Android 16 平台包含可能對應用程式造成影響的行為變更。無論 targetSdkVersion 為何,當應用程式在 Android 16 上執行時,下列行為變更將會套用至所有應用程式。您必須測試自己的應用程式,並視需要進行修改,以便在適當情況下支援這些變更。
另請務必查看僅對指定 Android 16 為目標版本的應用程式造成影響的行為變更。
核心功能
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列異動項目,這類變更會修改或擴充 Android 系統的各種核心功能。
JobScheduler 配額最佳化
從 Android 16 開始,我們會根據下列因素調整一般和快速工作執行的執行階段配額:
- 應用程式所屬的應用程式待機值區:在 Android 16 中,系統會開始透過充足的執行階段配額,強制執行有效待機值區。
- 如果工作在應用程式處於頂層狀態時開始執行:在 Android 16 中,如果工作是在應用程式向使用者顯示時啟動,且在應用程式隱藏後繼續執行,則會遵守工作執行時間配額。
- 如果工作在執行前景服務時執行:在 Android 16 中,與前景服務並行執行的工作會遵守工作執行階段配額。如果您使用工作進行使用者啟動的資料移轉,請考慮改用使用者啟動的資料移轉工作。
這項異動會影響使用 WorkManager、JobScheduler 和 DownloadManager 安排的工作。如要偵錯工作停止的原因,建議您呼叫 WorkInfo.getStopReason() (如果是 JobScheduler 工作,請呼叫 JobParameters.getStopReason()),記錄工作停止的原因。
如要瞭解應用程式狀態如何影響可使用的資源,請參閱「電源管理資源限制」。如要進一步瞭解如何以最佳方式節省電量,請參閱「針對工作排程 API 最佳化電池用量」指南。
此外,我們建議您運用 Android 16 中推出的新版 JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API,瞭解工作未執行的原因。
測試
如要測試應用程式的行為,只要應用程式在 Android 16 裝置上執行,您就可以啟用特定工作配額最佳化功能的覆寫功能。
如要停用「頂端狀態會遵守工作執行階段配額」的強制執行,請執行下列 adb 指令:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
如要停用「與前景服務同時執行的作業會遵守作業執行階段配額」的強制執行功能,請執行下列 adb 指令:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
如要測試特定應用程式待命值區行為,可以使用下列 adb 指令設定應用程式的應用程式待命值區:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
如要瞭解應用程式所屬的應用程式待命值區,可以使用下列 adb 指令取得應用程式的應用程式待命值區:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
因工作空白而停止的原因
當與工作相關聯的 JobParameters 物件已收集為垃圾,但未呼叫 JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) 來傳送工作完成信號時,就會發生遺棄的工作。這表示工作可能在未經應用程式察覺的情況下執行及重新排程。
依賴 JobScheduler 的應用程式不會維持對 JobParameters 物件的強參照,且超時現在會授予新的 STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED 工作停止原因,而非 STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT。
如果新棄站原因經常發生,系統會採取緩解措施來減少工作頻率。
應用程式應使用新的停止原因來偵測並減少遺失的工作。
如果您使用 WorkManager、AsyncTask 或 DownloadManager,則不會受到影響,因為這些 API 會代表應用程式管理工作生命週期。
完全淘汰 JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground
JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) 方法會在排程應用程式處於前景或暫時豁免背景限制時,指出工作的重要性。
自 Android 12 (API 級別 31) 起,此方法已淘汰。自 Android 16 起,這項方法不再有效,系統會忽略呼叫此方法的行為。
這項功能移除作業也適用於 JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground()。自 Android 16 起,如果呼叫該方法,該方法會傳回 false。
已排序的廣播優先順序範圍不再是全域
Android 應用程式可定義廣播接收器的優先順序,藉此控制接收器接收及處理廣播的順序。對於資訊清單宣告的接收器,應用程式可以使用 android:priority 屬性來定義優先順序,而對於內容註冊的接收器,應用程式可以使用 IntentFilter#setPriority() API 來定義優先順序。傳送廣播訊息時,系統會依優先順序 (由高至低) 將訊息傳送給接收器。
