Android 14, geliştiriciler için harika özellikler ve API'ler sunuyor. Aşağıdaki yardım kaynakları, uygulamalarınızdaki özellikler hakkında bilgi edinmenize ve ilgili API'leri kullanmaya başlamanıza yardımcı olur.
Eklenen, değiştirilen ve kaldırılan API'lerin ayrıntılı listesi için API farklılıkları raporunu inceleyin. Eklenen API'lerle ilgili ayrıntılar için Android API referansını ziyaret edin. Android 14 için API düzeyi 34'te eklenen API'leri bulun. Platform değişikliklerinin uygulamalarınızı etkileyebileceği alanlar hakkında bilgi edinmek için Android 14'ü hedefleyen uygulamalarda ve tüm uygulamalarda Android 14 davranış değişikliklerini inceleyin.
Uluslararası hale getirme
Uygulamaya özgü dil tercihleri
Android 14, Android 13'te (API düzeyi 33) kullanıma sunulan uygulama başına dil özelliklerini aşağıdaki ek özelliklerle genişletir:
Uygulamanın
localeConfigdosyasını otomatik olarak oluşturma: Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 ve AGP 8.1.0-alpha07'den itibaren uygulamanızı uygulama başına dil tercihlerini otomatik olarak destekleyecek şekilde yapılandırabilirsiniz. Android Gradle eklentisi, proje kaynaklarınızı temel alarakLocaleConfigdosyasını oluşturur ve nihai manifest dosyasına bu dosyaya referans ekler. Böylece artık dosyayı manuel olarak oluşturmanız veya güncellemeniz gerekmez. AGP,LocaleConfigdosyasına eklenecek yerel ayarları belirlemek için uygulama modüllerinizinresklasörlerindeki kaynakları ve kitaplık modülü bağımlılıklarını kullanır.Uygulamanın
localeConfigiçin dinamik güncellemeler:LocaleManager'dekisetOverrideLocaleConfig()vegetOverrideLocaleConfig()yöntemlerini kullanarak uygulamanızın desteklenen diller listesini cihazın sistem ayarlarında dinamik olarak güncelleyin. Bu esnekliği kullanarak bölgeye göre desteklenen diller listesini özelleştirebilir, A/B denemeleri çalıştırabilir veya uygulamanız yerelleştirme için sunucu tarafı push'ları kullanıyorsa güncellenmiş bir yerel ayar listesi sağlayabilirsiniz.Giriş yöntemi düzenleyiciler (IME'ler) için uygulama dili görünürlüğü: IME'ler, mevcut uygulamanın dilini kontrol etmek ve IME dilini bu dille eşleştirmek için
getApplicationLocales()yöntemini kullanabilir.
Grammatical Inflection API
3 milyar insan cinsiyete dayalı diller konuşuyor: İsim, fiil, sıfat ve edat gibi dil bilgisi kategorilerinin, konuştuğunuz veya bahsettiğiniz kişilerin ve nesnelerin cinsiyetine göre değiştiği diller. Cinsiyetli dillerin çoğunda, geleneksel olarak varsayılan veya genel cinsiyet olarak eril dil bilgisi cinsiyeti kullanılır.
Kullanıcılara yanlış dil bilgisi cinsiyetiyle hitap etmek (ör. kadınları eril dil bilgisi cinsiyetiyle hitap etmek) performanslarını ve tutumlarını olumsuz yönde etkileyebilir. Buna karşılık, kullanıcının dil bilgisi açısından cinsiyetini doğru yansıtan bir kullanıcı arayüzü, kullanıcı etkileşimini artırabilir ve daha kişiselleştirilmiş ve doğal bir kullanıcı deneyimi sunabilir.
Android 14, cinsiyetli diller için kullanıcı odaklı bir kullanıcı arayüzü oluşturmanıza yardımcı olmak amacıyla Gramatik Eğim API'yi kullanıma sunar. Bu API, uygulamanızı yeniden düzenlemeden dil bilgisi cinsiyeti desteği eklemenize olanak tanır.
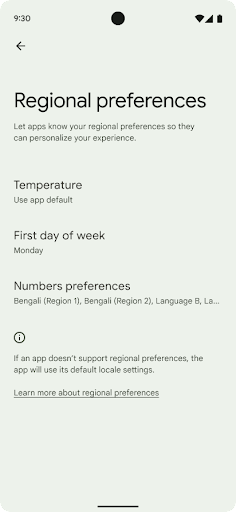
Bölgeye özgü tercihler
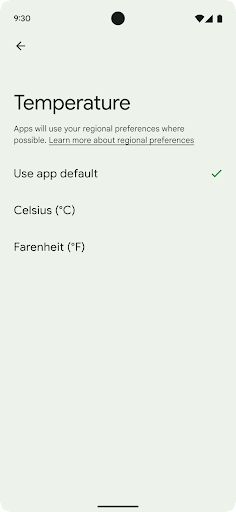
Bölgesel tercihler, kullanıcıların sıcaklık birimlerini, haftanın ilk gününü ve numaralandırma sistemlerini kişiselleştirmesine olanak tanır. ABD'de yaşayan Avrupalı sıcaklık biriminin Fahrenhayt yerine Santigrat cinsinden olmasını tercih edebilir ABD'de varsayılan gün yerine pazartesi günü kabul etmesini sağlayan uygulamalar Pazar.
