Android 16 platformu, uygulamanızı etkileyebilecek davranış değişiklikleri içerir.
Aşağıdaki davranış değişiklikleri, targetSdkVersion değerinden bağımsız olarak Android 16'da çalıştırılan tüm uygulamalar için geçerlidir. Uygulamanızı test etmeli ve uygun olduğu durumlarda bu değişiklikleri desteklemek için uygulamanızı gerektiği gibi değiştirmelisiniz.
Yalnızca Android 16'yı hedefleyen uygulamaları etkileyen davranış değişiklikleri listesini de incelemeyi unutmayın.
Temel işlevler
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), Android sisteminin çeşitli temel özelliklerini değiştiren veya genişleten aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
JobScheduler kota optimizasyonları
Android 16'dan itibaren, normal ve hızlandırılmış iş yürütme çalışma zamanı kotasını aşağıdaki faktörlere göre ayarlıyoruz:
- Uygulamanın hangi uygulama bekleme modunda olduğu: Android 16'da etkin bekleme modu grupları, cömert bir çalışma zamanı kotasıyla zorunlu kılınmaya başlanacak.
- İş, uygulama üst durumda iken yürütülmeye başlarsa: Android 16'da, uygulama kullanıcıya görünürken başlatılan ve uygulama görünmez hale geldikten sonra devam eden işler, işin çalışma süresi kotasına uyar.
- İş, ön plan hizmeti çalıştırılırken yürütülüyorsa: Android 16'da, ön plan hizmetiyle eşzamanlı olarak yürütülen işler, iş çalışma süresi kotasına uyar. Kullanıcı tarafından başlatılan veri aktarımı için işlerden yararlanıyorsanız bunun yerine kullanıcı tarafından başlatılan veri aktarımı işlerini kullanmayı düşünebilirsiniz.
Bu değişiklik, WorkManager, JobScheduler ve DownloadManager kullanılarak planlanan görevleri etkiler. Bir işin neden durdurulduğunu belirlemek için WorkInfo.getStopReason() işlevini çağırarak işinizin neden durdurulduğunu günlüğe kaydetmenizi öneririz (JobScheduler işleri için JobParameters.getStopReason() işlevini çağırın).
Uygulamanızın durumunun kullanabileceği kaynakları nasıl etkilediği hakkında bilgi edinmek için Güç yönetimi kaynak sınırları başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin. Pil kullanımını optimize etmeye yönelik en iyi uygulamalar hakkında daha fazla bilgi için görev planlama API'leri için pil kullanımını optimize etme ile ilgili yönergelere bakın.
Ayrıca, bir işin neden yürütülmediğini anlamak için Android 16'da kullanıma sunulan yeni JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API'den yararlanmanızı öneririz.
Test
Uygulamanızın davranışını test etmek için, uygulama Android 16 cihazda çalıştığı sürece belirli iş kotası optimizasyonlarının geçersiz kılınmasını etkinleştirebilirsiniz.
"En üst durum, iş çalışma zamanı kotasına uyar" kuralının uygulanmasını devre dışı bırakmak için aşağıdaki adb komutunu çalıştırın:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
"Ön plan hizmetiyle eşzamanlı olarak yürütülen işler, iş çalışma süresi kotasına uyar" kuralının uygulanmasını devre dışı bırakmak için aşağıdaki adb komutunu çalıştırın:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Belirli uygulama bekleme modu grubu davranışlarını test etmek için aşağıdaki adb komutunu kullanarak uygulamanızın uygulama bekleme modu grubunu ayarlayabilirsiniz:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
Uygulamanızın bulunduğu uygulama bekleme grubunu anlamak için aşağıdaki adb komutunu kullanarak uygulamanızın uygulama bekleme grubunu alabilirsiniz:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
Boş bırakılan işlerin durdurulma nedeni
İşle ilişkili JobParameters nesnesi çöp toplandıysa ancak iş tamamlandığını belirtmek için JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) çağrılmadıysa iş terk edilmiş olur. Bu, işin uygulamanın bilgisi olmadan çalıştığını ve yeniden planlandığını gösterir.
JobScheduler'ı kullanan uygulamalar JobParameters nesnesine güçlü bir referans sağlamaz ve zaman aşımı artık STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT yerine yeni iş durdurma nedeni STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED ile verilir.
Yeni terk edilmiş duraklatma nedeni sık sık gerçekleşirse sistem, iş sıklığını azaltmak için azaltma adımları atar.
Uygulamalar, terk edilmiş işleri tespit edip azaltmak için yeni durdurma nedenini kullanmalıdır.