在 Android 16 中,系統無法保證使用 android:priority 屬性或在不同程序中使用 IntentFilter#setPriority() 的廣播傳送順序。廣播優先順序只會在相同的應用程式程序中受到尊重,而不會跨所有程序。
此外,廣播優先順序會自動限制在 (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1) 的範圍內。只有系統元件可將 SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY、SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY 設為廣播優先順序。
如果您的應用程式執行下列任一操作,可能會受到影響:
- 您的應用程式已宣告多個使用相同廣播意圖的程序,並且預期會按照優先順序接收這些意圖。
- 您的應用程式程序會與其他程序互動,並預期以特定順序接收廣播意圖。
如果程序需要相互協調,則應使用其他協調管道進行通訊。
ART 內部變更
Android 16 包含 Android 執行階段 (ART) 的最新更新,可改善 Android 執行階段 (ART) 的效能,並提供其他 Java 功能的支援。透過 Google Play 系統更新,這些改善項目也適用於搭載 Android 12 (API 級別 31) 以上版本的十億部裝置。
隨著這些變更發布,依賴 ART 內部結構的程式庫和應用程式程式碼,可能無法在搭載 Android 16 的裝置上正常運作,也無法在透過 Google Play 系統更新更新 ART 模組的舊版 Android 上正常運作。
依賴內部結構 (例如 非 SDK 介面) 可能會導致相容性問題,但特別要避免依賴利用內部 ART 結構的程式碼 (或包含程式碼的程式庫),因為 ART 變更並未與裝置執行的平台版本綁定,且會透過 Google Play 系統更新傳送至十億部裝置。
所有開發人員都應在 Android 16 上徹底測試應用程式,檢查應用程式是否受到影響。此外,請檢查已知問題,瞭解您的應用程式是否依附我們已識別的任何程式庫,而這些程式庫又依附 ART 內部結構。如果確實有受到影響的應用程式程式碼或程式庫依附元件,請盡可能尋找公用 API 替代方案,並在問題追蹤工具中建立功能要求,為新的用途要求公用 API。
16 KB 頁面大小相容模式
Android 15 推出了 16 KB 記憶體分頁支援功能,以提升平台效能。Android 16 新增了相容模式,可讓為 4 KB 記憶體分頁建構的部分應用程式,在針對 16 KB 記憶體分頁設定的裝置上執行。
當應用程式在搭載 Android 16 以上版本的裝置上執行時,如果 Android 偵測到應用程式有 4 KB 對齊的記憶體分頁,就會自動使用相容性模式,並向使用者顯示通知對話方塊。在 AndroidManifest.xml 中設定 android:pageSizeCompat 屬性以啟用向後相容性模式,可防止應用程式啟動時顯示對話方塊。如要使用 android:pageSizeCompat 屬性,請使用 Android 16 SDK 編譯應用程式。
為獲得最佳效能、可靠性和穩定性,應用程式仍應以 16 KB 對齊。如要進一步瞭解如何更新應用程式以支援 16 KB 記憶體分頁,請參閱近期的網誌文章。
使用者體驗和系統 UI
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含下列變更,旨在打造更一致、直覺的使用者體驗。
淘汰令人混淆的無障礙工具公告
Android 16 已淘汰無障礙公告,這類公告的特色是使用 announceForAccessibility 或調度 TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT 無障礙事件。這可能會為 TalkBack 和 Android 螢幕閱讀器的使用者帶來不一致的使用者體驗,而替代方案可在各種 Android 輔助技術中,滿足更廣泛的使用者需求。
替代方案範例:
- 如要進行重大的 UI 變更 (例如變更視窗),請使用
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)和setAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)。在 Compose 中使用Modifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - 如要通知使用者關鍵 UI 的變更,請使用
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)。在 Compose 中使用Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}。這些事件應謹慎使用,因為每次 View 更新時,這些事件都可能產生通知。 - 如要通知使用者錯誤,請傳送
AccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERROR類型的AccessibilityEvent,並設定AccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence),或使用TextView#setError(CharSequence)。
