يعرض المكوّن Dialog رسائل منبثقة أو يطلب إدخال المستخدم في
طبقة فوق محتوى التطبيق الرئيسي. تؤدي إلى إنشاء تجربة واجهة مستخدم متداخلة لجذب انتباه المستخدمين.
تشمل حالات استخدام مربّع الحوار ما يلي:
- تأكيد إجراء المستخدم، مثل حذف ملف
- طلب إدخال المستخدم، مثل طلب إدخال بيانات في تطبيق قائمة المهام
- عرض قائمة خيارات للمستخدم لاختيارها، مثل اختيار بلد في إعداد الملف الشخصي
يقدّم هذا الموضوع عمليات التنفيذ التالية:
توافق الإصدار
يتطلّب هذا التنفيذ ضبط الحد الأدنى من إصدار حزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) لمشروعك على المستوى 21 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات أو مستوى أعلى.
التبعيات
إنشاء مربّع حوار تنبيه
يقدّم العنصر القابل للتجميع AlertDialog واجهة برمجة تطبيقات ملائمة لإنشاء مربع حوار
بتصميم مستوحى من أسلوب Material Design. ينفِّذ المثال التالي زرَّين في
مربّع حوار تنبيه، أحدهما لإغلاق مربّع الحوار والآخر لتأكيد
طلبه:
يشير هذا التنفيذ إلى عنصر مكوّن رئيسي يُرسِل الوسيطات إلى العنصر المكوّن الثانوي بهذه الطريقة:
النتائج
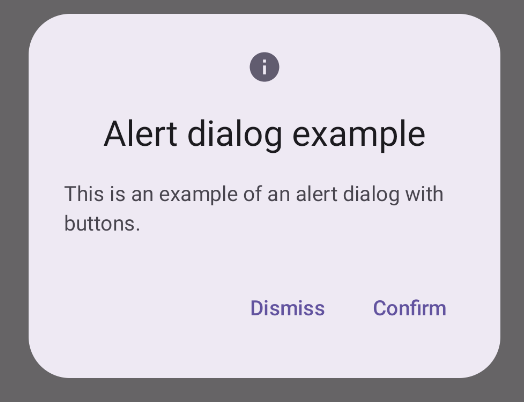
النقاط الرئيسية
يحتوي AlertDialog على مَعلمات محدّدة لمعالجة عناصر معيّنة من
المربّع الحواري. ومن بين هذه التحسينات ما يلي:
title: النص الذي يظهر في أعلى مربّع الحوارtext: النص الذي يظهر في وسط مربّع الحوارicon: الرسم الذي يظهر في أعلى مربّع الحوارonDismissRequest: الدالة التي يتمّ استدعاؤها عندما يغلِق المستخدِم مربّع الحوار، مثلاً من خلال النقر خارج مربّع الحوار-
dismissButton: عنصر قابل للتجميع يعمل كزر لإغلاق التطبيق confirmButton: عنصر قابل للتجميع يعمل كزر تأكيدعندما ينقر المستخدم على أيّ من الزرَّين، يتم إغلاق مربّع الحوار. عندما يُقرّ المستخدم على الإجراء، يتمّ استدعاء وظيفة تعالج أيضًا عملية التأكيد. في هذا المثال، الدالتان هما
onDismissRequest()وonConfirmRequest().في الحالات التي يتطلّب فيها مربّع الحوار مجموعة أكثر تعقيدًا من الأزرار، يمكنك الاستفادة من استخدام عنصر
Dialogالقابل للتجميع وملؤه بطريقة أكثر حرية.
إنشاء مربّع حوار
Dialog هو عنصر تركيبي أساسي لا يقدّم أيّ تنسيق أو
مواقع محدّدة مسبقًا للمحتوى. وهي حاوية بسيطة يجب
ملؤها بحاوية مثل Card. في ما يلي بعض المناقشات العميقة عن المَعلمات الرئيسية للمحادثة:
-
onDismissRequest: دالة lambda التي يتمّ استدعاؤها عندما يغلق المستخدِم مربّع الحوار -
properties: مثيلDialogPropertiesيقدّم بعض النطاق الإضافي للتخصيص
إنشاء مربّع حوار أساسي
المثال التالي هو عملية تنفيذ أساسية للعنصر القابل للتجميع Dialog. يُرجى ملاحظة
أنّه يستخدم Card كحاوية ثانوية. بدون الرمز Card، سيظهر المكوّن Text
بمفرده أعلى محتوى التطبيق الرئيسي.
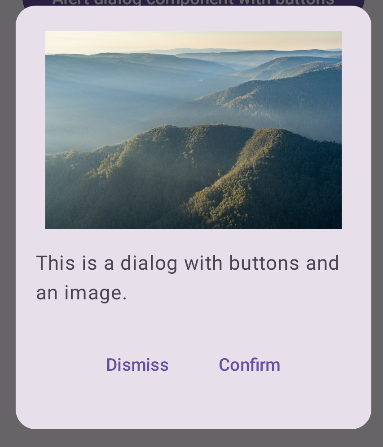
النتيجة
يُرجى العلم أنّه عندما يكون مربّع الحوار مفتوحًا، يظهر محتوى التطبيق الرئيسي تحته مظلمًا ورمماديًا:

إنشاء مربّع حوار متقدّم
في ما يلي تنفيذ أكثر تقدمًا للعنصر القابل للتجميع Dialog. في
هذا الحالة، ينفِّذ المكوّن يدويًا واجهة مشابهة للمثال السابق
AlertDialog.
النتيجة
المجموعات التي تتضمّن هذا الدليل
هذا الدليل هو جزء من مجموعات الأدلة السريعة المنظَّمة التي تتناول أهداف تطوير Android الأوسع نطاقًا:
النص الذي يظهر للمستخدم

طلب إدخال المستخدم



