يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 15 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات رائعة للمطوّرين. توضّح الأقسام التالية هذه الميزات لمساعدتك على البدء في استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات ذات الصلة.
للحصول على قائمة مفصّلة بواجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تمت إضافتها وتعديلها وإزالتها، يُرجى الاطّلاع على تقرير الاختلافات في واجهات برمجة التطبيقات. للحصول على تفاصيل حول واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المضافة، يُرجى الانتقال إلى مرجع واجهة برمجة تطبيقات Android. بالنسبة إلى Android 15، ابحث عن واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تمت إضافتها في المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات. للتعرّف على المجالات التي قد تؤثّر فيها تغييرات النظام الأساسي في تطبيقاتك، احرص على الاطّلاع على التغييرات في سلوك Android 15 للتطبيقات التي تستهدف Android 15 ولجميع التطبيقات.
الكاميرا والوسائط
يتضمّن Android 15 مجموعة متنوعة من الميزات التي تحسّن تجربة استخدام الكاميرا والوسائط، وتتيح لك الوصول إلى الأدوات والأجهزة التي تساعد صنّاع المحتوى في تنفيذ أفكارهم الإبداعية على Android.
لمزيد من المعلومات حول أحدث الميزات والحلول المتاحة للمطوّرين في ما يخص الوسائط والكاميرا على Android، يمكنك مشاهدة جلسة إنشاء تجارب حديثة في ما يخص الوسائط والكاميرا على Android من مؤتمر Google I/O.
تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 15 ميزة تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة، وهو وضع للتعرّض التلقائي للضوء متاح في كلاً من الكاميرا 2 وإضافة "الوضع الليلي" في الكاميرا. تعمل ميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة" على تعديل مستوى تعريض المعاينة المباشرة للشاشة في ظروف الإضاءة المنخفضة. يختلف ذلك عن طريقة إنشاء الصور الثابتة من خلال إضافة الكاميرا في "الوضع الليلي"، لأنّ "الوضع الليلي" يجمع سلسلة من الصور لإنشاء صورة واحدة محسّنة. على الرغم من أنّ وضع "الإضاءة المنخفضة" يعمل بشكلٍ جيد جدًا لإنشاء صورة ثابتة، إلا أنّه لا يمكنه إنشاء بثٍ متواصلٍ من اللقطات، ولكن يمكن لميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة" فعل ذلك. وبالتالي، توفّر ميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة" ميزات كاميرا ، مثل:
- توفير معاينة محسّنة للصور، ما يتيح للمستخدمين ضبط عناصر الصور المنخفضة الإضاءة بشكلٍ أفضل
- مسح رموز الاستجابة السريعة ضوئيًا في الإضاءة المنخفضة
في حال تفعيل ميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة"، يتم تفعيلها تلقائيًا عند انخفاض مستوى الإضاءة، ويتم إيقافها عند زيادة الإضاءة.
يمكن للتطبيقات تسجيل فيديو من المعاينة المباشرة على الشاشة في ظروف الإضاءة المنخفضة لحفظه بدرجة سطوع أفضل.
لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة.
عناصر التحكّم في الكاميرا داخل التطبيق
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 15 إضافة تتيح التحكّم بشكل أكبر في أجهزة الكاميرا و algoritms على الأجهزة المتوافقة:
- تعديلات متقدّمة لقوة الفلاش تتيح التحكّم بدقة في كثافة الفلاش في كلا الوضعَين
SINGLEوTORCHأثناء التقاط الصور
التحكّم في مساحة HDR
Android 15 chooses HDR headroom that is appropriate for the underlying device
capabilities and bit-depth of the panel. For pages that have lots of SDR
content, such as a messaging app displaying a single HDR thumbnail, this
behavior can end up adversely influencing the perceived brightness of the SDR
content. Android 15 lets you control the HDR headroom with
setDesiredHdrHeadroom to strike a balance between SDR
and HDR content.
التحكّم في مستوى الصوت

Android 15 introduces support for the CTA-2075 loudness standard to help you avoid audio loudness inconsistencies and ensure users don't have to constantly adjust volume when switching between content. The system leverages known characteristics of the output devices (headphones and speaker) along with loudness metadata available in AAC audio content to intelligently adjust the audio loudness and dynamic range compression levels.
To enable this feature, you need to ensure loudness metadata is available in
your AAC content and enable the platform feature in your app. For this, you
instantiate a LoudnessCodecController object by
calling its create factory method with the audio
session ID from the associated AudioTrack; this
automatically starts applying audio updates. You can pass an
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener to modify or filter
loudness parameters before they are applied on the
MediaCodec.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer will also be updated to use the
LoudnessCodecController APIs for a seamless app integration.
أجهزة MIDI 2.0 الافتراضية
أضاف نظام Android 13 إمكانية الاتصال ب أجهزة MIDI 2.0 باستخدام USB، والتي تتواصل باستخدام حِزم MIDI العالمية (UMP). يوفّر نظام التشغيل Android 15 دعمًا لبروتوكول UMP في تطبيقات MIDI الافتراضية، ما يتيح لتطبيقات إنشاء المحتوى التحكّم في تطبيقات المزج كجهاز MIDI 2.0 افتراضي تمامًا كما لو كانت تستخدم جهاز USB MIDI 2.0.
فك تشفير برامج AV1 بشكل أكثر كفاءة

dav1d هو برنامج فك ترميز AV1 الرائج من VideoLAN، وهو متاح لأجهزة Android التي لا تتيح فك ترميز AV1 في الأجهزة. ويحقّق برنامج dav1d أداءً أفضل بثلاث مرات مقارنةً ببرنامج فك ترميز AV1 القديم، ما يتيح تشغيل محتوى AV1 بدقة عالية لعدد أكبر من المستخدمين، بما في ذلك بعض الأجهزة المنخفضة ومتوسطة المستوى.
يجب أن يوافق تطبيقك على استخدام dav1d من خلال استدعائه بالاسم
"c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". سيتم استخدام dav1d كبرنامج الترميز والترميز التلقائي لبرنامج AV1 في تحديث لاحق. وتمّت إتاحة هذه الميزة بشكل موحّد ونشرها على
أجهزة Android 11 التي تتلقّى تحديثات نظام Google Play.
إنتاجية المطوّرين وأدواتهم
مع أنّ معظم جهودنا لتحسين إنتاجيتك تركّز على أدوات مثل استوديو Android وJetpack Compose ومكتبات Android Jetpack، إلا أنّنا نبحث دائمًا عن طرق في المنصة لمساعدتك في تحقيق أهدافك بسهولة أكبر.
