แพลตฟอร์ม Android 16 มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่อาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานต่อไปนี้มีผลกับแอปทั้งหมดเมื่อทำงานบน Android 16 โดยไม่คำนึงถึง targetSdkVersion คุณควรทดสอบแอปแล้วแก้ไขแอปตามที่จำเป็นเพื่อรองรับการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ (หากมี)
โปรดตรวจสอบรายการการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานที่ส่งผลต่อแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 16 เท่านั้นด้วย
ฟังก์ชันหลัก
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งแก้ไขหรือขยายความสามารถหลักต่างๆ ของระบบ Android
การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพโควต้า JobScheduler
Starting in Android 16, we're adjusting regular and expedited job execution runtime quota based on the following factors:
- Which app standby bucket the application is in: in Android 16, active standby buckets will start being enforced by a generous runtime quota.
- If the job starts execution while the app is in a top state: in Android 16, Jobs started while the app is visible to the user and continues after the app becomes invisible, will adhere to the job runtime quota.
- If the job is executing while running a Foreground Service: in Android 16, jobs that are executing while concurrently with a foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota. If you're leveraging jobs for user initiated data transfer, consider using user initiated data transfer jobs instead.
This change impacts tasks scheduled using WorkManager, JobScheduler, and
DownloadManager. To debug why a job was stopped, we recommend logging why your
job was stopped by calling WorkInfo.getStopReason() (for
JobScheduler jobs, call JobParameters.getStopReason()).
For information about how your app's state affects the resources it can use, see Power management resource limits. For more information on battery-optimal best practices, refer to guidance on optimize battery use for task scheduling APIs.
We also recommend leveraging the new
JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API introduced in
Android 16 to understand why a job has not executed.
Testing
To test your app's behavior, you can enable override of certain job quota optimizations as long as the app is running on an Android 16 device.
To disable enforcement of "top state will adhere to job runtime quota", run the
following adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To disable enforcement of "jobs that are executing while concurrently with a
foreground service will adhere to the job runtime quota", run the following
adb command:
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
To test certain app standby bucket behavior, you can set the app standby bucket
of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
To understand the app standby bucket your app is in, you can get the app standby
bucket of your app using the following adb command:
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
เหตุผลที่หยุดงานว่างเปล่าที่หยุดทำงาน
งานที่ถูกทิ้งจะเกิดขึ้นเมื่อมีการรวบรวมขยะจากออบเจ็กต์ JobParameters ที่เชื่อมโยงกับงาน แต่ไม่มีการเรียกใช้ JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) เพื่อส่งสัญญาณว่างานเสร็จสมบูรณ์ ซึ่งหมายความว่างานอาจกำลังทำงานและกำลังกำหนดเวลาใหม่โดยที่แอปไม่รู้
แอปที่อาศัย JobScheduler จะไม่เก็บการอ้างอิงแบบ Strong กับออบเจ็กต์ JobParameters และตอนนี้การหมดเวลาจะได้รับเหตุผลใหม่ในการหยุดงาน STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED แทน STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT
หากมีสาเหตุใหม่ของการหยุดกลางคันเกิดขึ้นบ่อยครั้ง ระบบจะดำเนินการตามขั้นตอนเพื่อลดความถี่ของงาน
