يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة رائعة للمطوّرين. توضّح الأقسام التالية هذه الميزات لمساعدتك على البدء في استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات ذات الصلة.
للحصول على قائمة مفصّلة بواجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة والمعدَّلة والمحذوفة، يُرجى الاطّلاع على تقرير الاختلافات في واجهات برمجة التطبيقات. للحصول على تفاصيل حول واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة، يُرجى الانتقال إلى مرجع واجهات برمجة تطبيقات Android، حيث يتم تمييز واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة لتسهيل العثور عليها.عليك أيضًا مراجعة الأقسام التي قد تؤثر فيها تغييرات النظام الأساسي في تطبيقاتك. لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على الصفحات التالية:
- التغييرات في السلوك التي تؤثّر في التطبيقات عند استهدافها الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android
- تغييرات في السلوك تؤثر في جميع التطبيقات بغض النظر عن
targetSdkVersion
الوظيفة الأساسية
يتضمّن Android واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة توسّع الإمكانات الأساسية لنظام التشغيل Android.
إصداران من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات لنظام التشغيل Android في عام 2025
- This preview is for the next major release of Android with a planned launch in Q2 of 2025. This release is similar to all of our API releases in the past, where we can have planned behavior changes that are often tied to a targetSdkVersion.
- We're planning the major release a quarter earlier (Q2 rather than Q3 in prior years) to better align with the schedule of device launches across our ecosystem, so more devices can get the major release of Android sooner. With the major release coming in Q2, you'll need to do your annual compatibility testing a few months earlier than in previous years to make sure your apps are ready.
- We plan to have another release in Q4 of 2025 which also will include new developer APIs. The Q2 major release will be the only release in 2025 to include planned behavior changes that could affect apps.
In addition to new developer APIs, the Q4 minor release will pick up feature updates, optimizations, and bug fixes; it will not include any app-impacting behavior changes.
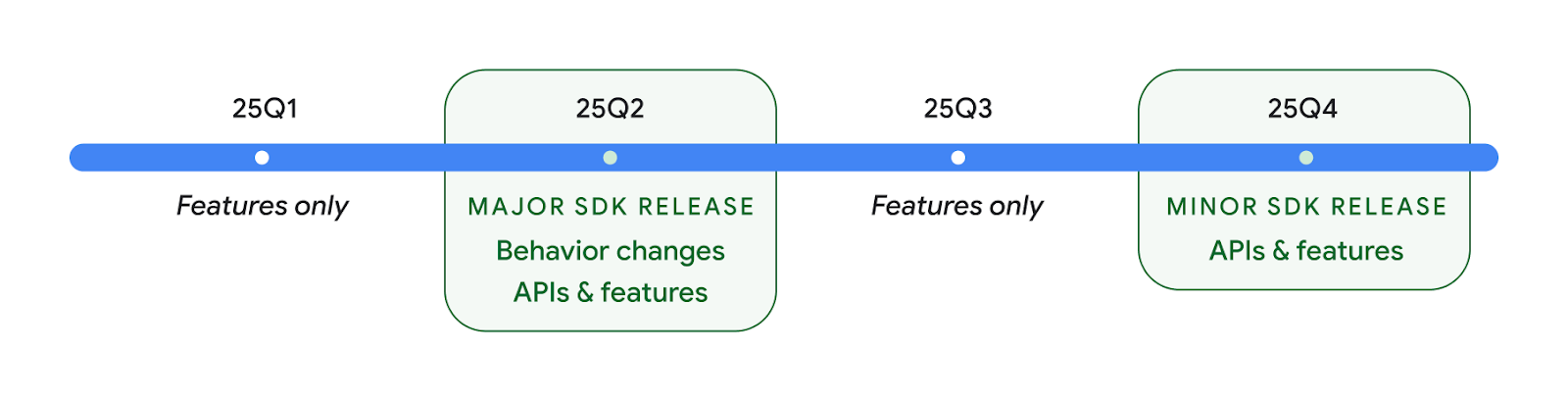
We'll continue to have quarterly Android releases. The Q1 and Q3 updates in-between the API releases will provide incremental updates to help ensure continuous quality. We're actively working with our device partners to bring the Q2 release to as many devices as possible.
Using new APIs with major and minor releases
Guarding a code block with a check for API level is done today using
the SDK_INT constant with
VERSION_CODES. This will continue
to be supported for major Android releases.
