Android XR 系统使用与移动应用和大屏幕应用类似的互动模型,以帮助用户了解如何使用 XR。其中包括主屏幕、应用概览、返回堆栈等已知模式。
为了帮助您打造无缝的一体化体验,Android XR 提供了自然的动作导航、多模式输入以及新的空间和 3D 功能。
Home Space 模式和 Full Space 模式
用户可在 Home Space 和 Full Space 两种模式下体验您的应用。在 Home Space 中,用户可以同时处理多个任务,您的应用可与其他应用并排运行。在 Full Space 中,您的应用是用户体验的焦点,可完全访问 Android XR 的沉浸式功能。
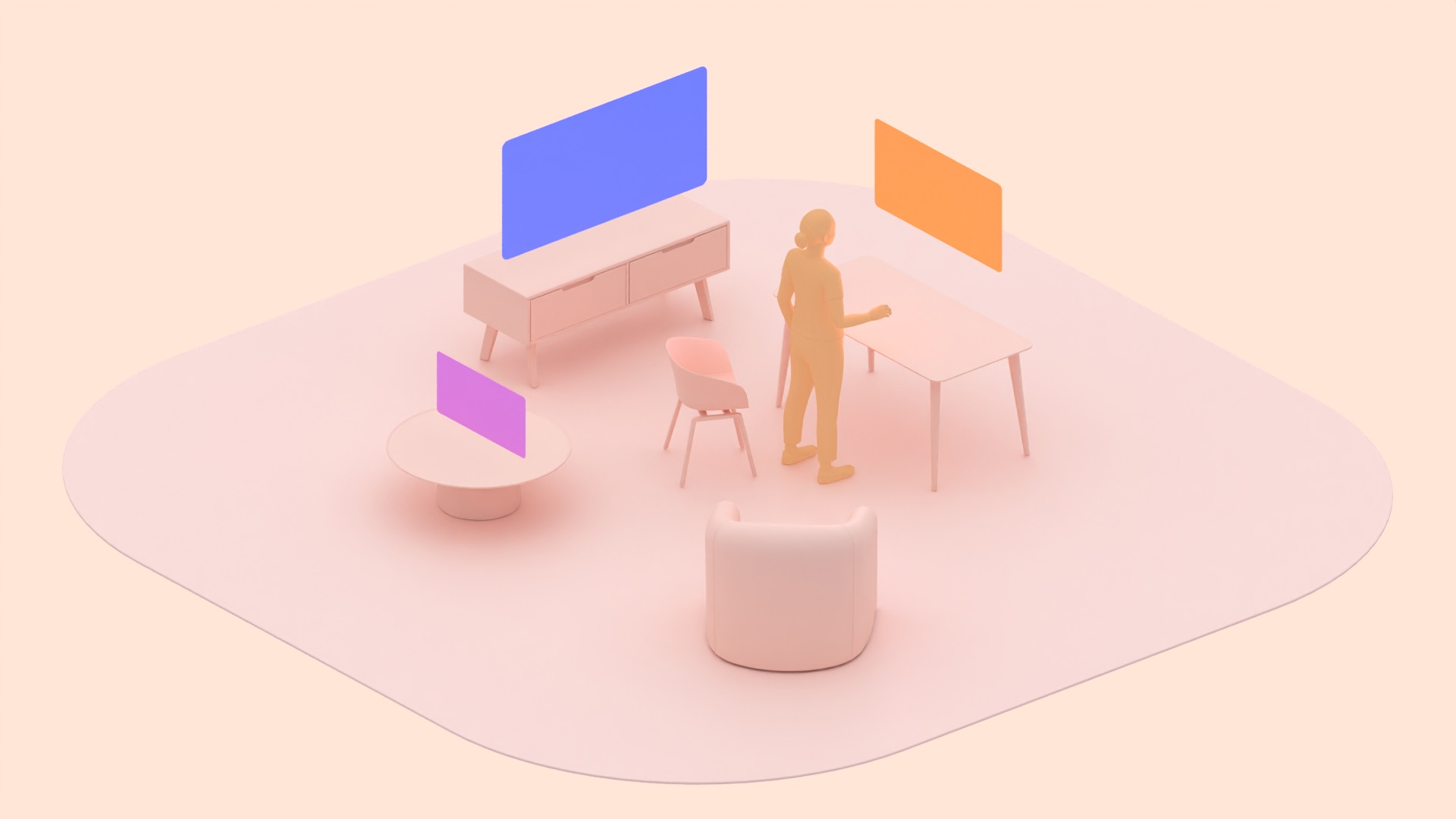

Home Space
- 多个应用可以并排运行,以便用户同时处理多个任务。
- 任何兼容的移动版或大屏幕版 Android 应用都可以在 Home Space 中运行,无需进行额外开发。
- 遵循针对大屏设备优化的指南开发的 Android 应用最适合进行自适应。
- Home Space 支持系统环境。它不支持空间面板、3D 模型或应用的空间环境。
- 应用具有受限边界。
- 默认大小:1024 x 720dp
- 最小尺寸 385 x 595dp,最大尺寸 2560 x 1800dp
- 应用在距离用户 1.75 米处启动。
让用户掌控自己的环境
在 Android XR 中,环境是指用户佩戴 XR 设备时看到的真实或虚拟空间。它不受移动设备和桌面设备屏幕的物理限制。
- 空间环境可模拟完全沉浸式的虚拟空间,取代用户的实际空间。仅适用于全屏聊天室。例如,用户在虚拟豪华影院中观看电影。
- 透视环境会向用户的实际环境添加数字元素。例如,用户打开多个大屏应用,同时查看真实的房间。
系统环境
用户可以选择 Android XR 系统提供的环境。这些系统环境可在 Home Space 或 Full Space 中使用。如果应用未定义特定环境,则会继承系统环境(在透传环境或虚拟环境中)。
了解系统手势
Android XR 将熟悉的移动操作(例如按压、双指张合和滑动)扩展到了基于手势的导航系统。
通过使用主手的食指和拇指进行捏合来选择内容,这在空间上相当于在触摸屏上点按或按下鼠标按钮。按住双指张合可滚动、移动或调整窗口大小,以及在 2D 和 3D 空间中选择和移动界面元素或对象。
