Giống như các bản phát hành trước, Android 16 có các thay đổi về hành vi có thể ảnh hưởng đến ứng dụng của bạn. Những thay đổi về hành vi sau đây chỉ áp dụng cho ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16 trở lên. Nếu ứng dụng của bạn nhắm đến Android 16 trở lên, bạn nên điều chỉnh ứng dụng để hỗ trợ những hành vi này (nếu cần).
Ngoài ra, hãy nhớ tham khảo danh sách các thay đổi về hành vi ảnh hưởng đến tất cả ứng dụng chạy trên Android 16 bất kể targetSdkVersion của ứng dụng.
Trải nghiệm người dùng và giao diện người dùng hệ thống
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có những thay đổi sau đây nhằm mang đến trải nghiệm người dùng nhất quán và trực quan hơn.
Chế độ chọn không hiển thị tràn viền sẽ không còn nữa
Android 15 thực thi chế độ hiển thị tràn viền cho các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 15 (API cấp 35), nhưng ứng dụng của bạn có thể chọn không sử dụng bằng cách đặt R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement thành true. Đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16 (API cấp 36), R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement sẽ không được dùng nữa và bị vô hiệu hoá, đồng thời ứng dụng của bạn không thể chọn không hiển thị tràn viền.
- Nếu ứng dụng của bạn nhắm đến Android 16 (API cấp 36) và đang chạy trên một thiết bị Android 15, thì
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementvẫn hoạt động. - Nếu ứng dụng của bạn nhắm đến Android 16 (API cấp 36) và đang chạy trên thiết bị Android 16, thì
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementsẽ bị tắt.
Để kiểm thử trong Android 16, hãy đảm bảo ứng dụng của bạn hỗ trợ chế độ hiển thị tràn viền và xoá mọi hoạt động sử dụng R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement để ứng dụng của bạn cũng hỗ trợ chế độ hiển thị tràn viền trên thiết bị Android 15. Để hỗ trợ chế độ hiển thị tràn viền, hãy xem hướng dẫn về Compose và Khung hiển thị.
Bạn phải di chuyển hoặc chọn không sử dụng tính năng xem trước thao tác quay lại
Đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16 (API cấp 36) trở lên và chạy trên thiết bị Android 16 trở lên, ảnh động hệ thống xem trước thao tác quay lại (quay lại trang chủ, giữa các tác vụ và giữa các hoạt động) sẽ được bật theo mặc định.
Ngoài ra, onBackPressed không được gọi và KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK không còn được gửi đi nữa.
Nếu ứng dụng của bạn chặn sự kiện quay lại và bạn chưa di chuyển sang tính năng xem trước thao tác quay lại, hãy cập nhật ứng dụng để sử dụng các API điều hướng quay lại được hỗ trợ hoặc tạm thời chọn không sử dụng bằng cách đặt thuộc tính android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback thành false trong thẻ <application> hoặc <activity> của tệp AndroidManifest.xml của ứng dụng.
Các API phông chữ Elegant không được dùng nữa và bị vô hiệu hoá
Các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 15 (API cấp 35) có thuộc tính elegantTextHeight
TextView được đặt thành true theo mặc định, thay thế phông chữ nhỏ gọn bằng một phông chữ dễ đọc hơn nhiều. Bạn có thể ghi đè điều này bằng cách đặt thuộc tính elegantTextHeight thành false.
Android 16 không dùng thuộc tính elegantTextHeight nữa và thuộc tính này sẽ bị bỏ qua khi ứng dụng của bạn nhắm đến Android 16. "Phông chữ giao diện người dùng" do các API này kiểm soát sẽ ngừng hoạt động, vì vậy, bạn nên điều chỉnh mọi bố cục để đảm bảo việc hiển thị văn bản nhất quán và không bị ảnh hưởng trong tương lai bằng tiếng Ả Rập, tiếng Lào, tiếng Miến Điện, tiếng Tamil, tiếng Gujarati, tiếng Kannada, tiếng Malayalam, tiếng Odia, tiếng Telugu hoặc tiếng Thái.
