Android 16 プラットフォームには、アプリに影響する可能性がある動作変更が含まれています。下記の動作変更は、targetSdkVersion に関係なく、Android 16 上で稼働するすべてのアプリに適用されます。該当する場合は、アプリをテストし、必要に応じて修正して、これらの変更に対応する必要があります。
Android 16 をターゲットとするアプリにのみ影響する動作変更のリストも必ずご確認ください。
コア機能
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、Android システムのさまざまなコア機能を変更または拡張する以下の変更が含まれています。
JobScheduler の割り当ての最適化
Android 16 以降では、次の要素に基づいて、通常のジョブと迅速なジョブの実行ランタイム割り当てを調整しています。
- アプリケーションが属するアプリ スタンバイ バケット: Android 16 では、アクティブなスタンバイ バケットは、十分なランタイム割り当てによって適用されるようになります。
- アプリが最上位の状態のときにジョブの実行が開始された場合: Android 16 では、アプリがユーザーに表示されている間に開始され、アプリが非表示になった後も継続されるジョブは、ジョブの実行時間割り当てに準拠します。
- フォアグラウンド サービスの実行中にジョブが実行されている場合: Android 16 では、フォアグラウンド サービスと同時に実行されているジョブは、ジョブの実行時間割り当てに準拠します。ジョブをユーザー開始型データ転送に活用している場合は、代わりにユーザー開始型データ転送ジョブの使用を検討してください。
この変更は、WorkManager、JobScheduler、DownloadManager を使用してスケジュール設定されたタスクに影響します。ジョブが停止した理由をデバッグするには、WorkInfo.getStopReason() を呼び出してジョブが停止した理由をロギングすることをおすすめします(JobScheduler ジョブの場合は JobParameters.getStopReason() を呼び出します)。
アプリの状態が使用できるリソースに与える影響については、電源管理のリソース制限をご覧ください。バッテリーを最適化するためのベスト プラクティスについて詳しくは、タスク スケジューリング API のバッテリー使用量を最適化するをご覧ください。
また、Android 16 で導入された新しい JobScheduler#getPendingJobReasonsHistory API を活用して、ジョブが実行されなかった理由を把握することをおすすめします。
テスト
アプリの動作をテストするには、アプリが Android 16 デバイスで実行されている場合に限り、特定のジョブ割り当ての最適化のオーバーライドを有効にできます。
「トップ状態はジョブ ランタイム割り当てに準拠する」の適用を無効にするには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_TOP_STARTED_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
「フォアグラウンド サービスと同時に実行されるジョブはジョブ ランタイム割り当てに準拠する」の適用を無効にするには、次の adb コマンドを実行します。
adb shell am compat enable OVERRIDE_QUOTA_ENFORCEMENT_TO_FGS_JOBS APP_PACKAGE_NAME
特定のアプリ スタンバイ バケットの動作をテストするには、次の adb コマンドを使用してアプリのアプリ スタンバイ バケットを設定します。
adb shell am set-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME active|working_set|frequent|rare|restricted
アプリが属するアプリ スタンバイ バケットを把握するには、次の adb コマンドを使用して、アプリのアプリ スタンバイ バケットを取得します。
adb shell am get-standby-bucket APP_PACKAGE_NAME
空のジョブが破棄された停止理由
An abandoned job occurs when the JobParameters object associated with the job
has been garbage collected, but JobService#jobFinished(JobParameters,
boolean) has not been called to signal job completion. This indicates that
the job may be running and being rescheduled without the app's awareness.
Apps that rely on JobScheduler, don't maintain a strong reference to the
JobParameters object, and timeout will now be granted the new job stop reason
STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT_ABANDONED, instead of STOP_REASON_TIMEOUT.
If there are frequent occurrences of the new abandoned stop reason, the system will take mitigation steps to reduce job frequency.
Apps should use the new stop reason to detect and reduce abandoned jobs.
If you're using WorkManager, AsyncTask, or DownloadManager, you aren't impacted because these APIs manage the job lifecycle on your app's behalf.