Bu tercihler için yeni Android Ayarlar menüleri, kullanıcılara uygulama tercihlerini değiştirebilecekleri keşfedilebilir ve merkezi bir konum sunar. Bu tercihler, yedekleme ve geri yükleme sırasında da korunur. Çeşitli API ve
hedefler (ör.
getTemperatureUnit
ve
getFirstDayOfWeek -
uygulamanıza kullanıcı tercihlerine okuma erişimi verebilirsiniz, böylece uygulamanız
bilgileri görüntüler. Ayrıca bir
BroadcastReceiver açık
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
kullanın.
Bu ayarları bulmak için Ayarlar uygulamasını açın ve Sistem > Diller ve giriş > Bölgesel tercihler.
Erişilebilirlik
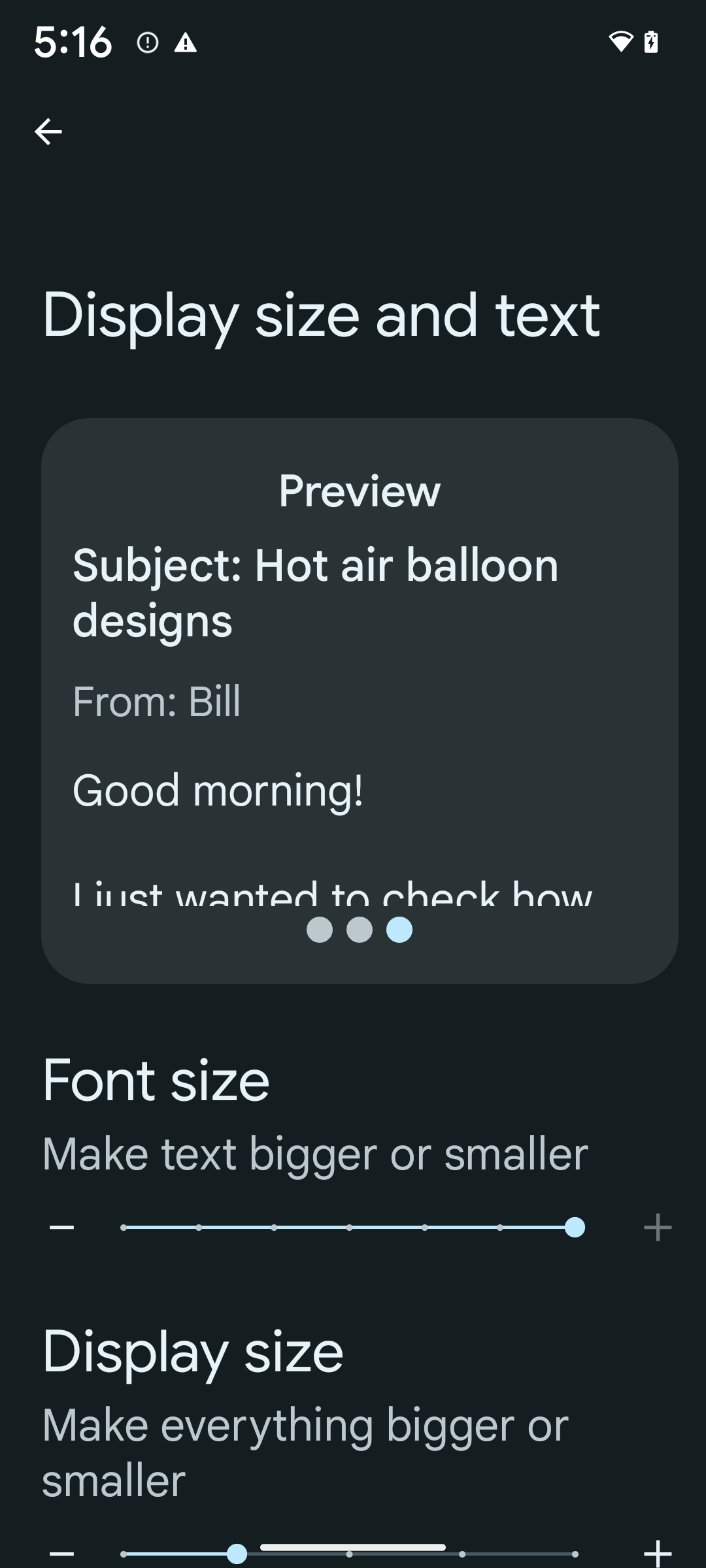
%200'e kadar doğrusal olmayan yazı tipi ölçeklendirme
Android 14'ten itibaren sistem, %200'e kadar yazı tipi ölçeklendirmeyi destekleyerek kullanıcılara ek erişilebilirlik seçenekleri sunar.
