แพลตฟอร์ม Android 16 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานต่อไปนี้จะมีผลกับแอปทั้งหมดเมื่อแอปทำงานบน Android 16
โดยไม่คำนึงถึง targetSdkVersion คุณควรทดสอบแอป แล้วแก้ไข
ตามที่จำเป็นเพื่อรองรับการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ หากเกี่ยวข้อง
อย่าลืมตรวจสอบรายการการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่มีผลกับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 เท่านั้นด้วย
ฟังก์ชันหลัก
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งจะแก้ไขหรือ ขยายความสามารถหลักต่างๆ ของระบบ Android
การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพโควต้า JobScheduler
ตั้งแต่ Android 16 เป็นต้นไป เราจะปรับโควต้าเวลาทำงานปกติและโควต้าเวลาทำงานแบบเร่งด่วน โดยอิงตามปัจจัยต่อไปนี้
- ถังพักแอปที่แอปพลิเคชันอยู่: ใน Android 16 ระบบจะเริ่มบังคับใช้ถังพักที่ใช้งานอยู่โดยมีโควต้าเวลาเรียกใช้ที่มาก
- หากงานเริ่มดำเนินการขณะที่แอปอยู่ในสถานะบนสุด: ใน Android 16 งานที่เริ่มขณะที่แอปแสดงต่อผู้ใช้และดำเนินการต่อหลังจาก แอปไม่แสดงแล้ว จะเป็นไปตามโควต้าเวลาทำงานของงาน
- หากงานกำลังดำเนินการขณะที่บริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าทำงาน: ใน Android 16 งานที่ดำเนินการพร้อมกันกับบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า จะยึดตามโควต้าเวลาทำงานของงาน หากคุณใช้ประโยชน์จากงานสำหรับการโอนข้อมูลที่เริ่มต้นโดยผู้ใช้ ให้พิจารณาใช้งานการโอนข้อมูลที่เริ่มต้นโดยผู้ใช้แทน
การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้ส่งผลต่องานที่กำหนดเวลาโดยใช้ WorkManager, JobScheduler และ DownloadManager หากต้องการแก้ไขข้อบกพร่องว่าเหตุใดงานจึงหยุดทำงาน เราขอแนะนำให้บันทึกเหตุผลที่งานหยุดทำงานโดยเรียกใช้ WorkInfo.getStopReason() (สำหรับงาน JobScheduler ให้เรียกใช้ JobParameters.getStopReason())
ดูข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับสถานะของแอปที่ส่งผลต่อทรัพยากรที่แอปใช้ได้ที่ขีดจำกัดของทรัพยากรการจัดการพลังงาน ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับแนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำในการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพแบตเตอรี่ได้ที่คำแนะนำเกี่ยวกับการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการใช้แบตเตอรี่สำหรับ API การตั้งเวลางาน
นอกจากนี้ เราขอแนะนำให้ใช้ประโยชน์จาก API JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory ใหม่ที่เปิดตัวใน Android 16 เพื่อทำความเข้าใจว่าเหตุใดจึงไม่มีการเรียกใช้ Job
การทดสอบ
