Come le release precedenti, Android 16 include modifiche al comportamento che potrebbero influire sulla tua app. Le seguenti modifiche al comportamento si applicano esclusivamente alle app che hanno come target Android 16 o versioni successive. Se la tua app ha come target Android 16 o versioni successive, devi modificarla per supportare questi comportamenti, ove applicabile.
Assicurati di esaminare anche l'elenco delle modifiche al comportamento che interessano tutte le app
in esecuzione su Android 16, indipendentemente dal targetSdkVersion della tua app.
Esperienza utente e UI di sistema
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche volte a creare un'esperienza utente più coerente e intuitiva.
Rimozione della disattivazione edge-to-edge
Android 15 ha imposto la modalità edge-to-edge per le app che hanno come target Android 15 (livello API 35), ma la tua app potrebbe disattivarla impostando
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement su true. Per le app
che hanno come target Android 16 (livello API 36),
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement è deprecato e disabilitato e la tua
app non può disattivare la visualizzazione edge-to-edge.
- Se la tua app ha come target Android 16 (livello API 36) ed è in esecuzione su un
dispositivo Android 15,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementcontinua a funzionare. - Se la tua app ha come target Android 16 (livello API 36) ed è in esecuzione su un
dispositivo Android 16,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementè disattivato.
Per i test in Android 16, assicurati che la tua app supporti la visualizzazione edge-to-edge e
rimuovi qualsiasi utilizzo di R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement in modo che la tua app
supporti la visualizzazione edge-to-edge anche su un dispositivo Android 15. Per supportare la visualizzazione da bordo a bordo,
consulta le indicazioni relative a Composizione e Visualizzazioni.
Migrazione o disattivazione richieste per la funzionalità Indietro predittivo
Per le app che hanno come target Android 16 (livello API 36) o versioni successive e in esecuzione su un
dispositivo Android 16 o versioni successive, le animazioni del sistema di navigazione predittiva
(torna alla schermata Home, passaggio da un'attività all'altra e passaggio da un'attività all'altra) sono attive per impostazione predefinita.
Inoltre, onBackPressed non viene chiamato e
KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK non viene più inviato.
Se la tua app intercetta l'evento Indietro e non hai ancora eseguito la migrazione alla navigazione
predittiva, aggiorna l'app per utilizzare le API di navigazione Indietro supportate oppure
disattiva temporaneamente la funzionalità impostando l'attributo
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback su false nel tag
<application> o <activity> del file AndroidManifest.xml dell'app.
API Elegant font deprecate e disabilitate
Le app che hanno come target Android 15 (livello API 35) hanno l'attributo
elegantTextHeight
TextView impostato su true per
impostazione predefinita, sostituendo il carattere compatto con uno molto più leggibile. Puoi
ignorare questa impostazione impostando l'attributo elegantTextHeight su false.
Android 16 ritira l'attributo
elegantTextHeight
e l'attributo verrà ignorato una volta che la tua app avrà come target Android 16. I "caratteri
dell'interfaccia utente" controllati da queste API verranno ritirati, pertanto devi adattare tutti
i layout per garantire il rendering del testo coerente e a prova di futuro in arabo, laotiano,
birmano, tamil, gujarati, kannada, malayalam, odia, telugu o tailandese.
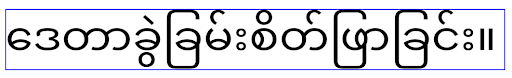
elegantTextHeight per le app che hanno come target Android
14 (livello API 34) e versioni precedenti o per le app che hanno come target Android 15 (livello API 35)
che hanno sostituito il valore predefinito impostando l'attributo elegantTextHeight su false.
elegantTextHeight per le app che hanno come target Android
16 (livello API 36) o per le app che hanno come target Android 15 (livello API 35) che non
hanno eseguito l'override del valore predefinito impostando l'attributo elegantTextHeight
su false.Funzionalità di base
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche che modificano o espandono varie funzionalità di base del sistema Android.
