Android 15 introduce fantastiche funzionalità e API per gli sviluppatori. Le seguenti sezioni riepilogano queste funzionalità per aiutarti a iniziare a utilizzare le API correlate.
Per un elenco dettagliato delle API aggiunte, modificate e rimosse, leggi il report API diff. Per informazioni dettagliate sulle API aggiunte, visita il riferimento API Android. Per Android 15, cerca le API aggiunte nel livello API 35. Per scoprire le aree in cui le modifiche alla piattaforma potrebbero influire sulle tue app, assicurati di consultare le modifiche al comportamento di Android 15 per le app che hanno come target Android 15 e per tutte le app.
Fotocamera e contenuti multimediali
Android 15 include una serie di funzionalità che migliorano l'esperienza con la fotocamera e i contenuti multimediali e che ti danno accesso a strumenti e hardware per supportare i creator nel dare vita alla loro visione su Android.
Per saperne di più sulle funzionalità e sulle soluzioni per sviluppatori più recenti per i contenuti multimediali e la fotocamera di Android, guarda il talk Building modern Android media and camera experiences di Google I/O.
Aumento luce
Android 15 introduce la funzionalità Low Light Boost, una modalità di esposizione automatica disponibile sia per Camera 2 sia per l'estensione della fotocamera con modalità notturna. Il potenziamento automatico regola l'esposizione dello stream di anteprima in condizioni di scarsa illuminazione. Questo è diverso da come l'estensione della fotocamera in modalità Notte crea immagini fisse, perché la modalità Notte combina una raffica di foto per creare un'unica immagine migliorata. Sebbene la modalità notturna sia molto efficace per creare un'immagine fissa, non può creare uno stream continuo di fotogrammi, ma lo può fare il miglioramento in condizioni di scarsa illuminazione. Pertanto, il miglioramento in condizioni di scarsa illuminazione consente di attivare le funzionalità della fotocamera, ad esempio:
- Fornire un'anteprima dell'immagine migliorata, in modo che gli utenti possano inquadrare meglio le foto in condizioni di scarsa illuminazione
- Scansione di codici QR in condizioni di scarsa illuminazione
Se attivi l'opzione Luce notturna, questa si attiva automaticamente quando il livello di illuminazione è basso e si disattiva quando c'è più luce.
Le app possono registrare l'anteprima stream quando la luce è bassa in modo che il video salvato sia più luminoso.
Per saperne di più, consulta Aumento luminosità in condizioni di scarsa illuminazione.
Controlli della videocamera in-app
Android 15 aggiunge un'estensione per un maggiore controllo sull'hardware e sugli algoritmi della fotocamera sui dispositivi supportati:
- Regolazioni avanzate dell'intensità del flash che consentono di controllare con precisione l'intensità del flash sia in modalità
SINGLEsia in modalitàTORCHdurante l'acquisizione delle immagini.
Controllo dell'headroom HDR
Android 15 sceglie un headroom HDR appropriato per le funzionalità del dispositivo di base e la profondità di bit del pannello. Per le pagine con molti contenuti SDR, ad esempio un'app di messaggistica che mostra una singola miniatura HDR, questo comportamento può influire negativamente sulla luminosità percepita dei contenuti SDR. Android 15 ti consente di controllare l'headroom HDR con
setDesiredHdrHeadroom per trovare un equilibrio tra i contenuti SDR
e HDR.
Controllo del loudness

Android 15 introduce il supporto per Standard per il volume CTA-2075 per aiutarti evitare incoerenze del volume audio e fare in modo che gli utenti non debbano controllare regolare il volume passando da un contenuto all'altro. Il sistema sfrutta le note alle caratteristiche dei dispositivi di uscita (cuffie e altoparlanti) insieme metadati del volume disponibili nei contenuti audio AAC per regolare in modo intelligente il volume audio e livelli di compressione dell'intervallo dinamico.
Per attivare questa funzionalità, devi assicurarti che i metadati relativi all'intensità siano disponibili nei contenuti AAC e attivare la funzionalità della piattaforma nella tua app. Per farlo, devi creare un oggetto LoudnessCodecController chiamando il relativo metodo di fabbrica create con l'ID sessione audio dell'elemento AudioTrack associato. In questo modo, inizieranno automaticamente ad applicarsi gli aggiornamenti audio. Puoi trasmettere un
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener per modificare o filtrare
i parametri di volume prima di essere applicati
MediaCodec.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
Anche ExoPlayer di AndroidX media3 verrà aggiornato per utilizzare le API LoudnessCodecController per un'integrazione perfetta delle app.
Dispositivi MIDI virtuali 2.0
Android 13 ha aggiunto il supporto per la connessione ai dispositivi MIDI 2.0 tramite USB, che comunicano utilizzando Universal MIDI Packets (UMP). Android 15 estende il supporto UMP alle app MIDI virtuali, consentendo alle app di composizione di controllare le app di sintesi come un dispositivo MIDI 2.0 virtuale, proprio come faresti con un dispositivo MIDI 2.0 USB.
Decodifica software AV1 più efficiente

dav1d, il popolare decodificatore software AV1 di VideoLAN, è disponibile per i dispositivi Android che non supportano la decodifica AV1 in hardware. dav1d è fino a 3 volte più performante del precedente decodificatore software AV1, il che consente la riproduzione di AV1 HD a un maggior numero di utenti, inclusi alcuni dispositivi di fascia bassa e media.
La tua app deve attivare l'utilizzo di dav1d invocandolo per nome"c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". In un aggiornamento successivo, dav1d diventerà il decodificatore software AV1 predefinito. Questo supporto è standardizzato e sottoposto a backporting sui dispositivi Android 11 che ricevono gli aggiornamenti di sistema di Google Play.
Produttività e strumenti per gli sviluppatori
Sebbene la maggior parte del nostro lavoro per migliorare la tua produttività si concentri su strumenti come Android Studio, Jetpack Compose e le librerie Android Jetpack, cerchiamo sempre modi nella piattaforma per aiutarti a realizzare più facilmente la tua visione.
Aggiornamenti di OpenJDK 17
Android 15 continua il lavoro di aggiornamento delle librerie di base di Android per allinearsi alle funzionalità delle ultime release LTS di OpenJDK.
Sono incluse le seguenti funzionalità e i seguenti miglioramenti principali:
- Miglioramenti della qualità della vita relativi ai buffer NIO
- Stream
- Metodi
mathestrictmathaggiuntivi - Aggiornamenti del pacchetto
util, inclusicollection,mapesetin sequenza - Supporto di
ByteBufferinDeflater - Aggiornamenti della sicurezza come
X500PrivateCredentiale aggiornamenti delle chiavi di sicurezza
Queste API vengono aggiornate su oltre un miliardo di dispositivi con Android 12 (livello API 31) o versioni successive tramite gli aggiornamenti di sistema di Google Play, in modo da poter scegliere come target le ultime funzionalità di programmazione.
