Android 15 では、デベロッパー向けに優れた機能と API が導入されました。以下のセクションでは、関連する API を使い始めるうえで役立つよう、これらの機能の概要を説明します。
追加、変更、削除された API の詳細な一覧については、API 差分レポートをご覧ください。追加された API について詳しくは、Android API リファレンスをご覧ください。Android 15 の場合は、API レベル 35 で追加された API をご確認ください。プラットフォームの変更がアプリに影響する可能性がある領域については、Android 15 の動作変更(Android 15 をターゲットとするアプリの場合とすべてのアプリの場合)をご確認ください。
カメラとメディア
Android 15 には、カメラとメディアのエクスペリエンスを向上させるさまざまな機能が含まれています。また、クリエイターが Android でビジョンを実現できるようサポートするツールやハードウェアにアクセスできます。
Android のメディアとカメラの最新機能とデベロッパー向けソリューションについて詳しくは、Google I/O の Building modern Android media and camera experiences の講演をご覧ください。
Low Light Boost
Android 15 introduces Low Light Boost, an auto-exposure mode available to both Camera 2 and the night mode camera extension. Low Light Boost adjusts the exposure of the Preview stream in low-light conditions. This is different from how the night mode camera extension creates still images, because night mode combines a burst of photos to create a single, enhanced image. While night mode works very well for creating a still image, it can't create a continuous stream of frames, but Low Light Boost can. Thus, Low Light Boost enables camera capabilities, such as:
- Providing an enhanced image preview, so users are better able to frame their low-light pictures
- Scanning QR codes in low light
If you enable Low Light Boost, it automatically turns on when there's a low light level, and turns off when there's more light.
Apps can record off the Preview stream in low-light conditions to save a brightened video.
For more information, see Low Light Boost.
アプリ内カメラ コントロール
Android 15 では、サポート対象デバイスのカメラ ハードウェアとそのアルゴリズムをより細かく制御するための拡張機能が追加されました。
HDR ヘッドルーム制御
Android 15 は、基盤となるデバイスの機能とパネルのビット深度に適した HDR ヘッドルームを指定します。1 つの HDR サムネイルを表示するメッセージ アプリなど、SDR コンテンツが多いページでは、この動作により、SDR コンテンツの明るさが認識されなくなる可能性があります。Android 15 では、setDesiredHdrHeadroom を使用して HDR ヘッドルームを制御し、SDR コンテンツと HDR コンテンツのバランスをとることができます。
音量調節

Android 15 introduces support for the CTA-2075 loudness standard to help you avoid audio loudness inconsistencies and ensure users don't have to constantly adjust volume when switching between content. The system leverages known characteristics of the output devices (headphones and speaker) along with loudness metadata available in AAC audio content to intelligently adjust the audio loudness and dynamic range compression levels.
To enable this feature, you need to ensure loudness metadata is available in
your AAC content and enable the platform feature in your app. For this, you
instantiate a LoudnessCodecController object by
calling its create factory method with the audio
session ID from the associated AudioTrack; this
automatically starts applying audio updates. You can pass an
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener to modify or filter
loudness parameters before they are applied on the
MediaCodec.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer will also be updated to use the
LoudnessCodecController APIs for a seamless app integration.
仮想 MIDI 2.0 デバイス
Android 13 added support for connecting to MIDI 2.0 devices using USB, which communicate using Universal MIDI Packets (UMP). Android 15 extends UMP support to virtual MIDI apps, enabling composition apps to control synthesizer apps as a virtual MIDI 2.0 device just like they would with an USB MIDI 2.0 device.
AV1 ソフトウェア デコードの効率化

dav1d は、VideoLAN の人気の高い AV1 ソフトウェア デコーダで、ハードウェアで AV1 デコードをサポートしていない Android デバイスで利用できます。dav1d は従来の AV1 ソフトウェア デコーダよりも最大 3 倍のパフォーマンスを発揮し、一部のローエンド デバイスやミッドレンジ デバイスを含む、より多くのユーザーが HD AV1 を再生できるようになります。
アプリは、dav1d の名前 "c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder" で呼び出して、dav1d の使用をオプトインする必要があります。dav1d は、今後のアップデートでデフォルトの AV1 ソフトウェア デコーダになります。このサポートは標準化され、Google Play システム アップデートを受信する Android 11 デバイスにバックポートされています。
デベロッパーの生産性とツール
生産性向上のための取り組みは、Android Studio、Jetpack Compose、Android Jetpack ライブラリなどのツールを中心に進められていますが、プラットフォームでビジョンをより簡単に実現できる方法も常に探しています。
OpenJDK 17 の更新
Android 15 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases.
The following key features and improvements are included:
- Quality-of-life improvements around NIO buffers
- Streams
- Additional
mathandstrictmathmethods utilpackage updates including sequencedcollection,map, andsetByteBuffersupport inDeflater- Security updates such as
X500PrivateCredentialand security key updates
These APIs are updated on over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher through Google Play System updates, so you can target the latest programming features.
