Android 15 mang đến cho nhà phát triển các tính năng và API mới hữu ích. Các phần sau đây tóm tắt những tính năng này để giúp bạn làm quen với các API liên quan.
Để biết danh sách chi tiết về các API đã thêm, sửa đổi và xoá, hãy đọc báo cáo điểm khác biệt về API. Để biết thông tin chi tiết về các API được thêm, hãy truy cập tài liệu tham khảo về API cho Android. Đối với Android 15, hãy tìm các API được thêm ở API cấp 35. Để tìm hiểu những thay đổi của nền tảng có thể tác động đến ứng dụng của bạn, hãy nhớ tham khảo các thay đổi về hành vi của Android 15 đối với ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 15 và tất cả ứng dụng.
Camera và nội dung nghe nhìn
Android 15 có nhiều tính năng giúp cải thiện trải nghiệm về camera và nội dung nghe nhìn, đồng thời cung cấp cho bạn quyền truy cập vào các công cụ và phần cứng để hỗ trợ nhà sáng tạo hiện thực hoá ý tưởng của họ trên Android.
Để biết thêm thông tin về các tính năng mới nhất và giải pháp dành cho nhà phát triển về nội dung nghe nhìn và camera trên Android, hãy xem bài nói chuyện Xây dựng trải nghiệm nội dung nghe nhìn và camera hiện đại trên Android tại Google I/O.
Tăng cường ánh sáng yếu
Android 15 introduces Low Light Boost, an auto-exposure mode available to both Camera 2 and the night mode camera extension. Low Light Boost adjusts the exposure of the Preview stream in low-light conditions. This is different from how the night mode camera extension creates still images, because night mode combines a burst of photos to create a single, enhanced image. While night mode works very well for creating a still image, it can't create a continuous stream of frames, but Low Light Boost can. Thus, Low Light Boost enables camera capabilities, such as:
- Providing an enhanced image preview, so users are better able to frame their low-light pictures
- Scanning QR codes in low light
If you enable Low Light Boost, it automatically turns on when there's a low light level, and turns off when there's more light.
Apps can record off the Preview stream in low-light conditions to save a brightened video.
For more information, see Low Light Boost.
Các chế độ điều khiển camera trong ứng dụng
Android 15 adds an extension for more control over the camera hardware and its algorithms on supported devices:
- Advanced flash strength adjustments enabling precise control of flash
intensity in both
SINGLEandTORCHmodes while capturing images.
Kiểm soát khoảng không gian trống của HDR
Android 15 chooses HDR headroom that is appropriate for the underlying device
capabilities and bit-depth of the panel. For pages that have lots of SDR
content, such as a messaging app displaying a single HDR thumbnail, this
behavior can end up adversely influencing the perceived brightness of the SDR
content. Android 15 lets you control the HDR headroom with
setDesiredHdrHeadroom to strike a balance between SDR
and HDR content.
Kiểm soát độ lớn âm thanh

Android 15 introduces support for the CTA-2075 loudness standard to help you avoid audio loudness inconsistencies and ensure users don't have to constantly adjust volume when switching between content. The system leverages known characteristics of the output devices (headphones and speaker) along with loudness metadata available in AAC audio content to intelligently adjust the audio loudness and dynamic range compression levels.
To enable this feature, you need to ensure loudness metadata is available in
your AAC content and enable the platform feature in your app. For this, you
instantiate a LoudnessCodecController object by
calling its create factory method with the audio
session ID from the associated AudioTrack; this
automatically starts applying audio updates. You can pass an
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener to modify or filter
loudness parameters before they are applied on the
MediaCodec.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer will also be updated to use the
LoudnessCodecController APIs for a seamless app integration.
Thiết bị MIDI 2.0 ảo
Android 13 added support for connecting to MIDI 2.0 devices using USB, which communicate using Universal MIDI Packets (UMP). Android 15 extends UMP support to virtual MIDI apps, enabling composition apps to control synthesizer apps as a virtual MIDI 2.0 device just like they would with an USB MIDI 2.0 device.
Giải mã phần mềm AV1 hiệu quả hơn

dav1d, the popular AV1 software decoder from VideoLAN is available for Android devices that don't support AV1 decode in hardware. dav1d is up to 3x more performant than the legacy AV1 software decoder, enabling HD AV1 playback for more users, including some low and mid tier devices.
Your app needs to opt-in to using dav1d by invoking it by name
"c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". dav1d will be made the default AV1 software
decoder in a subsequent update. This support is standardized and backported to
Android 11 devices that receive Google Play system updates.
Năng suất và công cụ dành cho nhà phát triển
Mặc dù hầu hết công việc của chúng tôi nhằm cải thiện năng suất của bạn đều xoay quanh các công cụ như Android Studio, Jetpack Compose và các thư viện Android Jetpack, nhưng chúng tôi luôn tìm cách giúp bạn dễ dàng hiện thực hoá ý tưởng của mình hơn trên nền tảng này.
Nội dung cập nhật OpenJDK 17
Android 15 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases.
The following key features and improvements are included:
- Quality-of-life improvements around NIO buffers
- Streams
- Additional
mathandstrictmathmethods utilpackage updates including sequencedcollection,map, andsetByteBuffersupport inDeflater- Security updates such as
X500PrivateCredentialand security key updates
These APIs are updated on over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher through Google Play System updates, so you can target the latest programming features.
Cải thiện tệp PDF
Android 15 includes substantial improvements to the PdfRenderer
APIs. Apps can incorporate advanced features such as rendering
password-protected files, annotations, form editing,
searching, and selection with copy. Linearized PDF
optimizations are supported to speed local PDF viewing and reduce resource use.
The Jetpack PDF library uses these APIs to simplify adding PDF
viewing capabilities to your app.
The PdfRenderer has been moved to a module that can be updated using Google
Play system updates independent of the platform release, and we're supporting
these changes back to Android 11 (API level 30) by creating a compatible
pre-Android 15 version of the API surface, called
PdfRendererPreV.
Tinh chỉnh tính năng tự động chuyển đổi ngôn ngữ
Android 14 added on-device, multi-language recognition in audio with automatic
switching between languages, but this can cause words to get dropped,
especially when languages switch with less of a pause between the two
utterances. Android 15 adds additional controls to help apps tune this switching
to their use case.