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
The new SDK_INT_FULL
constant can be used for API checks against both major and minor versions with
the new VERSION_CODES_FULL
enumeration.
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
You can also use the
Build.getMinorSdkVersion()
method to get just the minor SDK version.
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
These APIs have not yet been finalized and are subject to change, so please send us feedback if you have any concerns.
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يمنح نظام التشغيل Android 16 مطوّري التطبيقات والمستخدمين المزيد من التحكّم والمرونة في إعداد أجهزتهم بما يتناسب مع احتياجاتهم.
الإشعارات التي تركّز على مستوى التقدّم
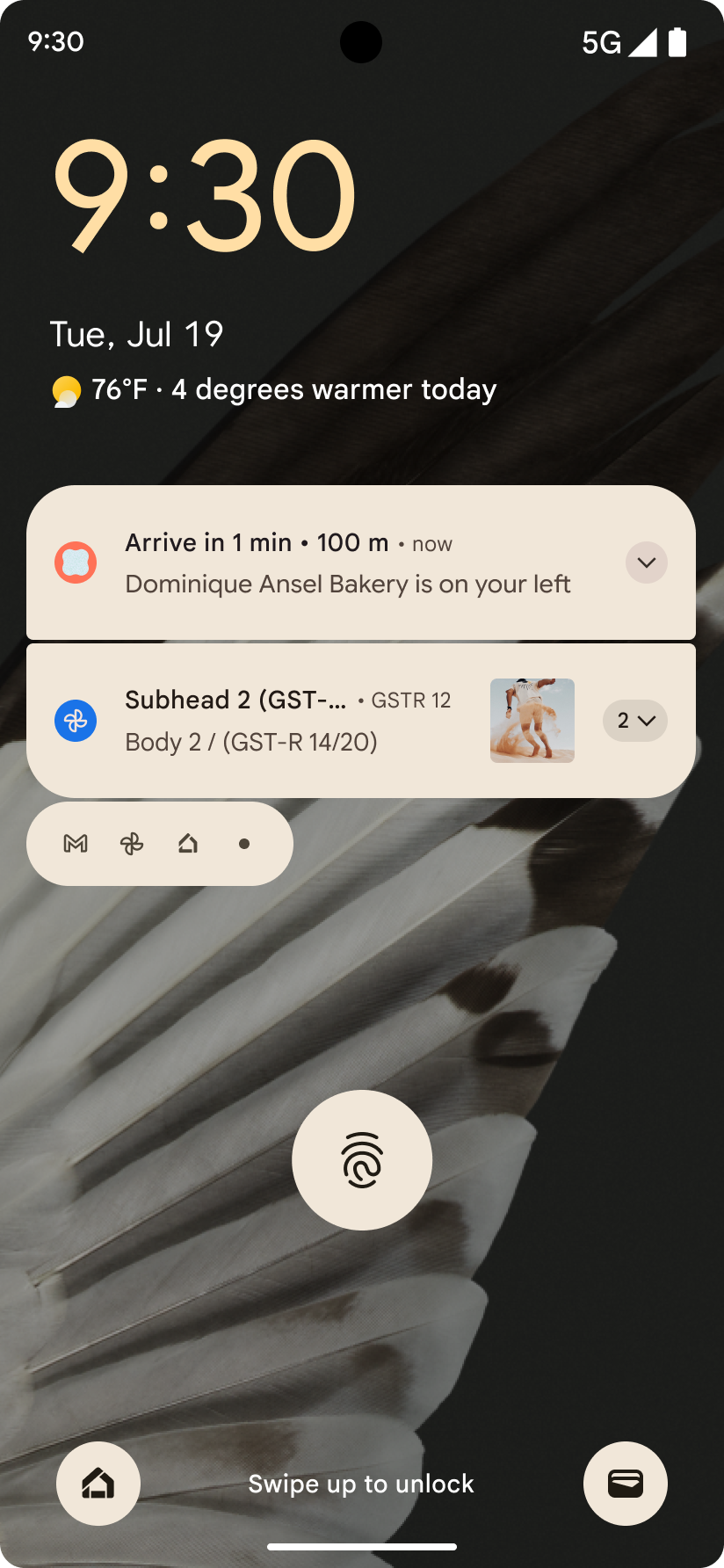
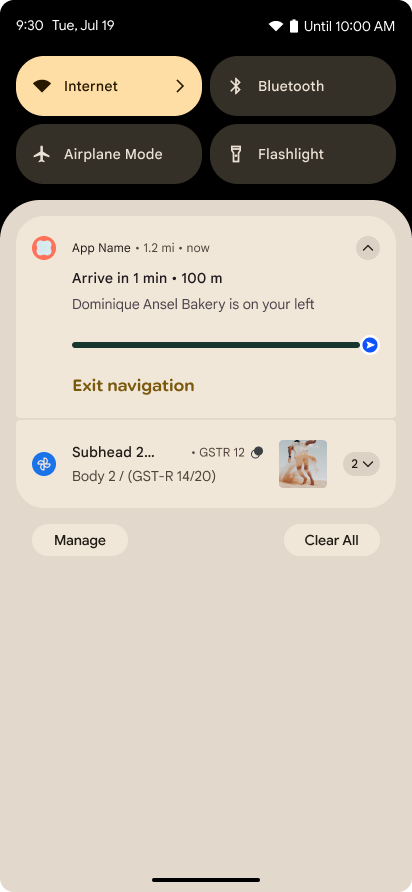
Android 16 introduces progress-centric notifications to help users seamlessly track user-initiated, start-to-end journeys.
