أشرطة التطبيقات هي حاويات في أعلى الشاشة أو أسفلها تمنح المستخدمين إمكانية الوصول إلى الميزات الرئيسية وعناصر التنقّل:
النوع |
المظهر |
الغرض |
|---|---|---|
| شريط التطبيق العلوي | في أعلى الشاشة |
يتيح الوصول إلى المهام والمعلومات الرئيسية. وعادةً ما يستضيف القسم عنوانًا وبنود إجراءات أساسية وعناصر تنقّل معيّنة. |
| شريط التطبيق السفلي | في أسفل الشاشة |
وعادةً ما تتضمّن عناصر التنقّل الأساسية. قد تمنح إمكانية الوصول إلى إجراءات أخرى، على سبيل المثال، باستخدام زر إجراء رئيسي. |
توافق الإصدار
يتطلّب هذا التنفيذ ضبط الحد الأدنى من إصدار حزمة SDK لمشروعك على المستوى 21 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات أو إصدار أحدث.
التبعيات
تنفيذ شريط تطبيق في أعلى الشاشة
يعرض الرمز التالي عمليات التنفيذ للأنواع الأربعة من أشرطة التطبيقات العلوية، بما في ذلك أمثلة متنوعة على كيفية التحكّم في سلوك الانتقال للأعلى أو للأسفل.
- شريط التطبيقات العلوي الصغير
- شريط التطبيق العلوي الذي تمّت محاذاته في الوسط
- شريط التطبيق العلوي المتوسط
- شريط التطبيق العلوي الكبير
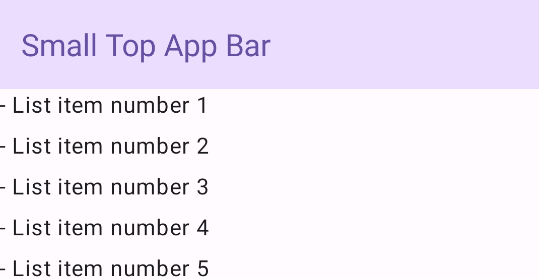
شريط التطبيق العلوي الصغير
لإنشاء شريط تطبيق صغير في أعلى الشاشة، استخدِم العنصر القابل للتجميع TopAppBar. هذا هو
أبسط شريط تطبيق علوي ممكن، وفي هذا المثال يحتوي على عنوان فقط.
لا يُرسِل المثال التالي إلى TopAppBar قيمة
scrollBehavior، لذا لا يستجيب شريط التطبيق العلوي للانتقال إلى
المحتوى الداخلي.
النتيجة
شريط التطبيق العلوي الذي تمت محاذاته في الوسط
شريط التطبيقات العلوي الذي تم ضبطه في المنتصف هو نفسه شريط التطبيقات الصغير،
باستثناء أنّ العنوان يكون في المنتصف داخل المكوّن. لتنفيذ ذلك، استخدِم العنصر القابل للتجميع المخصّص CenterAlignedTopAppBar.
يستخدم هذا المثال enterAlwaysScrollBehavior() للحصول على القيمة التي يتم تمريرها
لـ scrollBehavior. يتم تصغير الشريط عندما ينتقل المستخدم إلى
المحتوى الداخلي للإطار.
النتيجة

شريط التطبيق العلوي المتوسط
يضع شريط التطبيق العلوي المتوسط الحجم العنوان أسفل أي رموز إضافية. لإنشاء
واحد، استخدِم العنصر القابل للتجميع MediumTopAppBar.
مثل الرمز البرمجي السابق، يستخدم هذا المثال enterAlwaysScrollBehavior() لمحاولة
الحصول على القيمة التي يتم تمريرها إلى scrollBehavior.