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS
confines the automatic switching to the beginning of the audio session, while
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES deactivates the
language switching after a defined number of switches. These options are
particularly useful if you expect that there will be a single language spoken
during the session that should be autodetected.
Cải thiện OpenType Variable Font API
Android 15 improves the usability of the OpenType variable font. You can create
a FontFamily instance from a variable font without specifying weight axes
with the buildVariableFamily API. The text renderer overrides the value
of wght axis to match the displaying text.
Using the API simplifies the code for creating a Typeface considerably:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
Previously, to create the same Typeface, you would need much more code:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Here's an example of how a Typeface created with both the old and new APIs
renders:
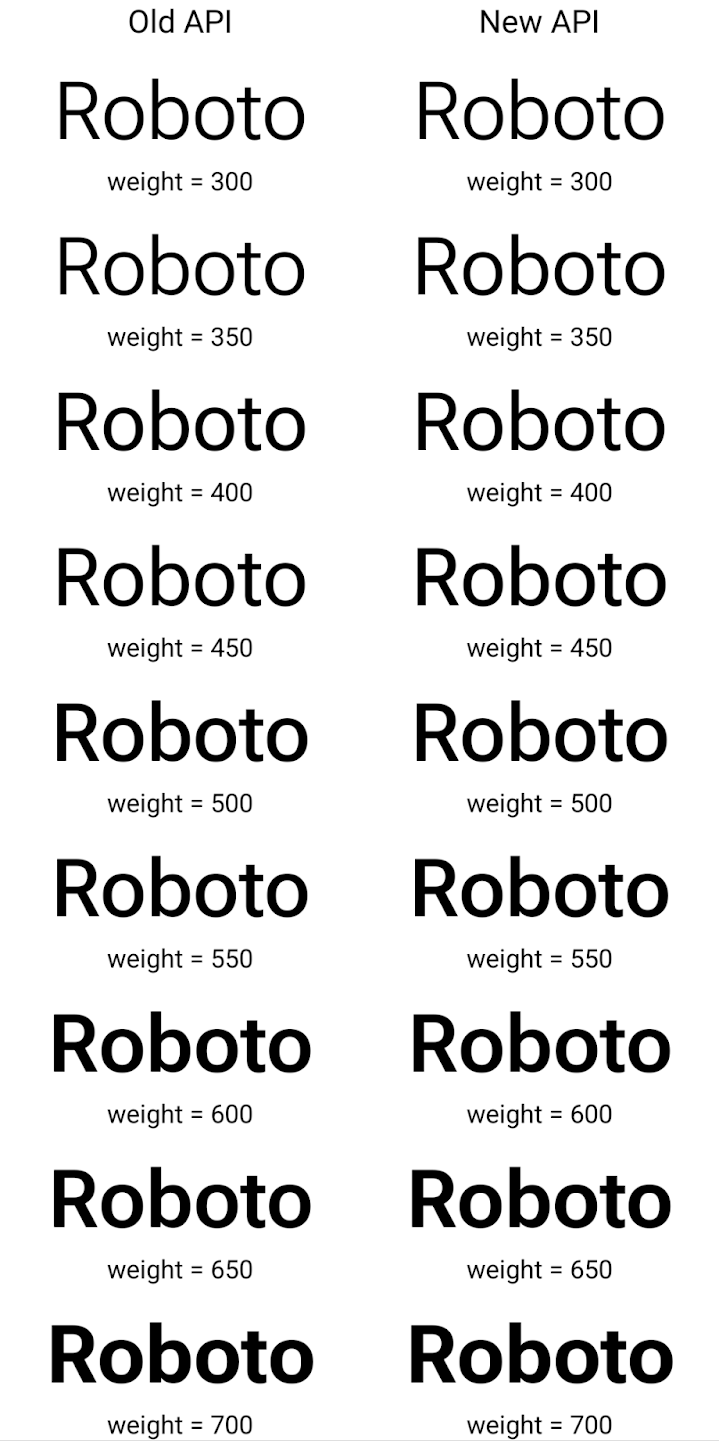
In this example, the Typeface created with the old API doesn't have the
capability to create accurate font weights for the 350, 450, 550 and 650
Font instances, so the renderer falls back to the closest weight. So in
this case, 300 is rendered instead of 350, 400 is rendered instead of 450, and
so on. By contrast, the Typeface created with the new APIs dynamically creates
a Font instance for a given weight, so accurate weights are rendered for 350,
450, 550, and 650 as well.
Các chế độ kiểm soát chi tiết dấu ngắt dòng
Kể từ Android 15, TextView và trình ngắt dòng cơ bản có thể giữ nguyên phần văn bản nhất định trong cùng một dòng để cải thiện khả năng đọc. Bạn có thể tận dụng tính năng tuỳ chỉnh ngắt dòng này bằng cách sử dụng thẻ <nobreak> trong tài nguyên chuỗi hoặc createNoBreakSpan. Tương tự, bạn có thể giữ nguyên các từ không bị xuống dòng bằng cách sử dụng thẻ <nohyphen> hoặc createNoHyphenationSpan.
Ví dụ: tài nguyên chuỗi sau đây không có dấu ngắt dòng và hiển thị với văn bản "Pixel 8 Pro" bị ngắt ở vị trí không mong muốn:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
Ngược lại, tài nguyên chuỗi này bao gồm thẻ <nobreak>, thẻ này gói cụm từ "Pixel 8 Pro" và ngăn chặn dấu ngắt dòng:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
Sự khác biệt trong cách hiển thị các chuỗi này được thể hiện trong các hình ảnh sau:

<nobreak>.
<nobreak>.Lưu trữ ứng dụng
Android và Google Play đã công bố hỗ trợ tính năng lưu trữ ứng dụng vào năm ngoái, cho phép người dùng giải phóng dung lượng bằng cách xoá một phần các ứng dụng ít dùng trên thiết bị được phát hành bằng Android App Bundle trên Google Play. Android 15 hỗ trợ cấp hệ điều hành để lưu trữ và huỷ lưu trữ ứng dụng, giúp tất cả các cửa hàng ứng dụng dễ dàng triển khai tính năng này.