WorkManager, AsyncTask veya DownloadManager kullanıyorsanız bu API'ler iş yaşam döngüsünü uygulamanız adına yönettiğinden bu değişiklikten etkilenmezsiniz.
JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground tamamen kullanımdan kaldırılıyor
JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) yöntemi, planlama uygulaması ön plandayken veya geçici olarak arka plan kısıtlamalarından muafken bir işin önemini belirtir.
Bu yöntem, Android 12 (API düzeyi 31) sürümünden itibaren kullanımdan kaldırılmıştır. Android 16'dan itibaren bu yöntem artık etkili bir şekilde çalışmaz ve bu yöntem çağrılırsa yoksayılır.
Bu işlev kaldırma işlemi JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground() için de geçerlidir. Android 16'dan itibaren, yöntem çağrılırsa false döndürülür.
Sıralı yayın önceliği kapsamı artık global değil
Android uygulamalarının, alıcılara yayını alma ve işleme sırasını kontrol etmek için yayın alıcılarında öncelikleri tanımlamasına izin verilir. Manifestte tanımlanan alıcılarda uygulamalar önceliği tanımlamak için android:priority özelliğini, bağlamda kaydedilen alıcılarda ise IntentFilter#setPriority() API'yi kullanabilir. Bir yayın gönderildiğinde sistem, yayını öncelik sırasına göre (en yüksekten en düşüğe) alıcılara iletir.
Android 16'da, farklı işlemlerde android:priority özelliğini veya IntentFilter#setPriority() değerini kullanan yayın sırası garanti edilmez. Yayın önceliklerine tüm süreçlerde değil, yalnızca aynı başvuru sürecinde uyulur.
Ayrıca yayın öncelikleri otomatik olarak (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1) aralığına sınırlandırılır. Yalnızca sistem bileşenlerinin SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY'ü yayın önceliği olarak ayarlamasına izin verilir.
Uygulamanız aşağıdakilerden birini yapıyorsa bu durumdan etkilenebilir:
- Uygulamanız aynı yayın intent'iyle birden fazla işlem tanımladı ve bu intent'leri önceliğe göre belirli bir sırada alma konusunda beklentileri var.
- Başvuru süreciniz diğer süreçlerle etkileşim kurar ve belirli bir sırada yayın amacı almayla ilgili beklentileri vardır.
İşlemlerin birbiriyle koordinasyon kurması gerekiyorsa diğer koordinasyon kanallarını kullanarak iletişim kurmalıdır.
ART ile ilgili dahili değişiklikler
Android 16, Android Runtime'da (ART) performansı artıran ve ek Java özellikleri için destek sağlayan en son güncellemeleri içerir. Google Play sistem güncellemeleri sayesinde bu iyileştirmeler, Android 12 (API düzeyi 31) ve sonraki sürümleri çalıştıran bir milyardan fazla cihazda da kullanılabilir.
Bu değişiklikler kullanıma sunulduğunda, ART'nin dahili yapılarına dayanan kitaplıklar ve uygulama kodları, Android 16 çalıştıran cihazların yanı sıra Google Play sistem güncellemeleri aracılığıyla ART modülünü güncelleyen önceki Android sürümlerinde düzgün çalışmayabilir.
Dahili yapılara (ör. SDK dışı arayüzler) güvenmek her zaman uyumluluk sorunlarına yol açabilir. Ancak ART değişiklikleri cihazın çalıştığı platform sürümüne bağlı olmadığı ve Google Play sistem güncellemeleri aracılığıyla bir milyardan fazla cihaza dağıtıldığı için özellikle dahili ART yapılarından yararlanan koda (veya kod içeren kitaplıklara) güvenmekten kaçınmak önemlidir.
Tüm geliştiriciler, uygulamalarını Android 16'da ayrıntılı bir şekilde test ederek uygulamalarının etkilenip etkilenmediğini kontrol etmelidir. Ayrıca, uygulamanızın dahili ART yapılarına dayalı olarak tespit ettiğimiz kitaplıklara bağımlı olup olmadığını görmek için bilinen sorunları kontrol edin. Etkilenen uygulama kodunuz veya kitaplık bağımlılıklarınız varsa mümkün olduğunda herkese açık API alternatifleri arayın ve sorun takipçimizde özellik isteği oluşturarak yeni kullanım alanları için herkese açık API'ler isteyin.
