Android 16 為開發人員推出了強大的新功能和 API。以下各節會簡要說明這些功能,協助您開始使用相關 API。
如需新增、修改及移除 API 的詳細清單,請參閱 API 差異比較表。如要進一步瞭解新的 API,請參閱 Android API 參考資料 - 新的 API 會醒目顯示,以利於查看。此外,也請查看平台變更可能對應用程式造成的影響。詳情請參閱下列頁面:
核心功能
Android 包含可擴充 Android 系統核心功能的新 API。
2025 年將發布兩項 Android API
- 這個預覽版適用於下一個 Android 主要版本,預計於 2025 年第 2 季推出。這個版本與我們過去的所有 API 版本類似,我們可以進行預定的行為變更,這些變更通常與 targetSdkVersion 相關。
- 我們預計將主要版本提前一個季發布 (第 2 季,而非以往的第 3 季),以便與生態系統中的裝置推出時程保持一致,讓更多裝置能盡早取得主要的 Android 版本。由於主要版本將於第 2 季推出,您需要比往年提早幾個月進行年度相容性測試,確保應用程式已準備就緒。
- 我們預計在 2025 年第 4 季推出另一個版本,其中也會納入新的開發人員 API。2025 年唯一會納入可能影響應用程式的行為變更計畫的版本,就是第 2 季主要版本。
除了新的開發人員 API,第 4 季次要版本還會推出功能更新、最佳化和錯誤修正,但不會包含任何會影響應用程式的行為變更。
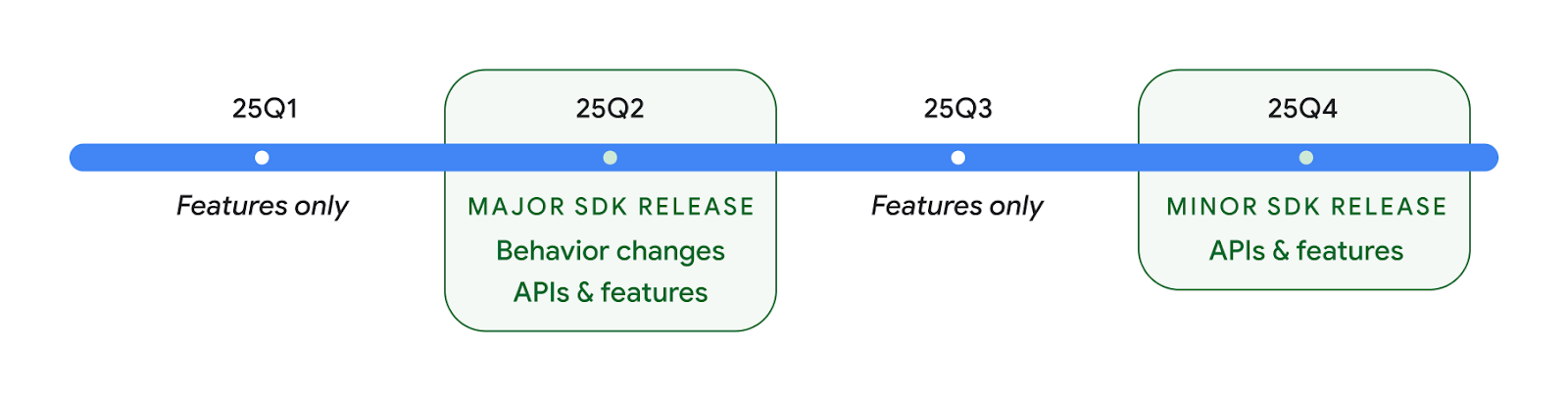
我們會持續每季發布 Android 版本。在 API 版本之間,第 1 季和第 3 季的更新會提供漸進式更新,有助確保持續提供高品質服務。我們正積極與裝置合作夥伴合作,盡可能讓 Q2 版本適用於更多裝置。
使用主要和次要版本的新 API
今天,您可以使用 SDK_INT 常數搭配 VERSION_CODES,保護含有 API 級別檢查的程式碼區塊。我們會持續為主要的 Android 版本提供支援。
if (SDK_INT >= VERSION_CODES.BAKLAVA) {
// Use APIs introduced in Android 16
}
新的 SDK_INT_FULL 常數可用於針對主要和次要版本進行 API 檢查,並搭配新的 VERSION_CODES_FULL 列舉。
if (SDK_INT_FULL >= VERSION_CODES_FULL.[MAJOR or MINOR RELEASE]) {
// Use APIs introduced in a major or minor release
}
您也可以使用 Build.getMinorSdkVersion() 方法,只取得 SDK 子版本。
val minorSdkVersion = Build.getMinorSdkVersion(VERSION_CODES_FULL.BAKLAVA)
這些 API 尚未定案,且可能有所變動,因此如果您有任何疑慮,請提供意見回饋。
使用者體驗和系統 UI
Android 16 可讓應用程式開發人員和使用者進一步控管及彈性設定裝置,以符合自身需求。
