كما هو الحال في الإصدارات السابقة، يتضمّن Android 16 تغييرات في السلوك قد تؤثّر في تطبيقك. تنطبق تغييرات السلوك التالية حصريًا على التطبيقات التي تستهدف Android 16 أو الإصدارات الأحدث. إذا كان تطبيقك يستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android أو الإصدارات الأحدث، عليك تعديل تطبيقك ليتوافق مع هذه السلوكيات، حيثما ينطبق ذلك.
احرص أيضًا على مراجعة قائمة التغييرات في السلوك التي تؤثر في جميع التطبيقات
التي تعمل على Android 16 بغض النظر عن targetSdkVersion لتطبيقك.
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية التي تهدف إلى توفير تجربة مستخدم أكثر اتساقًا وسهولة.
إيقاف مشاركة البيانات الشخصية في وضع ملء الشاشة
فرض Android 15 عرض التطبيقات من الحافة إلى الحافة للتطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، ولكن يمكن لتطبيقك إيقاف هذه الميزة من خلال ضبط R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement على true. بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، تم إيقاف R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement نهائيًا، ولا يمكن لتطبيقك إيقاف ميزة "العرض حتى حافة الشاشة".
- إذا كان تطبيقك يستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) ويعمل على جهاز Android 15، سيستمر عمل
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement. - إذا كان تطبيقك يستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) ويعمل على جهاز Android 16، سيتم إيقاف
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement.
لإجراء الاختبار على Android 16، تأكَّد من أنّ تطبيقك يتوافق مع وضع ملء الشاشة، وأزِل أي استخدام للرمز R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement لكي يتوافق تطبيقك أيضًا مع وضع ملء الشاشة على جهاز Android 15. للاستفادة من ميزة "من الحافة إلى الحافة"، اطّلِع على إرشادات Compose وViews.
يجب نقل البيانات أو إيقاف ميزة "الرجوع التوقّعي"
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأحدث وتعمل على جهاز Android 16 أو إصدار أحدث، يتم تفعيل الصور المتحركة التلقائية لنظام الرجوع التوقّعي (الرجوع إلى الشاشة الرئيسية والتنقّل بين المهام والتنقّل بين الأنشطة).
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، لا يتم استدعاء onBackPressed ولا يتم إرسال KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK بعد الآن.
إذا كان تطبيقك يعترض حدث الرجوع ولم تنتقل بعد إلى ميزة "الرجوع التوقّعي"، عليك تعديل تطبيقك لاستخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المتوافقة مع ميزة "الرجوع"، أو إيقاف الميزة مؤقتًا من خلال ضبط السمة android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback على false في العلامة <application> أو <activity> من ملف AndroidManifest.xml الخاص بتطبيقك.
إيقاف واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الخاصة بالخطوط الأنيقة نهائيًا
في التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، يتم ضبط السمة
elegantTextHeight
TextView على القيمة true تلقائيًا، ما يؤدي إلى استبدال الخط المضغوط بخط أكثر قابلية للقراءة. يمكنك إلغاء هذا الإعداد من خلال ضبط السمة elegantTextHeight على false.
في الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android، سيتم إيقاف السمة
elegantTextHeight،
وسيتم تجاهل السمة عندما يستهدف تطبيقك الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android. سيتم إيقاف "خطوط واجهة المستخدم" التي تتحكّم فيها واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه، لذا عليك تعديل أي تخطيطات لضمان عرض النص بشكل متسق ومناسب للمستقبل باللغات العربية أو اللاوية أو البورمية أو التاميلية أو الغوجاراتية أو الكنادية أو المالايالامية أو الأودية أو التيلوغوية أو التايلاندية.
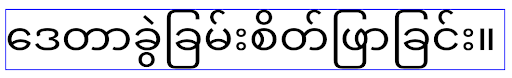 سلوك
سلوك elegantTextHeight للتطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 14 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 34 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأقدم، أو للتطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والتي تم فيها تجاهل الإعداد التلقائي من خلال ضبط السمة elegantTextHeight على false. سلوك
سلوك elegantTextHeight للتطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، أو للتطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والتي لم
تتجاوز الإعداد التلقائي من خلال ضبط السمة elegantTextHeight
على false.الوظيفة الأساسية
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية التي تعدّل أو توسّع العديد من الإمكانات الأساسية لنظام التشغيل Android.
