פלטפורמת Android 16 כוללת שינויים בהתנהגות שעשויים להשפיע על האפליקציה שלכם. שינויי ההתנהגות הבאים חלים על כל האפליקציות כשהן פועלות ב-Android 16, בלי קשר ל-targetSdkVersion. מומלץ לבדוק את האפליקציה ולשנות אותה לפי הצורך כדי לתמוך בשינויים האלה, במקרים הרלוונטיים.
חשוב גם לעיין ברשימת השינויים בהתנהגות שמשפיעים רק על אפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 16.
פונקציונליות עיקרית
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים, שמשנים או מרחיבים יכולות ליבה שונות של מערכת Android.
אופטימיזציה של מכסת JobScheduler
החל מ-Android 16, אנחנו משנים את מכסת זמן הריצה של ביצוע משימות רגילות ומזורזות על סמך הגורמים הבאים:
- באיזו קטגוריה של אפליקציות במצב המתנה האפליקציה נמצאת: ב-Android 16, קטגוריות פעילות של אפליקציות במצב המתנה ייאכפו על ידי מכסה נדיבה של זמן ריצה.
- אם העבודה מתחילה לפעול כשהאפליקציה במצב עליון: ב-Android 16, עבודות שהתחילו כשהאפליקציה גלויה למשתמשים וממשיכות אחרי שהאפליקציה הופכת ללא גלויה, יפעלו בהתאם למכסת זמן הריצה של העבודה.
- אם המשימה מתבצעת בזמן ששירות שפועל בחזית פועל: ב-Android 16, משימות שמתבצעות במקביל לשירות שפועל בחזית יפעלו בהתאם למכסת זמן הריצה של המשימה. אם אתם משתמשים במשימות להעברת נתונים שהמשתמשים יזמו, כדאי להשתמש במקום זאת במשימות להעברת נתונים שהמשתמשים יזמו.
השינוי הזה משפיע על משימות שמתוזמנות באמצעות WorkManager, JobScheduler ו-DownloadManager. כדי לנפות באגים ולגלות למה משימה הופסקה, מומלץ לתעד את הסיבה להפסקת המשימה באמצעות קריאה ל-WorkInfo.getStopReason() (למשימות JobScheduler, צריך לקרוא ל-JobParameters.getStopReason()).
במאמר מגבלות משאבים לניהול צריכת חשמל מוסבר איך מצב האפליקציה משפיע על המשאבים שהיא יכולה להשתמש בהם. למידע נוסף על שיטות מומלצות לאופטימיזציה של הסוללה, אפשר לעיין בהנחיות בנושא אופטימיזציה של השימוש בסוללה בממשקי API לתזמון משימות.
מומלץ גם להשתמש ב-API החדש JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory שהושק ב-Android 16 כדי להבין למה משימה לא בוצעה.
בדיקה
כדי לבדוק את התנהגות האפליקציה, אפשר להפעיל ביטול של אופטימיזציות מסוימות של מכסת העבודות, כל עוד האפליקציה פועלת במכשיר עם Android 16.
כדי להשבית את האכיפה של ההגדרה 'המצב העליון יפעל בהתאם למכסת זמן הריצה של העבודה', מריצים את הפקודה adb הבאה:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
כדי להשבית את האכיפה של 'משימות שמופעלות במקביל לשירות חזיתי יפעלו בהתאם למכסת זמן הריצה של המשימה', מריצים את הפקודה הבאה של adb:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
כדי לבדוק התנהגות מסוימת של דלי המתנה של האפליקציה, אפשר להגדיר את דלי המתנה של האפליקציה באמצעות הפקודה הבאה adb:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
כדי להבין באיזו קטגוריית המתנה של אפליקציות נמצאת האפליקציה שלכם, אתם יכולים להשתמש בפקודה adb הבאה כדי לקבל את קטגוריית המתנה של האפליקציה:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
הסיבה להפסקת עבודות ריקות שננטשו
An abandoned job occurs when the JobParameters object associated with the job
has been garbage collected, but JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) has not been called to signal job completion. This indicates that
the job may be running and being rescheduled without the app's awareness.
Apps that rely on JobScheduler, don't maintain a strong reference to the
JobParameters object, and timeout will now be granted the new job stop reason
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, instead of STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
If there are frequent occurrences of the new abandoned stop reason, the system will take mitigation steps to reduce job frequency.