以進度為主的通知
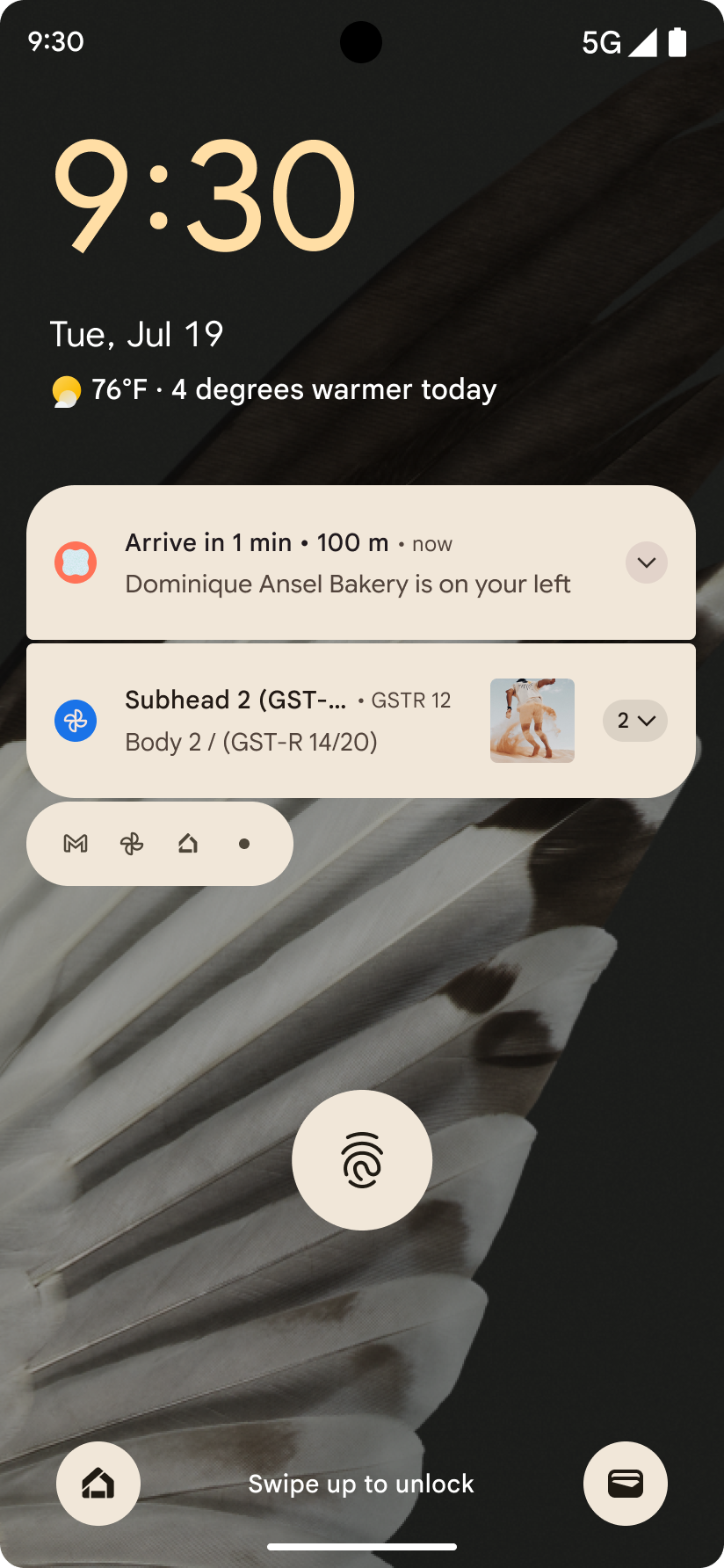
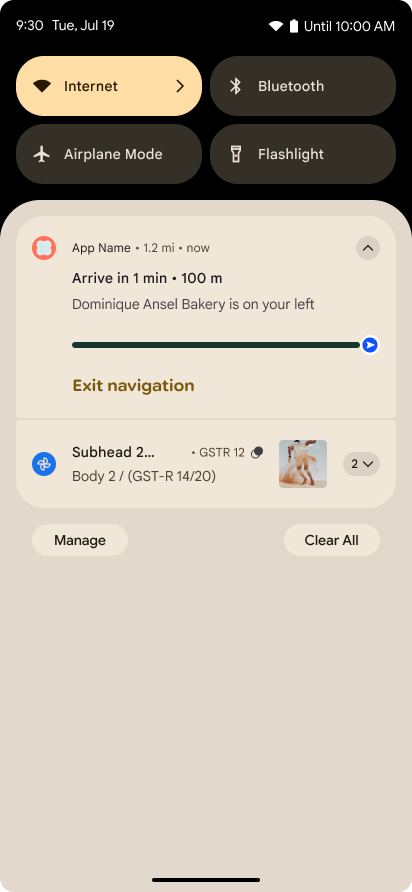
Android 16 推出以進度為主的通知,協助使用者順暢追蹤使用者啟動的端對端歷程。
Notification.ProgressStyle 是一種新的通知樣式,可讓您建立以進度為主的通知。主要用途包括共乘、外送和導航。在 Notification.ProgressStyle 類別中,您可以使用點和區隔,表示使用者歷程中的狀態和里程碑。
詳情請參閱「以進度為主軸的通知」說明文件。
預測返回更新
Android 16 新增了新的 API,可協助您在手勢導覽 (例如返回主畫面動畫) 中啟用預測返回系統動畫。使用新的 PRIORITY_SYSTEM_NAVIGATION_OBSERVER 註冊 onBackInvokedCallback,即可在系統處理返回導覽時讓應用程式接收一般 onBackInvoked 呼叫,且不會影響一般返回導覽流程。
Android 16 也新增了 finishAndRemoveTaskCallback() 和 moveTaskToBackCallback。只要將這些回呼註冊至 OnBackInvokedDispatcher,系統就能在使用者執行返回手勢時觸發特定行為,並播放相應的提前動畫。
更豐富的觸覺回饋
自推出以來,Android 就提供觸覺感應致動器控制項。
Android 11 新增了對更複雜的觸覺效果支援,進階的致動器可透過裝置定義語義原始類型的 VibrationEffect.Compositions 支援此類效果。
Android 16 新增觸覺 API,讓應用程式定義觸覺效果的振幅和頻率曲線,同時抽象化裝置功能之間的差異。
開發人員工作效率和工具
我們致力於提升開發人員的工作效率,因此主要著重於 Android Studio、Jetpack Compose 和 Android Jetpack 程式庫等工具。此外,我們也持續尋找平台上的各種方法,協助您實現願景。
動態桌布的內容處理方式
在 Android 16 中,動態桌布架構會獲得新的內容 API,以解決動態、使用者導向桌布的挑戰。目前,整合使用者提供內容的動態桌布需要複雜的服務專屬實作項目。Android 16 推出 WallpaperDescription 和 WallpaperInstance。您可以使用 WallpaperDescription 識別同一個服務中動態桌布的不同例項。舉例來說,如果桌布同時出現在主畫面和螢幕鎖定畫面,則兩者可能會顯示不同的內容。桌布挑選器和 WallpaperManager 會使用這項中繼資料,為使用者提供更優質的桌布,讓您能以更簡便的方式打造多樣化且個人化的動態桌布體驗。
效能和電池
Android 16 導入的 API 可協助您收集應用程式的深入分析資訊。
系統觸發的剖析
ProfilingManager 已在 Android 15 中新增,讓應用程式能夠在外部公開裝置上使用 Perfetto 要求收集分析資料。不過,由於這項剖析作業必須從應用程式啟動,因此應用程式很難或無法擷取啟動或 ANR 等重要流程。
