Платформа Android 15 включает изменения в поведении, которые могут повлиять на ваше приложение. Следующие изменения в поведении применяются ко всем приложениям, работающим на Android 15, независимо от targetSdkVersion . Вам следует протестировать свое приложение, а затем внести необходимые изменения для корректной поддержки этих изменений, где это применимо.
Обязательно ознакомьтесь также со списком изменений в поведении, которые затрагивают только приложения, ориентированные на Android 15 .
Основная функциональность
Android 15 изменяет или расширяет различные основные возможности системы Android.
Изменения в состоянии пакета остановлены.
Целью состояния пакета FLAG_STOPPED (которое пользователи могут использовать в сборках AOSP, нажав и удерживая значок приложения и выбрав «Принудительно остановить») всегда было сохранение приложений в этом состоянии до тех пор, пока пользователь явно не удалит приложение из этого состояния напрямую. запуск приложения или косвенное взаимодействие с приложением (через общий доступ или виджет, выбор приложения в качестве живых обоев и т. д.). В Android 15 мы обновили поведение системы, чтобы оно соответствовало предполагаемому поведению. Приложения следует выводить из остановленного состояния только прямым или косвенным действием пользователя.
Для поддержки предполагаемого поведения, в дополнение к существующим ограничениям, система также отменяет все ожидающие намерения, когда приложение переходит в состояние остановки на устройстве под управлением Android 15. Когда действия пользователя выводят приложение из состояния остановки, трансляция ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED доставлено в приложение, предоставляя возможность перерегистрировать любые ожидающие намерения.
Вы можете вызвать новый метод ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped() , чтобы подтвердить, было ли приложение переведено в состояние остановлено.
Поддержка страниц размером 16 КБ
Исторически Android поддерживал страницы памяти размером всего 4 КБ, что оптимизировало производительность системной памяти для среднего объёма памяти, обычно используемого устройствами Android. Начиная с Android 15, AOSP поддерживает устройства, настроенные на использование страниц размером 16 КБ (устройства с 16 КБ). Если ваше приложение использует библиотеки NDK , напрямую или косвенно через SDK, вам потребуется пересобрать приложение для его работы на устройствах с 16 КБ.
Поскольку производители устройств продолжают выпускать устройства с большим объёмом физической памяти (ОЗУ), многие из них будут использовать размер страницы 16 КБ (а в перспективе и больше) для оптимизации производительности. Добавление поддержки устройств с размером страницы 16 КБ позволит вашему приложению работать на этих устройствах и позволит использовать преимущества, связанные с повышением производительности. Без перекомпиляции приложения не будут работать на устройствах с 16 КБ в будущих версиях Android.
Чтобы помочь вам добавить поддержку для вашего приложения, мы предоставили рекомендации о том, как проверить, затронуто ли ваше приложение , как перестроить ваше приложение (если это применимо) и как протестировать ваше приложение в среде 16 КБ с помощью эмуляторов (включая образы системы Android 15 для эмулятора Android).
Преимущества и повышение производительности
Устройства, настроенные с размером страницы 16 КБ, в среднем используют немного больше памяти, но также получают различные улучшения производительности как для системы, так и для приложений:
- Сокращение времени запуска приложений, когда система испытывает нехватку памяти: в среднем на 3,16 % меньше, с более значительными улучшениями (до 30 %) для некоторых протестированных нами приложений.
- Снижение энергопотребления при запуске приложения: в среднем снижение на 4,56 %.
- Более быстрый запуск камеры: в среднем на 4,48 % более быстрый горячий запуск и в среднем на 6,60 % более быстрый холодный запуск.
- Улучшено время загрузки системы: в среднем улучшено на 8% (приблизительно 950 миллисекунд).
Эти улучшения основаны на нашем первоначальном тестировании, и результаты на реальных устройствах, вероятно, будут отличаться. По мере продолжения тестирования мы предоставим дополнительный анализ потенциальных преимуществ для приложений.
Проверьте, не затронуто ли ваше приложение
Если ваше приложение использует нативный код , вам следует пересобрать его с поддержкой устройств с памятью 16 КБ . Если вы не уверены, использует ли ваше приложение нативный код, вы можете использовать APK Analyzer для его определения, а затем проверить выравнивание сегментов ELF для любых обнаруженных общих библиотек . Android Studio также предоставляет функции, помогающие автоматически обнаруживать проблемы выравнивания .
Если ваше приложение использует только код, написанный на языке программирования Java или Kotlin, включая все библиотеки и SDK, то оно уже поддерживает устройства с 16 КБ. Тем не менее, мы рекомендуем протестировать приложение в среде с 16 КБ, чтобы убедиться в отсутствии непредвиденных регрессий в его поведении.
