פלטפורמת Android 15 כוללת שינויים בהתנהגות שעשויים להשפיע על האפליקציה שלכם. שינויי ההתנהגות הבאים חלים על כל האפליקציות כשהן פועלות ב-Android 15, בלי קשר ל-targetSdkVersion. מומלץ לבדוק את האפליקציה ולשנות אותה לפי הצורך כדי לתמוך בהן בצורה תקינה, במקרים הרלוונטיים.
חשוב גם לעיין ברשימת השינויים בהתנהגות שמשפיעים רק על אפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 15.
פונקציונליות עיקרית
Android 15 משנה או מרחיב יכולות ליבה שונות של מערכת Android.
שינויים במצב העצירה של החבילה
המטרה של מצב החבילה FLAG_STOPPED (המשתמש יכול להפעיל אותו בגרסאות build של AOSP בלחיצה ארוכה על סמל האפליקציה ובחירה באפשרות 'השבתה בכוח') הייתה תמיד להשאיר אפליקציות במצב הזה עד שהמשתמש יסיר אותן במפורש מהמצב הזה על ידי הפעלה ישירה של האפליקציה או אינטראקציה עקיפה עם האפליקציה (דרך חלונית השיתוף או ווידג'ט, בחירה באפליקציה כטפט חי וכו'). ב-Android 15 עדכנו את התנהגות המערכת כך שתתאים להתנהגות המיועדת הזו. אפליקציות צריכות להסיר מהמצב 'מושבת' רק כתוצאה מפעולת משתמש ישירה או עקיפה.
כדי לתמוך בהתנהגות הרצויה, בנוסף להגבלות הקיימות, המערכת מבטלת גם את כל כוונות הפנייה בהמתנה כשהאפליקציה נכנסת למצב מושהה במכשיר עם Android מגרסה 15 ואילך. כשהפעולות של המשתמש מסירות את האפליקציה מהמצב המושהה, ההודעה ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED מועברת לאפליקציה ומאפשרת לרשום מחדש את כל הכוונות בהמתנה.
אפשר להפעיל את השיטה החדשה ApplicationStartInfo.wasForceStopped() כדי לוודא שהאפליקציה הועברה למצב מושהה.
תמיכה בגודל דף של 16KB
בעבר, מערכת Android תמכה רק בדפים עם זיכרון בגודל 4KB, מה שאפשר למערכת לייעל את הביצועים של הזיכרון הכולל במכשירים עם נפח זיכרון ממוצע. החל מ-Android 15, AOSP תומך במכשירים שמגדירים בהם גודל דף של 16KB (מכשירים עם 16KB). אם האפליקציה שלך משתמשת בספריות NDK, באופן ישיר או בעקיפין דרך SDK, תצטרכו לבנות מחדש את האפליקציה כדי שהיא תפעל במכשירים האלה עם 16 KB.
יצרני המכשירים ממשיכים לפתח מכשירים עם נפחים גדולים יותר של זיכרון פיזי (RAM). במכשירים רבים כאלה יוטמעו דפים בגודל 16KB (ובסופו של דבר בגודל גדול יותר) כדי לשפר את הביצועים של המכשיר. הוספת תמיכה במכשירים עם גודל דף של 16KB מאפשרת לאפליקציה לפעול במכשירים האלה, וליהנות משיפורי הביצועים שקשורים לכך. בלי קומפילציה מחדש, האפליקציות לא יפעלו במכשירים עם 16 KB בגרסאות עתידיות של Android.
כדי לעזור לכם להוסיף תמיכה לאפליקציה, סיפקנו הנחיות בנושא בדיקה אם יש השפעה על האפליקציה, בנייה מחדש של האפליקציה (אם רלוונטי) ובדיקת האפליקציה בסביבה של 16KB באמצעות אמולטורים (כולל תמונות מערכת של Android 15 לאמולטור של Android).
יתרונות ושיפור בביצועים
במכשירים שמוגדרים בהם דפים בגודל 16KB, נעשה שימוש במעט יותר זיכרון בממוצע, אבל יש גם שיפורים שונים בביצועים של המערכת ושל האפליקציות:
- זמני השקה קצרים יותר של אפליקציות בזמן שהמערכת נמצאת בלחץ על הזיכרון: נמוך ב-3.16% בממוצע, עם שיפורים משמעותיים יותר (עד 30%) בחלק מהאפליקציות שבדקנו
- צריכת חשמל מופחתת במהלך השקת האפליקציה: הפחתה של 4.56% בממוצע
- הפעלה מהירה יותר של המצלמה: הפעלה מתוך הזיכרון (hot start) מהירה יותר ב-4.48% בממוצע, והפעלה מחדש (cold start) מהירה יותר ב-6.60% בממוצע
- זמן הפעלה משופר של המערכת: שיפור של 8% (כ-950 אלפיות השנייה) בממוצע
השיפורים האלה מבוססים על הבדיקה הראשונית שלנו, וסביר להניח שהתוצאות במכשירים בפועל יהיו שונות. נמשיך לספק ניתוח נוסף של היתרונות הפוטנציאליים של האפליקציות.
