이전 버전과 마찬가지로 Android 16에는 앱에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 동작 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다. 다음 동작 변경사항은 Android 16 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱에만 적용됩니다. 앱이 Android 16 이상을 타겟팅하는 경우 이러한 동작을 지원하도록 앱을 수정해야 합니다(해당하는 경우).
앱의 targetSdkVersion과 관계없이 Android 16에서 실행되는 모든 앱에 영향을 미치는 동작 변경사항 목록도 검토해야 합니다.
사용자 환경 및 시스템 UI
Android 16(API 수준 36)에는 더 일관되고 직관적인 사용자 환경을 만들기 위한 다음 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
더 넓은 화면 선택 해제 지원 종료
Android 15에서는 Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하는 앱에 더 넓은 화면을 강제 적용했지만, R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement을 true로 설정하여 앱에서 선택 해제할 수 있었습니다. Android 16 (API 수준 36)을 타겟팅하는 앱의 경우 R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement가 지원 중단되고 사용 중지되며 앱에서 더 이상 전체 화면 모드를 선택 해제할 수 없습니다.
- 앱이 Android 16 (API 수준 36)을 타겟팅하고 Android 15 기기에서 실행되는 경우
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement는 계속 작동합니다. - 앱이 Android 16 (API 수준 36)을 타겟팅하고 Android 16 기기에서 실행되는 경우
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement가 사용 중지됩니다.
Android 16에서 테스트하려면 앱이 더 넓은 화면을 지원하는지 확인하고 R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement 사용을 삭제하여 앱이 Android 15 기기에서도 더 넓은 화면을 지원하도록 합니다. 더 넓은 화면을 지원하려면 Compose 및 Views 안내를 참고하세요.
뒤로 탐색 예측을 위해 이전 또는 선택 해제 필요
Android 16 (API 수준 36) 이상을 타겟팅하고 Android 16 이상 기기에서 실행되는 앱의 경우 예측 뒤로 탐색 시스템 애니메이션(홈으로 돌아가기, 교차 작업, 교차 활동)이 기본적으로 사용 설정됩니다.
또한 onBackPressed이 호출되지 않고 KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK이 더 이상 디스패치되지 않습니다.
앱이 뒤로 이벤트를 가로채고 아직 뒤로 탐색 예측으로 이전하지 않은 경우 지원되는 뒤로 탐색 API를 사용하도록 앱을 업데이트하거나 앱의 AndroidManifest.xml 파일의 <application> 또는 <activity> 태그에서 android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback 속성을 false로 설정하여 일시적으로 선택 해제하세요.
elegant font API 지원 중단 및 사용 중지
Android 15 (API 수준 35)를 타겟팅하는 앱의 경우 elegantTextHeight
TextView 속성이 기본적으로 true로 설정되어 있어 간결한 글꼴이 가독성이 훨씬 높은 글꼴로 대체됩니다. elegantTextHeight 속성을 false로 설정하여 이를 재정의할 수 있습니다.
Android 16에서는 elegantTextHeight 속성이 지원 중단되며 앱이 Android 16을 타겟팅하면 속성이 무시됩니다. 이러한 API로 제어되는 'UI 글꼴'이 지원 중단되므로 아랍어, 라오어, 미얀마어, 타밀어, 구자라트어, 칸나다어, 말라얄람어, 오디아어, 텔루구어 또는 태국어에서 일관되고 미래에 대비할 수 있는 텍스트 렌더링을 보장하도록 레이아웃을 조정해야 합니다.
elegantTextHeight 속성을 false로 설정하여 기본값을 재정의한 앱의 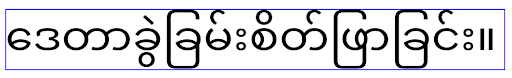
elegantTextHeight 동작elegantTextHeight 속성을 false로 설정하여 기본값을 재정의하지 않은 앱의 
elegantTextHeight 동작핵심 기능
Android 16(API 수준 36)에는 Android 시스템의 다양한 핵심 기능을 수정하거나 확장하는 다음과 같은 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
고정 속도 작업 예약 방식 최적화
Android 16을 타겟팅하기 전에는 scheduleAtFixedRate가 유효한 프로세스 수명 주기를 벗어나기 때문에 작업 실행을 놓쳤을 때 앱이 유효한 수명 주기로 돌아가면 누락된 실행이 모두 즉시 실행되었습니다.