為協助您完成這項工作,Android 16 為 ProfilingManager 導入系統觸發的剖析功能。應用程式可以註冊對特定觸發事件 (例如冷啟動 reportFullyDrawn 或 ANR) 的追蹤記錄興趣,系統就會代替應用程式啟動及停止追蹤記錄。追蹤記錄完成後,結果會傳送至應用程式的資料目錄。
ApplicationStartInfo 中的啟動元件
ApplicationStartInfo 已在 Android 15 中新增,可讓應用程式查看程序啟動原因、啟動類型、啟動時間、節流和其他實用的診斷資料。Android 16 新增了 getStartComponent(),用於區分觸發啟動的元件類型,這有助於最佳化應用程式的啟動流程。
更深入瞭解工作
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReason() API 會傳回工作可能處於待處理狀態的原因。不過,工作可能會因多種原因而處於待處理狀態。
在 Android 16 中,我們推出了全新的 API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasons(int jobId),可傳回工作處於待處理狀態的多種原因,包括開發人員設定的明確限制,以及系統設定的隱含限制。
我們也推出 JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory(int jobId),可傳回最新約束條件變更的清單。
建議您使用 API 來偵測工作未執行的原因,特別是當您發現特定工作成功率降低,或特定工作完成時間延遲時,就需要進行偵錯。例如,在背景更新小工具時發生錯誤,或是在應用程式啟動前無法呼叫預先擷取工作。
這也能協助您進一步瞭解,某些工作是否因系統定義的限制而無法完成,而非明確設定的限制。
自動調整刷新率
在 Android 15 中推出的適應性重新整理率 (ARR) 可讓支援硬體的螢幕重新整理率,透過獨立的 VSync 步驟調整至內容影格速率。這麼做可降低耗電量,同時避免需要切換模式,進而導致卡頓現象。
Android 16 在還原 getSupportedRefreshRates() 時,會引入 hasArrSupport() 和 getSuggestedFrameRate(int),讓應用程式更容易利用 ARR。RecyclerView 1.4 在從彈跳或平滑捲動中進行調整時,會在內部支援 ARR,我們也持續致力於將 ARR 支援功能加入更多 Jetpack 程式庫。這篇關於影格速率的文章介紹許多可用來設定影格速率的 API,讓應用程式能直接使用 ARR。
ADPF 中的 Headroom API
SystemHealthManager 引進 getCpuHeadroom 和 getGpuHeadroom API,旨在為遊戲和資源密集型應用程式提供可用 CPU 和 GPU 資源的預估值。這些方法可讓您評估應用程式或遊戲如何最佳化系統健康狀況,尤其是與其他Android 動態效能架構 (ADPF) API 搭配使用時,這些 API 可偵測熱控調節。
