Android 15 มาพร้อมฟีเจอร์และ API ที่ยอดเยี่ยมสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป ส่วนต่อไปนี้ จะสรุปฟีเจอร์เหล่านี้เพื่อช่วยให้คุณเริ่มต้นใช้งาน API ที่เกี่ยวข้องได้
ดูรายการ API ที่เพิ่ม แก้ไข และนำออกโดยละเอียดได้ในรายงานความแตกต่างของ API ดูรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับ API ที่เพิ่มได้ที่เอกสารอ้างอิง Android API — สำหรับ Android 15 ให้มองหา API ที่เพิ่มใน API ระดับ 35 หากต้องการดูข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับส่วนที่การเปลี่ยนแปลงแพลตฟอร์มอาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ โปรดดูการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทํางานของ Android 15 สําหรับแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 และสําหรับแอปทั้งหมด
กล้องและสื่อ
Android 15 มีฟีเจอร์มากมายที่ช่วยปรับปรุงประสบการณ์การใช้งานกล้องและสื่อ รวมถึงให้คุณเข้าถึงเครื่องมือและฮาร์ดแวร์เพื่อสนับสนุนครีเอเตอร์ในการ ทำให้วิสัยทัศน์ของตนเป็นจริงบน Android
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับฟีเจอร์ล่าสุดและโซลูชันสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอปสำหรับสื่อและกล้องของ Android ได้ที่ทอล์กการสร้างประสบการณ์การใช้งานสื่อและกล้องที่ทันสมัยใน Android จาก Google I/O
การเพิ่มแสงในสภาวะแสงน้อย
Android 15 เปิดตัวการเพิ่มคุณภาพในโหมดแสงน้อย ซึ่งเป็นโหมดการรับแสงอัตโนมัติที่ใช้ได้กับทั้ง Camera 2 และส่วนขยายกล้องโหมดกลางคืน การเพิ่มแสงในสภาวะแสงน้อยจะปรับการเปิดรับแสงของสตรีมตัวอย่างในสภาวะที่มีแสงน้อย ซึ่งแตกต่างจากวิธีที่ส่วนขยายกล้องโหมดกลางคืนสร้างภาพนิ่ง เนื่องจากโหมดกลางคืนจะรวมภาพถ่ายหลายรูปเข้าด้วยกันเพื่อสร้างรูปภาพเดียวที่ปรับปรุงแล้ว แม้ว่าโหมดกลางคืนจะทำงานได้ดีกับการสร้างภาพนิ่ง แต่ก็ไม่สามารถสร้างเฟรมอย่างต่อเนื่อง แต่โหมดเพิ่มคุณภาพในที่แสงน้อยทำได้ การเพิ่มคุณภาพในที่แสงน้อยจึงเปิดใช้ความสามารถของกล้อง เช่น
- แสดงตัวอย่างรูปภาพที่ปรับปรุงแล้วเพื่อให้ผู้ใช้จัดเฟรมรูปภาพที่มีแสงน้อยได้ดียิ่งขึ้น
- การสแกนคิวอาร์โค้ดในที่แสงน้อย
หากเปิดใช้การเพิ่มแสงในสภาวะแสงน้อย ฟีเจอร์นี้จะเปิดโดยอัตโนมัติเมื่อมีระดับแสงต่ำ และปิดเมื่อมีแสงมากขึ้น
แอปสามารถบันทึกจากสตรีมตัวอย่างในสภาพแสงน้อยเพื่อบันทึกวิดีโอที่สว่างขึ้น
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่การเพิ่มคุณภาพในโหมดแสงน้อย
การควบคุมกล้องในแอป
Android 15 เพิ่มส่วนขยายเพื่อให้ควบคุมฮาร์ดแวร์กล้องและอัลกอริทึมของกล้องได้มากขึ้นในอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับ ดังนี้
- การปรับความแรงของแฟลชขั้นสูงที่ช่วยควบคุมความเข้มของแฟลชได้อย่างแม่นยำทั้งในโหมด
SINGLEและTORCHขณะถ่ายภาพ
การควบคุมส่วนหัวของ HDR
Android 15 จะเลือก Headroom ของ HDR ที่เหมาะสมกับความสามารถของอุปกรณ์และความละเอียดของบิตของแผง สำหรับหน้าเว็บที่มีเนื้อหา SDR จำนวนมาก เช่น แอปรับส่งข้อความที่แสดงภาพขนาดย่อ HDR รายการเดียว ลักษณะการทำงานนี้อาจส่งผลเสียต่อความสว่างที่รับรู้ของเนื้อหา SDR Android 15 ให้คุณควบคุม Headroom ของ HDR ด้วย setDesiredHdrHeadroom เพื่อรักษาสมดุลระหว่างเนื้อหา SDR กับ HDR
การควบคุมความดัง

Android 15 เพิ่มการรองรับ มาตรฐานความดัง CTA-2075 เพื่อช่วยคุณ หลีกเลี่ยงความดังของเสียงที่ไม่สอดคล้องกัน และทำให้ผู้ใช้ไม่ต้องคอยฟัง ปรับระดับเสียงเมื่อสลับระหว่างเนื้อหา ระบบใช้ประโยชน์จากลักษณะที่ทราบของอุปกรณ์เอาต์พุต (หูฟังและลำโพง) พร้อมกับข้อมูลเมตาระดับเสียงที่มีอยู่ในเนื้อหาเสียง AAC เพื่อปรับระดับความดังของเสียงและการบีบอัดช่วงไดนามิกอย่างชาญฉลาด
หากต้องการเปิดใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้ คุณต้องตรวจสอบว่าข้อมูลเมตาระดับเสียงพร้อมใช้งานในเนื้อหา AAC และเปิดใช้ฟีเจอร์แพลตฟอร์มในแอป โดยคุณจะต้องสร้างอินสแตนซ์ออบเจ็กต์ LoudnessCodecController ด้วยการเรียกใช้เมธอด create ของฟีเจอร์ดังกล่าวพร้อมด้วยรหัสเซสชันเสียงจาก AudioTrack ที่เชื่อมโยง ซึ่งจะเริ่มใช้การอัปเดตเสียงโดยอัตโนมัติ คุณสามารถส่ง OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener เพื่อแก้ไขหรือกรองพารามิเตอร์ระดับเสียงก่อนที่จะนำไปใช้กับ MediaCodec
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
นอกจากนี้ AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer จะได้รับการอัปเดตให้ใช้ LoudnessCodecControllerAPI เพื่อการผสานรวมแอปอย่างราบรื่น
อุปกรณ์ MIDI 2.0 เสมือน
Android 13 เพิ่มการรองรับการเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์ MIDI 2.0 โดยใช้ USB ซึ่งสื่อสารโดยใช้แพ็กเก็ต MIDI สากล (UMP) Android 15 ขยายการรองรับ UMP ไปยังแอป MIDI เสมือน ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปแต่งเพลงควบคุมแอปซินธิไซเซอร์ได้เสมือนเป็นอุปกรณ์ MIDI 2.0 เสมือนจริง เช่นเดียวกับที่ควบคุมอุปกรณ์ USB MIDI 2.0
การถอดรหัสซอฟต์แวร์ AV1 ที่มีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น

dav1d ซึ่งเป็นโปรแกรมถอดรหัส AV1 ยอดนิยมจาก VideoLAN พร้อมให้ใช้งานในอุปกรณ์ Android ที่ไม่รองรับการถอดรหัส AV1 ในฮาร์ดแวร์แล้ว โดยมีประสิทธิภาพมากกว่าโปรแกรมถอดรหัสซอฟต์แวร์ AV1 รุ่นเดิมถึง 3 เท่า ซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้จำนวนมากขึ้นสามารถเล่น AV1 แบบ HD ได้ รวมถึงอุปกรณ์ระดับกลางและระดับล่างบางรุ่น
แอปของคุณต้องเลือกใช้ dav1d โดยเรียกใช้ตามชื่อ
"c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder" เราจะกำหนดให้ dav1d เป็นโปรแกรมถอดรหัสซอฟต์แวร์ AV1 เริ่มต้นในการอัปเดตครั้งถัดไป การรองรับนี้ได้รับการกำหนดมาตรฐานและพอร์ตไปยังเวอร์ชันเก่าสำหรับอุปกรณ์ Android 11 ที่ได้รับการอัปเดตระบบ Google Play