แอปควรใช้เหตุผลในการหยุดใหม่เพื่อตรวจหาและลดงานที่หยุดกลางคัน
หากคุณใช้ WorkManager, AsyncTask หรือ DownloadManager คุณจะได้รับผลกระทบเนื่องจาก API เหล่านี้จัดการวงจรงานในนามของแอป
เลิกใช้งาน JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground อย่างสมบูรณ์
วิธีการ JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) จะระบุความสำคัญของงานขณะที่แอปกำหนดเวลาอยู่เบื้องหน้าหรือเมื่อได้รับการยกเว้นจากข้อจำกัดของเบื้องหลังชั่วคราว
เราเลิกใช้งานเมธอดนี้ตั้งแต่ Android 12 (API ระดับ 31) ตั้งแต่ Android 16 เป็นต้นไป วิธีการนี้จะใช้งานไม่ได้อีกต่อไป และระบบจะไม่สนใจการเรียกใช้เมธอดนี้
การนําฟังก์ชันการทำงานนี้ออกจะมีผลกับJobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground() ด้วย ตั้งแต่ Android 16 เป็นต้นไป หากมีการเรียกใช้เมธอด เมธอดจะแสดงผลลัพธ์เป็น false
ขอบเขตลําดับความสําคัญของประกาศตามลําดับไม่ได้เป็นแบบทั่วโลกอีกต่อไป
แอป Android ได้รับอนุญาตให้กำหนดลำดับความสำคัญในเครื่องรับการออกอากาศเพื่อควบคุมลำดับที่เครื่องรับจะรับและประมวลผลการออกอากาศ สําหรับตัวรับที่ประกาศในไฟล์ Manifest แอปสามารถใช้แอตทริบิวต์ android:priority เพื่อกําหนดลําดับความสําคัญ และสำหรับตัวรับที่ลงทะเบียนตามบริบท แอปสามารถใช้ IntentFilter#setPriority() API เพื่อกําหนดลําดับความสําคัญ เมื่อส่งการออกอากาศ ระบบจะส่งการออกอากาศไปยังผู้รับตามลําดับความสําคัญจากสูงไปต่ำ
ใน Android 16 ระบบจะไม่รับประกันลำดับการนำส่งแบบออกอากาศที่ใช้แอตทริบิวต์ android:priority หรือ IntentFilter#setPriority() ในกระบวนการต่างๆ ระบบจะพิจารณาลำดับความสำคัญของการออกอากาศภายในกระบวนการสมัครเดียวกันเท่านั้น ไม่ใช่ในทุกกระบวนการ
นอกจากนี้ ระบบจะจำกัดลําดับความสําคัญของรายการออกอากาศให้อยู่ในช่วง (SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1) โดยอัตโนมัติ เฉพาะคอมโพเนนต์ของระบบเท่านั้นที่จะได้รับอนุญาตให้ตั้งค่า SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY เป็นลำดับความสำคัญของการออกอากาศ
แอปของคุณอาจได้รับผลกระทบหากมีลักษณะการทำงานอย่างใดอย่างหนึ่งต่อไปนี้
- แอปพลิเคชันของคุณประกาศกระบวนการหลายรายการที่มี Intent การออกอากาศเดียวกัน และคาดหวังที่จะได้รับการส่ง Intent เหล่านั้นตามลำดับที่แน่นอนโดยอิงตามลําดับความสําคัญ
- กระบวนการสมัครของคุณจะโต้ตอบกับกระบวนการอื่นๆ และมีสิ่งที่คาดหวังเกี่ยวกับการรับ Intent การออกอากาศตามลําดับที่กําหนด
หากกระบวนการต่างๆ จำเป็นต้องประสานงานกัน ทีมควรสื่อสารโดยใช้ช่องทางประสานงานอื่นๆ
การเปลี่ยนแปลงภายในของ ART
Android 16 includes the latest updates to the Android Runtime (ART) that improve the Android Runtime's (ART's) performance and provide support for additional Java features. Through Google Play System updates, these improvements are also available to over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher.
As these changes are released, libraries and app code that rely on internal structures of ART might not work correctly on devices running Android 16, along with earlier Android versions that update the ART module through Google Play system updates.
Relying on internal structures (such as non-SDK interfaces) can always lead to compatibility problems, but it's particularly important to avoid relying on code (or libraries containing code) that leverages internal ART structures, since ART changes aren't tied to the platform version the device is running on and they go out to over a billion devices through Google Play system updates.
All developers should check whether their app is impacted by testing their apps thoroughly on Android 16. In addition, check the known issues to see if your app depends on any libraries that we've identified that rely on internal ART structures. If you do have app code or library dependencies that are affected, seek public API alternatives whenever possible and request public APIs for new use cases by creating a feature request in our issue tracker.