تعديلات OpenJDK 17
Android 15 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases.
The following key features and improvements are included:
- Quality-of-life improvements around NIO buffers
- Streams
- Additional
mathandstrictmathmethods utilpackage updates including sequencedcollection,map, andsetByteBuffersupport inDeflater- Security updates such as
X500PrivateCredentialand security key updates
These APIs are updated on over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher through Google Play System updates, so you can target the latest programming features.
تحسينات على ملفات PDF
Android 15 includes substantial improvements to the PdfRenderer
APIs. Apps can incorporate advanced features such as rendering
password-protected files, annotations, form editing,
searching, and selection with copy. Linearized PDF
optimizations are supported to speed local PDF viewing and reduce resource use.
The Jetpack PDF library uses these APIs to simplify adding PDF
viewing capabilities to your app.
The PdfRenderer has been moved to a module that can be updated using Google
Play system updates independent of the platform release, and we're supporting
these changes back to Android 11 (API level 30) by creating a compatible
pre-Android 15 version of the API surface, called
PdfRendererPreV.
تحسينات على التبديل التلقائي للغات
أضاف نظام التشغيل Android 14 ميزة التعرّف على محتوى الصوت بعدّة لغات على الجهاز مع التبديل التلقائي بين اللغات، ولكن قد يؤدي ذلك إلى حذف كلمات، خاصةً عند التبديل بين اللغات بدون فترة راحة بين العبارة والعبارة الأخرى. يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 15 عناصر تحكّم إضافية لمساعدة التطبيقات في ضبط عملية التبديل هذه
حسب حالة الاستخدام.
يحدّد الخيار EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS
التبديل التلقائي ببداية جلسة الصوت، بينما يؤدي الخيار
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES إلى إيقاف
تبديل اللغة بعد عدد محدّد من عمليات التبديل. تكون هذه الخيارات مفيدة بشكلٍ خاص إذا كنت تتوقّع أن يتم التحدّث بلغة واحدة
أثناء الجلسة التي من المفترض أن يتم رصدها تلقائيًا.
تحسين واجهة برمجة التطبيقات OpenType Variable Font
يعمل نظام التشغيل Android 15 على تحسين سهولة استخدام الخط المتغيّر OpenType. يمكنك إنشاء
مثيل FontFamily من خط متغيّر بدون تحديد محاور الوزن
باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات buildVariableFamily. يلغي عارض النص القيمة
من المحور wght لمطابقة النص المعروض.
يؤدي استخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات إلى تبسيط الرمز البرمجي لإنشاء Typeface بشكل كبير:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
في السابق، لكي تتمكّن من إنشاء Typeface نفسها، كنت تحتاج إلى مزيد من الرموز البرمجية:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
في ما يلي مثال على كيفية عرض Typeface تم إنشاؤه باستخدام كلّ من واجهتَي برمجة التطبيقات القديمة والجديدة:
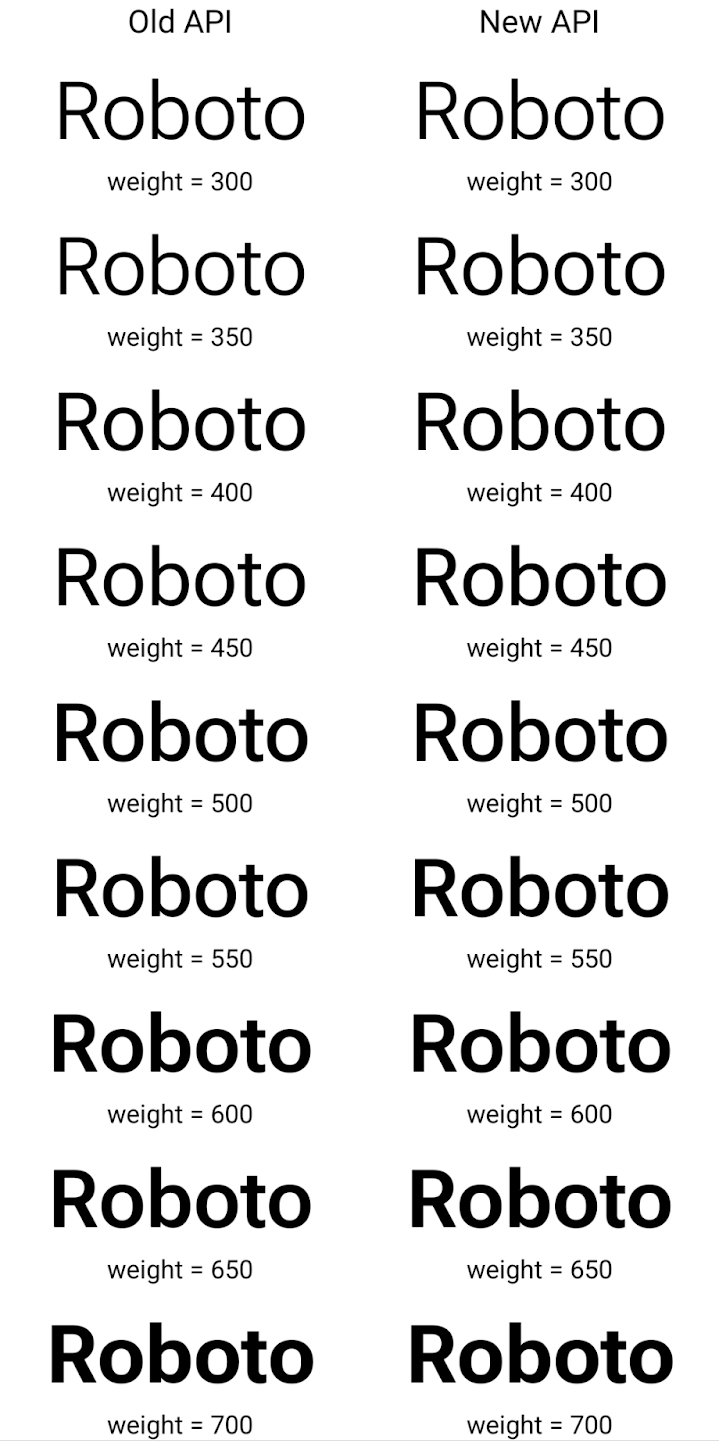
في هذا المثال، لا تملك Typeface التي تم إنشاؤها باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات القديمة
القدرة على إنشاء قيم دقيقة لوزن الخط لحالات Font التي تبلغ 350 و450 و550 و650
، لذا يعود مُنشئ العرض إلى أقرب قيمة لوزن الخط. ففي
في هذه الحالة، يتم عرض العدد 300 بدلاً من 350، ويتم عرض 400 بدلاً من 450،
وهكذا. في المقابل، فإنّ Typeface الذي تم إنشاؤه باستخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة ينشئ ديناميكيًا
مثيل Font لوزن معين، لذا يتم عرض الترجيحات الدقيقة بقيمة 350،
450 و550 و650 أيضًا.