Miglioramenti al PDF
Android 15 include miglioramenti sostanziali a PdfRenderer
su quelle di livello inferiore. Le app possono incorporare funzionalità avanzate come il rendering
file protetti da password, annotazioni, modifica di moduli,
ricerca e selezione con testo. Sono supportate le ottimizzazioni dei PDF linearizzati per velocizzare la visualizzazione dei PDF locali e ridurre l'utilizzo delle risorse.
La libreria Jetpack PDF utilizza queste API per semplificare l'aggiunta di file PDF
funzionalità di visualizzazione per la tua app.
PdfRenderer è stato spostato in un modulo che può essere aggiornato utilizzando gli aggiornamenti di sistema di Google Play indipendentemente dalla release della piattaforma e supportiamo queste modifiche fino ad Android 11 (livello API 30) creando una versione compatibile pre-Android 15 dell'API, chiamata PdfRendererPreV.
Miglioramenti al cambio di lingua automatico
Android 14 ha aggiunto il riconoscimento multilingue on-device nell'audio con il passaggio automatico tra le lingue, ma questo può causare l'eliminazione di parole, soprattutto quando le lingue cambiano con una pausa minore tra le due frasi. Android 15 aggiunge controlli aggiuntivi per aiutare le app a ottimizzare questo passaggio in base al loro caso d'uso.
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS limita il passaggio automatico all'inizio della sessione audio, mentre EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES disattiva il passaggio di lingua dopo un numero definito di passaggi. Queste opzioni sono particolarmente utili se prevedi che durante la sessione verrà parlata una sola lingua che deve essere rilevata automaticamente.
API per i caratteri variabili OpenType migliorata
Android 15 migliora l'usabilità dei caratteri variabili OpenType. Puoi creare
un'istanza FontFamily da un carattere variabile senza specificare gli assi di spessore
con l'API buildVariableFamily. Il renderer di testo sostituisce il valore
su wght asse per corrispondere al testo visualizzato.
L'utilizzo dell'API semplifica notevolmente il codice per la creazione di una Typeface:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
In precedenza, per creare lo stesso Typeface, era necessario molto più codice:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Di seguito è riportato un esempio di come viene visualizzato un Typeface creato sia con le API precedenti sia con quelle nuove:
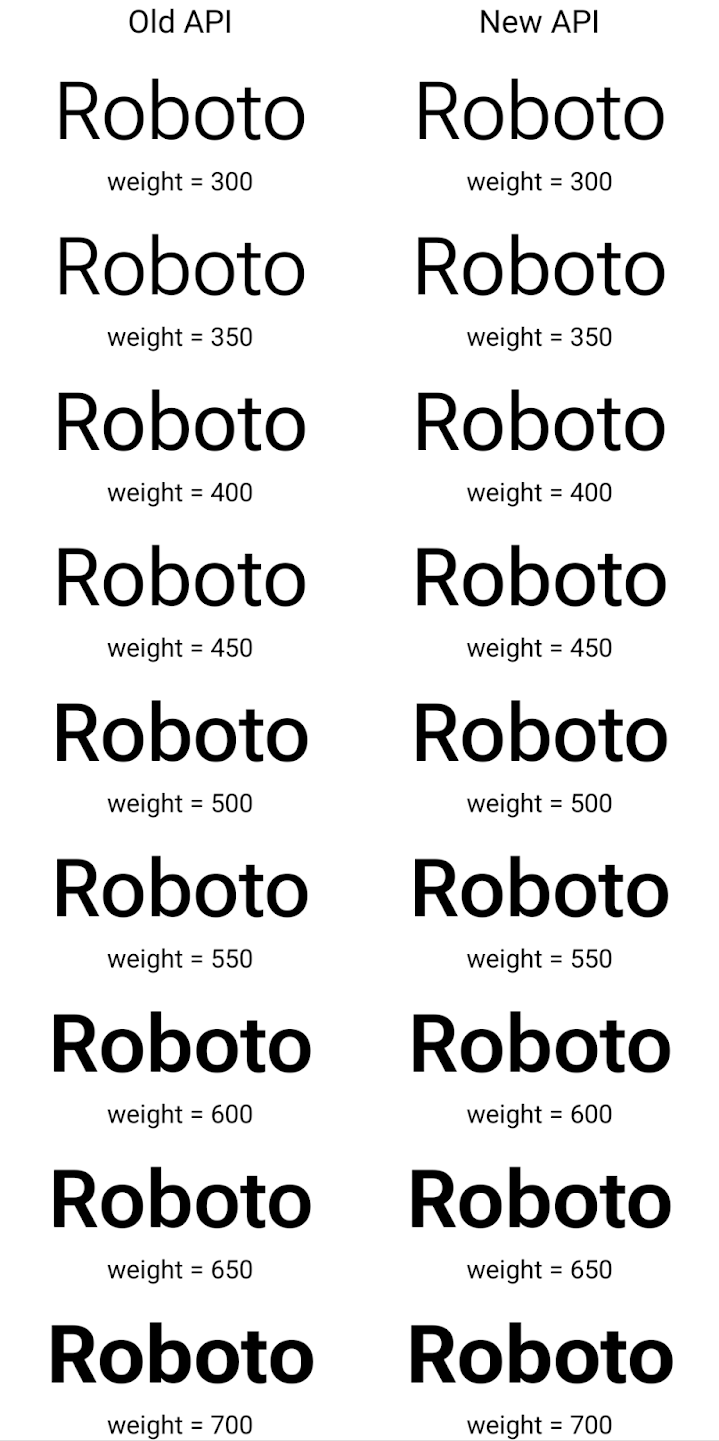
In questo esempio, il Typeface creato con l'API precedente non ha il valore
capacità di creare spessori di carattere precisi per i modelli 350, 450, 550 e 650
Font, quindi il renderer torna al peso più vicino. Quindi
In questo caso, viene eseguito il rendering di 300 anziché 350, di 400 invece di 450 e
così via. Al contrario, l'elemento Typeface creato con le nuove API crea in modo dinamico
un'istanza Font per un determinato peso, in modo che le ponderazioni siano accurate per 350,
450, 550 e 650.
Controlli granulari delle interruzioni di riga
A partire da Android 15, un TextView e l'interruzione di riga sottostante possono conservare la parte di testo specificata nella stessa riga per migliorare la leggibilità. Puoi sfruttare questa personalizzazione dell'interruzione di riga utilizzando il tag <nobreak> nelle risorse stringa o createNoBreakSpan. Analogamente, puoi impedire la suddivisione delle parole in sillabe utilizzando il tag <nohyphen> o createNoHyphenationSpan.