تحسين جدولة العمل بمعدّل ثابت
قبل استهداف الإصدار 16 من Android، عندما يفوت scheduleAtFixedRate
تنفيذ مهمة بسبب عدم التزامه بدورة حياة
صالحة للعمليات، يتم تنفيذ جميع عمليات التنفيذ الفائتة
على الفور عند عودة التطبيق إلى دورة حياة صالحة.
عند استهداف Android 16، يتم تنفيذ مرة واحدة على الأكثر من عملية تنفيذ
scheduleAtFixedRate الفائتة على الفور عندما يعود التطبيق
إلى دورة حياة صالحة. من المتوقّع أن يؤدي تغيير السلوك هذا إلى تحسين أداء التطبيق. يمكنك اختبار هذا السلوك في تطبيقك لمعرفة ما إذا كان تطبيقك متأثرًا.
يمكنك أيضًا إجراء الاختبار باستخدام إطار عمل توافق التطبيقات
وتفعيل علامة التوافق STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS.
أشكال الأجهزة
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية للتطبيقات عند عرضها على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة.
التنسيقات التكيّفية
بما أنّ تطبيقات Android تعمل الآن على مجموعة متنوعة من الأجهزة (مثل الهواتف والأجهزة اللوحية والأجهزة القابلة للطي وأجهزة الكمبيوتر والسيارات وأجهزة التلفزيون) وأوضاع عرض المحتوى في النافذة الحالية على الشاشات الكبيرة (مثل وضع تقسيم الشاشة والعرض في نافذة)، على المطوّرين إنشاء تطبيقات Android تتكيّف مع أي حجم للشاشة والنافذة، بغض النظر عن اتجاه الجهاز. إنّ نماذج التصميم، مثل حصر الاتجاه وإمكانية تغيير الحجم، أصبحت مقيّدة جدًا في عالم اليوم الذي يضم أجهزة متعددة.
تجاهُل قيود الاتجاه وإمكانية تغيير الحجم ونسبة العرض إلى الارتفاع
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، لن تنطبق قيود الاتجاه وتغيير الحجم ونسبة العرض إلى الارتفاع على الشاشات التي يبلغ عرضها الأصغر 600 وحدة بكسل مستقلة الكثافة (dp) أو أكثر. تملأ التطبيقات نافذة العرض بأكملها، بغض النظر عن نسبة العرض إلى الارتفاع أو الاتجاه المفضّل لدى المستخدم، ولا يتم استخدام وضع "العمودين الجانبيين".
يقدّم هذا التغيير سلوكًا جديدًا موحّدًا للمنصة. يتجه نظام التشغيل Android نحو نموذج يُتوقّع فيه أن تتكيّف التطبيقات مع مختلف الاتجاهات وأحجام العرض ونِسب العرض إلى الارتفاع. فالقيود، مثل الاتجاه الثابت أو إمكانية تغيير الحجم المحدودة، تعيق قدرة التطبيق على التكيّف. اجعل تطبيقك قابلاً للتكيّف لتقديم أفضل تجربة مستخدم ممكنة.
يمكنك أيضًا اختبار هذا السلوك باستخدام
اختبار توافق التطبيقات وتفعيل
علامة التوافق UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT.
التغييرات الشائعة التي قد تؤدي إلى أعطال
قد يؤدي تجاهل قيود الاتجاه وإمكانية تغيير الحجم ونسبة العرض إلى الارتفاع إلى التأثير في واجهة المستخدم لتطبيقك على بعض الأجهزة، خاصةً العناصر المصمَّمة للتنسيقات الصغيرة التي تكون في الوضع العمودي فقط، مثل المشاكل المتعلقة بالتنسيقات الممدودة والرسوم المتحركة والمكوّنات التي تظهر خارج الشاشة. يمكن أن تتسبّب أي افتراضات بشأن نسبة العرض إلى الارتفاع أو اتجاه الشاشة في حدوث مشاكل مرئية في تطبيقك. مزيد من المعلومات حول كيفية تجنُّب هذه المشاكل وتحسين السلوك التكيّفي لتطبيقك
يؤدي السماح بتدوير الجهاز إلى إعادة إنشاء المزيد من الأنشطة، ما قد يؤدي إلى فقدان حالة المستخدم إذا لم يتم الاحتفاظ بها بشكل صحيح. تعرَّف على كيفية حفظ حالة واجهة المستخدم بشكل صحيح في مقالة حفظ حالات واجهة المستخدم.