Для поддержки приватного пространства некоторым приложениям необходимы изменения.
Личное пространство — это новая функция Android 15, которая позволяет пользователям создавать на своем устройстве отдельное пространство, где они могут хранить конфиденциальные приложения вдали от посторонних глаз под дополнительным уровнем аутентификации. Поскольку приложения в личном пространстве имеют ограниченную видимость, некоторым типам приложений необходимо предпринять дополнительные шаги, чтобы иметь возможность видеть приложения в личном пространстве пользователя и взаимодействовать с ними.
Все приложения
Поскольку приложения в личном пространстве хранятся в отдельном профиле пользователя, аналогично рабочим профилям , приложения не должны предполагать, что любые установленные копии их приложений, которых нет в основном профиле, находятся в рабочем профиле. Если в вашем приложении есть логика, связанная с приложениями рабочего профиля, которые делают это предположение, вам необходимо настроить эту логику.
Медицинские приложения
Когда пользователь блокирует личное пространство, все приложения в нем останавливаются, и эти приложения не могут выполнять приоритетные или фоновые действия, включая показ уведомлений. Такое поведение может критически повлиять на использование и функционирование медицинских приложений, установленных в личном пространстве.
При настройке частного пространства пользователи предупреждаются о том, что частное пространство не подходит для приложений, которым необходимо выполнять критически важные действия в приоритетном или фоновом режиме, например показывать уведомления от медицинских приложений. Однако приложения не могут определить, используются ли они в личном пространстве, поэтому они не могут показать пользователю предупреждение в этом случае.
По этим причинам, если вы разрабатываете медицинское приложение, проанализируйте, как эта функция может повлиять на ваше приложение, и примите соответствующие меры (например, проинформируйте пользователей о том, что не следует устанавливать ваше приложение в личном пространстве), чтобы избежать нарушения критически важных функций приложения.
Приложения для запуска
Если вы разрабатываете приложение запуска, вам необходимо сделать следующее, прежде чем приложения в личном пространстве станут видимыми:
- Ваше приложение должно быть назначено в качестве приложения запуска по умолчанию для устройства, то есть иметь роль
ROLE_HOME. - Ваше приложение должно объявить обычное разрешение
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESв файле манифеста вашего приложения .
Приложения запуска, объявляющие разрешение ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES , должны обрабатывать следующие случаи использования частного пространства:
- Ваше приложение должно иметь отдельный контейнер запуска для приложений, установленных в личном пространстве. Используйте метод
getLauncherUserInfo(), чтобы определить, какой тип профиля пользователя обрабатывается. - Пользователь должен иметь возможность скрывать и показывать контейнер частного пространства.
- Пользователь должен иметь возможность блокировать и разблокировать контейнер личного пространства. Используйте метод
requestQuietModeEnabled()чтобы заблокировать (передавtrue) или разблокировать (передавfalse) личное пространство. Когда приложение заблокировано, никакие приложения в контейнере частного пространства не должны быть видимыми или обнаруживаемыми с помощью таких механизмов, как поиск. Ваше приложение должно зарегистрировать получателя для широковещательных рассылок
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEиACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLEи обновить пользовательский интерфейс в вашем приложении при изменении заблокированного или разблокированного состояния контейнера частного пространства. Обе эти трансляции включаютEXTRA_USER, который ваше приложение может использовать для обращения к пользователю частного профиля.Вы также можете использовать метод
isQuietModeEnabled()чтобы проверить, заблокирован ли профиль частного пространства или нет.
Приложения из магазина приложений
Личное пространство включает кнопку «Установить приложения», которая запускает неявное намерение установить приложения в личное пространство пользователя. Чтобы ваше приложение могло получить это неявное намерение, объявите <intent-filter> в файле манифеста вашего приложения с <category> CATEGORY_APP_MARKET .
Удалён шрифт эмодзи на основе PNG.
Устаревший файл шрифта Emoji на основе PNG ( NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf ) был удален, остался только векторный файл. Начиная с Android 13 (уровень API 33), файл шрифта эмодзи, используемый системным средством рендеринга эмодзи , изменился с файла на основе PNG на векторный файл . Система сохранила файл устаревшего шрифта в Android 13 и 14 по соображениям совместимости, чтобы приложения с собственными средствами визуализации шрифтов могли продолжать использовать файл устаревшего шрифта до тех пор, пока они не смогут обновиться.
Чтобы проверить, не затронуто ли ваше приложение, найдите в коде вашего приложения ссылки на файл NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf .
Вы можете адаптировать свое приложение несколькими способами:
- Используйте API платформы для рендеринга текста. Вы можете визуализировать текст на
Canvasс растровым изображением и при необходимости использовать его для получения необработанного изображения. - Добавьте поддержку шрифтов COLRv1 в свое приложение. Библиотека с открытым исходным кодом FreeType поддерживает COLRv1 версии 2.13.0 и выше.
- В крайнем случае, вы можете связать устаревший файл шрифта эмодзи (
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) с вашим APK, хотя в этом случае в вашем приложении будут отсутствовать последние обновления эмодзи. Дополнительную информацию можно найти на странице проекта Noto Emoji на GitHub .
Повышена минимальная целевая версия SDK с 23 до 24.
Android 15 основывается на изменениях, внесенных в Android 14, и еще больше расширяет эту безопасность. В Android 15 приложения с targetSdkVersion ниже 24 установить невозможно. Требование, чтобы приложения соответствовали современным уровням API, помогает обеспечить лучшую безопасность и конфиденциальность.
Вредоносное ПО часто нацелено на более низкие уровни API, чтобы обойти защиту безопасности и конфиденциальности, представленную в более поздних версиях Android. Например, некоторые вредоносные приложения используют targetSdkVersion , равный 22, чтобы избежать применения модели разрешений во время выполнения, представленной в 2015 году в Android 6.0 Marshmallow (уровень API 23). Из-за этого изменения в Android 15 вредоносным программам становится сложнее избежать улучшений безопасности и конфиденциальности. Попытка установить приложение, ориентированное на более низкий уровень API, приводит к сбою установки, и в Logcat появляется сообщение, подобное следующему:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
На устройствах, обновляющихся до Android 15, все приложения с targetSdkVersion ниже 24 остаются установленными.
Если вам нужно протестировать приложение, ориентированное на более старый уровень API, используйте следующую команду ADB:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
Безопасность и конфиденциальность
В Android 15 представлены надежные меры по борьбе с мошенничеством с использованием одноразовых паролей (OTP) и защите конфиденциального контента пользователя, уделяя особое внимание усилению службы прослушивания уведомлений и защите совместного использования экрана. Ключевые улучшения включают в себя удаление одноразовых паролей из уведомлений, доступных ненадежным приложениям, скрытие уведомлений во время совместного использования экрана и защиту действий приложений при публикации одноразовых паролей. Эти изменения направлены на защиту конфиденциального контента пользователя от несанкционированных действий.
Разработчикам необходимо учитывать следующее, чтобы обеспечить совместимость своих приложений с изменениями в Android 15:
Редактирование OTP
Android не позволит ненадежным приложениям, реализующим NotificationListenerService , читать неотредактированный контент из уведомлений, в которых был обнаружен OTP. Доверенные приложения, такие как ассоциации диспетчера сопутствующих устройств, освобождаются от этих ограничений.
Защита совместного использования экрана
- Содержимое уведомлений скрывается во время сеансов совместного использования экрана, чтобы сохранить конфиденциальность пользователя. Если приложение реализует
setPublicVersion(), Android показывает общедоступную версию уведомления, которая служит заменой уведомления в небезопасных контекстах. В противном случае содержимое уведомления будет отредактировано без какого-либо дополнительного контекста. - Конфиденциальный контент, например ввод пароля, скрыт от удаленных зрителей, чтобы предотвратить раскрытие конфиденциальной информации пользователя.
- Действия приложений, которые публикуют уведомления во время совместного использования экрана, где был обнаружен OTP, будут скрыты. Содержимое приложения скрыто от удаленного просмотра при запуске.
- Помимо автоматической идентификации конфиденциальных полей в Android, разработчики могут вручную помечать части своего приложения как конфиденциальные с помощью
setContentSensitivity, который скрыт от удаленных зрителей во время совместного использования экрана. - Разработчики могут включить параметр « Отключить защиту общего доступа к экрану» в разделе «Параметры разработчика» , чтобы освободиться от защиты общего доступа к экрану в целях демонстрации или тестирования. Системный рекордер экрана по умолчанию освобожден от этих изменений, поскольку записи остаются на устройстве.
В Android 15 представлены надежные меры по борьбе с мошенничеством с использованием одноразовых паролей (OTP) и защите конфиденциального контента пользователя, уделяя особое внимание усилению службы прослушивания уведомлений и защите совместного использования экрана. Ключевые улучшения включают в себя удаление одноразовых паролей из уведомлений, доступных ненадежным приложениям, скрытие уведомлений во время совместного использования экрана и защиту действий приложений при публикации одноразовых паролей. Эти изменения направлены на защиту конфиденциального контента пользователя от несанкционированных действий.