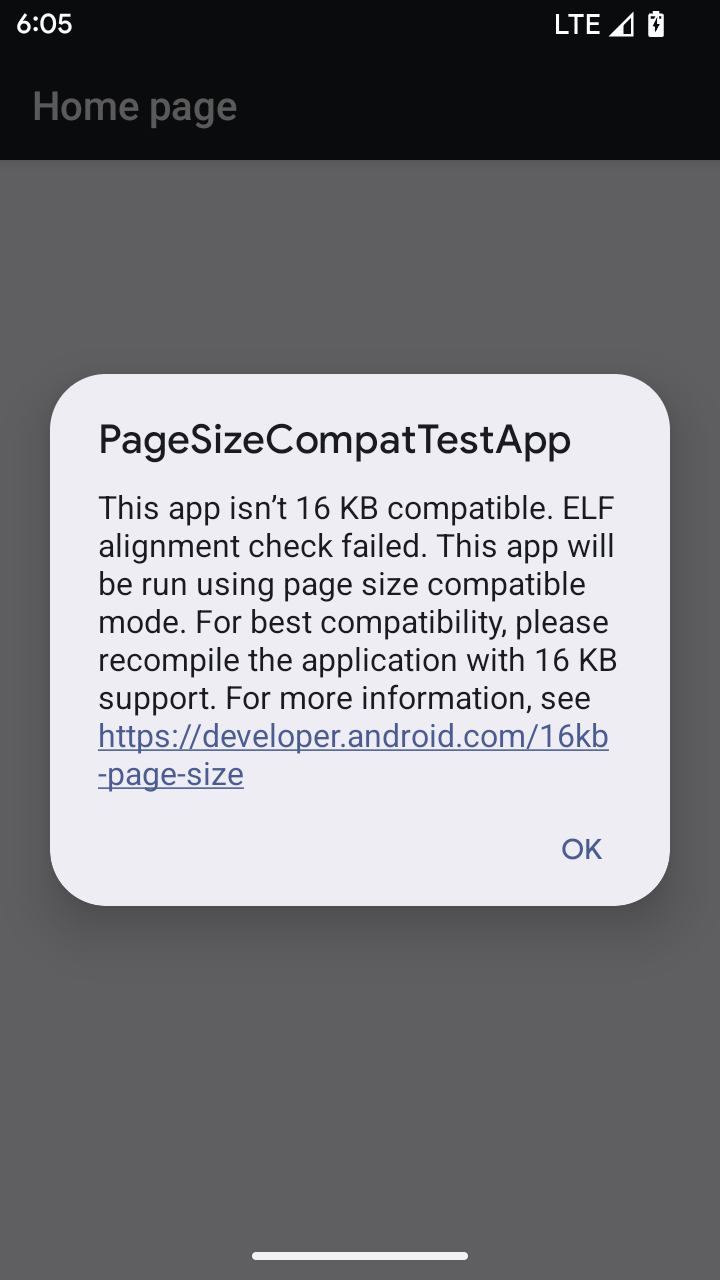
16 KB sayfa boyutu uyumluluk modu
Android 15, platformun performansını optimize etmek için 16 KB bellek sayfası desteğini kullanıma sundu. Android 16, 4 KB bellek sayfaları için geliştirilmiş bazı uygulamaların 16 KB bellek sayfaları için yapılandırılmış bir cihazda çalışmasına olanak tanıyan bir uyumluluk modu ekler.
Uygulamanız Android 16 veya sonraki bir sürümün yüklü olduğu bir cihazda çalışırken Android, uygulamanızda 4 KB'lık hizalanmış bellek sayfaları olduğunu algılarsa otomatik olarak uyumluluk modunu kullanır ve kullanıcıya bir bildirim iletişim kutusu gösterir. AndroidManifest.xml özelliğini AndroidManifest.xml içinde geriye dönük uyumluluk modunu etkinleştirecek şekilde ayarlamak, uygulamanız başlatıldığında iletişim kutusunun gösterilmesini engeller.android:pageSizeCompat android:pageSizeCompat mülkünü kullanmak için uygulamanızı Android 16 SDK'sını kullanarak derleyin.
En iyi performans, güvenilirlik ve kararlılık için uygulamanız 16 KB'ya hizalanmış olmalıdır. Uygulamalarınızı 16 KB bellek sayfalarını destekleyecek şekilde güncellemeyle ilgili daha fazla bilgi için son blog yayınımıza göz atın.
Kullanıcı deneyimi ve sistem arayüzü
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), daha tutarlı ve sezgisel bir kullanıcı deneyimi oluşturmayı amaçlayan aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Kullanımı engelleyen erişilebilirlik duyurularının desteğinin sonlandırılması
Android 16, announceForAccessibility kullanımı veya TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT erişilebilirlik etkinliklerinin gönderilmesiyle karakterize edilen erişilebilirlik duyurularını desteklememektedir. Bu durum, TalkBack ve Android'in ekran okuyucusunun kullanıcıları için tutarsız kullanıcı deneyimleri oluşturabilir. Alternatifler ise Android'in çeşitli yardımcı teknolojileri genelinde daha geniş bir kullanıcı ihtiyacı yelpazesine daha iyi hizmet eder.