Notification.ProgressStyle is a new notification
style that lets you create progress-centric notifications. Key use cases include
rideshare, delivery, and navigation. Within the Notification.ProgressStyle
class, you can denote states and milestones in a user journey using
points and segments.
لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على صفحة مستندات الإشعارات التي تركّز على مستوى التقدّم.
تعديلات على إيماءة الرجوع إلى الخلف التنبؤية
يضيف الإصدار 16 من Android واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة لمساعدتك في تفعيل الصور المتحركة في النظام لإيماءة الرجوع إلى الخلف التنبؤية في أثناء التنقّل باستخدام الإيماءات، مثل الصورة المتحركة للرجوع إلى الشاشة الرئيسية. من خلال تسجيل
onBackInvokedCallback باستخدام الرمز الجديد
PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER، يمكن لتطبيقكتلقّي طلب onBackInvoked العادي كلما تعامل النظام مع عملية الرجوع بدون التأثير في سير عملية الرجوع العادي.
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 أيضًا رمزَي
finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() و
moveTaskToBackCallback. من خلال تسجيل عمليات الاستدعاء هذه
باستخدام OnBackInvokedDispatcher، يمكن للنظام بدء
سلوكيات معيّنة وتشغيل الصور المتحركة المقابلة مسبقًا عند تنفيذ رمز الإيماءة
للرجوع.
تجاوب حسّي أكثر ثراءً
Android has exposed control over the haptic actuator ever since its inception.
Android 11 added support for more complex haptic effects that more advanced
actuators could support through
VibrationEffect.Compositions of device-defined semantic
primitives.
Android 16 adds haptic APIs that let apps define the amplitude and frequency curves of a haptic effect while abstracting away differences between device capabilities.
إنتاجية المطوّرين وأدواتهم
مع أنّ معظم جهودنا لتحسين إنتاجيتك تركّز على أدوات مثل استوديو Android وJetpack Compose ومكتبات Android Jetpack، إلا أنّنا نبحث دائمًا عن طرق في النظام الأساسي لمساعدتك في تحقيق أهدافك.
التعامل مع المحتوى في الخلفيات المتحركة
In Android 16, the live wallpaper framework is gaining a new content API to
address the challenges of dynamic, user-driven wallpapers. Currently, live
wallpapers incorporating user-provided content require complex, service-specific
implementations. Android 16 introduces
WallpaperDescription and
WallpaperInstance. WallpaperDescription lets you
identify distinct instances of a live wallpaper from the same service. For
example, a wallpaper that has instances on both the home screen and on the lock
screen may have unique content in both places. The wallpaper picker and
WallpaperManager use this metadata to better present
wallpapers to users, streamlining the process for you to create diverse and
personalized live wallpaper experiences.
الأداء والبطارية
يقدّم الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تساعد في جمع إحصاءات حول تطبيقاتك.
تحديد المواصفات الشخصية لصاحب البيانات من خلال النظام
ProfilingManager was
added in Android 15, giving apps the ability to
request profiling data collection using Perfetto on public devices in the field.
However, since this profiling must be started from the app, critical flows such
as startups or ANRs would be difficult or impossible for apps to capture.