Các ứng dụng có quyền REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES có thể gọi
PackageInstaller requestArchive để yêu cầu lưu trữ một
đã cài đặt gói ứng dụng. Thao tác này sẽ xoá APK và mọi tệp đã lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm nhưng vẫn tồn tại
dữ liệu người dùng. Các ứng dụng đã lưu trữ được trả về dưới dạng ứng dụng có thể hiển thị thông qua các API LauncherApps; người dùng sẽ thấy một cách xử lý giao diện người dùng để làm nổi bật rằng các ứng dụng đó đã được lưu trữ. Nếu người dùng nhấn vào một ứng dụng đã lưu trữ, trình cài đặt chịu trách nhiệm sẽ nhận được yêu cầu huỷ lưu trữ ứng dụng đó và quá trình khôi phục có thể được theo dõi bằng thông báo truyền tin ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED.
Bật chế độ 16 KB trên thiết bị bằng cách sử dụng tuỳ chọn cho nhà phát triển
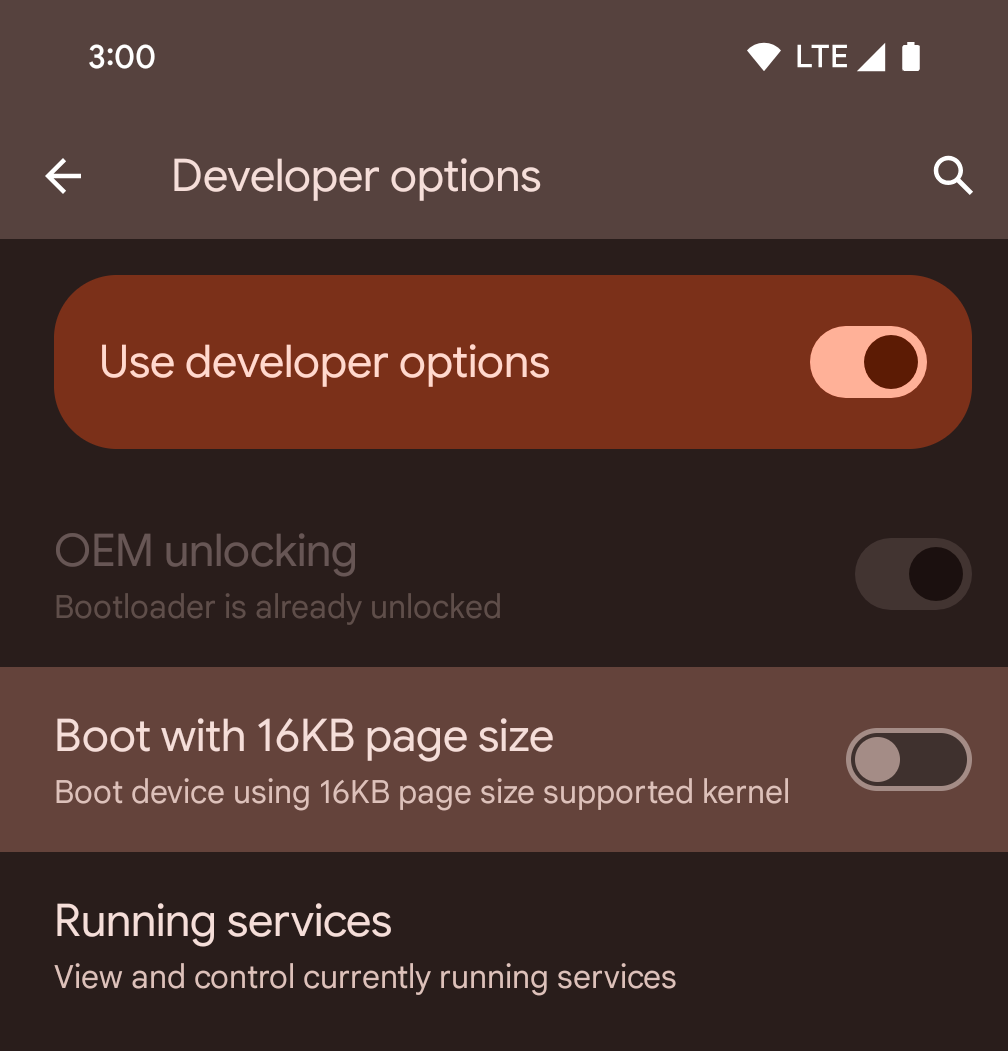
Bật/tắt lựa chọn cho nhà phát triển Khởi động với kích thước trang 16 KB để khởi động thiết bị ở chế độ 16 KB.
Trong các phiên bản QPR của Android 15, bạn có thể sử dụng tùy chọn cho nhà phát triển có trên một số thiết bị để khởi động thiết bị ở chế độ 16 KB và thực hiện kiểm thử trên thiết bị. Trước khi sử dụng tuỳ chọn cho nhà phát triển, hãy chuyển đến phần Cài đặt > Hệ thống > Bản cập nhật phần mềm rồi áp dụng mọi bản cập nhật hiện có.
Tuỳ chọn cho nhà phát triển này có trên các thiết bị sau:
Pixel 8 và 8 Pro (chạy Android 15 QPR1 trở lên)
Pixel 8a (chạy Android 15 QPR1 trở lên)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro và 9 Pro XL (chạy Android 15 QPR2 trở lên)
Pixel 9a (chạy Android 16 trở lên)
Đồ hoạ
Android 15 mang đến những điểm cải tiến mới nhất về đồ hoạ, bao gồm cả ANGLE và các điểm bổ sung cho hệ thống đồ hoạ Canvas.
Hiện đại hoá quyền truy cập vào GPU của Android

Android hardware has evolved quite a bit from the early days where the core OS would run on a single CPU and GPUs were accessed using APIs based on fixed-function pipelines. The Vulkan® graphics API has been available in the NDK since Android 7.0 (API level 24) with a lower-level abstraction that better reflects modern GPU hardware, scales better to support multiple CPU cores, and offers reduced CPU driver overhead — leading to improved app performance. Vulkan is supported by all modern game engines.
Vulkan is Android's preferred interface to the GPU. Therefore, Android 15 includes ANGLE as an optional layer for running OpenGL® ES on top of Vulkan. Moving to ANGLE will standardize the Android OpenGL implementation for improved compatibility, and, in some cases, improved performance. You can test out your OpenGL ES app stability and performance with ANGLE by enabling the developer option in Settings -> System -> Developer Options -> Experimental: Enable ANGLE on Android 15.