用户将惯用手的手掌朝向自己,然后捏合并按住食指和拇指即可进行导航。用户将手指向上、向下、向左或向右移动,然后松开手指即可选择选项。用户可以在输入设置中设置主手偏好设置。
用户可以随时随地打开手势导航菜单,执行以下操作:
- 返回:与 Android 移动设备上的返回堆栈相同,用于返回上一个项。
- 启动器:将用户定向到主屏幕。
- 最近用过:用户可以打开、关闭和切换应用。
设计多模态输入
设计可供广大用户访问的沉浸式应用至关重要。您应允许用户自定义输入法,以适应其个人偏好和能力。
为帮助您实现这一目标,Android XR 支持多种输入方法,包括手部和眼球跟踪、语音指令、蓝牙连接的键盘、传统鼠标和自适应鼠标、触控板和六自由度 (6DoF) 控制器。您的应用应自动支持这些内置模式。
请务必针对您选择的任何交互模型提供视觉或音频反馈,以确认用户操作。
手部跟踪功能可实现自然互动。在开发 OpenXR 应用时,您可以向系统请求直接访问手部跟踪功能并添加自己的自定义手势的权限。这些操作应易于学习、记忆和执行。
在设计手势时,请注意手势应能够轻松重复执行,并且不需要大范围地移动手部或频繁抬起手臂,否则可能会让人感到疲倦。如果您添加了虚拟手,请确保系统能够准确跟踪它们。
您还可以设计模仿现实世界中操作(例如提起或投掷)的手势。使用熟悉的手势可能有助于用户更快地了解互动。
请注意,与系统手势相似可能会导致冲突或意外激活系统功能。
语音指令非常适合免触摸互动。用户可以通过 Gemini 口述文本输入内容,并通过语音指令执行某些应用互动。例如,用户可以说“打开 Google 地图”来打开该应用。
眼动跟踪可实现轻松互动,例如通过注视对象来选择对象。为了尽量减少眼睛疲劳,您可以提供其他输入方法。
外围设备。Android XR 支持蓝牙键盘、鼠标和 6DoF 控制器等外部设备。对于控制器,请确保按钮映射直观,并考虑允许用户重新映射按钮以符合其偏好设置。
隐私注意事项
Android 的隐私权建议适用于构建 XR 应用。请务必先征得用户同意,然后再收集任何个人身份信息,并将用户数据收集范围限制在必要范围内,并安全地存储这些数据。
OpenXR™ 和 OpenXR 徽标是 Khronos Group Inc. 拥有的商标,已在中国、欧盟、日本和英国注册为商标。