To help with this, Android 16 introduces system-triggered profiling to
ProfilingManager. Apps can register interest in receiving traces for certain
triggers such as cold start reportFullyDrawn
or ANRs, and then the system starts and stops a trace on the app's behalf. After
the trace completes, the results are delivered to the app's data directory.
بدء المكوّن في ApplicationStartInfo
تم إضافةApplicationStartInfo في الإصدار
15 من Android، ما يتيح للتطبيق الاطّلاع على أسباب
بدء العملية ونوع البدء وأوقات البدء والحدّ من السرعة وغيرها من بيانات التشخيص مفيدة. يضيف الإصدار 16 من Android رمزًا برمجيًا هو
getStartComponent()
لتمييز نوع المكوّن الذي بدأ عملية التشغيل، ما قد يكون مفيدًا في
تحسين عملية بدء تشغيل تطبيقك.
تحسين فحص المهام
تعرض واجهة برمجة التطبيقات JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() سبب احتمال أن تكون إحدى المهام في انتظار المراجعة. ومع ذلك، قد تكون المهمة في انتظار المراجعة لعدة أسباب.
في Android 16، نقدّم واجهة برمجة تطبيقات جديدة
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId)، وهي تعرض عدة
أسباب لتعليق إحدى المهام، وذلك بسبب القيود الصريحة التي يحدّدها المطوّر والقيود الضمنية التي يحدّدها النظام.
نقدّم أيضًا الرمز
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId) الذي يعرض قائمة
بأحدث تغييرات القيود.
ننصحك باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات لمساعدتك في تصحيح الأخطاء المتعلّقة بعدم تنفيذ مهامك، خاصةً إذا لاحظت انخفاضًا في معدّلات نجاح مهام معيّنة أو إذا واجهت أخطاء تتعلّق بالوقت المستغرَق لإكمال مهام معيّنة. على سبيل المثال، تعذّر تعديل التطبيقات المصغّرة في الخلفية أو تعذّر استدعاء مهمة التحميل المُسبَق قبل بدأ التطبيق.
ويمكن أن يساعدك ذلك أيضًا في معرفة ما إذا كانت بعض المهام لا تكتمل بسبب قيود محدّدة من النظام مقارنةً بالقيود المحدّدة بوضوح.
معدّل التحديث التكيّفي
إنّ معدل إعادة التحميل التكيُّفي (ARR) الذي تم تقديمه في Android 15 يتيح لمعدل إعادة تحميل الشاشة على الأجهزة المتوافقة التكيُّف مع معدل عرض اللقطات للمحتوى باستخدام خطوات فاصل عرض اللقطات المنفصلة. ويؤدي ذلك إلى تقليل استهلاك الطاقة مع التخلص من الحاجة إلى التبديل بين الأوضاع الذي قد يؤدي إلى حدوث تقطُّع في الأداء.
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 hasArrSupport() و
getSuggestedFrameRate(int) مع استعادة
getSupportedRefreshRates() لتسهيل استفادة تطبيقاتك من ميزة ARR. يتيح RecyclerView
1.4 استخدام ميزة ARR داخليًا عند الانتقال من التمرير السريع أو
الانتقال السلس، ونحن نواصل عملنا لإضافة ميزة ARR
إلى المزيد من مكتبات Jetpack. تتناول مقالة معدّل عرض اللقطات هذه
العديد من واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي يمكنك استخدامها لضبط معدّل عرض اللقطات كي يتمكّن تطبيقك من استخدام ميزة "معدل عرض الإعلانات" مباشرةً.
واجهات برمجة تطبيقات Headroom في ADPF
The SystemHealthManager introduces the
getCpuHeadroom and
getGpuHeadroom APIs, designed to provide games and
resource-intensive apps with estimates of available CPU and GPU resources. These
methods offer a way for you to gauge how your app or game can best improve
system health, particularly when used in conjunction with other Android Dynamic
Performance Framework (ADPF) APIs that detect thermal
throttling.
By using CpuHeadroomParams and
GpuHeadroomParams on supported devices, you can
customize the time window used to compute the headroom and select between
average or minimum resource availability. This can help you reduce your CPU or
GPU resource usage accordingly, leading to better user experiences and improved
battery life.
تسهيل الاستخدام
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة لتسهيل الاستخدام يمكن أن تساعدك في توفير تطبيقك لجميع المستخدمين.
واجهات برمجة تطبيقات محسَّنة لتسهيل الاستخدام
Android 16 adds additional APIs to enhance UI semantics that help improve consistency for users that rely on accessibility services, such as TalkBack.