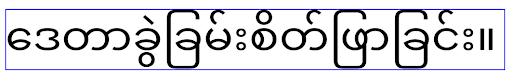 Hành vi
Hành vi elegantTextHeight đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 14 (API cấp 34) trở xuống hoặc đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 15 (API cấp 35) đã ghi đè giá trị mặc định bằng cách đặt thuộc tính elegantTextHeight thành false. Hành vi
Hành vi elegantTextHeight đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16 (API cấp 36) hoặc đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 15 (API cấp 35) không ghi đè giá trị mặc định bằng cách đặt thuộc tính elegantTextHeight thành false.Chức năng cốt lõi
Android 16 (API cấp 36) bao gồm những thay đổi sau đây giúp sửa đổi hoặc mở rộng nhiều chức năng cốt lõi của hệ thống Android.
Tối ưu hoá lịch làm việc theo mức giá cố định
Trước khi nhắm đến Android 16, khi scheduleAtFixedRate bỏ lỡ một lần thực thi tác vụ do nằm ngoài vòng đời quy trình hợp lệ, tất cả các lần thực thi bị bỏ lỡ sẽ thực thi ngay khi ứng dụng quay lại một vòng đời hợp lệ.
Khi nhắm đến Android 16, tối đa một lần thực thi bị bỏ lỡ của scheduleAtFixedRate sẽ được thực thi ngay lập tức khi ứng dụng quay lại một vòng đời hợp lệ. Thay đổi về hành vi này dự kiến sẽ cải thiện hiệu suất của ứng dụng. Kiểm thử hành vi này trong ứng dụng để xem ứng dụng của bạn có bị ảnh hưởng hay không.
Bạn cũng có thể kiểm thử bằng cách sử dụng khung tương thích của ứng dụng và bật cờ tương thích STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS.
Kiểu dáng thiết bị
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có những thay đổi sau đây đối với các ứng dụng khi hiển thị trên thiết bị có màn hình lớn.
Bố cục thích ứng (Adaptive Layouts)
Giờ đây, các ứng dụng Android chạy trên nhiều thiết bị (chẳng hạn như điện thoại, máy tính bảng, thiết bị có thể gập lại, máy tính, ô tô và TV) và các chế độ tạo cửa sổ trên màn hình lớn (chẳng hạn như chế độ chia đôi màn hình và chế độ tạo cửa sổ trên máy tính), nhà phát triển nên tạo các ứng dụng Android thích ứng với mọi kích thước màn hình và cửa sổ, bất kể hướng thiết bị. Các mô hình như hạn chế hướng và khả năng đổi kích thước quá hạn chế trong thế giới đa thiết bị ngày nay.
Bỏ qua các quy định hạn chế về hướng, khả năng đổi kích thước và tỷ lệ khung hình
Đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16 (API cấp 36), các quy tắc hạn chế về hướng, khả năng đổi kích thước và tỷ lệ khung hình sẽ không còn áp dụng trên những màn hình có chiều rộng nhỏ nhất >= 600 dp. Ứng dụng lấp đầy toàn bộ cửa sổ hiển thị, bất kể tỷ lệ khung hình hay hướng mà người dùng muốn và không sử dụng hiệu ứng hòm thư.
Thay đổi này giới thiệu một hành vi tiêu chuẩn mới của nền tảng. Android đang hướng tới một mô hình mà các ứng dụng dự kiến sẽ thích ứng với nhiều hướng, kích thước màn hình và tỷ lệ khung hình. Các quy tắc hạn chế như hướng cố định hoặc khả năng đổi kích thước hạn chế sẽ cản trở khả năng thích ứng của ứng dụng. Giúp ứng dụng của bạn có khả năng thích ứng để mang đến trải nghiệm tốt nhất có thể cho người dùng.
Bạn cũng có thể kiểm thử hành vi này bằng cách sử dụng khung tương thích của ứng dụng và bật cờ tương thích UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT.
Các thay đổi có thể gây lỗi thường gặp
Việc bỏ qua các hạn chế về hướng, khả năng thay đổi kích thước và tỷ lệ khung hình có thể ảnh hưởng đến giao diện người dùng của ứng dụng trên một số thiết bị, đặc biệt là những phần tử được thiết kế cho bố cục nhỏ ở chế độ dọc: ví dụ: các vấn đề như bố cục bị kéo giãn và các thành phần cũng như ảnh động ngoài màn hình. Mọi giả định về tỷ lệ khung hình hoặc hướng đều có thể gây ra vấn đề về hình ảnh cho ứng dụng của bạn. Tìm hiểu thêm về cách tránh những vấn đề này và cải thiện hành vi thích ứng của ứng dụng.