The Android ANGLE on Vulkan roadmap
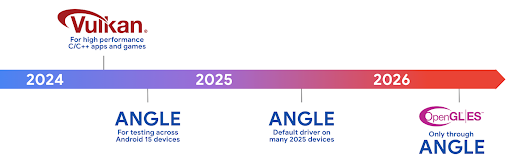
As part of streamlining our GPU stack, going forward we will be shipping ANGLE as the GL system driver on more new devices, with the future expectation that OpenGL/ES will be only available through ANGLE. That being said, we plan to continue support for OpenGL ES on all devices.
Recommended next steps
Use the developer options to select the ANGLE driver for OpenGL ES and test your app. For new projects, we strongly encourage using Vulkan for C/C++.
Những điểm cải tiến cho Canvas
Android 15 continues our modernization of Android's Canvas graphics system with additional capabilities:
Matrix44provides a 4x4 matrix for transforming coordinates that should be used when you want to manipulate the canvas in 3D.clipShaderintersects the current clip with the specified shader, whileclipOutShadersets the clip to the difference of the current clip and the shader, each treating the shader as an alpha mask. This supports the drawing of complex shapes efficiently.
Hiệu suất và pin
Android tiếp tục tập trung vào việc giúp bạn cải thiện hiệu suất và chất lượng của ứng dụng. Android 15 giới thiệu các API giúp thực hiện các tác vụ trong ứng dụng của bạn hiệu quả hơn, tối ưu hoá hiệu suất ứng dụng và thu thập thông tin chi tiết về ứng dụng của bạn.
Để biết các phương pháp hay nhất giúp tiết kiệm pin, gỡ lỗi mức sử dụng mạng và điện năng, cũng như thông tin chi tiết về cách chúng tôi cải thiện hiệu suất sử dụng pin của hoạt động ở chế độ nền trong Android 15 và các phiên bản Android gần đây, hãy xem bài nói chuyện Cải thiện hiệu suất sử dụng pin của hoạt động ở chế độ nền trên Android trong Google I/O.
ApplicationStartInfo API
In previous versions of Android, app startup has been a bit of a mystery. It was
challenging to determine within your app whether it started from a cold, warm,
or hot state. It was also difficult to know how long your app spent during the
various launch phases: forking the process, calling onCreate, drawing the
first frame, and more. When your Application class was instantiated, you had no
way of knowing whether the app started from a broadcast, a content provider, a
job, a backup, boot complete, an alarm, or an Activity.
The ApplicationStartInfo API on Android 15 provides
all of this and more. You can even choose to add your own timestamps into the
flow to help collect timing data in one place. In addition to collecting
metrics, you can use ApplicationStartInfo to help directly optimize app
startup; for example, you can eliminate the costly instantiation of UI-related
libraries within your Application class when your app is starting up due to a
broadcast.
Thông tin chi tiết về kích thước ứng dụng
Since Android 8.0 (API level 26), Android has included the
StorageStats.getAppBytes API that summarizes the installed
size of an app as a single number of bytes, which is a sum of the APK size, the
size of files extracted from the APK, and files that were generated on the
device such as ahead-of-time (AOT) compiled code. This number is not very
insightful in terms of how your app is using storage.
Android 15 adds the
StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API, which lets
you get insight into how your app is using up all that space, including APK file
splits, AOT and speedup related code, dex metadata, libraries, and guided
profiles.
Lập hồ sơ do ứng dụng quản lý
Android 15 bao gồm lớp ProfilingManager, cho phép bạn thu thập thông tin phân tích tài nguyên từ trong ứng dụng, chẳng hạn như tệp báo lỗi, hồ sơ vùng nhớ khối xếp, lấy mẫu ngăn xếp, v.v. Mã này cung cấp lệnh gọi lại cho ứng dụng kèm theo thẻ đã cung cấp để xác định tệp đầu ra. Tệp này được phân phối đến thư mục tệp của ứng dụng. API này giới hạn tốc độ để giảm thiểu tác động đến hiệu suất.
Để đơn giản hoá việc tạo các yêu cầu phân tích tài nguyên trong ứng dụng, bạn nên sử dụng API AndroidX Profiling tương ứng, có trong Core 1.15.0-rc01 trở lên.
Cải tiến cơ sở dữ liệu SQLite
Android 15 giới thiệu các API SQLite hiển thị các tính năng nâng cao từ công cụ SQLite cơ bản nhắm đến các vấn đề hiệu suất cụ thể có thể xuất hiện trong ứng dụng. Các API này đi kèm với bản cập nhật SQLite cho phiên bản 3.44.3.
Nhà phát triển nên tham khảo các phương pháp hay nhất về hiệu suất SQLite để khai thác tối đa cơ sở dữ liệu SQLite, đặc biệt là khi làm việc với các cơ sở dữ liệu lớn hoặc khi chạy các truy vấn nhạy cảm với độ trễ.
- Giao dịch bị hoãn chỉ có thể đọc: khi thực hiện các giao dịch có
chỉ đọc (không bao gồm câu lệnh ghi), hãy sử dụng
beginTransactionReadOnly()vàbeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)để phát hành giao dịchDEFERREDchỉ đọc. Các giao dịch như vậy có thể chạy đồng thời với nhau và nếu cơ sở dữ liệu ở chế độ WAL, chúng có thể chạy đồng thời với các giao dịchIMMEDIATEhoặcEXCLUSIVE. - Số lượng hàng và mã nhận dạng: Các API được thêm vào để truy xuất số lượng hàng đã thay đổi
hàng hoặc mã hàng được chèn gần đây nhất mà không tạo thêm truy vấn.
getLastChangedRowCount()trả về số lượng hàng được chèn, cập nhật hoặc xoá bởi câu lệnh SQL gần đây nhất trong giao dịch hiện tại, trong khigetTotalChangedRowCount()sẽ trả về số lượng trên kết nối hiện tại.getLastInsertRowId()trả vềrowidcủa hàng cuối cùng cần chèn vào kết nối hiện tại. - Câu lệnh thô: phát hành một câu lệnh SQlite thô, bỏ qua các trình bao bọc thuận tiện và mọi chi phí xử lý bổ sung mà chúng có thể phát sinh.