عناصر تحكّم دقيقة في فواصل الأسطر
بدءًا من Android 15، يمكن لرمز TextView وفاصل السطر الأساسي
الحفاظ على الجزء المحدّد من النص في السطر نفسه لتحسين قراءة النص. يمكنك الاستفادة من هذا التخصيص لفاصل السطر باستخدام علامة
<nobreak> في موارد السلاسل أو
createNoBreakSpan. بالمثل، يمكنك منع الواصلة بين الكلمات باستخدام العلامة <nohyphen> أو العلامة createNoHyphenationSpan.
على سبيل المثال، لا يتضمّن مورد السلسلة التالي فاصل سطر، ويؤدي إلى عرض النص "Pixel 8 Pro" مقطوعًا في مكان غير مرغوب فيه:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
في المقابل، يتضمّن مورد السلسلة هذا العلامة <nobreak> التي تلتف حول العبارة "Pixel 8 Pro" وتمنع استخدام فواصل الأسطر:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
يظهر الفرق في طريقة عرض هذه السلاسل في الصور التالية:

<nobreak>
<nobreak>أرشفة التطبيقات
تم الإعلان عن إتاحة أرشفة التطبيقات في Android وGoogle Play أخيرًا عام، ما يتيح للمستخدمين إخلاء بعض المساحة من خلال إزالة التطبيقات المستخدمة بشكل غير متكرر من الجهاز الذي تم نشره باستخدام تطبيق Android حزمة على Google Play. يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 15 ميزة أرشفة التطبيقات وإلغاء أرشفتها على مستوى نظام التشغيل، ما يسهّل على جميع متاجر التطبيقات تنفيذ هذه الميزة.
يمكن للتطبيقات التي لديها إذن REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES طلب البيانات من
PackageInstaller requestArchive لطلب أرشفة
حزمة تطبيق مثبَّتة تؤدي إلى إزالة حزمة APK وأي ملفات مخزَّنة مؤقتًا ولكنها تظل قائمة
بيانات المستخدمين. يتم عرض التطبيقات المؤرشفة كتطبيقات قابلة للعرض من خلال واجهات برمجة التطبيقات
LauncherApps، وسيظهر للمستخدمين تنسيق واجهة مستخدم يُبرز أنّه تم أرشفة
هذه التطبيقات. إذا نقر أحد المستخدمين على تطبيق مؤرشَف، يكون أداة التثبيت المسؤولة
طلبًا لـ إخراجه من الأرشيف، ويمكن إكمال عملية استعادته
المراقبة بواسطة بث ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED.
تفعيل الوضع 16 كيلوبايت على جهاز باستخدام خيارات المطوّرين
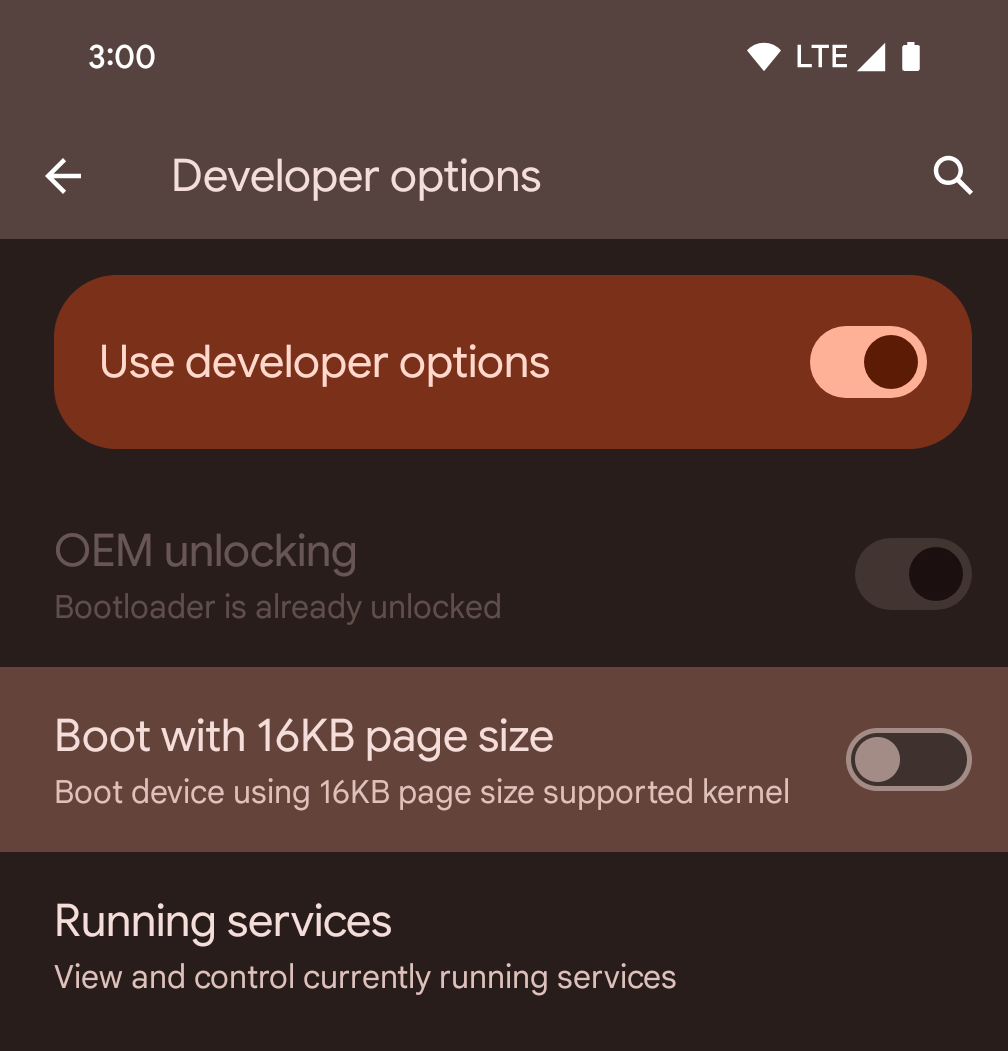
فعِّل خيار المطوّر التشغيل مع صفحات حجمها 16 كيلوبايت لتشغيل الجهاز في وضع 16 كيلوبايت.