JobInfo#setImportantWhileForeground のサポートを完全に終了
JobInfo.Builder#setImportantWhileForeground(boolean) メソッドは、スケジュール設定アプリがフォアグラウンドにある間、またはバックグラウンドの制限を一時的に免除されている間のジョブの重要度を示します。
このメソッドは、Android 12(API レベル 31)で非推奨になりました。Android 16 以降では、このメソッドは効果的に機能しなくなり、このメソッドの呼び出しは無視されます。
この機能の削除は JobInfo#isImportantWhileForeground() にも適用されます。Android 16 以降では、メソッドが呼び出されると、メソッドは false を返します。
順序付きブロードキャストの優先度のスコープがグローバルではなくなった
Android apps are allowed to define priorities on broadcast receivers to control
the order in which the receivers receive and process the broadcast. For
manifest-declared receivers, apps can use the
android:priority attribute to define the priority and for
context-registered receivers, apps can use the
IntentFilter#setPriority() API to define the priority. When
a broadcast is sent, the system delivers it to receivers in order of their
priority, from highest to lowest.
In Android 16, broadcast delivery order using the android:priority attribute
or IntentFilter#setPriority() across different processes will not be
guaranteed. Broadcast priorities will only be respected within the same
application process rather than across all processes.
Also, broadcast priorities will be automatically confined to the range
(SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY + 1,
SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY - 1). Only system components will be
allowed to set SYSTEM_LOW_PRIORITY, SYSTEM_HIGH_PRIORITY as broadcast
priority.
Your app might be impacted if it does either of the following:
- Your application has declared multiple processes with the same broadcast intent, and has expectations around receiving those intents in a certain order based on the priority.
- Your application process interacts with other processes and has expectations around receiving a broadcast intent in a certain order.
If the processes need to coordinate with each other, they should communicate using other coordination channels.
ART の内部変更
Android 16 includes the latest updates to the Android Runtime (ART) that improve the Android Runtime's (ART's) performance and provide support for additional Java features. Through Google Play System updates, these improvements are also available to over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher.
As these changes are released, libraries and app code that rely on internal structures of ART might not work correctly on devices running Android 16, along with earlier Android versions that update the ART module through Google Play system updates.
Relying on internal structures (such as non-SDK interfaces) can always lead to compatibility problems, but it's particularly important to avoid relying on code (or libraries containing code) that leverages internal ART structures, since ART changes aren't tied to the platform version the device is running on and they go out to over a billion devices through Google Play system updates.
All developers should check whether their app is impacted by testing their apps thoroughly on Android 16. In addition, check the known issues to see if your app depends on any libraries that we've identified that rely on internal ART structures. If you do have app code or library dependencies that are affected, seek public API alternatives whenever possible and request public APIs for new use cases by creating a feature request in our issue tracker.
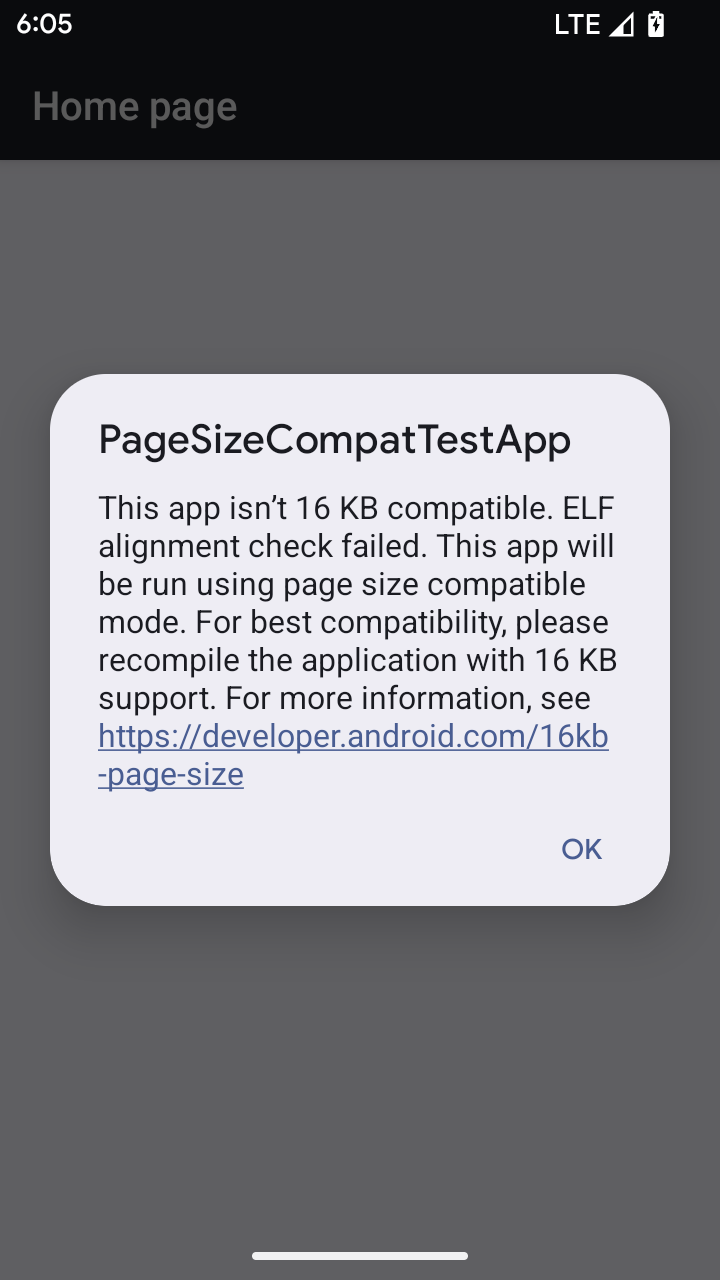
16 KB ページサイズの互換モード
Android 15 introduced support for 16 KB memory pages to optimize performance of the platform. Android 16 adds a compatibility mode, allowing some apps built for 4 KB memory pages to run on a device configured for 16 KB memory pages.
