يتضمّن الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android تغييرات في السلوك قد تؤثّر في تطبيقك.
تنطبق تغييرات السلوك التالية على جميع التطبيقات عند تشغيلها على الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android،
بغض النظر عن targetSdkVersion. عليك اختبار تطبيقك ثم تعديله حسب الحاجة ليتوافق مع هذه التغييرات، حيثما ينطبق ذلك.
احرص أيضًا على مراجعة قائمة التغييرات في السلوك التي تؤثّر فقط في التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android.
الوظيفة الأساسية
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية التي تعدّل أو توسّع العديد من الإمكانات الأساسية لنظام Android.
تحسينات حصص JobScheduler
اعتبارًا من Android 16، سنعدّل حصة وقت التشغيل المخصّصة لتنفيذ المهام العادية والمستعجلة استنادًا إلى العوامل التالية:
- حزمة التطبيق الاحتياطية التي يندرج فيها التطبيق: في Android 16، سيتم فرض حِزم التطبيقات الاحتياطية النشطة من خلال حصة سخية لوقت التشغيل.
- إذا بدأ تنفيذ المهمة بينما يكون التطبيق في حالة نشطة: في نظام التشغيل Android 16، ستلتزم المهام التي تبدأ أثناء ظهور التطبيق للمستخدم وتستمر بعد أن يصبح التطبيق غير مرئي بحصة وقت تشغيل المهمة.
- إذا كانت المهمة قيد التنفيذ أثناء تشغيل خدمة تعمل في المقدّمة: في Android 16، ستلتزم المهام التي يتم تنفيذها بشكل متزامن مع خدمة تعمل في المقدّمة بحصة وقت تشغيل المهمة. إذا كنت تستخدم المهام لنقل البيانات التي يبدأها المستخدم، ننصحك باستخدام مهام نقل البيانات التي يبدأها المستخدم بدلاً من ذلك.
يؤثّر هذا التغيير في المهام المُجدوَلة باستخدام WorkManager وJobScheduler وDownloadManager. لتحديد سبب إيقاف مهمة، ننصح بتسجيل سبب إيقاف مهمتك من خلال استدعاء WorkInfo.getStopReason() (بالنسبة إلى مهام JobScheduler، استدعِ JobParameters.getStopReason()).
للحصول على معلومات حول كيفية تأثير حالة تطبيقك في الموارد التي يمكنه استخدامها، اطّلِع على حدود موارد إدارة الطاقة. لمزيد من المعلومات حول أفضل الممارسات المتعلقة بتحسين استهلاك البطارية، يُرجى الرجوع إلى الإرشادات حول تحسين استخدام البطارية لواجهات برمجة التطبيقات الخاصة بجدولة المهام.
ننصحك أيضًا بالاستفادة من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory التي تم طرحها في Android 16 لمعرفة سبب عدم تنفيذ مهمة.
الاختبار
لاختبار سلوك تطبيقك، يمكنك تفعيل إلغاء بعض تحسينات حصة المهام طالما أنّ التطبيق يعمل على جهاز Android 16.
لإيقاف فرض "الالتزام بحصة وقت التشغيل المخصّصة للوظيفة"، نفِّذ الأمر adb التالي:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
لإيقاف فرض "المهام التي يتم تنفيذها بشكل متزامن مع خدمة تعمل في المقدّمة ستلتزم بحصة وقت تشغيل المهمة"، شغِّل الأمر adb التالي:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
لاختبار سلوك معيّن لحزمة التطبيق في وضع الاستعداد، يمكنك ضبط حزمة التطبيق في وضع الاستعداد باستخدام الأمر adb التالي:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
لمعرفة فئة وضع الاستعداد التي يندرج فيها تطبيقك، يمكنك الحصول على فئة وضع الاستعداد لتطبيقك باستخدام الأمر adb التالي:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
سبب إيقاف المهام الفارغة التي تم التخلي عنها
An abandoned job occurs when the JobParameters object associated with the job
has been garbage collected, but JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) has not been called to signal job completion. This indicates that
the job may be running and being rescheduled without the app's awareness.