في إصدارات QPR من نظام التشغيل Android 15، يمكنك استخدام خيار المطوّرين المتاح على أجهزة معيّنة لإعادة تشغيل الجهاز في وضع 16 كيلوبايت وإجراء اختبار على الجهاز فقط. قبل استخدام خيار المطوّرين، انتقِل إلى الإعدادات > النظام > تحديثات البرامج وطبِّق أي تحديثات متوفّرة.
يتوفّر خيار المطوّرين هذا على الأجهزة التالية:
Pixel 8 وPixel 8 Pro (مع الإصدار 1 من حزمة إصلاح الأخطاء في نظام Android 15 أو إصدار أحدث)
Pixel 8a (مع الإصدار 1 من حزمة إصلاح الأخطاء في نظام Android 15 أو إصدار أحدث)
Pixel 9 و9 Pro و9 Pro XL (مع الإصدار الثاني من حزمة Android 15 QPR أو إصدار أحدث)
Pixel 9a (مع نظام التشغيل Android 16 أو إصدار أحدث)
الرسومات
يوفّر Android 15 أحدث التحسينات على الرسومات، بما في ذلك ANGLE وإضافات إلى نظام رسومات Canvas.
تحديث طريقة وصول Android إلى وحدة معالجة الرسومات

Android hardware has evolved quite a bit from the early days where the core OS would run on a single CPU and GPUs were accessed using APIs based on fixed-function pipelines. The Vulkan® graphics API has been available in the NDK since Android 7.0 (API level 24) with a lower-level abstraction that better reflects modern GPU hardware, scales better to support multiple CPU cores, and offers reduced CPU driver overhead — leading to improved app performance. Vulkan is supported by all modern game engines.
Vulkan is Android's preferred interface to the GPU. Therefore, Android 15 includes ANGLE as an optional layer for running OpenGL® ES on top of Vulkan. Moving to ANGLE will standardize the Android OpenGL implementation for improved compatibility, and, in some cases, improved performance. You can test out your OpenGL ES app stability and performance with ANGLE by enabling the developer option in Settings -> System -> Developer Options -> Experimental: Enable ANGLE on Android 15.
The Android ANGLE on Vulkan roadmap
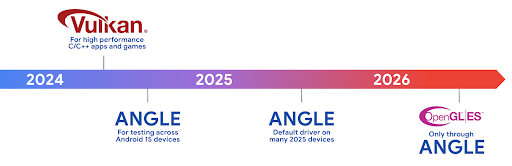
As part of streamlining our GPU stack, going forward we will be shipping ANGLE as the GL system driver on more new devices, with the future expectation that OpenGL/ES will be only available through ANGLE. That being said, we plan to continue support for OpenGL ES on all devices.
Recommended next steps
Use the developer options to select the ANGLE driver for OpenGL ES and test your app. For new projects, we strongly encourage using Vulkan for C/C++.
تحسينات على Canvas
يواصل نظام Android 15 جهودنا لتطوير نظام الرسومات Canvas في Android من خلال إضافة ميزات إضافية:
- يوفّر
Matrix44مصفوفة 4×4 لتحويل الإحداثيات التي يجب استخدامها عندما تريد التحكّم في اللوحة في المساحات الثلاثية الأبعاد. - يقاطع
clipShaderالمقطع الحالي بالshader المحدّد، في حين يضبطclipOutShaderالمقطع على اختلاف المقطع الحالي والshader، مع اعتبار كل منهما shader على أنّه قناع شفافية. يتيح ذلك رسم أشكال معقّدة بكفاءة.
الأداء والبطارية
يواصل نظام التشغيل Android التركيز على مساعدتك في تحسين أداء تطبيقاتك وجودتها. يقدِّم نظام التشغيل Android 15 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تساعد في تنفيذ المهام في تطبيقك بكفاءة أكبر، وتحسين أداء التطبيق، وجمع إحصاءات حول تطبيقاتك.
للاطّلاع على أفضل الممارسات التي تساهم في الحفاظ على البطارية وتصحيح أخطاء استخدام الشبكة والطاقة، بالإضافة إلى تفاصيل حول كيفية تحسين كفاءة البطارية عند تنفيذ العمليات في الخلفية في Android 15 والإصدارات الحديثة من Android، يمكنك مشاهدة جلسة تحسين كفاءة البطارية عند تنفيذ العمليات في الخلفية على Android من مؤتمر Google I/O.
ApplicationStartInfo API
في الإصدارات السابقة من Android، كان تشغيل التطبيقات عملية غير معروفة إلى حدٍ ما. كان من الصعوبة تحديد ما إذا كان تطبيقك قد بدأ من حالة التشغيل على البارد أو إعادة التشغيل البطيء
أو إعادة التشغيل السريع. كان من الصعب أيضًا معرفة المدة التي استغرقها تطبيقك أثناء
مراحل الإطلاق المختلفة: إنشاء نسخة من العملية، واستدعاء onCreate، ورسم
الإطار الأول، وغير ذلك. عند إنشاء مثيل لفئة Application، لم يكن لديك
طريقة لمعرفة ما إذا كان التطبيق قد بدأ من بث أو مقدّم محتوى أو
عملية أو خدمة احتياطية أو اكتمال عملية التمهيد أو منبّه أو Activity.
توفّر واجهة برمجة التطبيقات ApplicationStartInfo على Android 15 كل هذه الميزات والمزيد. يمكنك أيضًا اختيار إضافة الطوابع الزمنية الخاصة بك إلى السلسلة للمساعدة في جمع بيانات التوقيت في مكان واحد. بالإضافة إلى جمع القياسات، يمكنك استخدام ApplicationStartInfo للمساعدة في تحسين بدء تشغيل التطبيق مباشرةً. على سبيل المثال، يمكنك إزالة عمليات إنشاء المثيلات المكلّفة للمكتبات ذات الصلة بواجهة المستخدم ضمن فئة Application عند بدء تشغيل تطبيقك بسبب بث.
معلومات مفصّلة عن حجم التطبيق
منذ الإصدار 8.0 من Android (المستوى 26 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، يتضمّن Android واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
StorageStats.getAppBytes التي تلخّص حجم التطبيق المثبَّت كعدد واحد من البايتات، وهو مجموع حجم حزمة APK وحجم الملفات المستخرَجة من حزمة APK والملفات التي تم إنشاؤها على
الجهاز، مثل الرموز البرمجية المجمَّعة مسبقًا (AOT). لا يقدّم هذا الرقم معلومات مفيدة بشأن كيفية استخدام تطبيقك لمساحة التخزين.
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 15 واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type])، التي تتيح
لك الحصول على إحصاءات عن كيفية استخدام تطبيقك لكل هذه المساحة، بما في ذلك عمليات تقسيم ملف APK، والرموز البرمجية ذات الصلة بميزة AOT والتسريع، والبيانات الوصفية لملف dex، والمكتبات، والملفات الشخصية الإرشادية.