Outline text for maximum text contrast
Users with low vision often have reduced contrast sensitivity, making it challenging to distinguish objects from their backgrounds. To help these users, Android 16 introduces outline text, replacing high contrast text, which draws a larger contrasting area around text to greatly improve legibility.
Android 16 contains new AccessibilityManager APIs to let
your apps check or register a listener to
see if this mode is enabled. This is primarily for UI Toolkits like Compose to
offer a similar visual experience. If you maintain a UI Toolkit library or your
app performs custom text rendering that bypasses the
android.text.Layout class then you can use this to know
when outline text is enabled.
Duration added to TtsSpan
Android 16 extends TtsSpan with a TYPE_DURATION,
consisting of ARG_HOURS, ARG_MINUTES,
and ARG_SECONDS. This lets you directly annotate time
duration, ensuring accurate and consistent text-to-speech output with services
like TalkBack.
Support elements with multiple labels
Android currently allows UI elements to derive their accessibility label from
another, and now offers the ability for multiple labels to be associated, a
common scenario in web content. By introducing a list-based API within
AccessibilityNodeInfo, Android can directly support these
multi-label relationships. As part of this change, we've deprecated
AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy and
#getLabeledBy in favor of
#addLabeledBy, #removeLabeledBy, and
#getLabeledByList.
Improved support for expandable elements
Android 16 adds accessibility APIs that allow you to convey the expanded or
collapsed state of interactive elements, such as menus and expandable lists. By
setting the expanded state using setExpandedState and
dispatching TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents
with a CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED content change type,
you can ensure that screen readers like TalkBack announce
state changes, providing a more intuitive and inclusive user experience.
Indeterminate ProgressBars
Android 16 adds RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE, giving a way for
you to expose RangeInfo for both determinate and
indeterminate ProgressBar widgets, allowing services like
TalkBack to more consistently provide feedback for progress
indicators.
Tri-state CheckBox
The new AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked and setChecked(int)
methods in Android 16 now support a "partially checked" state in addition to
"checked" and "unchecked." This replaces the deprecated boolean
isChecked and setChecked(boolean).
Supplemental descriptions
When an accessibility service describes a ViewGroup, it
combines content labels from its child views. If you provide a
contentDescription for the ViewGroup, accessibility services assume you are
also overriding the description of non-focusable child views. This can be
problematic if you want to label things like a drop-down (for example, "Font
Family") while preserving the current selection for accessibility (for example,
"Roboto"). Android 16 adds setSupplementalDescription so
you can provide text that provides information about a ViewGroup without
overriding information from its children.
Required form fields
Android 16 adds setFieldRequired to
AccessibilityNodeInfo so apps can tell an accessibility
service that input to a form field is required. This is an important scenario
for users filling out many types of forms, even things as simple as a required
terms and conditions checkbox, helping users to consistently identify and
quickly navigate between required fields.
استخدام الهاتف كميكروفون لإجراء مكالمات صوتية باستخدام سماعات الأذن الطبية المزودة بتقنية LEA
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 إمكانية السماح لمستخدمي سمّاعات الأذن الطبية المزوّدة بتقنية LE Audio بالتبديل بين الميكروفونات المدمجة في سمّاعات الأذن الطبية والميكروفون في الهاتف لإجراء المكالمات الصوتية. يمكن أن يكون ذلك مفيدًا في البيئات الصاخبة أو في حالات أخرى قد لا تعمل فيها ميكروفونات سماعة الأذن الطبية بشكل جيد.
عناصر التحكّم في مستوى الصوت المحيط لسماعات الأذن الطبية المتوافقة مع LEA
Android 16 adds the capability for users of LE Audio hearing aids to adjust the volume of ambient sound that is picked up by the hearing aid's microphones. This can be helpful in situations where background noise is too loud or too quiet.
الكاميرا
يحسِّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 إمكانية استخدام الكاميرات الاحترافية، ما يتيح التعريض التلقائي المختلط إلى جانب إجراء تعديلات دقيقة على درجة حرارة الألوان ودرجة اللون. يساعد مؤشر وضع الليل الجديد تطبيقك في معرفة الوقت المناسب للتبديل إلى جلسة كاميرا في وضع الليل أو إيقافها. تسهّل الإجراءات الجديدة Intent التقاط صور متحركة،
ونواصل تحسين صور Ultra HDR من خلال توفير توافق مع ترميز HEIC
ومَعلمات جديدة من مسودة معيار ISO 21496-1.