Ottimizzazione della pianificazione del lavoro a tariffa fissa
Prima di scegliere come target Android 16, quando scheduleAtFixedRate
mancava un'esecuzione di attività perché non rientrava in un
ciclo di vita del processo valido, tutte le esecuzioni mancate venivano eseguite immediatamente
quando l'app tornava a un ciclo di vita valido.
Quando scegli come target Android 16, al massimo una esecuzione mancata di
scheduleAtFixedRate viene eseguita immediatamente quando l'app
torna a un ciclo di vita valido. Questa modifica del comportamento dovrebbe migliorare il rendimento dell'app. Testa questo comportamento nella tua app per verificare se è interessata.
Puoi anche eseguire il test utilizzando il framework di compatibilità delle app e attivando il flag di compatibilità STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS.
Fattori di forma dei dispositivi
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche per le app quando vengono visualizzate su dispositivi con schermi di grandi dimensioni.
Layout adattivi
Ora le app per Android vengono eseguite su una vasta gamma di dispositivi (come smartphone, tablet, pieghevoli, computer, auto e TV) e modalità di visualizzazione a finestre su schermi di grandi dimensioni (come la visualizzazione a schermo diviso e a finestre sul computer). Gli sviluppatori devono creare app per Android che si adattino a qualsiasi dimensione dello schermo e della finestra, indipendentemente dall'orientamento del dispositivo. Paradigmi come la limitazione dell'orientamento e del ridimensionamento sono troppo restrittivi nel mondo multidevice di oggi.
Ignora le limitazioni relative a orientamento, ridimensionamento e proporzioni
Per le app che hanno come target Android 16 (livello API 36), Android 16 include modifiche al modo in cui il sistema gestisce le limitazioni di orientamento, ridimensionamento e proporzioni. Sui display con larghezza minima >= 600 dp, le limitazioni non si applicano più. Inoltre, le app riempiono l'intera finestra di visualizzazione, indipendentemente dalle proporzioni o dall'orientamento preferito dall'utente, e non viene utilizzato il pillarbox.
Questa modifica introduce un nuovo comportamento standard della piattaforma. Android sta passando a un modello in cui le app devono adattarsi a vari orientamenti, dimensioni di visualizzazione e proporzioni. Limitazioni come l'orientamento fisso o il ridimensionamento limitato ostacolano l'adattabilità dell'app, pertanto ti consigliamo di rendere la tua app adattiva per offrire la migliore esperienza utente possibile.
Puoi anche testare questo comportamento utilizzando il
framework di compatibilità delle app e
attivando il flag di compatibilità UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT.
Modifiche che provocano un errore comuni
Ignorare le limitazioni di orientamento, ridimensionamento e proporzioni potrebbe influire sull'interfaccia utente della tua app su alcuni dispositivi, in particolare sugli elementi progettati per layout di piccole dimensioni bloccati in orientamento verticale: ad esempio, problemi come layout allungati e animazioni e componenti fuori schermo. Qualsiasi ipotesi sul formato o sull'orientamento può causare problemi visivi con la tua app. Scopri di più su come evitarli e migliorare il comportamento adattivo della tua app.
Se consenti la rotazione del dispositivo, si verifica una maggiore ricreazione dell'attività, che può comportare la perdita dello stato dell'utente se non viene conservato correttamente. Scopri come salvare correttamente lo stato dell'interfaccia utente in Salva stati dell'interfaccia utente.
Dettagli di implementazione
I seguenti attributi del manifest e API di runtime vengono ignorati sui dispositivi con schermo di grandi dimensioni in modalità a schermo intero e multi-finestra:
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
I seguenti valori per screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation() e
getRequestedOrientation() vengono ignorati:
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Per quanto riguarda il ridimensionamento del display, android:resizeableActivity="false",
android:minAspectRatio e android:maxAspectRatio non hanno alcun effetto.