หากต้องการทดสอบลักษณะการทำงานของแอป คุณสามารถเปิดใช้การลบล้างการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพโควต้าของงานบางอย่างได้ ตราบใดที่แอปทำงานบนอุปกรณ์ Android 16
หากต้องการปิดใช้การบังคับใช้ "สถานะสูงสุดจะยึดตามโควต้าเวลาทำงานของงาน" ให้เรียกใช้คำสั่งadbต่อไปนี้
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
หากต้องการปิดใช้การบังคับใช้ "งานที่ดำเนินการพร้อมกับบริการที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าจะยึดตามโควต้าเวลาทำงานของงาน" ให้เรียกใช้adbคำสั่งต่อไปนี้
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
หากต้องการทดสอบลักษณะการทำงานของ App Standby Bucket บางอย่าง คุณสามารถตั้งค่า App Standby Bucket
ของแอปได้โดยใช้adbคำสั่งต่อไปนี้
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
หากต้องการทำความเข้าใจที่เก็บข้อมูลสแตนด์บายแอปที่แอปของคุณอยู่ คุณสามารถรับที่เก็บข้อมูลสแตนด์บายแอปของแอปได้โดยใช้คำสั่ง adb ต่อไปนี้
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
เหตุผลที่หยุดงานที่ว่างเปล่าซึ่งถูกละทิ้ง
งานที่ถูกทิ้งจะเกิดขึ้นเมื่อมีการรวบรวมขยะจากออบเจ็กต์ JobParameters ที่เชื่อมโยงกับงาน แต่ไม่มีการเรียกใช้ JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) เพื่อส่งสัญญาณว่างานเสร็จสมบูรณ์ ซึ่งหมายความว่างานอาจกำลังทำงานและกำลังกำหนดเวลาใหม่โดยที่แอปไม่รู้
แอปที่อาศัย JobScheduler จะไม่เก็บการอ้างอิงแบบ Strong กับออบเจ็กต์ JobParameters และตอนนี้การหมดเวลาจะได้รับเหตุผลใหม่ในการหยุดงาน STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED แทน STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT
หากมีสาเหตุใหม่ของการหยุดกลางคันเกิดขึ้นบ่อยครั้ง ระบบจะดำเนินการตามขั้นตอนเพื่อลดความถี่ของงาน
แอปควรใช้เหตุผลในการหยุดใหม่เพื่อตรวจหาและลดงานที่หยุดกลางคัน
หากคุณใช้ WorkManager, AsyncTask หรือ DownloadManager คุณจะได้รับผลกระทบเนื่องจาก API เหล่านี้จัดการวงจรงานในนามของแอป
เลิกใช้งาน JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground อย่างสมบูรณ์
The JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean)
method indicates the importance of a job while the scheduling app is in the
foreground or when temporarily exempted from background restrictions.
This method has been deprecated since Android 12 (API level 31). Starting in Android 16, it no longer functions effectively and calling this method will be ignored.
This removal of functionality also applies to
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). Starting in Android