Việc cho phép xoay thiết bị sẽ dẫn đến việc tạo lại nhiều hoạt động hơn, điều này có thể dẫn đến mất trạng thái người dùng nếu không được duy trì đúng cách. Tìm hiểu cách lưu trạng thái giao diện người dùng một cách chính xác trong bài viết Lưu trạng thái giao diện người dùng.
Thông tin chi tiết về việc triển khai
Các thuộc tính tệp kê khai và API thời gian chạy sau đây sẽ bị bỏ qua trên các thiết bị màn hình lớn ở chế độ toàn màn hình và chế độ nhiều cửa sổ:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
Các giá trị sau đây cho screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation() và getRequestedOrientation() sẽ bị bỏ qua:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Về khả năng thay đổi kích thước màn hình, android:resizeableActivity="false", android:minAspectRatio và android:maxAspectRatio không có tác dụng.
Đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16 (API cấp 36), theo mặc định, các quy tắc hạn chế về hướng, khả năng đổi kích thước và tỷ lệ khung hình của ứng dụng sẽ bị bỏ qua trên màn hình lớn, nhưng mọi ứng dụng chưa sẵn sàng hoàn toàn đều có thể tạm thời ghi đè hành vi này bằng cách chọn không sử dụng (dẫn đến hành vi trước đó là được đặt ở chế độ tương thích).
Ngoại lệ
Các hạn chế về hướng, khả năng đổi kích thước và tỷ lệ khung hình của Android 16 không áp dụng trong những trường hợp sau:
- Trò chơi (dựa trên cờ
android:appCategory) - Người dùng chọn sử dụng rõ ràng hành vi mặc định của ứng dụng trong phần cài đặt tỷ lệ khung hình của thiết bị
- Màn hình có kích thước nhỏ hơn
sw600dp
Tạm thời không nhận
Để chọn không sử dụng một hoạt động cụ thể, hãy khai báo thuộc tính PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY của tệp kê khai:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
Nếu có quá nhiều phần trong ứng dụng của bạn chưa sẵn sàng cho Android 16, bạn có thể chọn không tham gia hoàn toàn bằng cách áp dụng cùng một thuộc tính ở cấp ứng dụng:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Sức khoẻ và thể chất
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có các thay đổi sau đây liên quan đến dữ liệu về sức khoẻ và thể dục.
Quyền đối với dữ liệu về sức khoẻ và thể dục
Đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16 (API cấp 36) trở lên, các quyền BODY_SENSORS sử dụng các quyền chi tiết hơn trong android.permissions.health, mà Health Connect cũng sử dụng. Kể từ Android 16, mọi API trước đây yêu cầu quyền BODY_SENSORS hoặc BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND đều yêu cầu quyền android.permissions.health tương ứng. Điều này ảnh hưởng đến các loại dữ liệu, API và loại dịch vụ trên nền trước sau đây:
HEART_RATE_BPMtừ Dịch vụ sức khoẻ trên Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEtừ Trình quản lý cảm biến AndroidheartRateAccuracyvàheartRateBpmtừProtoLayouttrên Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHtrong trường hợp cần có quyềnandroid.permission.healthtương ứng thay choBODY_SENSORS
Nếu sử dụng các API này, ứng dụng của bạn phải yêu cầu các quyền chi tiết tương ứng:
- Đối với hoạt động theo dõi Tần số tim, SpO2 hoặc Nhiệt độ trên da trong khi sử dụng: hãy yêu cầu quyền chi tiết trong
android.permissions.health, chẳng hạn nhưREAD_HEART_RATEthay vìBODY_SENSORS. - Đối với quyền truy cập vào cảm biến ở chế độ nền: hãy yêu cầu
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDthay vìBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
Các quyền này giống như những quyền bảo vệ quyền truy cập để đọc dữ liệu từ Health Connect, kho dữ liệu Android cho dữ liệu về sức khoẻ, hoạt động thể dục và thể chất.
Ứng dụng dành cho thiết bị di động
Các ứng dụng di động di chuyển để sử dụng READ_HEART_RATE và các quyền chi tiết khác cũng phải khai báo một hoạt động để hiển thị chính sách quyền riêng tư của ứng dụng. Đây cũng là yêu cầu đối với Health Connect.
