בדומה לגרסאות קודמות, Android 16 כולל שינויים בהתנהגות שעשויים להשפיע על האפליקציה שלכם. שינויי ההתנהגות הבאים רלוונטיים רק לאפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 16 ואילך. אם האפליקציה שלכם מטרגטת את Android מגרסה 16 ואילך, אתם צריכים לשנות את האפליקציה כדי שהיא תתמוך בהתנהגויות האלה, במקרים הרלוונטיים.
חשוב גם לבדוק את רשימת השינויים בהתנהגות שמשפיעים על כל האפליקציות שפועלות ב-Android 16, בלי קשר ל-targetSdkVersion של האפליקציה.
חוויית המשתמש וממשק המשתמש של המערכת
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים, שנועדו ליצור חוויית משתמש עקבית ואינטואיטיבית יותר.
האפשרות להסיר את התצוגה מקצה לקצה תבוטל
האפשרות 'מקצה לקצה' נאכפת ב-Android 15 באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35), אבל אפשר להשבית אותה באפליקציה על ידי הגדרת R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement ל-true. באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 16 (רמת API 36), R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement הוצא משימוש ומושבת, ולא ניתן לבטל את ההגדרה של תצוגה מקצה לקצה באפליקציה.
- אם האפליקציה מיועדת ל-Android 16 (רמת API 36) והיא פועלת במכשיר עם Android 15, הפונקציה
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementממשיכה לפעול. - אם האפליקציה מטרגטת ל-Android 16 (רמת API 36) והיא פועלת במכשיר עם Android 16, התכונה
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementמושבתת.
כדי לבדוק ב-Android 16, מוודאים שהאפליקציה תומכת בתצוגה מקצה לקצה ומסירים את השימוש ב-R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement כדי שהאפליקציה תתמוך בתצוגה מקצה לקצה גם במכשיר Android 15. הוראות לגבי תמיכה בתצוגה מקצה לקצה מופיעות במאמרים יצירת מסמכים ותצוגות.
כדי להשתמש בתכונה "חיזוי החזרה", צריך לבצע העברה או לבטל את ההסכמה
באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 16 (רמת API 36) ואילך ופועלות במכשיר עם Android 16 ואילך, מופעלות כברירת מחדל האנימציות של מערכת הניווט התחזיתי אחורה (חזרה למסך הבית, מעבר בין משימות ומעבר בין פעילויות).
בנוסף, לא מתבצעת קריאה ל-onBackPressed ולא מתבצעת יותר שליחה של KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK.
אם האפליקציה שלכם מיירטת את אירוע החזרה ואתם עדיין לא עברתם לניווט חזוי אחורה, עדכנו את האפליקציה כדי להשתמש בממשקי API נתמכים של ניווט אחורה, או השביתו את התכונה באופן זמני על ידי הגדרת המאפיין android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback לערך false בתג <application> או <activity> של קובץ AndroidManifest.xml של האפליקציה.
הוצאה משימוש והשבתה של ממשקי API אלגנטיים לגופנים
באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35), מאפיין elegantTextHeight TextView מוגדר כ-true כברירת מחדל, והגופן הקומפקטי מוחלף בגופן קריא הרבה יותר. אפשר לשנות את ההגדרה הזו על ידי הגדרת המאפיין elegantTextHeight לערך false.
ב-Android 16, המאפיין elegantTextHeight הוצא משימוש. המערכת תתעלם מהמאפיין הזה ברגע שהאפליקציה תטרגט ל-Android 16. ממשקי ה-API האלה שולטים ב'גופנים של ממשק המשתמש', אבל הם יוצאים משימוש. לכן, צריך להתאים את הפריסות כדי להבטיח עיבוד עקבי של טקסט בעברית, בלאית, במיאנמר, בטמילית, בגוג'ראטית, בקנאדה, במלאיאלאם, באודיה, בטלוגו או בתאילנדית.