Per le app che hanno come target Android 16 (livello API 36), l'orientamento, il ridimensionamento e i vincoli delle proporzioni delle app vengono ignorati sugli schermi di grandi dimensioni per impostazione predefinita, ma ogni app non completamente pronta può ignorare temporaneamente questo comportamento disattivandolo (il che comporta il comportamento precedente di essere inserita in modalità di compatibilità).
Eccezioni
Le limitazioni di orientamento, ridimensionamento e proporzioni di Android 16 non si applicano nelle seguenti situazioni:
- Giochi (in base alla bandiera
android:appCategory) - Utenti che attivano esplicitamente il comportamento predefinito dell'app nelle impostazioni delle proporzioni del dispositivo
- Schermi più piccoli di
sw600dp
Disattivare temporaneamente
Per disattivare un'attività specifica, dichiara la proprietà
PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY del manifest:
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
Se troppe parti della tua app non sono pronte per Android 16, puoi disattivare completamente la funzionalità applicando la stessa proprietà a livello di applicazione:
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Salute e fitness
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche relative ai dati di salute e fitness.
Autorizzazioni per salute e fitness
Per le app che hanno come target Android 16 (livello API 36) o versioni successive,
le autorizzazioni BODY_SENSORS utilizzano autorizzazioni più granulari
in android.permissions.health, che vengono utilizzate anche da Connessione Salute. A partire da Android 16, qualsiasi API che in precedenza richiedeva BODY_SENSORS
o BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND richiede invece l'autorizzazione
android.permissions.health corrispondente. Ciò influisce sui seguenti tipi di dati, API e tipi di servizi in primo piano:
HEART_RATE_BPMda Servizi per la salute su Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEda Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracyeheartRateBpmdaProtoLayoutsu Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHdove è necessaria la rispettiva autorizzazioneandroid.permission.healthal posto diBODY_SENSORS
Se la tua app utilizza queste API, deve richiedere le rispettive autorizzazioni granulari:
- Per il monitoraggio durante l'uso di battito cardiaco, SpO2 o temperatura cutanea:
richiedi l'autorizzazione granulare in
android.permissions.health, ad esempioREAD_HEART_RATEanzichéBODY_SENSORS. - Per l'accesso ai sensori in background, richiedi
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDanzichéBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
Queste autorizzazioni sono le stesse che proteggono l'accesso alla lettura dei dati da Connessione Salute, l'archivio dati Android per i dati relativi a salute, fitness e benessere.
App mobili
Le app mobile che eseguono la migrazione per utilizzare READ_HEART_RATE e altre autorizzazioni granulari
devono anche dichiarare un'attività per visualizzare
le norme sulla privacy dell'app. Si tratta dello stesso requisito di Connessione Salute.
Connettività
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche nello stack Bluetooth per migliorare la connettività con i dispositivi periferici.
Nuovi intent per gestire la perdita di accoppiamento e le modifiche alla crittografia
Nell'ambito della gestione migliorata della perdita del legame, Android 16 introduce anche due nuovi intent per fornire alle app una maggiore consapevolezza della perdita del legame e delle modifiche alla crittografia.
Le app che hanno come target Android 16 ora possono:
- Ricevere un'intenzione
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGquando viene rilevata la perdita del legame remoto, in modo da poter fornire un feedback più informativo agli utenti e intraprendere azioni appropriate. - Ricevere un'intenzione
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEogni volta che cambia lo stato della crittografia del collegamento. Sono incluse la modifica dello stato della crittografia, la modifica dell'algoritmo di crittografia e la modifica delle dimensioni della chiave di crittografia. Le app devono considerare il legame ripristinato se il link viene criptato correttamente al momento della ricezione dell'intentACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEin un secondo momento.
Adattamento alle diverse implementazioni degli OEM
Sebbene Android 16 introduca questi nuovi intent, la loro implementazione e la loro trasmissione possono variare in base ai diversi produttori di dispositivi (OEM). Per garantire che la tua app offra un'esperienza coerente e affidabile su tutti i dispositivi, gli sviluppatori devono progettare la gestione della perdita di legame in modo che si adatti in modo graduale a queste potenziali variazioni.