التعرّض التلقائي المختلط للضوء
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 أوضاعًا جديدة مختلطة للتعريض التلقائي إلى Camera2، ما يتيح لك التحكّم يدويًا في جوانب معيّنة من التعريض مع السماح لخوارزمية التعريض التلقائي (AE) بالتعامل مع الباقي. يمكنك التحكّم في درجة ISO + التعريض التلقائي ووقت التعريض + التعريض التلقائي، ما يوفّر مزيدًا من المرونة مقارنةً بالنهج الحالي الذي يتيح لك التحكّم يدوياً بالكامل أو الاعتماد بالكامل على التعريض التلقائي.
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
تعديلات دقيقة على درجة حرارة الألوان ودرجة اللون
Android 16 adds camera support for fine color temperature and tint adjustments
to better support professional video recording applications. In previous Android
versions, you could control white balance settings through
CONTROL_AWB_MODE, which contains options limited to a
preset list, such as Incandescent,
Cloudy, and Twilight. The
COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT enables the use of
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE and
COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT for precise adjustments of
white balance based on the correlated color temperature.
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
The following examples show how a photo would look after applying different color temperature and tint adjustments:





رصد المشاهد في "الوضع الليلي" للكاميرا
To help your app know when to switch to and from a night mode camera session,
Android 16 adds EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR. If
supported, it's available in the CaptureResult within
Camera2.
This is the API we briefly mentioned as coming soon in the How Instagram enabled users to take stunning low light photos blog post. That post is a practical guide on how to implement night mode together with a case study that links higher-quality in-app night mode photos with an increase in the number of photos shared from the in-app camera.
إجراءات Intent لالتقاط صور حيّة
Android 16 adds standard Intent actions —
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE, and
ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE — which request that
the camera application capture a motion photo and return
it.
You must either pass an extra EXTRA_OUTPUT to control
where the image will be written, or a Uri through
Intent.setClipData(ClipData). If you don't set a
ClipData, it will be copied there for you when calling
Context.startActivity(Intent).
تحسينات على صور UltraHDR

Android 16 continues our work to deliver dazzling image quality with UltraHDR
images. It adds support for UltraHDR images in the HEIC file
format. These images will get ImageFormat type
HEIC_ULTRAHDR and will contain an embedded gainmap similar
to the existing UltraHDR JPEG format. We're working on AVIF support for UltraHDR
as well, so stay tuned.
In addition, Android 16 implements additional parameters in UltraHDR from the ISO 21496-1 draft standard, including the ability to get and set the colorspace that gainmap math should be applied in, as well as support for HDR encoded base images with SDR gainmaps.
الرسومات
يتضمّن Android 16 أحدث التحسينات على الرسومات، مثل التأثيرات الرسومية المخصّصة باستخدام AGSL.
تأثيرات رسومية مخصّصة باستخدام AGSL
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 RuntimeColorFilter و
RuntimeXfermode، ما يتيح لك إنشاء تأثيرات معقّدة مثل
الحدّ الأدنى وتأثير "تشبيك الصورة" و"تشبع درجة اللون" وتطبيقها على طلبات الرسم. منذ الإصدار Android
13، أصبح بإمكانك استخدام AGSL لإنشاء
تأثيرات رسومية ديناميكية مخصّصة تمتد إلى Shader. تعكس واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة
هذا الإجراء، مع إضافة RuntimeColorFilter المستند إلى AGSL والتي
تُوسّع نطاق ColorFilter، وتأثير Xfermode الذي
يتيح لك تنفيذ عمليات دمج ومزج مخصّصة مستندة إلى AGSL بين وحدات البكسل المصدر
والوجهة.
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
إمكانية الاتصال
يعدّل Android 16 النظام الأساسي لمنح تطبيقك إمكانية الوصول إلى أحدث التطورات في تكنولوجيات الاتصال والشبكات اللاسلكية.
تحديد المدى مع مستوى أمان محسّن
Android 16 adds support for robust security features in Wi-Fi location on supported devices with Wi-Fi 6's 802.11az, allowing apps to combine the higher accuracy, greater scalability, and dynamic scheduling of the protocol with security enhancements including AES-256-based encryption and protection against MITM attacks. This allows it to be used more safely in proximity use cases, such as unlocking a laptop or a vehicle door. 802.11az is integrated with the Wi-Fi 6 standard, leveraging its infrastructure and capabilities for wider adoption and easier deployment.