在支援的裝置上使用 CpuHeadroomParams 和 GpuHeadroomParams,您可以自訂用於計算預留空間的時間視窗,並選擇平均或最低資源可用性。這麼做可以協助您相應減少 CPU 或 GPU 資源使用量,進而提供更優質的使用者體驗和更長的電池續航力。
無障礙設定
Android 16 新增了無障礙 API 和功能,可協助您為所有使用者提供應用程式。
改良的無障礙 API
Android 16 新增了其他 API,可強化使用者介面語意,協助依賴無障礙服務 (例如 TalkBack) 的使用者提升一致性。
加外框的文字,可盡可能提高文字對比度
低視力使用者通常對對比敏感度較低,因此很難從背景中辨識物體。為協助這類使用者,Android 16 引進了外框文字,取代高對比文字,這項功能會在文字周圍繪製較大的對比區域,大幅提升易讀性。
Android 16 包含新的 AccessibilityManager API,可讓應用程式檢查或註冊事件監聽器,瞭解是否已啟用此模式。這項功能主要適用於 Compose 等 UI 工具包,可提供類似的視覺體驗。如果您維護 UI 工具包程式庫,或應用程式執行會略過 android.text.Layout 類別的自訂文字算繪作業,則可使用此方法瞭解何時啟用輪廓文字。
新增至 TtsSpan 的時間長度
Android 16 會使用 TYPE_DURATION 擴充 TtsSpan,其中包含 ARG_HOURS、ARG_MINUTES 和 ARG_SECONDS。這可讓您直接註解時間長度,確保 TalkBack 等服務能提供準確且一致的文字轉語音輸出內容。
支援含有多個標籤的元素
Android 目前允許 UI 元素從其他元素衍生無障礙標籤,現在則提供多個標籤的關聯功能,這也是網路內容的常見情境。在 AccessibilityNodeInfo 中導入以清單為基礎的 API,Android 即可直接支援這些多標籤關係。在本次異動中,我們已淘汰 AccessibilityNodeInfo#setLabeledBy 和 #getLabeledBy,改用 #addLabeledBy、#removeLabeledBy 和 #getLabeledByList。
改善對可展開元素的支援
Android 16 新增了無障礙 API,可讓您傳達互動元素 (例如選單和可展開清單) 的展開或收合狀態。您可以使用 setExpandedState 設定展開狀態,並搭配 CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_EXPANDED 內容變更類型調度 TYPE_WINDOW_CONTENT_CHANGED AccessibilityEvents,確保 TalkBack 等螢幕閱讀器會宣告狀態變更,提供更直覺且全面的使用者體驗。
不確定進度列
Android 16 新增了 RANGE_TYPE_INDETERMINATE,讓您可以為確定和不確定的 ProgressBar 小工具公開 RangeInfo,讓 TalkBack 等服務能更一致地提供進度指標的意見回饋。
