Android 16 플랫폼에는 앱에 영향을 줄 수 있는 동작 변경사항이 있습니다. targetSdkVersion과 관계없이 Android 16에서 실행되는 모든 앱에 적용되는 동작 변경사항은 다음과 같습니다. 이러한 변경사항을 적절히 지원해야 하는 경우 앱을 테스트한 후 필요에 따라 수정해야 합니다.
또한 Android 16을 타겟팅하는 앱에만 영향을 주는 동작 변경사항 목록을 검토해야 합니다.
핵심 기능
Android 16 (API 수준 36)에는 Android 시스템의 다양한 핵심 기능을 수정하거나 확장하는 다음과 같은 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
JobScheduler 할당량 최적화
Android 16부터는 다음 요소를 기반으로 일반 및 신속 작업 실행 런타임 할당량이 조정됩니다.
- 애플리케이션이 속한 앱 대기 버킷: Android 16에서는 활성 대기 버킷이 넉넉한 런타임 할당량에 의해 적용되기 시작합니다.
- 앱이 상단 상태에 있는 동안 작업이 실행을 시작하는 경우: Android 16에서 앱이 사용자에게 표시되는 동안 시작되고 앱이 표시되지 않게 된 후에도 계속되는 작업은 작업 런타임 할당량을 준수합니다.
- 포그라운드 서비스를 실행하는 동안 작업이 실행되는 경우: Android 16에서 포그라운드 서비스와 동시에 실행되는 작업은 작업 런타임 할당량을 준수합니다. 사용자가 시작한 데이터 전송에 작업을 활용하는 경우 대신 사용자가 시작한 데이터 전송 작업을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
이 변경사항은 WorkManager, JobScheduler, DownloadManager를 사용하여 예약된 작업에 영향을 미칩니다. 작업이 중지된 이유를 디버깅하려면 WorkInfo.getStopReason()을 호출하여 작업이 중지된 이유를 로깅하는 것이 좋습니다 (JobScheduler 작업의 경우 JobParameters.getStopReason() 호출).
앱의 상태가 사용할 수 있는 리소스에 미치는 영향에 관한 자세한 내용은 전원 관리 리소스 제한을 참고하세요. 배터리 최적화 권장사항에 관한 자세한 내용은 작업 예약 API의 배터리 사용 최적화에 관한 안내를 참고하세요.
또한 Android 16에 도입된 새로운 JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API를 활용하여 작업이 실행되지 않은 이유를 파악하는 것이 좋습니다.
테스트
앱의 동작을 테스트하려면 앱이 Android 16 기기에서 실행되는 동안 특정 작업 할당량 최적화의 재정의를 사용 설정하면 됩니다.
'최상위 상태가 작업 런타임 할당량을 준수함'의 시행을 사용 중지하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행합니다.
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
'포그라운드 서비스와 동시에 실행되는 작업은 작업 런타임 할당량을 준수합니다'의 적용을 사용 중지하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 실행하세요.
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
특정 앱 대기 버킷 동작을 테스트하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 사용하여 앱의 앱 대기 버킷을 설정하면 됩니다.
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
앱이 속한 앱 대기 버킷을 확인하려면 다음 adb 명령어를 사용하여 앱의 앱 대기 버킷을 가져오면 됩니다.
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
비어 있는 작업 중지 이유가 삭제됨
포기된 작업은 작업과 연결된 JobParameters 객체가 가비지 컬렉션되었지만 JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean)가 호출되어 작업 완료를 알리지 않은 경우에 발생합니다. 이는 앱의 인식 없이 작업이 실행되고 재예약되고 있음을 나타냅니다.
JobScheduler를 사용하는 앱은 JobParameters 객체에 대한 강력한 참조를 유지하지 않으며 이제 제한 시간에 STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT 대신 새 작업 중지 이유 STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED가 부여됩니다.
새 중단된 중지 이유가 자주 발생하면 시스템은 작업 빈도를 줄이기 위한 완화 조치를 취합니다.
앱은 새 중지 이유를 사용하여 중단된 작업을 감지하고 줄여야 합니다.
WorkManager, AsyncTask 또는 DownloadManager를 사용하는 경우 이러한 API가 앱을 대신하여 작업 수명 주기를 관리하므로 영향을 받지 않습니다.
JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground 완전히 지원 중단
JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) 메서드는 예약 앱이 포그라운드에 있거나 일시적으로 백그라운드 제한사항에서 제외된 경우 작업의 중요도를 나타냅니다.
이 메서드는 Android 12 (API 수준 31)부터 지원 중단되었습니다. Android 16부터는 더 이상 효과적으로 작동하지 않으며 이 메서드를 호출해도 무시됩니다.
이 기능 삭제는 JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground()에도 적용됩니다. Android 16부터 메서드가 호출되면 메서드는 false를 반환합니다.
순서가 지정된 브로드캐스트 우선순위 범위가 더 이상 전역이 아님
Android 앱은 broadcast receiver의 우선순위를 정의하여 수신기가 브로드캐스트를 수신하고 처리하는 순서를 제어할 수 있습니다. 매니페스트 선언 수신기의 경우 앱은 android:priority 속성을 사용하여 우선순위를 정의할 수 있고 컨텍스트 등록 수신기의 경우 앱은 IntentFilter#setPriority() API를 사용하여 우선순위를 정의할 수 있습니다. 브로드캐스트가 전송되면 시스템은 우선순위 순으로(최상위부터 최하위 순으로) 수신기에 브로드캐스트를 전달합니다.
Android 16에서는 여러 프로세스에서 android:priority 속성 또는 IntentFilter#setPriority()를 사용하는 브로드캐스트 전송 순서가 보장되지 않습니다. 브로드캐스트 우선순위는 모든 프로세스 전반이 아닌 동일한 애플리케이션 프로세스 내에서만 적용됩니다.
또한 브로드캐스트 우선순위는 (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1) 범위로 자동으로 제한됩니다. 시스템 구성요소만 SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY를 브로드캐스트 우선순위로 설정할 수 있습니다.
앱이 다음 중 하나를 실행하는 경우 영향을 받을 수 있습니다.
- 애플리케이션이 동일한 브로드캐스트 인텐트로 여러 프로세스를 선언했으며 우선순위에 따라 이러한 인텐트를 특정 순서로 수신할 것으로 예상합니다.
- 애플리케이션 프로세스는 다른 프로세스와 상호작용하며 특정 순서로 브로드캐스트 인텐트를 수신하는 것에 관한 기대치를 갖습니다.
프로세스가 서로 조정해야 하는 경우 다른 조정 채널을 사용하여 통신해야 합니다.
ART 내부 변경사항
Android 16에는 Android 런타임 (ART)의 성능을 개선하고 추가 Java 기능을 지원하는 Android 런타임 (ART)의 최신 업데이트가 포함되어 있습니다. Google Play 시스템 업데이트를 통해 Android 12 (API 수준 31) 및 이후 버전을 실행하는 10억 대 이상의 기기에서도 이러한 개선사항을 사용할 수 있습니다.
이러한 변경사항이 출시되면 ART의 내부 구조를 사용하는 라이브러리와 앱 코드가 Android 16을 실행하는 기기와 Google Play 시스템 업데이트를 통해 ART 모듈을 업데이트하는 이전 Android 버전에서 제대로 작동하지 않을 수 있습니다.
내부 구조 (예: SDK 이외의 인터페이스)를 사용하면 항상 호환성 문제가 발생할 수 있지만, 내부 ART 구조를 활용하는 코드 (또는 코드가 포함된 라이브러리)를 사용하지 않는 것이 특히 중요합니다. ART 변경사항은 기기가 실행 중인 플랫폼 버전과 연결되지 않으며 Google Play 시스템 업데이트를 통해 10억 대 이상의 기기에 전송되기 때문입니다.
모든 개발자는 Android 16에서 앱을 철저히 테스트하여 앱이 영향을 받는지 확인해야 합니다. 또한 알려진 문제에서 앱이 내부 ART 구조를 사용하는 것으로 확인된 라이브러리에 종속되어 있는지 확인하세요. 영향을 받는 앱 코드 또는 라이브러리 종속 항목이 있는 경우 가능하면 공개 API 대안을 찾고 Issue Tracker에서 기능 요청을 생성하여 새로운 사용 사례에 사용할 공개 API를 요청하세요.