Apps should use the new stop reason to detect and reduce abandoned jobs.
If you're using WorkManager, AsyncTask, or DownloadManager, you aren't impacted because these APIs manage the job lifecycle on your app's behalf.
הוצאה מלאה משימוש של JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground
השיטה JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) מציינת את מידת החשיבות של משימה בזמן שאפליקציית התזמון נמצאת בחזית או כשהיא פטורה באופן זמני מההגבלות על משימות ברקע.
השיטה הזו הוצאה משימוש בגרסה Android 12 (רמת API 31). החל מגרסה Android 16, היא כבר לא פועלת בצורה יעילה והקריאה לשיטה הזו תתעלם.
הסרת הפונקציונליות הזו חלה גם על JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground(). החל מגרסה Android 16, אם השיטה נקראת, היא מחזירה את הערך false.
ההיקף של סדר העדיפויות של שידורים כבר לא גלובלי
Android apps are allowed to define priorities on broadcast receivers to control
the order in which the receivers receive and process the broadcast. For
manifest-declared receivers, apps can use the
android:priority attribute to define the priority and for
context-registered receivers, apps can use the
IntentFilter#setPriority() API to define the priority. When
a broadcast is sent, the system delivers it to receivers in order of their
priority, from highest to lowest.
In Android 16, broadcast delivery order using the android:priority attribute
or IntentFilter#setPriority() across different processes will not be
guaranteed. Broadcast priorities will only be respected within the same
application process rather than across all processes.
Also, broadcast priorities will be automatically confined to the range
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Only system components will be
allowed to set SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY as broadcast
priority.
Your app might be impacted if it does either of the following:
- Your application has declared multiple processes with the same broadcast intent, and has expectations around receiving those intents in a certain order based on the priority.
- Your application process interacts with other processes and has expectations around receiving a broadcast intent in a certain order.
If the processes need to coordinate with each other, they should communicate using other coordination channels.
שינויים פנימיים ב-ART
Android 16 כולל את העדכונים האחרונים ל-Android Runtime (ART), שמשפרים את הביצועים של Android Runtime (ART) ומספקים תמיכה בתכונות נוספות של Java. דרך עדכוני המערכת של Google Play, השיפורים האלה זמינים גם ליותר ממיליארד מכשירים עם Android 12 (רמת API 31) ואילך.
כשהשינויים האלה יפורסמו, יכול להיות שספריות וקוד של אפליקציות שמסתמכים על מבנים פנימיים של ART לא יפעלו כראוי במכשירים עם Android 16, וגם בגרסאות קודמות של Android שבהן מופעלים עדכוני מערכת של Google Play למודול ART.
תמיד יכולות להיות בעיות תאימות אם מסתמכים על מבנים פנימיים (כמו ממשקים שאינם SDK), אבל חשוב במיוחד להימנע מהסתמכות על קוד (או ספריות שמכילות קוד) שמשתמש במבנים פנימיים של ART, כי השינויים ב-ART לא קשורים לגרסה של הפלטפורמה שבה המכשיר פועל, והם מועברים ליותר ממיליארד מכשירים דרך עדכוני המערכת של Google Play.
כל המפתחים צריכים לבדוק אם האפליקציה שלהם מושפעת מהשינוי, על ידי בדיקה יסודית של האפליקציות ב-Android 16. בנוסף, כדאי לבדוק את הבעיות המוכרות כדי לראות אם האפליקציה שלכם תלויה בספריות שזיהינו שתלויה במבנים פנימיים של ART. אם יש לכם קוד אפליקציה או יחסי תלות בספרייה שמושפעים מהשינוי, כדאי לנסות למצוא חלופות לממשקי API ציבוריים כשהדבר אפשרי, ולבקש ממשקי API ציבוריים לתרחישי שימוש חדשים על ידי יצירת בקשה לתכונה באתר למעקב אחר בעיות.