تفاصيل التنفيذ
يتم تجاهل سمات البيان وواجهات برمجة التطبيقات لوقت التشغيل التالية على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة في وضعَي ملء الشاشة والنوافذ المتعددة:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
يتم تجاهل القيم التالية الخاصة بـ screenOrientation وsetRequestedOrientation() وgetRequestedOrientation():
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
في ما يتعلق بإمكانية تغيير حجم شاشة العرض، ليس هناك أي تأثير على android:resizeableActivity="false" وandroid:minAspectRatio وandroid:maxAspectRatio.
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار Android 16 (المستوى 36 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، يتم تلقائيًا تجاهل قيود اتجاه التطبيق وإمكانية تغيير حجمه ونسبة العرض إلى الارتفاع على الشاشات الكبيرة، ولكن يمكن لكل تطبيق غير جاهز تمامًا إلغاء هذا السلوك مؤقتًا من خلال إيقافه (ما يؤدي إلى السلوك السابق المتمثل في وضعه في وضع التوافق).
الاستثناءات
لا تنطبق قيود الاتجاه وتغيير الحجم ونسبة العرض إلى الارتفاع في نظام التشغيل Android 16 في الحالات التالية:
- الألعاب (استنادًا إلى علامة
android:appCategory) - المستخدمون الذين يوافقون صراحةً على السلوك التلقائي للتطبيق في إعدادات نسبة العرض إلى الارتفاع على الجهاز
- الشاشات التي يقل حجمها عن
sw600dp
إيقاف الميزة مؤقتًا
لإيقاف نشاط معيّن، عليك تعريف السمة
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY في ملف البيان:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
إذا لم تكن أجزاء كثيرة من تطبيقك جاهزة لنظام التشغيل Android 16، يمكنك إيقاف هذه الميزة تمامًا من خلال تطبيق السمة نفسها على مستوى التطبيق:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
الصحة واللياقة البدنية
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية المتعلّقة ببيانات الصحة واللياقة البدنية.
أذونات الصحة واللياقة البدنية
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأحدث، تستخدم أذونات
BODY_SENSORS أذونات أكثر دقة
ضمن android.permissions.health، والتي يستخدمها أيضًا Health Connect. اعتبارًا من الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android، أي واجهة برمجة تطبيقات كانت تتطلّب في السابق BODY_SENSORS
أو BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND أصبحت تتطلّب الإذن المقابل android.permissions.health بدلاً من ذلك. يؤثّر ذلك في أنواع البيانات وواجهات برمجة التطبيقات وأنواع الخدمات التي تعمل في المقدّمة التالية:
HEART_RATE_BPMمن "خدمات الصحة" على Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEمن "إدارة أجهزة الاستشعار في Android"heartRateAccuracyوheartRateBpmمنProtoLayoutعلى Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHحيث يجب منح الإذنandroid.permission.healthبدلاً منBODY_SENSORS
إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه، يجب أن يطلب الأذونات الدقيقة ذات الصلة:
- للمراقبة أثناء الاستخدام لمعدّل نبضات القلب أو نسبة الأكسجين بالدم أو درجة حرارة الجلد، اطلب الإذن الدقيق ضمن
android.permissions.health، مثلREAD_HEART_RATEبدلاً منBODY_SENSORS. - للوصول إلى أجهزة الاستشعار في الخلفية، استخدِم
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDبدلاً منBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
وهذه الأذونات هي نفسها التي تحمي إمكانية قراءة البيانات من Health Connect، وهو مستودع بيانات Android الخاص ببيانات الصحة واللياقة البدنية والعافية.
التطبيقات المتوافقة مع الأجهزة الجوّالة
يجب أيضًا أن تحدّد التطبيقات التي يتم نقلها لاستخدام الإذن READ_HEART_RATE والأذونات الأخرى الدقيقة نشاطًا لعرض سياسة الخصوصية الخاصة بالتطبيق. هذا هو الشرط نفسه الذي ينطبق على Health Connect.
إمكانية الاتصال
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) التغييرات التالية في حزمة بروتوكول البلوتوث لتحسين الاتصال بالأجهزة الطرفية.
أهداف جديدة للتعامل مع فقدان الربط والتغييرات في التشفير
كجزء من المعالجة المحسّنة لفقدان الربط، يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 16 أيضًا هدفَين جديدَين لمنح التطبيقات وعيًا أكبر بفقدان الربط وتغييرات التشفير.