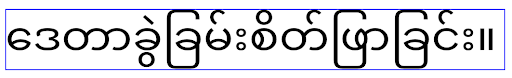 ההתנהגות של
ההתנהגות של elegantTextHeight באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android
14 (רמת API 34) ומטה, או באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35) ששינו את ברירת המחדל על ידי הגדרת המאפיין elegantTextHeight ל-false. התנהגות
התנהגות elegantTextHeight באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android
16 (רמת API 36), או באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35) שלא
ביטלו את ברירת המחדל על ידי הגדרת המאפיין elegantTextHeight לערך false.פונקציונליות עיקרית
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים, שמשנים או מרחיבים יכולות ליבה שונות של מערכת Android.
אופטימיזציה של תזמון פעולה בקצב קבוע
לפני הטירגוט ל-Android 16, אם scheduleAtFixedRate החמיץ ביצוע של משימה כי הוא לא היה במחזור חיים תקין של תהליך, כל הביצועים שהוחמצו מתבצעים באופן מיידי כשהאפליקציה חוזרת למחזור חיים תקין.
כשמטרגטים ל-Android 16, פעולה אחת שהוחמצה של scheduleAtFixedRate תושלם באופן מיידי כשהאפליקציה תחזור למחזור חיים תקין. שינוי ההתנהגות הזה צפוי לשפר את ביצועי האפליקציה. כדאי לבדוק את ההתנהגות הזו באפליקציה כדי לראות אם היא מושפעת.
אפשר גם לבדוק באמצעות מסגרת התאימות לאפליקציות ולהפעיל את הדגל STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS compat.
גורמי צורה של מכשירים
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים באפליקציות כשהן מוצגות במכשירים עם מסך גדול.
פריסות מותאמות
אפליקציות ל-Android פועלות עכשיו במגוון מכשירים (כמו טלפונים, טאבלטים, מכשירים מתקפלים, מחשבים, מכוניות וטלוויזיות) ובמצבי תצוגת חלונות במסכים גדולים (כמו מסך מפוצל וממשק מחשב). לכן, מפתחים צריכים ליצור אפליקציות ל-Android שמותאמות לכל גודל מסך וחלון, בלי קשר לכיוון המסך במכשיר. פרדיגמות כמו הגבלת כיוון המסך והגבלת שינוי הגודל כבר לא מתאימות לעולם של היום, שבו משתמשים במספר מכשירים.
התעלמות מהגבלות על כיוון, שינוי גודל ויחס גובה-רוחב
באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 16 (רמת API 36), ההגבלות על כיוון, שינוי גודל ויחס גובה-רוחב לא חלות יותר על מסכים עם רוחב מינימלי של 600dp ומעלה. האפליקציות ממלאות את חלון התצוגה, בלי קשר ליחס הגובה-רוחב או להעדפת הכיוון של המשתמש, ולא נעשה שימוש בבפורמט pillarbox.
השינוי הזה מציג התנהגות חדשה של הפלטפורמה. מערכת Android עוברת למודל שבו האפליקציות צריכות להתאים את עצמן לכיוונים, לגדלים של מסכים וליחסי גובה-רוחב שונים. כיוון מסך קבוע או שינוי גודל מוגבל מקשים על התאמת האפליקציה. כדי לספק את חוויית המשתמש הטובה ביותר, צריך להתאים את האפליקציה למצבים שונים.
אפשר גם לבדוק את ההתנהגות הזו באמצעות מסגרת התאימות של האפליקציה והפעלת דגל התאימות UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT.
שינויי תוכנה נפוצים שעלולים לגרום לכשלים
התעלמות מהגבלות על כיוון, שינוי גודל ויחס גובה-רוחב עלולה להשפיע על ממשק המשתמש של האפליקציה במכשירים מסוימים, במיוחד על רכיבים שנועדו לפריסות קטנות שמוגבלות לכיוון לאורך: לדוגמה, בעיות כמו פריסות מתוחות ואנימציות ורכיבים מחוץ למסך. הנחות לגבי יחס הגובה-רוחב או הכיוון עלולות לגרום לבעיות חזותיות באפליקציה. מידע נוסף על איך להימנע מבעיות כאלה ולשפר את יכולת ההתאמה של האפליקציה למצבים שונים.
כשמאפשרים סיבוב מכשיר, מתבצעות יותר יצירות מחדש של פעילויות, וזה עלול להוביל לאובדן מצב המשתמש אם הוא לא נשמר כראוי. במאמר שמירת מצבי ממשק המשתמש מוסבר איך לשמור אותם נכון.