三態核取方塊
Android 16 中的新 AccessibilityNodeInfo
getChecked 和 setChecked(int) 方法現在除了支援「已勾選」和「未勾選」之外,也支援「部分勾選」狀態。這會取代已淘汰的布林值 isChecked 和 setChecked(boolean)。
補充說明
無障礙服務說明 ViewGroup 時,會結合其子項檢視畫面的內容標籤。如果您為 ViewGroup 提供 contentDescription,無障礙服務會假設您也要覆寫無法聚焦的子項檢視畫面的說明。如果您想標示下拉式選單 (例如「字型系列」),同時保留現有無障礙選項 (例如「Roboto」),這可能會造成問題。Android 16 新增了 setSupplementalDescription,讓您可以提供文字,提供 ViewGroup 的相關資訊,而不會覆寫其子項的資訊。
必填表單欄位
Android 16 會將 setFieldRequired 新增至 AccessibilityNodeInfo,讓應用程式可向無障礙服務指出表單欄位需要輸入內容。對於填寫各種表單的使用者來說,這都是重要的情境,即使是像條款和條件核取方塊這類簡單的項目,也能協助使用者一貫地識別並快速瀏覽必要欄位。
將手機設為 LE Audio 助聽器的語音通話麥克風
Android 16 新增了 LE Audio 助聽器功能,使用者可在助聽器內建麥克風和手機麥克風之間切換,以便進行語音通話。這項功能在吵雜的環境或其他助聽器麥克風效能不佳的情況下特別實用。
控制 LEA 助聽器的環境音量
Android 16 新增了 LE Audio 助聽器功能,可調整助聽器麥克風收錄到的環境音量。在背景噪音過大或過小時,這項功能就非常實用。
相機
Android 16 強化了對專業相機使用者的支援,可進行混合式自動曝光,並精確調整色溫和色調。新的夜間模式指標可協助應用程式瞭解何時該切換至夜間模式攝影工作階段,以及何時該切換回來。新的 Intent 動作可讓您更輕鬆地拍攝動態相片,我們也持續改良 UltraHDR 影像,支援 HEIC 編碼和 ISO 21496-1 草案標準的新參數。
混合式自動曝光
Android 16 在 Camera2 中新增了混合式自動曝光模式,讓您可以手動控制曝光的特定層面,同時讓自動曝光 (AE) 演算法處理其餘部分。您可以控制 ISO + AE 和曝光時間 + AE,相較於目前必須完全手動控制或完全依賴自動曝光的做法,這項功能提供更大的彈性。
fun setISOPriority() {
// ... (Your existing code before the snippet) ...
val availablePriorityModes = mStaticInfo.characteristics.get(
CameraCharacteristics.CONTROL_AE_AVAILABLE_PRIORITY_MODES
)
// ... (Your existing code between the snippets) ...