يمكن للتطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 16 من Android الآن تنفيذ ما يلي:
- تلقّي نية
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGعند رصد فقدان الربط عن بُعد ، ما يتيح لهم تقديم ملاحظات أكثر إفادة للمستخدمين واتّخاذ الإجراءات المناسبة - تلقّي نية
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEعند تغيير حالة التشفير للرابط ويشمل ذلك تغيير حالة التشفير وتغيير خوارزمية التشفير وتغيير حجم مفتاح التشفير. يجب أن تُعتبر التطبيقات قد أعادت الربط إذا تم تشفير الرابط بنجاح عند تلقّيACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEintent لاحقًا.
التكيّف مع عمليات التنفيذ المختلفة التي يجريها المصنّعون الأصليون للأجهزة
على الرغم من أنّ الإصدار 16 من Android يقدّم هذه النوايا الجديدة، يمكن أن يختلف تنفيذها ونقلها على مستوى الشركات المصنّعة للأجهزة المختلفة. لضمان أن يقدّم تطبيقك تجربة متّسقة وموثوقة على جميع الأجهزة، على المطوّرين تصميم آلية معالجة فقدان الربط للتكيّف بسلاسة مع هذه الاختلافات المحتملة.
ننصحك باتّباع سلوكيات التطبيقات التالية:
في حال بثّ نية
ACTION_KEY_MISSING:سيقطع النظام ربط ACL (الربط غير المتزامن)، ولكن سيتم الاحتفاظ بمعلومات الربط للجهاز (على النحو описан هنا).
يجب أن يستخدم تطبيقك هذا الإذن كإشارة أساسية لرصد فقدان الربط وإرشاد المستخدم إلى التأكّد من أنّ الجهاز البعيد ضمن النطاق قبل بدء عملية محو بيانات الجهاز أو إعادة إقرانه.
إذا انقطع اتصال أحد الأجهزة بعد تلقّي
ACTION_KEY_MISSING، يجب أن يتعامل تطبيقك بحذر مع إعادة الاتصال، لأنّه قد لا يكون الجهاز مرتبطًا بالنظام بعد ذلك.في حال عدم بث نية
ACTION_KEY_MISSING:سيظل رابط ACL متصلاً، وسيزيل النظام معلومات الربط للجهاز، تمامًا كما هو الحال في Android 15.
في هذا السيناريو، من المفترض أن يواصل تطبيقك استخدام آليات التعامل مع فقدان الربط الحالية كما في إصدارات Android السابقة، لرصد أحداث فقدان الربط وإدارتها.
طريقة جديدة لإزالة ربط البلوتوث
يمكن الآن لجميع التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 16 من Android إلغاء إقران الأجهزة التي تتضمّن بلوتوث باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
العامة في CompanionDeviceManager. إذا كان يتم
إدارة جهاز مصاحب كربط إدارة الخدمات الجوّالة للمؤسسات، يمكن للتطبيق بدء
إزالة الربط عبر البلوتوث باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات removeBond(int) الجديدة
على الجهاز المرتبط. يمكن للتطبيق مراقبة التغييرات في حالة الربط من خلال
الاستماع إلى حدث البث لجهاز البلوتوث
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
الأمان
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) تغييرات الأمان التالية.
قفل إصدار MediaStore
بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android أو الإصدارات الأحدث، سيصبح MediaStore#getVersion()
فريدًا لكل تطبيق. ويؤدي ذلك إلى إزالة السمات التعريفية من سلسلة الإصدار
لمنع إساءة الاستخدام والاستفادة من تقنيات تحديد الهوية. ويجب ألا تفترض التطبيقات
أيّ شيء بشأن تنسيق هذا الإصدار. من المفترض أن تتمكّن التطبيقات من التعامل مع تغييرات الإصدار عند استخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات هذه، وفي معظم الحالات، لن تحتاج التطبيقات إلى تغيير سلوكها الحالي، ما لم يحاول المطوّر استنتاج معلومات إضافية تتجاوز النطاق المقصود لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات هذه.
Safer Intents
ميزة "نقل نوايا أكثر أمانًا" هي مبادرة أمان متعدّدة المراحل مصمَّمة لتحسين أمان آلية تحديد الغرض في Android. والهدف من ذلك هو حماية التطبيقات من الإجراءات الضارة من خلال إضافة عمليات تحقّق أثناء معالجة الأهداف وتصفية الأهداف التي لا تستوفي معايير معيّنة.