Ad esempio, la seguente risorsa stringa non include un a capo e viene visualizzata con il testo "Pixel 8 Pro" interrotto in un punto indesiderato:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
Al contrario, questa risorsa stringa include il tag <nobreak>, che inserisce un a capo nella frase "Pixel 8 Pro" e impedisce gli a capo:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
La differenza nel modo in cui queste stringhe vengono visualizzate è mostrata nelle seguenti immagini:

<nobreak>.
<nobreak>.Archiviazione app
L'anno scorso Android e Google Play hanno annunciato il supporto dell'archiviazione delle app, consentendo agli utenti di liberare spazio rimuovendo parzialmente dal dispositivo le app utilizzate di rado che sono state pubblicate utilizzando Android App Bundle su Google Play. Android 15 include il supporto a livello di sistema operativo per l'archiviazione delle app e l'annullamento dell'archiviazione, semplificando l'implementazione da parte di tutti gli store.
Le app con l'autorizzazione REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES possono chiamare il
PackageInstaller metodo requestArchive per richiedere l'archiviazione di un
pacchetto di app installato, che rimuove l'APK e gli eventuali file memorizzati nella cache, ma persiste
dati utente. Le app archiviate vengono restituite come app visualizzabili tramite la
API di LauncherApps; gli utenti vedranno un'interfaccia utente
per evidenziare che tali utenti
vengono archiviate. Se un utente tocca un'app archiviata, l'utente che ha eseguito l'installazione responsabile
riceverà una richiesta di annullamento dell'archiviazione del file e il processo di ripristino può
monitorate dalla trasmissione ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED.
Attivare la modalità a 16 kB su un dispositivo utilizzando le opzioni sviluppatore
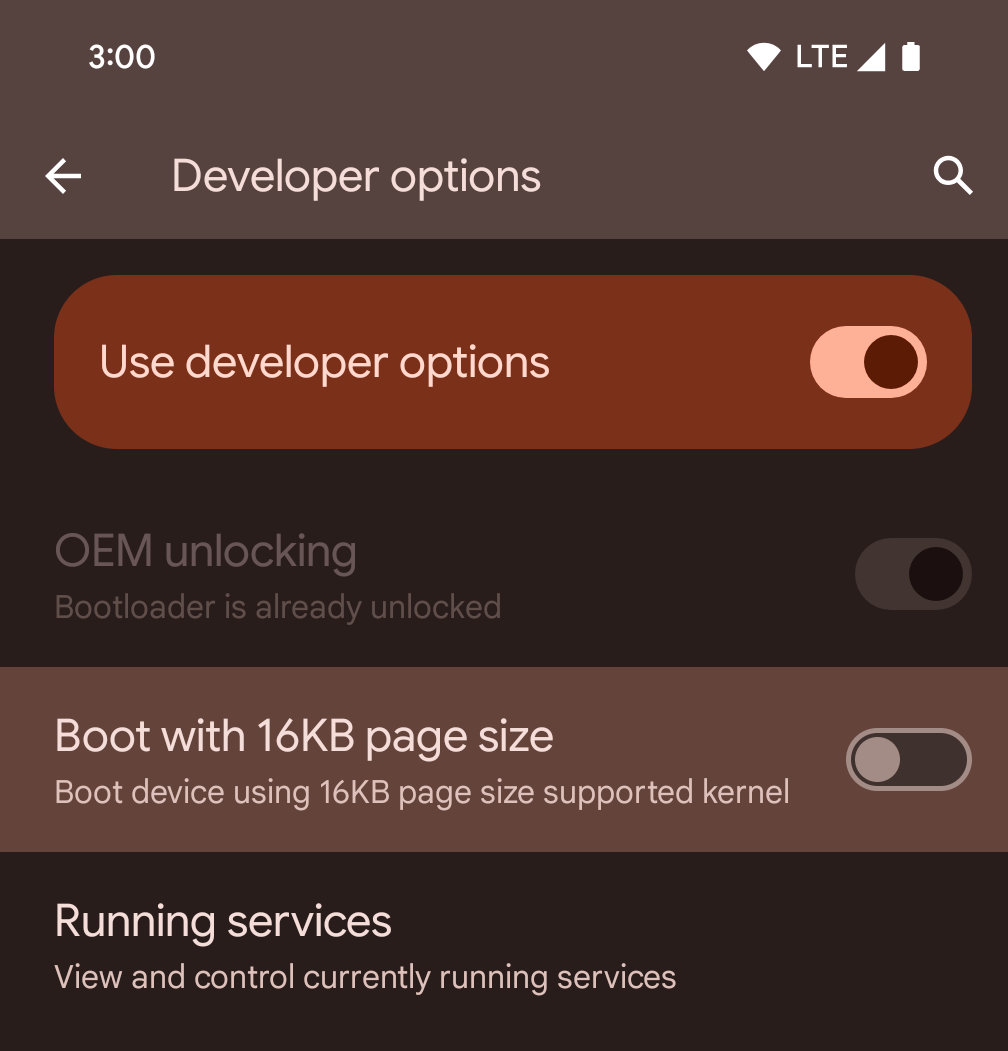
Attiva l'opzione per sviluppatori Avvia con dimensione pagina 16 kB per avviare un dispositivo in modalità a 16 kB.
Nelle versioni QPR di Android 15, puoi utilizzare l'opzione sviluppatore disponibile su alcuni dispositivi per avviare il dispositivo in modalità 16 KB ed eseguire test sul dispositivo. Prima di utilizzare l'opzione sviluppatore, vai a Impostazioni > Sistema > Aggiornamenti software e applica gli aggiornamenti disponibili.
Questa opzione sviluppatore è disponibile sui seguenti dispositivi:
Pixel 8 e 8 Pro (con Android 15 QPR1 o versioni successive)
Pixel 8a (con Android 15 QPR1 o versioni successive)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro e 9 Pro XL (con Android 15 QPR2 Beta 2 o versioni successive)
Grafica
Android 15 offre i più recenti miglioramenti grafici, tra cui ANGLE e aggiunte al sistema grafico Canvas.
Modernizzazione dell'accesso alla GPU di Android

L'hardware Android si è evoluto notevolmente rispetto ai primi tempi, quando il sistema operativo di base veniva eseguito su una singola CPU e si accedeva alle GPU utilizzando API basate su pipeline a funzioni fisse. L'API grafica Vulkan® è disponibile nel NDK da Android 7.0 (livello API 24) con un'astrazione di livello inferiore che riflette meglio l'hardware GPU moderno, si adatta meglio al supporto di più core CPU e offre un carico del driver della CPU ridotto, migliorando così le prestazioni dell'app. Vulkan è supportato da tutti i motori di gioco moderni.