Ekranda büyük metin öğelerinin çok fazla büyümesini önlemek için sistem doğrusal olmayan bir ölçeklendirme eğrisi uygular. Bu ölçeklendirme stratejisi, büyük metinlerin küçük metinlerle aynı oranda ölçeklenmediği anlamına gelir. Doğrusal olmayan yazı tipi ölçeklendirme, farklı boyutlardaki öğeler arasındaki orantılı hiyerarşinin korunmasına yardımcı olurken yüksek derecelerdeki doğrusal metin ölçeklendirmeyle ilgili sorunları (ör. metnin kesilmesi veya çok büyük ekran boyutları nedeniyle okunmasının zorlaşması) azaltır.
Uygulamanızı doğrusal olmayan yazı tipi ölçeklendirme ile test etme
Metin boyutunu tanımlamak için ölçeklendirilmiş piksel (sp) birimlerini kullanıyorsanız bu ek seçenekler ve ölçeklendirme iyileştirmeleri, uygulamanızdaki metne otomatik olarak uygulanır. Ancak, uygulamanızın yazı tipi boyutlarını doğru şekilde uyguladığından ve kullanılabilirliği etkilemeden daha büyük yazı tipi boyutlarını desteklediğinden emin olmak için kullanıcı arayüzü testini en büyük yazı tipi boyutu etkinleştirilmişken (%200) yapmanız gerekir.
%200 yazı tipi boyutunu etkinleştirmek için aşağıdaki adımları uygulayın:
- Ayarlar uygulamasını açıp Erişilebilirlik > Görüntü boyutu ve metin'e gidin.
- Yazı tipi boyutu seçeneği için bu bölüme eşlik eden resimde gösterildiği gibi, maksimum yazı tipi boyutu ayarı etkinleştirilene kadar artı (+) simgesine dokunun.
Metin boyutları için ölçeklendirilmiş piksel (sp) birimlerini kullanma
Metin boyutlarını her zaman sp birimleriyle belirtmeyi unutmayın. Uygulamanız sp birimlerini kullandığında Android, kullanıcının tercih ettiği metin boyutunu uygulayabilir ve uygun şekilde ölçeklendirebilir.
Dolgu için sp birimlerini kullanmayın veya görünüm yüksekliklerini dolaylı dolgu olduğunu varsayarak tanımlamayın: Doğrusal olmayan yazı tipi ölçeklendirmesinde sp boyutları orantılı olmayabilir. Bu nedenle, 4 sp + 20 sp, 24 sp'ye eşit olmayabilir.
Ölçeklendirilmiş piksel (sp) birimlerini dönüştürme
Sp birimlerinden piksele dönüştürmek için TypedValue.applyDimension(), pikselden sp'ye dönüştürmek için TypedValue.deriveDimension() işlevini kullanın. Bu yöntemler, uygun doğrusal olmayan ölçeklendirme eğrisini otomatik olarak uygular.
Configuration.fontScale veya DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity kullanarak denklemlere kod gömmekten kaçının. Yazı tipi ölçeklendirme doğrusal olmadığından scaledDensity alanı artık doğru değil. Yazı tipleri artık tek bir skaler değerle ölçeklendirilmediğinden fontScale alanı yalnızca bilgilendirme amaçlı kullanılmalıdır.
lineHeight için sp birimlerini kullanma
Satır yüksekliğinin metninizle birlikte ölçeklenmesi için android:lineHeight değerini her zaman dp yerine sp birimlerini kullanarak tanımlayın. Aksi takdirde, metniniz sp birimindeyse ancak lineHeight dp veya px birimindeyse ölçeklenmez ve sıkışık görünür.
TextView, lineHeight ve textSize birimleri sp olarak tanımlanmışsa amaçlanan oranların korunması için lineHeight birimini otomatik olarak düzeltir.
Kamera ve medya içerikleri
Resimler için Ultra HDR

Android 14, fotoğraf çekerken sensörden daha fazla bilginin korunmasını sağlayan ve canlı renkler ile daha yüksek kontrast sağlayan Yüksek Dinamik Aralık (HDR) resimleri için destek ekler. Android, JPEG resimleriyle tamamen geriye dönük uyumlu olan Ultra HDR biçimini kullanır. Bu biçim, uygulamaların HDR resimlerle sorunsuz bir şekilde birlikte çalışmasını sağlar ve gerektiğinde resimleri Standart Dinamik Aralık (SDR) olarak gösterir.