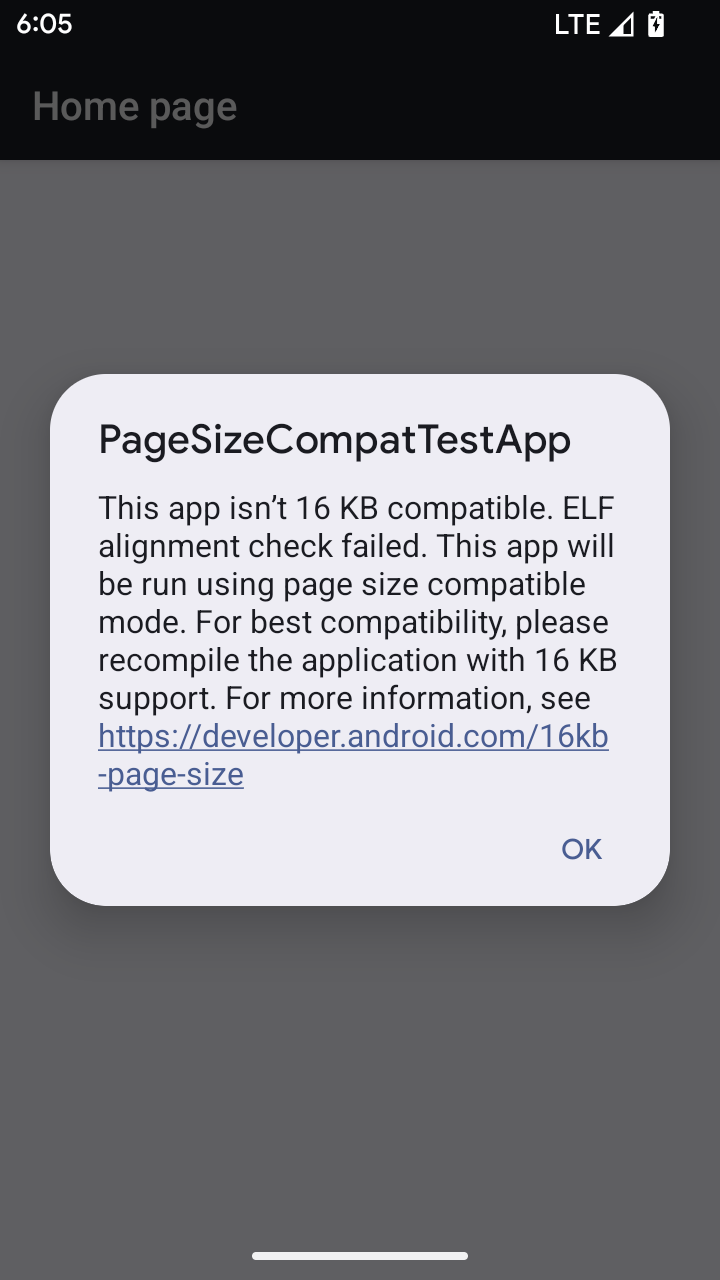
מצב תאימות לגודל דף של 16KB
ב-Android 15 נוספה תמיכה בדפים בזיכרון בגודל 16KB כדי לייעל את הביצועים של הפלטפורמה. ב-Android 16 נוספה תמיכה במצב תאימות, שמאפשר לאפליקציות מסוימות שנוצרו לדפים בזיכרון בנפח 4KB לפעול במכשיר שמוגדר לדפים בזיכרון בנפח 16KB.
כשהאפליקציה פועלת במכשיר עם Android מגרסה 16 ואילך, אם מערכת Android מזהה שהאפליקציה כוללת דפי זיכרון בגודל 4KB, היא משתמשת באופן אוטומטי במצב תאימות ומציגה למשתמש תיבת דו-שיח עם התראה. הגדרת המאפיין android:pageSizeCompat בקובץ AndroidManifest.xml כדי להפעיל את מצב התאימות לאחור תמנע את הצגת תיבת הדו-שיח כשהאפליקציה מופעלת. כדי להשתמש בנכס android:pageSizeCompat, צריך לקמפל את האפליקציה באמצעות Android 16 SDK.
כדי לקבל את הביצועים, האמינות והיציבות הטובים ביותר, עדיין צריך לבצע התאמה של האפליקציה ל-16 KB. פרטים נוספים זמינים בפוסט האחרון שלנו בבלוג בנושא עדכון האפליקציות כך שיתמכו בדפי זיכרון בגודל 16KB.
חוויית המשתמש וממשק המשתמש של המערכת
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים, שנועדו ליצור חוויית משתמש עקבית ואינטואיטיבית יותר.
