和先前版本一樣,Android 15 也包含可能會影響應用程式的行為變更。以下行為變更僅適用於指定 Android 15 以上版本的應用程式。如果您的應用程式指定 Android 15 以上版本,建議您視情況修改應用程式,以支援這些行為。
此外,無論應用程式的 targetSdkVersion 為何,請務必查看對所有 Android 15 應用程式有影響的行為變更清單。
核心功能
Android 15 會修改或擴充 Android 系統的各種核心功能。
前景服務異動
我們將對 Android 15 的前景服務進行下列異動。
資料同步處理前景服務逾時行為
Android 15 為指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 以上版本為目標版本的應用程式,在 dataSync 中導入新的逾時行為。這項行為也適用於新的mediaProcessing前景服務類型。
系統允許應用程式的 dataSync 服務在 24 小時內執行總共 6 小時,之後系統會呼叫執行中的服務 Service.onTimeout(int, int) 方法 (在 Android 15 中推出)。此時,服務有幾秒的時間可以呼叫 Service.stopSelf()。呼叫 Service.onTimeout() 後,系統就不會再將服務視為前景服務。如果服務未呼叫 Service.stopSelf(),系統會擲回內部例外狀況。例外狀況會記錄在 Logcat 中,並顯示以下訊息:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type dataSync did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
如要避免這項行為變更帶來的問題,您可以執行下列一或多項操作:
- 讓您的服務實作新的
Service.onTimeout(int, int)方法。應用程式收到回呼時,請務必在幾秒內呼叫stopSelf()。(如果您沒有立即停止應用程式,系統會產生失敗)。 - 確認應用程式的
dataSync服務在任何 24 小時內的執行時間不超過 6 小時 (除非使用者與應用程式互動,並重設計時器)。 - 只有在使用者直接互動時才啟動
dataSync前景服務;由於您的應用程式在服務啟動後位於前景,因此應用程式進入背景後,您的服務剩下六小時。 - 請改用其他 API,而非
dataSync前景服務。
如果應用程式的 dataSync 前景服務在過去 24 小時內已執行 6 小時,您就無法啟動其他 dataSync 前景服務,除非使用者將應用程式移至前景 (這樣會重設計時器)。如果您嘗試啟動另一項 dataSync 前景服務,系統會擲回 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException,並顯示錯誤訊息「Time limit is Of for 前景服務類型 dataSync」
測試
如要測試應用程式的行為,您可以啟用資料同步處理逾時,即使應用程式並非以 Android 15 為目標版本 (只要應用程式是在 Android 15 裝置上執行),也能啟用。如要啟用逾時值,請執行下列 adb 指令:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
您也可以調整逾時期限,方便測試應用程式在達到限制時的行為。如要設定新的逾時期限,請執行下列 adb 指令:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager data_sync_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
新的媒體處理前景服務類型
Android 15 推出了新的前景服務類型 mediaProcessing。此服務類型適合用於轉碼媒體檔案等作業。舉例來說,媒體應用程式可能會下載音訊檔案,需要將其轉換成其他格式後再播放。您可以使用 mediaProcessing 前景服務,確保即使應用程式處於背景執行狀態,轉換也能繼續進行。
系統允許應用程式的 mediaProcessing 服務在 24 小時內執行總共 6 小時,之後系統會呼叫執行中的服務 Service.onTimeout(int, int) 方法 (在 Android 15 中推出)。此時,服務有幾秒的時間可以呼叫 Service.stopSelf()。如果服務未呼叫 Service.stopSelf(),系統會擲回內部例外狀況。例外狀況會記錄在 Logcat 中,並顯示以下訊息:
Fatal Exception: android.app.RemoteServiceException: "A foreground service of
type mediaProcessing did not stop within its timeout: [component name]"
為避免例外狀況,您可以採取下列其中一種做法:
- 請讓服務實作新的
Service.onTimeout(int, int)方法。應用程式收到回呼時,請務必在幾秒內呼叫stopSelf()。(如果您沒有立即停止應用程式,系統會產生失敗)。 - 請確認應用程式的
mediaProcessing服務在任何 24 小時內的總執行時間不超過 6 小時 (除非使用者與應用程式互動,重新設定計時器)。 - 只有在使用者直接互動時才啟動
mediaProcessing前景服務;由於您的應用程式在服務啟動後位於前景,因此應用程式進入背景後,您的服務剩下六小時。 - 請改用 WorkManager 等其他 API,而非
mediaProcessing前景服務。
如果應用程式的 mediaProcessing 前景服務在過去 24 小時內已執行 6 小時,您就無法啟動其他 mediaProcessing 前景服務,除非使用者將應用程式移至前景 (這樣會重設計時器)。如果您嘗試啟動其他 mediaProcessing 前景服務,系統會擲回 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException,並顯示「前景服務類型 mediaProcessing 的時間限制已用盡」等錯誤訊息。
如要進一步瞭解 mediaProcessing 服務類型,請參閱「Android 15 的前景服務類型變更:媒體處理」。
測試
如要測試應用程式的行為,您可以啟用媒體處理逾時,即使應用程式並未以 Android 15 為目標版本 (只要應用程式在 Android 15 裝置上執行),也能啟用。如要啟用逾時值,請執行下列 adb 指令:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_INTRODUCE_TIME_LIMITS your-package-name
您也可以調整逾時期限,方便測試應用程式在達到上限時的行為。如要設定新的逾時期限,請執行下列 adb 指令:
adb shell device_config put activity_manager media_processing_fgs_timeout_duration duration-in-milliseconds
BOOT_COMPLETED 廣播接收器啟動前景服務的限制
BOOT_COMPLETED 廣播接收器啟動有一些新限制
前景服務BOOT_COMPLETED 接收器無法啟動
下列類型的前景服務:
dataSynccameramediaPlaybackphoneCallmediaProjectionmicrophone(我們已對microphone設下這項限制,自 Android 14)
如果 BOOT_COMPLETED 接收器嘗試啟動任何這些類型的前景
服務就會擲回 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException。
測試
如要測試應用程式的行為,即使應用程式並非以 Android 15 為目標版本 (只要應用程式是在 Android 15 裝置上執行),您也可以啟用這些新限制。執行下列 adb 指令:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_BOOT_COMPLETED_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
如要在不重新啟動裝置的情況下傳送「BOOT_COMPLETED」廣播訊息,請按照下列步驟操作:
執行下列 adb 指令:
adb shell am broadcast -a android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED your-package-name
應用程式擁有 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 權限時,啟動前景服務的限制
先前,如果應用程式擁有 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 權限,即使目前處於背景執行狀態,也能啟動前景服務 (如「背景啟動限制的例外狀況」一文所述)。
如果應用程式指定 Android 15 為目標版本,這項豁免權現在比較縮小。應用程式現在需要具備 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 權限,且也設有可見的重疊視窗。也就是說,應用程式必須先啟動 TYPE_APPLICATION_OVERLAY 視窗,「而且」必須先顯示該視窗,才能啟動前景服務。
如果應用程式嘗試從背景啟動前景服務,但不符合這些新要求 (且沒有其他例外狀況),系統會擲回 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException。