16, if the method is called, the method returns false.
ขอบเขตลำดับความสำคัญของการออกอากาศที่สั่งซื้อแล้วไม่ได้เป็นแบบทั่วโลกอีกต่อไป
แอป Android ได้รับอนุญาตให้กำหนดลำดับความสำคัญในเครื่องรับการออกอากาศเพื่อควบคุมลำดับที่เครื่องรับจะรับและประมวลผลการออกอากาศ สําหรับตัวรับที่ประกาศในไฟล์ Manifest แอปสามารถใช้แอตทริบิวต์ android:priority เพื่อกําหนดลําดับความสําคัญ และสำหรับตัวรับที่ลงทะเบียนตามบริบท แอปสามารถใช้ IntentFilter#setPriority() API เพื่อกําหนดลําดับความสําคัญ เมื่อส่งการออกอากาศ ระบบจะส่งการออกอากาศไปยังผู้รับตามลําดับความสําคัญจากสูงไปต่ำ
ใน Android 16 ระบบจะไม่รับประกันลำดับการนำส่งแบบออกอากาศที่ใช้แอตทริบิวต์ android:priority หรือ IntentFilter#setPriority() ในกระบวนการต่างๆ ระบบจะพิจารณาลำดับความสำคัญของการออกอากาศภายในกระบวนการสมัครเดียวกันเท่านั้น ไม่ใช่ในทุกกระบวนการ
นอกจากนี้ ระบบจะจำกัดลําดับความสําคัญของรายการออกอากาศให้อยู่ในช่วง (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1) โดยอัตโนมัติ เฉพาะคอมโพเนนต์ของระบบเท่านั้นที่จะได้รับอนุญาตให้ตั้งค่า SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY เป็นลำดับความสำคัญของการออกอากาศ
แอปของคุณอาจได้รับผลกระทบหากมีลักษณะการทำงานอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่งต่อไปนี้
- แอปพลิเคชันของคุณประกาศกระบวนการหลายรายการที่มี Intent การออกอากาศเดียวกัน และคาดหวังที่จะได้รับการส่ง Intent เหล่านั้นตามลำดับที่แน่นอนโดยอิงตามลําดับความสําคัญ
- กระบวนการสมัครของคุณจะโต้ตอบกับกระบวนการอื่นๆ และมีสิ่งที่คาดหวังเกี่ยวกับการรับ Intent การออกอากาศตามลําดับที่กําหนด
หากกระบวนการต่างๆ จำเป็นต้องประสานงานกัน ทีมควรสื่อสารโดยใช้ช่องทางประสานงานอื่นๆ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงภายในของ ART
Android 16 มีการอัปเดตล่าสุดสำหรับรันไทม์ Android (ART) ซึ่งจะปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพของรันไทม์ Android (ART) และรองรับฟีเจอร์ Java เพิ่มเติม การอัปเดตระบบ Google Play ยังช่วยให้อุปกรณ์กว่า 1 พันล้านเครื่องที่ใช้ Android 12 (API ระดับ 31) ขึ้นไปได้รับประโยชน์จากการปรับปรุงเหล่านี้ด้วย
เมื่อมีการเผยแพร่การเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ ไลบรารีและโค้ดแอปที่อาศัยโครงสร้างภายในของ ART อาจทํางานไม่ถูกต้องในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 16 รวมถึง Android เวอร์ชันเก่าที่อัปเดตข้อบังคับของ ART ผ่านการอัปเดตระบบของ Google Play