איך בודקים אם האפליקציה שלכם מושפעת
אם האפליקציה שלך משתמשת בקוד Native, עליך לבנות מחדש את האפליקציה עם תמיכה במכשירים עם דפי זיכרון בגודל 16 KB. אם אתם לא בטוחים אם האפליקציה שלכם משתמשת בקוד Native, אתם יכולים להשתמש בכלי APK Analyzer כדי לזהות אם יש קוד Native, ואז לבדוק את ההתאמה של פלחי ELF לכל הספריות המשותפות שמצאתם. ב-Android Studio יש גם תכונות שעוזרות לכם לזהות באופן אוטומטי בעיות שקשורות ליישור.
אם האפליקציה שלך משתמשת רק בקוד שנכתב בשפת התכנות Java או ב-Kotlin, כולל כל הספריות או ערכות ה-SDK, אז האפליקציה כבר תומכת במכשירים עם נפח אחסון של 16 KB. עם זאת, מומלץ לבצע בדיקה של האפליקציה בסביבה של 16 KB כדי לוודא שאין נסיגות לא צפויות בהתנהגות האפליקציה.
שינויים שנדרשים כדי שאפליקציות מסוימות יתמכו במרחב הפרטי
מרחב פרטי הוא תכונה חדשה ב-Android 15 שמאפשרת למשתמשים ליצור מרחב נפרד במכשיר שבו הם יכולים להסתיר אפליקציות עם מידע אישי רגיש, באמצעות שכבת אימות נוספת. מאחר שלאפליקציות במרחב הפרטי יש חשיפה מוגבלת, יש לבצע פעולות נוספות כדי שסוגי אפליקציות מסוימים יוכלו לראות את האפליקציות במרחב הפרטי של המשתמש ולנהל איתן אינטראקציה.
כל האפליקציות
מאחר שהאפליקציות במרחב הפרטי נשמרות בפרופיל משתמש נפרד, בדומה לפרופילים לעבודה, האפליקציות לא צריכות להניח שעותקים מותקנים של האפליקציה שלהן שלא נמצאים בפרופיל הראשי נמצאים בפרופיל העבודה. אם באפליקציה שלכם יש לוגיקה שקשורה לאפליקציות בפרופיל העבודה שמבוססת על ההנחה הזו, תצטרכו לשנות את הלוגיקה הזו.
אפליקציות רפואיות
כשמשתמש נועל את המרחב הפרטי, כל האפליקציות במרחב הפרטי מופסקות, והן לא יכולות לבצע פעילויות בחזית או ברקע, כולל הצגת התראות. ההתנהגות הזו עשויה להשפיע באופן משמעותי על השימוש ועל הפעולה של אפליקציות רפואיות שמותקנות במרחב הפרטי.
בתהליך ההגדרה של המרחב הפרטי, המשתמשים מקבלים אזהרה שהמרחב הפרטי לא מתאים לאפליקציות שצריכות לבצע פעילויות קריטיות בחזית או ברקע, כמו הצגת התראות מאפליקציות רפואיות. עם זאת, אפליקציות לא יכולות לקבוע אם נעשה בהן שימוש במרחב הפרטי, ולכן הן לא יכולות להציג אזהרה למשתמש במקרה כזה.
לכן, אם אתם מפתחים אפליקציה רפואית, כדאי לבדוק איך התכונה הזו עשויה להשפיע על האפליקציה שלכם ולנקוט את הפעולות המתאימות – למשל, להודיע למשתמשים לא להתקין את האפליקציה במרחב הפרטי – כדי למנוע שיבושים ביכולות החיוניות של האפליקציה.