הוצאה משימוש של הודעות נגישות מפריעות
ב-Android 16 הופסקה התמיכה בהודעות נגישות, שמתאפיינות בשימוש ב-announceForAccessibility או בשליחת אירועי נגישות מסוג TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT. כתוצאה מכך, חוויית המשתמש של משתמשי TalkBack וקורא המסך של Android עשויה להיות לא עקבית. חלופות יכולות לעזור לטפל בטווח רחב יותר של צרכים של משתמשים במגוון טכנולוגיות העזרה של Android.
דוגמאות לחלופות:
- לשינויים משמעותיים בממשק המשתמש, כמו שינויים בחלונות, צריך להשתמש ב-
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)וב-setAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). ב-Compose, משתמשים ב-Modifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - כדי להודיע למשתמש על שינויים בממשק המשתמש הקריטי, משתמשים ב-
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). בחלונית הכתיבה, משתמשים ב-Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. מומלץ להשתמש בהם במשורה, כי הם עלולים ליצור הודעות בכל פעם שנתונים מתעדכנים בתצוגה. - כדי להודיע למשתמשים על שגיאות, שולחים
AccessibilityEventמסוגAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORומגדירים אתAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence), או משתמשים ב-TextView#setError(CharSequence).
במסמכי העזרה של ממשק ה-API announceForAccessibility, שהוצא משימוש, מופיעים פרטים נוספים על חלופות מוצעות.
תמיכה בניווט באמצעות 3 לחצנים
Android 16 brings predictive back support to the 3-button navigation for apps that have properly migrated to predictive back. Long-pressing the back button initiates a predictive back animation, giving you a preview of where the back swipe takes you.
This behavior applies across all areas of the system that support predictive back animations, including the system animations (back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity).
סמלי אפליקציות מעוצבים באופן אוטומטי
החל מ-Android 16 QPR 2, מערכת Android מחילה אוטומטית ערכות נושא על סמלי אפליקציות כדי ליצור חוויית מסך בית מגובשת. הבעיה הזו מתרחשת אם אפליקציה לא מספקת סמל אפליקציה מעוצב משלה. אפליקציות יכולות לשלוט בעיצוב של סמל האפליקציה לפי ערכת הנושא על ידי הוספת שכבה מונוכרומטית לסמל האפליקציה הדינמי ותצוגה מקדימה של סמל האפליקציה ב-Android Studio.
גורמי צורה של מכשירים
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים באפליקציות כשהן מוצגות במסכים על ידי בעלי מכשירים וירטואליים.
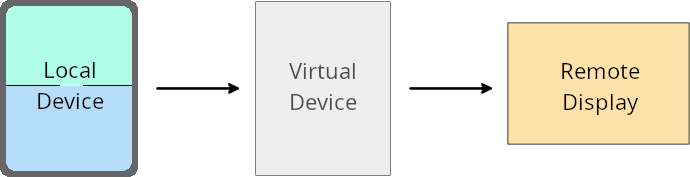
ביטול הגדרות של בעלי מכשיר וירטואלי
בעלים של מכשיר וירטואלי הוא אפליקציה מהימנה או בעלת הרשאות שיוצרת ומנהלת מכשיר וירטואלי. בעלי מכשירים וירטואליים מריצים אפליקציות במכשיר וירטואלי ואז מקרינים את האפליקציות על המסך של מכשיר מרוחק, כמו מחשב אישי, מכשיר מציאות מדומה או מערכת מידע ובידור ברכב. הבעלים של המכשיר הווירטואלי נמצא במכשיר מקומי, כמו טלפון נייד.
שינויים מברירת המחדל של המערכת לכל אפליקציה
במכשירים שמותקנת בהם גרסת Android 16 (API ברמה 36), בעלי מכשירים וירטואליים יכולים לשנות את הגדרות האפליקציה במכשירים וירטואליים נבחרים שהם מנהלים. לדוגמה, כדי לשפר את פריסת האפליקציות, בעלי מכשיר וירטואלי יכולים להתעלם מהגבלות על כיוון, יחס גובה-רוחב ושינוי גודל כשמציגים אפליקציות במסך חיצוני.
שינויי תוכנה נפוצים שעלולים לגרום לכשלים
ההתנהגות של Android 16 עשויה להשפיע על ממשק המשתמש של האפליקציה שלכם בגורמי צורה של מסכים גדולים, כמו מסכי רכב או Chromebook, במיוחד פריסות שנועדו למסכים קטנים במצב אנכי. במאמר מידע על פריסות דינמיות מוסבר איך להתאים את האפליקציה לכל סוגי המכשירים.