Vulkan è l'interfaccia preferita di Android per la GPU. Pertanto, Android 15 include ANGLE come livello facoltativo per l'esecuzione di OpenGL® ES su Vulkan. Il passaggio ad ANGLE standardizzerà l'implementazione di OpenGL per Android per una maggiore compatibilità e, in alcuni casi, per un miglioramento delle prestazioni. Puoi testare la stabilità e le prestazioni delle app OpenGL ES con ANGLE attivando l'opzione per gli sviluppatori in Impostazioni -> Sistema -> Opzioni sviluppatore -> Sperimentale: attiva ANGLE su Android 15.
Roadmap di Android ANGLE su Vulkan
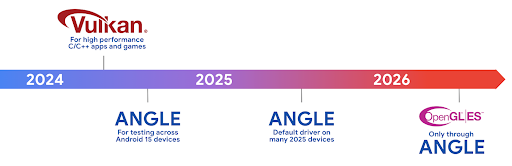
Nell'ambito dell'ottimizzazione del nostro stack GPU, in futuro forniremo ANGLE come driver di sistema GL su più nuovi dispositivi, con la previsione futura che OpenGL/ES sarà disponibile solo tramite ANGLE. Detto questo, prevediamo di mantenere il supporto di OpenGL ES su tutti i dispositivi.
Passi successivi consigliati
Utilizza le opzioni per gli sviluppatori per selezionare il driver ANGLE per OpenGL ES e testare la tua app. Per i nuovi progetti, ti consigliamo vivamente di utilizzare Vulkan per C/C++.
Miglioramenti per Canvas
Android 15 continua la nostra modernizzazione del sistema grafico Canvas di Android con funzionalità aggiuntive:
Matrix44fornisce una matrice 4x4 per la trasformazione delle coordinate da utilizzare quando vuoi manipolare la tela in 3D.clipShaderinterseca il clip corrente con lo shader specificato, mentreclipOutShaderimposta il clip sulla differenza tra il clip corrente e lo shader, trattando ciascuno lo shader come una maschera alfa. Ciò consente di disegnare in modo efficiente forme complesse.
Prestazioni e batteria
Android continua a concentrarsi sull'aiuto per migliorare le prestazioni e la qualità delle tue app. Android 15 introduce API che contribuiscono a rendere più efficienti le attività nella tua app, a ottimizzare le prestazioni dell'app e a raccogliere approfondimenti sulle tue app.
Per le best practice per l'efficienza della batteria, il debug dell'utilizzo di rete ed energia e dettagli su come stiamo migliorando l'efficienza della batteria del lavoro in background in Android 15 e nelle versioni recenti di Android, guarda il talk Migliorare l'efficienza della batteria del lavoro in background su Android di Google I/O.
API ApplicationStartInfo
Nelle versioni precedenti di Android, l'avvio delle app era un po' un mistero. È stato difficile determinare all'interno della tua app se è stata avviata da uno stato freddo, tiepido o caldo. Inoltre, era difficile sapere quanto tempo impiegava l'app durante le varie fasi di lancio: il fork del processo, la chiamata a onCreate, il disegno del primo frame e altro ancora. Quando è stata creata l'istanza della classe Application, non avevi modo di sapere se l'app era stata avviata da una trasmissione, da un fornitore di contenuti, da un job, da un backup, dall'avvio completo, da una sveglia o da un Activity.
L'API ApplicationStartInfo su Android 15 offre tutto questo e altro ancora. Puoi anche scegliere di aggiungere i tuoi timestamp nel
flussi per contribuire a raccogliere i dati relativi ai tempi in un unico posto. Oltre a raccogliere
le metriche, puoi utilizzare ApplicationStartInfo per ottimizzare direttamente l'avvio
dell'app. Ad esempio, puoi eliminare la costosa istanza di librerie
relative all'interfaccia utente all'interno della tua classe Application quando l'app si avvia a causa di una broadcasting.
Informazioni dettagliate sulle dimensioni dell'app
Da Android 8.0 (livello API 26), Android include l'API StorageStats.getAppBytes che riassume le dimensioni installate di un'app come un singolo numero di byte, ovvero la somma delle dimensioni dell'APK, delle dimensioni dei file estratti dall'APK e dei file generati sul dispositivo, come il codice compilato in anticipo (AOT). Questo numero non è molto utile per capire in che modo la tua app utilizza lo spazio di archiviazione.
Android 15 aggiunge l'API StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]), che consente di ottenere informazioni su come la tua app utilizza tutto questo spazio, inclusi i raggruppamenti dei file APK, il codice AOT e relativo all'accelerazione, i metadati dex, le librerie e i profili guidati.
Profilazione gestita dalle app
Android 15 include la classe ProfilingManager,
che ti consente di raccogliere informazioni sul profiling all'interno della tua app, ad esempio dump heap, profili heap, campionamento dello stack e altro ancora. Fornisce un callback alla tua app con un tag fornito per identificare il file di output, che viene inviato alla directory dei file della tua app. L'API limita la frequenza per ridurre al minimo
l'impatto sulle prestazioni.
Per semplificare la creazione di richieste di profilazione nella tua app, ti consigliamo di utilizzare l'Profiling API AndroidX corrispondente, disponibile in Core 1.15.0-rc01 o versioni successive.
Miglioramenti al database SQLite
Android 15 introduce le API SQLite che espongono funzionalità avanzate motore SQLite sottostante che ha come target specifici problemi di prestazioni che possono manifest nelle app. Queste API sono incluse nell'aggiornamento di SQLite alla versione 3.44.3.
Gli sviluppatori devono consultare le best practice per le prestazioni di SQLite per ottenere il massimo dal proprio database SQLite, in particolare quando si lavora con database di grandi dimensioni o quando si eseguono query sensibili alla latenza.
- Transazioni differite di sola lettura: quando emetti transazioni di sola lettura (non includono istruzioni di scrittura), utilizza
beginTransactionReadOnly()ebeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)per emettere transazioniDEFERREDdi sola lettura. Queste transazioni possono essere eseguite in contemporanea e, se il database è in modalità WAL, eseguita in concomitanza conIMMEDIATEoEXCLUSIVEtransazioni. - Conteggi e ID righe: sono state aggiunte API per recuperare il conteggio
righe o l'ultimo ID riga inserito senza inviare un'ulteriore query.
getLastChangedRowCount()restituisce il numero di righe che sono stati inseriti, aggiornati o eliminati dall'istruzione SQL più recente all'interno la transazione corrente egetTotalChangedRowCount()restituisce il conteggio della connessione corrente.getLastInsertRowId()restituiscerowiddell'ultima riga da inserire nella connessione corrente. - Istruzioni non elaborate: invia un'istruzione SQlite non elaborata, aggirando la convenienza e l'eventuale overhead di elaborazione aggiuntivo che potrebbe subire.