تحديد المواصفات الشخصية لصاحب البيانات من خلال التطبيق
Android 15 includes the ProfilingManager class,
which lets you collect profiling information from within your app such as heap
dumps, heap profiles, stack sampling, and more. It provides a callback to your
app with a supplied tag to identify the output file, which is delivered to your
app's files directory. The API does rate limiting to minimize the performance
impact.
To simplify constructing profiling requests in your app, we recommend using the
corresponding Profiling AndroidX API, available
in Core 1.15.0-rc01 or higher.
تحسينات على قاعدة بيانات SQLite
Android 15 introduces SQLite APIs that expose advanced features from the underlying SQLite engine that target specific performance issues that can manifest in apps. These APIs are included with the update of SQLite to version 3.44.3.
Developers should consult best practices for SQLite performance to get the most out of their SQLite database, especially when working with large databases or when running latency-sensitive queries.
- Read-only deferred transactions: when issuing transactions that are
read-only (don't include write statements), use
beginTransactionReadOnly()andbeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)to issue read-onlyDEFERREDtransactions. Such transactions can run concurrently with each other, and if the database is in WAL mode, they can run concurrently withIMMEDIATEorEXCLUSIVEtransactions. - Row counts and IDs: APIs were added to retrieve the count of changed
rows or the last inserted row ID without issuing an additional query.
getLastChangedRowCount()returns the number of rows that were inserted, updated, or deleted by the most recent SQL statement within the current transaction, whilegetTotalChangedRowCount()returns the count on the current connection.getLastInsertRowId()returns therowidof the last row to be inserted on the current connection. - Raw statements: issue a raw SQlite statement, bypassing convenience wrappers and any additional processing overhead that they may incur.
تحديثات "إطار عمل الأداء الديناميكي" في Android
Android 15 continues our investment in the Android Dynamic Performance Framework (ADPF), a set of APIs that allow games and performance intensive apps to interact more directly with power and thermal systems of Android devices. On supported devices, Android 15 adds ADPF capabilities:
- A power-efficiency mode for hint sessions to indicate that their associated threads should prefer power saving over performance, great for long-running background workloads.
- GPU and CPU work durations can both be reported in hint sessions, allowing the system to adjust CPU and GPU frequencies together to best meet workload demands.
- Thermal headroom thresholds to interpret possible thermal throttling status based on headroom prediction.
To learn more about how to use ADPF in your apps and games, head over to the documentation.
الخصوصية
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 15 مجموعة متنوّعة من الميزات التي تساعد مطوّري التطبيقات في حماية خصوصية المستخدمين.
رصد تسجيل الشاشة
Android 15 adds support for apps to detect that they are being recorded. A callback is invoked whenever the app transitions between being visible or invisible within a screen recording. An app is considered visible if activities owned by the registering process's UID are being recorded. This way, if your app is performing a sensitive operation, you can inform the user that they're being recorded.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
إمكانات IntentFilter الموسّعة
يتيح Android 15 توفير دقة Intent بدرجة أكبر من خلال واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
UriRelativeFilterGroup التي تتضمّن مجموعة من عناصر
UriRelativeFilter التي تشكّل مجموعة من قواعد Intent
مطابقة يجب استيفاؤها، بما في ذلك مَعلمات طلب البحث لعناوين URL وأجزاء عناوين URL
وقواعد الحظر أو الاستبعاد.
يمكن تحديد هذه القواعد في ملف XML الخاص بـ AndroidManifest باستخدام
العلامة <uri-relative-filter-group> التي يمكن أن تتضمّن اختياريًا علامة android:allow. يمكن أن تحتوي هذه العلامات على علامات <data> تستخدِم سمات علامات بيانات
الحالية بالإضافة إلى سمتَي android:query وandroid:fragment.
في ما يلي مثال على بنية AndroidManifest:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
المساحة الخاصّة
Private space lets users create a separate space on their device where they can keep sensitive apps away from prying eyes, under an additional layer of authentication. The private space uses a separate user profile. The user can choose to use the device lock or a separate lock factor for the private space.
Apps in the private space show up in a separate container in the launcher, and are hidden from the recents view, notifications, settings, and from other apps when the private space is locked. User-generated and downloaded content (such as media or files) and accounts are separated between the private space and the main space. The system sharesheet and the photo picker can be used to give apps access to content across spaces when the private space is unlocked.
Users can't move existing apps and their data into the private space. Instead, users select an install option in the private space to install an app using whichever app store they prefer. Apps in the private space are installed as separate copies from any apps in the main space (new copies of the same app).
When a user locks the private space, the profile is stopped. While the profile is stopped, apps in the private space are no longer active and can't perform foreground or background activities, including showing notifications.
We recommend that you test your app with private space to make sure your app works as expected, especially if your app falls into one of the following categories:
- Apps with logic for work profiles that assumes that any installed copies of their app that aren't in the main profile are in the work profile.
- Medical apps
- Launcher apps
- App store apps
طلب آخر اختيار للمستخدم في ما يخصّ إذن الوصول إلى "الصور المحدّدة"
يمكن للتطبيقات الآن إبراز الصور والفيديوهات التي تم اختيارها مؤخرًا فقط عند منح التطبيقات
إذن وصول جزئي إلى أذونات الوصول إلى الوسائط. يمكن أن تحسِّن هذه الميزة
تجربة المستخدم للتطبيقات التي تطلب الوصول إلى الصور
والفيديوهات بشكل متكرر. لاستخدام هذه الميزة في تطبيقك، فعِّل الوسيطة
QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY عند طلب MediaStore
من خلال ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
"مبادرة حماية الخصوصية" على Android
يتضمّن Android 15 أحدث إضافات "خدمات الإعلانات" من Android، بما في ذلك أحدث إصدار من مبادرة حماية الخصوصية على Android. تشكّل هذه الإضافة جزءًا من جهودنا لتطوير تقنيات تُحسِّن خصوصية المستخدمين وتتيح تجارب إعلانية مخصّصة فعّالة لتطبيقات الأجهزة الجوّالة. تتضمّن صفحة مبادرة حماية الخصوصية مزيدًا من المعلومات حول "مبادرة حماية الخصوصية" في برامج معاينة المطوّرين والإصدارات التجريبية من Android لمساعدتك في البدء.
Health Connect
Android 15 integrates the latest extensions around Health Connect by Android, a secure and centralized platform to manage and share app-collected health and fitness data. This update adds support for additional data types across fitness, nutrition, skin temperature, training plans, and more.