// Turn on AE mode to set priority mode
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_MODE_ON
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE,
CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AE_PRIORITY_MODE_SENSOR_SENSITIVITY_PRIORITY
)
reqBuilder.set(
CaptureRequest.SENSOR_SENSITIVITY,
TEST_SENSITIVITY_VALUE
)
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after the snippet) ...
}
精確調整色溫和色調
Android 16 新增相機支援功能,可調整精細的色溫和色調,以便更好地支援專業錄影應用程式。在先前的 Android 版本中,您可以透過 CONTROL_AWB_MODE 控制白平設定,其中包含的選項僅限於預設清單,例如 Incandescent、Cloudy 和 Twilight。COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT 可讓您使用 COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE 和 COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT,根據相關色溫精確調整白平。
fun setCCT() {
// ... (Your existing code before this point) ...
val colorTemperatureRange: Range<Int> =
mStaticInfo.characteristics[CameraCharacteristics.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE_RANGE]
// Set to manual mode to enable CCT mode
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.CONTROL_AWB_MODE] = CameraMetadata.CONTROL_AWB_MODE_OFF
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE] = CameraMetadata.COLOR_CORRECTION_MODE_CCT
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TEMPERATURE] = 5000
reqBuilder[CaptureRequest.COLOR_CORRECTION_COLOR_TINT] = 30
val request: CaptureRequest = reqBuilder.build()
// ... (Your existing code after this point) ...
}
以下範例顯示在套用不同色溫和色調調整後,相片的樣貌:





相機夜間模式場景偵測
為協助應用程式瞭解何時切換至夜間模式相機工作階段,Android 16 新增了 EXTENSION_NIGHT_MODE_INDICATOR。如果支援,則可在 Camera2 的 CaptureResult 中使用。
這是我們在「Instagram 如何讓使用者拍出令人驚豔的低光照相」網誌文章中,曾簡短提及的即將推出的 API。這篇文章是實用指南,說明如何實作夜間模式,並提供個案研究,說明如何透過應用程式內的相機,分享更多高品質的夜間模式相片。
動態相片拍攝意圖動作
Android 16 新增了標準意圖動作 ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE 和 ACTION_MOTION_PHOTO_CAPTURE_SECURE,可要求相機應用程式擷取動態相片並傳回。
您必須傳遞額外的 EXTRA_OUTPUT 來控制要寫入圖片的位置,或是透過 Intent.setClipData(ClipData) 傳遞 Uri。如果您未設定 ClipData,系統會在您呼叫 Context.startActivity(Intent) 時複製該值。
UltraHDR 圖片強化

Android 16 持續致力於透過 UltraHDR 圖片提供令人驚豔的圖像品質。新增對 HEIC 檔案格式中的 UltraHDR 圖片支援。這些圖片會取得 ImageFormat 類型的 HEIC_ULTRAHDR,並包含類似現有 UltraHDR JPEG 格式的內嵌增益圖。我們也正在努力讓 AVIF 支援 UltraHDR,敬請期待。