واجهات برمجة التطبيقات العامة لتحديد المدى
Android 16 includes the new RangingManager, which provides
ways to determine the distance and angle on supported hardware between the local
device and a remote device. RangingManager supports the usage of a variety of
ranging technologies such as BLE channel sounding, BLE RSSI-based ranging, Ultra
Wideband, and Wi-Fi round trip time.
توفّر الجهاز المصاحب في "أداة إدارة الأجهزة المصاحبة"
In Android 16, new APIs are being introduced for binding your companion app
service. Service will be bound when BLE is in range and Bluetooth is connected
and service will be unbound when BLE is out of range or Bluetooth is
disconnected. App will receives a new
'onDevicePresenceEvent()' callback based on various
of DevicePresenceEvent.
More details can be found in
'startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)'.
الوسائط
يتضمّن Android 16 مجموعة متنوعة من الميزات التي تحسّن تجربة استخدام الوسائط.
تحسينات على أداة اختيار الصور
The photo picker provides a safe, built-in way for users to grant your app access to selected images and videos from both local and cloud storage, instead of their entire media library. Using a combination of Modular System Components through Google System Updates and Google Play services, it's supported back to Android 4.4 (API level 19). Integration requires just a few lines of code with the associated Android Jetpack library.
Android 16 includes the following improvements to the photo picker:
- Embedded photo picker: New APIs that enable apps to embed the photo picker into their view hierarchy. This allows it to feel like a more integrated part of the app while still leveraging the process isolation that allows users to select media without the app needing overly broad permissions. To maximize compatibility across platform versions and simplify your integration, you'll want to use the forthcoming Android Jetpack library if you want to integrate the embedded photo picker.
- Cloud search in photo picker: New APIs that enable searching from the cloud media provider for the Android photo picker. Search functionality in the photo picker is coming soon.
فيديو احترافي متقدّم
يتيح نظام التشغيل Android 16 استخدام ترميز Advanced Professional Video (APV) المصمّم لاستخدامه في تسجيل الفيديوهات بجودة عالية على المستوى الاحترافي وعمليات ما بعد الإنتاج.
يتضمن معيار ترميز APV الميزات التالية:
- جودة فيديو بدون فقدان ملحوظ للبيانات (قريبة من جودة الفيديو الأصلي)
- ترميز داخل اللقطة فقط بدرجة منخفضة من التعقيد ومع معدل نقل بيانات مرتفع (بدون توقّع ملف هبوط حبيبات البكسل) لدعم سير عمل التعديل بشكل أفضل
- إتاحة نطاق معدل نقل بيانات مرتفع يصل إلى بضعة غيغابايت في الثانية للمحتوى بدقة 2K و4K و8K ، وذلك من خلال مخطّط ترميز معلومات منخفض الوزن
- تقسيم الإطارات للمحتوى الغامر وتفعيل الترميز والترميز الثنائي
- إتاحة تنسيقات مختلفة لتحليل الألوان ودرجات البت
- إتاحة عمليات فك ترميز وإعادة ترميز متعددة بدون تعريض الجودة المرئية للتدهّور الشديد
- إتاحة الفيديوهات المتعدّدة وأنواع الفيديوهات المساعِدة، مثل الفيديوهات التي تُظهر العمق والصور المموّهة والمعاينة
- التوافق مع تقنية HDR10/10+ والبيانات الوصفية التي يحدّدها المستخدم
يتم توفير تنفيذ مرجعي لـ APV من خلال مشروع OpenAPV. سيتيح نظام Android 16 استخدام الملف الشخصي APV 422-10 الذي يقدّم تحليل ألوان YUV 422 بالإضافة إلى ترميز 10 بت ومعدّلات نقل البيانات المستهدَفة التي تصل إلى 2 غيغابايت في الثانية.
الخصوصية
يتضمّن Android 16 مجموعة متنوّعة من الميزات التي تساعد مطوّري التطبيقات في حماية خصوصية المستخدمين.
تحديثات Health Connect
Health Connect adds ACTIVITY_INTENSITY, a data type defined according to World
Health Organization guidelines around moderate and vigorous activity. Each
record requires the start time, the end time, and whether the activity intensity
is moderate or vigorous.
Health Connect also contains updated APIs supporting medical records. This allows apps to read and write medical records in FHIR format with explicit user consent.