Aggiornamenti di Android Dynamic Performance Framework
Android 15 continua il nostro investimento nell'Android Dynamic Performance Framework (ADPF), un insieme di API che consente a giochi e app ad alte prestazioni di interagire più direttamente con i sistemi di alimentazione e termici dei dispositivi Android. Sui dispositivi supportati, Android 15 aggiunge le funzionalità ADPF:
- Una modalità di risparmio energetico per le sessioni di suggerimenti per indicare che i thread associati devono dare la priorità al risparmio energetico rispetto alle prestazioni, ideale per i carichi di lavoro in background di lunga durata.
- Le durate del lavoro della GPU e della CPU possono essere entrambe registrate nelle sessioni di suggerimenti, consentendo al sistema di regolare le frequenze della CPU e della GPU insieme per soddisfare al meglio le richieste del carico di lavoro.
- Soglie di headroom termico per interpretare il possibile stato di throttling termico in base alla previsione dell'headroom.
Per scoprire di più su come utilizzare ADPF nelle tue app e nei tuoi giochi, consulta la documentazione.
Privacy
Android 15 include una serie di funzionalità che aiutano gli sviluppatori di app a proteggere la privacy degli utenti.
Rilevamento della registrazione dello schermo
Android 15 aggiunge il supporto delle app per rilevare che vengono registrate. Un callback viene invocato ogni volta che l'app passa da visibile a invisibile all'interno di una registrazione dello schermo. Un'app è considerata visibile se vengono registrate attività di proprietà dell'UID della procedura di registrazione. In questo modo, se la tua app esegue un'operazione sensibile, puoi informare l'utente che è in corso una registrazione.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
Funzionalità ampliate di IntentFilter
Android 15 supporta la risoluzione Intent più precisa tramite
UriRelativeFilterGroup, che contiene un insieme di
UriRelativeFilter oggetti che formano un insieme di Intent
regole di corrispondenza che devono essere soddisfatte, inclusi i parametri di query dell'URL, i frammenti di URL e le regole di blocco o esclusione.
Queste regole possono essere definite nel file XML AndroidManifest con il
tag <uri-relative-filter-group>, che può includere facoltativamente un
tag android:allow. Questi tag possono contenere tag <data> che utilizzano attributi di tag dati esistenti,
nonché gli attributi android:query e android:fragment.
Ecco un esempio di sintassi di AndroidManifest:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
Spazio privato
Lo spazio privato consente agli utenti di creare uno spazio separato sul proprio dispositivo in cui possono proteggere le app sensibili da occhi indiscreti mediante un ulteriore livello di autenticazione. Lo spazio privato utilizza un profilo utente distinto. L'utente può scegliere di usare il blocco dispositivo o un fattore di blocco separato per lo spazio privato.
Le app nello spazio privato vengono visualizzate in un contenitore separato in Avvio app e, quando lo spazio privato è bloccato, non appaiono nelle viste di contenuti recenti, notifiche, impostazioni e altre app. I contenuti generati e scaricati dall'utente (ad esempio contenuti multimediali o file) e gli account sono separati tra lo spazio privato e lo spazio principale. Il foglio di condivisione del sistema e il selettore di foto possono essere usati per concedere alle app l'accesso ai contenuti tra gli spazi quando lo spazio privato è sbloccato.
Gli utenti non possono spostare le app esistenti e i relativi dati nello spazio privato. Gli utenti scelgono un'opzione di installazione nello spazio privato per installare un'app utilizzando l'app store che preferiscono. Le app nello spazio privato vengono installate come copie separate da qualsiasi app nello spazio principale (nuove copie della stessa app).
Quando un utente blocca lo spazio privato, il profilo viene interrotto. Quando il profilo è fermo, le app nello spazio privato non sono più attive e non possono eseguire attività in primo piano o in background, inclusa la visualizzazione di notifiche.
Ti consigliamo di testare l'app con lo spazio privato per assicurarti che funzioni come previsto, soprattutto se rientra in una delle seguenti categorie:
- App con logica per i profili di lavoro che presuppongono che tutte le copie installate dell'app che non si trovano nel profilo principale siano nel profilo di lavoro.
- App mediche
- App di avvio
- App dello Store
Eseguire query sulla selezione più recente dell'utente per l'accesso alle foto selezionate
Ora le app possono mettere in evidenza solo le foto e i video selezionati più di recente quando viene concesso l'accesso parziale alle autorizzazioni per i contenuti multimediali. Questa funzionalità può migliorare
l'esperienza utente per le app che richiedono spesso l'accesso a foto e
video. Per utilizzare questa funzionalità nella tua app, attiva l'argomento
QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY quando esegui query su MediaStore
tramite ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Privacy Sandbox su Android
Android 15 include le ultime estensioni di Android Ad Services, che incorporano la versione più recente di Privacy Sandbox su Android. Questa aggiunta fa parte del nostro impegno per sviluppare tecnologie che migliorino la privacy degli utenti e consentano esperienze pubblicitarie efficaci e personalizzate per le app mobile. Nella nostra pagina di Privacy Sandbox puoi trovare ulteriori informazioni su Privacy Sandbox su Android, sull'Anteprima per gli sviluppatori e sui programmi beta per iniziare.
Connessione Salute
Android 15 integra le ultime estensioni Connessione Salute di Android, un servizio sicuro e centralizzato per gestire e condividere i dati relativi a salute e fitness raccolti da app. Questo aggiornamento aggiunge il supporto per tipi di dati aggiuntivi in fitness, alimentazione, temperatura cutanea, piani di allenamento e altro ancora.
Il monitoraggio della temperatura cutanea consente agli utenti di memorizzare e condividere dati sulla temperatura più precisi da un dispositivo indossabile o da un altro dispositivo di monitoraggio.
I piani di allenamento sono programmi di allenamento strutturati per aiutare un utente a raggiungere i suoi obiettivi di fitness. Il supporto dei piani di allenamento include una serie di obiettivi di completamento e rendimento:
- Obiettivi di completamento relativi a calorie bruciate, distanza, durata, ripetizioni e passi.
- Obiettivi di rendimento relativi a il maggior numero possibile di ripetizioni (AMRAP), frequenza, battito cardiaco, alimentazione, tasso di sforzo percepito e velocità.
Scopri di più sugli ultimi aggiornamenti di Connessione Salute su Android nel Creare esperienze adattabili con Android Discussione sulla salute di Google I/O.
Condivisione della schermata dell'app
Android 15 supporta la condivisione dello schermo delle app, quindi gli utenti possono condividere o registrare solo una finestra dell'app anziché l'intero schermo del dispositivo. Questa funzionalità, attivata per la prima volta in Android 14 QPR2, include callback di MediaProjection che consentono alla tua app di personalizzare l'esperienza di condivisione schermo dell'app. Tieni presente che per le app che hanno come target Android 14 (livello API 34) o versioni successive, il consenso dell'utente è obbligatorio per ogni sessione di acquisizione MediaProjection.