Apps that rely on JobScheduler, don't maintain a strong reference to the
JobParameters object, and timeout will now be granted the new job stop reason
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, instead of STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
If there are frequent occurrences of the new abandoned stop reason, the system will take mitigation steps to reduce job frequency.
Apps should use the new stop reason to detect and reduce abandoned jobs.
If you're using WorkManager, AsyncTask, or DownloadManager, you aren't impacted because these APIs manage the job lifecycle on your app's behalf.
إيقاف JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground نهائيًا
تشير طريقة JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean)
إلى أهمية إحدى المهام عندما يكون تطبيق تحديد الموعد في
المقدّمة أو عندما يتم إعفاؤه مؤقتًا من القيود المفروضة على التطبيقات التي تعمل في الخلفية.
تم إيقاف هذه الطريقة نهائيًا منذ الإصدار 12 من Android (المستوى 31 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات). اعتبارًا من الإصدار Android 16، لم تعُد هذه الطريقة تعمل بفعالية، وسيتم تجاهل استدعاء هذه الطريقة.
تنطبق إزالة هذه الوظيفة أيضًا على
JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). بدءًا من الإصدار Android
16، إذا تم استدعاء الطريقة، ستُرجع الطريقة false.
لم يعُد نطاق أولوية البث المنظَّم عامًا
Android apps are allowed to define priorities on broadcast receivers to control
the order in which the receivers receive and process the broadcast. For
manifest-declared receivers, apps can use the
android:priority attribute to define the priority and for
context-registered receivers, apps can use the
IntentFilter#setPriority() API to define the priority. When
a broadcast is sent, the system delivers it to receivers in order of their
priority, from highest to lowest.
In Android 16, broadcast delivery order using the android:priority attribute
or IntentFilter#setPriority() across different processes will not be
guaranteed. Broadcast priorities will only be respected within the same
application process rather than across all processes.
Also, broadcast priorities will be automatically confined to the range
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Only system components will be
allowed to set SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY as broadcast
priority.
Your app might be impacted if it does either of the following:
- Your application has declared multiple processes with the same broadcast intent, and has expectations around receiving those intents in a certain order based on the priority.
- Your application process interacts with other processes and has expectations around receiving a broadcast intent in a certain order.
If the processes need to coordinate with each other, they should communicate using other coordination channels.
التغييرات الداخلية في ART
Android 16 includes the latest updates to the Android Runtime (ART) that improve the Android Runtime's (ART's) performance and provide support for additional Java features. Through Google Play System updates, these improvements are also available to over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher.
As these changes are released, libraries and app code that rely on internal structures of ART might not work correctly on devices running Android 16, along with earlier Android versions that update the ART module through Google Play system updates.
Relying on internal structures (such as non-SDK interfaces) can always lead to compatibility problems, but it's particularly important to avoid relying on code (or libraries containing code) that leverages internal ART structures, since ART changes aren't tied to the platform version the device is running on and they go out to over a billion devices through Google Play system updates.
All developers should check whether their app is impacted by testing their apps thoroughly on Android 16. In addition, check the known issues to see if your app depends on any libraries that we've identified that rely on internal ART structures. If you do have app code or library dependencies that are affected, seek public API alternatives whenever possible and request public APIs for new use cases by creating a feature request in our issue tracker.
