SDK 扩展利用模块化系统组件将 API 添加到之前发布的特定 API 级别的公共 SDK 中。当最终用户通过 Google Play 系统更新收到模块更新后,这些 API 即可在设备上使用。应用开发者可以在其应用中利用这些 API,以提供这些先前 Android 版本的 SDK 原本不支持的其他功能。
API 版本控制
从 Android 11(API 级别 30)开始,Android 设备就包含一组 SDK 扩展。添加的新 API 会包含在某个 API 级别中,但也可能包含在特定版本的 SDK 扩展中。例如,照片选择器的 ACTION_PICK_IMAGES API 添加到了 Android 13(API 级别 33)的公共 SDK 中,但它也可通过 SDK 扩展(从 R 扩展版本 2 开始)来使用。SDK 扩展名称对应一个整数常量(来自 Build.VERSION_CODES 的常量或 SdkExtensions 类中定义的常量,例如 SdkExtensions.AD_SERVICES)。
确定要使用的 SDK 扩展
您需要先确定哪些 SDK 包含支持您的应用的使用情形的 API,然后才能使用相应的 SDK Extension API。
SDK Extension API 的 API 参考文档页面指明了应用可用于访问特定 API 的最低 SDK 扩展版本。如果文档还指定了一个 Android 平台版本(用 API 级别指代),那么该 API 也适用于搭载相应 Android 版本或更高版本的所有设备。
例如,ACTION_PICK_IMAGES 在从 Android 13(API 级别 33)起的公共 SDK 中通常可用,但还适用于搭载 Android 11(API 级别 30)及更高版本的设备,只要该设备至少配有 R 扩展版本 2 即可。
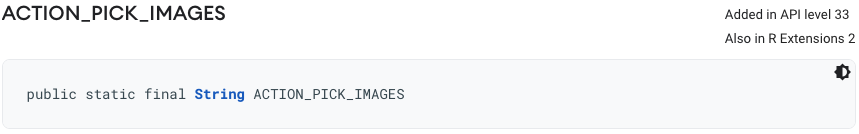
若要使用此 API,您需针对 API 级别至少为 33 或扩展级别至少为 2 的 SDK 进行编译。
若要使用某个扩展 SDK,请执行以下步骤:
- 查看要使用的 API 的功能文档及 API 参考文档,查找所需的最低扩展版本。
- 确定您的功能集所需的扩展版本后,在 Android Studio 中打开 SDK 管理器。
- 选择具有相应扩展版本(或更高版本,因为 API 可累加)的 Android SDK 平台条目。例如:Android SDK 平台 33,扩展级别 4。
在应用的
build.gradle.kts或build.gradle文件中声明这些值:Groovy
android { compileSdk 33 compileSdkExtension 4 ... }
Kotlin
android { compileSdk = 33 compileSdkExtension = 4 ... }
检查 SDK 扩展是否可用
您的应用可以在运行时检查哪些 SDK 扩展版本是可用的;在开发过程中,您可以使用 Android 调试桥 (adb) 命令查找扩展版本,如以下部分所述。
在运行时检查
您的应用可以在运行时使用 getExtensionVersion() 方法检查 SDK 扩展是否适用于某个给定的平台版本。例如,以下代码会检查 Android 11(API 级别 30)SDK 扩展的扩展版本 2 或更高版本是否可用:
Kotlin
fun isPhotoPickerAvailable(): Boolean { return SdkExtensions.getExtensionVersion(Build.VERSION_CODES.R) >= 2 // Safely use extension APIs that are available with Android 11 (API level 30) Extensions Version 2, such as Photo Picker. }
Java
public static final boolean isPhotoPickerAvailable() { return SdkExtensions.getExtensionVersion(Build.VERSION_CODES.R) >= 2; }
这类似于根据 Build.VERSION.SDK_INT 执行检查:
Kotlin
fun isPhotoPickerAvailable(): Boolean { return Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 33 }
Java
public static final boolean isPhotoPickerAvailable() { return Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 33; }
此 SDK_INT 检查仍然安全有效,但即使相应的扩展 API 可用,isPhotoPickerAvailable 在某些设备上也会返回 false。因此,SDK_INT 检查并不是最优方法,而扩展版本检查可以更好地检查 API 可用性。所有 SDK_INT 大于或等于 33(Android 13 或更高版本)的设备的公共 SDK 中都有照片选择器 API,但有些设备的 SDK_INT 低于 33(例如 Android 11、12 和 12L)也可以访问这些 API,前提是这些设备的 R 扩展版本不低于 2。
在这种情况下,采用扩展版本检查有助于您的应用为更多用户提供其他功能。如需获取可用于检查设备是否有特定 SDK 扩展的所有常量的列表,请参阅 SDK 扩展名称和常量。
广告服务扩展
与一般的 SDK 扩展类似,AdServices API 参考文档有时会指示某个 API 是“广告服务扩展”版本的一部分。与一般 SDK 扩展不同,广告服务扩展使用 SdkExtensions.AD_SERVICES 常量来确定设备上的扩展版本:
Kotlin
fun isAdServicesAvailable(): Boolean { return SdkExtensions.getExtensionVersion(SdkExtensions.AD_SERVICES) >= 4 }
Java
public static final boolean isAdServicesAvailable() { return SdkExtensions.getExtensionVersion(SdkExtensions.AD_SERVICES) >= 4; }
如需详细了解广告服务扩展中的功能以及如何开始使用,请参阅广告服务扩展文档。
实用程序方法
在某些情况下,SDK 扩展包含 Jetpack 实用程序方法,用于检查其 SDK Extension API 的可用性。例如,您可以使用 Jetpack 库函数检查 PhotoPicker 的可用性,从而可以忽略条件版本检查。
工具支持
在 Android Studio Flamingo | 2022.2.1 或更高版本中,lint 工具可以在其 NewAPI 检查过程中扫描 SDK 扩展版本的问题。此外,Android Studio 还可以为使用 SDK 扩展启动的 API 自动生成正确的版本检查。
SDK 扩展名称和常量
下表介绍了 API 参考文档中列出的不同 SDK 扩展集如何映射到应用可用于在运行时检查 API 可用性的常量。每个公开 SDK 的通用 SDK 扩展集会映射到 Build.VERSION_CODES 的值。
| SDK 扩展名称 | 常量 | 符合条件的设备 |
|---|---|---|
| R 扩展 | VERSION_CODES.R |
Android 11(API 级别 30)及更高版本 |
| S 扩展 | VERSION_CODES.S |
Android 12(API 级别 31)及更高版本 |
| T 扩展 | VERSION_CODES.TIRAMISU |
Android 13(API 级别 33)及更高版本 |
| U 扩展 | VERSION_CODES.UPSIDE_DOWN_CAKE |
Android 14(API 级别 34)及更高版本 |
| V 扩展 | VERSION_CODES.VANILLA_ICE_CREAM |
Android 15(API 级别 35)及更高版本 |
| 广告服务扩展 | SdkExtensions.AD_SERVICES |
Android 13(API 级别 33)及更高版本 |
使用 adb 检查
如需使用 adb 检查设备上的哪些 SDK 扩展可用,请运行以下命令:
adb shell getprop | grep build.version.extensions
运行该命令后,您会看到类似于以下内容的输出:
[build.version.extensions.r]: [3] # Android 11 (API level 30) and higher
[build.version.extensions.s]: [3] # Android 12 (API level 31) and higher
[build.version.extensions.t]: [3] # Android 13 (API level 33) and higher
每行都会显示设备上存在的 SDK 扩展及其对应的扩展版本号(在本例中为 3)。