如果您的應用程式聲明 SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW 權限,並從背景啟動前景服務,可能會受到這項變更的影響。如果應用程式收到 ForegroundServiceStartNotAllowedException,請檢查應用程式的運算順序,並確認應用程式在嘗試從背景啟動前景服務前,已擁有有效的疊加式視窗。您可以呼叫 View.getWindowVisibility(),檢查覆疊視窗目前是否可見,也可以覆寫 View.onWindowVisibilityChanged(),在可見度變更時收到通知。
測試
如要測試應用程式的行為,您可以啟用這些新限制,即使應用程式並非以 Android 15 為目標版本 (只要應用程式在 Android 15 裝置上執行) 也一樣。如要啟用這些新限制,以便從背景啟動前景服務,請執行下列 adb 指令:
adb shell am compat enable FGS_SAW_RESTRICTIONS your-package-name
變更應用程式修改零打擾模式全域狀態的時間
指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 以上版本的應用程式,將無法再變更裝置上的勿擾模式 (DND) 全域狀態或政策 (透過修改使用者設定或關閉勿擾模式)。相反地,應用程式必須提供 AutomaticZenRule,系統會將其與現有的最嚴格政策優先方案結合為全域政策。呼叫先前影響全域狀態的現有 API (setInterruptionFilter、setNotificationPolicy) 會導致建立或更新隱含的 AutomaticZenRule,而 AutomaticZenRule 的開啟和關閉狀態會根據這些 API 呼叫的呼叫週期而定。
請注意,只有在應用程式呼叫 setInterruptionFilter(INTERRUPTION_FILTER_ALL) 且預期該呼叫會停用先前由其擁有者啟用的 AutomaticZenRule 時,這項變更才會影響可觀察的行為。
OpenJDK API 變更
Android 15 持續更新 Android 核心程式庫,以便與最新版 OpenJDK LTS 中的功能保持一致。
如果應用程式指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35),以下部分變更可能會影響應用程式相容性:
字串格式化 API 的變更:使用下列
String.format()和Formatter.format()API 時,系統現在會更嚴格地驗證引數索引、旗標、寬度和精確度:String.format(String, Object[])String.format(Locale, String, Object[])Formatter.format(String, Object[])Formatter.format(Locale, String, Object[])
舉例來說,使用引數索引 0 (格式字串中的
%0) 時,會擲回下列例外狀況:IllegalFormatArgumentIndexException: Illegal format argument index = 0在這種情況下,使用引數索引 1 (格式字串中的
%1) 即可修正問題。Arrays.asList(...).toArray()的元件類型變更:使用Arrays.asList(...).toArray()時,產生的陣列元件類型現在是Object,而不是基礎陣列元素的類型。因此,下列程式碼會擲回ClassCastException:String[] elements = (String[]) Arrays.asList("one", "two").toArray();在這種情況下,如要將
String保留在產生的陣列中做為元件型別,可以使用Collection.toArray(Object[]):String[] elements = Arrays.asList("two", "one").toArray(new String[0]);語言代碼處理方式異動:使用
LocaleAPI 時,希伯來文、意第緒文和印尼文的語言代碼不會再轉換為舊版代碼 (希伯來文:iw、意第緒文:ji、印尼文:in)。指定這些語言的語言代碼時,請改用 ISO 639-1 的代碼 (希伯來文:he、意第緒文:yi、印尼文:id)。隨機整數序列的變更:根據 https://bugs.openjdk.org/browse/JDK-8301574 中所做的變更,下列
Random.ints()方法現在會傳回與Random.nextInt()方法不同的數字序列:一般來說,這項變更不會導致應用程式發生中斷行為,但您的程式碼不應預期從
Random.ints()方法產生的序列會與Random.nextInt()相符。
在應用程式的建構設定中更新 compileSdk,以使用 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 後,新的 SequencedCollection API 可能會影響應用程式的相容性:
與