ประสิทธิภาพการทำงานและเครื่องมือสำหรับนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์
แม้ว่างานส่วนใหญ่ของเราในการปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพการทำงานของคุณจะมุ่งเน้นไปที่เครื่องมือต่างๆ เช่น Android Studio, Jetpack Compose และไลบรารี Android Jetpack แต่เราก็มองหาวิธีต่างๆ ในแพลตฟอร์มอยู่เสมอเพื่อช่วยให้คุณตระหนักถึงวิสัยทัศน์ได้ง่ายขึ้น
การอัปเดต OpenJDK 17
Android 15 ยังคงดำเนินการรีเฟรชไลบรารีหลักของ Android เพื่อปรับให้สอดคล้องกับฟีเจอร์ใน OpenJDK LTS เวอร์ชันล่าสุด
ฟีเจอร์หลักและการปรับปรุงที่สำคัญมีดังนี้
- การปรับปรุงคุณภาพชีวิตเกี่ยวกับบัฟเฟอร์ NIO
- สตรีม
- วิธีเพิ่มเติมสำหรับ
mathและstrictmath - การอัปเดตแพ็กเกจ
utilซึ่งรวมถึงแพ็กเกจcollection,mapและset - การสนับสนุน
ByteBufferในDeflater - การอัปเดตความปลอดภัย เช่น
X500PrivateCredentialและการอัปเดตคีย์ความปลอดภัย
API เหล่านี้ได้รับการอัปเดตในอุปกรณ์กว่า 1 พันล้านเครื่องที่ใช้ Android 12 (API ระดับ 31) ขึ้นไปผ่านการอัปเดตระบบ Google Play เพื่อให้คุณกำหนดเป้าหมายฟีเจอร์การเขียนโปรแกรมล่าสุดได้
การปรับปรุง PDF
Android 15 มีการปรับปรุงที่สำคัญสำหรับ PdfRenderer
API แอปสามารถรวมฟีเจอร์ขั้นสูง เช่น การแสดงผลไฟล์ที่มีการป้องกันด้วยรหัสผ่าน คําอธิบายประกอบ การแก้ไขแบบฟอร์ม การค้นหา และการเลือกพร้อมการคัดลอก PDF เชิงเส้น
รองรับการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพเพื่อให้ดู PDF ในเครื่องได้เร็วขึ้นและลดการใช้ทรัพยากร
ไลบรารี PDF ของ Jetpack ใช้ API เหล่านี้เพื่อให้การเพิ่ม PDF เป็นเรื่องง่าย
ความสามารถในการดูแอปของคุณ
ย้าย PdfRenderer ไปยังโมดูลที่อัปเดตได้โดยใช้ Google แล้ว
การอัปเดตระบบ Play โดยไม่ขึ้นอยู่กับการเปิดตัวแพลตฟอร์ม และเราให้การสนับสนุน
การเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้กลับไปใช้ Android 11 (API ระดับ 30) โดยการสร้าง
แพลตฟอร์ม API ก่อน Android 15 ที่เรียกว่า
PdfRendererPreV
การปรับแต่งการสลับภาษาอัตโนมัติ
Android 14 เพิ่มการจดจำเสียงหลายภาษาในอุปกรณ์ด้วยการสลับระหว่างภาษาโดยอัตโนมัติ แต่วิธีนี้อาจทำให้คำพูดถูกละทิ้ง โดยเฉพาะเมื่อสลับภาษาโดยเว้นช่วงระหว่างคำพูดน้อยลง Android 15 เพิ่มการควบคุมเพิ่มเติมเพื่อช่วยแอปปรับการเปลี่ยนนี้ให้เหมาะกับกรณีการใช้งาน
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS
จำกัดการเปลี่ยนภาษาอัตโนมัติไว้ที่ช่วงต้นของเซสชันเสียง ส่วน EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES จะปิดใช้งานการเปลี่ยนภาษาหลังจากเปลี่ยนจำนวนครั้งที่กำหนด ตัวเลือกเหล่านี้มีประโยชน์อย่างยิ่งในกรณีที่คุณคาดว่าจะมีการใช้ภาษาเดียวในเซสชันที่ควรตรวจจับโดยอัตโนมัติ
API แบบอักษรที่ปรับแต่งได้ OpenType ที่ได้รับการปรับปรุง
Android 15 ปรับปรุงความสามารถในการใช้งานแบบอักษร OpenType แบบแปรผัน คุณสามารถสร้างอินสแตนซ์ FontFamily จากแบบอักษรแบบผันแปรได้โดยไม่ต้องระบุแกนน้ำหนักด้วย buildVariableFamily API ตัวแสดงผลข้อความจะลบล้างค่า
ของแกน wght เพื่อให้ตรงกับข้อความที่แสดง
การใช้ API ช่วยลดความซับซ้อนของโค้ดในการสร้าง Typeface อย่างมาก
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
ก่อนหน้านี้ หากต้องการสร้าง Typeface เดียวกัน คุณต้องใช้โค้ดมากกว่านี้มาก
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
ต่อไปนี้เป็นตัวอย่างการแสดงผลของ Typeface ที่สร้างขึ้นด้วยทั้ง API เก่าและใหม่
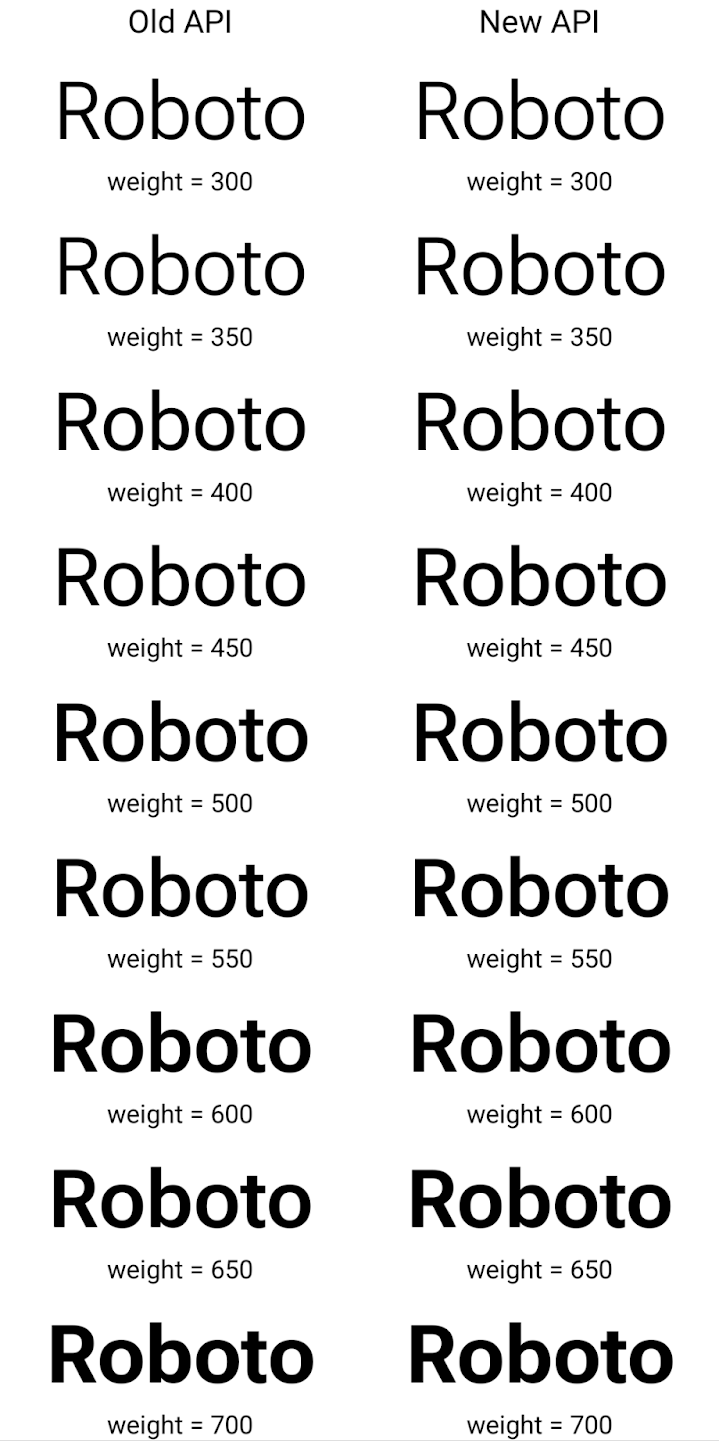
ในตัวอย่างนี้ Typeface ที่สร้างขึ้นด้วย API เก่าไม่มีความสามารถในการสร้างน้ำหนักแบบอักษรที่ถูกต้องสำหรับอินสแตนซ์ 350, 450, 550 และ 650 Font ดังนั้นโปรแกรมแสดงผลจึงใช้น้ำหนักแบบอักษรที่ใกล้เคียงที่สุด ดังนั้นใน
ในกรณีนี้ แสดงผล 300 แทน 350, แสดงผล 400 แทน 450 และ
เป็นต้น ในทางตรงกันข้าม Typeface ที่สร้างด้วย API ใหม่จะสร้าง
อินสแตนซ์ Font สำหรับน้ำหนักที่ระบุ ดังนั้นระบบจะแสดงผลน้ำหนักที่ถูกต้องเป็น 350
450, 550 และ 650 ด้วย
การควบคุมการขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่แบบละเอียด
ตั้งแต่ Android 15 เป็นต้นไป TextView และตัวแบ่งบรรทัดที่สำคัญจะเก็บรักษาข้อความที่ระบุในบรรทัดเดียวกันไว้เพื่อให้อ่านง่ายขึ้น คุณใช้ประโยชน์จากการปรับเปลี่ยนการขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่นี้ได้โดยการใช้แท็ก <nobreak> ในทรัพยากรสตริงหรือ createNoBreakSpan ในทำนองเดียวกัน คุณสามารถคงคำไม่ให้มีการแบ่งวรรคโดยใช้แท็ก <nohyphen> หรือ createNoHyphenationSpan
ตัวอย่างเช่น ทรัพยากรสตริงต่อไปนี้ไม่มีการขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่ และแสดงผลโดยตัดข้อความ "Pixel 8 Pro" ตรงที่ไม่ต้องการ
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
ในทางตรงกันข้าม ทรัพยากรสตริงนี้จะมีแท็ก <nobreak> ซึ่งตัดวลี "Pixel 8 Pro" และป้องกันการขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
ความแตกต่างของวิธีแสดงผลสตริงเหล่านี้จะแสดงอยู่ในรูปภาพต่อไปนี้

<nobreak>
<nobreak>การเก็บแอปถาวร
Android และ Google Play ได้ประกาศรองรับการเก็บถาวรของแอปไปเมื่อปีที่ผ่านมา ซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้เพิ่มพื้นที่ว่างได้ด้วยการนําแอปที่ไม่ได้ใช้บ่อยออกจากอุปกรณ์บางส่วน ซึ่งเผยแพร่โดยใช้ Android App Bundle ใน Google Play Android 15 มีการรองรับการเก็บถาวรแอปในระดับระบบปฏิบัติการ และยกเลิกการเก็บ ซึ่งจะทำให้ App Store ทั้งหมดติดตั้งใช้งานได้ง่ายขึ้น
แอปที่มีสิทธิ์ REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES สามารถเรียกใช้เมธอด requestArchive ของ PackageInstaller เพื่อขอเก็บถาวรแพ็กเกจแอปที่ติดตั้ง ซึ่งจะนำ APK และไฟล์แคชทั้งหมดออก แต่จะเก็บข้อมูลผู้ใช้ไว้ แอปที่เก็บถาวรจะแสดงผลเป็นแอปที่แสดงได้ผ่าน