קובצי עזר
אבטחה
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת שינויים שמקדמים את אבטחת המערכת כדי לעזור להגן על אפליקציות ומשתמשים מפני אפליקציות זדוניות.
אבטחה משופרת להגנה מפני התקפות של הפניית כוונות
Android 16 מספק אבטחה כברירת מחדל מפני Intentהתקפות כלליות של הפניה אוטומטית, עם דרישות מינימליות של תאימות ושינויים למפתחים.
אנחנו משיקים פתרונות לחיזוק האבטחה כברירת מחדל כדי למנוע ניצול לרעה של Intentהפניות אוטומטיות. ברוב המקרים, אפליקציות שמשתמשות ב-Intents לא ייתקלו בבעיות תאימות. אספנו מדדים לאורך תהליך הפיתוח כדי לעקוב אחרי אפליקציות שעלולות להיתקל בבעיות.
הפניה אוטומטית של Intent ב-Android מתרחשת כשהאקר יכול לשלוט באופן חלקי או מלא בתוכן של Intent שמשמש להפעלת רכיב חדש בהקשר של אפליקציה פגיעה, בזמן שאפליקציית הקורבן מפעילה Intent לא מהימן ברמת משנה בשדה תוספות של Intent ("ברמה העליונה"). הדבר עלול להוביל להפעלת רכיבים פרטיים בהקשר של אפליקציית הקורבן על ידי אפליקציית התוקף, להפעלת פעולות עם הרשאות מיוחדות או לקבלת גישת URI לנתונים רגישים, ועלול להוביל לגניבת נתונים ולהרצת קוד שרירותי.
ביטול ההסכמה לטיפול בהפניה אוטומטית של Intent
ב-Android 16 מוצג API חדש שמאפשר לאפליקציות לבטל את ההצטרפות להגנות אבטחה בהפעלה. יכול להיות שיהיה צורך בכך במקרים ספציפיים שבהם התנהגות האבטחה שמוגדרת כברירת מחדל מפריעה לתרחישי שימוש לגיטימיים באפליקציה.
לאפליקציות שעוברות הידור (compilation) עם SDK של Android 16 (רמת API 36) ומעלה
אפשר להשתמש ישירות בשיטה removeLaunchSecurityProtection() באובייקט Intent.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
לאפליקציות שמתבצעת בהן קומפילציה מול Android 15 (רמת API 35) ומטה
אפשר להשתמש ברפלקציה כדי לגשת לשיטה removeLaunchSecurityProtection(), אבל לא מומלץ לעשות את זה.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
האפליקציות הנלוות לא מקבלות יותר הודעות על פסק זמן לגילוי
Android 16 introduces a new behavior during
companion device pairing flow to protect the user's location
privacy from malicious apps. All companion apps running on Android 16 are no
longer directly notified of discovery timeout using
RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. Instead, the user is
notified of timeout events with a visual dialog. When the user dismisses
the dialog, the app is alerted of the association failure with
RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
The search duration has also been extended from the original 20 seconds, and the device discovery can be stopped by the user at any point during the search. If at least one device was discovered within the first 20 seconds of starting the search, the CDM stops searching for additional devices.
קישוריות
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים במערך Bluetooth כדי לשפר את הקישוריות למכשירים היקפיים.
טיפול משופר באובדן של קשרים
החל מגרסה 16 של Android, סטאק ה-Bluetooth עודכן כדי לשפר את האבטחה ואת חוויית המשתמש במקרה של איבוד חיבור מרחוק. בעבר, המערכת הייתה מסירה את הקישור באופן אוטומטי ומתחילה תהליך התאמה חדש, שעלול להוביל להתאמה מחדש לא מכוונת. גילינו במקרים רבים שאפליקציות לא מטפלות באירוע של אובדן ההתחייבות בצורה עקבית.
כדי לאחד את חוויית השימוש, מערכת Android 16 עברה שיפורים בטיפול באובדן קישורים. אם לא ניתן לאמת מכשיר Bluetooth שהיה מקושר בעבר במהלך החיבור מחדש, המערכת תנתק את הקישור, תשמור את פרטי הקישור המקומיים ותציג תיבת דו-שיח של המערכת שבה תודיע למשתמשים על אובדן הקישור ותנחה אותם לבצע התאמה מחדש.