Consigliamo i seguenti comportamenti delle app:
Se viene trasmesso l'intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSING:Il link ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less) verrà scollegato dal sistema, ma le informazioni sul legame del dispositivo verranno conservate (come descritto qui).
L'app deve utilizzare questo intent come indicatore principale per il rilevamento della perdita del legame e guidare l'utente a verificare che il dispositivo remoto sia nel raggio d'azione prima di avviare l'eliminazione o la nuova accoppiata del dispositivo.
Se un dispositivo si disconnette dopo aver ricevuto
ACTION_KEY_MISSING, la tua app deve essere cauta nel riconnettersi, poiché il dispositivo potrebbe non essere più associato al sistema.Se l'intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGNON viene trasmesso:Il link ACL rimarrà connesso e le informazioni sul legame del dispositivo verranno rimosse dal sistema, come accade in Android 15.
In questo scenario, l'app dovrebbe continuare a utilizzare i meccanismi di gestione della perdita di pacchetti esistenti, come nelle release Android precedenti, per rilevare e gestire gli eventi di perdita di pacchetti.
Nuovo modo per rimuovere l'accoppiamento Bluetooth
Tutte le app che hanno come target Android 16 ora possono disaccoppiare i dispositivi Bluetooth utilizzando un'API pubblica in CompanionDeviceManager. Se un dispositivo complementare viene gestito come associazione CDM, l'app può attivare la rimozione del legame Bluetooth utilizzando la nuova API removeBond(int) sul dispositivo associato. L'app può monitorare le modifiche dello stato del legame ascoltando l'evento di trasmissione del dispositivo Bluetooth
ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
Sicurezza
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche alla sicurezza.
Blocco della versione di MediaStore
Per le app destinate ad Android 16 o versioni successive, MediaStore#getVersion() sarà ora univoco per ogni app. In questo modo, le proprietà di identificazione vengono eliminate dalla stringa di versione per impedire l'uso improprio e l'utilizzo per le tecniche di fingerprinting. Le app non devono fare supposizioni sul formato di questa versione. Le app dovrebbero già gestire le modifiche delle versioni quando utilizzano questa API e nella maggior parte dei casi non dovrebbero dover cambiare il loro comportamento attuale, a meno che lo sviluppatore non abbia tentato di dedurre informazioni aggiuntive che vanno oltre lo scopo previsto di questa API.
Intenti più sicuri
La funzionalità Safer Intents è un'iniziativa di sicurezza in più fasi progettata per migliorare la sicurezza del meccanismo di risoluzione degli intent di Android. L'obiettivo è proteggere le app da azioni dannose aggiungendo controlli durante l'elaborazione degli intent e filtrando gli intent che non soddisfano criteri specifici.
In Android 15 la funzionalità si concentrava sull'app di invio, mentre con Android 16 il controllo passa all'app di ricezione, consentendo agli sviluppatori di attivare la risoluzione rigorosa degli intent utilizzando il manifest dell'app.
Verranno implementate due modifiche chiave:
Gli intent espliciti devono corrispondere al filtro per intent del componente di destinazione: se un intent ha come target esplicito un componente, deve corrispondere al filtro per intent di quel componente.
Gli intent senza un'azione non possono corrispondere ad alcun filtro per intent: gli intent che non hanno un'azione specificata non devono essere risolti in alcun filtro per intent.
Queste modifiche si applicano solo quando sono coinvolte più app e non influiscono sulla gestione degli intent all'interno di una singola app.
Impatto
La natura di attivazione significa che gli sviluppatori devono abilitarla esplicitamente nel manifest dell'app affinché diventi effettiva. Di conseguenza, l'impatto della funzionalità sarà limitato alle app i cui sviluppatori:
- Conoscono la funzionalità Safer Intents e i suoi vantaggi.
- Scegliere attivamente di incorporare pratiche di gestione degli intent più rigorose nelle proprie app.