Uygulamanız, etkinlik aralığı için HDR kullanıcı arayüzünü kullanmayı bir manifest girişi aracılığıyla veya çalışma zamanında Window.setColorMode() çağrısı yaparak etkinleştirdiğinde bu resimlerin kullanıcı arayüzünde HDR olarak oluşturulması çerçeve tarafından otomatik olarak yapılır. Desteklenen cihazlarda sıkıştırılmış Ultra HDR fotoğraflar da çekebilirsiniz. Sensörden daha fazla renk elde edildiğinde, düzenleme işlemi daha esnek olabilir. Ultra HDR resimlerle ilişkili Gainmap, OpenGL veya Vulkan kullanılarak oluşturulmak için kullanılabilir.
Kamera uzantılarında yakınlaştırma, odaklama, son görüntü ve daha fazlası
Android 14, kamera uzantılarını yükselterek ve iyileştirerek uygulamaların daha uzun işlem sürelerini yönetmesine olanak tanır. Bu sayede, desteklenen cihazlarda düşük ışıkta fotoğrafçılık gibi yoğun bilgi işlem gerektiren algoritmalar kullanılarak daha iyi görüntüler elde edilebilir. Bu özellikler, kamera uzantısı özelliklerini kullanırken kullanıcılara daha da güçlü bir deneyim sunar. Bu iyileştirmelere örnek olarak aşağıdakiler verilebilir:
- Dinamik fotoğraf çekme işlemi gecikmesi tahmini, mevcut sahneye ve çevre koşullarına göre çok daha doğru fotoğraf çekme işlemi gecikmesi tahminleri sağlar. İki gecikme tahmini yöntemi olan bir
StillCaptureLatencynesnesi almak içinCameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()işlevini çağırın.getCaptureLatency()yöntemi,onCaptureStartedileonCaptureProcessStarted()arasındaki tahmini gecikmeyi döndürür.getProcessingLatency()yöntemi iseonCaptureProcessStarted()ile işlenmiş son karenin kullanılabilir hale gelmesi arasındaki tahmini gecikmeyi döndürür. - Uygulamaların uzun süren, hareketsiz görüntü yakalama işlemlerinin mevcut ilerleme durumunu gösterebilmesi için yakalama ilerleme durumu geri çağırma işlevi desteği. Bu özelliğin
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailableile kullanılıp kullanılamayacağını kontrol edebilirsiniz. Kullanılabilirse ilerleme durumunun (0 ila 100 arasında) parametre olarak iletildiğionCaptureProcessProgressed()geri çağırma işlevini uygulayabilirsiniz. Uzantılara özel meta veriler (ör.
EXTENSION_BOKEHile arka plan bulanıklaştırma miktarı gibi bir uzantı efektinin miktarını ayarlamak içinCaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTH).Kamera uzantılarında sabit resim çekme için son görüntüden daha hızlı ve daha az işlenmiş bir görüntü sağlayan son görüntü özelliği. Bir uzantı, işleme gecikmesini artırdıysa kullanıcı deneyimini iyileştirmek için yer tutucu olarak bir görüntü sonrası resim sağlanabilir ve daha sonra nihai resimle değiştirilebilir. Bu özelliğin
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailableile kullanılıp kullanılamadığını kontrol edebilirsiniz. ArdındanExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration'e birOutputConfigurationiletebilirsiniz.Daha optimize ve enerji tasarruflu bir önizleme oluşturma yolu sağlayan
SurfaceViewdesteği.Uzantı kullanımı sırasında dokunarak odaklama ve yakınlaştırma desteği.
Sensör içi yakınlaştırma
CameraCharacteristics içindeki REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW içeriyorsa uygulamanız, akış kullanım alanı CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW olarak ayarlanmış bir RAW hedefi içeren CaptureRequest kullanarak kırpılmış bir RAW akışına tam görüş alanı ile aynı pikselleri vermek için gelişmiş sensör özelliklerini kullanabilir.
Güncellenen kamera, istek geçersiz kılma denetimlerini uygulayarak kullanıcılara diğer kamera kontrolleri hazır olmadan önce bile yakınlaştırma kontrolü sunar.
Kayıpsız USB ses
Android 14, USB kablolu kulaklıklarda ses kalitesini artıran kayıpsız ses biçimlerini destekler. USB cihazı tercih edilen karıştırıcı özellikleri için sorgulayabilir, tercih edilen karıştırıcı özelliklerindeki değişiklikler için bir dinleyici kaydedebilir ve AudioMixerAttributes sınıfını kullanarak karıştırıcı özelliklerini yapılandırabilirsiniz. Bu sınıf, ses karıştırıcının kanal maskesi, örnekleme hızı ve davranışı gibi biçimi temsil eder. Sınıf, karıştırma, ses seviyesi ayarı veya işleme efektleri olmadan seslerin doğrudan gönderilmesine olanak tanır.