PDF の改善
Android 15 では、PdfRenderer が大幅に改善されています。
APIアプリには、パスワードで保護されたファイルのレンダリング、アノテーション、フォームの編集、検索、コピー付きの選択などの高度な機能を組み込むことができます。リニア化された PDF の最適化がサポートされているため、ローカル PDF の表示が高速化され、リソースの使用量が削減されます。Jetpack PDF ライブラリでは、これらの API を使用して PDF を簡単に追加できます。
表示機能を追加できます。
PdfRenderer は、プラットフォームのリリースに依存せずに Google Play システム アップデートを使用して更新できるモジュールに移動されました。また、Android 15 より前のバージョンの API サーフェス(PdfRendererPreV)を作成することで、Android 11(API レベル 30)へのこれらの変更をサポートしています。
言語の自動切り替えの改善
Android 14 では、言語間の自動切り替えによる音声でのオンデバイスの複数言語認識が追加されましたが、特に 2 つの発話の間に短い休止時間がある場合、単語が欠落する可能性があります。Android 15 では、アプリがユースケースに合わせてこの切り替えを調整できるように、追加のコントロールが追加されています。EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS は自動切り替えを音声セッションの開始に限定します。EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES は、指定した回数切り替えた後に言語切り替えを無効にします。これらのオプションは、セッション中に自動検出される単一の言語が話されることが予想される場合に特に便利です。
OpenType 可変フォント API の改善
Android 15 では、OpenType 可変フォントのユーザビリティが改善されています。新しい
重み軸を指定しない可変フォントからの FontFamily インスタンス
buildVariableFamily API の場合。テキスト レンダラが値をオーバーライドする
の wght 軸を、表示テキストに合わせて調整します。
API を使用すると、Typeface の作成コードが大幅に簡素化されます。
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
以前は、同じ Typeface を作成するには、より多くのコードが必要でした。
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
新旧両方の API を使用して Typeface を作成する方法の例を次に示します。
レンダリング:
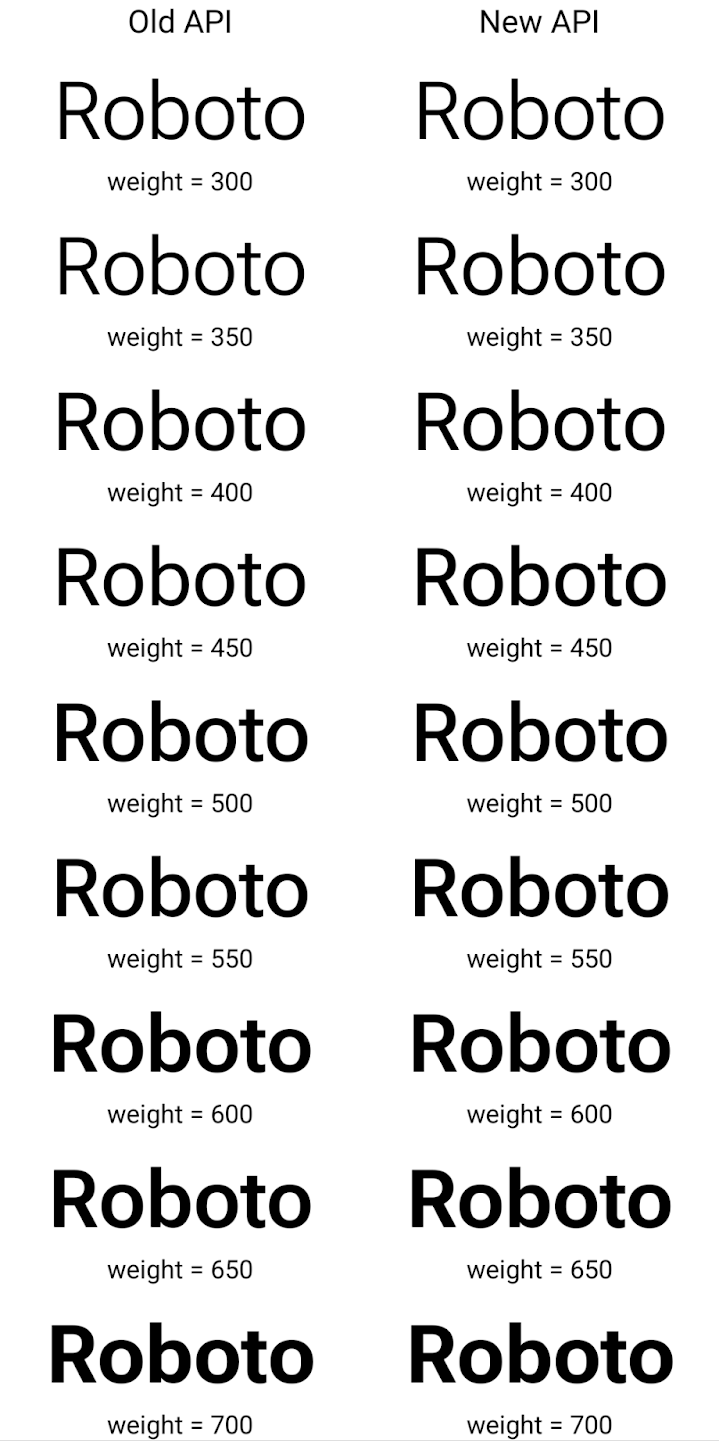
この例では、古い API で作成された Typeface に
350、450、550、650 のフォント ウェイトを正確に作成
Font インスタンスなので、レンダラは最も近い重みにフォールバックします。たとえば
この場合、350 ではなく 300 がレンダリングされ、450 ではなく 400 がレンダリングされます。
できます。一方、新しい API で作成された Typeface は、
指定された重みに対する Font インスタンス。350 度は正確な重みがレンダリングされます。
450、550、650 も選択できます
きめ細かい改行制御
Starting in Android 15, a TextView and the underlying
line breaker can preserve the given portion of text in the same line to improve
readability. You can take advantage of this line break customization by using
the <nobreak> tag in string resources or
createNoBreakSpan. Similarly, you can preserve words from
hyphenation by using the <nohyphen> tag or
createNoHyphenationSpan.