Bản cập nhật Khung hiệu suất động Android
Android 15 tiếp tục đầu tư vào Khung hiệu suất động Android (ADPF), một tập hợp API cho phép các trò chơi và ứng dụng cần nhiều hiệu suất tương tác trực tiếp hơn với hệ thống nguồn điện và nhiệt của thiết bị Android. Trên các thiết bị được hỗ trợ, Android 15 bổ sung các tính năng của ADPF:
- Chế độ tiết kiệm điện năng cho các phiên gợi ý để cho biết rằng các luồng liên kết của chúng nên ưu tiên tiết kiệm điện năng hơn là hiệu suất, rất phù hợp với khối lượng công việc trong nền chạy trong thời gian dài.
- Bạn có thể báo cáo cả thời lượng công việc của GPU và CPU trong các phiên gợi ý, cho phép hệ thống điều chỉnh tần suất CPU và GPU cùng nhau để đáp ứng tốt nhất nhu cầu về khối lượng công việc.
- Ngưỡng khoảng nhiệt để diễn giải trạng thái điều tiết nhiệt có thể xảy ra dựa trên dự đoán khoảng nhiệt.
Để tìm hiểu thêm về cách sử dụng ADPF trong ứng dụng và trò chơi, hãy truy cập vào tài liệu.
Quyền riêng tư
Android 15 có nhiều tính năng giúp nhà phát triển ứng dụng bảo vệ quyền riêng tư của người dùng.
Phát hiện bản ghi màn hình
Android 15 adds support for apps to detect that they are being recorded. A callback is invoked whenever the app transitions between being visible or invisible within a screen recording. An app is considered visible if activities owned by the registering process's UID are being recorded. This way, if your app is performing a sensitive operation, you can inform the user that they're being recorded.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
Các chức năng mở rộng của IntentFilter
Android 15 builds in support for more precise Intent resolution through
UriRelativeFilterGroup, which contains a set of
UriRelativeFilter objects that form a set of Intent
matching rules that must each be satisfied, including URL query parameters, URL
fragments, and blocking or exclusion rules.
These rules can be defined in the AndroidManifest XML file with the
<uri-relative-filter-group> tag, which can optionally include an
android:allow tag. These tags can contain <data> tags that use existing data
tag attributes as well as the android:query and android:fragment
attributes.
Here's an example of the AndroidManifest syntax:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
Không gian riêng tư
Không gian riêng tư cho phép người dùng tạo một không gian riêng biệt trên thiết bị của họ, nơi họ có thể bảo vệ các ứng dụng nhạy cảm khỏi những ánh mắt tò mò, nhờ một lớp xác thực bổ sung. Không gian riêng tư sử dụng một hồ sơ người dùng riêng biệt. Người dùng có thể chọn sử dụng phương thức khoá thiết bị hoặc một phương thức khoá riêng biệt cho không gian riêng tư.
Các ứng dụng trong không gian riêng tư sẽ xuất hiện trong một vùng chứa riêng biệt trong trình chạy và bị ẩn khỏi chế độ xem gần đây, thông báo, phần cài đặt và các ứng dụng khác khi không gian riêng tư bị khoá. Nội dung do người dùng tạo và tải xuống (chẳng hạn như nội dung nghe nhìn hoặc tệp) và tài khoản được tách riêng giữa không gian riêng tư và không gian chính. Bạn có thể dùng trang chia sẻ nội dung của hệ thống và công cụ chọn ảnh để cấp cho ứng dụng quyền truy cập vào nội dung trên các không gian khi không gian riêng tư được mở khoá.
Người dùng không thể di chuyển các ứng dụng hiện có và dữ liệu của ứng dụng vào không gian riêng tư. Thay vào đó, người dùng chọn một tuỳ chọn cài đặt trong không gian riêng tư để cài đặt ứng dụng bằng bất kỳ cửa hàng ứng dụng nào họ muốn. Các ứng dụng trong không gian riêng tư được cài đặt dưới dạng bản sao riêng biệt với mọi ứng dụng trong không gian chính (bản sao mới của cùng một ứng dụng).
Khi người dùng khoá không gian riêng tư, hồ sơ sẽ bị dừng. Khi hồ sơ bị dừng, các ứng dụng trong không gian riêng tư sẽ không còn hoạt động và không thể thực hiện các hoạt động trên nền trước hoặc trong nền, bao gồm cả việc hiển thị thông báo.
Bạn nên kiểm thử ứng dụng của mình trong không gian riêng tư để đảm bảo ứng dụng hoạt động như mong đợi, đặc biệt là nếu ứng dụng của bạn thuộc một trong các danh mục sau:
- Các ứng dụng có logic cho hồ sơ công việc giả định rằng mọi bản sao đã cài đặt của ứng dụng không có trong hồ sơ chính đều nằm trong hồ sơ công việc.
- Ứng dụng y tế
- Ứng dụng trình chạy
- Ứng dụng trên cửa hàng ứng dụng
Truy vấn lựa chọn gần đây nhất của người dùng đối với quyền truy cập vào ảnh đã chọn
Apps can now highlight only the most-recently-selected photos and videos when
partial access to media permissions is granted. This feature can improve
the user experience for apps that frequently request access to photos and
videos. To use this feature in your app, enable the
QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY argument when querying MediaStore
through ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Hộp cát về quyền riêng tư trên Android
Android 15 bao gồm các tiện ích Dịch vụ quảng cáo Android mới nhất, tích hợp phiên bản mới nhất của Hộp cát về quyền riêng tư trên Android. Việc bổ sung này là một phần trong nỗ lực phát triển các công nghệ giúp cải thiện quyền riêng tư của người dùng và mang lại trải nghiệm quảng cáo được cá nhân hoá hiệu quả cho các ứng dụng di động. Trang về hộp cát về quyền riêng tư của chúng tôi có thêm thông tin về các chương trình beta và bản dùng thử cho nhà phát triển của Hộp cát về quyền riêng tư trên Android để giúp bạn bắt đầu.
Health Connect
Android 15 integrates the latest extensions around Health Connect by Android, a secure and centralized platform to manage and share app-collected health and fitness data. This update adds support for additional data types across fitness, nutrition, skin temperature, training plans, and more.
Skin temperature tracking allows users to store and share more accurate temperature data from a wearable or other tracking device.
Training plans are structured workout plans to help a user achieve their fitness goals. Training plans support includes a variety of completion and performance goals:
- Completion goals around calories burned, distance, duration, repetition, and steps.