פרטי ההטמעה
במכשירים עם מסך גדול במצב מסך מלא ובמצב ריבוי חלונות, המערכת מתעלמת ממאפייני המניפסט וממשקי ה-API של זמן הריצה הבאים:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
המערכת מתעלמת מהערכים הבאים של screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation() ו-getRequestedOrientation():
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
לגבי שינוי הגודל של התצוגה, הערכים הבאים לא מושפעים: android:resizeableActivity="false", android:minAspectRatio ו-android:maxAspectRatio.
באפליקציות שמיועדות ל-Android 16 (API ברמה 36), המערכת מתעלמת כברירת מחדל מהגבלות על כיוון האפליקציה, שינוי הגודל ויחס הגובה-רוחב במסכים גדולים. אפשר לבטל את ההתנהגות הזו באופן זמני באפליקציות שעדיין לא מוכנות (וזה יגרום להצבה במצב תאימות, כמו בהתנהגות הקודמת).
חריגים
ההגבלות על כיוון, שינוי גודל ויחס גובה-רוחב ב-Android 16 לא חלות במצבים הבאים:
- משחקים (מבוססים על הדגל של
android:appCategory) - משתמשים שמביעים הסכמה מפורשת לפעולת ברירת המחדל של האפליקציה בהגדרות יחס הגובה-רוחב של המכשיר
- מסכים שקטנים מ-
sw600dp
ביטול זמני של ההסכמה
כדי לבטל את ההסכמה לפעילות ספציפית, צריך להצהיר על מאפיין המניפסט PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
אם יותר מדי חלקים באפליקציה לא מוכנים ל-Android 16, אפשר לבטל את ההסכמה באופן מלא על ידי החלת אותו מאפיין ברמת האפליקציה:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
בריאות וכושר
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים שקשורים לנתוני בריאות וכושר.
הרשאות ל"בריאות וכושר"
באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 16 (API level 36) ומעלה,
BODY_SENSORS נעשה שימוש בהרשאות יותר מפורטות
בקטע android.permissions.health, שגם Health Connect משתמש בהן. החל מ-Android 16, כל API שבעבר דרש את ההרשאות BODY_SENSORS
או BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND דורש במקום זאת את ההרשאה התואמת android.permissions.health. השינוי הזה משפיע על סוגי הנתונים, ממשקי ה-API וסוגי השירותים שפועלים בחזית הבאים:
HEART_RATE_BPMמתוך Health Services ב-Wear OS-
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEמ-Android Sensor Manager -
heartRateAccuracyו-heartRateBpmמ-ProtoLayoutב-Wear OS -
FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHבמקוםBODY_SENSORS, כשנדרשת ההרשאהandroid.permission.health
אם האפליקציה שלכם משתמשת בממשקי ה-API האלה, היא צריכה לבקש את ההרשאות הגרנולריות המתאימות:
- למעקב אחר קצב הלב, רמת החמצן בדם או טמפרטורת העור בזמן השימוש:
צריך לבקש את ההרשאה הגרנולרית בקטע
android.permissions.health, כמוREAD_HEART_RATEבמקוםBODY_SENSORS. - לגישה לחיישנים ברקע: צריך להשתמש ב-request
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDבמקום ב-requestBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
ההרשאות האלה זהות להרשאות שנדרשות כדי לקרוא נתונים מ-Health Connect, מאגר הנתונים של Android לנתוני בריאות, כושר ורווחה.
באפליקציות לנייד.
אפליקציות לנייד שעוברות לשימוש ב-READ_HEART_RATE ובהרשאות גרנולריות אחרות צריכות גם להצהיר על פעילות כדי להציג את מדיניות הפרטיות של האפליקציה. זו אותה דרישה כמו ב-Health Connect.
קישוריות
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים במערך Bluetooth כדי לשפר את הקישוריות למכשירים היקפיים.
כוונה חדשה לטיפול באובדן של קשר ובשינויים בהצפנה
כחלק משיפור הטיפול באירועים של אובדן קישור, ב-Android 16 נוספו גם 2 כוונות חדשות כדי לספק לאפליקציות מודעוּת רבה יותר לאובדן קישור ולשינויים בהצפנה.
אפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 16 יכולות עכשיו:
- לקבל כוונה מסוג
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGכשמתגלה אובדן של אבטחה מרחוק, כדי לספק משוב מפורט יותר מהמשתמשים ולבצע פעולות מתאימות. - לקבל כוונה מסוג
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEבכל פעם שסטטוס ההצפנה של הקישור משתנה. זה כולל שינוי בסטטוס ההצפנה, שינוי באלגוריתם ההצפנה ושינוי בגודל מפתח ההצפנה. אפליקציות צריכות להתייחס לאיחוד כמשוחזר אם הקישור מוצפן בהצלחה לאחר קבלת הכוונהACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGE.
התאמה להטמעות שונות של יצרני ציוד מקורי (OEM)
גרסת Android 16 כוללת את הכוונות החדשות האלה, אבל ההטמעה והשידור שלהן עשויים להשתנות בהתאם ליצרני המכשירים השונים (OEM). כדי לוודא שהאפליקציה מספקת חוויה עקבית ואמינה בכל המכשירים, המפתחים צריכים לתכנן את הטיפול באובדן הקשר כך שיתאים בצורה חלקה לשינויים הפוטנציאליים האלה.
מומלץ להשתמש בהתנהגויות הבאות באפליקציות:
אם המערכת משדרת את הכוונה
ACTION_KEY_MISSING:המערכת תנתק את הקישור של ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less), אבל פרטי הקישור של המכשיר יישמרו (כפי שמתואר כאן).
האפליקציה צריכה להשתמש בכוונה הזו כאות הראשי לזיהוי אובדן החיבור, ולהנחות את המשתמש לאשר שהמכשיר המרוחק נמצא בטווח לפני שהוא מתחיל למחוק את המכשיר או לבצע התאמה מחדש.
אם מכשיר מתנתק אחרי קבלת
ACTION_KEY_MISSING, האפליקציה צריכה להיזהר לפני שתנסה להתחבר מחדש, כי יכול להיות שהמכשיר כבר לא מקושר למערכת.אם הכוונה
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGלא משודרת:הקישור ל-ACL יישאר מחובר, ופרטי הקישור של המכשיר יוסרו על ידי המערכת, בדומה להתנהגות ב-Android 15.
בתרחיש הזה, האפליקציה צריכה להמשיך להשתמש במנגנונים הקיימים לטיפול באובדן אבטחה, כמו בגרסאות קודמות של Android, כדי לזהות אירועי אובדן אבטחה ולנהל אותם.
דרך חדשה להסרת שיוך Bluetooth
כל האפליקציות שמטרגטות את Android 16 יכולות עכשיו לבטל את ההתאמה של מכשירי Bluetooth באמצעות API ציבורי ב-CompanionDeviceManager. אם מכשיר נלווה מנוהל כשיוך CDM, האפליקציה יכולה להפעיל הסרה של קישור Bluetooth באמצעות ה-API החדש removeBond(int) במכשיר המשויך. האפליקציה יכולה לעקוב אחרי השינויים במצב החיבור על ידי האזנה לאירוע השידור של מכשיר ה-Bluetooth ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
אבטחה
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את שינויי האבטחה הבאים.
נעילת גרסה של MediaStore
For apps targeting Android 16 or higher, MediaStore#getVersion() will now
be unique to each app. This eliminates identifying properties from the version
string to prevent abuse and usage for fingerprinting techniques. Apps shouldn't
make any assumptions around the format of this version. Apps should already
handle version changes when using this API and in most cases shouldn't need to
change their current behavior, unless the developer has attempted to infer
additional information that is beyond the intended scope of this API.
כוונות בטוחות יותר
התכונה Safer Intents היא יוזמת אבטחה רב-שלבית שנועדה לשפר את האבטחה של מנגנון פתרון הכוונות ב-Android. המטרה היא להגן על אפליקציות מפני פעולות זדוניות על ידי הוספת בדיקות במהלך עיבוד הכוונות וסינון כוונות שלא עומדות בקריטריונים ספציפיים.