For example, the following string resource doesn't include a line break, and renders with the text "Pixel 8 Pro." breaking in an undesirable place:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
In contrast, this string resource includes the <nobreak> tag, which wraps the
phrase "Pixel 8 Pro." and prevents line breaks:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
The difference in how these strings are rendered is shown in the following images:

<nobreak> tag.
<nobreak> tag.アプリのアーカイブ
Android and Google Play announced support for app archiving last year, allowing users to free up space by partially removing infrequently used apps from the device that were published using Android App Bundle on Google Play. Android 15 includes OS level support for app archiving and unarchiving, making it easier for all app stores to implement it.
Apps with the REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES permission can call the
PackageInstaller requestArchive method to request archiving an
installed app package, which removes the APK and any cached files, but persists
user data. Archived apps are returned as displayable apps through the
LauncherApps APIs; users will see a UI treatment to highlight that those
apps are archived. If a user taps on an archived app, the responsible installer
will get a request to unarchive it, and the restoration process can be
monitored by the ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED broadcast.
開発者向けオプションを使用してデバイスで 16 KB モードを有効にする
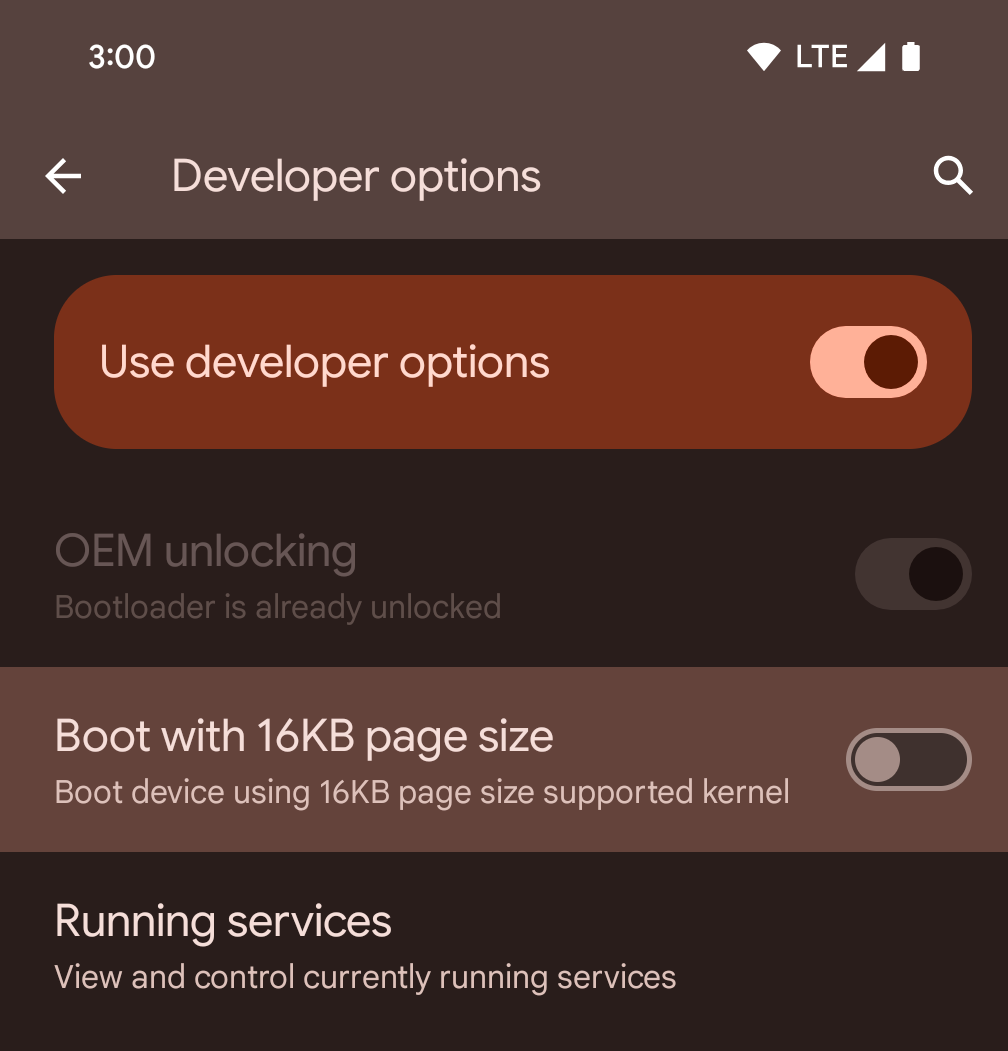
[16 KB ページサイズで起動する] デベロッパー オプションを切り替えて、デバイスを 16 KB モードで起動します。
Android 15 QPR1 以降では、特定のデバイスで利用可能なデベロッパー オプションを使用して、デバイスを 16 KB モードで起動し、デバイス上でテストを実行できます。開発者向けオプションを使用する前に、[設定] > [システム] > [ソフトウェア アップデート] に移動して、利用可能なアップデートを適用します。
この開発者向けオプションは、次のデバイスで利用できます。
Google Pixel 8、Google Pixel 8 Pro(Android 15 QPR1 以降)
Google Pixel 8a(Android 15 QPR1 以降)
Google Pixel 9、Google Pixel 9 Pro、Google Pixel 9 Pro XL(Android 15 QPR2 ベータ版 2 以降)
グラフィック
Android 15 では、ANGLE や Canvas グラフィック システムの追加など、最新のグラフィックの改善が導入されています。
Android の GPU アクセスを最新化

Android ハードウェアは、コア OS が単一の CPU で実行され、GPU に固定関数パイプラインに基づく API を使用してアクセスされていた初期の頃からかなり進化しています。Vulkan® グラフィック API は、Android 7.0(API レベル 24)以降、NDK で利用可能になりました。最新の GPU ハードウェアをより適切に反映する低レベルの抽象化により、複数の CPU コアをサポートするようにスケーリングが改善され、CPU ドライバのオーバーヘッドが削減され、アプリのパフォーマンスが向上します。Vulkan は、すべての最新のゲームエンジンでサポートされています。
Vulkan は、Android の GPU への優先インターフェースです。そのため、Android 15 には、Vulkan 上で OpenGL® ES を実行するためのオプション レイヤとして ANGLE が含まれています。ANGLE に移行することで、Android OpenGL の実装が標準化され、互換性が向上し、場合によってはパフォーマンスも向上します。Android 15 で [設定] -> [システム] -> [開発者向けオプション] -> [試験運用版: ANGLE を有効にする] で開発者向けオプションを有効にすると、ANGLE で OpenGL ES アプリの安定性とパフォーマンスをテストできます。
Android ANGLE on Vulkan のロードマップ
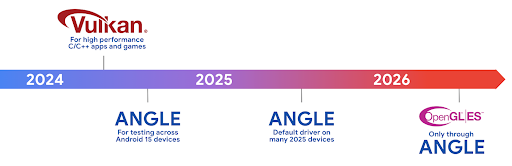
GPU スタックの効率化の一環として、今後はさらに多くの新しいデバイスで GL システム ドライバとして ANGLE を搭載する予定です。今後、OpenGL/ES は ANGLE でのみ利用可能になる見込みです。ただし、すべてのデバイスで OpenGL ES のサポートを継続する予定です。