في Android 15، ركّزت الميزة على تطبيق المرسِل، ولكن مع Android 16، أصبح تطبيق المتلقي هو الذي يتحكّم في العملية، ما يتيح للمطوّرين تفعيل ميزة تحليل الأهداف بدقة باستخدام بيان التطبيق.
سيتم تطبيق تغييران رئيسيان:
يجب أن تتطابق الأهداف الصريحة (Explicit Intents) مع فلتر Intent الخاص بالمكوِّن المستهدف: إذا كانت الأهداف الصريحة تستهدف مكوِّنًا بشكل صريح، يجب أن تتطابق مع فلتر Intent الخاص بهذا المكوِّن.
لا يمكن أن تتطابق الأهداف التي لا تتضمّن إجراءً مع أي فلتر Intent: يجب ألا يتم تحليل الأهداف التي لا تتضمّن إجراءً محدّدًا إلى أي فلتر Intent.
لا تنطبق هذه التغييرات إلا عند استخدام تطبيقات متعددة، ولا تؤثّر في معالجة الأهداف داخل تطبيق واحد.
التأثير
ويعني ذلك أنّ المطوّرين يجب أن يفعّلوا هذه الميزة صراحةً في بيان التطبيق لكي تصبح سارية. نتيجةً لذلك، سيقتصر تأثير الميزة على التطبيقات التي يستوفي مطوّروها الشروط التالية:
- أن تكون على دراية بميزة "نوايا أكثر أمانًا" وفوائدها
- اختيار تضمين ممارسات أكثر صرامة للتعامل مع الأهداف في تطبيقاتهم
يقلّل نهج الموافقة هذا من خطر تعطيل التطبيقات الحالية التي قد تعتمد على السلوك الحالي الأقل أمانًا في حلّ الأهداف.
على الرغم من أنّ التأثير الأوّلي لمبادرة "نوايا أكثر أمانًا" في Android 16 قد يكون محدودًا، إلا أنّ هناك خارطة طريق لتحقيق تأثير أوسع في إصدارات Android المستقبلية. ونخطّط في النهاية لجعل حلّ النية الصارمة هو السلوك التلقائي.
يمكن أن تؤدي ميزة "نقل نوايا أكثر أمانًا" إلى تحسين أمان منظومة Android المتكاملة بشكل كبير من خلال الحد من قدرة التطبيقات الضارة على استغلال الثغرات الأمنية في آلية تحديد الغرض.
ومع ذلك، يجب إدارة عملية الانتقال إلى خيار إيقاف ميزة "النسخ الاحتياطي" وفرضها بشكل إلزامي بعناية لمعالجة المشاكل المحتملة المتعلّقة بالتوافق مع التطبيقات الحالية.
التنفيذ
على المطوّرين تفعيل ميزة مطابقة الأهداف الأكثر صرامة بشكلٍ صريح باستخدام السمة intentMatchingFlags في بيان التطبيق.
في ما يلي مثال على حالة تكون فيها الميزة متاحة في التطبيق بأكمله، ولكنها غير مفعّلة أو تم إيقافها في جهاز استقبال:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
مزيد من المعلومات عن العلامات المتوافقة:
| اسم العلامة | الوصف |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | فرض مطابقة أكثر صرامة لرسائل Intent الواردة |
| لا شيء | يؤدي ذلك إلى إيقاف جميع قواعد المطابقة الخاصة للطلبات الواردة. عند تحديد علامات متعدّدة، يتم حل القيم المتعارضة من خلال منح الأولوية للعلامة "none". |
| allowNullAction | يخفّف من قواعد المطابقة للسماح بمطابقة الأهداف بدون إجراء. يجب استخدام هذا الخيار مع الخيار "enforceIntentFilter" لتحقيق سلوك معيّن. |
الاختبار وتصحيح الأخطاء
عندما يكون التنفيذ نشطًا، من المفترض أن تعمل التطبيقات بشكل صحيح إذا كان برنامج الاتصال الذي يستدعي الغرض قد ملأ الغرض بشكل صحيح.
ومع ذلك، ستؤدي النوايا المحظورة إلى ظهور رسائل تحذيرية في سجلّ الأخطاء، مثل
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" و"Access blocked:"
مع العلامة "PackageManager."
يشير ذلك إلى مشكلة محتملة قد تؤثر في التطبيق وتتطلّب
الانتباه.