النتيجة
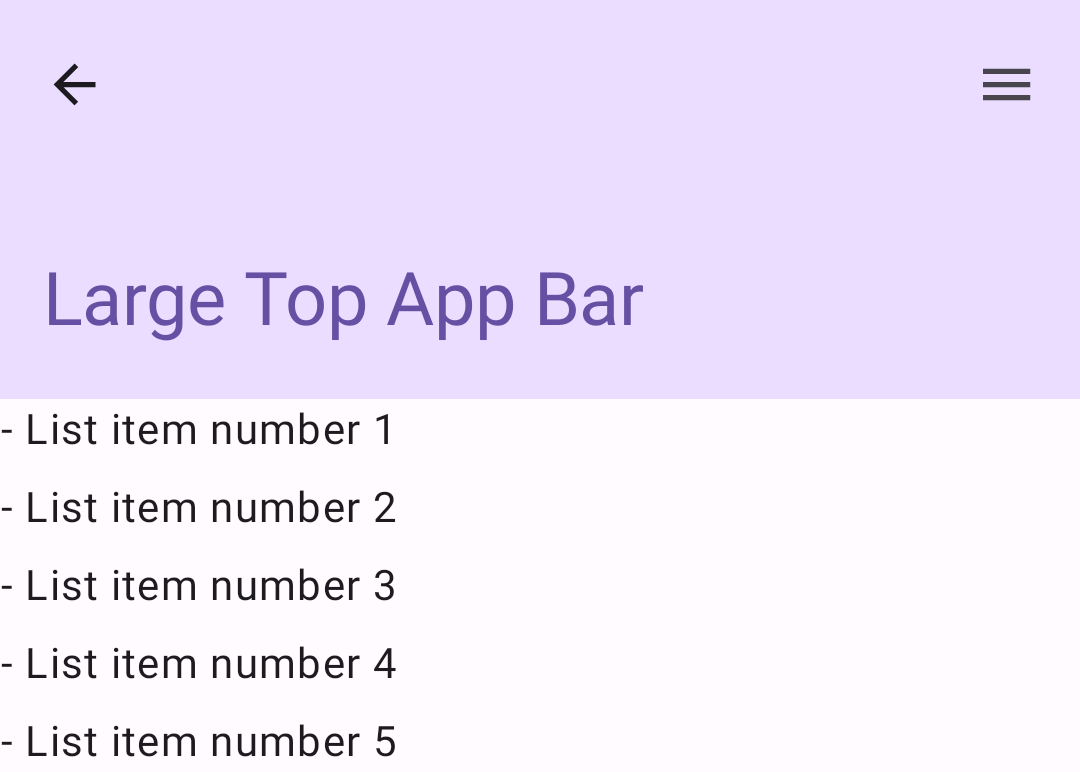
enterAlwaysScrollBehaviorشريط التطبيق العلوي الكبير
يشبه شريط التطبيقات العلوي الكبير الشريط المتوسط، إلا أنّ المسافة الفارغة بين
العنوان والرموز أكبر، كما أنّه يشغل مساحة أكبر على الشاشة بشكل عام. ل
إنشاء نموذج، استخدِم العنصر القابل للتجميع LargeTopAppBar ).
يستخدِم هذا المثال
exitUntilCollapsedScrollBehavior() للحصول على القيمة التي يتم تمريرها
scrollBehavior. ينكمش الشريط عندما ينتقل المستخدم إلى
المحتوى الداخلي للإطار، ولكن يتم توسيعه عندما ينتقل المستخدم إلى نهاية
المحتوى الداخلي.
النتيجة
تنفيذ شريط تطبيق سفلي
لإنشاء شريط تطبيق سفلي، استخدِم العنصر القابل للتجميع BottomAppBar، وهو مشابه لعنصر شريط التطبيق العلوي القابل للتجميع.
يمكنك تمرير العناصر القابلة للتجميع للسمَتَين التاليتَين:
actions: سلسلة من الرموز التي تظهر على يمين الشريط وعادةً ما تكون هذه الإجراءات إما إجراءات رئيسية للشاشة المحدّدة أو عناصر تنقّل.floatingActionButton: زر الإجراء الرئيسي العائم الذي يظهر على الجانب الأيمن من الشريط
النتيجة

النقاط الرئيسية
- بشكل عام، يتم تمرير أشرطة التطبيقات إلى العنصر القابل للتجميع
Scaffoldالذي يحتوي على معلمات محدّدة لتلقّيها. تشترك العناصر القابلة للتجميع التي تستخدمها لتنفيذ شريط التطبيقات العلوي في المَعلمات الرئيسية التالية:
title: النص الذي يظهر في شريط التطبيقnavigationIcon: الرمز الأساسي للتنقّل، والذي يظهر على يسار شريط التطبيقactions: الرموز التي تمنح المستخدم إمكانية الوصول إلى الإجراءات الرئيسية، والتي تظهر على يسار شريط التطبيق-
scrollBehavior: لتحديد كيفية استجابة شريط التطبيق العلوي لتحريك المحتوى الداخلي للإطار. -
colors: لتحديد كيفية ظهور شريط التطبيق
يمكنك التحكّم في كيفية استجابة شريط التطبيق عندما ينتقل المستخدم إلى المحتوى الداخلي للإطار. لإجراء ذلك، أنشئ مثيلًا من
TopAppBarScrollBehaviorوأرسِله إلى شريط التطبيق العلوي للمَعلمةscrollBehavior. هناك ثلاثة أنواع منTopAppBarScrollBehavior:enterAlwaysScrollBehavior: عندما يسحب المستخدم المحتوى الداخلي لإطار العمل، يتم تصغير شريط التطبيق العلوي. يتم توسيع شريط التطبيق عندما يجذب المستخدم المحتوى الداخلي للأسفل.exitUntilCollapsedScrollBehavior: يشبهenterAlwaysScrollBehavior، مع أنّ شريط التطبيق يتوسّع أيضًا عندما يصل المستخدم إلى نهاية المحتوى الداخلي للإطار.pinnedScrollBehavior: يبقى شريط التطبيقات في مكانه ولا يستجيب للتنقل.
المجموعات التي تتضمّن هذا الدليل
هذا الدليل هو جزء من مجموعات الأدلة السريعة المنظَّمة التي تتناول أهداف تطوير Android الأوسع نطاقًا: