في Material Design، الهيكل الأساسي هو بنية أساسية توفّر منصّة مُعيارًا لواجهات المستخدم المعقدة. ويجمع هذا المظهر بين مختلف أجزاء واجهة المستخدم، مثل أشرطة التطبيقات والأزرار التفاعلية العائمة، ما يمنح التطبيقات مظهرًا وأسلوبًا متسقَين.
توافق الإصدار
يتطلّب هذا التنفيذ ضبط الحد الأدنى من إصدار حزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) لمشروعك على المستوى 21 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات أو إصدار أحدث.
التبعيات
إنشاء إطار عمل
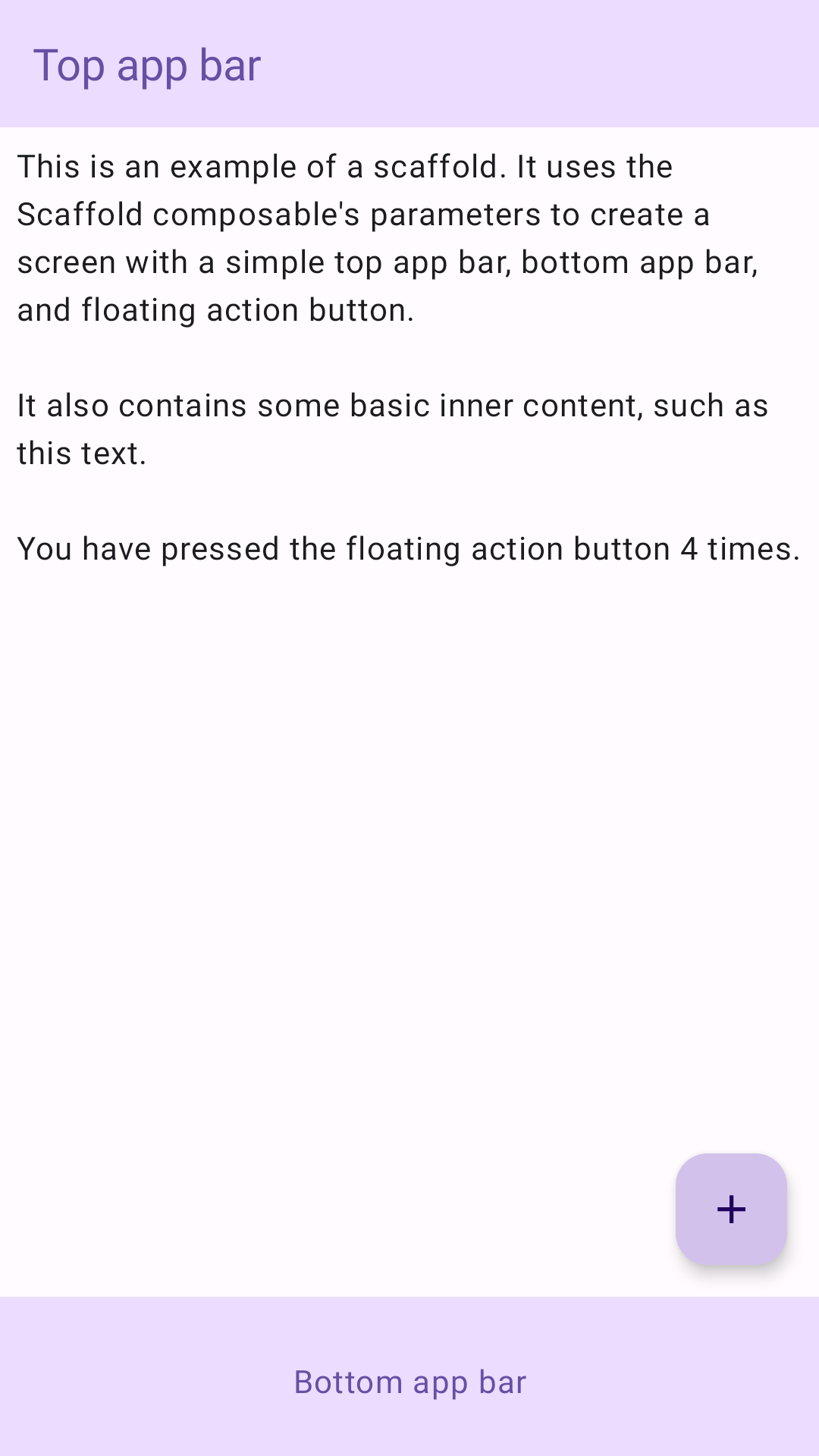
يقدّم المثال التالي مثالاً كاملاً على كيفية تنفيذ
Scaffold. يحتوي على شريط تطبيق في أعلى الشاشة وشريط تطبيق في أسفلها وزر إجراء عائم
يتفاعل مع الحالة الداخلية لتطبيق Scaffold.
النتائج
النقاط الرئيسية
توفّر العناصر القابلة للتجميع Scaffold واجهة برمجة تطبيقات مباشرة يمكنك استخدامها لجمع بنية تطبيقك بسرعة وفقًا لإرشادات Material Design.
تقبل Scaffold العديد من العناصر القابلة للإنشاء كمَعلمات. ومن بين هذه الشروط:
topBar: شريط التطبيق في أعلى الشاشةbottomBar: شريط التطبيق في أسفل الشاشةfloatingActionButton: زرّ يمرّر فوق أسفل يسار الشاشة ويُظهر الإجراءات الرئيسية.
للحصول على أمثلة أكثر تفصيلاً حول كيفية تنفيذ كلٍّ من أشرطة التطبيقات في أعلى الشاشة وفي أسفلها، يُرجى الاطّلاع على صفحة أشرطة التطبيقات.
يمكنك أيضًا تمرير محتوى Scaffold كما تفعل مع الحاويات الأخرى. وتُمرِّر
قيمة innerPadding إلى دالة lambda content التي يمكنك استخدامها بعد ذلك في العناصر المكوّنة
التابعة.
المجموعات التي تتضمّن هذا الدليل
هذا الدليل هو جزء من مجموعات الأدلة السريعة المنظَّمة التي تتناول أهداف تطوير Android الأوسع نطاقًا:
إنشاء إطار عمل للشاشة الرئيسية