LauncherApps API ผู้ใช้จะเห็นตัวเลือก UI เพื่อไฮไลต์
เก็บแอปพลิเคชันแล้ว หากผู้ใช้แตะแอปที่เก็บไว้ ผู้ติดตั้งที่รับผิดชอบจะได้รับคําขอให้ยกเลิกการเก็บ และสามารถตรวจสอบกระบวนการกู้คืนได้โดยการออกอากาศ ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED
เปิดใช้โหมด 16 KB ในอุปกรณ์โดยใช้ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป
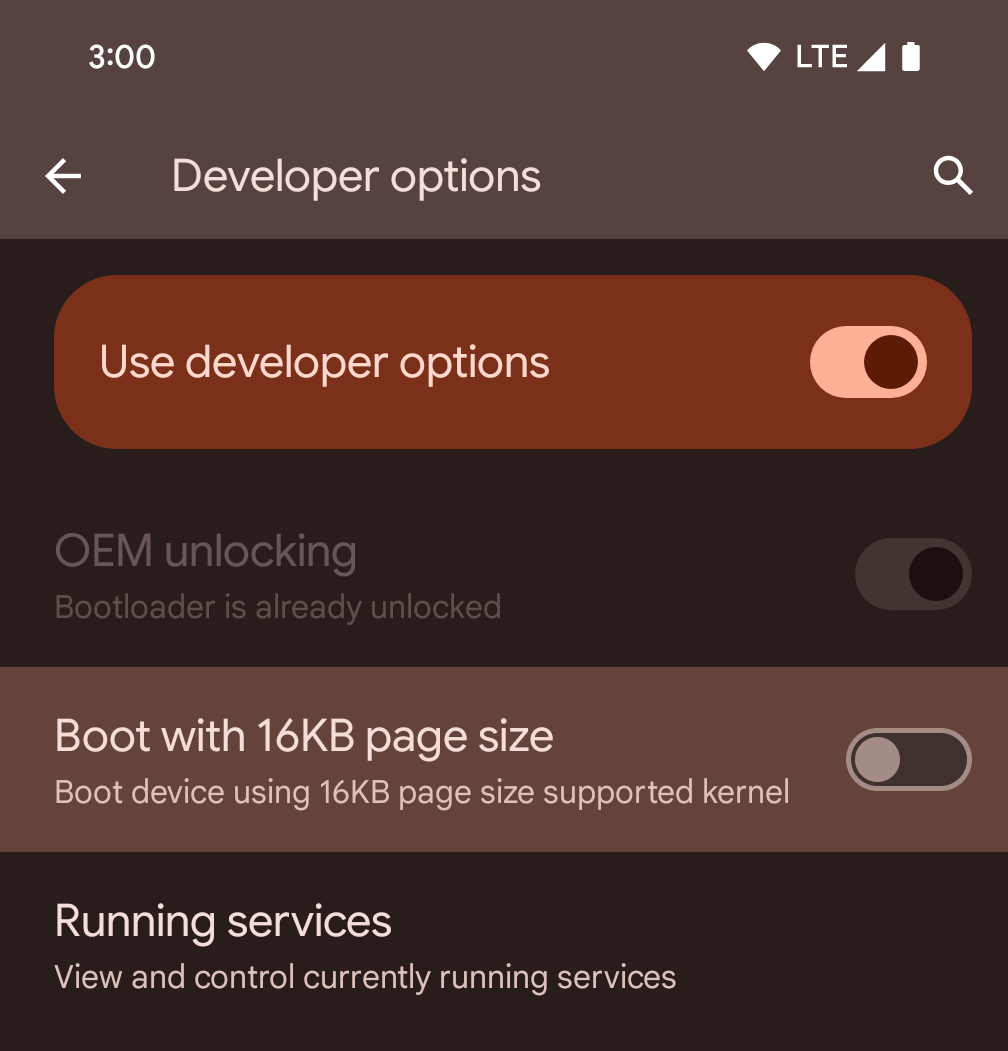
สลับตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอปบูตโดยใช้หน้าหน่วยความจำขนาด 16 KB เพื่อบูตอุปกรณ์ในโหมด 16 KB
ใน Android 15 เวอร์ชัน QPR คุณสามารถใช้ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอปที่มีในอุปกรณ์บางรุ่นเพื่อบูตอุปกรณ์ในโหมด 16 KB และทำการทดสอบในอุปกรณ์ได้ ก่อนใช้ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป ให้ไปที่การตั้งค่า > ระบบ > การอัปเดต ซอฟต์แวร์ แล้วใช้การอัปเดตที่มี
ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอปนี้พร้อมใช้งานในอุปกรณ์ต่อไปนี้
Pixel 8 และ 8 Pro (ที่ใช้ Android 15 QPR1 ขึ้นไป)
Pixel 8a (ใช้ Android 15 QPR1 ขึ้นไป)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro และ 9 Pro XL (ใช้ Android 15 QPR2 Beta 2 ขึ้นไป)
กราฟิก
Android 15 มาพร้อมการปรับปรุงกราฟิกล่าสุด ซึ่งรวมถึง ANGLE และการเพิ่มระบบกราฟิก Canvas
การปรับปรุงการเข้าถึง GPU ของ Android

ฮาร์ดแวร์ Android พัฒนาไปมากจากยุคแรกๆ ที่ระบบปฏิบัติการหลักจะทำงานบน CPU เพียงตัวเดียวและเข้าถึง GPU โดยใช้ API ตามไปป์ไลน์ฟังก์ชันคงที่ Vulkan® graphics API พร้อมใช้งานใน NDK ตั้งแต่ Android 7.0 (API ระดับ 24) โดยใช้การแยกระดับที่ต่ำลงซึ่งแสดงถึงฮาร์ดแวร์ GPU สมัยใหม่ได้ดียิ่งขึ้น ปรับขนาดได้ดียิ่งขึ้นเพื่อรองรับแกน CPU หลายแกน และลดค่าใช้จ่ายเพิ่มเติมของไดรเวอร์ CPU ซึ่งส่งผลให้แอปมีประสิทธิภาพดีขึ้น เครื่องมือเกมสมัยใหม่ทั้งหมดรองรับ Vulkan
Vulkan เป็นอินเทอร์เฟซที่ Android แนะนำสำหรับ GPU ดังนั้น Android 15 จึงรวม ANGLE ไว้เป็นเลเยอร์ที่ไม่บังคับสําหรับการเรียกใช้ OpenGL® ES บน Vulkan การเปลี่ยนไปใช้ ANGLE จะทำให้การใช้งาน OpenGL ของ Android เป็นมาตรฐานเดียวกันเพื่อการทำงานร่วมกันได้ดียิ่งขึ้น และปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพในบางกรณี คุณสามารถทดสอบความเสถียรและประสิทธิภาพของแอป OpenGL ES โดยใช้ ANGLE ได้โดยเปิดใช้ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอปในการตั้งค่า -> ระบบ -> ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป -> ทดลอง: เปิดใช้ ANGLE ใน Android 15
แผนพัฒนา ANGLE บน Vulkan ของ Android
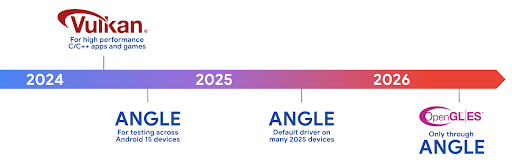
ในอนาคตเราจะจัดส่ง ANGLE เป็นไดรเวอร์ระบบ GL ในอุปกรณ์ใหม่จำนวนมากขึ้นเพื่อปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพของ GPU โดยคาดว่า OpenGL/ES จะใช้งานได้ผ่าน ANGLE เท่านั้น อย่างไรก็ตาม เราวางแผนที่จะรองรับ OpenGL ES บนอุปกรณ์ทุกเครื่องต่อไป
ขั้นตอนถัดไปที่แนะนำ
ใช้ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอปเพื่อเลือกไดรเวอร์ ANGLE สำหรับ OpenGL ES และทดสอบแอป สำหรับโปรเจ็กต์ใหม่ เราขอแนะนำให้ใช้ Vulkan สำหรับ C/C++
การปรับปรุงสำหรับ Canvas
Android 15 สานต่อการพัฒนาระบบกราฟิก Canvas ของ Android ให้ทันสมัยยิ่งขึ้นด้วยความสามารถเพิ่มเติมต่อไปนี้
Matrix44มีเมทริกซ์ 4x4 สำหรับการเปลี่ยนรูปแบบพิกัดที่ควรใช้เมื่อคุณต้องการจัดการผืนผ้าใบใน 3 มิติclipShaderจะตัดกันระหว่างคลิปปัจจุบันกับชิเดอร์ที่ระบุ ขณะที่clipOutShaderจะตั้งค่าคลิปเป็นความแตกต่างระหว่างคลิปปัจจุบันกับชิเดอร์ โดยแต่ละรายการจะถือว่าชิเดอร์เป็นมาสก์อัลฟ่า ซึ่งรองรับการวาดรูปทรงที่ซับซ้อนได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
ประสิทธิภาพและแบตเตอรี่
Android ยังคงมุ่งเน้นที่การช่วยคุณปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพและคุณภาพ ของแอป Android 15 เปิดตัว API ที่ช่วยให้การทำงานในแอปมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพของแอป และรวบรวมข้อมูลเชิงลึกเกี่ยวกับ แอปของคุณ
ดูแนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำเพื่อประสิทธิภาพแบตเตอรี่ การแก้ไขข้อบกพร่องของเครือข่ายและการใช้พลังงาน รวมถึง รายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับวิธีที่เราปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพแบตเตอรี่ของงานที่ทำงานเบื้องหลังใน Android 15 และ Android เวอร์ชันล่าสุดได้ที่ทอล์กการปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพแบตเตอรี่ของ งานที่ทำงานเบื้องหลังใน Android จาก Google I/O
ApplicationStartInfo API
ใน Android เวอร์ชันก่อนหน้า การเริ่มต้นแอปเป็นเรื่องที่เข้าใจยากอยู่บ้าง เราพบว่าการระบุภายในแอปว่าแอปเริ่มต้นจากสถานะเย็น อุ่น หรือร้อนนั้นเป็นเรื่องยาก นอกจากนี้ คุณยังทราบระยะเวลาที่แอปใช้ในการดำเนินการต่างๆ ในระยะเริ่มต้น เช่น การแยกกระบวนการ การเรียก onCreate การวาดเฟรมแรก และอื่นๆ ได้ไม่ชัดเจน เมื่อสร้างอินสแตนซ์คลาส Application แล้ว คุณจะไม่มีทางรู้ว่าแอปเริ่มต้นจากบรีดแคสต์ ผู้ให้บริการเนื้อหา งาน การสำรองข้อมูล การบูตเสร็จสมบูรณ์ การปลุก หรือ Activity
ApplicationStartInfo API ใน Android 15 มีฟีเจอร์ทั้งหมดนี้และอีกมากมาย คุณยังเลือกเพิ่มการประทับเวลาของคุณเองลงในขั้นตอนเพื่อรวบรวมข้อมูลการกําหนดเวลาในที่เดียวได้ด้วย นอกจากการเก็บรวบรวมเมตริกแล้ว คุณยังใช้ ApplicationStartInfo เพื่อช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการเริ่มต้นของแอปได้โดยตรง เช่น คุณอาจลดการสร้างอินสแตนซ์ของไลบรารีที่เกี่ยวข้องกับ UI ในคลาส Application ที่ไม่จำเป็นได้เมื่อแอปเริ่มต้นขึ้นเนื่องจากการออกอากาศ