- Performance goals around as many repetitions as possible (AMRAP), cadence, heart rate, power, perceived rate of exertion, and speed.
Learn more about the latest updates to Health Connect in Android in the Building adaptable experiences with Android Health talk from Google I/O.
Chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng
Android 15 hỗ trợ tính năng chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng để người dùng có thể chỉ chia sẻ hoặc ghi lại một cửa sổ ứng dụng thay vì toàn bộ màn hình thiết bị. Tính năng này được bật lần đầu trong Android 14 QPR2, bao gồm các lệnh gọi lại MediaProjection cho phép ứng dụng của bạn tuỳ chỉnh trải nghiệm chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng. Xin lưu ý rằng đối với các ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 14 (API cấp 34) trở lên, bạn phải có sự đồng ý của người dùng đối với mỗi phiên chụp MediaProjection.
Trải nghiệm người dùng và giao diện người dùng hệ thống
Android 15 mang đến cho nhà phát triển ứng dụng và người dùng nhiều quyền kiểm soát và tính linh hoạt hơn khi định cấu hình thiết bị cho phù hợp với nhu cầu của họ.
Để tìm hiểu thêm về cách sử dụng những điểm cải tiến mới nhất trong Android 15 nhằm cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng của ứng dụng, hãy xem bài nói chuyện Cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng trong ứng dụng Android tại Google I/O.
Bản xem trước tiện ích phong phú hơn nhờ Generated Previews API
Trước Android 15, cách duy nhất để cung cấp bản xem trước bộ chọn tiện ích là chỉ định một hình ảnh hoặc tài nguyên bố cục tĩnh. Các bản xem trước này thường khác biệt đáng kể với giao diện của tiện ích thực tế khi được đặt trên màn hình chính. Ngoài ra, không thể tạo tài nguyên tĩnh bằng Jetpack Glance, vì vậy tính năng Glance nhà phát triển phải chụp ảnh màn hình tiện ích của họ hoặc tạo bố cục XML để có một bản xem trước tiện ích.
Android 15 bổ sung tính năng hỗ trợ cho bản xem trước đã tạo. Điều này có nghĩa là trình cung cấp tiện ích ứng dụng có thể tạo RemoteViews để dùng làm bản xem trước bộ chọn, thay vì tài nguyên tĩnh.
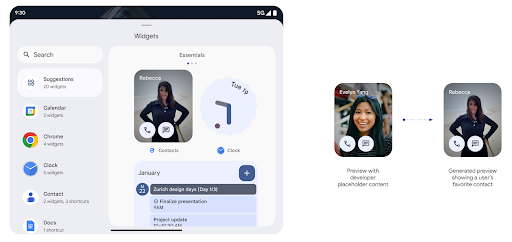
API Đẩy
Ứng dụng có thể cung cấp bản xem trước đã tạo thông qua API đẩy. Ứng dụng có thể cung cấp bản xem trước tại bất kỳ thời điểm nào trong vòng đời và không nhận được yêu cầu rõ ràng từ máy chủ lưu trữ để cung cấp bản xem trước. Bản xem trước được lưu trữ trong AppWidgetService và máy chủ lưu trữ có thể yêu cầu bản xem trước theo yêu cầu. Ví dụ sau đây tải tài nguyên bố cục tiện ích XML và đặt tài nguyên đó làm bản xem trước:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
Quy trình dự kiến là:
- Nhà cung cấp tiện ích sẽ gọi
setWidgetPreviewbất cứ lúc nào. Các bản xem trước được cung cấp sẽ được lưu trữ trongAppWidgetServicecùng với thông tin khác của nhà cung cấp. setWidgetPreviewthông báo cho máy chủ lưu trữ về bản xem trước đã cập nhật thông qua lệnh gọi lạiAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged. Để phản hồi, máy chủ của tiện ích sẽ tải lại tất cả thông tin của nhà cung cấp.- Khi hiển thị bản xem trước của tiện ích, máy chủ lưu trữ sẽ kiểm tra
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategoriesvà nếu được chọn có sẵn danh mục, hãy gọiAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewtới trả về bản xem trước đã lưu cho ứng dụng nhà cung cấp này.
Thời điểm gọi setWidgetPreview
Do không có lệnh gọi lại để cung cấp bản xem trước, ứng dụng có thể chọn gửi bản xem trước bất kỳ lúc nào khi chúng đang chạy. Tần suất cập nhật bản xem trước phụ thuộc vào trường hợp sử dụng tiện ích.
Danh sách sau đây mô tả hai danh mục chính của trường hợp sử dụng bản xem trước:
- Những nhà cung cấp cho thấy dữ liệu thực trong bản xem trước tiện ích, chẳng hạn như dữ liệu được cá nhân hoá hoặc thông tin gần đây. Các nhà cung cấp này có thể thiết lập bản xem trước sau khi người dùng đăng nhập hoặc đã định cấu hình ban đầu trong ứng dụng của họ. Sau đó, họ có thể thiết lập một tác vụ định kỳ để cập nhật bản xem trước theo tần suất mà họ chọn. Ví dụ về loại tiện ích này có thể là ảnh, lịch, thời tiết hoặc tin tức tiện ích.
- Các trình cung cấp hiển thị thông tin tĩnh trong bản xem trước hoặc tiện ích thao tác nhanh mà không hiển thị bất kỳ dữ liệu nào. Các nhà cung cấp này có thể đặt bản xem trước một lần, khi khởi chạy ứng dụng lần đầu tiên. Ví dụ về loại tiện ích này bao gồm trình đơn nhanh tiện ích hành động hoặc tiện ích lối tắt Chrome.
Một số nhà cung cấp có thể hiển thị bản xem trước tĩnh trên bộ chọn chế độ thiết bị trung tâm, nhưng thực tế thông tin trên bộ chọn màn hình chính. Các nhà cung cấp này phải tuân theo hướng dẫn cho cả hai trường hợp sử dụng này để đặt bản xem trước.
Hình trong hình
Android 15 introduces changes in Picture-in-Picture (PiP) ensuring an even smoother transition when entering into PiP mode. This will be beneficial for apps having UI elements overlaid on top of their main UI, which goes into PiP.
Developers use the onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to define logic
that toggles the visibility of the overlaid UI elements. This callback is
triggered when the PiP enter or exit animation is completed. Beginning in
Android 15, the PictureInPictureUiState class includes another state.