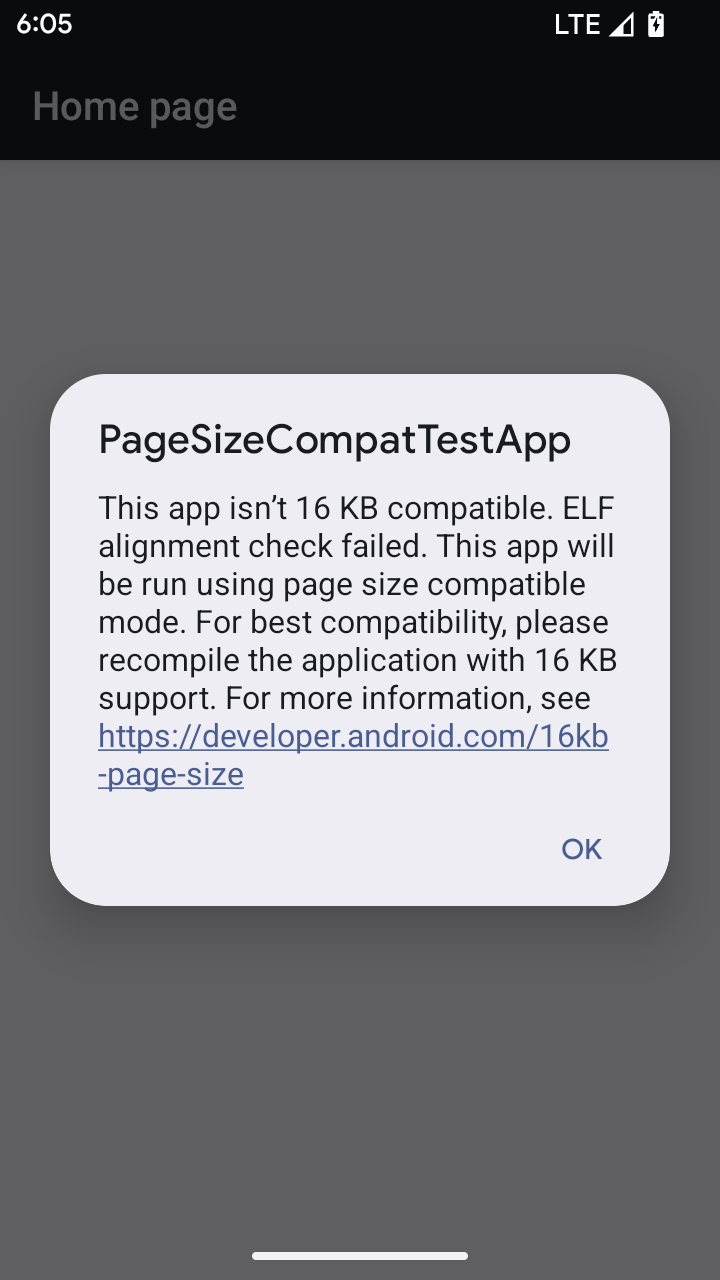
โหมดความเข้ากันได้กับขนาดหน้า 16 KB
Android 15 introduced support for 16 KB memory pages to optimize performance of the platform. Android 16 adds a compatibility mode, allowing some apps built for 4 KB memory pages to run on a device configured for 16 KB memory pages.
When your app is running on a device with Android 16 or higher, if Android
detects that your app has 4 KB aligned memory pages, it automatically uses
compatibility mode and display a notification dialog to the user. Setting the
android:pageSizeCompat property in the AndroidManifest.xml to enable the
backwards compatibility mode will prevent the display of the dialog when your
app launches. To use the android:pageSizeCompat property, compile your app
using the Android 16 SDK.
For best performance, reliability, and stability, your app should still be 16 KB aligned. Check out our recent blog post on updating your apps to support 16 KB memory pages for more details.
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ซึ่งมีจุดประสงค์เพื่อมอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่สม่ำเสมอและใช้งานง่ายยิ่งขึ้นแก่ผู้ใช้
การเลิกใช้งานการประกาศการช่วยเหลือพิเศษที่รบกวน
Android 16 deprecates accessibility announcements, characterized by the use of
announceForAccessibility or the dispatch of
TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT accessibility events. These can create
inconsistent user experiences for users of TalkBack and Android's screen reader,
and alternatives better serve a broader range of user needs across a variety of
Android's assistive technologies.
Examples of alternatives:
- For significant UI changes like window changes, use
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)andsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence). In Compose, useModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" } - To inform the user of changes to critical UI, use
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int). In Compose, useModifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}. These should be used sparingly as they may generate announcements every time a View is updated. - To notify users about errors, send an
AccessibilityEventof typeAccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORand setAccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence), or useTextView#setError(CharSequence).
The reference documentation for the deprecated
announceForAccessibility API includes more details about
suggested alternatives.