Skin temperature tracking allows users to store and share more accurate temperature data from a wearable or other tracking device.
Training plans are structured workout plans to help a user achieve their fitness goals. Training plans support includes a variety of completion and performance goals:
- Completion goals around calories burned, distance, duration, repetition, and steps.
- Performance goals around as many repetitions as possible (AMRAP), cadence, heart rate, power, perceived rate of exertion, and speed.
Learn more about the latest updates to Health Connect in Android in the Building adaptable experiences with Android Health talk from Google I/O.
مشاركة شاشة التطبيق
يتيح نظام التشغيل Android 15 مشاركة شاشة التطبيق كي يتمكّن المستخدمون من مشاركة أو تسجيل
نافذة التطبيق فقط بدلاً من شاشة الجهاز بالكامل. تم تفعيل هذه الميزة لأول مرة في ملف APK لنظام التشغيل
Android 14 QPR2، وتشمل MediaProjection طلبات إعادة الاتصال التي تسمح لتطبيقك
بتخصيص تجربة مشاركة شاشة التطبيق. يُرجى العلم أنّه بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 14 من Android (المستوى 34 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأحدث، يجب الحصول على موافقة المستخدم لكل جلسة رصد MediaProjection.
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يمنح نظام التشغيل Android 15 مطوّري التطبيقات والمستخدمين المزيد من التحكّم والمرونة في إعداد أجهزتهم بما يتناسب مع احتياجاتهم.
لمزيد من المعلومات حول كيفية استخدام أحدث التحسينات في Android 15 لتحسين تجربة المستخدم في تطبيقك، يمكنك مشاهدة جلسة تحسين تجربة المستخدم في تطبيق Android من مؤتمر Google I/O.
معاينات تطبيقات مصغّرة أكثر تفصيلاً باستخدام Generated Previews API
Before Android 15, the only way to provide widget picker previews was to specify a static image or layout resource. These previews often differ significantly from the look of the actual widget when it is placed on the home screen. Also, static resources can't be created with Jetpack Glance, so a Glance developer had to screenshot their widget or create an XML layout to have a widget preview.
Android 15 adds support for generated previews. This means that app widget
providers can generate RemoteViews to use as the picker preview, instead
of a static resource.
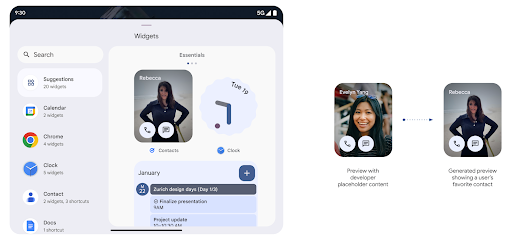
Push API
Apps can provide generated previews through a push API. Apps can provide
previews at any point in their lifecycle, and don't receive an explicit request
from the host to provide previews. Previews are persisted in AppWidgetService,
and hosts can request them on-demand. The following example loads an XML widget
layout resource and sets it as the preview:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
The expected flow is:
- At any time, the widget provider calls
setWidgetPreview. The provided previews are persisted inAppWidgetServicewith other provider info. setWidgetPreviewnotifies hosts of an updated preview through theAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChangedcallback. In response, the widget host reloads all of its provider information.- When displaying a widget preview, the host checks
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories, and if the chosen category is available, callsAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewto return the saved preview for this provider.
When to call setWidgetPreview
Because there is no callback to provide previews, apps can choose to send previews at any point when they are running. How often to update the preview depends on the widget's use case.
The following list describes the two main categories of preview use cases:
- Providers that show real data in their widget previews, such as personalized or recent information. These providers can set the preview once the user has signed in or has done initial configuration in their app. After this, they can set up a periodic task to update the previews at their chosen cadence. Examples of this type of widget could be a photo, calendar, weather or news widget.
- Providers that show static information in previews or quick-action widgets that don't display any data. These providers can set previews once, when the app first launches. Examples of this type of widget include a drive quick actions widget or chrome shortcuts widget.
Some providers might show static previews on the hub mode picker, but real information on the homescreen picker. These providers should follow the guidance for both of these use cases to set previews.
نافذة ضمن النافذة
Android 15 introduces changes in Picture-in-Picture (PiP) ensuring an even smoother transition when entering into PiP mode. This will be beneficial for apps having UI elements overlaid on top of their main UI, which goes into PiP.
Developers use the onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to define logic
that toggles the visibility of the overlaid UI elements. This callback is
triggered when the PiP enter or exit animation is completed. Beginning in
Android 15, the PictureInPictureUiState class includes another state.
With this UI state, apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) will observe the
Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback being invoked with
isTransitioningToPip() as soon as the PiP animation starts. There are
many UI elements that are not relevant for the app when it is in PiP mode, for
example views or layout that include information such as suggestions, upcoming
video, ratings, and titles. When the app goes to PiP mode, use the
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback to hide these UI elements. When the
app goes to full screen mode from the PiP window, use
onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to unhide these elements, as shown in
the following examples:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
This quick visibility toggle of irrelevant UI elements (for a PiP window) helps ensure a smoother and flicker-free PiP enter animation.
قواعد محسّنة لميزة "عدم الإزعاج"
AutomaticZenRule lets apps customize Attention
Management (Do Not Disturb) rules and decide when to activate or deactivate
them. Android 15 greatly enhances these rules with the goal of improving the
user experience. The following enhancements are included:
- Adding types to
AutomaticZenRule, allowing the system to apply special treatment to some rules. - Adding an icon to
AutomaticZenRule, helping to make the modes be more recognizable. - Adding a
triggerDescriptionstring toAutomaticZenRulethat describes the conditions on which the rule should become active for the user. - Added
ZenDeviceEffectstoAutomaticZenRule, allowing rules to trigger things like grayscale display, night mode, or dimming the wallpaper.
ضبط VibrationEffect لقنوات الإشعارات
يتيح Android 15 ضبط اهتزازات تفاعلية للإشعارات الواردة من خلال
قناة تستخدم NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect، لذلك
يستطيع المستخدمون التمييز بين الأنواع المختلفة من الإشعارات بدون
الاضطرار إلى النظر إلى أجهزتهم.
شريحة شريط الحالة لعرض الوسائط والإيقاف التلقائي
يمكن أن تؤدي ميزة "إلقاء الوسائط" إلى الكشف عن معلومات المستخدمين الخاصة. شريحة بارزة جديدة للحالة تُعلم المستخدمين بأي بث شاشة جارٍ. يمكن للمستخدمين النقر على الشريحة لإيقاف بث الشاشة أو مشاركتها أو تسجيلها. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، لتوفير تجربة مستخدم أكثر سهولة، يتم الآن تلقائيًا إيقاف أي عملية بث شاشة قيد التنفيذ عند قفل شاشة الجهاز.