การใช้โครงสร้างภายใน (เช่น อินเทอร์เฟซที่ไม่ใช่ SDK) อาจทำให้เกิดปัญหาความเข้ากันได้เสมอ แต่สิ่งสําคัญอย่างยิ่งคือหลีกเลี่ยงการใช้โค้ด (หรือไลบรารีที่มีโค้ด) ที่ใช้โครงสร้างภายในของ ART เนื่องจากการเปลี่ยนแปลง ART ไม่ได้เชื่อมโยงกับเวอร์ชันแพลตฟอร์มที่อุปกรณ์ใช้อยู่ และการเปลี่ยนแปลงดังกล่าวจะเผยแพร่ไปยังอุปกรณ์กว่า 1 พันล้านเครื่องผ่านการอัปเดตระบบของ Google Play
นักพัฒนาแอปทุกรายควรตรวจสอบว่าแอปของตนได้รับผลกระทบหรือไม่โดยการทดสอบแอปอย่างละเอียดใน Android 16 นอกจากนี้ ให้ตรวจสอบปัญหาที่ทราบเพื่อดูว่าแอปของคุณใช้ไลบรารีที่เราพบว่าใช้โครงสร้าง ART ภายในหรือไม่ หากคุณมีโค้ดแอปหรือไลบรารีที่ส่งผลต่อการใช้งาน ให้หา API สาธารณะทางเลือกทุกครั้งที่เป็นไปได้ และขอ API สาธารณะสำหรับ Use Case ใหม่โดยสร้างคำขอฟีเจอร์ในเครื่องมือติดตามปัญหา
โหมดความเข้ากันได้กับขนาดหน้า 16 KB
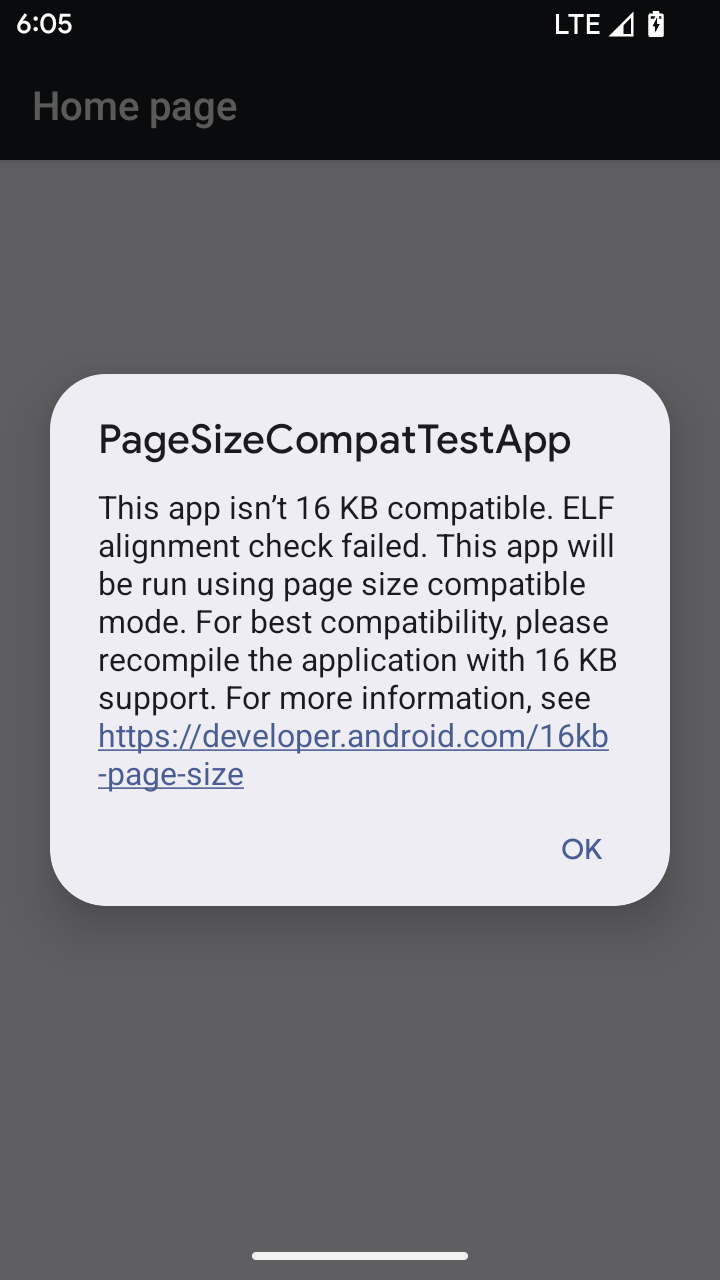
Android 15 รองรับหน้าหน่วยความจำขนาด 16 KB เพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพแพลตฟอร์ม Android 16 เพิ่มโหมดความเข้ากันได้ ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปบางแอปที่สร้างขึ้นสำหรับหน้าหน่วยความจำขนาด 4 KB ทำงานในอุปกรณ์ที่กำหนดค่าไว้สำหรับหน้าหน่วยความจำขนาด 16 KB ได้
เมื่อแอปทำงานในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 16 ขึ้นไป หาก Android ตรวจพบว่าแอปของคุณมีหน้าหน่วยความจำที่ปรับแนวขนาด 4 KB ระบบจะใช้โหมดเข้ากันได้โดยอัตโนมัติและแสดงกล่องโต้ตอบการแจ้งเตือนต่อผู้ใช้ การตั้งค่าพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ android:pageSizeCompat ใน AndroidManifest.xml เพื่อเปิดใช้โหมดความเข้ากันได้แบบย้อนหลังจะป้องกันไม่ให้กล่องโต้ตอบแสดงเมื่อแอปเปิดขึ้น หากต้องการใช้พร็อพเพอร์ตี้ android:pageSizeCompat ให้คอมไพล์แอปโดยใช้ Android 16 SDK
แอปของคุณควรยังคงมีขนาด 16 KB เพื่อให้มีประสิทธิภาพ ความน่าเชื่อถือ และความเสถียรที่ดีที่สุด ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมได้ในบล็อกโพสต์ล่าสุดเกี่ยวกับการอัปเดตแอปให้รองรับหน้าหน่วยความจำ 16 KB
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งมีจุดประสงค์ เพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ที่สอดคล้องกันและใช้งานง่ายยิ่งขึ้น
การเลิกใช้งานการประกาศการช่วยเหลือพิเศษที่รบกวนผู้ใช้
Android 16 เลิกใช้งานการประกาศการช่วยเหลือพิเศษ ซึ่งมีลักษณะการใช้งาน announceForAccessibility หรือการส่งเหตุการณ์การช่วยเหลือพิเศษ TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT การดำเนินการเหล่านี้อาจทำให้ผู้ใช้ TalkBack และโปรแกรมอ่านหน้าจอของ Android ได้รับประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ไม่สอดคล้องกัน และทางเลือกอื่นๆ จะตอบสนองความต้องการของผู้ใช้ได้หลากหลายมากขึ้นในเทคโนโลยีความช่วยเหลือพิเศษต่างๆ ของ Android
