Önceki sürümlerde olduğu gibi Android 16 da uygulamanızı etkileyebilecek davranış değişiklikleri içerir. Aşağıdaki davranış değişiklikleri yalnızca Android 16 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen uygulamalar için geçerlidir. Uygulamanız Android 16 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefliyorsa uygulanabilir durumlarda bu davranışları destekleyecek şekilde uygulamanızı değiştirmeniz gerekir.
Uygulamanızın targetSdkVersion değerinden bağımsız olarak, Android 16'da çalışan tüm uygulamaları etkileyen davranış değişiklikleri listesini de incelemeyi unutmayın.
Kullanıcı deneyimi ve sistem arayüzü
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), daha tutarlı ve sezgisel bir kullanıcı deneyimi oluşturmak için aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Uçtan uca kapsam dışında kalma özelliği kaldırılıyor
Android 15 enforced edge-to-edge for apps targeting Android 15 (API
level 35), but your app could opt-out by setting
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement to true. For apps
targeting Android 16 (API level 36),
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement is deprecated and disabled, and your
app can't opt-out of going edge-to-edge.
- If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 15 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementcontinues to work. - If your app targets Android 16 (API level 36) and is running on an
Android 16 device,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementis disabled.
For testing in Android 16, ensure your app supports edge-to-edge and
remove any use of R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement so that your app
also supports edge-to-edge on an Android 15 device. To support edge-to-edge,
see the Compose and Views guidance.
Tahmin edilen geri gitme özelliği için taşıma veya devre dışı bırakma işlemi gerekir
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher and running on an
Android 16 or higher device, the predictive back system animations
(back-to-home, cross-task, and cross-activity) are enabled by default.
Additionally, onBackPressed is not called and
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK is not dispatched anymore.
If your app intercepts the back event and you haven't migrated to predictive
back yet, update your app to use supported back navigation APIs, or
temporarily opt out by setting the
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback attribute to false in the
<application> or <activity> tag of your app's AndroidManifest.xml file.
Elegant Font API'leri kullanımdan kaldırıldı ve devre dışı bırakıldı
Apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) have the
elegantTextHeight
TextView attribute set to true by
default, replacing the compact font with one that is much more readable. You
could override this by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute to false.
Android 16 deprecates the
elegantTextHeight attribute,
and the attribute will be ignored once your app targets Android 16. The "UI
fonts" controlled by these APIs are being discontinued, so you should adapt any
layouts to ensure consistent and future proof text rendering in Arabic, Lao,
Myanmar, Tamil, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Telugu or Thai.
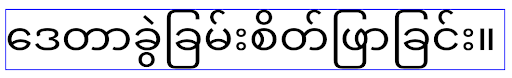
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
14 (API level 34) and lower, or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35)
that overrode the default by setting the elegantTextHeight
attribute to false.
elegantTextHeight behavior for apps targeting Android
16 (API level 36), or for apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) that didn't
override the default by setting the elegantTextHeight attribute
to false.Temel işlevler
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), Android sisteminin çeşitli temel özelliklerini değiştiren veya genişleten aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Sabit ücretli iş planlaması optimizasyonu
Prior to targeting Android 16, when scheduleAtFixedRate
missed a task execution due to being outside a valid
process lifecycle, all missed executions immediately
execute when the app returns to a valid lifecycle.
When targeting Android 16, at most one missed execution of
scheduleAtFixedRate is immediately executed when the app
returns to a valid lifecycle. This behavior change is expected to improve app
performance. Test this behavior in your app to check if your app is impacted.
You can also test by using the app compatibility framework
and enabling the STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS compat flag.
Cihaz form faktörleri
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), büyük ekranlı cihazlarda gösterilen uygulamalar için aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Uyarlanabilir düzenler
With Android apps now running on a variety of devices (such as phones, tablets, foldables, desktops, cars, and TVs) and windowing modes on large screens (such as split screen and desktop windowing), developers should build Android apps that adapt to any screen and window size, regardless of device orientation. Paradigms like restricting orientation and resizability are too restrictive in today's multidevice world.