Khả năng kết nối
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có những thay đổi sau đây trong ngăn xếp Bluetooth để cải thiện khả năng kết nối với các thiết bị ngoại vi.
Các ý định mới để xử lý tình trạng mất liên kết và thay đổi chế độ mã hoá
Trong phần Cải thiện khả năng xử lý việc mất liên kết, Android 16 cũng giới thiệu 2 ý định mới để giúp ứng dụng nhận biết rõ hơn về việc mất liên kết và các thay đổi về mã hoá.
Ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16 hiện có thể:
- Nhận ý định
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGkhi phát hiện mất liên kết từ xa, cho phép họ cung cấp ý kiến phản hồi chi tiết hơn cho người dùng và thực hiện các hành động thích hợp. - Nhận ý định
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEbất cứ khi nào trạng thái mã hoá của đường liên kết thay đổi. Điều này bao gồm thay đổi trạng thái mã hoá, thay đổi thuật toán mã hoá và thay đổi kích thước khoá mã hoá. Các ứng dụng phải xem xét việc khôi phục liên kết nếu đường liên kết được mã hoá thành công sau khi nhận được ý địnhACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGE.
Điều chỉnh cho phù hợp với nhiều cách triển khai của nhà sản xuất thiết bị gốc (OEM)
Mặc dù Android 16 giới thiệu các ý định mới này, nhưng cách triển khai và truyền tin của các ý định này có thể khác nhau tuỳ theo nhà sản xuất thiết bị gốc (OEM). Để đảm bảo ứng dụng của bạn mang lại trải nghiệm nhất quán và đáng tin cậy trên tất cả thiết bị, nhà phát triển nên thiết kế cách xử lý việc mất liên kết để thích ứng linh hoạt với những biến thể tiềm ẩn này.
Bạn nên áp dụng các hành vi sau đây cho ứng dụng:
Nếu ý định
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGđược truyền tin:Hệ thống sẽ ngắt kết nối liên kết ACL (Không có kết nối không đồng bộ), nhưng thông tin liên kết cho thiết bị sẽ được giữ lại (như mô tả tại đây).
Ứng dụng của bạn nên sử dụng ý định này làm tín hiệu chính để phát hiện mất liên kết và hướng dẫn người dùng xác nhận thiết bị từ xa nằm trong phạm vi trước khi bắt đầu quên thiết bị hoặc ghép nối lại.
Nếu một thiết bị ngắt kết nối sau khi nhận được
ACTION_KEY_MISSING, thì ứng dụng của bạn nên thận trọng khi kết nối lại, vì thiết bị có thể không còn liên kết với hệ thống nữa.Nếu ý định
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGKHÔNG được truyền tin:Đường liên kết ACL sẽ vẫn được kết nối và hệ thống sẽ xoá thông tin liên kết cho thiết bị, tương tự như hành vi trong Android 15.
Trong trường hợp này, ứng dụng của bạn sẽ tiếp tục các cơ chế xử lý mất liên kết hiện có như trong các bản phát hành Android trước, để phát hiện và quản lý các sự kiện mất liên kết.
Cách mới để xoá mối liên kết Bluetooth
Giờ đây, tất cả ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16 đều có thể huỷ ghép nối thiết bị Bluetooth bằng cách sử dụng API công khai trong CompanionDeviceManager. Nếu một thiết bị đồng hành đang được quản lý dưới dạng liên kết CDM, thì ứng dụng có thể kích hoạt việc xoá liên kết Bluetooth bằng cách sử dụng API removeBond(int) mới trên thiết bị được liên kết. Ứng dụng có thể theo dõi các thay đổi về trạng thái liên kết bằng cách nghe sự kiện truyền tin của thiết bị Bluetooth ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
Bảo mật
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có những thay đổi sau đây về bảo mật.
Khoá phiên bản MediaStore
Đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 16 trở lên, MediaStore#getVersion() hiện sẽ là duy nhất cho mỗi ứng dụng. Điều này giúp loại bỏ các thuộc tính nhận dạng khỏi chuỗi phiên bản để ngăn chặn việc lợi dụng và sử dụng cho các kỹ thuật tạo vân tay số. Ứng dụng không được đưa ra bất kỳ giả định nào về định dạng của phiên bản này. Các ứng dụng phải xử lý các thay đổi về phiên bản khi sử dụng API này và trong hầu hết các trường hợp, không cần thay đổi hành vi hiện tại, trừ phi nhà phát triển đã cố gắng suy luận thêm thông tin nằm ngoài phạm vi dự kiến của API này.