Alternatiflere örnekler:
- Pencere değişiklikleri gibi önemli kullanıcı arayüzü değişiklikleri için
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)vesetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)değerlerini kullanın. Oluştur'daModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" }simgesini kullanarak - Kullanıcıyı kritik kullanıcı arayüzündeki değişiklikler hakkında bilgilendirmek için
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)simgesini kullanın. Oluştur'daModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}simgesini kullanın . Bu bildirimler, bir görünüm her güncellendiğinde bildirim oluşturabileceğinden, dikkatli bir şekilde kullanılmalıdır. - Kullanıcıları hatalar hakkında bilgilendirmek için
AccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORtüründeki birAccessibilityEventgönderin veAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)değerini ayarlayın veyaTextView#setError(CharSequence)kullanın.
Kullanımdan kaldırılan announceForAccessibility API'nin referans dokümanlarında, önerilen alternatifler hakkında daha fazla bilgi verilmektedir.
3 düğmeli gezinme desteği
Android 16, tahmini geriye doğru geçişi doğru şekilde gerçekleştiren uygulamalarda 3 düğmeli gezinme için tahmini geri desteği sunar. Geri düğmesine uzun bastığınızda tahmini geri animasyonu başlatılır. Bu animasyon, geri kaydırmanın sizi nereye götüreceğinin önizlemesini gösterir.
Bu davranış, sistem animasyonları (ana sayfaya geri gitme, görevler arası ve etkinlikler arası) dahil olmak üzere sistemin tahmine dayalı geri animasyonlarını destekleyen tüm alanlarında geçerlidir.
Otomatik temalı uygulama simgeleri
Android 16 QPR 2'den itibaren Android, tutarlı bir ana ekran deneyimi oluşturmak için uygulama simgelerine otomatik olarak temalar uygular. Bu durum, bir uygulama kendi temalı uygulama simgesini sağlamadığında ortaya çıkar. Uygulamalar, temalı uygulama simgelerinin tasarımını uyarlanabilir simgelerine tek renkli bir katman ekleyerek ve uygulama simgelerinin Android Studio'da nasıl görüneceğini önizleyerek kontrol edebilir.
Cihaz form faktörleri
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), sanal cihaz sahipleri tarafından ekranlara yansıtılan uygulamalar için aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Sanal cihaz sahibinin geçersiz kılma işlemleri
Sanal cihaz sahibi, sanal cihaz oluşturan ve yöneten güvenilir veya ayrıcalıklı bir uygulamadır. Sanal cihaz sahipleri, uygulamaları sanal cihazda çalıştırıp kişisel bilgisayar, sanal gerçeklik cihazı veya araba bilgi-eğlence sistemi gibi uzak bir cihazın ekranına yansıtır. Sanal cihaz sahibi, cep telefonu gibi yerel bir cihaz kullanıyordur.
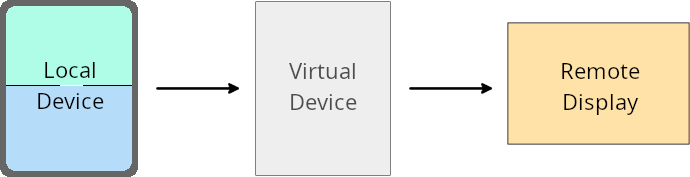
Uygulama bazında geçersiz kılmalar
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36) çalıştıran cihazlarda sanal cihaz sahipleri, sanal cihaz sahiplerinin yönettiği belirli sanal cihazlardaki uygulama ayarlarını geçersiz kılabilir. Örneğin, uygulama düzenini iyileştirmek için sanal cihaz sahibi, uygulamaları harici bir ekrana yansıtırken yön, en-boy oranı ve yeniden boyutlandırma kısıtlamalarını yoksayabilir.
Sık karşılaşılan zarar veren değişiklikler
Android 16'daki bu davranış, özellikle dikey yönde küçük ekranlar için tasarlanmış düzenlerde olmak üzere, araba ekranları veya Chromebook'lar gibi büyük ekranlı form faktörlerinde uygulamanızın kullanıcı arayüzünü etkileyebilir. Uygulamanızı tüm cihaz form faktörlerine uyarlanabilir hale getirme hakkında bilgi edinmek için Uyarlanabilir düzenler hakkında başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin.