Android 16을 타겟팅하는 경우 앱이 유효한 수명 주기로 돌아가면 누락된 scheduleAtFixedRate 실행이 최대 1회 즉시 실행됩니다. 이 동작 변경으로 앱 성능이 개선될 것으로 예상됩니다. 앱에서 이 동작을 테스트하여 앱이 영향을 받는지 확인합니다.
앱 호환성 프레임워크를 사용하고 STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS 호환성 플래그를 사용 설정하여 테스트할 수도 있습니다.
기기 폼 팩터
Android 16(API 수준 36)에는 대형 화면 기기에 표시될 때 앱에 적용되는 다음과 같은 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
적응형 레이아웃
이제 Android 앱이 다양한 기기 (예: 휴대전화, 태블릿, 폴더블, 데스크톱, 자동차, TV)와 대형 화면의 창 모드 (예: 화면 분할, 데스크톱 창)에서 실행되므로 개발자는 기기 방향과 관계없이 모든 화면 및 창 크기에 적응하는 Android 앱을 빌드해야 합니다. 방향과 크기 조절을 제한하는 것과 같은 패러다임은 오늘날의 멀티 디바이스 세계에서 너무 제한적입니다.
방향, 크기 조절 가능 여부, 가로세로 비율 제한 무시
Android 16 (API 수준 36)을 타겟팅하는 앱의 경우 최소 너비가 600dp 이상인 디스플레이에는 방향, 크기 조절, 가로세로 비율 제한이 더 이상 적용되지 않습니다. 앱이 가로세로 비율이나 사용자가 선호하는 방향과 관계없이 전체 디스플레이 창을 채우고 필러박스는 사용되지 않습니다.
이 변경사항은 새로운 표준 플랫폼 동작을 도입합니다. Android는 앱이 다양한 방향, 디스플레이 크기, 가로세로 비율에 적응해야 하는 모델로 이동하고 있습니다. 고정된 방향이나 제한된 크기 조절 가능 여부와 같은 제한사항은 앱 적응성을 저해합니다. 앱을 적응형으로 만들어 최상의 사용자 환경을 제공하세요.
앱 호환성 프레임워크를 사용하고 UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT 호환성 플래그를 사용 설정하여 이 동작을 테스트할 수도 있습니다.
일반적인 주요 변경사항
방향, 크기 조절 가능 여부, 가로세로 비율 제한을 무시하면 일부 기기에서 앱의 UI에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다. 특히 세로 모드로 잠긴 작은 레이아웃을 위해 설계된 요소의 경우 레이아웃이 늘어나고 화면 밖 애니메이션과 구성요소가 표시되는 등의 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다. 가로세로 비율이나 방향에 관한 가정은 앱에 시각적 문제를 일으킬 수 있습니다. 이러한 문제를 방지하고 앱의 적응형 동작을 개선하는 방법을 자세히 알아보세요.
기기 회전을 허용하면 활동이 더 많이 재생성되므로 제대로 보존되지 않으면 사용자 상태가 손실될 수 있습니다. UI 상태 저장에서 UI 상태를 올바르게 저장하는 방법을 알아보세요.
구현 세부정보
다음 매니페스트 속성과 런타임 API는 전체 화면 및 멀티 윈도우 모드의 대형 화면 기기에서 무시됩니다.
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation(), getRequestedOrientation()의 다음 값은 무시됩니다.
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
디스플레이 크기 조절과 관련하여 android:resizeableActivity="false", android:minAspectRatio, android:maxAspectRatio는 영향을 미치지 않습니다.
Android 16 (API 수준 36)을 타겟팅하는 앱의 경우 기본적으로 대형 화면에서 앱 방향, 크기 조절 가능 여부, 가로세로 비율 제약 조건이 무시되지만 완전히 준비되지 않은 모든 앱은 선택 해제하여 이 동작을 일시적으로 재정의할 수 있습니다 (호환성 모드로 배치되는 이전 동작이 발생함).
예외
다음 상황에서는 Android 16 방향, 크기 조정, 가로세로 비율 제한이 적용되지 않습니다.