With this UI state, apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) will observe the
Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback being invoked with
isTransitioningToPip() as soon as the PiP animation starts. There are
many UI elements that are not relevant for the app when it is in PiP mode, for
example views or layout that include information such as suggestions, upcoming
video, ratings, and titles. When the app goes to PiP mode, use the
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback to hide these UI elements. When the
app goes to full screen mode from the PiP window, use
onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to unhide these elements, as shown in
the following examples:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
This quick visibility toggle of irrelevant UI elements (for a PiP window) helps ensure a smoother and flicker-free PiP enter animation.
Cải thiện quy tắc Không làm phiền
AutomaticZenRule cho phép các ứng dụng tuỳ chỉnh các quy tắc Quản lý sự chú ý (Không làm phiền) và quyết định thời điểm kích hoạt hoặc huỷ kích hoạt các quy tắc đó. Android 15 cải thiện đáng kể các quy tắc này với mục tiêu cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng. Các điểm cải tiến sau đây:
- Thêm các loại vào
AutomaticZenRule, cho phép hệ thống áp dụng các loại đặc biệt xử lý tín dụng đối với một số quy tắc. - Thêm một biểu tượng vào
AutomaticZenRule, giúp cải thiện các chế độ có thể nhận ra. - Thêm một chuỗi
triggerDescriptionvàoAutomaticZenRuleđể mô tả các điều kiện mà quy tắc sẽ bắt đầu hoạt động cho người dùng. - Thêm
ZenDeviceEffectsvàoAutomaticZenRule, cho phép các quy tắc kích hoạt những tính năng như hiển thị thang màu xám, chế độ ban đêm hoặc giảm độ sáng hình nền.
Đặt VibrationEffect cho các kênh thông báo
Android 15 supports setting rich vibrations for incoming notifications by
channel using NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect, so
your users can distinguish between different types of notifications without
having to look at their device.
Khối nội dung trên thanh trạng thái của tính năng chiếu nội dung nghe nhìn và tính năng tự động dừng
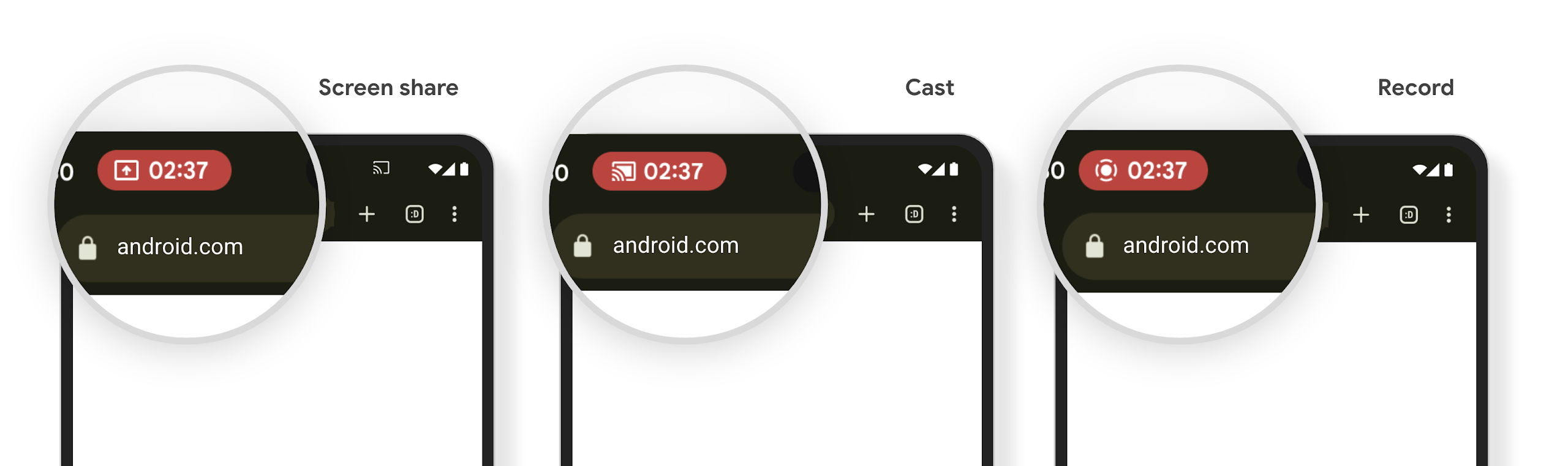
Media projection can expose private user information. A new, prominent status bar chip makes users aware of any ongoing screen projection. Users can tap the chip to stop screen casting, sharing, or recording. Also, for a more intuitive user experience, any in‑progress screen projection now automatically stops when the device screen is locked.
Màn hình lớn và kiểu dáng
Android 15 hỗ trợ các ứng dụng của bạn khai thác tối đa các kiểu dáng của Android, bao gồm cả màn hình lớn, thiết bị có thể lật và thiết bị có thể gập lại.
Cải thiện khả năng đa nhiệm trên màn hình lớn
Android 15 gives users better ways to multitask on large screen devices. For example, users can save their favorite split-screen app combinations for quick access and pin the taskbar on screen to quickly switch between apps. This means that making sure your app is adaptive is more important than ever.
Google I/O has sessions on Building adaptive Android apps and Building UI with the Material 3 adaptive library that can help, and our documentation has more to help you Design for large screens.
Hỗ trợ màn hình ngoài
Your app can declare a property that Android 15 uses to
allow your Application or Activity to be presented on the small cover
screens of supported flippable devices. These screens are too small to be
considered as compatible targets for Android apps to run on, but your app can
opt in to supporting them, making your app available in more places.
Khả năng kết nối
Android 15 cập nhật nền tảng để ứng dụng của bạn có thể sử dụng những tiến bộ mới nhất về công nghệ truyền thông và không dây.
Hỗ trợ vệ tinh
Android 15 tiếp tục mở rộng khả năng hỗ trợ nền tảng cho khả năng kết nối vệ tinh và bao gồm một số thành phần trên giao diện người dùng để đảm bảo trải nghiệm người dùng nhất quán trên bối cảnh kết nối vệ tinh.