Ignore orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions no longer apply on displays with smallest width >= 600dp. Apps fill the entire display window, regardless of aspect ratio or a user's preferred orientation, and pillarboxing isn't used.
This change introduces a new standard platform behavior. Android is moving toward a model where apps are expected to adapt to various orientations, display sizes, and aspect ratios. Restrictions like fixed orientation or limited resizability hinder app adaptability. Make your app adaptive to deliver the best possible user experience.
You can also test this behavior by using the
app compatibility framework and enabling the
UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT compat flag.
Common breaking changes
Ignoring orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions might impact your app's UI on some devices, especially elements that were designed for small layouts locked in portrait orientation: for example, issues like stretched layouts and off-screen animations and components. Any assumptions about aspect ratio or orientation can cause visual issues with your app. Learn more about how to avoid them and improve your app's adaptive behaviour.
Allowing device rotation results in more activity re-creation, which can result in losing user state if not properly preserved. Learn how to correctly save UI state in Save UI states.
Implementation details
The following manifest attributes and runtime APIs are ignored across large screen devices in full-screen and multi-window modes:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
The following values for screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation(), and
getRequestedOrientation() are ignored:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Regarding display resizability, android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio, and android:maxAspectRatio have no effect.
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36), app orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio constraints are ignored on large screens by default, but every app that isn't fully ready can temporarily override this behavior by opting out (which results in the previous behavior of being placed in compatibility mode).
Exceptions
The Android 16 orientation, resizability, and aspect ratio restrictions don't apply in the following situations:
- Games (based on the
android:appCategoryflag) - Users explicitly opting in to the app's default behavior in aspect ratio settings of the device
- Screens that are smaller than
sw600dp
Opt out temporarily
To opt out a specific activity, declare the
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY manifest property:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
If too many parts of your app aren't ready for Android 16, you can opt out completely by applying the same property at the application level:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Sağlık ve fitness
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), sağlık ve fitness verileriyle ilgili aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Sağlık ve fitness izinleri
For apps targeting Android 16 (API level 36) or higher,
BODY_SENSORS permissions use more granular permissions
under android.permissions.health, which Health Connect
also uses. As of Android 16, any API previously requiring BODY_SENSORS
or BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND requires the corresponding
android.permissions.health permission instead. This affects the following data
types, APIs, and foreground service types:
HEART_RATE_BPMfrom Health Services on Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEfrom Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracyandheartRateBpmfromProtoLayouton Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHwhere the respectiveandroid.permission.healthpermission is needed in place ofBODY_SENSORS
If your app uses these APIs, it should request the respective granular permissions:
- For while-in-use monitoring of Heart Rate, SpO2, or Skin Temperature:
request the granular permission under
android.permissions.health, such asREAD_HEART_RATEinstead ofBODY_SENSORS. - For background sensor access: request
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDinstead ofBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
These permissions are the same as those that guard access to reading data from Health Connect, the Android datastore for health, fitness, and wellness data.
Mobile apps
Mobile apps migrating to use the READ_HEART_RATE and other granular
permissions must also declare an activity to display
the app's privacy policy. This is the same requirement as Health Connect.
Bağlantı
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36), çevre birimi cihazlarla bağlantıyı iyileştirmek için Bluetooth yığınında aşağıdaki değişiklikleri içerir.
Bağlantı kaybı ve şifreleme değişikliklerini işlemek için yeni amaçlar
Daha iyi bağ kaybı yönetimi kapsamında Android 16, uygulamalara bağ kaybı ve şifreleme değişiklikleri hakkında daha fazla bilgi sağlamak için 2 yeni intent de sunar.
Android 16'yı hedefleyen uygulamalar artık:
- Uzaktan bağ kaybı algılandığında
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent'i alır. Bu sayede daha bilgilendirici kullanıcı geri bildirimleri sağlayabilir ve uygun işlemleri yapabilirler. - Bağlantının şifreleme durumu değiştiğinde bir
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent'i alın. Şifreleme durumu değişikliği, şifreleme algoritması değişikliği ve şifreleme anahtarı boyutu değişikliği buna dahildir. Uygulamalar, daha sonraACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent'i aldıktan sonra bağlantı başarıyla şifrelenirse bağın geri yüklendiğini dikkate almalıdır.