此外,Android 16 會根據 ISO 21496-1 草稿標準,在 UltraHDR 中實作其他參數,包括取得及設定應套用的增益圖數值空間,以及支援 HDR 編碼的基礎圖片,並使用 SDR 增益圖。
圖形
Android 16 包含最新的圖像改善功能,例如使用 AGSL 的自訂圖像效果。
使用 AGSL 自訂圖像效果
Android 16 新增了 RuntimeColorFilter 和 RuntimeXfermode,讓您可以製作複雜的效果 (例如閾值、棕褐色和色調飽和度),並套用至繪圖呼叫。自 Android 13 起,您可以使用 AGSL 建立可擴充 Shader 的自訂 RuntimeShaders。新的 API 會反映這項情況,新增由 AGSL 提供動力的 RuntimeColorFilter,可擴充 ColorFilter,以及 Xfermode 效果,讓您在來源和目的地像素之間實作以 AGSL 為基礎的自訂合成和混合效果。
private val thresholdEffectString = """
uniform half threshold;
half4 main(half4 c) {
half luminosity = dot(c.rgb, half3(0.2126, 0.7152, 0.0722));
half bw = step(threshold, luminosity);
return bw.xxx1 * c.a;
}"""
fun setCustomColorFilter(paint: Paint) {
val filter = RuntimeColorFilter(thresholdEffectString)
filter.setFloatUniform(0.5);
paint.colorFilter = filter
}
連線能力
Android 16 會更新平台,讓應用程式使用通訊和無線技術的最新進展。
採用強化安全性的測距功能
Android 16 新增了對 Wi-Fi 6 的 802.11az 支援裝置 Wi-Fi 位置資訊的強大安全性功能支援,讓應用程式可結合更高的精確度、更大的可擴充性和動態排程的通訊協定,以及 AES-256 加密和防範中間人攻擊的安全性強化功能。這可讓使用者在近距離用途 (例如解鎖筆電或車門) 時,更安全地使用這項功能。802.11az 已整合 Wi-Fi 6 標準,可利用其基礎架構和功能,讓採用率更廣泛,部署作業也更輕鬆。
一般測距 API
Android 16 包含新的 RangingManager,可用於判斷本機裝置與遠端裝置之間的距離和角度,前提是裝置支援硬體。RangingManager 支援各種測距技術,例如 BLE 通道測試、BLE RSSI 測距、超寬頻和 Wi-Fi 往返時間。
隨附裝置管理工具裝置狀態
在 Android 16 中,我們推出了新的 API,用於繫結隨附應用程式服務。當 BLE 在範圍內且已連上藍牙時,服務就會繫結;當 BLE 超出範圍或藍牙已中斷連線時,服務就會解除繫結。應用程式會根據各種 DevicePresenceEvent 接收新的 'onDevicePresenceEvent()' 回呼。如需更多詳細資訊,請參閱「startObservingDevicePresence(ObservingDevicePresenceRequest)」一文。
媒體
Android 16 包含多項功能,可提升媒體體驗。
相片挑選工具改良功能
相片挑選工具提供內建的安全方法,讓使用者授予應用程式存取權,以便存取本機和雲端儲存空間中的所選圖片和影片,而非整個媒體庫。透過 Google 系統更新和 Google Play 服務,結合使用模組化系統元件,可支援 Android 4.4 (API 級別 19) 以下版本。整合作業只需要幾行程式碼和相關的 Android Jetpack 程式庫。
Android 16 對相片挑選工具進行了以下改善:
- 內嵌式相片挑選器:新 API,可讓應用程式將相片挑選器嵌入其檢視區塊階層。這樣一來,使用者就能感受到應用程式更整合的部分,同時仍可利用程序隔離功能,讓使用者能夠選取媒體,而應用程式不需要過度廣泛的權限。如要盡可能提高各平台版本的相容性並簡化整合作業,如果您想整合內嵌的相片挑選工具,請使用即將推出的 Android Jetpack 程式庫。
- 相片挑選器中的雲端搜尋功能:新的 API 可讓 Android 相片挑選器從雲端媒體供應器搜尋內容。相片挑選工具中的搜尋功能即將推出。
進階專業影片
Android 16 推出了對進階專業影片 (APV) 轉碼器的支援,該轉碼器專為專業級高品質影片錄製和後製作業而設計。
APV 編碼器標準具有下列功能:
- 感知上無損的影片品質 (接近原始影片品質)
- 低複雜度和高吞吐量的單一影格編碼 (不含像素網域預測),以便更妥善支援編輯工作流程
- 支援高位元速率範圍 (最高可達數 Gbps),適用於 2K、4K 和 8K 解析度的內容,可透過輕量化熵值編碼方案啟用
- 為沉浸式內容和啟用平行編碼/解碼作業的框架平鋪作業
- 支援各種色度取樣格式和位元深度