推奨される次のステップ
デベロッパー オプションを使用して OpenGL ES の ANGLE ドライバを選択し、アプリをテストします。新しいプロジェクトでは、C/C++ に Vulkan を使用することを強くおすすめします。
キャンバスの改善
Android 15 continues our modernization of Android's Canvas graphics system with additional capabilities:
Matrix44provides a 4x4 matrix for transforming coordinates that should be used when you want to manipulate the canvas in 3D.clipShaderintersects the current clip with the specified shader, whileclipOutShadersets the clip to the difference of the current clip and the shader, each treating the shader as an alpha mask. This supports the drawing of complex shapes efficiently.
パフォーマンスとバッテリー
Android は、アプリのパフォーマンスと品質の向上を支援することに引き続き注力しています。Android 15 では、アプリ内のタスクの実行を効率化し、アプリのパフォーマンスを最適化し、アプリに関する分析情報を収集するのに役立つ API が導入されています。
バッテリー効率に関するベスト プラクティス、ネットワークと電力の使用量のデバッグ、Android 15 と最近のバージョンの Android でバックグラウンド作業のバッテリー効率を改善する方法について詳しくは、Google I/O の Android でのバックグラウンド作業のバッテリー効率の改善に関するトークをご覧ください。
ApplicationStartInfo API
In previous versions of Android, app startup has been a bit of a mystery. It was
challenging to determine within your app whether it started from a cold, warm,
or hot state. It was also difficult to know how long your app spent during the
various launch phases: forking the process, calling onCreate, drawing the
first frame, and more. When your Application class was instantiated, you had no
way of knowing whether the app started from a broadcast, a content provider, a
job, a backup, boot complete, an alarm, or an Activity.
The ApplicationStartInfo API on Android 15 provides
all of this and more. You can even choose to add your own timestamps into the
flow to help collect timing data in one place. In addition to collecting
metrics, you can use ApplicationStartInfo to help directly optimize app
startup; for example, you can eliminate the costly instantiation of UI-related
libraries within your Application class when your app is starting up due to a
broadcast.
アプリサイズの詳細情報
Android 8.0(API レベル 26)以降、Android には、アプリのインストール サイズを 1 つのバイト数として要約する StorageStats.getAppBytes API が含まれています。これは、APK のサイズ、APK から抽出されたファイルのサイズ、デバイスで生成されたファイル(事前(AOT)コンパイル済みコードなど)の合計です。この数値は、アプリがストレージをどのように使用しているかを把握するうえではあまり有用ではありません。
Android 15 では StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API が追加され、APK ファイルの分割、AOT と高速化関連のコード、dex メタデータ、ライブラリ、ガイド付きプロファイルなど、アプリがそのスペースをどのように使用しているかを把握できるようになります。
アプリ管理のプロファイリング
Android 15 には ProfilingManager クラスが含まれています。これにより、ヒープダンプ、ヒープ プロファイル、スタック サンプリングなどのプロファイリング情報をアプリ内から収集できます。出力ファイルを識別するタグが指定されたコールバックがアプリに提供され、アプリのファイル ディレクトリに配信されます。この API は、パフォーマンスへの影響を最小限に抑えるためにレート制限を行います。
アプリでのプロファイリング リクエストの作成を簡素化するには、Core 1.15.0-rc01 以降で利用可能な、対応する Profiling AndroidX API を使用することをおすすめします。
SQLite データベースの改善
Android 15 introduces SQLite APIs that expose advanced features from the underlying SQLite engine that target specific performance issues that can manifest in apps. These APIs are included with the update of SQLite to version 3.44.3.