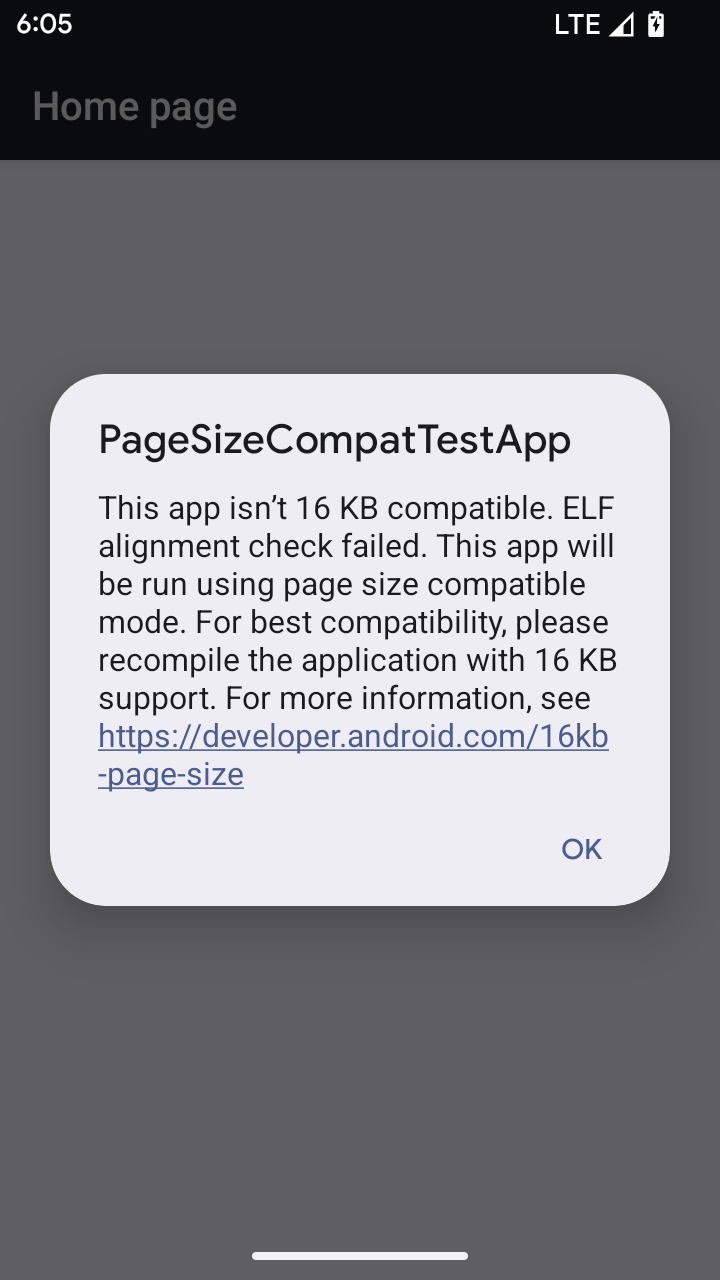
وضع التوافق مع حجم الصفحة البالغ 16 كيلوبايت
Android 15 introduced support for 16 KB memory pages to optimize performance of the platform. Android 16 adds a compatibility mode, allowing some apps built for 4 KB memory pages to run on a device configured for 16 KB memory pages.
When your app is running on a device with Android 16 or higher, if Android
detects that your app has 4 KB aligned memory pages, it automatically uses
compatibility mode and display a notification dialog to the user. Setting the
android:pageSizeCompat property in the AndroidManifest.xml to enable the
backwards compatibility mode will prevent the display of the dialog when your
app launches. To use the android:pageSizeCompat property, compile your app
using the Android 16 SDK.
For best performance, reliability, and stability, your app should still be 16 KB aligned. Check out our recent blog post on updating your apps to support 16 KB memory pages for more details.
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية التي تهدف إلى توفير تجربة مستخدم أكثر اتساقًا وسهولة.
إيقاف الإشعارات الخطيرة المتعلّقة بإمكانية الوصول نهائيًا
يوقف نظام التشغيل Android 16 نهائيًا إعلانات تسهيل الاستخدام التي تتميز باستخدام
announceForAccessibility أو إرسال
TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT أحداث تسهيل الاستخدام. ويمكن أن تؤدي هذه العناصر إلى اختلاف تجربتَي المستخدمين في TalkBack وقارئ شاشة Android،
وتعمل العناصر البديلة بشكل أفضل على تلبية مجموعة أوسع من احتياجات المستخدمين في مجموعة متنوعة من
التكنولوجيات المساعِدة في Android.
أمثلة على الحلول البديلة:
- بالنسبة إلى التغييرات المهمة في واجهة المستخدم، مثل التغييرات في النوافذ، استخدِم
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)وsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). في الكتابة، استخدِمModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - لإعلام المستخدم بالتغييرات في واجهة المستخدم المهمة، استخدِم رمز
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). في ميزة "إنشاء"، استخدِم رمزModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. يجب استخدام هذه الإعدادات بقدر معقول، لأنّها قد تؤدي إلى إنشاء إشعارات في كل مرة يتم فيها تعديل أحد "المشاهدات". - لإعلام المستخدمين بالأخطاء، أرسِل
AccessibilityEventمن النوعAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORواضبطAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)، أو استخدِمTextView#setError(CharSequence).