ข้อมูลขนาดแอปโดยละเอียด
ตั้งแต่ Android 8.0 (API ระดับ 26) เป็นต้นไป Android ได้รวม StorageStats.getAppBytes API ที่สรุปขนาดของแอปที่ติดตั้งเป็นจำนวนไบต์เดียว ซึ่งเป็นผลรวมของขนาด APK, ขนาดของไฟล์ที่ดึงมาจาก APK และไฟล์ที่สร้างในอุปกรณ์ เช่น โค้ดที่คอมไพล์ล่วงหน้า (AOT) ตัวเลขนี้ไม่ได้ให้ข้อมูลเชิงลึกมากนักเกี่ยวกับวิธีที่แอปใช้พื้นที่เก็บข้อมูล
Android 15 เพิ่ม StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API ซึ่งจะช่วยให้คุณได้รับข้อมูลเชิงลึกเกี่ยวกับวิธีที่แอปใช้พื้นที่ทั้งหมดนั้น รวมถึงการแยกไฟล์ APK, AOT และโค้ดที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการเร่งความเร็ว, ข้อมูลเมตา dex, ไลบรารี และโปรไฟล์ที่แนะนำ
การทำโปรไฟล์ที่แอปจัดการ
Android 15 มีคลาส ProfilingManager ซึ่งช่วยให้คุณรวบรวมข้อมูลการโปรไฟล์จากภายในแอปได้ เช่น การดัมพ์กอง โปรไฟล์กอง สุ่มตัวอย่างสแต็ก และอื่นๆ โดยจะทำการเรียกกลับไปยังแอปด้วยแท็กที่ระบุเพื่อระบุไฟล์เอาต์พุต ซึ่งระบบจะส่งไปยังไดเรกทอรีไฟล์ของแอป API จะจำกัดอัตราเพื่อลดผลกระทบด้านประสิทธิภาพ
เราขอแนะนําให้ใช้ Profiling AndroidX API ที่เกี่ยวข้องเพื่อลดความซับซ้อนในการสร้างคําขอโปรไฟล์ในแอป ซึ่งพร้อมใช้งานใน Core 1.15.0-rc01 ขึ้นไป
การปรับปรุงฐานข้อมูล SQLite
Android 15 เปิดตัว SQLite API ที่แสดงฟีเจอร์ขั้นสูงจากเครื่องมือ SQLite ที่อยู่เบื้องหลังซึ่งมุ่งเน้นปัญหาด้านประสิทธิภาพที่เฉพาะเจาะจงซึ่งอาจแสดงในแอป API เหล่านี้มาพร้อมกับการอัปเดต SQLite เป็นเวอร์ชัน 3.44.3
นักพัฒนาแอปควรอ่านแนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำสำหรับประสิทธิภาพของ SQLite เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์จากฐานข้อมูล SQLite ให้ได้สูงสุด โดยเฉพาะเมื่อทำงานกับ หรือเมื่อเรียกใช้การค้นหาที่คำนึงถึงเวลาในการตอบสนอง
- ธุรกรรมที่รอดำเนินการแบบอ่านอย่างเดียว: เมื่อออกธุรกรรมแบบอ่านอย่างเดียว (ไม่มีคำสั่งเขียน) ให้ใช้
beginTransactionReadOnly()และbeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)เพื่อออกธุรกรรมDEFERREDแบบอ่านอย่างเดียว ธุรกรรมดังกล่าวทำงานได้ พร้อมๆ กัน และถ้าฐานข้อมูลอยู่ในโหมด WAL จะสามารถส่ง ทำงานพร้อมกันกับธุรกรรมIMMEDIATEหรือEXCLUSIVE - จำนวนแถวและรหัส: มีการเพิ่ม API เพื่อเรียกข้อมูลจำนวนที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลง
หรือรหัสแถวที่แทรกล่าสุดโดยไม่ต้องส่งคำขอเพิ่มเติม
getLastChangedRowCount()จะแสดงจํานวนแถวที่แทรก อัปเดต หรือลบโดยคำสั่ง SQL ล่าสุดภายในธุรกรรมปัจจุบัน ส่วนgetTotalChangedRowCount()จะแสดงจํานวนการเชื่อมต่อปัจจุบันgetLastInsertRowId()แสดงผลrowidของแถวสุดท้าย ที่จะแทรกลงในการเชื่อมต่อปัจจุบัน - ข้อความดิบ: ออกคำสั่ง SQlite ดิบโดยหลีกเลี่ยงความสะดวก Wrapper และค่าใช้จ่ายในการประมวลผลเพิ่มเติมอื่นๆ ที่อาจเกิดขึ้น
การอัปเดตเฟรมเวิร์กประสิทธิภาพแบบไดนามิกของ Android
Android 15 ยังคงลงทุนใน Android Dynamic Performance Framework (ADPF) ซึ่งเป็นชุด API ที่ช่วยให้เกมและแอปที่เน้นประสิทธิภาพสามารถโต้ตอบกับระบบพลังงานและความร้อนของอุปกรณ์ Android ได้โดยตรงยิ่งขึ้น Android 15 เพิ่มความสามารถต่อไปนี้ของ ADPF ในอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับ
- โหมดประหยัดพลังงานสำหรับเซสชันคำแนะนำเพื่อบ่งบอกว่าชุดข้อความที่เกี่ยวข้องควรให้ความสำคัญกับการประหยัดพลังงานมากกว่าประสิทธิภาพ ซึ่งเหมาะสำหรับเวิร์กโหลดที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหลังเป็นเวลานาน
- คุณรายงานระยะเวลาการทำงานของ GPU และ CPU ได้ในเซสชันคำแนะนำ ซึ่งช่วยให้ระบบปรับความถี่ของ CPU และ GPU ร่วมกันเพื่อตอบสนองดีมานด์ของปริมาณงานได้ดีที่สุด
- เกณฑ์ Headroom ความร้อนเพื่อตีความสถานะการจำกัดความร้อนที่เป็นไปได้ตามการคาดการณ์ Headroom
หากต้องการดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธีใช้ ADPF ในแอปและเกม โปรดไปที่เอกสารประกอบ
ความเป็นส่วนตัว
Android 15 มีฟีเจอร์มากมายที่จะช่วยนักพัฒนาแอปปกป้องความเป็นส่วนตัวของผู้ใช้
การตรวจหาการบันทึกหน้าจอ
Android 15 เพิ่มการรองรับแอปเพื่อตรวจจับว่ามีการบันทึกเสียง ระบบจะเรียกใช้การเรียกกลับทุกครั้งที่แอปเปลี่ยนสถานะระหว่างมองเห็นหรือไม่มองเห็นภายในการบันทึกหน้าจอ แอปคือ ถือว่ามองเห็นได้หากกิจกรรมที่เป็นของ UID ของกระบวนการลงทะเบียนนั้น มีการบันทึก วิธีนี้ช่วยให้คุณแจ้งให้ผู้ใช้ทราบว่ามีการบันทึกเสียงอยู่ได้ หากแอปของคุณดําเนินการที่มีความละเอียดอ่อน
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
ความสามารถของ IntentFilter ที่เพิ่มขึ้น
Android 15 รองรับความละเอียดของ Intent ที่แม่นยำยิ่งขึ้นผ่าน UriRelativeFilterGroup ซึ่งมีชุดออบเจ็กต์ UriRelativeFilter ที่ประกอบขึ้นเป็นชุดกฎการจับคู่ Intent ที่ต้องปฏิบัติตามแต่ละส่วน เช่น พารามิเตอร์การค้นหา URL, ส่วนย่อยของ URL และกฎการบล็อกหรือการยกเว้น
คุณกำหนดกฎเหล่านี้ในไฟล์ XML AndroidManifest ได้ด้วยแท็ก <uri-relative-filter-group> ซึ่งอาจรวมแท็ก android:allow หรือไม่ก็ได้ แท็กเหล่านี้อาจมีแท็ก <data> ที่ใช้แอตทริบิวต์แท็กที่มีอยู่ รวมถึงแอตทริบิวต์ android:query และ android:fragment
ตัวอย่างไวยากรณ์ AndroidManifest
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
พื้นที่ส่วนตัว
พื้นที่ส่วนตัวช่วยให้ผู้ใช้สร้างพื้นที่แยกต่างหากในอุปกรณ์ ซึ่งสามารถซ่อนแอปที่มีความละเอียดอ่อนเพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้ผู้อื่นแอบดูได้ภายใต้การตรวจสอบสิทธิ์อีกชั้น พื้นที่ส่วนตัวจะใช้โปรไฟล์ผู้ใช้แยกต่างหาก ผู้ใช้สามารถเลือกใช้การล็อกอุปกรณ์หรือปัจจัยการล็อกแยกต่างหากสำหรับพื้นที่ส่วนตัว