การรองรับการไปยังส่วนต่างๆ แบบ 3 ปุ่ม
Android 16 รองรับการกดย้อนกลับแบบคาดการณ์ในการนําทางด้วยปุ่ม 3 ปุ่มสําหรับแอปที่ย้ายข้อมูลไปยังการกดย้อนกลับแบบคาดการณ์อย่างถูกต้อง การกดปุ่มย้อนกลับค้างไว้จะเป็นการเริ่มภาพเคลื่อนไหวย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดา ซึ่งจะแสดงตัวอย่างตำแหน่งที่คุณจะไปเมื่อปัดกลับ
ลักษณะการทำงานนี้มีผลกับทุกส่วนของระบบที่รองรับภาพเคลื่อนไหวแบบคาดเดาของการย้อนกลับ รวมถึงภาพเคลื่อนไหวของระบบ (การย้อนกลับไปยังหน้าจอหลัก การข้ามงาน และการทำงานข้ามแอป)
รูปแบบของอุปกรณ์
Android 16 (ระดับ API 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้สำหรับแอปเมื่อเจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือนฉายภาพไปยังจอแสดงผล
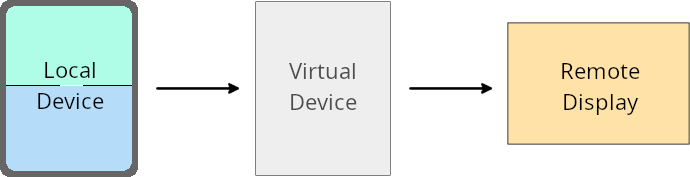
การลบล้างของเจ้าของอุปกรณ์เสมือนจริง
A virtual device owner is a trusted or privileged app that creates and manages a virtual device. Virtual device owners run apps on a virtual device and then project the apps to the display of a remote device, such as a personal computer, virtual reality device, or car infotainment system. The virtual device owner is on a local device, such as a mobile phone.
Per-app overrides
On devices running Android 16 (API level 36), virtual device owners can override app settings on select virtual devices that the virtual device owners manage. For example, to improve app layout, a virtual device owner can ignore orientation, aspect ratio, and resizability restrictions when projecting apps onto an external display.
Common breaking changes
The Android 16 behavior might impact your app's UI on large screen form factors such as car displays or Chromebooks, especially layouts that were designed for small displays in portrait orientation. To learn how to make your app adaptive for all device form factors, see About adaptive layouts.
References
ความปลอดภัย
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงที่ส่งเสริมความปลอดภัยของระบบเพื่อช่วยปกป้องแอปและผู้ใช้จากแอปที่เป็นอันตราย
ปรับปรุงความปลอดภัยเพื่อป้องกันการโจมตีด้วยการเปลี่ยนเส้นทาง Intent
Android 16 provides default security against general Intent redirection
attacks, with minimum compatibility and developer changes required.
We are introducing by-default security hardening solutions to Intent
redirection exploits. In most cases, apps that use intents normally won't
experience any compatibility issues; we've gathered metrics throughout our
development process to monitor which apps might experience breakages.
Intent redirection in Android occurs when an attacker can partly or fully control the contents of an intent used to launch a new component in the context of a vulnerable app, while the victim app launches an untrusted sub-level intent in an extras field of an ("top-level") Intent. This can lead to the attacker app launching private components in the context of the victim app, triggering privileged actions, or gaining URI access to sensitive data, potentially leading to data theft and arbitrary code execution.
Opt out of Intent redirection handling
Android 16 introduces a new API that allows apps to opt out of launch security protections. This might be necessary in specific cases where the default security behavior interferes with legitimate app use cases.
For applications compiling against Android 16 (API level 36) SDK or higher
You can directly use the removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method on the Intent
object.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
For applications compiling against Android 15 (API level 35) or lower
While not recommended, you can use reflection to access the
removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
แอปที่ใช้ร่วมกันจะไม่ได้รับการแจ้งเตือนเกี่ยวกับการหมดเวลาการค้นหาอีกต่อไป
Android 16 introduces a new behavior during
companion device pairing flow to protect the user's location
privacy from malicious apps. All companion apps running on Android 16 are no
longer directly notified of discovery timeout using
RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. Instead, the user is
notified of timeout events with a visual dialog. When the user dismisses
the dialog, the app is alerted of the association failure with
RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
The search duration has also been extended from the original 20 seconds, and the device discovery can be stopped by the user at any point during the search. If at least one device was discovered within the first 20 seconds of starting the search, the CDM stops searching for additional devices.
การเชื่อมต่อ
Android 16 (API ระดับ 36) มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงต่อไปนี้ในสแต็กบลูทูธเพื่อปรับปรุงการเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ต่อพ่วง
การจัดการการสูญเสียพันธบัตรที่ดีขึ้น
Starting in Android 16, the Bluetooth stack has been updated to improve security and user experience when a remote bond loss is detected. Previously, the system would automatically remove the bond and initiate a new pairing process, which could lead to unintentional re-pairing. We have seen in many instances apps not taking care of the bond loss event in a consistent way.
To unify the experience, Android 16 improved the bond loss handling to the system. If a previously bonded Bluetooth device could not be authenticated upon reconnection, the system will disconnect the link, retain local bond information, and display a system dialog informing users of the bond loss and directing them to re-pair.