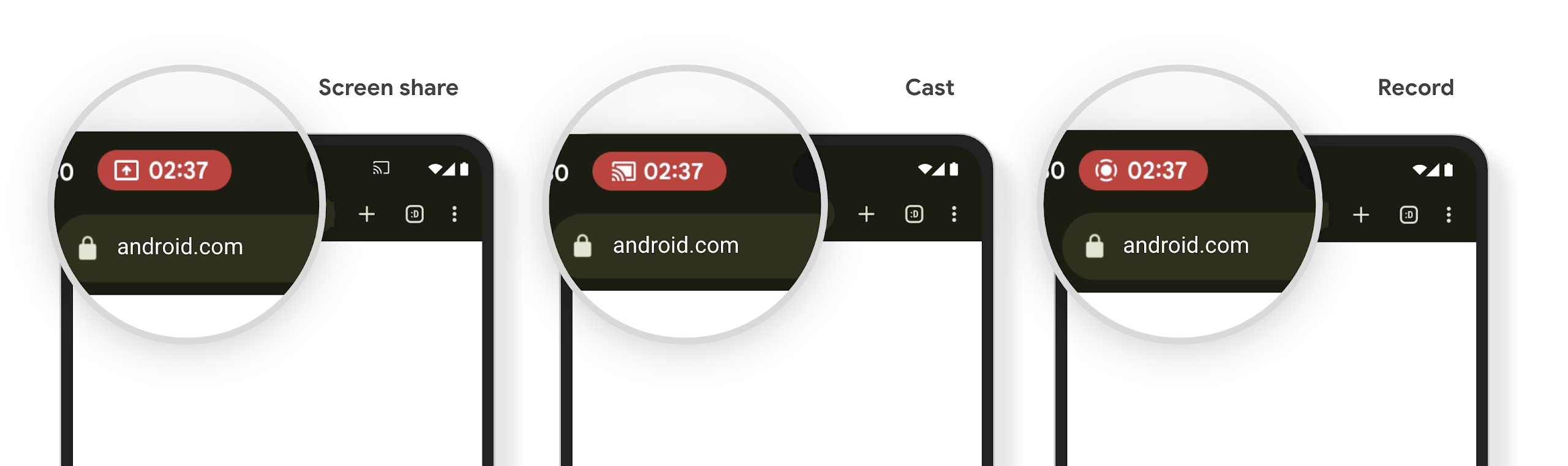
الشاشات الكبيرة وأشكال الأجهزة
يوفّر نظام التشغيل Android 15 لتطبيقاتك إمكانية الاستفادة إلى أقصى حدّ من عوامل الشكل في Android، بما في ذلك الشاشات الكبيرة والأجهزة القابلة للطي والأجهزة القابلة للطي والفتح.
تحسين تعدُّد المهام على الشاشات الكبيرة
Android 15 gives users better ways to multitask on large screen devices. For example, users can save their favorite split-screen app combinations for quick access and pin the taskbar on screen to quickly switch between apps. This means that making sure your app is adaptive is more important than ever.
Google I/O has sessions on Building adaptive Android apps and Building UI with the Material 3 adaptive library that can help, and our documentation has more to help you Design for large screens.
إمكانية استخدام الشاشة الخارجية
يمكن لتطبيقك تعريف خاصية يستخدمها نظام التشغيل Android 15 لسماحApplication أو Activity بعرض المحتوى على الشاشات الصغيرة المخصّصة للغلاف في الأجهزة القابلة للطي المتوافقة. هذه الشاشات صغيرة جدًا لكي يتم
اعتبارها استهدافات متوافقة لتشغيل تطبيقات Android عليها، ولكن يمكن لتطبيقك
تفعيل توافقها، ما يجعل تطبيقك متاحًا في المزيد من الأماكن.
إمكانية الاتصال
يعدّل Android 15 النظام الأساسي لمنح تطبيقك إمكانية الوصول إلى أحدث التطورات في تكنولوجيات الاتصال والشبكات اللاسلكية.
التوافق مع الأقمار الصناعية
يواصل نظام Android 15 توسيع نطاق توفّر المنصة للاتصال عبر الأقمار الصناعية ويضمّ بعض عناصر واجهة المستخدم لضمان تجربة مستخدم متّسقة على مستوى منظومة الاتصال عبر الأقمار الصناعية.
يمكن للتطبيقات استخدام ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() لرصد الحالات التي يكون فيها الجهاز متصلاً بأحد الأقمار الصناعية، ما يمنح التطبيقات المزيد من المعلومات عن سبب عدم توفّر خدمات الشبكة الكاملة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يقدّم الإصدار 15 من Android
توافقًا مع تطبيقات الرسائل القصيرة ورسائل الوسائط المتعددة، بالإضافة إلى تطبيقات RCS المحمَّلة مسبقًا لاستخدام
الاتصال عبر الأقمار الصناعية لإرسال الرسائل واستلامها.
تجارب أكثر سلاسة باستخدام تقنية NFC
يعمل نظام التشغيل Android 15 على تحسين تجربة الدفع بدون تلامس الأجهزة وجعلها أكثر سلاسة وموثوقية، مع مواصلة توفير منظومة التطبيقات المتكاملة لتقنية NFC القوية في Android. على
الأجهزة المتوافقة، يمكن للتطبيقات أن تطلب من NfcAdapter الدخول إلى
وضع المراقبة، حيث يستمع الجهاز إلى قراء
NFC ولكنه لا يستجيب لهم، ويرسل خدمة NFC الخاصة بالتطبيق PollingFrame
العناصر لمعالجتها. يمكن استخدام عناصر PollingFrame لمنح الإذن
قبل إجراء عملية التواصل الأولى مع قارئ NFC، ما يتيح إجراء معاملة
بنقرة واحدة في العديد من الحالات.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكن للتطبيقات تسجيل فلتر على الأجهزة المتوافقة لكي تتم إعلامها بنشاط حلقة الاستطلاع، ما يتيح التشغيل السلس مع تطبيقات متعددة متوافقة مع NFC.
دور المحفظة
Android 15 introduces a Wallet role that allows tighter integration with the user's preferred wallet app. This role replaces the NFC default contactless payment setting. Users can manage the Wallet role holder by navigating to Settings > Apps > Default Apps.
The Wallet role is used when routing NFC taps for AIDs registered in the payment category. Taps always go to the Wallet role holder unless another app that is registered for the same AID is running in the foreground.
This role is also used to determine where the Wallet Quick Access tile should go when activated. When the role is set to "None", the Quick Access tile isn't available and payment category NFC taps are only delivered to the foreground app.