16KB 페이지 크기 호환성 모드
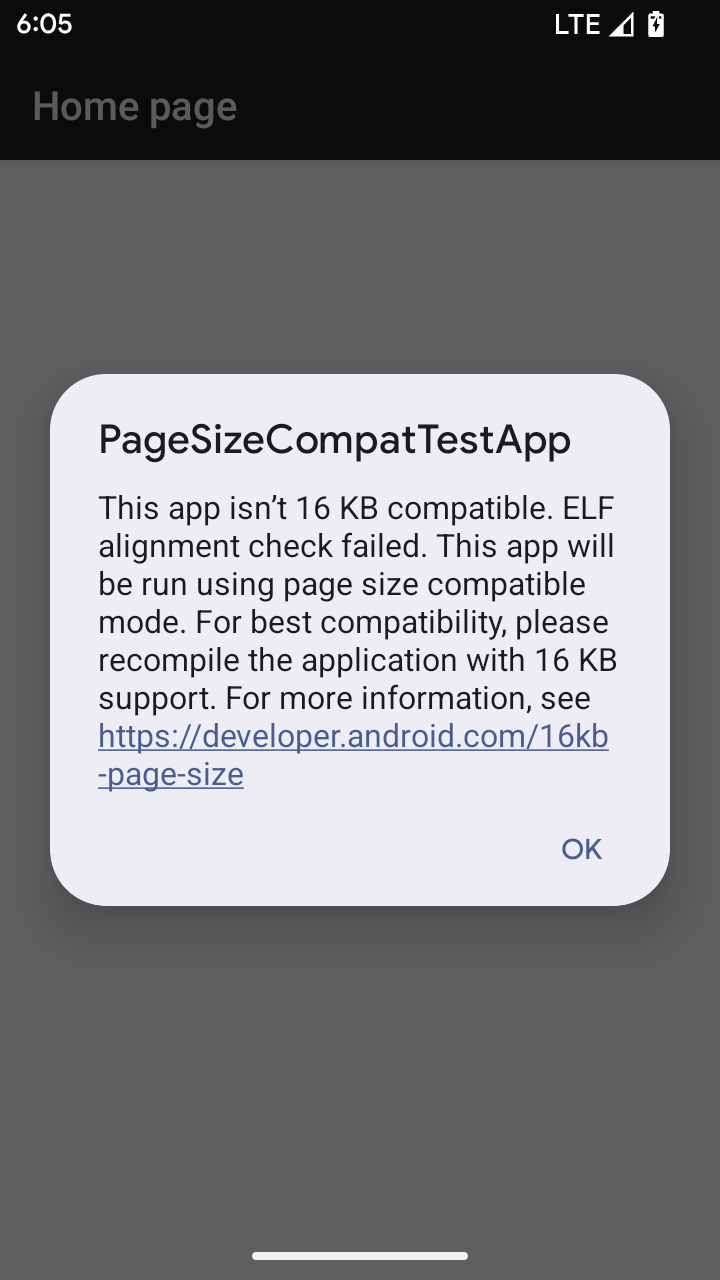
Android 15에서는 플랫폼의 성능을 최적화하기 위해 16KB 메모리 페이지 지원을 도입했습니다. Android 16에서는 4KB 메모리 페이지용으로 빌드된 일부 앱이 16KB 메모리 페이지용으로 구성된 기기에서 실행될 수 있도록 하는 호환성 모드를 추가합니다.
앱이 Android 16 이상을 실행하는 기기에서 실행 중일 때 Android에서 앱에 4KB 정렬 메모리 페이지가 있음을 감지하면 자동으로 호환성 모드를 사용하고 사용자에게 알림 대화상자를 표시합니다. AndroidManifest.xml에서 android:pageSizeCompat 속성을 설정하여 이전 버전과의 호환성 모드를 사용 설정하면 앱이 실행될 때 대화상자가 표시되지 않습니다. android:pageSizeCompat 속성을 사용하려면 Android 16 SDK를 사용하여 앱을 컴파일하세요.
최상의 성능, 안정성, 안정성을 위해 앱은 계속 16KB 정렬되어야 합니다. 16KB 메모리 페이지를 지원하도록 앱을 업데이트하는 방법에 관한 최근 블로그 게시물을 참고하세요.