Geliştirici üretkenliği ve araçları
Kimlik Bilgisi Yöneticisi
Android 14, platform API'si olarak Kimlik Bilgisi Yöneticisi'ni ekler. Google Play Hizmetleri'ni kullanan bir Jetpack Kitaplığı aracılığıyla Android 4.4 (API düzeyi 19) cihazlara ek destek sağlanır. Kimlik Bilgisi Yöneticisi, kimlik bilgilerini kullanıcı tarafından yapılandırılmış kimlik bilgisi sağlayıcılarla alan ve depolayan API'lerle kullanıcıların oturum açmasını kolaylaştırmayı amaçlar. Kimlik Bilgisi Yöneticisi, tek bir API'de kullanıcı adı ve şifre, geçiş anahtarları ve birleşik oturum açma çözümleri (ör. Google ile oturum açma) gibi birden fazla oturum açma yöntemini destekler.
Geçiş anahtarları birçok avantaj sağlar. Örneğin, geçiş anahtarları endüstri standartlarına göre tasarlanmıştır, farklı işletim sistemlerinde ve tarayıcı ekosistemlerinde çalışabilir, hem web sitelerinde hem de uygulamalarda kullanılabilir.
Daha fazla bilgi için Kimlik Bilgisi Yöneticisi ve geçiş anahtarları belgelerine ve Kimlik Bilgisi Yöneticisi ve geçiş anahtarları hakkındaki blog yayınına göz atın.
ve geri yükleme
Health Connect, kullanıcıların sağlık ve fitness verilerini saklayan cihaz üzerinde bir depolama alanıdır. Bu sayede kullanıcılar, en sevdikleri uygulamalar arasında veri paylaşabilir ve bu uygulamalarla hangi verileri paylaşmak istediklerini tek bir yerden kontrol edebilir.
Android 14'ten önceki Android sürümlerini çalıştıran cihazlarda Health Connect, Google Play Store'dan uygulama olarak indirilebilir. Android 14'ten itibaren Health Connect, platformun bir parçasıdır ve ayrı bir indirme işlemi gerektirmeden Google Play sistem güncellemeleri aracılığıyla güncelleme alır. Bu sayede Health Connect sık sık güncellenebilir ve uygulamalarınız, Health Connect'in Android 14 veya sonraki sürümleri çalıştıran cihazlarda kullanılabildiğinden emin olabilir. Kullanıcılar, sistem ayarlarına entegre edilmiş gizlilik denetimleriyle cihazlarındaki Ayarlar'dan Health Connect'e erişebilir.
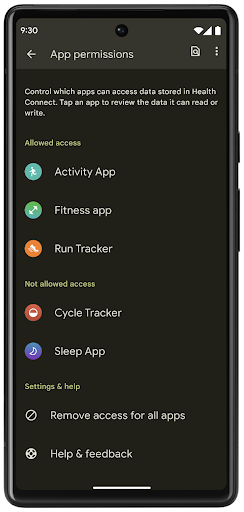
Health Connect, Android 14'te egzersiz rotaları gibi çeşitli yeni özellikler içerir. Bu özellikler sayesinde kullanıcılar, egzersiz rotalarını harita üzerinde görselleştirerek paylaşabilir. Rota, belirli bir zaman aralığında kaydedilen konumların listesi olarak tanımlanır. Uygulamanız, rotaları egzersiz oturumlarına ekleyerek bunları birbirine bağlayabilir. Kullanıcıların bu hassas veriler üzerinde tam kontrole sahip olması için kullanıcıların, rotaların tek tek diğer uygulamalarla paylaşılmasına izin vermesi gerekir.
Daha fazla bilgi için Health Connect dokümanlarına ve Android Sağlık'ta yenilikler başlıklı blog yayınına göz atın.
OpenJDK 17 güncellemeleri
Android 14, Android'in temel kitaplıklarını en son OpenJDK LTS sürümlerindeki özelliklerle uyumlu hale getirmek için yenileme çalışmalarına devam ediyor. Bu çalışmalara hem kitaplık güncellemeleri hem de uygulama ve platform geliştiricileri için Java 17 dil desteği dahildir.
Aşağıdaki özellikler ve iyileştirmeler dahildir:
- Yaklaşık 300
java.basesınıfı Java 17 desteği için güncellendi. - Java programlama diline çok satırlı dize değişmezleri getiren metin blokları.
- instanceof için kalıp eşleştirme: Bir nesnenin
instanceofiçinde ek değişkenler olmadan belirli bir türe sahipmiş gibi değerlendirilmesine olanak tanır. - Hangi sınıfların ve arayüzlerin bunları genişletebileceğini veya uygulayabileceğini kısıtlamanıza olanak tanıyan mühürlü sınıflar.