ב-Android 15 התכונה התמקדה באפליקציה השולחת, ועכשיו ב-Android 16, השליטה עוברת לאפליקציה המקבלת, ומאפשרת למפתחים להביע הסכמה לפתרון קפדני של כוונות באמצעות מניפסט האפליקציה שלהם.
אנחנו מטמיעים שני שינויים חשובים:
אובייקטים מסוג Intent מפורש חייבים להתאים למסנן ה-Intent של רכיב היעד: אם אובייקט Intent מכוון במפורש לרכיב מסוים, הוא צריך להתאים למסנן ה-Intent של הרכיב הזה.
אובייקטים מסוג Intent ללא פעולה לא יכולים להתאים למסנן Intent כלשהו: אובייקטים מסוג Intent שלא צוינה להם פעולה לא אמורים להיות מזוהים כמסנן Intent כלשהו.
השינויים האלה חלים רק כשמעורבות כמה אפליקציות, והם לא משפיעים על הטיפול ב-Intent באפליקציה אחת.
השפעה
התכונה היא אופציונלית, ולכן מפתחים צריכים להפעיל אותה באופן מפורש במניפסט האפליקציה כדי שהיא תיכנס לתוקף. כתוצאה מכך, ההשפעה של התכונה תוגבל לאפליקציות שהמפתחים שלהן:
- מכירים את התכונה 'כוונות בטוחות יותר' ואת היתרונות שלה.
- בוחרים באופן פעיל לשלב באפליקציות שלהם שיטות לטיפול בהצהרות כוונות בצורה מחמירה יותר.
הגישה הזו מאפשרת להפעיל את התכונה רק אם רוצים, וכך מצמצמת את הסיכון לשיבוש של אפליקציות קיימות שעשויות להסתמך על ההתנהגות הנוכחית של זיהוי כוונות, שהיא פחות מאובטחת.
יכול להיות שההשפעה הראשונית ב-Android 16 תהיה מוגבלת, אבל ליוזמת Safer Intents יש תוכנית להשפעה רחבה יותר בגרסאות עתידיות של Android. התוכנית היא שבסופו של דבר, התנהגות ברירת המחדל תהיה זיהוי כוונות מדויק.
התכונה Safer Intents (העברות Intent בטוחות יותר) יכולה לשפר באופן משמעותי את האבטחה של מערכת Android, כי היא מקשה על אפליקציות זדוניות לנצל פרצות במנגנון של פתרון Intent.
עם זאת, צריך לנהל את המעבר לביטול ההסכמה ולאכיפה המחייבת בזהירות כדי לטפל בבעיות תאימות אפשריות עם אפליקציות קיימות.
הטמעה
המפתחים צריכים להפעיל באופן מפורש התאמה מחמירה יותר של Intent באמצעות המאפיין intentMatchingFlags בקובץ המניפסט של האפליקציה.
הנה דוגמה למצב שבו התכונה מופעלת בהסכמה לכל האפליקציה,
אבל מושבתת או שבוטלה בהסכמה במקלט:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
מידע נוסף על הדגלים הנתמכים:
| שם ההתרעה | תיאור |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | התנאי הזה מחייב התאמה מדויקת יותר של כוונות נכנסות |
| ללא | השבתה של כל כללי ההתאמה המיוחדים לכוונות נכנסות. כשמציינים כמה דגלים, ערכים סותרים נפתרים על ידי מתן עדיפות לדגל 'none' |
| allowNullAction | הכלל הזה מרחיב את כללי ההתאמה כדי לאפשר התאמה של כוונות ללא פעולה. הדגל הזה משמש בשילוב עם enforceIntentFilter כדי להשיג התנהגות ספציפית |
בדיקה וניפוי באגים
כשהאכיפה פעילה, האפליקציות אמורות לפעול בצורה תקינה אם המתקשר של הכוונה מילא את הכוונה בצורה תקינה.
עם זאת, כוונות חסומות יפעילו הודעות אזהרה ביומן כמו
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" ו-"Access blocked:"
עם התג "PackageManager."
המשמעות היא שיש בעיה פוטנציאלית שעלולה להשפיע על האפליקציה ונדרש טיפול בה.