When your app is running on a device with Android 16 or higher, if Android
detects that your app has 4 KB aligned memory pages, it automatically uses
compatibility mode and display a notification dialog to the user. Setting the
android:pageSizeCompat property in the AndroidManifest.xml to enable the
backwards compatibility mode will prevent the display of the dialog when your
app launches. To use the android:pageSizeCompat property, compile your app
using the Android 16 SDK.
For best performance, reliability, and stability, your app should still be 16 KB aligned. Check out our recent blog post on updating your apps to support 16 KB memory pages for more details.
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、より一貫性のある直感的なユーザー エクスペリエンスを実現するための以下の変更が含まれています。
妨げになるユーザー補助の読み上げの非推奨化
Android 16 では、announceForAccessibility の使用や TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT ユーザー補助イベントのディスパッチを特徴とするユーザー補助通知が非推奨になりました。これにより、TalkBack と Android のスクリーン リーダーのユーザーに対して一貫性のないユーザー エクスペリエンスが生じる可能性があります。代替手段を使用すると、さまざまな Android 支援技術で幅広いユーザーのニーズに対応できます。
代替手段の例:
- ウィンドウの変更など、UI の大幅な変更の場合は、
Activity.setTitle(CharSequence)とsetAccessibilityPaneTitle(java.lang.CharSequence)を使用します。Compose でModifier.semantics { paneTitle = "paneTitle" }を使用する - 重要な UI の変更をユーザーに通知するには、
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int)を使用します。Compose では、Modifier.semantics { liveRegion = LiveRegionMode.[Polite|Assertive]}を使用します。ビューが更新されるたびにお知らせが生成される可能性があるため、これらの関数は慎重に使用する必要があります。 - エラーをユーザーに通知するには、タイプ
AccessibilityEvent#CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_ERRORのAccessibilityEventを送信し、AccessibilityNodeInfo#setError(CharSequence)を設定するか、TextView#setError(CharSequence)を使用します。
非推奨の announceForAccessibility API のリファレンス ドキュメントには、推奨される代替方法の詳細が記載されています。
3 ボタン ナビゲーションのサポート
Android 16 brings predictive back support to the 3-button navigation for apps that have properly migrated to predictive back. Long-pressing the back button initiates a predictive back animation, giving you a preview of where the back swipe takes you.
This behavior applies across all areas of the system that support predictive back animations, including the system animations (back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity).
テーマ別アプリアイコンの自動生成
Beginning with Android 16 QPR 2, Android automatically applies themes to app icons to create a cohesive home screen experience. This occurs if an app does not provide its own themed app icon. Apps can control the design of their themed app icon by including a monochrome layer within their adaptive icon and previewing what their app icon will look like in Android Studio.
デバイスのフォーム ファクタ
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、仮想デバイスの所有者がディスプレイに投影したアプリに対して、次の変更が行われます。
仮想デバイス所有者のオーバーライド
A virtual device owner is a trusted or privileged app that creates and manages a virtual device. Virtual device owners run apps on a virtual device and then project the apps to the display of a remote device, such as a personal computer, virtual reality device, or car infotainment system. The virtual device owner is on a local device, such as a mobile phone.