Developers should consult best practices for SQLite performance to get the most out of their SQLite database, especially when working with large databases or when running latency-sensitive queries.
- Read-only deferred transactions: when issuing transactions that are
read-only (don't include write statements), use
beginTransactionReadOnly()andbeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)to issue read-onlyDEFERREDtransactions. Such transactions can run concurrently with each other, and if the database is in WAL mode, they can run concurrently withIMMEDIATEorEXCLUSIVEtransactions. - Row counts and IDs: APIs were added to retrieve the count of changed
rows or the last inserted row ID without issuing an additional query.
getLastChangedRowCount()returns the number of rows that were inserted, updated, or deleted by the most recent SQL statement within the current transaction, whilegetTotalChangedRowCount()returns the count on the current connection.getLastInsertRowId()returns therowidof the last row to be inserted on the current connection. - Raw statements: issue a raw SQlite statement, bypassing convenience wrappers and any additional processing overhead that they may incur.
Android Dynamic Performance Framework の更新
Android 15 では、Android Dynamic Performance Framework(ADPF)への投資が継続されています。ADPF は、ゲームやパフォーマンスを必要とするアプリが Android デバイスの電力システムや温度システムをより直接的に操作できるようにする API のセットです。サポートされているデバイスでは、Android 15 に ADPF 機能が追加されます。
- ヒント セッションの省電力モード。関連するスレッドでパフォーマンスよりも省電力を優先すべきことを示します。長時間実行されるバックグラウンド ワークロードに適しています。
- GPU と CPU の作業時間はヒント セッションで報告できるため、システムはワークロードの需要に最適に合わせて CPU と GPU の周波数を調整できます。
- サーマル ヘッドルームしきい値: ヘッドルーム予測に基づいて、サーマル スロットリングが発生する可能性のあるステータスを解釈します。
アプリやゲームで ADPF を使用する方法について詳しくは、ドキュメントをご覧ください。
プライバシー
Android 15 には、アプリ デベロッパーがユーザーのプライバシーを保護するのに役立つさまざまな機能が含まれています。
画面録画の検出
Android 15 adds support for apps to detect that they are being recorded. A callback is invoked whenever the app transitions between being visible or invisible within a screen recording. An app is considered visible if activities owned by the registering process's UID are being recorded. This way, if your app is performing a sensitive operation, you can inform the user that they're being recorded.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
IntentFilter の機能の拡張
Android 15 builds in support for more precise Intent resolution through
UriRelativeFilterGroup, which contains a set of
UriRelativeFilter objects that form a set of Intent
matching rules that must each be satisfied, including URL query parameters, URL
fragments, and blocking or exclusion rules.
These rules can be defined in the AndroidManifest XML file with the
<uri-relative-filter-group> tag, which can optionally include an
android:allow tag. These tags can contain <data> tags that use existing data
tag attributes as well as the android:query and android:fragment
attributes.
Here's an example of the AndroidManifest syntax:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
プライベート スペース
Private space lets users create a separate space on their device where they can keep sensitive apps away from prying eyes, under an additional layer of authentication. The private space uses a separate user profile. The user can choose to use the device lock or a separate lock factor for the private space.
Apps in the private space show up in a separate container in the launcher, and are hidden from the recents view, notifications, settings, and from other apps when the private space is locked. User-generated and downloaded content (such as media or files) and accounts are separated between the private space and the main space. The system sharesheet and the photo picker can be used to give apps access to content across spaces when the private space is unlocked.
Users can't move existing apps and their data into the private space. Instead, users select an install option in the private space to install an app using whichever app store they prefer. Apps in the private space are installed as separate copies from any apps in the main space (new copies of the same app).
When a user locks the private space, the profile is stopped. While the profile is stopped, apps in the private space are no longer active and can't perform foreground or background activities, including showing notifications.
We recommend that you test your app with private space to make sure your app works as expected, especially if your app falls into one of the following categories:
- Apps with logic for work profiles that assumes that any installed copies of their app that aren't in the main profile are in the work profile.
- Medical apps
- Launcher apps
- App store apps
選択した写真へのアクセスに関するユーザーの最新の選択をクエリする
Apps can now highlight only the most-recently-selected photos and videos when
partial access to media permissions is granted. This feature can improve
the user experience for apps that frequently request access to photos and
videos. To use this feature in your app, enable the
QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY argument when querying MediaStore
through ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Android 版プライバシー サンドボックス
Android 15 includes the latest Android Ad Services extensions, incorporating the latest version of the Privacy Sandbox on Android. This addition is part of our work to develop technologies that improve user privacy and enable effective, personalized advertising experiences for mobile apps. Our privacy sandbox page has more information about the Privacy Sandbox on Android developer preview and beta programs to help you get started.
ヘルスコネクト
Android 15 では、 Android のヘルスコネクト: 安全で一元化された アプリが収集した健康とフィットネスに関するデータを管理、共有するプラットフォームです。今回の更新 フィットネス全体に対応するデータ型のサポートを追加します。 栄養、皮膚温、トレーニング計画など。
皮膚温の測定では、ウェアラブル デバイスなどの測定デバイスからより正確な温度データを保存して共有できます。
トレーニング プランは、ユーザーがフィットネスの目標を達成できるようにするための体系的なワークアウト プランです。トレーニング プランのサポートには、さまざまな達成目標とパフォーマンス目標が含まれます。
Android のヘルスコネクトの最新アップデートについて詳しくは、以下をご覧ください。 Android で適応性の高いエクスペリエンスを構築する Google I/O の健康に関するトピックです。
アプリの画面共有
Android 15 supports app screen sharing so users can share or record just an
app window rather than the entire device screen. This feature, first enabled in
Android 14 QPR2, includes
MediaProjection callbacks that allow your app
to customize the app screen sharing experience. Note that for apps targeting
Android 14 (API level 34) or higher,
user consent is required for each
MediaProjection capture session.