Google Play sistem güncellemeleri (Mainline projesi) sayesinde 600 milyondan fazla cihaz, bu değişiklikleri içeren en son Android Runtime (ART) güncellemelerini alabilir. Bu, uygulamalara cihazlar genelinde daha tutarlı ve güvenli bir ortam sunma ve kullanıcılara platform sürümlerinden bağımsız olarak yeni özellikler ve özellikler sunma taahhüdümüzün bir parçasıdır.
Java ve OpenJDK, Oracle ve/veya satış ortaklarının ticari markaları ya da tescilli ticari markalarıdır.
Uygulama mağazalarıyla ilgili iyileştirmeler
Android 14, uygulama mağazalarının kullanıcı deneyimini iyileştirmesine olanak tanıyan çeşitli PackageInstaller API'leri sunar.
İndirmeden önce yükleme onayı isteme
Uygulama yüklemek veya güncellemek için kullanıcı onayı gerekebilir.
Örneğin, REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES iznini kullanan bir yükleyici yeni bir uygulama yüklemeye çalıştığında. Önceki Android sürümlerinde uygulama mağazaları, yalnızca APK'lar yükleme oturumuna yazıldıktan ve oturum taahhüt edildikten sonra kullanıcı onayı isteyebilir.
Android 14'ten itibaren requestUserPreapproval() yöntemi, yükleyicilerin yükleme oturumunu önce kullanıcı onayı istemesine olanak tanır. Bu iyileştirme, uygulama mağazalarının APK'ları yüklemeyi, yükleme işlemi kullanıcı tarafından onaylanana kadar ertelemelerine olanak tanır. Ayrıca, kullanıcı yüklemeyi onayladıktan sonra uygulama mağazası, kullanıcıyı rahatsız etmeden uygulamayı arka planda indirip yükleyebilir.
Gelecekteki güncellemeler için sorumluluk alma
setRequestUpdateOwnership() yöntemi, yükleyicinin yüklediği bir uygulamanın gelecekteki güncellemelerinden sorumlu olmayı amaçladığını sisteme belirtmesine olanak tanır. Bu özellik, güncelleme sahipliği yaptırımını etkinleştirir. Bu sayede, uygulamaya otomatik güncelleme yüklenmesine yalnızca güncelleme sahibinin izin verilir. Güncelleme sahipliği yaptırımı, kullanıcıların yalnızca beklenen uygulama mağazasından güncelleme almasını sağlar.
INSTALL_PACKAGES iznini kullananlar da dahil olmak üzere diğer tüm yükleyicilerin, güncelleme yüklemek için açık kullanıcı onayı alması gerekir. Kullanıcı başka bir kaynaktan güncelleme yapmaya karar verirse güncelleme sahipliği kaybedilir.
Uygulamaları kullanıcıların günlük rutinini etkilemeyecek zamanlarda güncelleme
Uygulama mağazaları, etkin olarak kullanılan bir uygulamanın güncellenmesini genellikle istemez. Bunun nedeni, uygulamanın çalışan işlemlerinin sonlandırılmasıdır. Bu da kullanıcının yaptığı işlemi kesintiye uğratabilir.
Android 14'ten itibaren InstallConstraints API, yükleyicilere uygulama güncellemelerinin uygun bir zamanda yapılmasını sağlamanın bir yolunu sunar. Örneğin, bir uygulama mağazası, bir güncellemenin yalnızca kullanıcı söz konusu uygulamayla etkileşimde bulunmadığında kaydolmasını sağlamak için commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() yöntemini çağırabilir.
İsteğe bağlı bölmelerin sorunsuz şekilde yüklenmesi
Bölünmüş APK'lar sayesinde, bir uygulamanın özellikleri tek bir APK yerine ayrı APK dosyalarında yayınlanabilir. Bölünmüş APK'lar, uygulama mağazalarının farklı uygulama bileşenlerinin dağıtımını optimize etmesine olanak tanır. Örneğin, uygulama mağazaları hedef cihazın özelliklerine göre optimizasyon yapabilir. PackageInstaller API, API düzeyi 22'de kullanıma sunulmasından bu yana bölünmeleri desteklemektedir.
Android 14'te setDontKillApp() yöntemi, yükleyicinin yeni bölümler yüklenirken uygulamanın çalışan işlemlerinin sonlandırılmaması gerektiğini belirtmesine olanak tanır. Uygulama mağazaları, kullanıcı uygulamayı kullanırken uygulamanın yeni özelliklerini sorunsuz bir şekilde yüklemek için bu özelliği kullanabilir.
Uygulama meta verileri paketleri
Android 14'ten itibaren Android paket yükleyici, Google Play gibi uygulama mağazası sayfalarına dahil edilecek uygulama meta verilerini (ör. veri güvenliği uygulamaları) belirtmenize olanak tanır.
