To begin recording your device screen, run the screenrecord command to record the video. Then, run the pull command to download the video from the device to the host computer. Here's an example recording session:
$ adb shell shell@ $ screenrecord --verbose /sdcard/demo.mp4 (press Control + C to stop) shell@ $ exit $ adb pull /sdcard/demo.mp4
The screenrecord utility can record at any supported resolution and bit rate you request, while retaining the aspect ratio of the device display. The utility records at the native display resolution and orientation by default, with a maximum length of three minutes.
Limitations of the screenrecord utility:
- Audio is not recorded with the video file.
- Video recording is not available for devices running Wear OS.
- Some devices might not be able to record at their native display resolution. If you encounter problems with screen recording, try using a lower screen resolution.
- Rotation of the screen during recording is not supported. If the screen does rotate during recording, some of the screen is cut off in the recording.
Table 4. screenrecord options
| বিকল্পগুলি | বিবরণ |
|---|---|
--help | Display command syntax and options |
--size width x height | Set the video size: 1280x720 . The default value is the device's native display resolution (if supported), 1280x720 if not. For best results, use a size supported by your device's Advanced Video Coding (AVC) encoder. |
--bit-rate rate | Set the video bit rate for the video, in megabits per second. The default value is 20Mbps. You can increase the bit rate to improve video quality, but doing so results in larger movie files. The following example sets the recording bit rate to 6Mbps: screenrecord --bit-rate 6000000 /sdcard/demo.mp4 |
--time-limit time | Set the maximum recording time, in seconds. The default and maximum value is 180 (3 minutes). |
--rotate | Rotate the output 90 degrees. This feature is experimental. |
--verbose | Display log information on the command-line screen. If you do not set this option, the utility does not display any information while running. |
Read ART profiles for apps
Starting in Android 7.0 (API level 24), the Android Runtime (ART) collects execution profiles for installed apps, which are used to optimize app performance. Examine the collected profiles to understand which methods are executed frequently and which classes are used during app startup.
Note: It is only possible to retrieve the execution profile filename if you have root access to the file system, for example, on an emulator.
To produce a text form of the profile information, use the following command:
adb shell cmd package dump-profiles package
To retrieve the file produced, use:
adb pull /data/misc/profman/package.prof.txt
Reset test devices
If you test your app across multiple test devices, it may be useful to reset your device between tests, for example, to remove user data and reset the test environment. You can perform a factory reset of a test device running Android 10 (API level 29) or higher using the testharness adb shell command, as shown:
adb shell cmd testharness enable
When restoring the device using testharness , the device automatically backs up the RSA key that allows debugging through the current workstation in a persistent location. That is, after the device is reset, the workstation can continue to debug and issue adb commands to the device without manually registering a new key.
Additionally, to help make it easier and more secure to keep testing your app, using the testharness to restore a device also changes the following device settings:
- The device sets up certain system settings so that initial device setup wizards do not appear. That is, the device enters a state from which you can quickly install, debug, and test your app.
- Settings:
- Disables lock screen.
- Disables emergency alerts.
- Disables auto-sync for accounts.
- Disables automatic system updates.
- অন্যান্য:
- Disables preinstalled security apps.
If your app needs to detect and adapt to the default settings of the testharness command, use the ActivityManager.isRunningInUserTestHarness() .
স্ক্লাইট
sqlite3 starts the sqlite command-line program for examining SQLite databases. It includes commands such as .dump to print the contents of a table and .schema to print the SQL CREATE statement for an existing table. You can also execute SQLite commands from the command line, as shown:
$ adb -s emulator-5554 shell $ sqlite3 /data/data/com.example.app/databases/rssitems.db SQLite version 3.3.12 Enter ".help" for instructions
Note: It is only possible to access a SQLite database if you have root access to the file system, for example, on an emulator.
For more information, see the sqlite3 command line documentation .
adb USB backends
The adb server can interact with the USB stack through two backends. It can either use the native backend of the OS (Windows, Linux, or macOS) or it can use the libusb backend. Some features, such as attach , detach , and USB speed detection, are only available when using libusb backend.
You can choose a backend by using the ADB_LIBUSB environment variable. If it isn't set, adb uses its default backend. The default behavior varies among OS. Starting with ADB v34 , the liubusb backend is used by default on all OS except Windows, where the native backend is used by default. If ADB_LIBUSB is set, it determines whether the native backend or libusb is used. See the adb manual page for more information about adb environment variables.
adb mDNS backends
ADB can use the multicast DNS protocol to automatically connect the server and devices. The ADB server ships with two backends, Bonjour (Apple's mdnsResponder) and Openscreen.
The Bonjour backend needs a daemon to be running on the host machine. On macOS Apple's built-in daemon is always running, but on Windows and Linux, the user must make sure the mdnsd daemon is up and running. If the command adb mdns check returns an error, it is likely that ADB is using the Bonjour backend but there is no Bonjour daemon running.
The Openscreen backend does not need a daemon to be running on the machine. Support for the Openscreen backend on macOS starts at ADB v35. Windows and Linux are supported as of ADB v34.
By default ADB uses the Bonjour backend. This behavior can be changed using the environment variable ADB_MDNS_OPENSCREEN (set to 1 or 0 ). See the ADB manual page for further details.
adb Burst Mode (starting with ADB 36.0.0)
Burst Mode is an experimental feature that lets ADB to keep on sending packets to a device even before the device has responded to the previous packet. This greatly increases the throughput of ADB when transferring large files and also reduces latency while debugging.
Burst Mode is disabled by default. To enable the feature, do one of the following:
- Set the environment variable
ADB_BURST_MODEto1. - In Android Studio, go to the debugger settings at File (or Android Studio on macOS) > Settings > Build, Execution, Deployment > Debugger and set ADB Server Burst Mode to Enabled .