ตัวอย่างทางเลือกมีดังนี้
- สำหรับการเปลี่ยนแปลง UI ที่สำคัญ เช่น การเปลี่ยนแปลงหน้าต่าง ให้ใช้
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)และsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)ในโหมดเขียน ให้ใช้Modifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - หากต้องการแจ้งให้ผู้ใช้ทราบถึงการเปลี่ยนแปลง UI ที่สำคัญ ให้ใช้
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)ในโหมดเขียน ให้ใช้Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}คุณควรใช้ฟีเจอร์เหล่านี้อย่างจำกัดเนื่องจากอาจสร้างประกาศทุกครั้งที่มีการอัปเดตมุมมอง - หากต้องการแจ้งให้ผู้ใช้ทราบเกี่ยวกับข้อผิดพลาด ให้ส่ง
AccessibilityEventประเภทAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORและตั้งค่าAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)หรือใช้TextView#setError(CharSequence)
เอกสารอ้างอิงสําหรับ announceForAccessibility API ที่เลิกใช้งานแล้วมีรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับทางเลือกที่แนะนํา
รองรับการนำทางแบบ 3 ปุ่ม
Android 16 รองรับการกดย้อนกลับแบบคาดการณ์ในการนําทางด้วยปุ่ม 3 ปุ่มสําหรับแอปที่ย้ายข้อมูลไปยังการกดย้อนกลับแบบคาดการณ์อย่างถูกต้อง การกดปุ่มย้อนกลับค้างไว้จะเป็นการเริ่มภาพเคลื่อนไหวย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดา ซึ่งจะแสดงตัวอย่างตำแหน่งที่คุณจะไปเมื่อปัดกลับ
ลักษณะการทำงานนี้มีผลกับทุกส่วนของระบบที่รองรับภาพเคลื่อนไหวแบบคาดเดาของการย้อนกลับ รวมถึงภาพเคลื่อนไหวของระบบ (การย้อนกลับไปยังหน้าจอหลัก การข้ามงาน และการทำงานข้ามแอป)
ไอคอนแอปแบบมีธีมอัตโนมัติ
ตั้งแต่ Android 16 QPR 2 เป็นต้นไป Android จะใช้ธีมกับไอคอนแอปโดยอัตโนมัติเพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์หน้าจอหลักที่สอดคล้องกัน กรณีนี้จะเกิดขึ้นหากแอปไม่ได้ระบุไอคอนแอปตามธีมของแอปเอง แอปสามารถควบคุมการออกแบบไอคอนแอปที่เข้าชุดกันได้โดยใส่เลเยอร์ขาวดำไว้ในไอคอนแบบปรับอัตโนมัติ และดูตัวอย่างลักษณะไอคอนแอปใน Android Studio
รูปแบบของอุปกรณ์
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้สำหรับแอปเมื่อ เจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือนฉายภาพไปยังจอแสดงผล
การลบล้างเจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือนจริง
เจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือนคือแอปที่เชื่อถือได้หรือมีสิทธิ์ซึ่งสร้างและจัดการ อุปกรณ์เสมือน เจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือนจะเรียกใช้แอปในอุปกรณ์เสมือน แล้ว ฉายแอปไปยังจอแสดงผลของอุปกรณ์ระยะไกล เช่น คอมพิวเตอร์ส่วนตัว อุปกรณ์เสมือนจริง หรือระบบสาระบันเทิงในรถยนต์ เจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือน อยู่ในอุปกรณ์ในพื้นที่ เช่น โทรศัพท์มือถือ