Questo approccio di attivazione riduce al minimo il rischio di interrompere le app esistenti che potrebbero fare affidamento sul comportamento di risoluzione degli intent meno sicuro attuale.
Sebbene l'impatto iniziale in Android 16 possa essere limitato, l'iniziativa Safer Intents prevede una roadmap per un impatto più ampio nelle future release di Android. Il piano è quello di rendere la risoluzione rigorosa dell'intent il comportamento predefinito.
La funzionalità Safer Intents ha il potenziale per migliorare significativamente la sicurezza dell'ecosistema Android rendendo più difficile per le app dannose sfruttare le vulnerabilità nel meccanismo di risoluzione degli intent.
Tuttavia, la transizione al ritiro e all'applicazione obbligatoria deve essere gestita con attenzione per risolvere potenziali problemi di compatibilità con le app esistenti.
Implementazione
Gli sviluppatori devono attivare esplicitamente la corrispondenza degli intent più rigorosa utilizzando l'attributo
intentMatchingFlags nel file manifest dell'app.
Ecco un esempio in cui la funzionalità è attivata per l'intera app,
ma disattivata/disattivabile su un ricevitore:
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
Scopri di più sui flag supportati:
| Nome del flag | Descrizione |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Applica una corrispondenza più rigorosa per gli intent in entrata |
| nessuno | Disattiva tutte le regole di corrispondenza speciali per gli intent in entrata. Quando vengono specificati più flag, i valori in conflitto vengono risolti dando la precedenza al flag "none". |
| allowNullAction | Rilassa le regole di corrispondenza per consentire la corrispondenza delle intenzioni senza un'azione. Questo flag da utilizzare in combinazione con "enforceIntentFilter" per ottenere un comportamento specifico |
Test e debug
Quando l'applicazione è attiva, le app dovrebbero funzionare correttamente se il chiamante dell'intent
ha compilato correttamente l'intent.
Tuttavia, gli intent bloccati attiveranno messaggi di log di avviso come
"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" e "Access blocked:"
con il tag "PackageManager."
Ciò indica un potenziale problema che potrebbe influire sull'app e richiede
attenzione.
Filtro logcat:
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
Privacy
Android 16 (livello API 36) include le seguenti modifiche alla privacy.
Autorizzazione di accesso alla rete locale
I dispositivi sulla LAN sono accessibili a qualsiasi app con l'autorizzazione INTERNET.
In questo modo, le app possono connettersi facilmente ai dispositivi locali, ma ciò ha anche implicazioni per la privacy, ad esempio la creazione di un'impronta dell'utente e la funzione di proxy per la posizione.
Il progetto Protezioni rete locale mira a proteggere la privacy dell'utente limitando l'accesso alla rete locale tramite una nuova autorizzazione di runtime.
Piano di rilascio
Questa modifica verrà implementata tra due versioni, 25Q2 e TBD rispettivamente. È fondamentale che gli sviluppatori seguano queste indicazioni per il 25Q2 e condividano feedback perché queste protezioni verranno applicate in una release Android successiva. Inoltre, dovranno aggiornare gli scenari che dipendono dall'accesso implicito alla rete locale utilizzando le seguenti indicazioni e prepararsi al rifiuto e alla revoca della nuova autorizzazione da parte degli utenti.
Impatto
Nella fase attuale, LNP è una funzionalità di attivazione, il che significa che saranno interessate solo le app che la attivano. L'obiettivo della fase di attivazione è consentire agli sviluppatori di app di comprendere quali parti della loro app dipendono dall'accesso implicito alla rete locale in modo da prepararsi a proteggerle con le autorizzazioni per la prossima release.