- 게임 (
android:appCategory플래그 기반) - 사용자가 기기의 가로세로 비율 설정에서 앱의 기본 동작을 명시적으로 선택하는 경우
sw600dp보다 작은 화면
일시적으로 선택 해제
특정 활동을 선택 해제하려면 PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY 매니페스트 속성을 선언하세요.
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
앱의 너무 많은 부분이 Android 16에 대비되어 있지 않다면 애플리케이션 수준에서 동일한 속성을 적용하여 완전히 선택 해제할 수 있습니다.
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
건강 및 피트니스
Android 16(API 수준 36)에는 건강 및 피트니스 데이터와 관련된 다음과 같은 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
건강 및 피트니스 권한
Android 16 (API 수준 36) 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱의 경우 BODY_SENSORS 권한은 android.permissions.health 아래의 더 세분화된 권한을 사용하며, 이는 헬스 커넥트에서도 사용됩니다. Android 16부터 이전에 BODY_SENSORS 또는 BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND가 필요했던 API에는 대신 해당하는 android.permissions.health 권한이 필요합니다. 이는 다음 데이터 유형, API, 포그라운드 서비스 유형에 영향을 미칩니다.
- Wear OS의 건강 관리 서비스에서
HEART_RATE_BPM - Android 센서 관리자의
Sensor.TYPE_HEART_RATE - Wear OS의
ProtoLayout에서heartRateAccuracy및heartRateBpm FOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTH:BODY_SENSORS대신 해당android.permission.health권한이 필요한 경우
앱이 이러한 API를 사용하는 경우 세부 권한을 요청해야 합니다.
- 심박수, SpO2 또는 피부 온도의 사용 중 모니터링의 경우
BODY_SENSORS대신android.permissions.health아래의 상세 권한(예:READ_HEART_RATE)을 요청합니다. - 백그라운드 센서 액세스의 경우
BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND대신READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUND를 요청합니다.
이러한 권한은 건강, 피트니스, 웰니스 데이터를 위한 Android 데이터 저장소인 헬스 커넥트에서 데이터를 읽는 액세스를 보호하는 권한과 동일합니다.
모바일 앱
READ_HEART_RATE 및 기타 세부 권한을 사용하도록 이전하는 모바일 앱은 앱의 개인정보처리방침을 표시하기 위해 활동을 선언해야 합니다. 이는 헬스 커넥트와 동일한 요구사항입니다.
연결
Android 16(API 수준 36)에는 주변기기와의 연결을 개선하기 위해 블루투스 스택에 다음과 같은 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
연결 해제 및 암호화 변경을 처리하는 새로운 인텐트
연결 손실 처리 개선의 일환으로 Android 16에서는 앱에 연결 손실 및 암호화 변경사항에 대한 더 나은 인식을 제공하는 두 가지 새로운 인텐트를 도입합니다.
이제 Android 16을 타겟팅하는 앱은 다음을 실행할 수 있습니다.
- 원격 결합 손실이 감지되면
ACTION_KEY_MISSING인텐트를 수신하여 더 많은 정보를 제공하는 사용자 의견을 제공하고 적절한 조치를 취할 수 있습니다. - 링크의 암호화 상태가 변경될 때마다
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGE인텐트를 수신합니다. 여기에는 암호화 상태 변경, 암호화 알고리즘 변경, 암호화 키 크기 변경이 포함됩니다. 나중에ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGE인텐트를 수신할 때 연결이 성공적으로 암호화되면 앱은 결합이 복원되었다고 간주해야 합니다.
다양한 OEM 구현에 맞게 조정
Android 16에서는 이러한 새 인텐트를 도입하지만 구현 및 브로드캐스트는 기기 제조업체 (OEM)마다 다를 수 있습니다. 앱이 모든 기기에서 일관되고 안정적인 환경을 제공하려면 개발자는 이러한 잠재적 변형에 원활하게 적응하도록 결합 손실 처리를 설계해야 합니다.
다음과 같은 앱 동작을 권장합니다.
ACTION_KEY_MISSING인텐트가 브로드캐스트되면 다음이 실행됩니다.ACL (비동기 비연결) 링크는 시스템에서 연결 해제되지만 기기의 결합 정보는 유지됩니다 (여기에 설명).