Kullanıcıların cihaz ekran görüntüsü aldığını algılama
Android 14, ekran görüntülerinin algılanması için daha standart bir deneyim oluşturmak amacıyla gizliliği korumaya yönelik bir ekran görüntüsü algılama API'si sunuyor. Bu API, uygulamaların etkinlik bazında geri çağırma işlevleri kaydetmesine olanak tanır. Bu geri çağırmalar, kullanıcı bu etkinlik görünürken ekran görüntüsü aldığında çağrılır ve kullanıcı bilgilendirilir.
Kullanıcı deneyimi
Paylaşım sayfasındaki özel işlemler ve iyileştirilmiş sıralama
Android 14, sistem paylaşım sayfasını özel uygulama işlemlerini ve kullanıcılar için daha bilgilendirici önizleme sonuçlarını destekleyecek şekilde günceller.
Özel işlem ekleme
Android 14 ile uygulamanız, çağırdığı sistem paylaşım sayfasına özel işlemler ekleyebilir.
Doğrudan Paylaşım hedeflerinin sıralamasını iyileştirme
Android 14, kullanıcıya daha faydalı sonuçlar sunmak için doğrudan paylaşım hedeflerinin sıralamasını belirlemek amacıyla uygulamalardan daha fazla sinyal kullanır. Sıralama için en faydalı sinyali sağlamak üzere doğrudan paylaşım hedeflerinizin sıralamalarına ilişkin yönergeleri uygulayın. İletişim uygulamaları, giden ve gelen mesajlar için kısayol kullanımını da bildirebilir.
Tahmine dayalı geri hareketi için yerleşik ve özel animasyon desteği
Android 13, geliştirici seçeneğiyle birlikte tahmine dayalı ana sayfaya geri gitme animasyonunu kullanıma sundu. Geliştirici seçeneği etkinleştirilmiş desteklenen bir uygulamada geri kaydırılırken, geri hareketinin uygulamadan çıkıp ana ekrana döndüğünü belirten bir animasyon gösterilir.
Android 14, Tahmini Geri özelliği için birden fazla iyileştirme ve yeni rehberlik içerir:
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueayarını, uygulamanın tamamı yerine etkinlik başına tahmine dayalı geri sistem animasyonlarını etkinleştirmek için ayarlayabilirsiniz.- Android 13'teki ana sayfaya geri gitme animasyonuna eşlik edecek yeni sistem animasyonları ekledik. Yeni sistem animasyonları, etkinlik ve görevler arasıdır ve Tahmine Dayalı Geri Gitme'ye geçtikten sonra otomatik olarak sunulur.
- Alt sayfalar, yan sayfalar ve Arama için yeni Material bileşen animasyonlarını ekledik.
- Özel uygulama içi animasyonlar ve geçişler oluşturmak için tasarım kılavuzu hazırladık.
- Özel uygulama içi geçiş animasyonlarını desteklemek için yeni API'ler ekledik:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Kullanıcı geri kaydırdığında yanıt veren geçişler için
overridePendingTransitionyerineoverrideActivityTransitionkullanın.
Bu Android 14 önizleme sürümünde, Tahmini Geri Yükleme'nin tüm özellikleri geliştirici seçeneği olarak sunulur. Uygulamanızı tahmini geriye taşıma ile ilgili geliştirici kılavuzunu ve özel uygulama içi geçişler oluşturma ile ilgili geliştirici kılavuzunu inceleyin.
Büyük ekranlı cihaz üreticilerinin uygulama başına geçersiz kılmaları
Uygulama başına geçersiz kılma, cihaz üreticilerinin büyük ekranlı cihazlardaki uygulamaların davranışını değiştirmesine olanak tanır. Örneğin, FORCE_RESIZE_APP geçersiz kılması, uygulama manifest'inde resizeableActivity="false" ayarlanmış olsa bile sisteme uygulamayı ekran boyutlarına sığacak şekilde yeniden boyutlandırması (boyut uyumluluk modundan kaçınarak) talimatını verir.
Geçersiz kılma işlemleri, büyük ekranlarda kullanıcı deneyimini iyileştirmeyi amaçlar.
Yeni manifest özellikleri, uygulamanız için bazı cihaz üreticisi geçersiz kılma işlemlerini devre dışı bırakmanızı sağlar.
Büyük ekran kullanıcıları için uygulama başına geçersiz kılmalar
Uygulama başına geçersiz kılmalar, büyük ekranlı cihazlardaki uygulamaların davranışını değiştirir. Örneğin, OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE cihaz üreticisi geçersiz kılma, uygulamanın yapılandırmasından bağımsız olarak uygulamanın en-boy oranını 16:9 olarak ayarlar.