فلتر Logcat:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
فلترة طلبات النظام لوحدة معالجة الرسومات
لتعزيز أمان واجهة Mali GPU، تم حظر عمليات إدخال/إخراج وحدة معالجة الرسومات Mali التي تم إيقافها نهائيًا أو التي تم تصميمها فقط لتطوير وحدة معالجة الرسومات في إصدارات الإنتاج. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تم حصر استخدام IOCTLs في إنشاء ملفات تعريف وحدة معالجة الرسومات على عملية shell أو التطبيقات التي يمكن تصحيح أخطائها. يُرجى الرجوع إلى التعديل على "اتفاقية المطوّرين الخاصة بتطبيقات Android" لمعرفة المزيد من التفاصيل حول السياسة على مستوى المنصة.
يتم إجراء هذا التغيير على هواتف Pixel التي تستخدم وحدة معالجة الرسومات Mali (من Pixel 6 إلى Pixel 9). قدّمت شركة Arm تصنيفًا رسميًا لرموز IOCTL في Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst من الإصدار r54p2. وسيتم مواصلة صيانة هذه القائمة في إصدارات برامج التشغيل المستقبلية.
لا يؤثّر هذا التغيير في واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المتوافقة مع الرسومات (بما في ذلك Vulkan وOpenGL)، ومن غير المتوقّع أن يؤثّر في المطوّرين أو التطبيقات الحالية. لن تتأثر أدوات تحليل أداء وحدة معالجة الرسومات، مثل Streamline Performance Analyzer وAndroid GPU Inspector.
الاختبار
إذا ظهر لك رفض SELinux مشابه لما يلي، من المحتمل أن يكون هذا التغيير قد أثّر في تطبيقك:
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
إذا كان تطبيقك بحاجة إلى استخدام IOCTLs محظورة، يُرجى الإبلاغ عن الخطأ وتعيينه إلى android-partner-security@google.com.
الأسئلة الشائعة
هل ينطبق هذا التغيير في السياسة على جميع الشركات المصنّعة الأصلية للأجهزة؟ سيكون هذا التغيير اختياريًا، ولكنّه سيكون متاحًا لأي مصنّعين أصليين للأجهزة يريدون استخدام طريقة الحماية هذه. يمكنك الاطّلاع على تعليمات تنفيذ التغيير في مستندات التنفيذ.
هل من الضروري إجراء تغييرات في قاعدة الرموز البرمجية للمصنّع الأصلي للأجهزة لتنفيذ ذلك، أم أنّها تأتي مع إصدار جديد من "مشروع Android المفتوح المصدر" (AOSP) تلقائيًا؟ سيتم طرح التغيير على مستوى النظام الأساسي مع إصدار جديد من AOSP تلقائيًا. يمكن للمورّدين الموافقة على هذا التغيير في قاعدة الرموز البرمجية إذا كانوا يريدون تطبيقه.
هل يكون مورّدو الأنظمة على الرقاقات مسؤولين عن تعديل قائمة IOCTL؟ على سبيل المثال، إذا كان جهازي يستخدم وحدة معالجة الرسومات ARM Mali، هل عليّ التواصل مع ARM لإجراء أي من التغييرات؟ يجب أن تعدّل أنظمة SoC الفردية قوائم IOCTL لكل جهاز عند إصدار برنامج التشغيل. على سبيل المثال، ستعدّل ARM قائمة IOCTL المنشورة عند تحديث برامج التشغيل. ومع ذلك، على المصنّعين الأصليين للأجهزة التأكّد من تضمين التعديلات في سياسة SELinux، وإضافة أي أوامر IOCTL مخصّصة تم اختيارها إلى القوائم حسب الحاجة.
هل يتم تطبيق هذا التغيير تلقائيًا على جميع أجهزة Pixel المتوفرة في السوق، أم يجب أن يتّخذ المستخدم إجراءً لتفعيل خيار ما من أجل تطبيق هذا التغيير؟ ينطبق هذا التغيير على جميع أجهزة Pixel المتوفّرة في السوق والتي تستخدم وحدة معالجة الرسومات Mali (Pixel 6-9). ليس على المستخدم اتّخاذ أي إجراء لتطبيق هذا التغيير.
هل سيؤثر استخدام هذه السياسة في أداء برنامج تشغيل النواة؟ تم اختبار هذه السياسة على وحدة معالجة الرسومات Mali باستخدام GFXBench، ولم يتم رصد أي تغيير قابل للقياس في أداء وحدة معالجة الرسومات.