앱은 이 인텐트를 결합 손실 감지의 기본 신호로 사용하고 기기 잊기 또는 재페어링을 시작하기 전에 사용자가 원격 기기가 범위 내에 있는지 확인하도록 안내해야 합니다.
ACTION_KEY_MISSING이 수신된 후 기기가 연결 해제되면 기기가 더 이상 시스템과 결합되지 않을 수 있으므로 앱은 다시 연결하는 데 주의해야 합니다.ACTION_KEY_MISSING인텐트가 브로드캐스트되지 않은 경우:ACL 링크는 연결된 상태로 유지되며 기기의 결합 정보는 Android 15의 동작과 마찬가지로 시스템에서 삭제됩니다.
이 시나리오에서 앱은 이전 Android 버전과 마찬가지로 기존의 결합 손실 처리 메커니즘을 계속 사용하여 결합 손실 이벤트를 감지하고 관리해야 합니다.
블루투스 연결을 삭제하는 새로운 방법
이제 Android 16을 타겟팅하는 모든 앱은 CompanionDeviceManager의 공개 API를 사용하여 블루투스 기기를 페어링 해제할 수 있습니다. 호환 기기가 CDM 연결로 관리되는 경우 앱은 연결된 기기에서 새 removeBond(int) API를 사용하여 블루투스 결합 삭제를 트리거할 수 있습니다. 앱은 블루투스 기기 브로드캐스트 이벤트 ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED를 리슨하여 결합 상태 변경사항을 모니터링할 수 있습니다.
보안
Android 16(API 수준 36)에는 다음과 같은 보안 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
MediaStore 버전 잠금
Android 16 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱의 경우 이제 MediaStore#getVersion()가 각 앱마다 고유합니다. 이렇게 하면 버전 문자열에서 식별 속성이 제거되어 지문 식별 기법의 악용과 사용을 방지할 수 있습니다. 앱은 이 버전의 형식을 가정해서는 안 됩니다. 앱은 이 API를 사용할 때 이미 버전 변경을 처리해야 하며, 개발자가 이 API의 의도된 범위를 벗어난 추가 정보를 추론하려고 시도하지 않는 한 대부분의 경우 현재 동작을 변경할 필요가 없습니다.
더 안전한 인텐트
더 안전한 인텐트 기능은 Android의 인텐트 해결 메커니즘의 보안을 개선하기 위해 설계된 다단계 보안 이니셔티브입니다. 목표는 인텐트 처리 중에 검사를 추가하고 특정 기준을 충족하지 않는 인텐트를 필터링하여 악의적인 행위로부터 앱을 보호하는 것입니다.
Android 15에서 이 기능은 전송 앱에 중점을 두었지만 이제 Android 16에서는 제어를 수신 앱으로 전환하여 개발자가 앱 매니페스트를 사용하여 엄격한 인텐트 해결을 선택할 수 있습니다.
두 가지 주요 변경사항이 구현됩니다.
명시적 인텐트는 타겟 구성요소의 인텐트 필터와 일치해야 합니다. 인텐트가 구성요소를 명시적으로 타겟팅하는 경우 해당 구성요소의 인텐트 필터와 일치해야 합니다.
작업이 없는 인텐트는 인텐트 필터와 일치할 수 없음: 작업이 지정되지 않은 인텐트는 인텐트 필터로 확인되지 않아야 합니다.
이러한 변경사항은 여러 앱이 관련되어 있는 경우에만 적용되며 단일 앱 내의 인텐트 처리에는 영향을 미치지 않습니다.
영향
선택적 특성은 개발자가 앱 매니페스트에서 명시적으로 사용 설정해야 적용된다는 의미입니다. 따라서 이 기능의 영향은 개발자가 다음을 충족하는 앱으로 제한됩니다.
- 더 안전한 인텐트 기능과 그 이점을 알고 있습니다.
- 더 엄격한 인텐트 처리 관행을 앱에 통합하도록 적극적으로 선택합니다.
이 선택 방식은 현재 보안 수준이 낮은 인텐트 해결 동작을 사용할 수 있는 기존 앱이 중단될 위험을 최소화합니다.
Android 16에서의 초기 영향은 제한적일 수 있지만 더 안전한 인텐트 이니셔티브에는 향후 Android 버전에서 더 광범위한 영향을 미치기 위한 로드맵이 있습니다. 궁극적으로는 엄격한 인텐트 해결을 기본 동작으로 만들 계획입니다.