- 支援多重解碼和重新編碼,且不會嚴重降低視覺品質
- 支援多視角影片和輔助影片,例如深度、alpha 和預覽
- 支援 HDR10/10+ 和使用者定義的中繼資料
OpenAPV 專案提供 APV 的參考實作項目。Android 16 將實作支援 APV 422-10 設定檔,提供 YUV 422 色彩取樣功能,以及 10 位元編碼和最高 2 Gbps 的目標位元率。
隱私權
Android 16 包含多項功能,可協助應用程式開發人員保護使用者隱私權。
健康資料同步更新
Health Connect 新增了 ACTIVITY_INTENSITY,這是根據世界衛生組織針對中度和劇烈活動制定的規範所定義的資料類型。每個記錄都需要開始時間、結束時間,以及活動強度是屬於中等或劇烈。
Health Connect 也包含支援醫療記錄的更新版 API。這樣一來,應用程式就能在取得使用者的明確同意後,以 FHIR 格式讀取及寫入醫療記錄。
Android 版 Privacy Sandbox
Android 16 整合了最新版本的 Android 版 Privacy Sandbox,這是我們持續開發技術的一部分,讓使用者知道自己的隱私權受到保護。網站提供更多 Android 版 Privacy Sandbox 開發人員 Beta 版計畫的相關資訊,協助您開始使用。請查看 SDK 執行階段,讓 SDK 在專屬的執行階段環境中執行,而非在服務的應用程式中執行,以便在收集和分享使用者資料時提供更完善的防護。
安全性
Android 16 包含多項功能,可協助您提升應用程式安全性及保護應用程式資料。
金鑰共用 API
Android 16 新增了 API,可支援與其他應用程式共用 Android KeyStore 金鑰的存取權。新的 KeyStoreManager 類別支援應用程式 uid 授予和撤銷金鑰存取權,並包含可讓應用程式存取共用金鑰的 API。
裝置板型規格
Android 16 可讓應用程式充分運用 Android 的板型規格。
電視的標準化影像和音訊品質架構
Android 16 中的新 MediaQuality 套件公開一組標準化 API,可存取音訊和相片設定檔,以及硬體相關設定。這可讓串流應用程式查詢設定檔,並動態套用至媒體:
- 採用更廣動態範圍進行調色的電影,需要更高色彩準確度,才能看見陰影中的細微細節,並調整環境光線,因此適合使用偏好色彩準確度而非亮度的設定檔。
- 體育賽事直播通常會以較窄的動態範圍進行調色,但觀眾通常會在日間觀看,因此如果設定檔將亮度優先於色彩準確度,就能獲得更好的效果。
- 完全互動式內容需要盡可能減少處理作業以縮短延遲時間,並需要更高的影格速率,這也是許多電視機上會提供遊戲設定檔的原因。
這個 API 可讓應用程式切換設定檔,使用者也能根據內容調整支援的電視。
國際化
Android 16 新增多項功能,可提升使用者在不同語言環境下的裝置使用體驗。
直書文字
Android 16 新增了對垂直顯示和測量文字的低階支援功能,為程式庫開發人員提供基本的垂直書寫支援。這項功能特別適合日文等常使用直式書寫系統的語言。Paint 類別已新增旗標 VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG。使用 Paint.setFlags 設定這個標記時,Paint 的文字測量 API 會回報垂直進度,而非水平進度,而 Canvas 會垂直繪製文字。
val text = "「春は、曙。」"
Box(
Modifier.padding(innerPadding).background(Color.White).fillMaxSize().drawWithContent {
drawIntoCanvas { canvas ->
val paint = Paint().apply { textSize = 64.sp.toPx() }
// Draw text vertically
paint.flags = paint.flags or VERTICAL_TEXT_FLAG
val height = paint.measureText(text)
canvas.nativeCanvas.drawText(
text,
0,
text.length,
size.width / 2,
(size.height - height) / 2,
paint
)
}
}
) {}
自訂計量系統
使用者現在可以在「設定」中,透過區域偏好設定自訂測量系統。使用者偏好設定會納入語言代碼,因此您可以在 ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED 上註冊 BroadcastReceiver,以便在地區偏好設定變更時,處理語言代碼設定的變更。
使用格式化工具可協助您提供符合當地體驗的服務。舉例來說,如果使用者將手機設為英文 (美國),或使用英文 (美國) 並將公制系統設為偏好的測量系統,則英文 (美國) 中的「0.5 英寸」會顯示為「12.7 公釐」。
如要找到這些設定,請開啟「設定」應用程式,並依序前往「系統」>「語言與地區」。