ユーザー エクスペリエンスとシステム UI
Android 15 では、アプリ デベロッパーとユーザーがニーズに合わせてデバイスを構成するための制御と柔軟性が向上しています。
Android 15 の最新の改善点を使用してアプリのユーザー エクスペリエンスを向上させる方法について詳しくは、Google I/O の Android アプリのユーザー エクスペリエンスを高めるをご覧ください。
Generated Previews API によるリッチなウィジェットのプレビュー
Before Android 15, the only way to provide widget picker previews was to specify a static image or layout resource. These previews often differ significantly from the look of the actual widget when it is placed on the home screen. Also, static resources can't be created with Jetpack Glance, so a Glance developer had to screenshot their widget or create an XML layout to have a widget preview.
Android 15 adds support for generated previews. This means that app widget
providers can generate RemoteViews to use as the picker preview, instead
of a static resource.
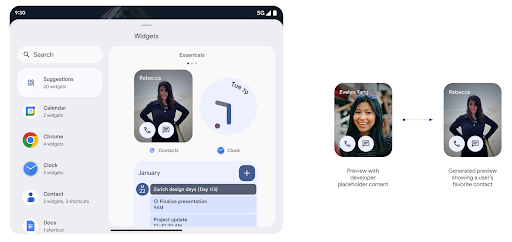
Push API
Apps can provide generated previews through a push API. Apps can provide
previews at any point in their lifecycle, and don't receive an explicit request
from the host to provide previews. Previews are persisted in AppWidgetService,
and hosts can request them on-demand. The following example loads an XML widget
layout resource and sets it as the preview:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
The expected flow is:
- At any time, the widget provider calls
setWidgetPreview. The provided previews are persisted inAppWidgetServicewith other provider info. setWidgetPreviewnotifies hosts of an updated preview through theAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChangedcallback. In response, the widget host reloads all of its provider information.- When displaying a widget preview, the host checks
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories, and if the chosen category is available, callsAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewto return the saved preview for this provider.
When to call setWidgetPreview
Because there is no callback to provide previews, apps can choose to send previews at any point when they are running. How often to update the preview depends on the widget's use case.
The following list describes the two main categories of preview use cases:
- Providers that show real data in their widget previews, such as personalized or recent information. These providers can set the preview once the user has signed in or has done initial configuration in their app. After this, they can set up a periodic task to update the previews at their chosen cadence. Examples of this type of widget could be a photo, calendar, weather or news widget.
- Providers that show static information in previews or quick-action widgets that don't display any data. These providers can set previews once, when the app first launches. Examples of this type of widget include a drive quick actions widget or chrome shortcuts widget.
Some providers might show static previews on the hub mode picker, but real information on the homescreen picker. These providers should follow the guidance for both of these use cases to set previews.
ピクチャー イン ピクチャー
Android 15 introduces changes in Picture-in-Picture (PiP) ensuring an even smoother transition when entering into PiP mode. This will be beneficial for apps having UI elements overlaid on top of their main UI, which goes into PiP.
Developers use the onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to define logic
that toggles the visibility of the overlaid UI elements. This callback is
triggered when the PiP enter or exit animation is completed. Beginning in
Android 15, the PictureInPictureUiState class includes another state.
With this UI state, apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) will observe the
Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback being invoked with
isTransitioningToPip() as soon as the PiP animation starts. There are
many UI elements that are not relevant for the app when it is in PiP mode, for
example views or layout that include information such as suggestions, upcoming
video, ratings, and titles. When the app goes to PiP mode, use the
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback to hide these UI elements. When the
app goes to full screen mode from the PiP window, use
onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to unhide these elements, as shown in
the following examples:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
This quick visibility toggle of irrelevant UI elements (for a PiP window) helps ensure a smoother and flicker-free PiP enter animation.
サイレント モード ルールの改善
AutomaticZenRule lets apps customize Attention
Management (Do Not Disturb) rules and decide when to activate or deactivate
them. Android 15 greatly enhances these rules with the goal of improving the
user experience. The following enhancements are included:
- Adding types to
AutomaticZenRule, allowing the system to apply special treatment to some rules. - Adding an icon to
AutomaticZenRule, helping to make the modes be more recognizable. - Adding a
triggerDescriptionstring toAutomaticZenRulethat describes the conditions on which the rule should become active for the user. - Added
ZenDeviceEffectstoAutomaticZenRule, allowing rules to trigger things like grayscale display, night mode, or dimming the wallpaper.