더 안전한 인텐트 기능은 악성 앱이 인텐트 해결 메커니즘의 취약점을 악용하기 어렵게 하여 Android 생태계의 보안을 크게 향상할 수 있습니다.
하지만 선택 해제 및 필수 시행으로의 전환은 기존 앱과의 잠재적인 호환성 문제를 해결하기 위해 신중하게 관리해야 합니다.
구현
개발자는 앱 매니페스트에서 intentMatchingFlags 속성을 사용하여 더 엄격한 인텐트 일치를 명시적으로 사용 설정해야 합니다.
다음은 전체 앱에 대해 기능이 선택되어 있지만 수신기에서 사용 중지/선택 해제된 예입니다.
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
지원되는 플래그에 대한 자세한 내용은 다음을 참고하세요.
| 플래그 이름 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | 수신 인텐트에 더 엄격한 일치를 적용합니다. |
| 없음 | 수신 인텐트의 모든 특수 일치 규칙을 사용 중지합니다. 여러 플래그를 지정할 때 'none' 플래그에 우선순위를 부여하여 충돌하는 값을 해결합니다. |
| allowNullAction | 작업이 없는 인텐트가 일치하도록 일치 규칙을 완화합니다. 특정 동작을 달성하기 위해 'enforceIntentFilter'와 함께 사용되는 플래그 |
테스트 및 디버깅
시행이 활성화된 경우 인텐트 호출자가 인텐트를 올바르게 채웠다면 앱이 올바르게 작동해야 합니다.
하지만 차단된 인텐트는 "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" 및 "Access blocked:"과 같은 경고 로그 메시지를 "PackageManager." 태그와 함께 트리거합니다. 이는 앱에 영향을 미칠 수 있는 잠재적인 문제를 나타내며 주의가 필요합니다.
Logcat 필터:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
GPU syscall 필터링
Mali GPU 노출 영역을 강화하기 위해 지원 중단되었거나 GPU 개발 전용인 Mali GPU IOCTL이 프로덕션 빌드에서 차단되었습니다. 또한 GPU 프로파일링에 사용되는 IOCTL이 셸 프로세스나 디버깅 가능한 애플리케이션으로 제한되었습니다. 플랫폼 수준 정책에 관한 자세한 내용은 SAC 업데이트를 참고하세요.
이 변경사항은 Mali GPU를 사용하는 Pixel 기기 (Pixel 6~9)에서 발생합니다. Arm은 r54p2 출시의 Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst에 IOCTL의 공식 분류를 제공했습니다. 이 목록은 향후 드라이버 출시에서도 계속 유지됩니다.
이 변경사항은 지원되는 그래픽 API (Vulkan 및 OpenGL 포함)에 영향을 미치지 않으며 개발자나 기존 애플리케이션에도 영향을 미치지 않을 것으로 예상됩니다. Streamline Performance Analyzer 및 Android GPU 검사기와 같은 GPU 프로파일링 도구는 영향을 받지 않습니다.
테스트
다음과 유사한 SELinux 거부가 표시되면 이 변경사항이 애플리케이션에 영향을 미쳤을 가능성이 높습니다.
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
애플리케이션에서 차단된 IOCTL을 사용해야 하는 경우 버그를 신고하고 android-partner-security@google.com에 할당하세요.
FAQ
이 정책 변경사항이 모든 OEM에 적용되나요? 이 변경사항은 선택사항이지만 이 강화 방법을 사용하려는 OEM은 사용할 수 있습니다. 변경사항 구현에 관한 안내는 구현 문서를 참고하세요.
이를 구현하기 위해 OEM 코드베이스를 변경해야 하나요? 아니면 기본적으로 새로운 AOSP 출시와 함께 제공되나요? 플랫폼 수준 변경사항은 기본적으로 새로운 AOSP 출시와 함께 제공됩니다. 공급업체는 이 변경사항을 적용하려는 경우 코드베이스에서 선택할 수 있습니다.