แอปในพื้นที่ส่วนตัวจะปรากฏในคอนเทนเนอร์แยกต่างหากใน Launcher และถูกซ่อนจากมุมมองรายการล่าสุด การแจ้งเตือน การตั้งค่า และแอปอื่นๆ เมื่อล็อกพื้นที่ส่วนตัวไว้ เนื้อหาที่ผู้ใช้สร้างขึ้นและดาวน์โหลด (เช่น สื่อหรือไฟล์) และบัญชีจะแยกกันระหว่างพื้นที่ส่วนตัวและพื้นที่หลัก คุณสามารถใช้ระบบ Sharesheet และเครื่องมือเลือกรูปภาพเพื่อให้แอปเข้าถึงเนื้อหาในพื้นที่ต่างๆ ได้เมื่อปลดล็อกพื้นที่ส่วนตัว
ผู้ใช้จะย้ายแอปที่มีอยู่และข้อมูลของแอปไปยังพื้นที่ส่วนตัวไม่ได้ แต่ผู้ใช้จะเลือกตัวเลือกการติดตั้งในพื้นที่ส่วนตัวเพื่อติดตั้งแอปโดยใช้ App Store ที่ต้องการแทน แอปในพื้นที่ส่วนตัวจะติดตั้งเป็นสำเนาแยกต่างหากจากแอปในพื้นที่หลัก (สำเนาใหม่ของแอปเดียวกัน)
เมื่อผู้ใช้ล็อกพื้นที่ส่วนตัว โปรไฟล์จะหยุดทำงาน เมื่อโปรไฟล์หยุดทำงาน แอปในพื้นที่ส่วนตัวจะไม่ทำงานอีกต่อไปและไม่สามารถดําเนินกิจกรรมในเบื้องหน้าหรือเบื้องหลัง รวมถึงแสดงการแจ้งเตือน
เราขอแนะนำให้คุณทดสอบแอปด้วยพื้นที่ส่วนตัวเพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าแอปทำงานได้ตามที่คาดไว้ โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งหากแอปของคุณจัดอยู่ในหมวดหมู่ใดหมวดหมู่หนึ่งต่อไปนี้
- แอปที่มีตรรกะสำหรับโปรไฟล์งานซึ่งถือว่าสำเนาของแอปที่ติดตั้งไว้ซึ่งไม่ได้อยู่ในโปรไฟล์หลักอยู่ในโปรไฟล์งาน
- แอปทางการแพทย์
- แอป Launcher
- แอป App Store
ค้นหาการเลือกของผู้ใช้ล่าสุดสำหรับการเข้าถึงรูปภาพที่เลือก
ตอนนี้แอปจะไฮไลต์ได้เฉพาะรูปภาพและวิดีโอที่เลือกล่าสุดเมื่อได้รับสิทธิ์การเข้าถึงบางส่วนในสื่อ ฟีเจอร์นี้ช่วยปรับปรุง
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้สำหรับแอปที่มักขอเข้าถึงรูปภาพและ
วิดีโอ หากต้องการใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้ในแอป ให้เปิดใช้อาร์กิวเมนต์ QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY เมื่อค้นหา MediaStore ผ่าน ContentResolver
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Privacy Sandbox ใน Android
Android 15 มีชิ้นงานบริการโฆษณา Android เวอร์ชันล่าสุด ซึ่งรวม Privacy Sandbox ใน Android เวอร์ชันล่าสุด การเปิดตัวครั้งนี้เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของความพยายามของเราในการพัฒนาเทคโนโลยีที่ช่วยเพิ่มความเป็นส่วนตัวของผู้ใช้ และสร้างประสบการณ์ใช้งานโฆษณาที่ปรับตามโปรไฟล์ของผู้ใช้ให้มีประสิทธิภาพยิ่งขึ้นสำหรับแอปบนอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนที่ หน้า Privacy Sandbox มีข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับ Privacy Sandbox ในโปรแกรมทดลองใช้ก่อนเปิดตัวและโปรแกรมเบต้าสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป Android เพื่อช่วยให้คุณเริ่มต้นใช้งาน
Health Connect
Android 15 ผสานรวมส่วนขยายล่าสุดเกี่ยวกับ Health Connect โดย Android ซึ่งเป็นแพลตฟอร์มที่ปลอดภัยและเป็นศูนย์กลางสำหรับจัดการและแชร์ข้อมูลสุขภาพและการออกกำลังกายที่แอปรวบรวม การอัปเดตนี้ เพิ่มการรองรับประเภทข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมในฟิตเนส ข้อมูลโภชนาการ อุณหภูมิผิวหนัง แผนการออกกำลังกาย และอื่นๆ
การติดตามอุณหภูมิผิวหนังช่วยให้ผู้ใช้จัดเก็บและแชร์ได้แม่นยำยิ่งขึ้น ข้อมูลอุณหภูมิจากอุปกรณ์ที่สวมใส่ได้หรืออุปกรณ์ติดตามอื่นๆ
แผนการออกกำลังกายคือแผนการออกกำลังกายที่มีโครงสร้างเพื่อช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ออกกำลังกายได้เต็มที่ เป้าหมาย การรองรับแผนการฝึกอบรมจะรวมถึงการสำเร็จหลักสูตรและประสิทธิภาพที่หลากหลาย เป้าหมาย:
- เป้าหมายที่สำเร็จเกี่ยวกับแคลอรี่ที่ใช้ไป ระยะทาง, ระยะเวลา การทำซ้ำและจำนวนก้าว
- เป้าหมายด้านประสิทธิภาพที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการทำซ้ำให้ได้มากที่สุด (AMRAP), ความถี่, อัตราการเต้นของหัวใจ, กำลัง, ระดับความเหนื่อยล้าที่รับรู้ และความเร็ว
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการอัปเดตล่าสุดของ Health Connect ใน Android ใน การสร้างประสบการณ์การใช้งานแบบปรับเปลี่ยนได้ด้วย Android การพูดคุยด้านสุขภาพจาก Google I/O
การแชร์หน้าจอแอป
Android 15 รองรับการแชร์หน้าจอแอปเพื่อให้ผู้ใช้แชร์หรือบันทึกเฉพาะหน้าต่างแอปแทนทั้งหน้าจอของอุปกรณ์ได้ ฟีเจอร์นี้เปิดใช้ใน Android 14 QPR2 เป็นครั้งแรก โดยมีMediaProjectionการเรียกกลับที่ช่วยให้แอปของคุณปรับแต่งประสบการณ์การแชร์หน้าจอของแอปได้ โปรดทราบว่าแอปที่กําหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 14 (API ระดับ 34) ขึ้นไปต้องได้รับความยินยอมจากผู้ใช้สําหรับเซสชันการจับภาพ MediaProjection แต่ละเซสชัน
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้และ UI ของระบบ
Android 15 ช่วยให้นักพัฒนาแอปและผู้ใช้ควบคุมและปรับแต่ง การกำหนดค่าอุปกรณ์ให้เหมาะกับความต้องการของตนได้มากขึ้น
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับวิธีใช้การปรับปรุงล่าสุดใน Android 15 เพื่อปรับปรุง ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้แอปได้ที่การบรรยายปรับปรุงประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้แอป Android จาก Google I/O
ตัวอย่างวิดเจ็ตที่สมบูรณ์ยิ่งขึ้นด้วย Generated Previews API
ก่อน Android 15 วิธีเดียวในการแสดงตัวอย่างเครื่องมือเลือกวิดเจ็ตคือต้องระบุทรัพยากรรูปภาพหรือเลย์เอาต์แบบคงที่ ตัวอย่างเหล่านี้มักจะแตกต่างจากลักษณะของวิดเจ็ตจริงเมื่อวางไว้ในหน้าจอหลักอย่างมาก นอกจากนี้ ทรัพยากรแบบคงที่ไม่อาจสร้างได้ด้วย Jetpack Glance ดังนั้นข้อมูลโดยย่อ นักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์ต้องจับภาพหน้าจอวิดเจ็ตของตน หรือสร้างเค้าโครง XML เพื่อให้ ตัวอย่างวิดเจ็ต
Android 15 เพิ่มการรองรับตัวอย่างที่สร้างขึ้น ซึ่งหมายความว่าผู้ให้บริการวิดเจ็ตแอปสามารถสร้าง RemoteViews เพื่อใช้เป็นตัวอย่างเครื่องมือเลือกแทนทรัพยากรแบบคงที่