kotlin-stdlib中的MutableList.removeFirst()和MutableList.removeLast()擴充函式發生衝突Java 中的
List型別會對應至 Kotlin 中的MutableList型別。由於 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 已推出List.removeFirst()和List.removeLast()API,Kotlin 編譯器會將函式呼叫 (例如list.removeFirst()) 靜態解析為新的ListAPI,而不是kotlin-stdlib中的擴充功能函式。如果應用程式重新編譯時,將
compileSdk設為35,並將minSdk設為34以下,然後在 Android 14 以下版本執行,就會擲回執行階段錯誤:java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: No virtual method removeFirst()Ljava/lang/Object; in class Ljava/util/ArrayList;Android Gradle 外掛程式中的現有
NewApilint 選項可以偵測這些新 API 用法。./gradlew lintMainActivity.kt:41: Error: Call requires API level 35 (current min is 34): java.util.List#removeFirst [NewApi] list.removeFirst()如要修正執行階段例外狀況和 Lint 錯誤,請在 Kotlin 中將
removeFirst()和removeLast()函式呼叫分別替換為removeAt(0)和removeAt(list.lastIndex)。如果您使用 Android Studio Ladybug | 2024.1.3 以上版本,系統也會提供這些錯誤的快速修正選項。如果已停用 Lint 選項,請考慮移除
@SuppressLint("NewApi")和lintOptions { disable 'NewApi' }。與 Java 中的其他方法發生衝突
現有型別已新增方法,例如
List和Deque。這些新方法可能與其他介面和類別中,名稱和引數類型相同的方法不相容。如果方法簽章與不相容的項目發生衝突,javac編譯器會輸出建構時間錯誤。例如:錯誤示例 1:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:135: error: removeLast() in MyList cannot implement removeLast() in List public void removeLast() { ^ return type void is not compatible with Object where E is a type-variable: E extends Object declared in interface List錯誤示例 2:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:7: error: types Deque<Object> and List<Object> are incompatible; public class MyList implements List<Object>, Deque<Object> { both define reversed(), but with unrelated return types 1 error錯誤示例 3:
javac MyList.javaMyList.java:43: error: types List<E#1> and MyInterface<E#2> are incompatible; public static class MyList implements List<Object>, MyInterface<Object> { class MyList inherits unrelated defaults for getFirst() from types List and MyInterface where E#1,E#2 are type-variables: E#1 extends Object declared in interface List E#2 extends Object declared in interface MyInterface 1 error如要修正這些建構錯誤,實作這些介面的類別應使用相容的回傳型別覆寫方法。例如:
@Override public Object getFirst() { return List.super.getFirst(); }
安全性
Android 15 包含多項變更,可提升系統安全性,協助保護應用程式和使用者免受惡意應用程式侵害。
受限的 TLS 版本