Разработчикам необходимо учитывать следующее, чтобы их приложения были совместимы с изменениями в Android 15:
Редактирование OTP
Android не позволит ненадежным приложениям, реализующим NotificationListenerService , читать неотредактированный контент из уведомлений, в которых был обнаружен OTP. Доверенные приложения, такие как ассоциации диспетчера сопутствующих устройств, освобождаются от этих ограничений.
Защита совместного использования экрана
- Содержимое уведомлений скрывается во время сеансов совместного использования экрана, чтобы сохранить конфиденциальность пользователя. Если приложение реализует
setPublicVersion(), Android показывает общедоступную версию уведомления, которая служит заменой уведомления в небезопасных контекстах. В противном случае содержимое уведомления будет отредактировано без какого-либо дополнительного контекста. - Конфиденциальный контент, например ввод пароля, скрыт от удаленных зрителей, чтобы предотвратить раскрытие конфиденциальной информации пользователя.
- Действия приложений, которые публикуют уведомления во время совместного использования экрана, где был обнаружен OTP, будут скрыты. Содержимое приложения скрыто от удаленного просмотра при запуске.
- Помимо автоматической идентификации конфиденциальных полей в Android, разработчики могут вручную помечать части своего приложения как конфиденциальные с помощью
setContentSensitivity, который скрыт от удаленных зрителей во время совместного использования экрана. - Разработчики могут включить параметр « Отключить защиту общего доступа к экрану» в разделе «Параметры разработчика» , чтобы освободиться от защиты общего доступа к экрану в целях демонстрации или тестирования. Системный рекордер экрана по умолчанию освобожден от этих изменений, поскольку записи остаются на устройстве.
Камера и медиа
В Android 15 внесены следующие изменения в работу камеры и мультимедийных приложений.
При достижении пределов ресурсов воспроизведение аудио напрямую или с выгрузкой ресурсов становится недействительным при воспроизведении аудиодорожек, ранее открытых в режиме прямого или выгруженного воспроизведения.
До Android 15, если приложение запрашивало прямое воспроизведение звука или разгрузку звука, пока другое приложение воспроизводило звук и были достигнуты ограничения ресурсов, приложение не могло открыть новый AudioTrack .
Начиная с Android 15, когда приложение запрашивает прямое воспроизведение или воспроизведение с разгрузкой и достигаются ограничения ресурсов, система аннулирует все открытые в данный момент объекты AudioTrack , которые препятствуют выполнению запроса на новую дорожку.
(Прямая аудиодорожка и аудиодорожки с выгрузкой обычно открываются для воспроизведения сжатых аудиоформатов. Общие случаи использования прямого воспроизведения аудио включают потоковое воспроизведение закодированного звука через HDMI на телевизор. Дорожки с разгрузкой обычно используются для воспроизведения сжатого аудио на мобильном устройстве с аппаратным DSP. ускорение.)
Пользовательский опыт и пользовательский интерфейс системы
В Android 15 внесены некоторые изменения, призванные обеспечить более согласованный и интуитивно понятный пользовательский интерфейс.
Функция предиктивной анимации возврата включена для приложений, которые дали на это согласие.
Начиная с Android 15, опция разработчика для прогнозируемой анимации спины была удалена. Системные анимации, такие как возврат домой, перекрестная задача и перекрестная активность, теперь отображаются для приложений, которые включили интеллектуальный жест возврата либо полностью, либо на уровне активности. Если ваше приложение затронуто, выполните следующие действия:
- Убедитесь, что ваше приложение правильно перенесено для использования интеллектуального жеста назад.
- Убедитесь, что переходы фрагментов работают с прогнозирующей обратной навигацией.
- Откажитесь от анимации и переходов фреймворка и вместо этого используйте переходы Animator и androidx.
- Мигрируйте из бэк-стеков, о которых
FragmentManagerне знает. Вместо этого используйте обратные стеки, управляемыеFragmentManagerили компонентом навигации.
Виджеты отключаются, когда пользователь принудительно останавливает приложение.
Если пользователь принудительно останавливает приложение на устройстве под управлением Android 15, система временно отключает все виджеты приложения. Виджеты выделены серым цветом, и пользователь не может с ними взаимодействовать. Это связано с тем, что, начиная с Android 15, система отменяет все ожидающие намерения приложения, когда приложение принудительно остановлено.
Система повторно включает эти виджеты при следующем запуске приложения пользователем.
Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Изменения состояния остановки пакета .
Индикатор состояния медиапроектора оповещает пользователей о совместном использовании экрана, трансляции и записи.