Referanslar
Güvenlik
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), uygulamaları ve kullanıcıları kötü amaçlı uygulamalardan korumaya yardımcı olmak için sistem güvenliğini artıran değişiklikler içerir.
Niyet yönlendirme saldırılarına karşı gelişmiş güvenlik
Android 16, genel Intent yönlendirme saldırılarına
karşı varsayılan güvenlik sağlar. Minimum uyumluluk ve geliştirici değişiklikleri gerektirir.
Intent
Yönlendirme saldırılarına karşı varsayılan olarak güvenlik sağlamlaştırma çözümleri sunuyoruz. Çoğu durumda, amaçları kullanan uygulamalarda normalde herhangi bir uyumluluk sorunu yaşanmaz. Hangi uygulamalarda sorun yaşanabileceğini izlemek için geliştirme sürecimiz boyunca metrikler topladık.
Android'de Intent yönlendirmesi, saldırganın savunmasız bir uygulama bağlamında yeni bir bileşeni başlatmak için kullanılan bir Intent'in içeriğini kısmen veya tamamen kontrol edebildiği, kurban uygulamanın ise bir ("üst düzey") Intent'in ekstralar alanında güvenilmeyen bir alt düzey Intent başlattığı durumlarda gerçekleşir. Bu durum, saldırgan uygulamanın kurban uygulaması bağlamında özel bileşenler başlatmasına, ayrıcalıklı işlemleri tetiklemesine veya hassas verilere URI erişimi kazanmasına yol açabilir. Bu da veri hırsızlığına ve rastgele kod yürütmeye neden olabilir.
Intent yönlendirme işleme özelliğini devre dışı bırakma
Android 16, uygulamaların başlatma güvenlik korumalarını devre dışı bırakmasına olanak tanıyan yeni bir API sunuyor. Bu, varsayılan güvenlik davranışının meşru uygulama kullanım alanlarını engellediği belirli durumlarda gerekli olabilir.
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36) SDK'sına veya sonraki sürümlere göre derlenen uygulamalar için
Intent nesnesinde doğrudan removeLaunchSecurityProtection() yöntemini kullanabilirsiniz.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Android 15 (API düzeyi 35) veya önceki sürümlere göre derlenen uygulamalar için
Önerilmese de removeLaunchSecurityProtection() yöntemine erişmek için yansıtma kullanabilirsiniz.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Tamamlayıcı uygulamalar artık keşif zaman aşımları hakkında bildirim almayacak
Android 16, kullanıcının konum gizliliğini kötü amaçlı uygulamalardan korumak için yardımcı cihaz eşleme akışında yeni bir davranış sunar. Android 16'da çalışan tüm tamamlayıcı uygulamalar artık RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT kullanılarak keşif zaman aşımı hakkında doğrudan bilgilendirilmez. Bunun yerine, kullanıcıya görsel bir iletişim kutusu gösterilerek zaman aşımı etkinlikleri bildirilir. Kullanıcı iletişim kutusunu kapattığında uygulama, RESULT_USER_REJECTED ile ilişkilendirme hatası konusunda uyarılır.
Arama süresi de orijinal 20 saniyeden uzatıldı ve cihaz bulma işlemi, arama sırasında kullanıcı tarafından herhangi bir noktada durdurulabilir. Aramanın başlatılmasından sonraki ilk 20 saniye içinde en az bir cihaz bulunursa CDM başka cihaz aramayı durdurur.
Bağlantı
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), çevre birimi cihazlarıyla bağlantıyı iyileştirmek için Bluetooth yığınında aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Geliştirilmiş tahvil kaybı işleme
Android 16'dan itibaren Bluetooth yığını, uzak bağlantı kaybı algılandığında güvenliği ve kullanıcı deneyimini iyileştirmek için güncellendi. Daha önce sistem, bağı otomatik olarak kaldırır ve yeni bir eşleme işlemi başlatırdı. Bu da istemeden yeniden eşlemeye neden olabilirdi. Birçok durumda, uygulamaların bağ kaybı etkinliğini tutarlı bir şekilde ele almadığını tespit ettik.
Android 16, deneyimi birleştirmek için sistemde bağ kaybının ele alınmasını iyileştirdi. Daha önce bağlanmış bir Bluetooth cihazı yeniden bağlandığında kimliği doğrulanamazsa sistem bağlantıyı keser, yerel bağlantı bilgilerini saklar ve kullanıcıları bağlantı kaybı hakkında bilgilendirip yeniden eşlemeye yönlendiren bir sistem iletişim kutusu gösterir.