מסנן Logcat:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
סינון של קריאות מערכת (syscall) ב-GPU
כדי להקשיח את פני השטח של Mali GPU, Mali GPU IOCTLs שהוצאו משימוש או שמיועדים אך ורק לפיתוח GPU נחסמו בגרסאות ייצור. בנוסף, פקודות IOCTL שמשמשות ליצירת פרופיל של GPU הוגבלו לתהליך המעטפת או לאפליקציות שניתנות לניפוי באגים. פרטים נוספים על המדיניות ברמת הפלטפורמה זמינים בעדכון בנושא SAC.
השינוי הזה מתבצע במכשירי Pixel עם מעבד גרפי Mali (Pixel 6-9). חברת Arm סיפקה סיווג רשמי של פקודות ה-IOCTL שלה בDocumentation/ioctl-categories.rst של גרסת r54p2 שלה. הרשימה הזו תמשיך להתעדכן בגרסאות עתידיות של מנהלי ההתקנים.
השינוי הזה לא משפיע על ממשקי API נתמכים של גרפיקה (כולל Vulkan ו-OpenGL), ולא צפוי להשפיע על מפתחים או על אפליקציות קיימות. השינוי לא ישפיע על כלי פרופיל של GPU, כמו Streamline Performance Analyzer ו-Android GPU Inspector.
בדיקה
אם מופיעה לכם דחייה של SELinux שדומה לזו שמופיעה בהמשך, סביר להניח שהשינוי הזה השפיע על האפליקציה שלכם:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
אם האפליקציה שלכם צריכה להשתמש ב-IOCTLs חסומים, עליכם לדווח על באג ולהקצות אותו לכתובת android-partner-security@google.com.
שאלות נפוצות
האם השינוי הזה במדיניות חל על כל יצרני הציוד המקורי? השינוי הזה יהיה אופציונלי, אבל הוא יהיה זמין לכל יצרני הציוד המקורי שירצו להשתמש בשיטת האבטחה הזו. הוראות להטמעת השינוי מופיעות במסמכי ההטמעה.
האם חובה לבצע שינויים בבסיס הקוד של יצרן הציוד המקורי כדי להטמיע את התכונה הזו, או שהיא מגיעה עם גרסה חדשה של AOSP כברירת מחדל? השינוי ברמת הפלטפורמה יגיע עם מהדורת AOSP חדשה כברירת מחדל. ספקים יכולים להחיל את השינוי הזה על בסיס הקוד שלהם אם הם רוצים.
האם מערכות SoC אחראיות לעדכון רשימת ה-IOCTL? לדוגמה, אם במכשיר שלי נעשה שימוש ב-GPU מסוג ARM Mali, האם אצטרך לפנות אל ARM כדי לבצע שינויים כלשהם? מערכות SoC נפרדות צריכות לעדכן את רשימות ה-IOCTL שלהן לכל מכשיר עם פרסום מנהל ההתקן. לדוגמה, ARM תעדכן את רשימת ה-IOCTL שפורסמה שלה אחרי עדכוני מנהלי התקנים. עם זאת, יצרני ציוד מקורי (OEM) צריכים לוודא שהם משלבים את העדכונים ב-SEPolicy שלהם, ומוסיפים לרשימות את כל פקודות ה-IOCTL המותאמות אישית שנבחרו, לפי הצורך.
האם השינוי הזה חל אוטומטית על כל מכשירי Pixel שזמינים למכירה, או שנדרשת פעולה של המשתמש כדי להפעיל משהו וליישם את השינוי? השינוי הזה חל על כל מכשירי Pixel שזמינים כרגע לרכישה ומשתמשים במעבד גרפי מסוג Mali (מכשירי Pixel 6 עד Pixel 9). לא נדרשת פעולה מצד המשתמש כדי להחיל את השינוי הזה.
האם השימוש במדיניות הזו ישפיע על הביצועים של מנהל ההתקן של ליבת מערכת ההפעלה? המדיניות הזו נבדקה ב-GPU מסוג Mali באמצעות GFXBench, ולא נצפה שינוי מדיד בביצועי ה-GPU.