Esperienza utente e UI di sistema
Android 15 offre a sviluppatori di app e utenti maggiore controllo e flessibilità per configurare il dispositivo in base alle proprie esigenze.
Per scoprire di più su come utilizzare i più recenti miglioramenti di Android 15 per migliorare l'esperienza utente della tua app, guarda la presentazione Migliorare l'esperienza utente della tua app Android di Google I/O.
Anteprime dei widget più ricche con l'API Generated Previews
Prima di Android 15, l'unico modo per fornire anteprime del selettore widget era specificare una risorsa immagine o layout statica. Queste anteprime spesso sono diverse molto dall'aspetto del widget reale quando è posizionato sulla home page schermo. Inoltre, non è possibile creare risorse statiche con Jetpack Glance, quindi Riepilogo uno sviluppatore ha dovuto fare uno screenshot del widget o creare un layout XML l'anteprima del widget.
Android 15 aggiunge il supporto per le anteprime generate. Ciò significa che il widget dell'app
i provider possono generare RemoteViews da usare come anteprima del selettore,
di una risorsa statica.
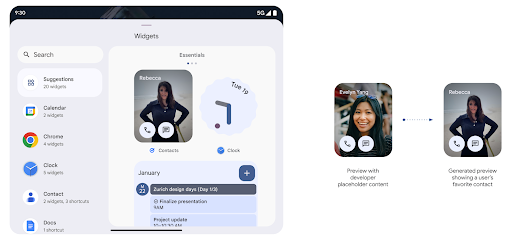
API Push
Le app possono fornire anteprime generate tramite un'API push. Le app possono fornire anteprime in qualsiasi momento del loro ciclo di vita e non ricevono una richiesta esplicita dall'host per fornire anteprime. Le anteprime vengono conservate in AppWidgetService e gli autori possono richiederle on demand. L'esempio seguente carica una risorsa di layout del widget XML e la imposta come anteprima:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
Il flusso previsto è:
- In qualsiasi momento, il fornitore del widget chiama
setWidgetPreview. Le anteprime fornite vengono conservate inAppWidgetServiceinsieme ad altre informazioni del fornitore. setWidgetPreviewinvia una notifica agli host di un'anteprima aggiornata tramite il callbackAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged. In risposta, l'host del widget ricarica tutte le informazioni del fornitore.- Quando viene visualizzata un'anteprima del widget, l'host controlla
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategoriese, se la categoria scelta è disponibile, chiamaAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewper restituire l'anteprima salvata per questo fornitore.
Quando chiamare setWidgetPreview
Poiché non è necessario richiamare le anteprime, le app possono scegliere di inviare vengono visualizzate in qualsiasi momento quando sono in esecuzione. La frequenza con cui aggiornare l'anteprima dipende dal caso d'uso del widget.
L'elenco seguente descrive le due categorie principali di casi d'uso di anteprima:
- Fornitori che mostrano dati reali nelle anteprime dei widget, ad esempio informazioni personalizzate o recenti. Questi fornitori possono impostare l'anteprima dopo che l'utente ha eseguito l'accesso o ha completato la configurazione iniziale nella propria app. Dopodiché, possono configurare un'attività periodica per aggiornare le anteprime con la cadenza scelta. Esempi di questo tipo di widget possono essere foto, calendario, meteo o notizie.
- Fornitori che mostrano informazioni statiche nelle anteprime o nei widget di azioni rapide che non mostrano dati. Questi fornitori possono impostare le anteprime una sola volta, quando viene avviata per la prima volta. Alcuni esempi di questo tipo di widget includono una guida rapida widget azioni o widget scorciatoie di Chrome.
Alcuni fornitori potrebbero mostrare anteprime statiche nel selettore della modalità Hub, ma informazioni reali nel selettore della schermata Home. Questi fornitori devono seguire le indicazioni per entrambi i casi d'uso per impostare le anteprime.
Picture in picture
Android 15 introduce modifiche in Picture in picture (PIP) per garantire una transizione più fluida quando entri in modalità PIP. Ciò sarà vantaggioso per app con elementi UI sovrapposti alla UI principale, che passa in PIP.
Gli sviluppatori utilizzano il callback onPictureInPictureModeChanged per definire la logica
che attiva/disattiva la visibilità
degli elementi UI sovrapposti. Questo callback viene attivato al termine dell'animazione di entrata o uscita in PiP. Inizia tra
Android 15, la classe PictureInPictureUiState include un altro stato.
Con questo stato della UI, le app destinate ad Android 15 (livello API 35) osserveranno
Richiamato callback Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged con
isTransitioningToPip() all'avvio dell'animazione PIP. Esistono
molti elementi UI non pertinenti all'app in modalità PIP, ad esempio
visualizzazioni o layout di esempio che includono informazioni come suggerimenti,
video, valutazioni e titoli. Quando l'app passa in modalità PIP, usa
Callback onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged per nascondere questi elementi UI. Quando l'app passa alla modalità a schermo intero dalla finestra PiP, utilizza il callback onPictureInPictureModeChanged per mostrare nuovamente questi elementi, come mostrato nei seguenti esempi:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
Questa rapida attivazione/disattivazione della visibilità di elementi UI non pertinenti (per una finestra PIP) per garantire un'animazione di inserimento in PIP più fluida e senza sfarfallii.
Regole Non disturbare migliorate
AutomaticZenRule consente alle app di personalizzare la funzionalità Attenzione
Gestione delle regole (Non disturbare) e decidere quando attivarle o disattivarle
che li rappresentano. Android 15 migliora notevolmente queste regole con l'obiettivo di migliorare
un'esperienza utente positiva. Sono inclusi i seguenti miglioramenti:
- Aggiunta di tipi a
AutomaticZenRule, in modo che il sistema possa applicare tipi per alcune regole. - L'aggiunta di un'icona a
AutomaticZenRule, che contribuisce a rendere le modalità più riconoscibili. - Aggiunta a
AutomaticZenRuledi una stringatriggerDescriptionche descriva le condizioni in cui la regola deve diventare attiva per l'utente. - Aggiunta
ZenDeviceEffectsaAutomaticZenRule, consentendo alle regole di attivare elementi come scala di grigi schermo, modalità notturna o attenuazione dello sfondo.
Impostare VibrationEffect per i canali di notifica
Android 15 supporta l'impostazione di vibrazioni intense per le notifiche in arrivo tramite
canale utilizzando NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect,
i tuoi utenti possano distinguere tra diversi tipi di notifiche senza
dover guardare il proprio dispositivo.