هل من الضروري أن تتوافق قائمة IOCTL مع إصدارات مساحة المستخدم وبرنامج تشغيل النواة الحالية؟ نعم، يجب مزامنة قائمة IOCTL المسموح بها مع IOCTL المتوافقة مع برامج تشغيل مساحة المستخدم وبرامج تشغيل النواة. في حال تعديل IOCTLs في مساحة المستخدم أو برنامج تشغيل النواة، يجب تعديل قائمة SEPolicy IOCTL لتتطابق مع التعديل.
صنّفت ARM عمليات IOCTL على أنّها "محظورة" أو "أدوات قياس"، ولكنّنا نريد استخدام بعضها في حالات الاستخدام الفعلي و/أو رفض البعض الآخر. يتحمّل مصنّعو المعدات الأصلية/أنظمة التشغيل على الرقاقة الفردية مسؤولية تحديد كيفية تصنيف IOCTL التي يستخدمونها، وذلك استنادًا إلى إعدادات مكتبات Mali الخاصة بمساحة المستخدم. يمكن استخدام قائمة ARM للمساعدة في تحديد هذه الحالات، ولكن قد تختلف حالة الاستخدام لكل مصنّع معدات أصلية/نظام على شريحة.
الخصوصية
يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 16 (المستوى 36 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) تغييرات الخصوصية التالية.
إذن الوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية
يمكن لأي تطبيق لديه إذن INTERNET الوصول إلى الأجهزة على الشبكة المحلية.
يسهّل ذلك على التطبيقات الاتصال بالأجهزة المحلية، ولكن له أيضًا آثار على الخصوصية، مثل إنشاء بصمة للمستخدم، والعمل كخادم وكيل للموقع الجغرافي.
يهدف مشروع "حماية الشبكة المحلية" إلى حماية خصوصية المستخدم من خلال حصر الوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية بإذن جديد أثناء التشغيل.
خطة الإصدار
سيتم طرح هذا التغيير بين إصدارَين، 25Q2 و26Q2 على التوالي. من الضروري أن يلتزم المطوّرون بهذه الإرشادات في الربع الثاني من عام 2025 وأن يشاركوا ملاحظاتهم لأنّ هذه الحمايات سيتم فرضها في إصدار Android لاحق. علاوةً على ذلك، سيحتاجون إلى تعديل السيناريوهات التي تعتمد على الوصول الضمني إلى الشبكة المحلية باتّباع الإرشادات التالية والاستعداد لرفض المستخدم وإلغاء الإذن الجديد.
التأثير
في المرحلة الحالية، ميزة "الشبكة المحلية فقط" هي ميزة اختيارية، ما يعني أنّ التطبيقات التي تفعّلها فقط ستتأثر بها. والهدف من مرحلة الموافقة هو أن يتعرّف مطوّرو التطبيقات على الأجزاء التي تعتمد على الوصول الضمني إلى الشبكة المحلية، وذلك حتى يتمكّنوا من إعدادها لتكون محمية بإذن في الإصدار التالي.
ستتأثر التطبيقات إذا كانت تصل إلى الشبكة المحلية للمستخدم باستخدام:
- الاستخدام المباشر أو استخدام المكتبة للمقابس الأولية على عناوين الشبكة المحلية (مثل بروتوكول mDNS أو SSDP لاكتشاف الخدمات)
- استخدام فئات على مستوى إطار العمل يمكنها الوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية (مثل NsdManager)
يتطلّب نقل البيانات إلى عنوان شبكة محلية ومنه منح الإذن بالوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية. يسرد الجدول التالي بعض الحالات الشائعة:
| عمليات الشبكة المنخفضة المستوى في التطبيق | يجب منح الإذن بالوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية |
|---|---|
| إجراء اتصال TCP صادر | نعم |
| قبول اتصالات TCP الواردة | نعم |
| إرسال بث أحادي أو بث متعدّد أو بث عادي عبر UDP | نعم |
| تلقّي بث أحادي أو متعدد أو عادي وارد عبر UDP | نعم |
يتم تنفيذ هذه القيود في أعماق حزمة الشبكات، وبالتالي تسري على جميع واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المتعلقة بالشبكات. ويشمل ذلك المقابس التي تم إنشاؤها في الرموز البرمجية الأصلية أو المُدارة، ومكتبات الشبكات مثل Cronet وOkHttp، وأي واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تم تنفيذها فوق هذه المكتبات. ستتطلّب محاولة حلّ الخدمات على الشبكة المحلية (أي تلك التي تتضمّن اللاحقة .local) إذنًا بالوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية.