تتضمّن المستندات المرجعية لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات
announceForAccessibility المتوقّفة نهائيًا مزيدًا من التفاصيل حول
البدائل المقترَحة.
إتاحة التنقّل باستخدام ثلاثة أزرار
يتيح نظام Android 16 ميزة "الرجوع التوقّعي" في ميزة التنقّل باستخدام 3 أزرار للتطبيقات التي تم نقلها بشكل صحيح إلى ميزة "الرجوع التوقّعي". يؤدي الضغط مع الاستمرار على زر الرجوع إلى تشغيل صورة متحركة تنبؤية للرجوع، ما يمنحك معاينة للصفحة التي يؤدي التمرير السريع للخلف إلى عرضها.
ينطبق هذا السلوك على جميع أقسام النظام التي تتيح استخدام الصور المتحركة التنبؤية للرجوع، بما في ذلك الصور المتحركة في النظام (للرجوع إلى الشاشة الرئيسية والتنقّل بين المهام وتنفيذ عدة أنشطة في الوقت نفسه).
رموز تطبيقات مستوحاة من موضوع معيّن تلقائيًا
بدءًا من الإصدار الثاني من Android 16 QPR، يطبّق Android تلقائيًا المظاهر على رموز التطبيقات لتوفير تجربة متسقة على الشاشة الرئيسية. يحدث ذلك إذا لم يوفّر التطبيق رمزًا مستوحى من موضوع معيّن. يمكن للتطبيقات التحكّم في تصميم رمز التطبيق المتوافق مع المظهر من خلال تضمين طبقة أحادية اللون في الرمز التكيّفي ومعاينة الشكل الذي سيبدو عليه رمز التطبيق في استوديو Android.
أشكال الأجهزة
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية للتطبيقات عند عرضها على الشاشات من قِبل مالكي الأجهزة الافتراضية.
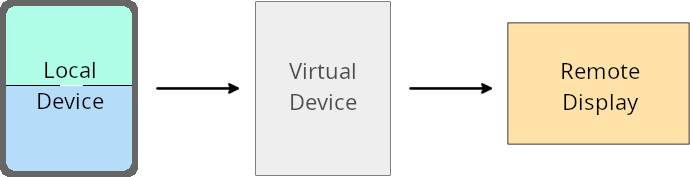
تجاهل مالك الجهاز الافتراضي
مالك الجهاز الافتراضي هو تطبيق موثوق به أو لديه امتيازات، وهو ينشئ جهازًا افتراضيًا ويديره. يشغّل مالكو الأجهزة الافتراضية التطبيقات على جهاز افتراضي ثم يعرضونها على شاشة جهاز بعيد، مثل جهاز كمبيوتر شخصي أو جهاز واقع افتراضي أو نظام معلومات وترفيه في السيارة. يكون مالك الجهاز الافتراضي على جهاز محلي، مثل هاتف جوّال.
عمليات التجاوز على مستوى التطبيق
على الأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، يمكن لمالكي الأجهزة الافتراضية إلغاء إعدادات التطبيقات على أجهزة افتراضية محدّدة يديرها مالكو الأجهزة الافتراضية. على سبيل المثال، لتحسين تخطيط التطبيق، يمكن لمالك جهاز افتراضي تجاهل القيود المتعلقة بالاتجاه ونسبة العرض إلى الارتفاع وإمكانية تغيير الحجم عند عرض التطبيقات على شاشة خارجية.
التغييرات الشائعة التي قد تؤدي إلى أعطال
قد يؤثّر سلوك Android 16 في واجهة المستخدم لتطبيقك على أجهزة ذات شاشات كبيرة، مثل شاشات السيارات أو أجهزة Chromebook، خاصةً التصاميم التي تم إنشاؤها لشاشات صغيرة في الوضع العمودي. للتعرّف على كيفية جعل تطبيقك متوافقًا مع جميع أشكال الأجهزة، يمكنك الاطّلاع على لمحة عن التصاميم المتجاوبة.