האם רשימת ה-IOCTL צריכה להיות תואמת לגרסאות הנוכחיות של מרחב המשתמש ושל מנהל ההתקן של ליבת המערכת? כן, צריך לסנכרן את רשימת ה-IOCTL המותרים עם ה-IOCTL שנתמכים על ידי מנהלי ההתקנים של מרחב המשתמש ושל ליבת מערכת ההפעלה. אם פקודות ה-IOCTL במרחב המשתמש או במנהל ההתקן של ליבת המערכת מעודכנות, צריך לעדכן את רשימת פקודות ה-IOCTL של SEPolicy כך שתתאים להן.
חברת ARM סיווגה את פקודות ה-IOCTL כ 'מוגבלות' או כ'מכשירים', אבל אנחנו רוצים להשתמש בחלק מהן בתרחישי שימוש בייצור, ו/או לדחות אחרות. יצרני ציוד מקורי (OEM) ומערכות על שבב (SoC) אחראים להחליט איך לסווג את פקודות ה-IOCTL שבהן הם משתמשים, על סמך ההגדרה של ספריות Mali במרחב המשתמשים שלהם. אפשר להשתמש ברשימה של ARM כדי לקבל החלטות לגביהם, אבל יכול להיות שתרחישי השימוש של כל יצרן ציוד מקורי או SoC יהיו שונים.
פרטיות
Android 16 (API ברמה 36) כוללת את השינויים הבאים שקשורים לפרטיות.
הרשאה לגישה לרשת המקומית
כל אפליקציה שיש לה הרשאה INTERNET יכולה לגשת למכשירים ברשת המקומית.
כך קל לאפליקציות להתחבר למכשירים מקומיים, אבל יש לכך גם השלכות על הפרטיות, כמו יצירת טביעת אצבע של המשתמש ושימוש ב-proxy למיקום.
מטרת הפרויקט Local Network Protections (הגנות על הרשת המקומית) היא להגן על פרטיות המשתמש באמצעות הגבלת הגישה לרשת המקומית מאחורי הרשאת זמן ריצה חדשה.
תוכנית ההשקה
השינוי הזה יוטמע בין שתי גרסאות, 25Q2 ו-26Q2 בהתאמה. חשוב מאוד שהמפתחים יפעלו לפי ההנחיות האלה ב-25Q2 וישתפו משוב, כי אמצעי ההגנה האלה יאכפו בגרסת Android מאוחרת יותר. בנוסף, הם יצטרכו לעדכן תרחישים שתלויים בגישה מרומזת לרשת מקומית באמצעות ההנחיות הבאות, ולהתכונן לדחייה של ההרשאה החדשה על ידי המשתמשים ולביטול שלה.
השפעה
בשלב הנוכחי, ניוד מספרים הוא תכונה אופציונלית, כלומר היא תשפיע רק על האפליקציות שהביעו הסכמה לשימוש בה. המטרה של שלב ההצטרפות היא לאפשר למפתחי אפליקציות להבין אילו חלקים באפליקציה שלהם תלויים בגישה משתמעת לרשת המקומית, כדי שיוכלו להתכונן להגנה על ההרשאות בגרסה הבאה.
האפליקציות יושפעו אם הן ניגשות לרשת המקומית של המשתמש באמצעות:
- שימוש ישיר או שימוש בספרייה בשקעים גולמיים בכתובות של רשת מקומית (למשל, פרוטוקול גילוי שירותים mDNS או SSDP)
- שימוש במחלקות ברמת המסגרת שיש להן גישה לרשת המקומית (למשל, NsdManager)
כדי להעביר תנועה אל כתובת ברשת מקומית וממנה, נדרשת הרשאת גישה לרשת המקומית. בטבלה הבאה מפורטים כמה מקרים נפוצים:
| פעולה ברשת ברמה נמוכה באפליקציה | נדרשת הרשאת גישה לרשת המקומית |
|---|---|
| יצירת חיבור TCP יוצא | כן |
| אישור חיבורי TCP נכנסים | כן |
| שליחת שידור יחיד, שידור לקבוצה או שידור לכולם ב-UDP | כן |
| קבלת שידור יחיד, שידור מרובה או שידור לכל ברשת ב-UDP | כן |
ההגבלות האלה מוטמעות עמוק במערך של רכיבי הרשת, ולכן הן חלות על כל ממשקי ה-API של הרשת. הנתונים כוללים שקעים שנוצרו בקוד מקורי או בקוד מנוהל, ספריות רשת כמו Cronet ו-OkHttp, וכל ממשקי API שהוטמעו מעל אלה. כדי לפתור בעיות בשירותים ברשת המקומית (כלומר, שירותים עם הסיומת .local), צריך הרשאה לרשת המקומית.