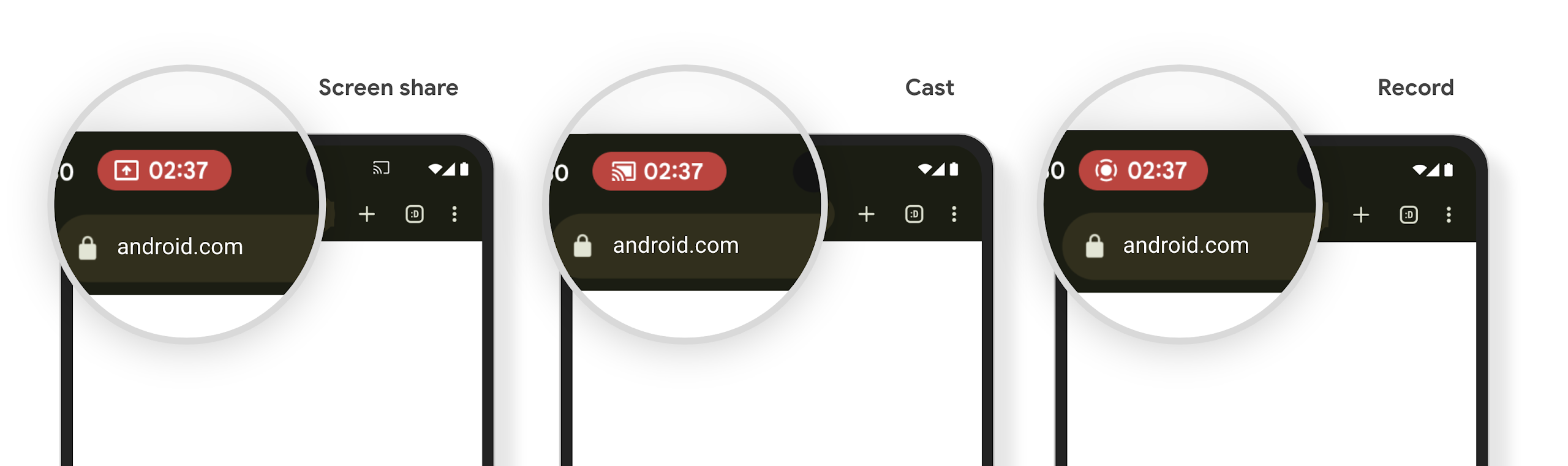
Etichetta della barra di stato della proiezione di contenuti multimediali e arresto automatico
La proiezione di contenuti multimediali può esporre informazioni private degli utenti. Un nuovo chip della barra di stato in evidenza informa gli utenti di eventuali proiezioni dello schermo in corso. Gli utenti possono toccare il chip per interrompere la trasmissione, la condivisione o la registrazione dello schermo. Inoltre, per un'esperienza utente più intuitiva, qualsiasi proiezione dello schermo in corso ora si interrompe automaticamente quando lo schermo del dispositivo è bloccato.
Schermi grandi e fattori di forma
Android 15 offre alle tue app il supporto per sfruttare al meglio i fattori di forma di Android, inclusi schermi di grandi dimensioni, smartphone con apertura a libro e pieghevoli.
Multitasking migliore su schermo grande
Android 15 offre agli utenti modi migliori per svolgere più attività contemporaneamente su dispositivi con schermi grandi. Ad esempio, gli utenti possono salvare le combinazioni di app con schermo diviso preferite per accedervi rapidamente e fissare la barra delle app sullo schermo per passare rapidamente da un'app all'altra. Ciò significa rendere l'app adattiva più importante che mai.
Google I/O offre sessioni su Creazione di app Android adattabili e Creazione di UI con la libreria adattabile Material 3 che possono essere utili. La nostra documentazione contiene ulteriori informazioni per aiutarti a creare design per schermi di grandi dimensioni.
Supporto dello schermo della cover
La tua app può dichiarare una proprietà utilizzata da Android 15 per consentire la visualizzazione di Application o Activity sulle piccole schermate di copertina dei dispositivi pieghevoli supportati. Questi schermi sono troppo piccoli per essere considerati come target compatibili per l'esecuzione delle app per Android, ma la tua app può attivare il loro supporto, rendendola disponibile in più luoghi.
Connettività
Android 15 aggiorna la piattaforma per consentire alla tua app di accedere agli ultimi progressi nelle tecnologie di comunicazione e wireless.
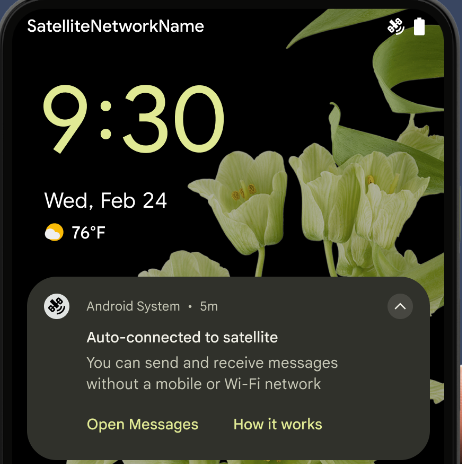
Supporto satellitare
Android 15 continua a estendere il supporto delle piattaforme per la connettività satellitare e include alcuni elementi dell'interfaccia utente per garantire un'esperienza utente coerente panorama della connettività satellitare.
Le app possono utilizzare ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() per rilevare quando un dispositivo è connesso a un satellite, in modo da avere una maggiore consapevolezza del motivo per cui i servizi di rete completi potrebbero non essere disponibili. Inoltre, Android 15 supporta le app SMS e MMS, nonché le app RCS precaricate, per utilizzare la connettività satellitare per l'invio e la ricezione di messaggi.
Esperienze NFC più fluide
Android 15 si impegna a rendere l'esperienza di pagamento contactless più fluida e affidabile, continuando a supportare il solido ecosistema di app NFC di Android. Sui dispositivi supportati, le app possono richiedere al NfcAdapter di entrare in modalità di osservazione, in cui il dispositivo ascolta, ma non risponde ai lettori NFC, inviando gli oggetti PollingFrame del servizio NFC dell'app da elaborare. Gli oggetti PollingFrame possono essere utilizzati per l'autenticazione prima della prima comunicazione con il lettore NFC, consentendo in molti casi una transazione con un solo tocco.
Inoltre, le app possono registrare un filtro sui dispositivi supportati in modo da ricevere una notifica dell'attività del loop di polling, il che consente un funzionamento regolare con più applicazioni compatibili con NFC.
Ruolo del portafoglio
Android 15 introduce un ruolo Wallet che consente un'integrazione più stretta con l'app Wallet preferita dall'utente. Questo ruolo sostituisce l'impostazione di pagamento contactless predefinita NFC. Gli utenti possono gestire il proprietario del ruolo Wallet andando a Impostazioni > App > App predefinite.