사용자 경험 및 시스템 UI
Android 16 (API 수준 36)에는 더 일관되고 직관적인 사용자 환경을 만들기 위한 다음 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
방해가 되는 접근성 안내 지원 중단
Android 16에서는 announceForAccessibility 사용 또는 TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT 접근성 이벤트 전송으로 특징되는 접근성 공지사항을 지원 중단합니다. 이로 인해 TalkBack 및 Android의 스크린 리더 사용자에게 일관되지 않은 사용자 환경이 발생할 수 있으며, 대안은 다양한 Android의 보조 기술에서 더 광범위한 사용자 요구사항을 충족합니다.
대안의 예:
- 창 변경과 같은 중요한 UI 변경의 경우
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)및setAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)를 사용하세요. Compose에서Modifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" }를 사용합니다. - 중요한 UI 변경사항을 사용자에게 알리려면
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)를 사용하세요. Compose에서는Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}를 사용합니다 . 뷰가 업데이트될 때마다 공지사항이 생성될 수 있으므로 이러한 공지사항은 가급적 사용하지 않는 것이 좋습니다. - 사용자에게 오류를 알리려면
AccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERROR유형의AccessibilityEvent를 전송하고AccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)를 설정하거나TextView#setError(CharSequence)를 사용하세요.
지원 중단된 announceForAccessibility API의 참조 문서에는 추천 대안에 관한 자세한 내용이 포함되어 있습니다.
3버튼 탐색 지원
Android 16에서는 뒤로 탐색 예측으로 적절하게 이전한 앱의 3버튼 탐색에 뒤로 탐색 예측을 지원합니다. 뒤로 버튼을 길게 누르면 뒤로 탐색 예측 애니메이션이 시작되어 뒤로 스와이프하면 이동할 위치를 미리 볼 수 있습니다.
이 동작은 시스템 애니메이션 (홈으로 돌아가기, 교차 작업, 교차 활동)을 비롯하여 뒤로 탐색 예측 애니메이션을 지원하는 시스템의 모든 영역에 적용됩니다.
자동 테마 앱 아이콘
Android 16 QPR 2부터 Android는 앱 아이콘에 테마를 자동으로 적용하여 일관된 홈 화면 환경을 만듭니다. 이는 앱에서 자체 테마 앱 아이콘을 제공하지 않는 경우 발생합니다. 앱은 적응형 아이콘 내에 단색 레이어를 포함하고 Android 스튜디오에서 앱 아이콘이 어떻게 표시되는지 미리 봄으로써 테마가 적용된 앱 아이콘의 디자인을 제어할 수 있습니다.
기기 폼 팩터
Android 16 (API 수준 36)에는 가상 기기 소유자가 디스플레이에 투영할 때 앱에 적용되는 다음과 같은 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
가상 기기 소유자 재정의
가상 기기 소유자는 가상 기기를 만들고 관리하는 신뢰할 수 있는 앱 또는 권한이 있는 앱입니다. 가상 기기 소유자는 가상 기기에서 앱을 실행한 다음 개인용 컴퓨터, 가상 현실 기기, 자동차 인포테인먼트 시스템과 같은 원격 기기의 디스플레이에 앱을 투영합니다. 가상 기기 소유자는 휴대전화와 같은 로컬 기기에 있습니다.
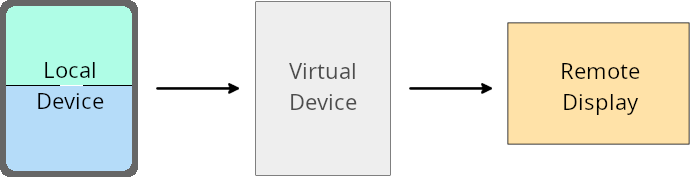
앱별 재정의
Android 16 (API 레벨 36)을 실행하는 기기에서 가상 기기 소유자는 가상 기기 소유자가 관리하는 일부 가상 기기의 앱 설정을 재정의할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 앱 레이아웃을 개선하기 위해 가상 기기 소유자는 앱을 외부 디스플레이에 투영할 때 방향, 가로세로 비율, 크기 조절 제한을 무시할 수 있습니다.
일반적인 주요 변경사항
Android 16 동작은 자동차 디스플레이나 Chromebook과 같은 대형 화면 폼 팩터의 앱 UI에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다. 특히 세로 방향의 소형 디스플레이용으로 설계된 레이아웃의 경우 더욱 그렇습니다. 모든 기기 폼 팩터에 맞게 앱을 적응형으로 만드는 방법을 알아보려면 적응형 레이아웃 정보를 참고하세요.