Ý định an toàn hơn
Safer Intents là một sáng kiến bảo mật nhiều giai đoạn được thiết kế để cải thiện tính bảo mật của cơ chế phân giải ý định của Android. Mục tiêu là bảo vệ ứng dụng khỏi các hành động độc hại bằng cách thêm các bước kiểm tra trong quá trình xử lý ý định và lọc những ý định không đáp ứng các tiêu chí cụ thể.
Trong Android 15, tính năng này tập trung vào ứng dụng gửi. Giờ đây, với Android 16, tính năng này chuyển quyền kiểm soát sang ứng dụng nhận, cho phép nhà phát triển chọn sử dụng tính năng phân giải ý định nghiêm ngặt bằng tệp kê khai ứng dụng của họ.
Chúng tôi sẽ triển khai 2 thay đổi chính:
Ý định tường minh phải khớp với bộ lọc ý định của thành phần đích: Nếu một ý định nhắm đến một thành phần một cách tường minh, thì ý định đó phải khớp với bộ lọc ý định của thành phần đó.
Ý định không có hành động không thể khớp với bất kỳ bộ lọc ý định nào: Những ý định không chỉ định hành động sẽ không được phân giải thành bất kỳ bộ lọc ý định nào.
Những thay đổi này chỉ áp dụng khi có nhiều ứng dụng liên quan và không ảnh hưởng đến việc xử lý ý định trong một ứng dụng duy nhất.
Tác động
Bản chất của việc chọn sử dụng có nghĩa là nhà phát triển phải bật tính năng này một cách rõ ràng trong tệp kê khai ứng dụng để tính năng có hiệu lực. Do đó, tác động của tính năng này sẽ chỉ giới hạn ở những ứng dụng mà nhà phát triển:
- Biết về tính năng Ý định an toàn hơn và lợi ích của tính năng này.
- Chủ động chọn áp dụng các phương pháp xử lý ý định nghiêm ngặt hơn vào ứng dụng của họ.
Phương pháp chọn tham gia này giúp giảm thiểu nguy cơ làm hỏng các ứng dụng hiện có có thể dựa vào hành vi phân giải ý định kém an toàn hiện tại.
Mặc dù tác động ban đầu trong Android 16 có thể bị hạn chế, nhưng Sáng kiến Safer Intents (Ý định an toàn hơn) có một lộ trình để mang lại tác động rộng hơn trong các bản phát hành Android trong tương lai. Kế hoạch là cuối cùng sẽ đặt độ phân giải ý định nghiêm ngặt làm hành vi mặc định.
Tính năng Safer Intents có khả năng cải thiện đáng kể tính bảo mật của hệ sinh thái Android bằng cách khiến các ứng dụng độc hại khó khai thác các lỗ hổng trong cơ chế phân giải ý định hơn.
Tuy nhiên, bạn phải quản lý cẩn thận quá trình chuyển đổi sang lựa chọn không tham gia và biện pháp thực thi bắt buộc để giải quyết các vấn đề có thể xảy ra về khả năng tương thích với các ứng dụng hiện có.
Triển khai
Nhà phát triển cần bật rõ ràng tính năng so khớp ý định nghiêm ngặt hơn bằng cách sử dụng thuộc tính intentMatchingFlags trong tệp kê khai ứng dụng.
Sau đây là ví dụ về trường hợp tính năng này được chọn tham gia cho toàn bộ ứng dụng, nhưng bị tắt/chọn không tham gia trên một receiver:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
Thông tin thêm về các cờ được hỗ trợ:
| Tên cờ | Mô tả |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Thực thi tính năng so khớp nghiêm ngặt hơn cho các ý định đến |
| không có | Tắt tất cả các quy tắc so khớp đặc biệt cho các ý định đến. Khi chỉ định nhiều cờ, các giá trị xung đột sẽ được giải quyết bằng cách ưu tiên cờ "none" |
| allowNullAction | Nới lỏng các quy tắc so khớp để cho phép các ý định không có hành động trùng khớp. Cờ này được dùng cùng với "enforceIntentFilter" để đạt được một hành vi cụ thể |
Kiểm thử và gỡ lỗi
Khi quy trình thực thi đang hoạt động, các ứng dụng sẽ hoạt động bình thường nếu phương thức gọi ý định đã điền đúng ý định.