المراجع
الأمان
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) تغييرات تعزّز أمان النظام للمساعدة في حماية التطبيقات والمستخدمين من التطبيقات الضارة.
تحسين الأمان ضد هجمات إعادة توجيه Intent
يوفر نظام التشغيل Android 16 حماية تلقائية من هجمات إعادة التوجيه العامة Intent، مع الحد الأدنى من التوافق والتغييرات المطلوبة من المطوّرين.
نحن بصدد طرح حلول لتعزيز الأمان بشكل تلقائي بهدف الحماية من استغلال عمليات إعادة التوجيه.Intent في معظم الحالات، لن تواجه التطبيقات التي تستخدم الأهداف أي مشاكل في التوافق، إذ جمعنا مقاييس خلال عملية التطوير لمراقبة التطبيقات التي قد تواجه مشاكل.
تحدث عملية إعادة توجيه Intent في نظام التشغيل Android عندما يتمكّن أحد المهاجمين من التحكّم جزئيًا أو كليًا في محتوى Intent المستخدَم لإطلاق مكوِّن جديد في سياق تطبيق معرَّض للخطر، بينما يطلق تطبيق الضحية Intent غير موثوق به على مستوى فرعي في حقل التطبيقات الإضافية من Intent ("على المستوى الأعلى"). ويمكن أن يؤدي ذلك إلى أن يطلق تطبيق المهاجم مكوّنات خاصة في سياق تطبيق الضحية، أو أن يؤدي إلى تشغيل إجراءات ذات امتيازات، أو الحصول على إذن الوصول إلى بيانات حساسة باستخدام معرّف الموارد الموحّد (URI)، ما قد يؤدي إلى سرقة البيانات وتنفيذ رموز برمجية عشوائية.
إيقاف معالجة إعادة التوجيه المستندة إلى Intent
يقدّم Android 16 واجهة برمجة تطبيقات جديدة تتيح للتطبيقات إيقاف ميزات الحماية الأمنية عند التشغيل. وقد يكون ذلك ضروريًا في حالات معيّنة يتداخل فيها السلوك الأمني التلقائي مع حالات استخدام التطبيق المشروعة.
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي يتم تجميعها باستخدام حزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) لنظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأحدث
يمكنك استخدام طريقة removeLaunchSecurityProtection() مباشرةً في عنصر Intent.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي يتم تجميعها باستخدام الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأقدم
مع أنّنا لا ننصح بذلك، يمكنك استخدام الانعكاس للوصول إلى الطريقة removeLaunchSecurityProtection().
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
لم تعُد التطبيقات المصاحبة تتلقّى إشعارات بانتهاء مهلة البحث عن الأجهزة
Android 16 introduces a new behavior during
companion device pairing flow to protect the user's location
privacy from malicious apps. All companion apps running on Android 16 are no
longer directly notified of discovery timeout using
RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. Instead, the user is
notified of timeout events with a visual dialog. When the user dismisses
the dialog, the app is alerted of the association failure with
RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
The search duration has also been extended from the original 20 seconds, and the device discovery can be stopped by the user at any point during the search. If at least one device was discovered within the first 20 seconds of starting the search, the CDM stops searching for additional devices.
إمكانية الاتصال
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية في حزمة بروتوكول البلوتوث لتحسين إمكانية الاتصال بالأجهزة الطرفية.
تحسين معالجة فقدان الاتصال
بدءًا من Android 16، تم تعديل حِزمة البلوتوث لتحسين الأمان وتجربة المستخدم عند رصد فقدان الربط عن بُعد. في السابق، كان النظام يزيل الربط تلقائيًا ويُطلق عملية إقران جديدة، ما قد يؤدي إلى إعادة إقران غير مقصودة. لقد لاحظنا في العديد من الحالات أنّ التطبيقات لا تهتم بحدث فقدان الارتباط بطريقة متّسقة.
لتوحيد التجربة، حسّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 معالجة فقدان الربط في النظام. إذا تعذّر مصادقة جهاز بلوتوث سبق ربطه عند إعادة الربط، سيقطع النظام الرابط ويحتفظ بمعلومات الربط المحلية ويعرض مربّع حوار للنظام يُعلم المستخدمين بفقدان الربط ويوجّههم إلى إعادة الإقران.