참조
보안
Android 16 (API 수준 36)에는 악성 앱으로부터 앱과 사용자를 보호하는 데 도움이 되는 시스템 보안을 촉진하는 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
인텐트 리디렉션 공격에 대한 보안 개선
Android 16은 일반적인 Intent 리디렉션 공격에 대한 기본 보안을 제공하며, 최소한의 호환성과 개발자 변경사항이 필요합니다.
Intent 리디렉션 악용에 기본적으로 보안 강화 솔루션을 도입합니다. 대부분의 경우 인텐트를 사용하는 앱에는 호환성 문제가 발생하지 않습니다. Google에서는 개발 프로세스 전반에 걸쳐 측정항목을 수집하여 중단이 발생할 수 있는 앱을 모니터링했습니다.
Android의 인텐트 리디렉션은 공격자가 취약한 앱의 컨텍스트에서 새 구성요소를 실행하는 데 사용되는 인텐트의 콘텐츠를 부분적으로 또는 완전히 제어할 수 있는 반면 피해자 앱은 ("최상위") 인텐트의 extras 필드에서 신뢰할 수 없는 하위 수준 인텐트를 실행할 때 발생합니다. 이로 인해 공격자 앱이 피해자 앱의 컨텍스트에서 비공개 구성요소를 실행하거나, 권한이 있는 작업을 트리거하거나, 민감한 데이터에 대한 URI 액세스 권한을 획득하여 데이터 도용 및 임의의 코드 실행으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
인텐트 리디렉션 처리 선택 해제
Android 16에서는 앱이 실행 보안 보호를 선택 해제할 수 있는 새로운 API를 도입합니다. 기본 보안 동작이 합법적인 앱 사용 사례를 방해하는 특정 경우에는 필요할 수 있습니다.
Android 16 (API 수준 36) SDK 이상을 기준으로 컴파일하는 애플리케이션
Intent 객체에서 removeLaunchSecurityProtection() 메서드를 직접 사용할 수 있습니다.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
Android 15 (API 수준 35) 이하를 기준으로 컴파일하는 애플리케이션
권장되지는 않지만 리플렉션을 사용하여 removeLaunchSecurityProtection() 메서드에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
호환 앱에 더 이상 검색 시간 제한 알림이 전송되지 않음
Android 16에서는 악성 앱으로부터 사용자의 위치 개인 정보를 보호하기 위해 컴패니언 기기 페어링 흐름 중에 새로운 동작을 도입합니다. Android 16에서 실행되는 모든 호환 앱은 더 이상 RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT를 사용하여 검색 시간 초과에 관해 직접 알림을 받지 않습니다. 대신 사용자에게 시각적 대화상자를 통해 시간 초과 이벤트가 알림으로 전송됩니다. 사용자가 대화상자를 닫으면 앱에 RESULT_USER_REJECTED와의 연결 실패에 관한 알림이 전송됩니다.
검색 시간도 원래 20초에서 연장되었으며, 검색 중 언제든지 사용자가 기기 검색을 중지할 수 있습니다. 검색을 시작한 후 처음 20초 이내에 기기가 하나 이상 감지되면 CDM은 추가 기기 검색을 중지합니다.
연결
Android 16 (API 수준 36)에는 주변기기와의 연결을 개선하기 위해 블루투스 스택에 다음과 같은 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
결합 손실 처리 개선
Android 16부터 원격 결합 손실이 감지될 때 보안 및 사용자 환경을 개선하기 위해 블루투스 스택이 업데이트되었습니다. 이전에는 시스템이 자동으로 결합을 삭제하고 새 페어링 프로세스를 시작하여 의도치 않은 재페어링이 발생할 수 있었습니다. 앱이 결합 해제 이벤트를 일관된 방식으로 처리하지 않는 경우가 많았습니다.
환경을 통합하기 위해 Android 16에서는 시스템에 대한 결합 손실 처리를 개선했습니다. 이전에 페어링된 블루투스 기기를 다시 연결할 때 인증할 수 없는 경우 시스템은 링크를 연결 해제하고 로컬 페어링 정보를 유지하며 사용자에게 페어링 손실에 관해 알리고 다시 페어링하도록 안내하는 시스템 대화상자를 표시합니다.