אפליקציות מרכז האפליקציות
אם אתם מפתחים אפליקציית מרכז אפליקציות, עליכם לבצע את הפעולות הבאות כדי שהאפליקציות במרחב הפרטי יהיו גלויות:
- האפליקציה שלכם צריכה להיות מוקצית כאפליקציית ברירת המחדל של מרכז האפליקציות במכשיר, כלומר, היא צריכה להיות מוקצית לתפקיד
ROLE_HOME. - באפליקציה צריך להצהיר על ההרשאה הרגילה
ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILESבקובץ המניפסט של האפליקציה.
אפליקציות מרכז האפליקציות שמצהירות על ההרשאה ACCESS_HIDDEN_PROFILES חייבות לטפל בתרחישי השימוש הבאים במרחב הפרטי:
- לאפליקציה צריך להיות מאגר נפרד במרכז האפליקציות לאפליקציות שמותקנות במרחב הפרטי. משתמשים ב-method
getLauncherUserInfo()כדי לקבוע איזה סוג של פרופיל משתמש מנוהל. - המשתמש צריך להיות מסוגל להסתיר ולהציג את הקונטיינר של המרחב הפרטי.
- המשתמש צריך להיות מסוגל לנעול ולפתוח את המרחב הפרטי. משתמשים ב-method
requestQuietModeEnabled()כדי לנעול (על ידי העברתtrue) או לבטל את הנעילה (על ידי העברתfalse) של המרחב הפרטי. כשהמרחב הפרטי נעול, אף אפליקציה במאגר שלו לא אמורה להיות גלויה או ניתנת לגילוי באמצעות מנגנונים כמו חיפוש. האפליקציה צריכה לרשום מקלט לשידורים של
ACTION_PROFILE_AVAILABLEושלACTION_PROFILE_UNAVAILABLE, ולעדכן את ממשק המשתמש באפליקציה כשהסטטוס של המרחב הפרטי (נעול או לא נעול) משתנה. שתי השידורים האלה כוללים את הערךEXTRA_USER, שבעזרתו האפליקציה יכולה להפנות למשתמש בפרופיל הפרטי.אפשר גם להשתמש ב-method
isQuietModeEnabled()כדי לבדוק אם פרופיל המרחב הפרטי נעול או לא.
אפליקציות מחנות האפליקציות
המרחב הפרטי כולל לחצן 'התקנת אפליקציות' שמפעיל כוונה משתמעת להתקין אפליקציות במרחב הפרטי של המשתמש. כדי שהאפליקציה תקבל את הכוונה המשתמעת הזו, צריך להצהיר על <intent-filter> בקובץ המניפסט של האפליקציה עם <category> של CATEGORY_APP_MARKET.
הוסר גופן אמוג'י מבוסס PNG
קובץ הגופן הקודם של אמוג'י (NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf) שמבוסס על קובץ PNG הוסר, ונותר רק הקובץ המבוסס על וקטור. החל מ-Android 13 (רמת API 33), קובץ הגופן של האמוג'י שמשמש את המערכת להצגת אמוג'י השתנה מקובץ מבוסס-PNG לקובץ מבוסס-וקטור. המערכת שמרה את קובץ הגופן הקודם ב-Android 13 וב-Android 14 מסיבות תאימות, כדי שאפליקציות עם מנועי גופן משלהם יוכלו להמשיך להשתמש בקובץ הגופן הקודם עד שהן יוכלו לשדרג.
כדי לבדוק אם האפליקציה שלכם מושפעת, מחפשים בקוד של האפליקציה הפניות לקובץ NotoColorEmojiLegacy.ttf.
יש כמה דרכים להתאים את האפליקציה:
- שימוש ב-API של פלטפורמות לעיבוד טקסט. אפשר להעביר טקסט ל-
Canvasשמבוסס על bitmap ולהשתמש בו כדי לקבל תמונה גולמית, אם צריך. - מוסיפים לאפליקציה תמיכה בגופנים מסוג COLRv1. ספריית FreeType בקוד פתוח תומכת ב-COLRv1 בגרסה 2.13.0 ואילך.
- כחלופה אחרונה, אפשר לצרף את קובץ הגופן הקודם של אמוג'י (
NotoColorEmoji.ttf) לקובץ ה-APK, אבל במקרה כזה באפליקציה לא יוצגו עדכוני האמוג'י האחרונים. למידע נוסף, אפשר לעיין בדף הפרויקט של Noto Emoji ב-GitHub.
הגדלנו את גרסת ה-SDK המינימלית לטירגוט מ-23 ל-24
Android 15 מבוסס על השינויים שבוצעו ב-Android 14 ומרחיב את האבטחה הזו. ב-Android 15, אפליקציות עם
לא ניתן להתקין את התוסף targetSdkVersion שמכיל פחות מ-24.