Farklı OEM uygulamalarında uyum sağlama
Android 16 bu yeni intent'leri kullanıma sunsa da bunların uygulanması ve yayınlanması farklı cihaz üreticilerine (OEM'ler) göre değişiklik gösterebilir. Uygulamanızın tüm cihazlarda tutarlı ve güvenilir bir deneyim sunmasını sağlamak için geliştiricilerin, bağlantı kaybı işlemelerini bu olası varyasyonlara sorunsuz bir şekilde uyum sağlayacak şekilde tasarlamaları gerekir.
Aşağıdaki uygulama davranışlarını öneririz:
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent'i yayınlanırsa:ACL (Asenkron Bağlantısız) bağlantısının bağlantısı sistem tarafından kesilir ancak cihazın bağ bilgileri saklanır (burada açıklandığı gibi).
Uygulamanız, bağlantı kaybı algılama için birincil sinyal olarak bu intent'i kullanmalı ve cihazı unutma veya yeniden eşleme işlemini başlatmadan önce kullanıcıyı uzak cihazın kapsama alanında olduğunu onaylamasına yönlendirmelidir.
Bir cihaz
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGalındıktan sonra bağlantısını keserse uygulamanız, cihaz artık sistemle bağlı olmayabileceğinden yeniden bağlantı kurarken dikkatli olmalıdır.ACTION_KEY_MISSINGintent'i yayınlanmıyorsa:ACL bağlantısı bağlı kalır ve Android 15'teki davranışla aynı şekilde cihazın bağ bilgileri sistem tarafından kaldırılır.
Bu senaryoda, uygulamanız, bağ kaybı etkinliklerini algılayıp yönetmek için önceki Android sürümlerindeki mevcut bağ kaybı işleme mekanizmalarını kullanmaya devam etmelidir.
Bluetooth eşlemesini kaldırmanın yeni yolu
All apps targeting Android 16 are now able to unpair bluetooth devices using a
public API in CompanionDeviceManager. If a companion device is
being managed as a CDM association, then the app can trigger
bluetooth bond removal by using the new removeBond(int) API
on the associated device. The app can monitor the bond state changes by
listening to the bluetooth device broadcast event
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
Güvenlik
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36) aşağıdaki güvenlik değişikliklerini içerir.
MediaStore sürüm kilitleme
For apps targeting Android 16 or higher, MediaStore#getVersion() will now
be unique to each app. This eliminates identifying properties from the version
string to prevent abuse and usage for fingerprinting techniques. Apps shouldn't
make any assumptions around the format of this version. Apps should already
handle version changes when using this API and in most cases shouldn't need to
change their current behavior, unless the developer has attempted to infer
additional information that is beyond the intended scope of this API.
Daha güvenli intent'ler
The Safer Intents feature is a multi-phase security initiative designed to improve the security of Android's intent resolution mechanism. The goal is to protect apps from malicious actions by adding checks during intent processing and filtering intents that don't meet specific criteria.
In Android 15 the feature focused on the sending app, now with Android 16, shifts control to the receiving app, allowing developers to opt-in to strict intent resolution using their app manifest.
Two key changes are being implemented:
Explicit Intents Must Match the Target Component's Intent Filter: If an intent explicitly targets a component, it should match that component's intent filter.
Intents Without an Action Cannot Match any Intent Filter: Intents that don't have an action specified shouldn't be resolved to any intent filter.
These changes only apply when multiple apps are involved and don't affect intent handling within a single app.
Impact
The opt-in nature means that developers must explicitly enable it in their app manifest for it to take effect. As a result, the feature's impact will be limited to apps whose developers:
- Are aware of the Safer Intents feature and its benefits.
- Actively choose to incorporate stricter intent handling practices into their apps.
This opt-in approach minimizes the risk of breaking existing apps that may rely on the current less-secure intent resolution behavior.
While the initial impact in Android 16 may be limited, the Safer Intents initiative has a roadmap for broader impact in future Android releases. The plan is to eventually make strict intent resolution the default behavior.