Tuy nhiên, các ý định bị chặn sẽ kích hoạt thông báo nhật ký cảnh báo như "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" và "Access blocked:" bằng thẻ "PackageManager.". Điều này cho thấy một vấn đề tiềm ẩn có thể ảnh hưởng đến ứng dụng và cần được chú ý.
Bộ lọc Logcat:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
Lọc lệnh gọi hệ thống GPU
Để tăng cường bảo mật cho bề mặt GPU Mali, các IOCTL GPU Mali đã ngừng hoạt động hoặc chỉ dành cho việc phát triển GPU đã bị chặn trong các bản dựng phát hành công khai. Ngoài ra, các IOCTL được dùng để lập hồ sơ GPU đã bị hạn chế đối với quy trình shell hoặc các ứng dụng có thể gỡ lỗi. Hãy tham khảo thông tin cập nhật về SAC để biết thêm thông tin về chính sách ở cấp nền tảng.
Thay đổi này diễn ra trên các thiết bị Pixel sử dụng GPU Mali (Pixel 6 – 9). Arm đã cung cấp danh mục chính thức về các IOCTL trong Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst của bản phát hành r54p2. Danh sách này sẽ tiếp tục được duy trì trong các bản phát hành trình điều khiển trong tương lai.
Thay đổi này không ảnh hưởng đến các API đồ hoạ được hỗ trợ (bao gồm cả Vulkan và OpenGL), đồng thời không ảnh hưởng đến nhà phát triển hoặc các ứng dụng hiện có. Các công cụ lập hồ sơ GPU như Streamline Performance Analyzer và Android GPU Inspector sẽ không bị ảnh hưởng.
Thử nghiệm
Nếu bạn thấy một thông báo từ chối SELinux tương tự như sau, thì có thể ứng dụng của bạn đã chịu ảnh hưởng của thay đổi này:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
Nếu ứng dụng của bạn cần sử dụng các IOCTL bị chặn, vui lòng báo cáo lỗi và chỉ định lỗi đó cho android-partner-security@google.com.
Câu hỏi thường gặp
Thay đổi chính sách này có áp dụng cho tất cả các OEM không? Thay đổi này sẽ là lựa chọn không bắt buộc, nhưng có sẵn cho mọi OEM muốn sử dụng phương thức tăng cường này. Bạn có thể xem hướng dẫn triển khai thay đổi trong tài liệu triển khai.
Tôi có bắt buộc phải thay đổi cơ sở mã của OEM để triển khai tính năng này hay tính năng này có trong bản phát hành AOSP mới theo mặc định không? Theo mặc định, thay đổi ở cấp nền tảng sẽ đi kèm với một bản phát hành AOSP mới. Các nhà cung cấp có thể chọn áp dụng thay đổi này trong cơ sở mã của họ nếu muốn.
SoC có chịu trách nhiệm cập nhật danh sách IOCTL không? Ví dụ: nếu thiết bị của tôi sử dụng GPU ARM Mali, thì tôi có cần liên hệ với ARM để yêu cầu thay đổi không? Từng SoC phải cập nhật danh sách IOCTL cho mỗi thiết bị khi phát hành trình điều khiển. Ví dụ: ARM sẽ cập nhật danh sách IOCTL đã xuất bản khi có bản cập nhật trình điều khiển. Tuy nhiên, các OEM phải đảm bảo rằng họ kết hợp các bản cập nhật trong SEPolicy và thêm mọi IOCTL tuỳ chỉnh đã chọn vào danh sách nếu cần.
Thay đổi này có tự động áp dụng cho tất cả thiết bị Pixel đang bán trên thị trường không, hay người dùng cần thực hiện thao tác để bật/tắt một chế độ nào đó nhằm áp dụng thay đổi này? Thay đổi này áp dụng cho tất cả thiết bị Pixel đang bán trên thị trường sử dụng GPU Mali (Pixel 6 – 9). Người dùng không cần làm gì để áp dụng thay đổi này.
Việc sử dụng chính sách này có ảnh hưởng đến hiệu suất của trình điều khiển nhân không? Chính sách này đã được kiểm thử trên GPU Mali bằng GFXBench và không có thay đổi nào đáng kể về hiệu suất GPU.