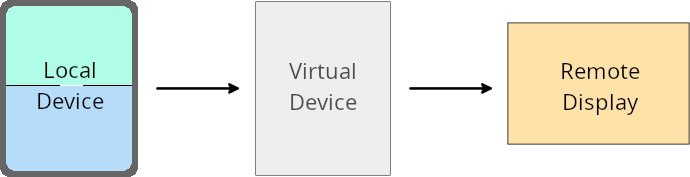
การลบล้างต่อแอป
ในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) เจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือนจะ ลบล้างการตั้งค่าแอปในอุปกรณ์เสมือนบางเครื่องที่เจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือน จัดการได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น เจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือนสามารถ ละเว้นข้อจำกัดด้านการวางแนว อัตราส่วนภาพ และการปรับขนาดเมื่อฉาย แอปไปยังจอแสดงผลภายนอกเพื่อปรับปรุงเลย์เอาต์ของแอป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ส่งผลกับส่วนอื่นในระบบที่พบบ่อย
ลักษณะการทำงานของ Android 16 อาจส่งผลต่อ UI ของแอปในรูปแบบหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ เช่น จอแสดงผลในรถยนต์หรือ Chromebook โดยเฉพาะเลย์เอาต์ที่ออกแบบมาสำหรับจอแสดงผลขนาดเล็กในแนวนอน ดูวิธีทําให้แอปปรับเปลี่ยนตามรูปแบบของอุปกรณ์ทั้งหมดได้ที่เกี่ยวกับเลย์เอาต์ที่ปรับเปลี่ยนได้
ข้อมูลอ้างอิง
ความปลอดภัย
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ส่งเสริมความปลอดภัยของระบบเพื่อ ช่วยปกป้องแอปและผู้ใช้จากแอปที่เป็นอันตราย
ปรับปรุงความปลอดภัยเพื่อป้องกันการโจมตีโดยการเปลี่ยนเส้นทาง Intent
Android 16 มีการรักษาความปลอดภัยเริ่มต้นเพื่อป้องกันการโจมตีโดยIntentการเปลี่ยนเส้นทาง
ทั่วไป โดยต้องมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงความเข้ากันได้และนักพัฒนาแอปขั้นต่ำ
เราจะเปิดตัวโซลูชันการปิดช่องโหว่เพื่อความปลอดภัยโดยค่าเริ่มต้นสำหรับIntent
การใช้ประโยชน์จากการเปลี่ยนเส้นทาง ในกรณีส่วนใหญ่ แอปที่ใช้ Intent จะไม่พบปัญหาความเข้ากันได้ใดๆ เราได้รวบรวมเมตริกตลอดกระบวนการพัฒนาเพื่อตรวจสอบว่าแอปใดอาจพบปัญหา
การเปลี่ยนเส้นทาง Intent ใน Android จะเกิดขึ้นเมื่อผู้โจมตีสามารถควบคุมเนื้อหาของ Intent ที่ใช้เปิดตัวคอมโพเนนต์ใหม่ในบริบทของแอปที่มีช่องโหว่ได้บางส่วนหรือทั้งหมด ในขณะที่แอปเหยื่อเปิดตัว Intent ระดับย่อยที่ไม่น่าเชื่อถือ ในฟิลด์ส่วนเพิ่มเติมของ Intent ("ระดับบนสุด") ซึ่งอาจทำให้แอปของผู้โจมตี เปิดใช้คอมโพเนนต์ส่วนตัวในบริบทของแอปเหยื่อ ทริกเกอร์การดำเนินการที่มีสิทธิ์ หรือรับสิทธิ์เข้าถึง URI ไปยังข้อมูลที่ละเอียดอ่อน ซึ่งอาจนำไปสู่การขโมยข้อมูลและการดำเนินการโค้ดโดยพลการ
เลือกไม่ใช้การจัดการการเปลี่ยนเส้นทางตามความตั้งใจ