Le app saranno interessate se accedono alla rete locale dell'utente utilizzando:
- Utilizzo diretto o di libreria di socket non elaborati su indirizzi di rete locali (ad es. protocollo di rilevamento del servizio mDNS o SSDP)
- Utilizzo di classi a livello di framework che accedono alla rete locale (ad es. NsdManager)
Il traffico verso e da un indirizzo di rete locale richiede l'autorizzazione di accesso alla rete locale. La seguente tabella elenca alcuni casi comuni:
| Operazione di rete di basso livello dell'app | Autorizzazione di accesso alla rete locale richiesta |
|---|---|
| Creazione di una connessione TCP in uscita | sì |
| Accettare connessioni TCP in entrata | sì |
| Invio di un unicast, multicast, broadcast UDP | sì |
| Ricezione di un unicast, multicast o broadcast UDP in entrata | sì |
Queste limitazioni sono implementate in profondità nello stack di rete, e quindi si applicano a tutte le API di rete. Ciò include i socket creati in codice nativo o gestito, le librerie di rete come Cronet e OkHttp e qualsiasi API implementata sopra queste. Il tentativo di risolvere i servizi sulla rete locale (ovvero quelli con suffisso .local) richiederà l'autorizzazione di accesso alla rete locale.
Eccezioni alle regole riportate sopra:
- Se il server DNS di un dispositivo si trova su una rete locale, il traffico da o verso il dispositivo (sulla porta 53) non richiede l'autorizzazione di accesso alla rete locale.
- Le applicazioni che utilizzano Output Switcher come selettore in-app non avranno bisogno di autorizzazioni di rete locale (ulteriori indicazioni verranno fornite nel quarto trimestre del 2025).
Indicazioni per gli sviluppatori (attivazione)
Per attivare le limitazioni della rete locale:
- Esegui il flash del dispositivo con una build con 25Q2 Beta 3 o versioni successive.
- Installa l'app da testare.
Attiva/disattiva il flag Appcompat in adb:
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Riavvia il dispositivo
Ora l'accesso dell'app alla rete locale è limitato e qualsiasi tentativo di accedere alla rete locale genererà errori di socket. Se utilizzi API che eseguono operazioni di rete locale al di fuori del processo dell'app (ad es. NsdManager), non saranno interessate durante la fase di attivazione.
Per ripristinare l'accesso, devi concedere all'app l'autorizzazione a NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- Assicurati che l'app dichiari l'autorizzazione
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESnel file manifest. - Vai a Impostazioni > App > [Nome applicazione] > Autorizzazioni > Dispositivi nelle vicinanze > Consenti.
Ora l'accesso dell'app alla rete locale dovrebbe essere ripristinato e tutti gli scenari dovrebbero funzionare come prima dell'attivazione dell'app.
Una volta iniziato l'applicazione della protezione della rete locale, ecco come verrà interessato il traffico di rete dell'app.
| Autorizzazione | Richiesta LAN in uscita | Richiesta internet in uscita/in entrata | Inbound LAN Request |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concesso | Works | Works | Works |
| Non concesso | Fallimenti | Works | Fallimenti |
Utilizza il seguente comando per disattivare il flag App-Compat
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Errori
Gli errori derivanti da queste limitazioni verranno restituiti al socket chiamante ogni volta che richiama send o una variante di send a un indirizzo di rete locale.
Esempi di errori:
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Definizione di rete locale
Una rete locale in questo progetto si riferisce a una rete IP che utilizza un'interfaccia di rete in grado di trasmettere, ad esempio Wi-Fi o Ethernet, ma esclude le connessioni cellulari (WWAN) o VPN.
Le seguenti sono considerate reti locali:
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Link Local
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Link-local
- Route connesse direttamente
- Reti stub come Thread
- Più subnet (da definire)
Inoltre, sia gli indirizzi multicast (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) sia l'indirizzo di broadcast IPv4 (255.255.255.255) sono classificati come indirizzi di rete locali.
Foto di proprietà dell'app
Quando un'app che ha come target l'SDK 36 o versioni successive richiede le autorizzazioni per foto e video su dispositivi con Android 16 o versioni successive, gli utenti che scelgono di limitare l'accesso ai contenuti multimediali selezionati vedranno le foto di proprietà dell'app preselezionate nel selettore di foto. Gli utenti possono deselezionare uno di questi elementi preselezionati, revocando così l'accesso dell'app a foto e video.