通知チャンネルの VibrationEffect を設定する
Android 15 では、着信通知に対するリッチ バイブレーションの設定がサポートされています。
NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect を使用してチャンネルを作成するので、
ユーザーは通知の種類を
区別できるように
ユーザーがデバイスを見る必要はありません
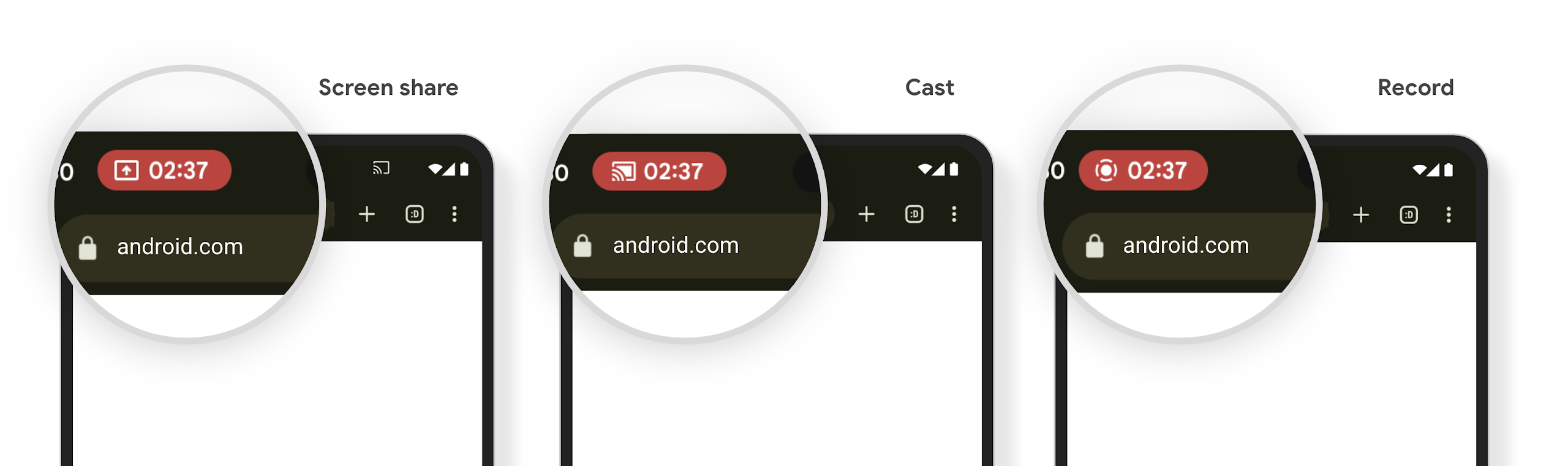
メディア プロジェクションのステータスバー チップと自動停止
Media projection can expose private user information. A new, prominent status bar chip makes users aware of any ongoing screen projection. Users can tap the chip to stop screen casting, sharing, or recording. Also, for a more intuitive user experience, any in‑progress screen projection now automatically stops when the device screen is locked.
大画面とフォーム ファクタ
Android 15 では、大画面、フリップ式、折りたたみ式など、Android のフォーム ファクタを最大限に活用するためのサポートがアプリに提供されます。
大画面でのマルチタスクを改善
Android 15 では、大画面デバイスでのマルチタスク機能が改善されています。対象 たとえば、ユーザーはお気に入りの分割画面のアプリの組み合わせを保存して、 画面上のタスクバーにアクセスしたり、固定したりすることで、アプリをすばやく切り替えられます。つまり アプリをアダプティブにすることの重要性が これまで以上に高まっています
Google I/O では、アダプティブな Android の構築に関するセッションを開催しています。 およびマテリアル 3 を使用した UI の作成 アダプティブ ライブラリ また、Google のドキュメントでは大規模な できます。
カバー画面のサポート
Your app can declare a property that Android 15 uses to
allow your Application or Activity to be presented on the small cover
screens of supported flippable devices. These screens are too small to be
considered as compatible targets for Android apps to run on, but your app can
opt in to supporting them, making your app available in more places.
接続
Android 15 では、プラットフォームが更新され、アプリで最新の通信技術やワイヤレス技術を利用できるようになります。
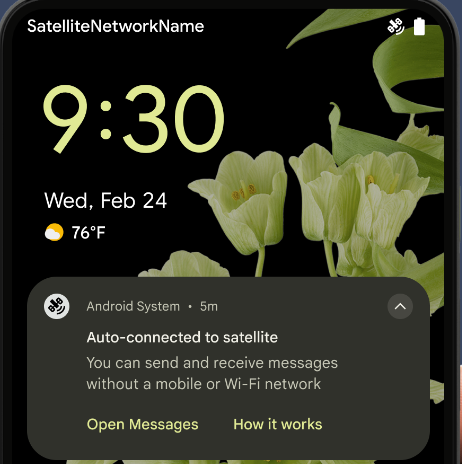
衛星通信のサポート
Android 15 continues to extend platform support for satellite connectivity and includes some UI elements to ensure a consistent user experience across the satellite connectivity landscape.
Apps can use ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() to
detect when a device is connected to a satellite, giving them more awareness of
why full network services might be unavailable. Additionally, Android 15
provides support for SMS and MMS apps as well as preloaded RCS apps to use
satellite connectivity for sending and receiving messages.
NFC のエクスペリエンスの向上
Android 15 では、Android の堅牢な NFC アプリ エコシステムを引き続きサポートしながら、タッチ決済のエクスペリエンスをよりシームレスで信頼性の高いものにする取り組みを進めています。サポートされているデバイスでは、アプリは NfcAdapter に観察モードに入るようリクエストできます。このモードでは、デバイスはリッスンしますが NFC リーダーには応答せず、アプリの NFC サービス PollingFrame
オブジェクトを送信して処理します。PollingFrame オブジェクトを使用すると、NFC リーダーへの最初の通信の前に認証を行うことができ、多くの場合、ワンタップ取引が可能になります。
さらに、アプリはサポートされているデバイスにフィルタを登録して、ポーリング ループ アクティビティを通知できます。これにより、複数の NFC 対応アプリケーションでスムーズに動作できます。
ウォレットの役割
Android 15 introduces a Wallet role that allows tighter integration with the user's preferred wallet app. This role replaces the NFC default contactless payment setting. Users can manage the Wallet role holder by navigating to Settings > Apps > Default Apps.