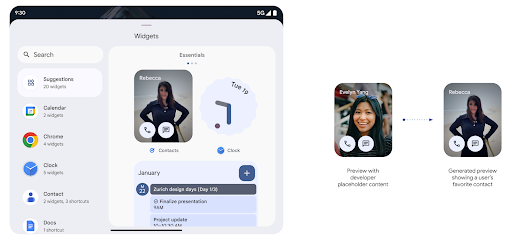
Push API
แอปสามารถแสดงตัวอย่างที่สร้างขึ้นผ่าน Push API แอปช่วยคุณได้
แสดงตัวอย่างได้ทุกเมื่อในวงจร และไม่ได้รับคำขอที่ชัดแจ้ง
จากโฮสต์เพื่อแสดงตัวอย่าง ระบบจะเก็บตัวอย่างเพลงไว้ใน AppWidgetService
และผู้จัดการประชุมจะขอตัวอย่างเพลงได้แบบออนดีมานด์ ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้จะโหลดทรัพยากรเลย์เอาต์วิดเจ็ต XML และตั้งค่าเป็นตัวอย่าง
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
ขั้นตอนที่คาดไว้มีดังนี้
- ผู้ให้บริการวิดเจ็ตเรียก
setWidgetPreviewได้ทุกเมื่อ ระบบจะเก็บตัวอย่างเพลงที่ระบุไว้ในAppWidgetServiceไว้พร้อมกับข้อมูลอื่นๆ ของผู้ให้บริการ setWidgetPreviewจะแจ้งโฮสต์เกี่ยวกับตัวอย่างที่อัปเดตแล้วผ่าน การติดต่อกลับของAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChangedในการตอบสนอง วิดเจ็ต โฮสต์จะโหลดข้อมูลผู้ให้บริการทั้งหมดซ้ำ- เมื่อแสดงตัวอย่างวิดเจ็ต โฮสต์จะตรวจสอบ
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategoriesและหากเลือก มีหมวดหมู่ ติดต่อAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewไปยัง ให้แสดงตัวอย่างที่บันทึกไว้สำหรับผู้ให้บริการรายนี้
กรณีที่ควรโทรหา setWidgetPreview
เนื่องจากไม่มีคอลแบ็กให้แสดงตัวอย่าง แอปจึงเลือกส่งตัวอย่างได้ทุกเมื่อขณะที่ทำงานอยู่ ความถี่ในการอัปเดตตัวอย่างจะขึ้นอยู่กับกรณีการใช้งานวิดเจ็ต
รายการต่อไปนี้อธิบายกรณีการใช้งานตัวอย่างเพลงหลัก 2 หมวดหมู่
- ผู้ให้บริการที่แสดงข้อมูลจริงในตัวอย่างวิดเจ็ต เช่น หรือข้อมูลล่าสุด ผู้ให้บริการเหล่านี้สามารถตั้งค่าตัวอย่างเพลงได้เมื่อผู้ใช้ลงชื่อเข้าใช้หรือทำการกําหนดค่าเริ่มต้นในแอปแล้ว หลังจากนั้น ผู้ให้บริการจะตั้งค่างานเป็นระยะเพื่ออัปเดตตัวอย่างเพลงตามช่วงเวลาที่เลือกได้ ตัวอย่างของวิดเจ็ตประเภทนี้อาจเป็นรูปภาพ ปฏิทิน สภาพอากาศ หรือข่าว วิดเจ็ต
- ผู้ให้บริการที่แสดงข้อมูลแบบคงที่ในตัวอย่างหรือวิดเจ็ตการดำเนินการด่วนซึ่งไม่แสดงข้อมูลใดๆ ผู้ให้บริการเหล่านี้สามารถ ตั้งค่าการแสดงตัวอย่างได้ 1 ครั้งเมื่อ เปิดแอปครั้งแรก ตัวอย่างของวิดเจ็ตประเภทนี้ ได้แก่ ไดรฟ์ไวท์ วิดเจ็ตการดำเนินการ หรือวิดเจ็ตทางลัดของ Chrome
ผู้ให้บริการบางรายอาจแสดงตัวอย่างแบบคงที่ในเครื่องมือเลือกโหมดฮับ แต่แสดงจริง ในเครื่องมือเลือกหน้าจอหลัก ผู้ให้บริการเหล่านี้ควรปฏิบัติตามคำแนะนำ สำหรับกรณีการใช้งานทั้ง 2 อย่างนี้ในการตั้งค่าตัวอย่าง
การแสดงภาพซ้อนภาพ
Android 15 เปิดตัวการเปลี่ยนแปลงในการแสดงภาพซ้อนภาพ (PIP) เพื่อให้ การเปลี่ยนผ่านที่ราบรื่นขึ้นเมื่อเข้าสู่โหมด PIP ซึ่งจะเป็นประโยชน์สำหรับแอปที่มีองค์ประกอบ UI วางซ้อนอยู่ด้านบนของ UI หลักซึ่งจะเข้าสู่โหมด PIP
นักพัฒนาแอปใช้ Callback onPictureInPictureModeChanged เพื่อกำหนดตรรกะ
ที่เปิด/ปิดการมองเห็นองค์ประกอบ UI ที่ซ้อนอยู่ การเรียกกลับนี้
ทริกเกอร์เมื่อภาพเคลื่อนไหวการป้อนหรือออกจาก PIP เสร็จสมบูรณ์ จะเริ่มต้นใน
Android 15 คลาส PictureInPictureUiState จะมีสถานะอื่นรวมอยู่ด้วย
ด้วยสถานะ UI นี้ แอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 15 (API ระดับ 35) จะสังเกตเห็น
มีการเรียกใช้ Callback Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged ด้วย
isTransitioningToPip() ทันทีที่ภาพเคลื่อนไหว PIP เริ่มขึ้น องค์ประกอบ UI จำนวนมากไม่เกี่ยวข้องกับแอปเมื่ออยู่ในโหมด PiP เช่น มุมมองหรือเลย์เอาต์ที่มีข้อมูล เช่น วิดีโอแนะนำ วิดีโอที่กำลังจะเผยแพร่ การจัดประเภท และชื่อ เมื่อแอปเข้าสู่โหมด PIP ให้ใช้
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged Callback เพื่อซ่อนองค์ประกอบ UI เหล่านี้ เมื่อ
แอปเข้าสู่โหมดเต็มหน้าจอจากหน้าต่าง PIP ให้ใช้
onPictureInPictureModeChanged Callback เพื่อเลิกซ่อนองค์ประกอบเหล่านี้ ดังที่แสดงใน
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
การเปิด/ปิดการแสดงผลองค์ประกอบ UI ที่ไม่เกี่ยวข้องอย่างรวดเร็ว (สำหรับหน้าต่าง PiP) นี้จะช่วยให้ภาพเคลื่อนไหวของ PiP ปรากฏขึ้นอย่างราบรื่นและไม่มีภาพกะพริบ
กฎห้ามรบกวนที่ปรับปรุงใหม่
AutomaticZenRule อนุญาตให้แอปปรับแต่งความสนใจได้
การจัดการกฎ (ห้ามรบกวน) และเลือกว่าจะเปิดหรือปิดใช้งานเมื่อใด
ให้พวกเขา Android 15 ช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพให้กฎเหล่านี้อย่างมาก โดยมีเป้าหมายเพื่อปรับปรุง
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ การปรับปรุงเหล่านี้มีดังนี้
- กำลังเพิ่มประเภทลงใน
AutomaticZenRuleเพื่อให้ระบบใช้แบบพิเศษได้ กับกฎบางอย่าง - การเพิ่มไอคอนลงใน
AutomaticZenRuleช่วยให้โหมดต่างๆ เป็นที่รู้จักมากขึ้น - การเพิ่มสตริง
triggerDescriptionในAutomaticZenRuleที่อธิบาย เงื่อนไขที่กฎควรทำงานสำหรับผู้ใช้ - เพิ่มเมื่อ
ZenDeviceEffectsเป็นAutomaticZenRuleเพื่อให้กฎเรียกใช้สิ่งต่างๆ เช่น โทนสีเทา จอแสดงผล โหมดกลางคืน หรือการหรี่แสงวอลเปเปอร์
ตั้งค่า VibrationEffect สำหรับช่องทางการแจ้งเตือน
Android 15 รองรับการตั้งค่าการสั่นแบบริชมีเดียสำหรับการแจ้งเตือนขาเข้าตามแชแนลโดยใช้ NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect เพื่อให้ผู้ใช้แยกแยะการแจ้งเตือนประเภทต่างๆ ได้โดยไม่ต้องมองที่อุปกรณ์
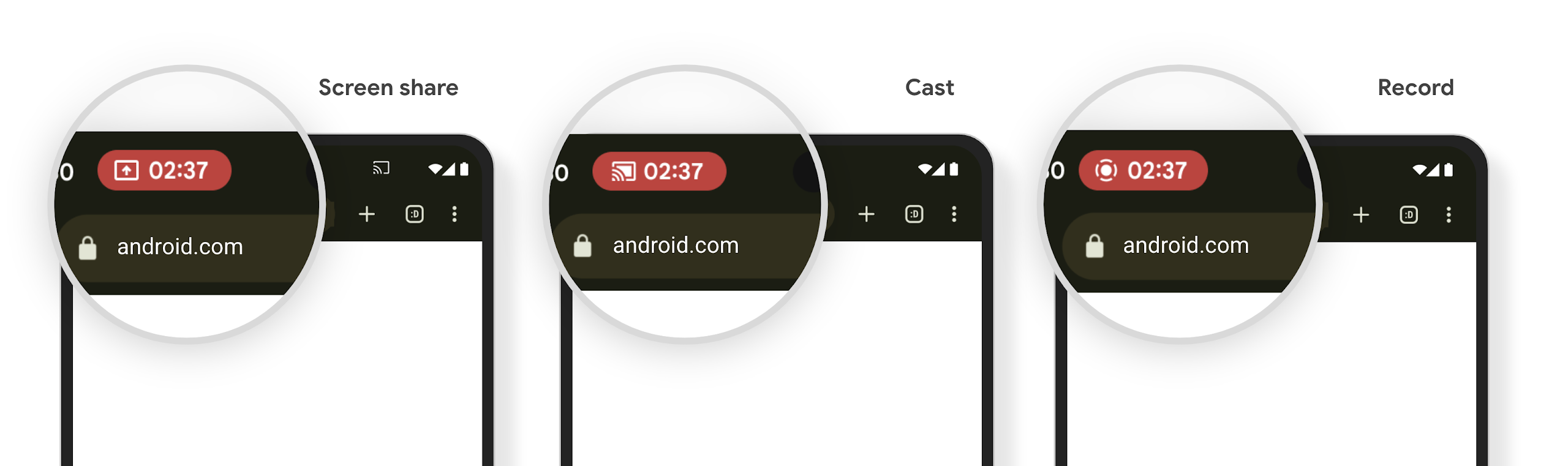
ชิปแถบสถานะการฉายภาพสื่อและการหยุดอัตโนมัติ
การฉายสื่ออาจเปิดเผยข้อมูลส่วนตัวของผู้ใช้ ชิปแถบสถานะใหม่ที่เห็นได้ชัดจะช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ทราบถึงการฉายหน้าจอที่ดำเนินอยู่ ผู้ใช้สามารถแตะชิปเพื่อหยุดแคสต์ แชร์ หรือบันทึกหน้าจอ นอกจากนี้ การแสดงภาพหน้าจอที่ดำเนินการอยู่จะหยุดโดยอัตโนมัติเมื่อหน้าจออุปกรณ์ล็อกอยู่เพื่อให้ผู้ใช้ได้รับประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ใช้งานง่ายยิ่งขึ้น
หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่และรูปแบบของอุปกรณ์
Android 15 ช่วยให้แอปของคุณรองรับรูปแบบ ต่างๆ ของ Android ได้อย่างเต็มที่ ซึ่งรวมถึงหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ อุปกรณ์แบบฝาพับ และอุปกรณ์แบบพับได้
การทำงานหลายอย่างพร้อมกันบนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ที่ได้รับการปรับปรุง
Android 15 ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ทำงานหลายอย่างพร้อมกันในอุปกรณ์หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ได้ดียิ่งขึ้น สำหรับ เช่น ผู้ใช้สามารถบันทึกชุดแอปที่ใช้ร่วมกันที่ชอบเพื่อใช้โหมดแยกหน้าจอได้อย่างรวดเร็ว เข้าถึงและปักหมุดแถบงานบนหน้าจอเพื่อสลับไปมาระหว่างแอปต่างๆ ได้อย่างรวดเร็ว ซึ่งหมายความว่า การทำให้แอปของคุณปรับเปลี่ยนได้นั้นสำคัญกว่าที่เคย
Google I/O มีเซสชันเกี่ยวกับการสร้าง Android แบบปรับอัตโนมัติ แอปและการสร้าง UI ด้วย Material 3 ไลบรารีแบบปรับอัตโนมัติ ที่ช่วยได้ และเอกสารของเรายังมีสิ่งอื่นๆ ที่ช่วยคุณออกแบบ
รองรับหน้าจอด้านนอก
แอปสามารถประกาศพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ที่ Android 15 ใช้เพื่ออนุญาตให้แสดง Application หรือ Activity บนหน้าจอฝาพับขนาดเล็กของอุปกรณ์แบบพลิกได้ หน้าจอเหล่านี้มีขนาดเล็กเกินกว่าที่จะถือว่าเป็นเป้าหมายที่เข้ากันได้สำหรับแอป Android ที่จะทำงานได้ แต่แอปของคุณสามารถเลือกที่จะรองรับหน้าจอเหล่านี้ได้ ซึ่งจะทำให้แอปพร้อมให้บริการในอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ มากขึ้น
การเชื่อมต่อ
Android 15 อัปเดตแพลตฟอร์มเพื่อให้แอปของคุณเข้าถึงความก้าวหน้าล่าสุด ในเทคโนโลยีการสื่อสารและไร้สาย
การรองรับดาวเทียม
Android 15 ยังคงขยายการรองรับแพลตฟอร์มสำหรับการเชื่อมต่อผ่านดาวเทียมต่อไป และ มีองค์ประกอบ UI บางอย่างเพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าผู้ใช้จะได้รับประสบการณ์ที่สอดคล้องกันทั่วทั้ง การเชื่อมต่อผ่านดาวเทียม
แอปสามารถใช้ ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() เพื่อ
ตรวจจับเมื่ออุปกรณ์เชื่อมต่อกับดาวเทียม ทำให้อุปกรณ์รับรู้ถึง
สาเหตุที่บริการเครือข่ายเต็มรูปแบบอาจใช้ไม่ได้ นอกจากนี้ Android 15 ยังรองรับแอป SMS และ MMS รวมถึงแอป RCS ที่โหลดไว้ล่วงหน้าเพื่อใช้การเชื่อมต่อผ่านดาวเทียมสำหรับส่งและรับข้อความ
ประสบการณ์การใช้งาน NFC ที่ราบรื่นยิ่งขึ้น
Android 15 กำลังพัฒนาประสบการณ์การแตะเพื่อจ่ายให้ราบรื่นและเชื่อถือได้มากขึ้น ในขณะเดียวกันก็ยังคงรองรับระบบนิเวศแอป NFC ที่มีประสิทธิภาพของ Android ในอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับ แอปจะขอให้ NfcAdapter เข้าสู่โหมดสังเกตการณ์ ซึ่งอุปกรณ์จะฟังแต่ไม่ตอบสนองต่อเครื่องอ่าน NFC โดยส่งออบเจ็กต์บริการ NFC ของแอป PollingFrame ไปประมวลผล คุณสามารถใช้ออบเจ็กต์ PollingFrame เพื่อตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ก่อนการสื่อสารกับเครื่องอ่าน NFC ครั้งแรก ซึ่งจะช่วยให้ทำธุรกรรมแบบแตะครั้งเดียวได้ในกรณีหลายกรณี
นอกจากนี้ แอปยังลงทะเบียนตัวกรองในอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับเพื่อให้ได้รับการแจ้งเตือนเกี่ยวกับกิจกรรมของลูปการสำรวจ ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปพลิเคชันที่รองรับ NFC หลายรายการทำงานได้อย่างราบรื่น
บทบาทของ Wallet
Android 15 เปิดตัวบทบาท Wallet ที่ช่วยให้ผสานรวมกับแอป Wallet ที่ต้องการของผู้ใช้ได้ดียิ่งขึ้น บทบาทนี้จะแทนที่การตั้งค่าการชำระเงินแบบไม่ต้องสัมผัสเริ่มต้นของ NFC ผู้ใช้สามารถจัดการผู้ถือบทบาท Wallet ได้โดยไปที่การตั้งค่า > แอป > แอปเริ่มต้น
ระบบจะใช้บทบาท Wallet เมื่อกำหนดเส้นทางการแตะ NFC สำหรับ AID ที่ลงทะเบียนไว้ในหมวดหมู่การชำระเงิน การแตะจะไปยังผู้ถือบทบาท Wallet เสมอ เว้นแต่ว่าแอปอื่นที่ลงทะเบียนสำหรับ AID เดียวกันจะทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้า
บทบาทนี้ยังใช้เพื่อกำหนดตําแหน่งการ์ดการเข้าถึงด่วนของ Wallet เมื่อเปิดใช้งาน เมื่อตั้งค่าบทบาทเป็น "ไม่มี" การ์ดการเข้าถึงด่วนจะใช้งานไม่ได้และการแตะ NFC หมวดหมู่การชำระเงินจะแสดงในแอปที่ทำงานอยู่เบื้องหน้าเท่านั้น
ความปลอดภัย
Android 15 ช่วยให้คุณปรับปรุงความปลอดภัยของแอป ปกป้องข้อมูลของแอป และ ให้ความโปร่งใสแก่ผู้ใช้มากขึ้น รวมถึงช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ควบคุมข้อมูลของตนได้ ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับสิ่งที่เรากำลังทำเพื่อปรับปรุงการปกป้องผู้ใช้และ ปกป้องแอปของคุณจากภัยคุกคามใหม่ๆ ได้จากทอล์กเรื่องการปกป้อง ความปลอดภัยของผู้ใช้ใน Android จาก Google I/O
ผสานรวม Credential Manager กับการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ
ตั้งแต่ Android 15 เป็นต้นไป นักพัฒนาแอปสามารถลิงก์มุมมองที่เฉพาะเจาะจง เช่น ช่องชื่อผู้ใช้หรือรหัสผ่านกับคำขอของเครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบได้ ซึ่งทำให้มอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับผู้ใช้ได้ง่ายขึ้นในระหว่างกระบวนการลงชื่อเข้าใช้ เมื่อผู้ใช้โฟกัสที่มุมมองใดมุมมองหนึ่ง ระบบจะส่งคําขอที่เกี่ยวข้องไปยังเครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบ ระบบจะรวบรวมข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบที่ได้จากผู้ให้บริการต่างๆ และแสดงใน UI สำรองสำหรับการป้อนข้อความอัตโนมัติ เช่น คำแนะนำในบรรทัดหรือคำแนะนำแบบเมนูแบบเลื่อนลง ไลบรารี androidx.credentials ของ Jetpack เป็นปลายทางที่นักพัฒนาแอปควรใช้ และจะพร้อมใช้งานเพื่อปรับปรุงฟีเจอร์นี้ใน Android 15 ขึ้นไปในเร็วๆ นี้
ผสานรวมการลงชื่อสมัครใช้และการลงชื่อเข้าใช้ด้วยการแตะครั้งเดียวกับข้อความแจ้งไบโอเมตริก
เครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบผสานรวมพรอมต์ข้อมูลไบโอเมตริกเข้ากับการสร้างข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบ และลงชื่อเข้าใช้ ทำให้ผู้ให้บริการไม่ต้องจัดการ พรอมต์ข้อมูลไบโอเมตริก ด้วยเหตุนี้ ผู้ให้บริการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบจึงต้องมุ่งเน้นที่ ผลลัพธ์ของการสร้างและรับโฟลว์ ซึ่งเสริมด้วยผลลัพธ์โฟลว์ข้อมูลไบโอเมตริก กระบวนการที่ง่ายขึ้นนี้จะช่วยให้การสร้างและการเรียกข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบมีประสิทธิภาพและสะดวกยิ่งขึ้น
การจัดการคีย์สำหรับการเข้ารหัสจากต้นทางถึงปลายทาง
เราขอแนะนำ E2eeContactKeysManager ใน Android 15 ซึ่งจะช่วยอำนวยความสะดวกในการเข้ารหัสจากต้นทางถึงปลายทาง (E2EE) ในแอป Android ของคุณด้วย API ระดับระบบปฏิบัติการสำหรับจัดเก็บคีย์สาธารณะการเข้ารหัส
E2eeContactKeysManager ได้รับการออกแบบมาให้ผสานรวมกับแอปรายชื่อติดต่อของแพลตฟอร์มเพื่อให้ผู้ใช้มีวิธีแบบรวมศูนย์ในการจัดการและยืนยันคีย์สาธารณะของรายชื่อติดต่อ
การตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ใน URI ของเนื้อหา
Android 15 เปิดตัวชุด API ที่ดำเนินการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ใน URI ของเนื้อหา ดังนี้
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: การดำเนินการนี้จะตรวจสอบสิทธิ์อย่างเต็มรูปแบบใน URI เนื้อหาActivityแอตทริบิวต์ไฟล์ ManifestrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: บังคับใช้สิทธิ์ที่ระบุใน URI ของเนื้อหาที่ระบุเมื่อเปิดใช้งานกิจกรรม- คลาส
ComponentCallerสําหรับผู้เรียกActivity: แสดงแอปที่เปิดใช้งานกิจกรรม
การช่วยเหลือพิเศษ
Android 15 เพิ่มฟีเจอร์ที่ปรับปรุงการช่วยเหลือพิเศษสำหรับผู้ใช้
อักษรเบรลล์ที่ดีขึ้น
ใน Android 15 เราได้ทำให้ TalkBack รองรับจอแสดงผลอักษรเบรลล์ที่ใช้มาตรฐาน HID ผ่านทั้ง USB และบลูทูธที่ปลอดภัย
มาตรฐานนี้ซึ่งคล้ายกับมาตรฐานที่ใช้กับเมาส์และแป้นพิมพ์จะช่วยให้ Android รองรับจอแสดงผลอักษรเบรลล์ได้หลากหลายมากขึ้นในอนาคต
การทำให้เป็นสากล
Android 15 เพิ่มฟีเจอร์และความสามารถที่ช่วยเสริมประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้ เมื่อใช้อุปกรณ์ในภาษาต่างๆ
แบบอักษรที่ปรับแต่งได้ของ CJK
ตั้งแต่ Android 15 เป็นต้นไป ไฟล์แบบอักษรสำหรับภาษาจีน ญี่ปุ่น และเกาหลี (CJK) อย่าง NotoSansCJK จะเป็นแบบอักษรที่เปลี่ยนแปลงได้ แบบอักษรแบบแปรผันเปิดโอกาสให้นักออกแบบตัวอักษรได้สร้างสรรค์งานในภาษา CJK นักออกแบบสามารถสำรวจสไตล์ที่หลากหลายมากขึ้นและสร้างเลย์เอาต์ที่สะดุดตาซึ่งก่อนหน้านี้ทำได้ยากหรือเป็นไปไม่ได้

การจัดชิดตัวอักษร
ใน Android 15 เป็นต้นไป คุณสามารถปรับข้อความให้ชิดขอบโดยใช้ระยะห่างของตัวอักษรได้โดย
ด้วย JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER การให้เหตุผลระหว่างคำเดิมคือ
เปิดตัวครั้งแรกใน Android 8.0 (API ระดับ 26) และระหว่างอักขระ
เหตุผลรองรับมีความสามารถที่คล้ายกันสำหรับภาษาที่ใช้
อักขระช่องว่างในการแบ่งกลุ่ม เช่น ภาษาจีน ภาษาญี่ปุ่น และอื่นๆ

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTERการกำหนดค่าการขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่โดยอัตโนมัติ
Android เริ่มรองรับการขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่ด้วยวลีสำหรับภาษาญี่ปุ่นและเกาหลีใน
Android 13 (API ระดับ 33) อย่างไรก็ตาม ขณะที่ตัวแบ่งบรรทัดแบบวลีจะปรับปรุง
ความสะดวกในการอ่านข้อความบรรทัดสั้นๆ จะทำงานได้ไม่ดีกับข้อความยาวๆ
ใน Android 15 แอปจะใช้ตัวแบ่งบรรทัดแบบวลีได้เฉพาะกับบรรทัดสั้นๆ เท่านั้น
โดยใช้ฟังก์ชัน LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
ตัวเลือก ตัวเลือกนี้จะเลือกตัวเลือกรูปแบบคำที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับข้อความ
สำหรับบรรทัดข้อความสั้นๆ จะมีการใช้ตัวแบ่งบรรทัดโดยใช้วลี โดยทำงานเหมือนเดิม
เป็น LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE ดังที่แสดงใน
รูปภาพต่อไปนี้:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTOจะใช้การแบ่งบรรทัดตามวลีเพื่อปรับปรุงความอ่านง่ายของข้อความ
เช่นเดียวกับการสมัคร
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASEสำหรับบรรทัดข้อความที่ยาวขึ้น LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO จะใช้โอเปอเรเตอร์
รูปแบบการขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่ ทำงานเหมือนกับ
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE ดังที่แสดงใน
รูปภาพต่อไปนี้:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
ไม่ใช้รูปแบบการขึ้นบรรทัดใหม่ เพื่อทำให้ข้อความอ่านง่ายขึ้น
เช่นเดียวกับการสมัคร
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONEแบบอักษรเฮนไทกานะภาษาญี่ปุ่นเพิ่มเติม
ใน Android 15 ไฟล์แบบอักษรของฮิรางานะญี่ปุ่นรุ่นเก่า (หรือที่เรียกว่า Hentaigana) จะได้รับการรวมกลุ่มไว้โดยค่าเริ่มต้น รูปทรงที่เป็นเอกลักษณ์ของตัวละคร Hentaigana สามารถเพิ่ม สำนวนของงานศิลปะหรือการออกแบบที่โดดเด่น ในขณะเดียวกันก็ช่วยให้คงความถูกต้องแม่นยำ การถ่ายทอดและความเข้าใจเกี่ยวกับเอกสารโบราณของญี่ปุ่น

กรวย VideoLAN แสดงลิขสิทธิ์ (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN ทุกคนสามารถใช้หรือแก้ไขโลโก้นี้หรือเวอร์ชันที่แก้ไขแล้วเพื่ออ้างอิงถึงโปรเจ็กต์ VideoLAN หรือผลิตภัณฑ์ใดๆ ที่พัฒนาโดยทีม VideoLAN แต่ไม่ได้บ่งบอกถึงการรับรองจากโปรเจ็กต์
Vulkan และโลโก้ Vulkan เป็นเครื่องหมายการค้าจดทะเบียนของ Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL เป็นเครื่องหมายการค้าจดทะเบียนและโลโก้ OpenGL ES เป็นเครื่องหมายการค้าของ Hewlett Packard Enterprise ซึ่ง Khronos ใช้โดยได้รับอนุญาต