Android 15 會限制 TLS 1.0 和 1.1 版本的使用。這些版本先前已在 Android 中淘汰,但現在已禁止用於指定 Android 15 為目標版本的應用程式。
安全啟動背景活動
Android 15 新增了多項變更,可防止惡意背景應用程式將其他應用程式帶到前景、提升權限及濫用使用者互動,進而保護使用者免受惡意應用程式侵害,並讓使用者進一步控管裝置。自 Android 10 (API 級別 29) 起,系統會限制啟動背景活動。
其他變更
- 將
PendingIntent建立者變更為預設封鎖背景活動啟動程序。這有助於防止應用程式意外建立PendingIntent,避免惡意人士濫用。 - 除非
PendingIntent傳送者允許,否則請勿將應用程式移至前景。這項異動旨在防止惡意應用程式濫用在背景啟動活動的功能。根據預設,應用程式不得將工作堆疊帶到前景,除非建立者允許啟動背景活動的權限,或傳送者具有啟動背景活動的權限。 - 控制工作堆疊頂端活動完成工作的方式。如果頂端活動完成工作,Android 會返回上次啟用的工作。此外,如果非頂端活動完成任務,Android 會返回主畫面,不會封鎖這個非頂端活動的完成作業。
- 防止其他應用程式在您的工作階段中啟動任意活動。這項異動可防止惡意應用程式建立看似來自其他應用程式的活動,藉此網路釣魚。
- 禁止將非可見視窗納入背景活動啟動程序。這樣一來,惡意應用程式就無法濫用背景活動啟動功能,向使用者顯示不當或惡意內容。
更安全的意圖
Android 15 推出意圖的 StrictMode。
如要查看 Intent 用量違規的詳細記錄,請使用下列方法:
Kotlin
fun onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build() ) }
Java
public void onCreate() { StrictMode.setVmPolicy(new VmPolicy.Builder() .detectUnsafeIntentLaunch() .build()); }
使用者體驗和系統 UI
Android 15 包含一些變更,旨在打造更一致、直覺的使用者體驗。
視窗插邊變更
Android 15 有兩項與視窗內嵌相關的變更:預設會強制執行邊到邊,且有設定變更,例如系統列的預設設定。
邊緣到邊緣強制執行
如果應用程式以 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 為目標版本,在搭載 Android 15 的裝置上預設會顯示無邊框模式。
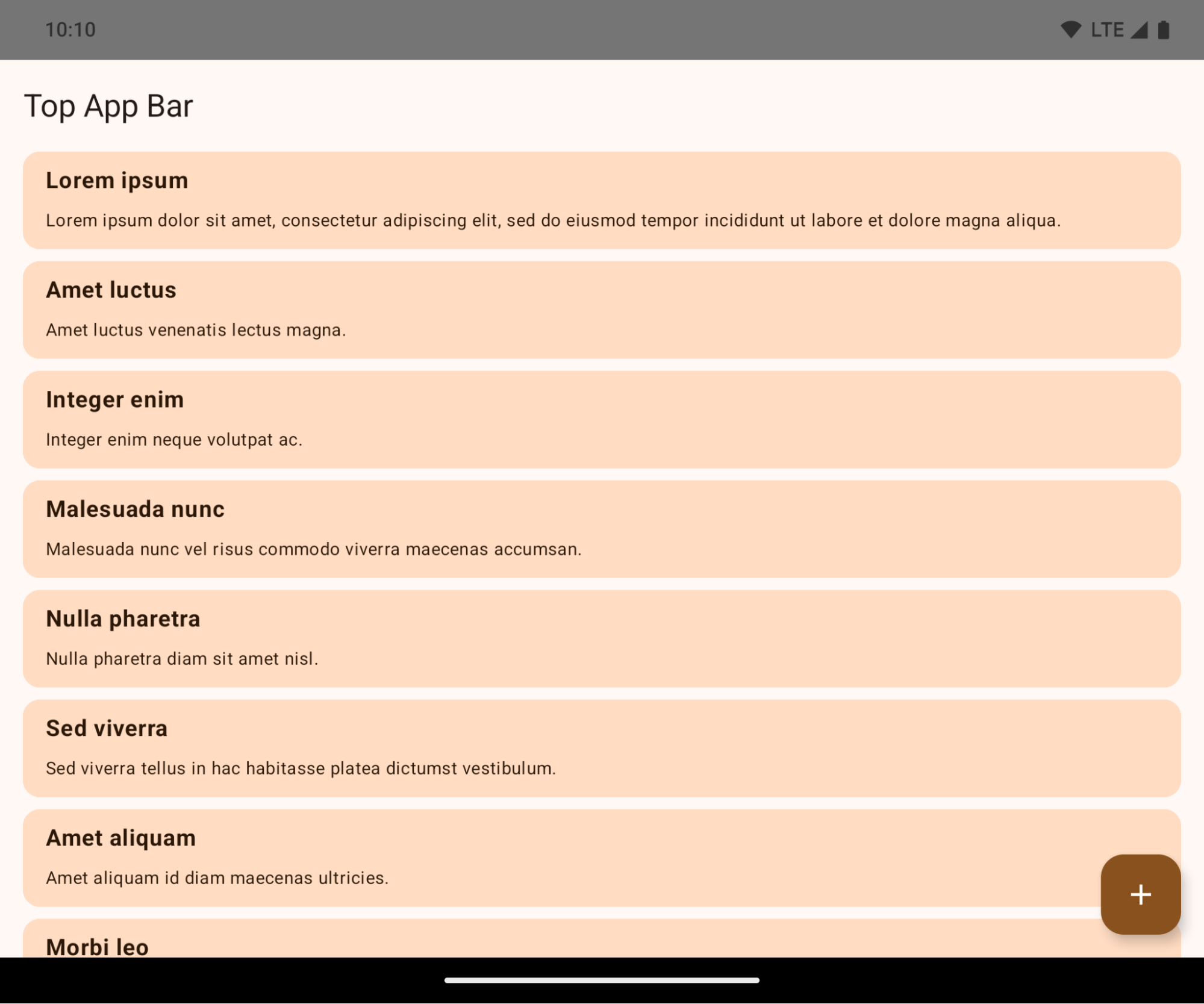
這項重大變更可能會對應用程式的 UI 造成負面影響。這項異動會影響下列 UI 區域:
- 手勢控點導覽列
- 預設為透明。
- 底部位移已停用,因此內容會在系統導覽列後方繪製,除非套用插邊。
setNavigationBarColor和R.attr#navigationBarColor已淘汰,不會影響手勢操作模式。setNavigationBarContrastEnforced和R.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforced仍不會影響手勢操作模式。
- 三按鈕操作
- 預設不透明度為 80%,顏色可能與視窗背景相符。
- 底部偏移已停用,因此內容會在系統導覽列後方繪製,除非套用插邊。
setNavigationBarColor和R.attr#navigationBarColor預設會設為與視窗背景相符。如要套用此預設值,視窗背景必須是顏色可繪項目。這個 API 已淘汰,但仍會影響三按鈕操作模式。setNavigationBarContrastEnforced和R.attr#navigationBarContrastEnforced預設為 true,這會在三按鈕操作列中加入 80% 不透明的背景。
- 狀態列
- 預設為透明。
- 頂端位移已停用,因此除非套用插邊,否則內容會在狀態列後方繪製。
setStatusBarColor和R.attr#statusBarColor已遭淘汰,對 Android 15 沒有影響。setStatusBarContrastEnforced和R.attr#statusBarContrastEnforced已淘汰,但仍會影響 Android 15。
- 螢幕凹口
- 非浮動視窗的
layoutInDisplayCutoutMode必須為LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS。SHORT_EDGES、NEVER和DEFAULT會解譯為ALWAYS,這樣使用者就不會看到因螢幕凹口而產生的黑邊,且畫面會顯示到螢幕邊框。
- 非浮動視窗的
以下範例顯示應用程式在指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 前後,以及套用插邊前後的樣貌。這個範例並不完整,Android Auto 上的顯示方式可能有所不同。
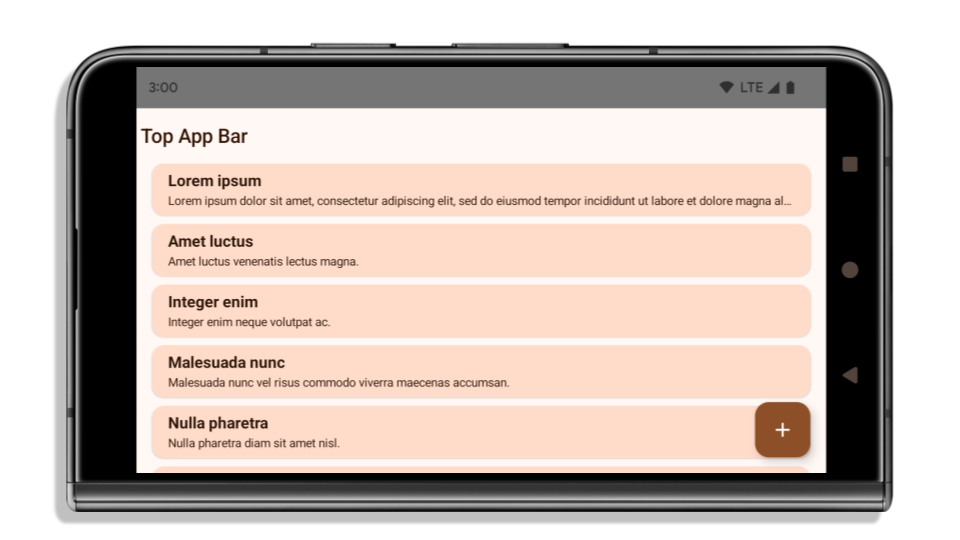