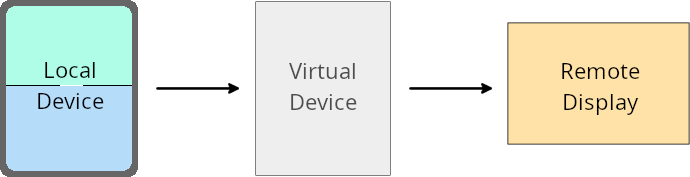
Per-app overrides
On devices running Android 16 (API level 36), virtual device owners can override app settings on select virtual devices that the virtual device owners manage. For example, to improve app layout, a virtual device owner can ignore orientation, aspect ratio, and resizability restrictions when projecting apps onto an external display.
Common breaking changes
The Android 16 behavior might impact your app's UI on large screen form factors such as car displays or Chromebooks, especially layouts that were designed for small displays in portrait orientation. To learn how to make your app adaptive for all device form factors, see About adaptive layouts.
References
セキュリティ
Android 16(API レベル 36)には、システム セキュリティを強化し、アプリとユーザーを悪意のあるアプリから保護するための変更が含まれています。
インテント リダイレクト攻撃に対するセキュリティの強化
Android 16 provides default security against general Intent redirection
attacks, with minimum compatibility and developer changes required.
We are introducing by-default security hardening solutions to Intent
redirection exploits. In most cases, apps that use intents normally won't
experience any compatibility issues; we've gathered metrics throughout our
development process to monitor which apps might experience breakages.
Intent redirection in Android occurs when an attacker can partly or fully control the contents of an intent used to launch a new component in the context of a vulnerable app, while the victim app launches an untrusted sub-level intent in an extras field of an ("top-level") Intent. This can lead to the attacker app launching private components in the context of the victim app, triggering privileged actions, or gaining URI access to sensitive data, potentially leading to data theft and arbitrary code execution.
Opt out of Intent redirection handling
Android 16 introduces a new API that allows apps to opt out of launch security protections. This might be necessary in specific cases where the default security behavior interferes with legitimate app use cases.
For applications compiling against Android 16 (API level 36) SDK or higher
You can directly use the removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method on the Intent
object.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent")
iSublevel?.removeLaunchSecurityProtection() // Opt out from hardening
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
For applications compiling against Android 15 (API level 35) or lower
While not recommended, you can use reflection to access the
removeLaunchSecurityProtection() method.
val i = intent
val iSublevel: Intent? = i.getParcelableExtra("sub_intent", Intent::class.java)
try {
val removeLaunchSecurityProtection = Intent::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("removeLaunchSecurityProtection")
removeLaunchSecurityProtection.invoke(iSublevel)
} catch (e: Exception) {
// Handle the exception, e.g., log it
} // Opt-out from the security hardening using reflection
iSublevel?.let { startActivity(it) }
コンパニオン アプリに検出タイムアウトが通知されなくなった
Android 16 introduces a new behavior during
companion device pairing flow to protect the user's location
privacy from malicious apps. All companion apps running on Android 16 are no
longer directly notified of discovery timeout using
RESULT_DISCOVERY_TIMEOUT. Instead, the user is
notified of timeout events with a visual dialog. When the user dismisses
the dialog, the app is alerted of the association failure with
RESULT_USER_REJECTED.
The search duration has also been extended from the original 20 seconds, and the device discovery can be stopped by the user at any point during the search. If at least one device was discovered within the first 20 seconds of starting the search, the CDM stops searching for additional devices.
接続
Android 16(API レベル 36)では、周辺機器との接続性を改善するために、Bluetooth スタックに次の変更が加えられています。
債券損失の処理を改善
Android 16 以降、Bluetooth スタックが更新され、リモート ボンディングの損失が検出されたときのセキュリティとユーザー エクスペリエンスが改善されました。以前は、システムが自動的にボンディングを削除し、新しいペア設定プロセスを開始していたため、意図しない再ペア設定が発生する可能性がありました。多くのアプリで、債券の損失イベントが一貫した方法で処理されていないことが確認されています。
エクスペリエンスを統一するため、Android 16 ではシステムへのボンディング損失の処理が改善されました。以前にペア設定した Bluetooth デバイスを再接続時に認証できなかった場合、システムはリンクを切断し、ローカルのペア設定情報を保持します。また、ペア設定が解除されたことをユーザーに通知し、ペア設定をやり直すよう求めるシステム ダイアログを表示します。