SoC가 IOCTL 목록을 최신 상태로 유지해야 하나요? 예를 들어 내 기기에서 ARM Mali GPU를 사용하는 경우 변경사항에 대해 ARM에 문의해야 하나요? 개별 SoC는 드라이버 출시 시 기기별로 IOCTL 목록을 업데이트해야 합니다. 예를 들어 ARM은 드라이버 업데이트 시 게시된 IOCTL 목록을 업데이트합니다. 하지만 OEM은 SEPolicy에 업데이트를 통합하고 필요에 따라 선택한 맞춤 IOCTL을 목록에 추가해야 합니다.
이 변경사항은 판매 중인 모든 Pixel 기기에 자동으로 적용되나요? 아니면 이 변경사항을 적용하려면 사용자가 설정을 전환해야 하나요? 이 변경사항은 Mali GPU를 사용하는 모든 Pixel 시장 내 기기(Pixel 6~9)에 적용됩니다. 이번 변경사항을 적용하기 위해 사용자가 별도로 취해야 할 조치는 없습니다.
이 정책을 사용하면 커널 드라이버의 성능에 영향을 미치나요? 이 정책은 GFXBench를 사용하여 Mali GPU에서 테스트되었으며 GPU 성능에 측정 가능한 변화가 관찰되지 않았습니다.
IOCTL 목록이 현재 사용자 공간 및 커널 드라이버 버전과 일치해야 하나요? 예, 허용된 IOCTL 목록은 사용자 공간과 커널 드라이버 모두에서 지원하는 IOCTL과 동기화되어야 합니다. 사용자 공간이나 커널 드라이버의 IOCTL이 업데이트되면 SEPolicy IOCTL 목록을 업데이트하여 일치시켜야 합니다.
ARM은 IOCTL을 '제한됨'/ '계측'으로 분류했지만 프로덕션 사용 사례에서 일부를 사용하거나 다른 일부를 거부하고 싶습니다. 개별 OEM/SoC는 사용자 공간 Mali 라이브러리 구성에 따라 사용하는 IOCTL을 분류하는 방법을 결정해야 합니다. ARM 목록을 사용하여 이를 결정할 수 있지만 각 OEM/SoC의 사용 사례는 다를 수 있습니다.
개인 정보 보호
Android 16(API 수준 36)에는 다음과 같은 개인 정보 보호 변경사항이 포함되어 있습니다.
로컬 네트워크 권한
LAN에 있는 기기는 INTERNET 권한이 있는 앱에서 액세스할 수 있습니다.
이를 통해 앱이 로컬 기기에 쉽게 연결할 수 있지만 사용자의 지문을 형성하고 위치의 프록시가 되는 등 개인 정보 보호 관련 영향도 있습니다.
로컬 네트워크 보호 프로젝트는 새로운 런타임 권한 뒤에 로컬 네트워크 액세스를 제한하여 사용자의 개인 정보를 보호하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
출시 계획
이 변경사항은 각각 25Q2와 26Q2 두 출시 사이에 배포됩니다. 개발자는 25Q2에 이 안내를 따르고 의견을 공유해야 합니다. 이러한 보호 조치는 향후 Android 출시에서 적용될 예정이기 때문입니다. 또한 다음 안내를 사용하여 암시적 로컬 네트워크 액세스에 의존하는 시나리오를 업데이트하고 사용자의 거부 및 새 권한 취소에 대비해야 합니다.
영향
현재 단계에서 LNP는 선택 기능이므로 선택한 앱에만 영향을 미칩니다. 선택 단계의 목표는 앱 개발자가 앱의 어떤 부분이 암시적 로컬 네트워크 액세스에 의존하는지 파악하여 다음 출시를 위해 권한으로 보호할 수 있도록 하는 것입니다.
다음 방법을 사용하여 사용자의 로컬 네트워크에 액세스하는 앱은 영향을 받습니다.
- 로컬 네트워크 주소 (예: mDNS 또는 SSDP 서비스 검색 프로토콜)에서 원시 소켓을 직접 또는 라이브러리 사용
- 로컬 네트워크에 액세스하는 프레임워크 수준 클래스 사용 (예: NsdManager)
로컬 네트워크 주소로 및 로컬 네트워크 주소에서 전송되는 트래픽에는 로컬 네트워크 액세스 권한이 필요합니다. 다음 표에는 몇 가지 일반적인 사례가 나와 있습니다.