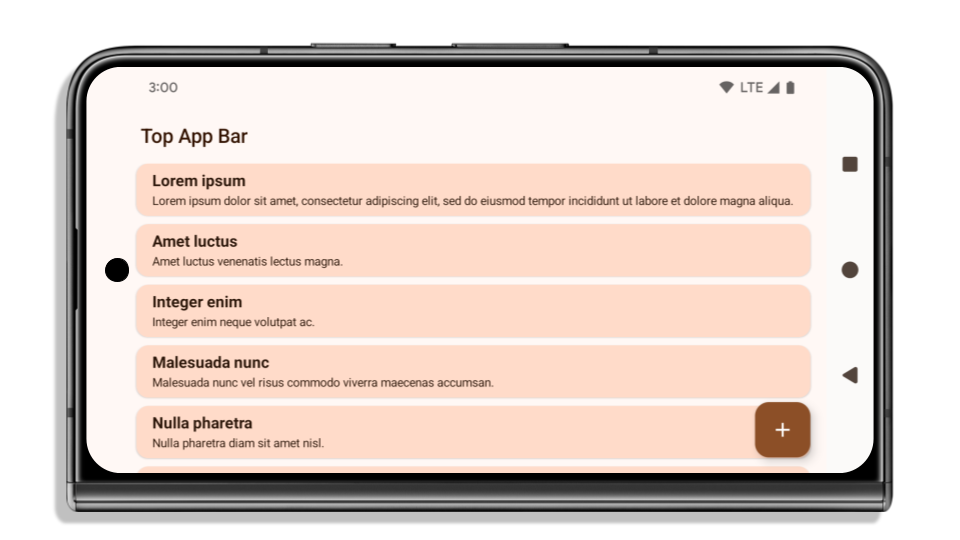
如果應用程式已採用無邊框設計,請檢查以下項目
如果您的應用程式已無邊框並套用插邊,則大多不受影響,但下列情況除外。不過,即使您認為自己不受影響,我們仍建議測試應用程式。
- 您有非浮動視窗,例如使用
SHORT_EDGES、NEVER或DEFAULT而不是LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS的Activity。如果應用程式在啟動時當機,可能是因為啟動畫面。您可以將核心啟動畫面依附元件升級至 1.2.0-alpha01 以上版本,或設定window.attributes.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = WindowManager.LayoutInDisplayCutoutMode.always。 - 流量較低的畫面可能會有 UI 遮蔽問題。確認這些較少造訪的畫面沒有遭到遮蔽的 UI。流量較低的螢幕包括:
- 新手上路或登入畫面
- 設定頁面
如果應用程式尚未採用無邊框設計,請檢查下列項目
如果您的應用程式尚未採用無邊框設計,很可能就會受到影響。除了已採用無邊框設計的應用程式情境,您也應考量下列事項:
- 如果應用程式在 Compose 中使用 Material 3 元件 (
androidx.compose.material3),例如TopAppBar、BottomAppBar和NavigationBar,這些元件可能會不受影響,因為它們會自動處理插邊。 - 如果應用程式使用 Compose 的 Material 2 元件 (
androidx.compose.material),這類元件本身不會自動處理插邊。不過,您可以存取插邊,然後手動套用。在 androidx.compose.material 1.6.0 以上版本,請使用windowInsets參數,為BottomAppBar、TopAppBar、BottomNavigation和NavigationRail手動套用插邊。同樣地,對Scaffold也是使用contentWindowInsets參數。 - 如果應用程式使用 Views 和 Material 元件 (
com.google.android.material),您可能不需採取額外行動,因為大多數以 Views 為基礎的 Material 元件 (例如BottomNavigationView、BottomAppBar、NavigationRailView或NavigationView) 都會處理插邊。不過,如果您使用AppBarLayout,就需要新增android:fitsSystemWindows="true"。 - 如果是自訂可組合函式,請手動將插邊套用為邊框間距。如果內容位於
Scaffold內,您可以使用Scaffold邊框間距值取用插邊。否則,請使用WindowInsets套用邊框間距。 - 如果應用程式使用 Views 和
BottomSheet、SideSheet或自訂容器,請使用ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener套用邊框間距。對於RecyclerView,也請使用這個事件監聽器套用邊框間距,同時新增clipToPadding="false"。
如果應用程式必須提供自訂背景保護功能,請檢查下列事項
如果應用程式必須為三按鈕操作模式或狀態列提供自訂背景保護措施,應用程式應使用 WindowInsets.Type#tappableElement() 將可組合函式或檢視區塊放在系統列後方,以取得三按鈕操作模式導覽列高度或 WindowInsets.Type#statusBars。
其他無邊框資源
如要進一步瞭解如何套用插邊,請參閱「無邊框檢視區塊」和「無邊框 Compose」指南。
已淘汰的 API
下列 API 已淘汰,但仍可使用:
R.attr#enforceStatusBarContrastR.attr#navigationBarColor(適用於三按鈕操作模式,且 alpha 值為 80%)Window#isStatusBarContrastEnforcedWindow#setNavigationBarColor(適用於三按鈕操作模式,透明度為 80%)Window#setStatusBarContrastEnforced
下列 API 已停用:
R.attr#navigationBarColor(手勢操作模式)R.attr#navigationBarDividerColorR.attr#statusBarColorWindow#setDecorFitsSystemWindowsWindow#getNavigationBarColorWindow#getNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#getStatusBarColorWindow#setNavigationBarColor(手勢操作模式)Window#setNavigationBarDividerColorWindow#setStatusBarColor