דרישה שהאפליקציות צריכות לעמוד ברמות API מודרניות עוזרת לשמור על אבטחה טובה יותר
פרטיות.
תוכנות זדוניות מכוונות לעיתים קרובות לרמות נמוכות יותר של API כדי לעקוף את האבטחה והפרטיות
באמצעי ההגנה שהוכנסו לשימוש בגרסאות מתקדמות יותר של Android. לדוגמה, אפליקציות זדוניות מסוימות משתמשות ב-targetSdkVersion של 22 כדי להימנע מהתחייבות למודל ההרשאות בסביבת זמן הריצה שהוצג ב-2015 ב-Android 6.0 Marshmallow (רמת API 23). השינוי הזה ב-Android 15 מקשה על תוכנות זדוניות להימנע מאבטחה
ושיפורים בפרטיות. ניסיון להתקין אפליקציה שמטרגטת ממשק API נמוך יותר
יוביל לכשל בהתקנה, ותופיע הודעה כמו ההודעה הבאה
מופיע ב-Logcat:
INSTALL_FAILED_DEPRECATED_SDK_VERSION: App package must target at least SDK version 24, but found 7
במכשירים ששודרגו ל-Android 15, אפליקציות עם targetSdkVersion נמוך מ-24 יישארו מותקנות.
אם צריך לבדוק אפליקציה שמטרגטת רמת API ישנה יותר, אפשר להשתמש ב-ADB הבא הפקודה:
adb install --bypass-low-target-sdk-block FILENAME.apk
אבטחה ופרטיות
בגרסה 15 של Android נוספו אמצעים חזקים למאבק בתרמית של סיסמה חד-פעמית (OTP) ולהגנה על התוכן הרגיש של המשתמשים, תוך התמקדות בשיפור ההגנות על שיתוף המסך ועל שירות ההאזנה להתראות. שיפורים מרכזיים כוללים הסרת קודי אימות חד-פעמיים מהתראות שגלויות לאפליקציות לא מהימנות, הסתרת התראות במהלך שיתוף המסך ואבטחת הפעילויות באפליקציות כשפורסמים קודי אימות חד-פעמיים. מטרת השינויים האלה היא להגן על התוכן הרגיש של המשתמשים מפני גורמים לא מורשים.
כדי לוודא שהאפליקציות שלהם תואמות לשינויים ב-Android 15, המפתחים צריכים לשים לב לנקודות הבאות:
השמטת סיסמה חד-פעמית
מערכת Android תמנע מאפליקציות לא מהימנות שמטמיעות את NotificationListenerService לקרוא תוכן לא ערוך מהתראות שבהן זוהה קוד אימות חד-פעמי. אפליקציות מהימנות, כמו שותפים לניהול מכשירי נלווים, פטורות מההגבלות האלה.
הגנה על שיתוף המסך
- תוכן ההתראות מוסתר במהלך סשנים של שיתוף מסך כדי לשמור על הפרטיות של המשתמש. אם האפליקציה מטמיעה את
setPublicVersion(), מערכת Android מציגה את הגרסה הציבורית של ההתראה, שמשמשת כהתראה חלופית בהקשרים לא מאובטחים. אחרת, תוכן ההתראה יימחק ללא הקשר נוסף. - תוכן רגיש, כמו הזנת סיסמה, מוסתר מהצופים מרחוק כדי למנוע חשיפת המידע הרגיש של המשתמש.
- פעילויות מאפליקציות ששולחות התראות במהלך שיתוף המסך, שבהן זוהתה OTP, יוסתרו. תוכן האפליקציה מוסתר מהצופה מרחוק כשהיא מופעלת.
- בנוסף לזיהוי האוטומטי של שדות רגישים ב-Android, מפתחים יכולים לסמן באופן ידני חלקים באפליקציה שלהם כתוכן רגיש באמצעות
setContentSensitivity. התוכן הזה יהיה מוסתר לצופים מרחוק במהלך שיתוף המסך. - מפתחים יכולים להחליף את המצב של האפשרות השבתת ההגנות של שיתוף המסך בקטע אפשרויות למפתחים כדי לקבל פטור מההגנות על שיתוף המסך למטרות הדגמה או בדיקה. מכשיר הקלטת המסך שמוגדר כברירת מחדל לא מושפע מהשינויים האלה, כי ההקלטות נשארות במכשיר.
מצלמה ומדיה
ב-Android 15 בוצעו השינויים הבאים בהתנהגות של המצלמה והמדיה בכל האפליקציות.