Các ứng dụng có thể dùng ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() để
phát hiện thời điểm thiết bị được kết nối với vệ tinh, giúp thiết bị nhận biết rõ hơn về
lý do tại sao dịch vụ mạng đầy đủ có thể không khả dụng. Ngoài ra, Android 15 còn hỗ trợ các ứng dụng SMS và MMS cũng như các ứng dụng RCS được tải sẵn để sử dụng kết nối vệ tinh nhằm gửi và nhận tin nhắn.
Trải nghiệm NFC mượt mà hơn
Android 15 is working to make the tap to pay experience more seamless and
reliable while continuing to support Android's robust NFC app ecosystem. On
supported devices, apps can request the NfcAdapter to enter
observe mode, where the device listens but doesn't respond to NFC
readers, sending the app's NFC service PollingFrame
objects to process. The PollingFrame objects can be used to auth
ahead of the first communication to the NFC reader, allowing for a one tap
transaction in many cases.
In addition, apps can register a filter on supported devices so they can be notified of polling loop activity, which allows for smooth operation with multiple NFC-aware applications.
Vai trò trong Wallet
Android 15 introduces a Wallet role that allows tighter integration with the user's preferred wallet app. This role replaces the NFC default contactless payment setting. Users can manage the Wallet role holder by navigating to Settings > Apps > Default Apps.
The Wallet role is used when routing NFC taps for AIDs registered in the payment category. Taps always go to the Wallet role holder unless another app that is registered for the same AID is running in the foreground.
This role is also used to determine where the Wallet Quick Access tile should go when activated. When the role is set to "None", the Quick Access tile isn't available and payment category NFC taps are only delivered to the foreground app.
Bảo mật
Android 15 giúp bạn tăng cường tính bảo mật cho ứng dụng, bảo vệ dữ liệu của ứng dụng và mang đến cho người dùng sự minh bạch cũng như quyền kiểm soát đối với dữ liệu của họ. Xem bài nói chuyện Bảo vệ tính bảo mật của người dùng trên Android tại Google I/O để biết thêm về những việc chúng tôi đang làm nhằm cải thiện các biện pháp bảo vệ người dùng và bảo vệ ứng dụng của bạn trước các mối đe doạ mới.
Tích hợp Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực với tính năng tự động điền
Starting with Android 15, developers can link specific views like username or password fields with Credential Manager requests, making it easier to provide a tailored user experience during the sign-in process. When the user focuses on one of these views, a corresponding request is sent to Credential Manager. The resulting credentials are aggregated across providers and displayed in autofill fallback UIs, such as inline suggestions or drop-down suggestions. The Jetpack androidx.credentials library is the preferred endpoint for developers to use and will soon be available to further enhance this feature in Android 15 and higher.
Tích hợp tính năng đăng ký và đăng nhập bằng một lần nhấn với lời nhắc sinh trắc học
Credential Manager integrates biometric prompts into the credential creation and sign-in processes, eliminating the need for providers to manage biometric prompts. As a result, credential providers only need to focus on the results of the create and get flows, augmented with the biometric flow result. This simplified process creates a more efficient and streamlined credential creation and retrieval process.
Quản lý khoá để mã hoá hai đầu
Chúng tôi sẽ ra mắt E2eeContactKeysManager trong Android 15. API này hỗ trợ tính năng mã hoá hai đầu (E2EE) trong các ứng dụng Android của bạn bằng cách cung cấp API cấp hệ điều hành để lưu trữ khoá công khai mã hoá.
E2eeContactKeysManager được thiết kế để tích hợp với ứng dụng danh bạ của nền tảng nhằm cung cấp cho người dùng một cách tập trung để quản lý và xác minh khoá công khai của danh bạ.
Kiểm tra quyền đối với URI nội dung
Android 15 introduces a set of APIs that perform permission checks on content URIs:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: This performs a full permission check on content URIs.Activitymanifest attributerequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: This enforces specified permissions on the provided content URIs at activity launch.ComponentCallerclass forActivitycallers: This represents the app that launched the activity.
Hỗ trợ tiếp cận
Android 15 bổ sung các tính năng giúp cải thiện khả năng hỗ trợ tiếp cận cho người dùng.
Chữ nổi tốt hơn
In Android 15, we've made it possible for TalkBack to support Braille displays that are using the HID standard over both USB and secure Bluetooth.
This standard, much like the one used by mice and keyboards, will help Android support a wider range of Braille displays over time.
Quốc tế hoá
Android 15 bổ sung các tính năng và chức năng bổ trợ cho trải nghiệm người dùng khi thiết bị được dùng bằng nhiều ngôn ngữ.
Phông chữ biến đổi CJK
Starting with Android 15, the font file for Chinese, Japanese, and Korean (CJK) languages, NotoSansCJK, is now a variable font. Variable fonts open up possibilities for creative typography in CJK languages. Designers can explore a broader range of styles and create visually striking layouts that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve.

Căn chỉnh giữa các ký tự
Starting with Android 15, text can be justified utilizing letter spacing by
using JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. Inter-word justification was
first introduced in Android 8.0 (API level 26), and inter-character
justification provides similar capabilities for languages that use the
whitespace character for segmentation, such as Chinese, Japanese, and others.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.Cấu hình ngắt dòng tự động
Android started supporting phrase-based line breaks for Japanese and Korean in
Android 13 (API level 33). However, while phrase-based line breaks improve the
readability of short lines of text, they don't work well for long lines of text.
In Android 15, apps can apply phrase-based line breaks only for short lines
of text, using the LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
option. This option selects the best word style option for the text.
For short lines of text, phrase-based line breaks are used, functioning the same
as LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, as shown in the
following image:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
applies phrase-based line breaks to improve the readability of the text.
This is the same as applying
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.For longer lines of text, LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO uses a no
line-break word style, functioning the same as
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, as shown in the
following image:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
applies no line-break word style to improve the readability of the text.
This is the same as applying
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.Phông chữ Hentaigana tiếng Nhật bổ sung
In Android 15, a font file for old Japanese Hiragana (known as Hentaigana) is bundled by default. The unique shapes of Hentaigana characters can add a distinctive flair to artwork or design while also helping to preserve accurate transmission and understanding of ancient Japanese documents.

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. This logo or a modified version may be used or modified by anyone to refer to the VideoLAN project or any product developed by the VideoLAN team, but does not indicate endorsement by the project.
Vulkan and the Vulkan logo are registered trademarks of the Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL is a registered trademark and the OpenGL ES logo is a trademark of Hewlett Packard Enterprise used by permission by Khronos.