Có cần thiết phải điều chỉnh danh sách IOCTL cho phù hợp với phiên bản trình điều khiển hạt nhân và không gian người dùng hiện tại không? Có, danh sách IOCTL được phép phải được đồng bộ hoá với IOCTL mà cả không gian người dùng và trình điều khiển nhân đều hỗ trợ. Nếu IOCTL trong không gian người dùng hoặc trình điều khiển hạt nhân được cập nhật, thì danh sách IOCTL SEPolicy cũng phải được cập nhật cho phù hợp.
ARM đã phân loại IOCTL là "bị hạn chế" / "đo lường", nhưng chúng tôi muốn sử dụng một số IOCTL trong các trường hợp sử dụng thực tế và/hoặc từ chối những IOCTL khác. Từng OEM/SoC chịu trách nhiệm quyết định cách phân loại các IOCTL mà họ sử dụng, dựa trên cấu hình của các thư viện Mali trong không gian người dùng. Bạn có thể sử dụng danh sách của ARM để quyết định về những vấn đề này, nhưng trường hợp sử dụng của mỗi OEM/SoC có thể khác nhau.
Quyền riêng tư
Android 16 (API cấp 36) có những thay đổi sau đây về quyền riêng tư.
Quyền truy cập mạng cục bộ
Mọi ứng dụng có quyền INTERNET đều có thể truy cập vào các thiết bị trên mạng LAN.
Điều này giúp các ứng dụng dễ dàng kết nối với các thiết bị cục bộ, nhưng cũng gây ra những vấn đề về quyền riêng tư
, chẳng hạn như tạo dấu vân tay của người dùng và đóng vai trò là proxy cho
vị trí.
Dự án Bảo vệ mạng cục bộ (LNP) nhằm mục đích bảo vệ quyền riêng tư của người dùng bằng cách kiểm soát quyền truy cập vào mạng cục bộ thông qua một quyền mới trong thời gian chạy.
Kế hoạch phát hành
Thay đổi này sẽ được triển khai giữa hai bản phát hành, 25Q2 và 26Q2 lần lượt. Nhà phát triển bắt buộc phải làm theo hướng dẫn này cho 25Q2 và chia sẻ ý kiến phản hồi vì các biện pháp bảo vệ này sẽ được thực thi trong một bản phát hành Android sau này. Hơn nữa, họ sẽ cần cập nhật các tình huống phụ thuộc vào quyền truy cập ngầm ẩn vào mạng cục bộ bằng cách làm theo hướng dẫn sau đây và chuẩn bị cho trường hợp người dùng từ chối và thu hồi quyền mới.
Tác động
Ở giai đoạn hiện tại, LNP là một tính năng chọn tham gia, nghĩa là chỉ những ứng dụng chọn tham gia mới bị ảnh hưởng. Mục tiêu của giai đoạn chọn tham gia là để nhà phát triển ứng dụng hiểu được những phần nào của ứng dụng phụ thuộc vào quyền truy cập ngầm ẩn vào mạng cục bộ để họ có thể chuẩn bị bảo vệ quyền cho bản phát hành tiếp theo.
Các ứng dụng sẽ bị ảnh hưởng nếu truy cập vào mạng cục bộ của người dùng bằng:
- Sử dụng trực tiếp hoặc sử dụng thư viện các ổ cắm thô trên địa chỉ mạng cục bộ (ví dụ: giao thức khám phá dịch vụ mDNS hoặc SSDP)
- Sử dụng các lớp cấp khung truy cập vào mạng cục bộ (ví dụ: NsdManager)
Lưu lượng truy cập đến và từ một địa chỉ mạng cục bộ yêu cầu quyền truy cập mạng cục bộ. Bảng sau đây liệt kê một số trường hợp phổ biến:
| Hoạt động mạng cấp thấp của ứng dụng | Quyền truy cập mạng cục bộ bắt buộc |
|---|---|
| Tạo kết nối TCP đi | có |
| Chấp nhận kết nối TCP đến | có |
| Gửi một gói đơn hướng, đa hướng, quảng bá UDP | có |
| Nhận một gói đơn hướng, đa hướng, quảng bá UDP đến | có |
Các quy định hạn chế này được triển khai sâu trong ngăn xếp mạng, do đó, chúng áp dụng cho tất cả các API mạng. Điều này bao gồm các ổ cắm được tạo trong mã gốc hoặc mã được quản lý, các thư viện mạng như Cronet và OkHttp, cũng như mọi API được triển khai trên các thư viện đó. Việc cố gắng phân giải các dịch vụ trên mạng cục bộ (tức là những dịch vụ có hậu tố .local) sẽ yêu cầu quyền truy cập mạng cục bộ.