"مبادرة حماية الخصوصية" على Android
يتضمّن الإصدار 16 من Android أحدث إصدار من مبادرة حماية الخصوصية على Android، وهي جزء من عملنا المستمر لتطوير تقنيات تضمن للمستخدمين اتّخاذ خطوات لحماية خصوصيتهم. يمكنك زيارة موقعنا الإلكتروني للاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات عن "مبادرة حماية الخصوصية" في الإصدار التجريبي من برنامج "مطوّرو تطبيقات Android" لمساعدتك في البدء. اطّلِع على وقت تشغيل حزمة SDK الذي يتيح تشغيل حِزم SDK في بيئة وقت تشغيل مخصّصة منفصلة عن التطبيق الذي تقدّمه، ما يوفر وسائل حماية أقوى بشأن جمع بيانات المستخدمين ومشاركتها.
الأمان
يتضمّن Android 16 ميزات تساعدك في تعزيز أمان تطبيقك وحماية بياناته.
Key sharing API
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تتيح مشاركة إمكانية الوصول إلى مفاتيح
متجر مفاتيح Android مع التطبيقات الأخرى. تتيح فئة
KeyStoreManager الجديدة
منح وإبطال إذن الوصول إلى المفاتيح
حسب uid للتطبيق، وتتضمّن واجهة برمجة تطبيقات للتطبيقات للوصول إلى مفاتيح
المشترَكة.
أشكال الأجهزة
يوفّر Android 16 لتطبيقاتك إمكانية الاستفادة إلى أقصى حد من عوامل الشكل في Android.
إطار عمل موحّد لجودة الصورة والصوت في أجهزة التلفزيون
The new MediaQuality
package in Android 16 exposes
a set of standardized APIs for access to audio and picture profiles and
hardware-related settings. This allows streaming apps to query profiles and
apply them to media dynamically:
- Movies mastered with a wider dynamic range require greater color accuracy to see subtle details in shadows and adjust to ambient light, so a profile that prefers color accuracy over brightness may be appropriate.
- Live sporting events are often mastered with a narrow dynamic range, but are often watched in daylight, so a profile that preferences brightness over color accuracy can give better results.
- Fully interactive content wants minimal processing to reduce latency, and wants higher frame rates, which is why many TV's ship with a game profile.
The API allows apps to switch between profiles and users to enjoy tuning supported TVs to best suit their content.
التوافق مع أسواق عالمية
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 16 ميزات وإمكانات تكمل تجربة المستخدم عند استخدام الجهاز بلغات مختلفة.
نص عمودي
يضيف نظام Android 16 دعمًا من المستوى الأدنى لعرض النص وقياسه عموديًا بهدف
توفير دعم أساسي للكتابة العمودية لمطوّري المكتبات. ويفيد ذلك
بشكل خاص في اللغات التي تستخدم عادةً أنظمة كتابة عمودية، مثل اليابانية. تمت إضافة علامة جديدة،
VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG،
إلى فئة Paint. عند ضبط
هذا الإعداد باستخدام
Paint.setFlags، ستحدّد واجهات برمجة التطبيقات
لقياس النصوص في Paint التقدّم في الرسم بالاتجاه العمودي بدلاً من التقدّم في الرسم بالاتجاه الأفقي، وسيرسم Canvas النص
بالاتجاه العمودي.
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
تخصيص نظام القياس
يمكن للمستخدمين الآن تخصيص نظام القياس في الإعدادات المفضّلة على مستوى المنطقة ضمن
الإعدادات. يتم تضمين إعدادات المستخدم المفضّلة كجزء من رمز اللغة، لذا يمكنك تسجيل BroadcastReceiver على ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED للتعامل مع تغييرات إعدادات اللغة عند تغيير الإعدادات المفضّلة على مستوى المنطقة.
يمكن أن يساعد استخدام أدوات التنسيق في مطابقة التجربة المحلية. على سبيل المثال، تمثل القيمة "0.5 بوصة" باللغة الإنجليزية (الولايات المتحدة) القيمة "12.7 مم" لمستخدم ضبط لغة هاتفه على الإنجليزية (الدنمارك) أو يستخدم هاتفه باللغة الإنجليزية (الولايات المتحدة) مع استخدام النظام المتري كنظام القياس المفضّل.
للعثور على هذه الإعدادات، افتح تطبيق "الإعدادات" وانتقِل إلى النظام > اللغات والمنطقة.