הפעלה ישירה והעברה של הפעלת אודיו מבטלות את התוקף של טראקים קודמים של אודיו בהפעלה ישירה או בהעברה, כשמגיעים למגבלות המשאבים
לפני Android 15, אם אפליקציה ביקשה הפעלת אודיו ישירה או הפעלת אודיו בהעברה (offload) בזמן שאפליקציה אחרת הפעילה אודיו והגעתם למגבלות המשאבים, האפליקציה לא הצליחה לפתוח AudioTrack חדש.
החל מגרסה 15 של Android, כשאפליקציה מבקשת הפעלה ישירה או העברה לענן (offload) ומגיעים למגבלות המשאבים, המערכת מבטלת את התוקף של כל אובייקט AudioTrack פתוח שמונע את מילוי הבקשה להפעלת הטראק החדש.
(בדרך כלל, טראקים של אודיו ישיר והעברת אודיו נפתחים להפעלה של פורמטים של אודיו דחוס. תרחישים נפוצים לדוגמה להפעלת אודיו ישיר כוללים סטרימינג של אודיו מקודד דרך HDMI לטלוויזיה. בדרך כלל משתמשים בטראקים להעברה כדי להפעיל אודיו דחוס במכשיר נייד עם האצת DSP בחומרה).
חוויית המשתמש וממשק המשתמש של המערכת
Android 15 כוללת כמה שינויים שנועדו ליצור חוויית משתמש עקבית ואינטואיטיבית יותר.
אנימציות של חיזוי תנועת החזרה מופעלות באפליקציות שהביעו הסכמה
החל מגרסה 15 של Android, האפשרות למפתחים לאנימציות חיזוי של תנועת החזרה הוסרה. אנימציות מערכת כמו חזרה למסך הבית, מעבר בין משימות ופעילויות, מופיעות עכשיו באפליקציות שהסכימו להשתמש בתנועת החזרה החזוי, באופן מלא או ברמת הפעילות. אם האפליקציה שלכם מושפעת, עליכם לבצע את הפעולות הבאות:
- מוודאים שהאפליקציה הועברה בצורה תקינה כדי להשתמש בתנועת החזרה החזוי.
- מוודאים שהמעבר בין הקטעים פועל עם ניווט חזרה חזוי.
- עוברים משימוש באנימציות ובמעברים של מסגרות, ומשתמשים במקום זאת ב-Animator ובמעברים של androidx.
- להעביר את הקוד מסטאקים קודמים ש-
FragmentManagerלא מכיר. במקום זאת, כדאי להשתמש בסטאקים קודמים שמנוהלים על ידיFragmentManagerאו על ידי רכיב הניווט.
ווידג'טים מושבתים כשמשתמש סוגר אפליקציה בכוח
אם משתמש מפסיק אפליקציה בכוח במכשיר עם Android 15, המערכת משביתה באופן זמני את כל הווידג'טים של האפליקציה. הווידג'טים מופיעים באפור והמשתמשים לא יכולים לבצע איתם פעולות. הסיבה לכך היא שמתחילת Android 15, המערכת מבטלת את כל הכוונות בהמתנה של האפליקציה כשהיא מופסקת בכוח.
המערכת מפעילה מחדש את הווידג'טים האלה בפעם הבאה שהמשתמש מפעיל את האפליקציה.
מידע נוסף זמין במאמר שינויים במצב 'החבילה הופסקה'.
התראות צ'יפ בשורת הסטטוס של הקרנת מדיה מודיעות למשתמשים על שיתוף מסך, הפעלת Cast והקלטה
נקודות חולשה של הקרנת מסך חושפות נתונים פרטיים של משתמשים, כמו מידע פיננסי, כי המשתמשים לא מבינים שהמסך של המכשיר שלהם משותף.
באפליקציות שפועלות במכשירים עם Android 15 QPR1 ואילך, צ'יפ גדול ובולט בסרגל המצב מתריע למשתמשים על הקרנת מסך מתמשכת. המשתמשים יכולים להקיש על הצ'יפ כדי להפסיק את השיתוף, ההעברה או הצילום של המסך שלהם. בנוסף, הקרנת המסך תיפסק באופן אוטומטי כשמסך המכשיר יינעל.