Эксплойты проецирования экрана раскрывают личные данные пользователей, такие как финансовая информация, поскольку пользователи не осознают, что экран их устройства используется совместно.
Для приложений, работающих на устройствах с Android 15 QPR1 или более поздней версии, большая и заметная строка состояния предупреждает пользователей о любом текущем проецировании экрана. Пользователи могут коснуться чипа, чтобы запретить совместное использование, трансляцию или запись своего экрана. Кроме того, проецирование экрана автоматически прекращается, когда экран устройства заблокирован.
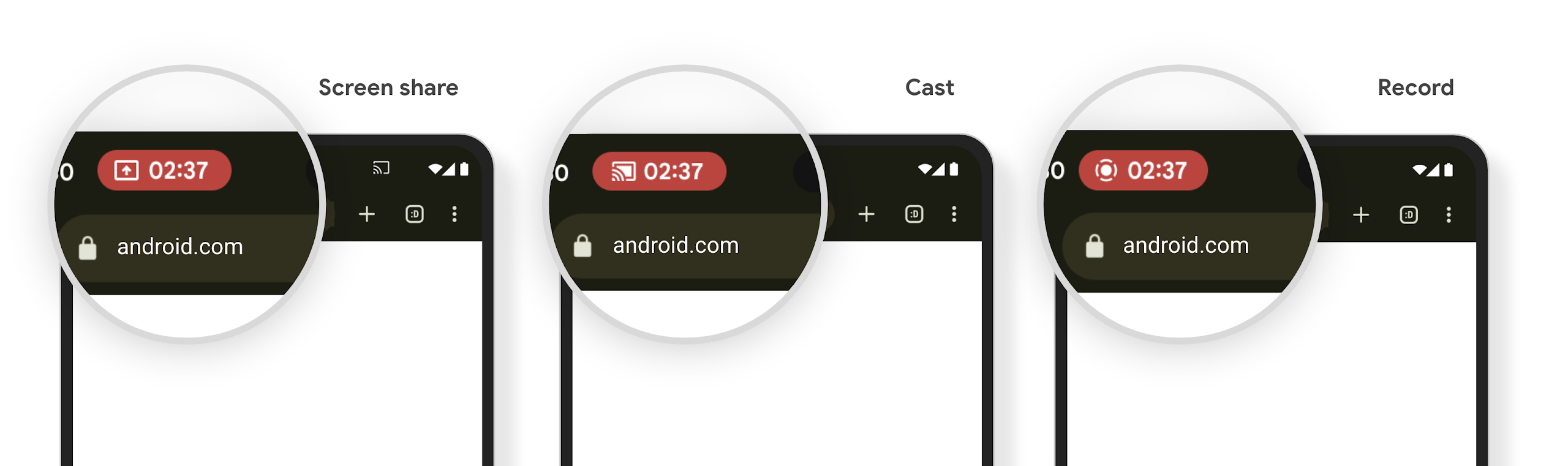
Проверьте, не затронуто ли ваше приложение
По умолчанию ваше приложение включает чип строки состояния и автоматически приостанавливает проецирование экрана при активации экрана блокировки.
Чтобы узнать больше о том, как протестировать приложение для этих вариантов использования, см. раздел Чип строки состояния и автоматическая остановка .
Ограничения доступа к сети в фоновом режиме
В Android 15 приложения, которые запускают сетевой запрос вне допустимого жизненного цикла процесса , получают исключение. Обычно это UnknownHostException или другое исключение IOException , связанное с сокетом. Сетевые запросы, которые происходят вне допустимого жизненного цикла, обычно происходят из-за того, что приложения по незнанию продолжают выполнять сетевой запрос даже после того, как приложение больше не активно.
Чтобы смягчить это исключение, убедитесь, что ваши сетевые запросы учитывают жизненный цикл и отменяются после выхода из действительного жизненного цикла процесса, используя компоненты, учитывающие жизненный цикл . Если важно, чтобы сетевой запрос выполнялся даже тогда, когда пользователь покидает приложение, рассмотрите возможность планирования сетевого запроса с помощью WorkManager или продолжения видимой для пользователя задачи с помощью Foreground Service .
Амортизация
С каждым релизом некоторые API Android могут устаревать или нуждаться в рефакторинге для улучшения пользовательского опыта разработчиков или поддержки новых возможностей платформы. В таких случаях мы официально объявляем устаревшие API устаревшими и рекомендуем разработчикам использовать альтернативные API.
«Устаревание» означает, что мы прекратили официальную поддержку этих API, но они по-прежнему будут доступны разработчикам. Чтобы узнать больше о важных устаревших функциях в этом выпуске Android, см. страницу «Устаревание» .