The Wallet role is used when routing NFC taps for AIDs registered in the payment category. Taps always go to the Wallet role holder unless another app that is registered for the same AID is running in the foreground.
This role is also used to determine where the Wallet Quick Access tile should go when activated. When the role is set to "None", the Quick Access tile isn't available and payment category NFC taps are only delivered to the foreground app.
セキュリティ
Android 15 では、アプリのセキュリティを強化し、アプリのデータを保護し、ユーザーがデータをより透明性をもって管理できるようになります。ユーザー保護を強化し、アプリを新たな脅威から保護するために Google が行っている取り組みについて詳しくは、Google I/O のAndroid でのユーザー セキュリティの保護に関するトークをご覧ください。
認証情報マネージャーを自動入力と統合する
Android 15 以降では、デベロッパーはユーザー名やパスワード フィールドなどの特定のビューを認証情報マネージャー リクエストにリンクできるため、ログイン プロセス中にカスタマイズされたユーザー エクスペリエンスを簡単に提供できます。ユーザーがこれらのビューのいずれかにフォーカスすると、対応するリクエストが認証情報マネージャーに送信されます。生成された認証情報はプロバイダ間で集約され、インライン候補やプルダウン候補などの自動入力のフォールバック UI に表示されます。Jetpack androidx.credentials ライブラリは、デベロッパーが使用するエンドポイントとして推奨されます。このライブラリはまもなく Android 15 以降で利用可能になり、この機能をさらに強化できるようになります。
シングルタップ登録とログインを生体認証プロンプトと統合する
Credential Manager integrates biometric prompts into the credential creation and sign-in processes, eliminating the need for providers to manage biometric prompts. As a result, credential providers only need to focus on the results of the create and get flows, augmented with the biometric flow result. This simplified process creates a more efficient and streamlined credential creation and retrieval process.
エンドツーエンドの暗号化の鍵管理
We are introducing the E2eeContactKeysManager in Android 15, which
facilitates end-to-end encryption (E2EE) in your Android apps by providing an
OS-level API for the storage of cryptographic public keys.
The E2eeContactKeysManager is designed to integrate with the platform
contacts app to give users a centralized way to manage and verify their
contacts' public keys.
コンテンツ URI の権限チェック
Android 15 introduces a set of APIs that perform permission checks on content URIs:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: This performs a full permission check on content URIs.Activitymanifest attributerequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: This enforces specified permissions on the provided content URIs at activity launch.ComponentCallerclass forActivitycallers: This represents the app that launched the activity.
ユーザー補助
Android 15 では、ユーザー補助機能を改善する機能が追加されています。
Better Braille
Android 15 では、TalkBack が USB とセキュア Bluetooth の両方で HID 標準を使用している点字ディスプレイをサポートできるようになりました。
この標準は、マウスやキーボードで使用されている標準とよく似ており、Android が今後、より幅広い点字ディスプレイをサポートするのに役立ちます。
多言語対応
Android 15 では、デバイスが異なる言語で使用される場合のユーザー エクスペリエンスを補完する機能が追加されています。
CJK 可変フォント
Android 15 以降、中国語、日本語、韓国語(CJK)言語のフォント ファイル NotoSansCJK が可変フォントになりました。可変フォントにより、CJK 言語でのクリエイティブなタイポグラフィの可能性が広がります。デザイナーは、より幅広いスタイルを試し、これまで実現が難しかった、または不可能だった視覚的に魅力的なレイアウトを作成できます。

文字間隔の調整
Android 15 以降では、文字間隔を使用してテキストを両端揃えできます。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER を使用します。変更前の単語間の両端揃え:
Android 8.0(API レベル 26)で初めて導入されました。
同様の機能は、
空白文字(中国語、日本語など)

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE を使用した日本語テキストのレイアウト。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE を使用した英語テキストのレイアウト。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD を使用した日本語テキストのレイアウト。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD を使用した英語テキストのレイアウト。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER を使用した日本語テキストのレイアウト。
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER を使用した英語テキストのレイアウト。自動改行の設定
Android started supporting phrase-based line breaks for Japanese and Korean in
Android 13 (API level 33). However, while phrase-based line breaks improve the
readability of short lines of text, they don't work well for long lines of text.
In Android 15, apps can apply phrase-based line breaks only for short lines
of text, using the LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
option. This option selects the best word style option for the text.
For short lines of text, phrase-based line breaks are used, functioning the same
as LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, as shown in the
following image:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
applies phrase-based line breaks to improve the readability of the text.
This is the same as applying
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.For longer lines of text, LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO uses a no
line-break word style, functioning the same as
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, as shown in the
following image:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
applies no line-break word style to improve the readability of the text.
This is the same as applying
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.追加の日本語変体仮名フォント
In Android 15, a font file for old Japanese Hiragana (known as Hentaigana) is bundled by default. The unique shapes of Hentaigana characters can add a distinctive flair to artwork or design while also helping to preserve accurate transmission and understanding of ancient Japanese documents.

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. This logo or a modified version may be used or modified by anyone to refer to the VideoLAN project or any product developed by the VideoLAN team, but does not indicate endorsement by the project.
Vulkan and the Vulkan logo are registered trademarks of the Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL is a registered trademark and the OpenGL ES logo is a trademark of Hewlett Packard Enterprise used by permission by Khronos.