The Safer Intents feature has the potential to significantly enhance the security of the Android ecosystem by making it more difficult for malicious apps to exploit vulnerabilities in the intent resolution mechanism.
However, the transition to opt-out and mandatory enforcement must be carefully managed to address potential compatibility issues with existing apps.
Implementation
Developers need to explicitly enable stricter intent matching using the
intentMatchingFlags attribute in their app manifest.
Here is an example where the feature is opt-in for the entire app,
but disabled/opt-out on a receiver:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
More on the supported flags:
| Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Enforces stricter matching for incoming intents |
| none | Disables all special matching rules for incoming intents. When specifying multiple flags, conflicting values are resolved by giving precedence to the "none" flag |
| allowNullAction | Relaxes the matching rules to allow intents without an action to match. This flag to be used in conjunction with "enforceIntentFilter" to achieve a specific behavior |
Testing and Debugging
When the enforcement is active, apps should function correctly if the intent
caller has properly populated the intent.
However, blocked intents will trigger warning log messages like
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" and "Access blocked:"
with the tag "PackageManager."
This indicates a potential issue that could impact the app and requires
attention.
Logcat filter:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
GPU sistem çağrısı filtreleme
To harden the Mali GPU surface, Mali GPU IOCTLs that have been deprecated or are intended solely for GPU development have been blocked in production builds. Additionally, IOCTLs used for GPU profiling have been restricted to the shell process or debuggable applications. Refer to the SAC update for more details on the platform-level policy.
This change takes place on Pixel devices using the Mali GPU (Pixel 6-9). Arm
has provided official categorization of their IOCTLs in
Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst of their r54p2 release. This
list will continue to be maintained in future driver releases.
This change does not impact supported graphics APIs (including Vulkan and OpenGL), and is not expected to impact developers or existing applications. GPU profiling tools such as the Streamline Performance Analyzer and the Android GPU Inspector won't be affected.
Testing
If you see a SELinux denial similar to the following, it is likely your application has been impacted by this change:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
If your application needs to use blocked IOCTLs, please file a bug and assign it to android-partner-security@google.com.
FAQ
Does this policy change apply to all OEMs? This change will be opt-in, but available to any OEMs who would like to use this hardening method. Instructions for implementing the change can be found in the implementation documentation.
Is it mandatory to make changes in the OEM codebase to implement this, or does it come with a new AOSP release by default? The platform-level change will come with a new AOSP release by default. Vendors may opt-in to this change in their codebase if they would like to apply it.
Are SoCs responsible for keeping the IOCTL list up to date? For example, if my device uses an ARM Mali GPU, would I need to reach out to ARM for any of the changes? Individual SoCs must update their IOCTL lists per device upon driver release. For example, ARM will update their published IOCTL list upon driver updates. However, OEMs should make sure that they incorporate the updates in their SEPolicy, and add any selected custom IOCTLs to the lists as needed.
Does this change apply to all Pixel in-market devices automatically, or is a user action required to toggle something to apply this change? This change applies to all Pixel in-market devices using the Mali GPU (Pixel 6-9). No user action is required to apply this change.
Will use of this policy impact the performance of the kernel driver? This policy was tested on the Mali GPU using GFXBench, and no measurable change to GPU performance was observed.
Is it necessary for the IOCTL list to align with the current userspace and kernel driver versions? Yes, the list of allowed IOCTLs must be synchronized with the IOCTLs supported by both the userspace and kernel drivers. If the IOCTLs in the user space or kernel driver are updated, the SEPolicy IOCTL list must be updated to match.
ARM has categorized IOCTLs as 'restricted' / 'instrumentation', but we want to use some of them in production use-cases, and/or deny others. Individual OEMs/SoCs are responsible for deciding on how to categorize the IOCTLs they use, based on the configuration of their userspace Mali libraries. ARM's list can be used to help decide on these, but each OEM/SoC's use-case may be different.
Gizlilik
Android 16 (API düzeyi 36) aşağıdaki gizlilik değişikliklerini içerir.
Yerel Ağ İzni
Devices on the LAN can be accessed by any app that has the INTERNET permission.