穩定設定
如果應用程式指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 以上版本,Configuration系統不會再排除系統資訊列。如果您在 Configuration 類別中使用螢幕大小進行版面配置計算,請視需求改用適當的 ViewGroup、WindowInsets 或 WindowMetricsCalculator 等更合適的替代方案。
Configuration 自 API 1 起就已推出,這項資訊通常來自 Activity.onConfigurationChanged。例如視窗密度、方向和大小。從 Configuration 傳回的視窗大小有一項重要特徵,就是先前會排除系統資訊列。
設定大小通常用於資源選取 (例如 /res/layout-h500dp),這仍是有效的用途。不過,我們一直不建議使用它來計算版面配置。如果這樣做,請立即遠離該裝置。視用途而定,您應將 Configuration 替換為更合適的項目。
如果使用它來計算版面配置,請使用適當的 ViewGroup,例如 CoordinatorLayout 或 ConstraintLayout。如要使用它判斷系統導覽列的高度,請使用 WindowInsets。如要瞭解應用程式視窗的目前大小,請使用 computeCurrentWindowMetrics。
下列清單說明受這項異動影響的欄位:
Configuration.screenWidthDp和screenHeightDp大小不再排除系統資訊列。Configuration.smallestScreenWidthDp會間接受到screenWidthDp和screenHeightDp變更的影響。Configuration.orientation會間接受到接近正方形裝置上screenWidthDp和screenHeightDp變更的影響。Display.getSize(Point)間接受到Configuration變更的影響。從 API 級別 30 開始,這項屬性已遭淘汰。- 自 API 級別 33 起,
Display.getMetrics()就已採用這種運作方式。
elegantTextHeight 屬性預設為 true
針對指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 的應用程式,elegantTextHeight TextView 屬性預設會變成 true,將預設使用的緊湊字型取代為具有大型垂直指標的某些指令碼,以便更容易閱讀。我們推出了精簡字型,以免版面配置中斷;Android 13 (API 級別 33) 允許文字版面配置利用 fallbackLineSpacing 屬性拉長垂直高度,藉此避免許多這類中斷情形。
在 Android 15 中,系統仍會保留精簡字型,因此應用程式可以將 elegantTextHeight 設為 false,以便取得與先前相同的行為,但未來版本不太可能支援這項功能。因此,如果您的應用程式支援下列文字:阿拉伯文、老撾文、緬甸文、泰米爾文、古吉拉特文、卡納達文、馬拉雅拉姆文、奧里雅文、泰盧固文或泰文,請將 elegantTextHeight 設為 true 來測試應用程式。
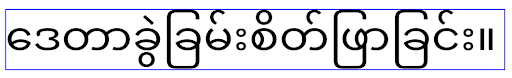
elegantTextHeight 指定 Android 14 (API 級別 34) 以下版本為目標版本的應用程式行為。
elegantTextHeight 指定 Android 15 為目標版本的應用程式行為。複雜字母形狀的 TextView 寬度變化
在舊版 Android 中,部分草書字型或形狀複雜的語言,可能會在前一個或下一個字元的區域中繪製字母。在某些情況下,這類信件會在開頭或結尾處遭到裁切。自 Android 15 起,TextView 會分配寬度,以便繪製這類字母的空間,並允許應用程式要求左側額外的邊框間距,以防裁剪。
由於這項變更會影響 TextView 決定寬度的做法,因此如果應用程式指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 以上版本,TextView 預設會分配更多寬度。您可以在 TextView 上呼叫 setUseBoundsForWidth API,啟用或停用這項行為。
由於新增左邊邊框間距可能會導致現有版面配置不對齊,因此即使應用程式指定 Android 15 以上版本,也不會預設新增邊框間距。不過,您可以呼叫 setShiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang 新增額外的邊框間距,避免發生裁剪情形。
以下範例說明這些變更如何改善部分字型和語言的文字版面配置。

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" />