如要進一步瞭解建議的替代方案,請參閱已淘汰的 announceForAccessibility API 參考說明文件。
支援三按鈕操作模式
Android 16 為已正確遷移至預測返回功能的應用程式,提供 3 鍵導覽的預測返回功能支援。長按返回按鈕會啟動預測返回動畫,讓您預覽返回滑動手勢會帶您前往的位置。
這項行為適用於系統中所有支援預測返回動畫的區域,包括系統動畫 (返回首頁、跨工作和跨活動)。
自動套用主題色應用程式圖示
從 Android 16 QPR 2 開始,Android 會自動將主題套用至應用程式圖示,打造一致的主畫面體驗。如果應用程式未提供自己的主題式應用程式圖示,就會發生這種情況。應用程式可以在自動調整式圖示中加入單色圖層,並在 Android Studio 中預覽應用程式圖示的外觀,藉此控制主題式應用程式圖示的設計。
裝置板型規格
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含以下變更,適用於虛擬裝置擁有者將應用程式投放到螢幕時。
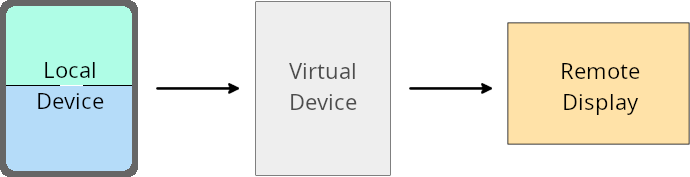
虛擬裝置擁有者覆寫
虛擬裝置擁有者是可信任或具備特殊權限的應用程式,可建立及管理虛擬裝置。虛擬裝置擁有者可以在虛擬裝置上執行應用程式,然後將應用程式投影到遠端裝置的螢幕上,例如個人電腦、虛擬實境裝置或車輛資訊娛樂系統。虛擬裝置擁有者使用本機裝置,例如手機。
個別應用程式覆寫值
在搭載 Android 16 (API 級別 36) 的裝置上,虛擬裝置擁有者可以覆寫所管理特定虛擬裝置的應用程式設定。舉例來說,為了改善應用程式版面配置,虛擬裝置擁有者在將應用程式投影到外部螢幕時,可以忽略方向、長寬比和可調整大小的限制。
常見的破壞性變更
Android 16 的這項行為可能會影響應用程式在大型螢幕 (例如車輛螢幕或 Chromebook) 上的 UI,尤其是專為直向小螢幕設計的版面配置。如要瞭解如何讓應用程式自動調整版面,以配合所有裝置板型規格,請參閱「關於自動調整版面」。
參考資料
安全性
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 包含多項異動,可提升系統安全性,協助保護應用程式和使用者免受惡意應用程式侵擾。
安全性提高,避免意圖重新導向攻擊
Android 16 提供預設安全性,可防範一般Intent重新導向攻擊,且只需進行最少的相容性調整和開發人員變更。
我們即將推出預設安全強化解決方案,以防範Intent
重新導向漏洞。在大多數情況下,使用意圖的應用程式通常不會遇到任何相容性問題;我們在開發過程中收集了各項指標,以監控哪些應用程式可能會發生中斷。
Android 發生意圖重新導向的情況,是指攻擊者可以部分或完整地控管某個意圖的內容,將該意圖用於在含有安全漏洞的應用程式環境中啟動新元件,而受害應用程式會在 ("頂層") Intent 的 Extras 欄位中啟動不受信任的次級意圖。這可能會導致攻擊者應用程式在受害者應用程式的環境中啟動私人元件、觸發具備特殊權限的動作,或取得機密資料的 URI 存取權,進而竊取資料及執行任意程式碼。
選擇不處理意圖重新導向
Android 16 導入新的 API,可讓應用程式選擇停用啟動安全防護措施。在特定情況下,預設安全性行為可能會干擾正當的應用程式用途,因此可能需要停用。
針對 Android 16 (API 級別 36) 以上 SDK 編譯的應用程式
您可以直接在 Intent 物件上使用 removeLaunchSecurityProtection() 方法。
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
針對 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 以下版本編譯的應用程式
雖然不建議,但您可以使用反射來存取 removeLaunchSecurityProtection() 方法。
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
隨附應用程式不會再收到探索逾時通知
Android 16 在配件裝置配對流程中導入了新行為,以保護使用者的所在位置隱私,避免遭到惡意應用程式竊取。所有在 Android 16 上執行的隨附應用程式,都不再直接透過 RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT 收到發現逾時的通知。而是透過視覺對話方塊通知使用者逾時事件。當使用者關閉對話方塊時,應用程式會收到關於 RESULT_USER_REJECTED 關聯失敗的警示。
搜尋時間也從原本的 20 秒延長,使用者可在搜尋期間的任何時間停止裝置探索。如果在開始搜尋的頭 20 秒內發現至少一台裝置,CDM 就會停止搜尋其他裝置。
連線能力
Android 16 (API 級別 36) 的藍牙堆疊包含下列變更,可提升與周邊裝置的連線能力。
改善債券損失處理方式
自 Android 16 起,我們已更新藍牙堆疊,以便在偵測到遠端連結遺失時,提升安全性和使用者體驗。先前系統會自動移除配對連結,並啟動新的配對程序,這可能會導致不小心重新配對。我們發現許多應用程式並未以一致的方式處理連結失效事件。
為統一使用體驗,Android 16 改善了系統的連結遺失處理方式。如果先前已配對的藍牙裝置無法在重新連線時驗證,系統會中斷連結、保留本機配對資訊,並顯示系統對話方塊,告知使用者配對失敗,並引導他們重新配對。