This makes it easy for apps to connect to local devices but it also has privacy
implications such as forming a fingerprint of the user, and being a proxy for
location.
The Local Network Protections project aims to protect the user's privacy by gating access to the local network behind a new runtime permission.
Release plan
This change will be deployed between two releases, 25Q2 and 26Q2 respectively. It is imperative that developers follow this guidance for 25Q2 and share feedback because these protections will be enforced at a later Android release. Moreover, they will need to update scenarios which depend on implicit local network access by using the following guidance and prepare for user rejection and revocation of the new permission.
Impact
At the current stage, LNP is an opt-in feature which means only the apps that opt in will be affected. The goal of the opt-in phase is for app developers to understand which parts of their app depend on implicit local network access such that they can prepare to permission guard them for the next release.
Apps will be affected if they access the user's local network using:
- Direct or library use of raw sockets on local network addresses (e.g. mDNS or SSDP service discovery protocol)
- Use of framework level classes that access the local network (e.g. NsdManager)
Traffic to and from a local network address requires local network access permission. The following table lists some common cases:
| App Low Level Network Operation | Local Network Permission Required |
|---|---|
| Making an outgoing TCP connection | yes |
| Accepting incoming TCP connections | yes |
| Sending a UDP unicast, multicast, broadcast | yes |
| Receiving an incoming UDP unicast, multicast, broadcast | yes |
These restrictions are implemented deep in the networking stack, and thus they apply to all networking APIs. This includes sockets created in native or managed code, networking libraries like Cronet and OkHttp, and any APIs implemented on top of those. Trying to resolve services on the local network (i.e. those with a .local suffix) will require local network permission.
Exceptions to the rules above:
- If a device's DNS server is on a local network, traffic to or from it (at port 53) doesn't require local network access permission.
- Applications using Output Switcher as their in-app picker won't need local network permissions (more guidance to come in 2025Q4).
Developer Guidance (Opt-in)
To opt into local network restrictions, do the following:
- Flash the device to a build with 25Q2 Beta 3 or later.
- Install the app to be tested.
Toggle the Appcompat flag in adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Reboot The device
Now your app's access to the local network is restricted and any attempt to access the local network will lead to socket errors. If you are using APIs that perform local network operations outside of your app process (ex: NsdManager), they won't be impacted during the opt-in phase.
To restore access, you must grant your app permission to NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- Ensure the app declares the
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESpermission in its manifest. - Go to Settings > Apps > [Application Name] > Permissions > Nearby devices > Allow.
Now your app's access to the local network should be restored and all your scenarios should work as they did prior to opting the app in.
Once enforcement for local network protection begins, here is how the app network traffic will be impacted.
| Permission | Outbound LAN Request | Outbound/Inbound Internet Request | Inbound LAN Request |
|---|---|---|---|
| Granted | Works | Works | Works |
| Not Granted | Fails | Works | Fails |
Use the following command to toggle-off the App-Compat flag
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Errors
Errors arising from these restrictions will be returned to the calling socket whenever it invokes send or a send variant to a local network address.
Example errors:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Local Network Definition
A local network in this project refers to an IP network that utilizes a broadcast-capable network interface, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet, but excludes cellular (WWAN) or VPN connections.
The following are considered local networks:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-local
- Directly-connected routes
- Stub networks like Thread
- Multiple-subnets (TBD)
Additionally, both multicast addresses (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) and the IPv4 broadcast address (255.255.255.255) are classified as local network addresses.
Uygulamaya ait fotoğraflar
Android 16 veya sonraki sürümleri çalıştıran cihazlarda SDK 36 veya sonraki sürümleri hedefleyen bir uygulama tarafından fotoğraf ve video izinleri istendiğinde, seçili medyaya erişimi sınırlamayı seçen kullanıcılar, uygulamaya ait tüm fotoğrafları fotoğraf seçicide önceden seçili olarak görür. Kullanıcılar önceden seçilmiş öğelerden herhangi birinin seçimini kaldırabilir. Bu durumda uygulamanın söz konusu fotoğraf ve videolara erişimi iptal edilir.