Các trường hợp ngoại lệ đối với các quy tắc ở trên:
- Nếu máy chủ DNS của thiết bị nằm trên mạng cục bộ, thì lưu lượng truy cập đến hoặc từ máy chủ đó (ở cổng 53) không yêu cầu quyền truy cập mạng cục bộ.
- Các ứng dụng sử dụng Trình chuyển đổi đầu ra làm trình chọn trong ứng dụng sẽ không cần quyền truy cập mạng cục bộ (sẽ có thêm hướng dẫn trong quý 4 năm 2025).
Hướng dẫn cho nhà phát triển (Chọn tham gia)
Để chọn tham gia các quy định hạn chế mạng cục bộ, hãy làm như sau:
- Cài đặt bản dựng có Beta 3 của 25Q2 trở lên vào thiết bị.
- Cài đặt ứng dụng cần kiểm thử.
Bật/tắt cờ Appcompat trong adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Khởi động lại thiết bị
Giờ đây, quyền truy cập của ứng dụng vào mạng cục bộ bị hạn chế và mọi nỗ lực truy cập vào mạng cục bộ sẽ dẫn đến lỗi ổ cắm. Nếu bạn đang sử dụng các API thực hiện các hoạt động mạng cục bộ bên ngoài quy trình ứng dụng (ví dụ: NsdManager), thì các API đó sẽ không bị ảnh hưởng trong giai đoạn chọn tham gia.
Để khôi phục quyền truy cập, bạn phải cấp cho ứng dụng quyền NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- Đảm bảo ứng dụng khai báo quyền
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICEStrong tệp kê khai. - Chuyển đến phần Cài đặt > Ứng dụng > [Tên ứng dụng] > Quyền > Thiết bị ở gần > Cho phép.
Giờ đây, quyền truy cập của ứng dụng vào mạng cục bộ sẽ được khôi phục và tất cả các tình huống của bạn sẽ hoạt động như trước khi chọn tham gia ứng dụng.
Sau khi việc thực thi biện pháp bảo vệ mạng cục bộ bắt đầu, lưu lượng truy cập mạng của ứng dụng sẽ bị ảnh hưởng như sau.
| Quyền | Yêu cầu LAN đi | Yêu cầu Internet đi/đến | Yêu cầu LAN đến |
|---|---|---|---|
| Đã cấp | Works | Works | Works |
| Không được cấp | Thất bại | Works | Thất bại |
Sử dụng lệnh sau để tắt cờ Tương thích ứng dụng
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Lỗi
Các lỗi phát sinh từ những quy định hạn chế này sẽ được trả về cho ổ cắm gọi bất cứ khi nào ổ cắm đó gọi lệnh gửi hoặc một biến thể gửi đến địa chỉ mạng cục bộ.
Ví dụ về lỗi:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Định nghĩa mạng cục bộ
Mạng cục bộ trong dự án này đề cập đến một mạng IP sử dụng giao diện mạng có khả năng quảng bá, chẳng hạn như Wi-Fi hoặc Ethernet, nhưng không bao gồm các kết nối di động (WWAN) hoặc VPN.
Sau đây được coi là mạng cục bộ:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Liên kết cục bộ
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Liên kết cục bộ
- Các tuyến được kết nối trực tiếp
- Các mạng gốc như Thread
- Nhiều mạng con (TBD)
Ngoài ra, cả địa chỉ đa hướng (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) và địa chỉ quảng bá IPv4 (255.255.255.255) đều được phân loại là địa chỉ mạng cục bộ.
Ảnh thuộc về ứng dụng
Khi một ứng dụng nhắm đến SDK 36 trở lên yêu cầu quyền truy cập vào ảnh và video trên các thiết bị chạy Android 16 trở lên, những người dùng chọn giới hạn quyền truy cập vào nội dung nghe nhìn đã chọn sẽ thấy mọi ảnh do ứng dụng sở hữu được chọn trước trong công cụ chọn ảnh. Người dùng có thể bỏ chọn bất kỳ mục nào trong số các mục được chọn trước này. Thao tác này sẽ thu hồi quyền truy cập của ứng dụng vào những ảnh và video đó.