الأمان
يساعدك نظام التشغيل Android 15 في تعزيز أمان تطبيقك وحماية بياناته، كما يوفّر للمستخدمين المزيد من الشفافية والتحكّم في بياناتهم. يمكنك مشاهدة جلسة الحفاظ على أمان المستخدمين على Android من مؤتمر Google I/O للتعرّف على المزيد من الإجراءات التي نتّخذها لتحسين وسائل حماية المستخدمين وحماية تطبيقك من التهديدات الجديدة.
دمج Credential Manager مع ميزة "الملء التلقائي"
Starting with Android 15, developers can link specific views like username or password fields with Credential Manager requests, making it easier to provide a tailored user experience during the sign-in process. When the user focuses on one of these views, a corresponding request is sent to Credential Manager. The resulting credentials are aggregated across providers and displayed in autofill fallback UIs, such as inline suggestions or drop-down suggestions. The Jetpack androidx.credentials library is the preferred endpoint for developers to use and will soon be available to further enhance this feature in Android 15 and higher.
دمج ميزة "نقرة واحدة لتسجيل الدخول أو إنشاء حساب" مع طلبات المقاييس الحيوية
مدير بيانات الاعتماد يدمج طلبات المقاييس الحيوية في إنشاء بيانات الاعتماد وتسجيل الدخول، ما يغنيك عن حاجة مقدّمي الخدمات إلى إدارة طلبات المقاييس الحيوية. نتيجةً لذلك، ما على موفّري بيانات الاعتماد سوى التركيز على نتائج مسارات الإنشاء والحصول، بالإضافة إلى نتيجة مسار البيانات الحيوية. توفّر هذه العملية المبسّطة بيانات اعتماد أكثر كفاءة وسلاسة. عملية الإنشاء والاسترجاع.
إدارة المفاتيح للتشفير التام بين الأطراف
نقدّم E2eeContactKeysManager في Android 15، وهو تنسيق ملف يسهّل التشفير التام بين الأطراف (E2EE) في تطبيقات Android من خلال توفير واجهة برمجة تطبيقات على مستوى نظام التشغيل لتخزين المفاتيح العامة للتشفير.
تم تصميم E2eeContactKeysManager للدمج مع تطبيق
جهات الاتصال في النظام الأساسي لمنح المستخدمين طريقة مركزية لإدارة مفاتيحهم المفتوحة
لجهات الاتصال وإثبات ملكيتها.
عمليات التحقّق من الأذونات على معرّفات الموارد المنتظمة للمحتوى
Android 15 introduces a set of APIs that perform permission checks on content URIs:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: This performs a full permission check on content URIs.Activitymanifest attributerequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: This enforces specified permissions on the provided content URIs at activity launch.ComponentCallerclass forActivitycallers: This represents the app that launched the activity.
تسهيل الاستخدام
يضيف Android 15 ميزات تعمل على تحسين إمكانية الوصول للمستخدمين.
تحسينات على لغة برايل
في الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android، أصبح بإمكان TalkBack إتاحة استخدام شاشات برايل التي تستخدم معيار HID عبر USB وBluetooth الآمن.
سيساعد هذا المعيار، مثل المعيار المستخدَم في الفئران ولوحات المفاتيح، نظام Android على إتاحة نطاق أوسع من أجهزة العرض بلغة برايل بمرور الوقت.
التوافق مع أسواق عالمية
يضيف Android 15 ميزات وإمكانات تكمل تجربة المستخدم عند استخدام الجهاز بلغات مختلفة.
خط CJK متغيّر
Starting with Android 15, the font file for Chinese, Japanese, and Korean (CJK) languages, NotoSansCJK, is now a variable font. Variable fonts open up possibilities for creative typography in CJK languages. Designers can explore a broader range of styles and create visually striking layouts that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve.

ضبط المسافة بين الأحرف
Starting with Android 15, text can be justified utilizing letter spacing by
using JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. Inter-word justification was
first introduced in Android 8.0 (API level 26), and inter-character
justification provides similar capabilities for languages that use the
whitespace character for segmentation, such as Chinese, Japanese, and others.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.إعدادات الفواصل التلقائية بين الأسطر
بدأ Android في إتاحة فواصل الأسطر المستندة إلى العبارة باللغتين اليابانية والكورية
Android 13 (المستوى 33) ومع ذلك، وبينما تعمل فواصل الأسطر المستندة إلى عبارة على تحسين
لسهولة قراءة السطور القصيرة من النص، فإنها لا تعمل بشكل جيد مع الأسطر الطويلة من النص.
في Android 15، يمكن للتطبيقات تطبيق فواصل الأسطر المستندة إلى العبارة على الأسطر القصيرة فقط.
من النص، باستخدام LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
. يحدد هذا الخيار أفضل خيار نمط كلمة للنص.
بالنسبة إلى الأسطر القصيرة من النص، يتم استخدام فواصل الأسطر المستندة إلى العبارة، وتعمل بالطريقة نفسها
كـ LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE، كما هو موضح في
الصورة التالية:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
يطبق فواصل الأسطر المستندة إلى العبارة لتحسين سهولة قراءة النص.
هذا مماثل لتطبيق
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.بالنسبة إلى أسطر النص الأطول، يستخدم LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO نمط كلمات بدون
فاصل سطر، ويعمل بالطريقة نفسها التي يعمل بها
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE، كما هو موضّح في
الصورة التالية:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
عدم تطبيق أي نمط من أنماط الكلمات بفواصل أسطر لتحسين إمكانية قراءة النص.
هذا مماثل لتطبيق
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.خط إضافي للغة اليابانية Hentaigana
في نظام التشغيل Android 15، ملف خط للهيرغانا اليابانية القديمة (المعروفة باسم Hentaigana) بشكل افتراضي. يمكن للأشكال الفريدة لأحرف الهينتيجانا إضافة طابعًا مميزًا للأعمال الفنية أو التصميم، مع المساعدة أيضًا في الحفاظ على دقة انتقال وفهم الوثائق اليابانية القديمة.

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. يمكن لأي شخص استخدام هذا الشعار أو نسخة معدَّلة منه أو تعديله للإشارة إلى مشروع VideoLAN أو أي منتج طوَّره فريق VideoLAN، ولكن لا يشير ذلك إلى موافقة المشروع.
Vulkan وشعار Vulkan علامتان تجاريتان مسجّلتان لشركة Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL هي علامة تجارية مسجّلة وشعار OpenGL ES هو علامة تجارية تابعة للشركة Hewlett Packard Enterprise وتستخدمها شركة Khronos بموجب إذن.