<TextView android:fontFamily="cursive" android:text="java" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" />

<TextView android:text="คอมพิวเตอร์" android:useBoundsForWidth="true" android:shiftDrawingOffsetForStartOverhang="true" />
EditText 的預設行高會因語言代碼而異
In previous versions of Android, the text layout stretched the height of the
text to meet the line height of the font that matched the current locale. For
example, if the content was in Japanese, because the line height of the Japanese
font is slightly larger than the one of a Latin font, the height of the text
became slightly larger. However, despite these differences in line heights, the
EditText element was sized uniformly, regardless
of the locale being used, as illustrated in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText is the same, even though these languages
have different line heights from each other.For apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35), a minimum line height is now
reserved for EditText to match the reference font for the specified Locale, as
shown in the following image:

EditText elements that
can contain text from English (en), Japanese (ja), and Burmese (my). The
height of the EditText now includes space to accommodate the
default line height for these languages' fonts.If needed, your app can restore the previous behavior by specifying the
useLocalePreferredLineHeightForMinimum attribute
to false, and your app can set custom minimum vertical metrics using the
setMinimumFontMetrics API in Kotlin and Java.
相機和媒體
Android 15 對指定 Android 15 以上版本的應用程式,進行了下列攝影機和媒體行為變更。
要求音訊焦點的限制
指定 Android 15 (API 級別 35) 為目標版本的應用程式必須是頂層應用程式,或執行前景服務,才能要求音訊焦點。如果應用程式在未符合上述任一規定的情況下嘗試要求焦點,則呼叫會傳回 AUDIOFOCUS_REQUEST_FAILED。
如要進一步瞭解音訊焦點,請參閱「管理音訊焦點」。
更新非 SDK 限制
基於與 Android 開發人員合作及最新的內部測試,Android 15 包含更新後的受限制非 SDK 介面清單。在限制非 SDK 介面之前,我們盡可能確保公開替代方案的可得性。
如果您的應用程式並不是以 Android 15 為目標版本,則此處所述的某些變更可能不會立即對您造成影響。不過,雖然應用程式視目標 API 級別而定,可以存取某些非 SDK 介面,但使用任何非 SDK 方法或欄位時,應用程式停止運作的風險極高。
如果不確定應用程式是否使用非 SDK 介面,可測試應用程式以便確認。如果應用程式仰賴非 SDK 介面,則應開始規劃遷移至 SDK 替代方案。我們瞭解有些應用程式可使用非 SDK 介面運作。如果您除了為應用程式中的某個功能使用非 SDK 介面外,已別無他法,則應要求新的公用 API。
如要進一步瞭解此 Android 版本中的變更,請參閱「Android 15 的非 SDK 介面限制更新內容」。如要進一步瞭解非 SDK 介面的一般資訊,請參閱「非 SDK 介面的限制」。