| 앱 하위 수준 네트워크 작업 | 로컬 네트워크 권한 필요 |
|---|---|
| 아웃바운드 TCP 연결 만들기 | 예 |
| 수신 TCP 연결 수락 | 예 |
| UDP 유니캐스트, 멀티캐스트, 브로드캐스트 전송 | 예 |
| 수신 UDP 유니캐스트, 멀티캐스트, 브로드캐스트 수신 | 예 |
이러한 제한사항은 네트워킹 스택 깊숙이 구현되므로 모든 네트워킹 API에 적용됩니다. 여기에는 네이티브 또는 관리 코드에서 생성된 소켓, Cronet 및 OkHttp와 같은 네트워킹 라이브러리, 이러한 라이브러리 위에 구현된 API가 포함됩니다. 로컬 네트워크에서 서비스 (예: .local 접미사가 있는 서비스)를 확인하려면 로컬 네트워크 권한이 필요합니다.
위 규칙의 예외:
- 기기의 DNS 서버가 로컬 네트워크에 있는 경우 포트 53에서 오가는 트래픽에는 로컬 네트워크 액세스 권한이 필요하지 않습니다.
- 출력 전환기를 인앱 선택기로 사용하는 애플리케이션에는 로컬 네트워크 권한이 필요하지 않습니다 (2025년 4분기에 자세한 안내 제공 예정).
개발자 안내 (선택)
로컬 네트워크 제한을 선택하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- 기기를 25Q2 베타 3 이상의 빌드로 플래시합니다.
- 테스트할 앱을 설치합니다.
adb에서 Appcompat 플래그를 전환합니다.
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>기기 재부팅
이제 앱의 로컬 네트워크 액세스가 제한되며 로컬 네트워크에 액세스하려고 하면 소켓 오류가 발생합니다. 앱 프로세스 외부에서 로컬 네트워크 작업을 실행하는 API (예: NsdManager)를 사용하는 경우 선택 단계에서는 영향을 받지 않습니다.
액세스 권한을 복원하려면 앱에 NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES 권한을 부여해야 합니다.
- 앱이 매니페스트에서
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES권한을 선언하는지 확인합니다. - 설정 > 앱 > [애플리케이션 이름] > 권한 > 근처 기기 > 허용으로 이동합니다.
이제 앱의 로컬 네트워크 액세스가 복원되고 모든 시나리오가 앱 선택 전과 같이 작동합니다.
로컬 네트워크 보호 시행이 시작되면 앱 네트워크 트래픽은 다음과 같이 영향을 받습니다.
| 권한 | 아웃바운드 LAN 요청 | 아웃바운드/인바운드 인터넷 요청 | 인바운드 LAN 요청 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 승인됨 | 작동의 원리 | 작동의 원리 | 작동의 원리 |
| 허용되지 않음 | 실패 경험 | 작동의 원리 | 실패 경험 |
다음 명령어를 사용하여 앱 호환성 플래그를 사용 중지합니다.
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
오류
이러한 제한으로 인해 발생하는 오류는 로컬 네트워크 주소에 send 또는 send 변형을 호출할 때마다 호출 소켓에 반환됩니다.
오류 예시:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
로컬 네트워크 정의
이 프로젝트의 로컬 네트워크는 Wi-Fi 또는 이더넷과 같이 브로드캐스트 지원 네트워크 인터페이스를 사용하지만 셀룰러 (WWAN) 또는 VPN 연결은 제외하는 IP 네트워크를 의미합니다.
다음은 로컬 네트워크로 간주됩니다.
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // 링크 로컬
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- 링크-로컬
- 직접 연결된 경로
- 스레드와 같은 스텁 네트워크
- 멀티 서브넷 (미정)
또한 멀티캐스트 주소 (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8)와 IPv4 브로드캐스트 주소 (255.255.255.255)는 모두 로컬 네트워크 주소로 분류됩니다.
앱 소유 사진
Android 16 이상을 실행하는 기기에서 SDK 36 이상을 타겟팅하는 앱에서 사진 및 동영상 권한을 요청하는 메시지가 표시되면 선택한 미디어에 대한 액세스를 제한하는 사용자에게는 앱이 소유한 사진이 사진 선택 도구에서 미리 선택된 상태로 표시됩니다. 사용자는 이러한 사전 선택된 항목을 선택 해제할 수 있으며, 이 경우 앱의 사진 및 동영상 액세스 권한이 취소됩니다.