Android 16 เปิดตัว API ใหม่ที่อนุญาตให้แอปเลือกไม่ใช้การรักษาความปลอดภัยในการเปิดตัว ซึ่งอาจจำเป็นในบางกรณีที่ลักษณะการทำงานด้านความปลอดภัยเริ่มต้น รบกวน Use Case ที่ถูกต้องของแอป
สำหรับแอปพลิเคชันที่คอมไพล์กับ SDK ของ Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) ขึ้นไป
คุณสามารถใช้วิธี removeLaunchSecurityProtection() กับออบเจ็กต์ Intent
ได้โดยตรง
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
สำหรับแอปพลิเคชันที่คอมไพล์กับ Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) หรือต่ำกว่า
แม้ว่าเราจะไม่แนะนำ แต่คุณก็สามารถใช้การสะท้อนเพื่อเข้าถึงเมธอด removeLaunchSecurityProtection() ได้
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
แอปที่ใช้ร่วมกันจะไม่ได้รับการแจ้งเตือนเกี่ยวกับการหมดเวลาการค้นพบอีกต่อไป
Android 16 เปิดตัวลักษณะการทำงานใหม่ในขั้นตอนการจับคู่อุปกรณ์เสริมเพื่อปกป้องความเป็นส่วนตัวของตำแหน่งของผู้ใช้จากแอปที่เป็นอันตราย แอปที่ใช้ร่วมกันทั้งหมดที่ทำงานบน Android 16 จะไม่ได้รับการแจ้งเตือนโดยตรงอีกต่อไปเมื่อหมดเวลาในการค้นหาโดยใช้ RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT แต่ผู้ใช้จะได้รับการแจ้งเตือนเกี่ยวกับเหตุการณ์หมดเวลาด้วยกล่องโต้ตอบแบบภาพแทน เมื่อผู้ใช้ปิดกล่องโต้ตอบ แอปจะได้รับการแจ้งเตือนเกี่ยวกับการเชื่อมโยงกับ RESULT_USER_REJECTED ไม่สำเร็จ
นอกจากนี้ ระยะเวลาการค้นหายังเพิ่มขึ้นจากเดิม 20 วินาที และผู้ใช้สามารถหยุดการค้นหาอุปกรณ์ได้ทุกเมื่อในระหว่างการค้นหา หากพบอุปกรณ์อย่างน้อย 1 เครื่องภายใน 20 วินาทีแรกของการเริ่มค้นหา CDM จะหยุดค้นหาอุปกรณ์เพิ่มเติม
การเชื่อมต่อ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ในสแต็กบลูทูธ เพื่อปรับปรุงการเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ต่อพ่วง
การจัดการการขาดทุนจากพันธบัตรที่ดีขึ้น
ตั้งแต่ Android 16 เป็นต้นไป สแต็กบลูทูธได้รับการอัปเดตเพื่อปรับปรุงความปลอดภัยและประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้เมื่อตรวจพบการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงระยะไกล ก่อนหน้านี้ ระบบจะนำการจับคู่ออกโดยอัตโนมัติและเริ่มกระบวนการจับคู่ใหม่ ซึ่งอาจนำไปสู่การจับคู่อีกครั้งโดยไม่ตั้งใจ เราพบว่ามีหลายครั้งที่แอปไม่ได้จัดการเหตุการณ์การสูญเสียพันธบัตรอย่างสม่ำเสมอ
Android 16 ได้ปรับปรุงการจัดการการสูญเสียการเชื่อมโยงกับระบบเพื่อรวมประสบการณ์การใช้งาน หากไม่สามารถตรวจสอบสิทธิ์อุปกรณ์บลูทูธที่จับคู่ไว้ก่อนหน้านี้เมื่อเชื่อมต่ออีกครั้ง ระบบจะยกเลิกการเชื่อมต่อ เก็บข้อมูลการจับคู่ในเครื่อง และแสดงกล่องโต้ตอบของระบบเพื่อแจ้งให้ผู้ใช้ทราบถึงการสูญเสียการจับคู่และนำผู้ใช้ไปยังการจับคู่อีกครั้ง