Il ruolo Wallet viene utilizzato per instradare i tocchi NFC per gli AID registrati nella categoria pagamenti. I tocchi vanno sempre al titolare del ruolo Wallet, a meno che un'altra app registrata per lo stesso AID non sia in esecuzione in primo piano.
Questo ruolo viene utilizzato anche per determinare dove deve essere inserito il riquadro di accesso rapido a Wallet quando viene attivato. Quando il ruolo è impostato su "Nessuna", il riquadro Accesso rapido non è disponibile e i tocchi NFC per la categoria di pagamento vengono inviati solo all'app in primo piano.
Sicurezza
Android 15 ti aiuta a migliorare la sicurezza della tua app, proteggere i dati dell'app e offre agli utenti maggiore trasparenza e controllo sui propri dati. Guarda il talk Safeguarding user security on Android di Google I/O per scoprire di più su cosa stiamo facendo per migliorare le misure di salvaguardia degli utenti e proteggere la tua app da nuove minacce.
Integrare Gestore delle credenziali con la compilazione automatica
A partire da Android 15, gli sviluppatori possono collegare viste specifiche, come i campi nome utente o password, alle richieste di Gestore delle credenziali, semplificando la fornitura di un'esperienza utente personalizzata durante la procedura di accesso. Quando l'utente si concentra su una di queste visualizzazioni, viene inviata una richiesta corrispondente a Credential Manager. Le credenziali risultanti vengono aggregate tra i fornitori e visualizzate nelle UI di riserva per la compilazione automatica, come i suggerimenti in linea o i suggerimenti del menu a discesa. La libreria Jetpack androidx.credentials è l'endpoint preferito per gli sviluppatori e sarà presto disponibile per migliorare ulteriormente questa funzionalità in Android 15 e versioni successive.
Integrare la registrazione e l'accesso con un solo tocco con le richieste biometriche
Gestore delle credenziali integra i prompt biometrici nella creazione delle credenziali e i processi di accesso, eliminando così la necessità da parte dei provider di gestire di prompt biometrici. Di conseguenza, i fornitori di credenziali devono concentrarsi solo i risultati dei flussi create e get, aumentati con il risultato del flusso biometrico. Questo processo semplificato crea credenziali più efficienti e semplificate processo di creazione e recupero.
Gestione delle chiavi per la crittografia end-to-end
Stiamo introducendo E2eeContactKeysManager in Android 15, che facilita la crittografia end-to-end (E2EE) nelle tue app per Android fornendo un'API a livello di sistema operativo per lo stoccaggio delle chiavi pubbliche di crittografia.
E2eeContactKeysManager è progettato per integrarsi con l'app Contatti della piattaforma per offrire agli utenti un modo centralizzato per gestire e verificare le chiavi pubbliche dei loro contatti.
Controlli delle autorizzazioni sugli URI dei contenuti
Android 15 introduce un insieme di API che eseguono controlli delle autorizzazioni sugli URI dei contenuti:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: viene eseguito un controllo completo delle autorizzazioni sugli URI dei contenuti.- Attributo manifest
ActivityrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: consente di applicare le autorizzazioni specificate agli URI dei contenuti forniti al momento del lancio dell'attività. - Classe
ComponentCallerper gli utenti che hanno chiamatoActivity: rappresenta l'app che ha avviato l'attività.
Accessibilità
Android 15 aggiunge funzionalità che migliorano l'accessibilità per gli utenti.
Braille migliorato
In Android 15, abbiamo reso possibile per TalkBack supportare i display braille che utilizzano lo standard HID sia tramite USB che tramite Bluetooth sicuro.
Questo standard, molto simile a quello utilizzato da mouse e tastiere, aiuterà Android a supportare nel tempo una gamma più ampia di display braille.
Internazionalizzazione
Android 15 aggiunge funzionalità e capacità che completano l'esperienza utente quando un dispositivo viene utilizzato in lingue diverse.
Carattere variabile CJK
A partire da Android 15, il file del carattere per le lingue cinese, giapponese e coreano (CJK), NotoSansCJK, è ora un carattere variabile. I caratteri variabili aprono nuove possibilità per la tipografia creativa nelle lingue CJK. I designer possono esplorare una gamma più ampia di stili e creare layout visivamente accattivanti che in precedenza erano difficili o impossibili da realizzare.

Giustificazione tra caratteri
A partire da Android 15, il testo può essere giustificato utilizzando la spaziatura tra le lettere
utilizzando JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. La giustificazione tra parole era
introdotto per la prima volta in Android 8.0 (livello API 26) e
giustificazione offre funzionalità simili per i linguaggi che utilizzano
spazio vuoto per la segmentazione, ad esempio cinese, giapponese e altri.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.Configurazione dell'interruzione di riga automatica
Android ha iniziato a supportare le interruzioni di riga basate su frase per il giapponese e il coreano in
Android 13 (livello API 33). Tuttavia, mentre le interruzioni di riga basate su frase migliorano
leggibilità di brevi righe di testo, non sono ideali per righe di testo lunghe.
In Android 15, le app possono applicare interruzioni di riga basate su frase solo per le righe brevi
di testo, utilizzando la classe LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
. Questa opzione seleziona lo stile della parola migliore per il testo.
Per brevi righe di testo, vengono utilizzate le interruzioni di riga basate su frase, che funzionano nello stesso modo
come LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, come mostrato in
immagine seguente:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
applica interruzioni di riga basate su frase per migliorare la leggibilità del testo.
È come applicare
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.Per le righe di testo più lunghe, LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO utilizza uno stile di parola senza interruzione di riga, che funziona come LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, come mostrato nell'immagine seguente:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
non applica alcun tipo di interruzione di riga per migliorare la leggibilità del testo.
Equivale ad applicare
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.Carattere Hentaigana giapponese aggiuntivo
In Android 15, un file del carattere per l'hiragana giapponese antico (noto come hentaigana) è incluso per impostazione predefinita. Le forme uniche dei caratteri hentaigana possono aggiungere un tocco distintivo all'artwork o al design, contribuendo al contempo a preservare la trasmissione e la comprensione accurate dei documenti giapponesi antichi.

Cono VideoLAN Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. Questo logo o una versione modificata può essere utilizzato o modificato da chiunque per fare riferimento al progetto VideoLAN o a qualsiasi prodotto sviluppato dal team di VideoLAN, ma non indica l'approvazione del progetto.
Vulkan e il logo Vulkan sono marchi registrati di Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL è un marchio registrato e il logo OpenGL ES è un marchio di Hewlett Packard Enterprise utilizzato con l'autorizzazione di Khronos.