استثناءات للقواعد أعلاه:
- إذا كان خادم DNS الخاص بالجهاز على شبكة محلية، لن تتطلّب حركة البيانات الواردة إليه أو الصادرة منه (على المنفذ 53) إذن الوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية.
- لن تحتاج التطبيقات التي تستخدم أداة Output Switcher كأداة اختيار داخل التطبيق إلى أذونات الوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية (ستتوفّر المزيد من الإرشادات في الربع الرابع من عام 2025).
إرشادات المطوّرين (تفعيل)
لفرض قيود على الشبكة المحلية، اتّبِع الخطوات التالية:
- تثبيت إصدار يتضمّن الإصدار التجريبي 3 من 25Q2 أو إصدار أحدث على الجهاز
- ثبِّت التطبيق الذي تريد اختباره.
بدِّل علامة Appcompat في adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>إعادة تشغيل الجهاز
سيتم الآن تقييد وصول تطبيقك إلى الشبكة المحلية، وسيؤدي أي محاولة للوصول إلى الشبكة المحلية إلى حدوث أخطاء في المقبس. إذا كنت تستخدم واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تنفّذ عمليات على الشبكة المحلية خارج عملية تطبيقك (مثل NsdManager)، لن تتأثّر هذه العمليات خلال مرحلة الموافقة.
لاستعادة إمكانية الوصول، يجب منح تطبيقك الإذن بالوصول إلى NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- تأكَّد من أنّ التطبيق يعلن عن إذن
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESفي بيان التطبيق. - انتقِل إلى الإعدادات > التطبيقات > [اسم التطبيق] > الأذونات > الأجهزة القريبة > السماح.
من المفترض الآن أن يكون قد تم استعادة إذن وصول تطبيقك إلى الشبكة المحلية، وأن تعمل جميع السيناريوهات كما كانت قبل منح التطبيق الإذن.
بعد بدء تطبيق ميزة "الحماية من شبكات الجيل الثاني"، سيتم التأثير في عدد الزيارات الواردة إلى شبكة التطبيق على النحو التالي:
| الإذن | Outbound LAN Request | طلب الإنترنت الصادر/الوارد | طلب شبكة LAN وارد |
|---|---|---|---|
| تم منح الأذونات | Works | Works | Works |
| لم يتم المنح | الإخفاقات | Works | الإخفاقات |
استخدِم الأمر التالي لإيقاف علامة App-Compat
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
الأخطاء
سيتم عرض الأخطاء الناتجة عن هذه القيود في مقبس الاتصال الذي تم استدعاؤه عندما يتم استدعاء الأمر send أو أحد متغيراته إلى عنوان شبكة محلية.
أمثلة على الأخطاء:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
تعريف الشبكة المحلية
تشير الشبكة المحلية في هذا المشروع إلى شبكة IP تستخدم واجهة شبكة متوافقة مع البث، مثل Wi-Fi أو Ethernet، ولكنها لا تشمل اتصالات شبكة الجوّال (WWAN) أو شبكة VPN.
تُعدّ الشبكات التالية شبكات محلية:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-local
- المسارات المرتبطة مباشرةً
- شبكات الأجهزة الوهمية، مثل Thread
- الشبكات الفرعية المتعددة (يُحدَّد لاحقًا)
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يتم تصنيف كل من عناوين البث المتعدد (224.0.0.0/4 وff00::/8) وعنوان البث IPv4 (255.255.255.255) كعناوين شبكة محلية.
الصور التي يملكها التطبيق
عندما يطلب تطبيق يستهدف الإصدار 36 من حزمة SDK أو إصدارًا أحدث على الأجهزة التي تعمل بالإصدار 16 من نظام التشغيل Android أو إصدارًا أحدث أذونات الوصول إلى الصور والفيديوهات، سيظهر للمستخدمين الذين يختارون حصر الوصول إلى الوسائط المحدّدة أي صور يملكها التطبيق تم اختيارها مسبقًا في أداة اختيار الصور. يمكن للمستخدمين إلغاء اختيار أي من هذه العناصر المحدّدة مسبقًا، ما سيؤدي إلى إبطال إذن وصول التطبيق إلى هذه الصور والفيديوهات.