חריגים לכללים שלמעלה:
- אם שרת ה-DNS של המכשיר נמצא ברשת מקומית, לא נדרשת הרשאת גישה לרשת המקומית כדי להעביר תנועה אל השרת או ממנו (בפורט 53).
- אפליקציות שמשתמשות בבוחר הפלט כבוחר בתוך האפליקציה לא יצטרכו הרשאות גישה לרשת המקומית (הנחיות נוספות יפורסמו ברבעון הרביעי של 2025).
הנחיות למפתחים (אופציונלי)
כדי להפעיל את ההגבלות על הגישה לרשת המקומית:
- מבצעים פלאשינג למכשיר לגרסה עם 25Q2 Beta 3 ואילך.
- מתקינים את האפליקציה שרוצים לבדוק.
מחליפים את מצב הדגל Appcompat ב-adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>הפעלה מחדש של המכשיר
עכשיו הגישה של האפליקציה לרשת המקומית מוגבלת, וכל ניסיון לגשת לרשת המקומית יוביל לשגיאות בשקע. אם אתם משתמשים בממשקי API שמבצעים פעולות ברשת המקומית מחוץ לתהליך של האפליקציה (לדוגמה: NsdManager), הם לא יושפעו במהלך שלב ההצטרפות.
כדי לשחזר את הגישה, צריך לתת לאפליקציה הרשאה ל-NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- מוודאים שהאפליקציה מצהירה על ההרשאה
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESבמניפסט שלה. - עוברים אל הגדרות > אפליקציות > [שם האפליקציה] > הרשאות > מכשירים בקרבת מקום > אישור.
עכשיו הגישה של האפליקציה לרשת המקומית אמורה לחזור, וכל התרחישים אמורים לפעול כמו לפני שהאפליקציה נכללה בהחרגה.
אחרי שהאכיפה של ההגנה על הרשת המקומית תתחיל, כך תושפע תנועת הרשת של האפליקציה.
| הרשאה | בקשה יוצאת ב-LAN | בקשה יוצאת/נכנסת לאינטרנט | בקשה נכנסת ב-LAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| הוענקה | Microsoft Works | Microsoft Works | Microsoft Works |
| לא הוענקה גישה | פספוסים | Microsoft Works | פספוסים |
כדי להשבית את הדגל App-Compat, משתמשים בפקודה הבאה
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
שגיאות
שגיאות שנובעות מההגבלות האלה יוחזרו לשקע הקורא בכל פעם שהוא מפעיל שליחה או גרסה שונה של שליחה לכתובת ברשת המקומית.
דוגמאות לשגיאות:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
הגדרה של רשת מקומית
רשת מקומית בפרויקט הזה היא רשת IP שמשתמשת בממשק רשת עם יכולת שידור, כמו Wi-Fi או Ethernet, אבל לא כוללת חיבורים סלולריים (WWAN) או חיבורי VPN.
הרשתות הבאות נחשבות לרשתות מקומיות:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- קישור מקומי
- מסלולים שמקושרים ישירות
- רשתות Stub כמו Thread
- Multiple-subnets (TBD)
בנוסף, גם כתובות מולטיקאסט (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) וכתובת ה-IPv4 לשידור (255.255.255.255) מסווגות ככתובות של רשת מקומית.
תמונות בבעלות האפליקציה
כשמוצגת בקשה להענקת הרשאות גישה לתמונות ולסרטונים מאפליקציה שתואמת ל-SDK מגרסה 36 ואילך במכשירים עם Android מגרסה 16 ואילך, משתמשים שבוחרים להגביל את הגישה למדיה שנבחרה יראו את כל התמונות שבבעלות האפליקציה שנבחרו מראש בבורר התמונות. המשתמשים יכולים לבטל את הבחירה של כל אחד מהפריטים שנבחרו מראש, וכך לבטל את הגישה של האפליקציה לתמונות ולסרטונים האלה.