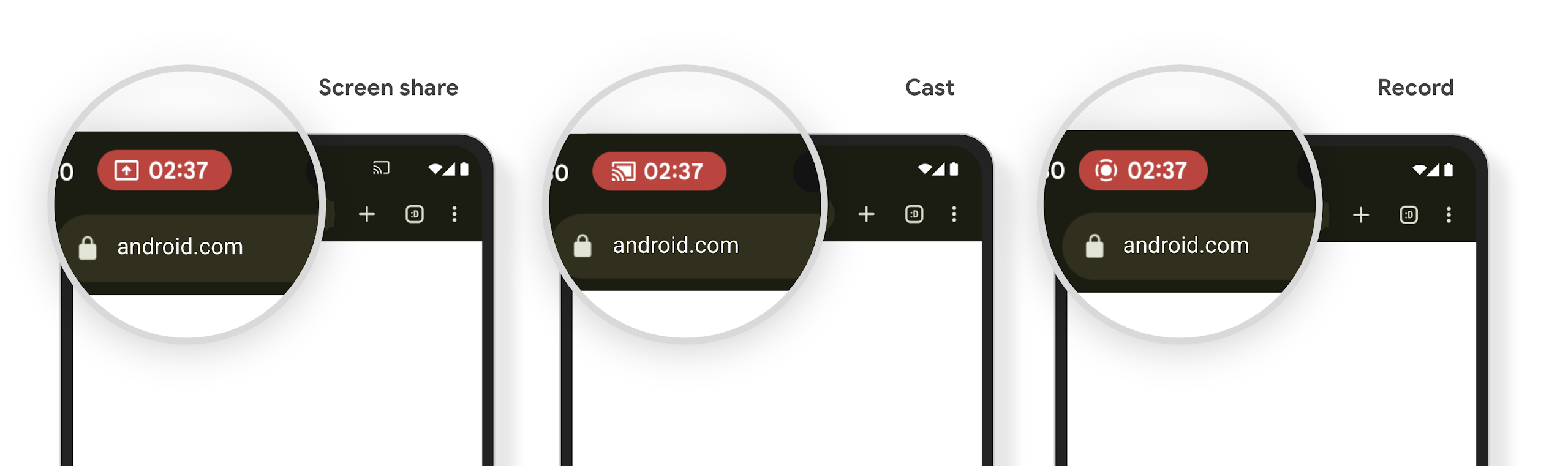
איך בודקים אם האפליקציה שלכם מושפעת
כברירת מחדל, האפליקציה כוללת את הצ'יפ של שורת הסטטוס ומפסיקה אוטומטית את הקרנת המסך כשמסך הנעילה מופעל.
מידע נוסף על בדיקת האפליקציה לגבי התרחישים לדוגמה האלה זמין במאמר צ'יפ בסרגל הסטטוס והפסקה אוטומטית.
הגבלות על גישה לרשת ברקע
ב-Android 15, אפליקציות שמתחילות בקשת רשת מחוץ למחזור החיים של התהליך מקבלות חריגה. בדרך כלל, UnknownHostException או IOException אחר שקשור ליציאה. בדרך כלל, בקשות לרשת שמתרחשות מחוץ למחזור חיים תקין נובעות מאפליקציות שממשיכות לשלוח בקשות לרשת בלי ידיעת המשתמשים, גם אחרי שהאפליקציה כבר לא פעילה.
כדי לצמצם את ההחרגה הזו, צריך לוודא שבקשות הרשת מותאמות למחזור החיים שלהן, ושהן מבוטלות כשהן יוצאות ממחזור חיים תקין של תהליך, באמצעות רכיבים שמותאמים למחזור חיים. אם חשוב לכם שהבקשה לרשת תתבצע גם כשהמשתמש יוצא מהאפליקציה, כדאי לתזמן את הבקשה לרשת באמצעות WorkManager או להמשיך במשימה שגלויה למשתמש באמצעות שירות שפועל בחזית.
הפסקת תמיכה
יכול להיות שבכל גרסה של Android, ממשקי API ספציפיים של Android יהפכו למיושנים או יצטרכו לעבור שינוי כדי לספק חוויית פיתוח טובה יותר או לתמוך ביכולות חדשות של הפלטפורמה. במקרים כאלה, אנחנו מוציאים משימוש באופן רשמי את ממשקי ה-API שיצאו משימוש ומפנים את המפתחים לממשקי API חלופיים שבהם הם יכולים להשתמש במקום זאת.
הוצאה משימוש פירושה שסיימנו את התמיכה הרשמית בממשקי ה-API, אבל הם ימשיכו להיות זמינים למפתחים. מידע נוסף על הוצאות משימוש חשובות בגרסה הזו של Android זמין בדף ההוצאות משימוש.