Android 14 QPR1, kullanıcıların büyük ekranlı cihazlarda yeni bir ayarlar menüsü aracılığıyla uygulama başına geçersiz kılma işlemleri uygulamasını sağlar.
Uygulama ekran paylaşımı
Uygulama ekran paylaşımı, kullanıcıların ekran içeriği kaydı sırasında cihaz ekranının tamamı yerine bir uygulama penceresini paylaşmasını sağlar.
Uygulama ekranı paylaşımında durum çubuğu, gezinme çubuğu, bildirimler ve diğer sistem kullanıcı arayüzü öğeleri paylaşılan ekrandan hariç tutulur. Yalnızca seçilen uygulamanın içeriği paylaşılır.
Uygulama ekranı paylaşımı, kullanıcıların birden fazla uygulamayı çalıştırmasına olanak tanır ancak içerik paylaşımını tek bir uygulamayla sınırlandırır. Bu sayede üretkenliği ve gizliliği artırır.
Pixel 8 Pro'da Gboard'da LLM destekli Akıllı Yanıt
Aralık ayı özellik güncellemesini alan Pixel 8 Pro cihazlarda geliştiriciler, Google Tensor'da çalışan cihaz üzerinde büyük dil modelleri (LLM) tarafından desteklenen Gboard'da daha yüksek kaliteli akıllı yanıtları deneyebilir.
Bu özellik, WhatsApp, Line ve KakaoTalk'ta ABD İngilizcesi için sınırlı bir önizleme olarak sunulmaktadır. Klavyeniz olarak Gboard'u kullanan bir Pixel 8 Pro cihaz kullanmanız gerekir.
Bu özelliği denemek için önce Ayarlar > Geliştirici Seçenekleri > AICore Ayarları > Aicore Kalıcı'yı Etkinleştir'i seçerek özelliği etkinleştirin.
Ardından, desteklenen bir uygulamada bir ileti dizisi açın. Gboard'un öneri şeridinde, gelen iletilere yanıt olarak LLM destekli Akıllı Yanıt'ı görebilirsiniz.
Grafik
Yollar sorgulanabilir ve enterpolasyon yapılabilir
Android'in Path API'si, vektör grafikleri oluşturmaya ve oluşturmaya yönelik güçlü ve esnek bir mekanizmadır. Bir yolu çizme veya doldurma, çizgi segmentlerinden veya ikinci dereceden ya da kübik eğrilerden yol oluşturma, daha da karmaşık şekiller elde etmek için boole işlemleri veya bunların tümünü eş zamanlı olarak gerçekleştirme yeteneğine sahip. Bunun bir sınırlaması, Yol nesnesinde gerçekte neyin olduğunu bulma yeteneğidir. Nesnenin iç kısımları, oluşturulduktan sonra arayanlar için opak olur.
Path oluşturmak için moveTo(), lineTo() ve cubicTo() gibi yöntemleri çağırarak yol segmentleri ekleyebilirsiniz. Ancak bu yolda segmentlerin ne olduğunu sormanın bir yolu olmadığından, bu bilgileri oluşturma sırasında saklamanız gerekir.
Android 14'ten itibaren, içinde ne olduğunu öğrenmek için yolları sorgulayabilirsiniz.
Öncelikle, Path.getPathIterator API'yi kullanarak bir PathIterator nesnesi almanız gerekir:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Daha sonra, segmentleri tek tek güncellemek ve her bir segment için gerekli tüm verileri almak üzere PathIterator öğesini çağırabilirsiniz. Bu örnekte, verileri sizin için paketleyen PathIterator.Segment nesneleri kullanılmaktadır:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator, nokta verilerini tutmak için bir arabellek iletebileceğiniz, next()'un ayırt etmeyen bir sürümüne de sahiptir.
Path verilerini sorgulamanın önemli kullanım alanlarından biri de kesme noktasıdır. Örneğin, iki farklı yol arasında animasyon (veya morph) oluşturmak isteyebilirsiniz. Bu kullanım alanını daha da basitleştirmek için Android 14, Path üzerinde interpolate() yöntemini de içerir. İki yolun aynı dahili yapıya sahip olduğu varsayıldığında interpolate() yöntemi, ara değer alınan bu sonuçla yeni bir Path oluşturur. Bu örnek, şekli path ile otherPath arasında yarı yolda olan (0,5 değerinin doğrusal bir kesişimi) bir yol döndürür:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Jetpack graphics-path kitaplığı, Android'in önceki sürümleri için de benzer API'leri etkinleştirir.
Köşe ve parça gölgelendiricileri içeren özel ağlar
Android, özel gölgelemeyle üçgen ağ çizmeyi uzun süredir destekliyordu ancak giriş ağı biçimi, önceden tanımlanmış birkaç özellik kombinasyonuyla sınırlıydı. Android 14, üçgenler veya üçgen şeritler olarak tanımlanabilen ve isteğe bağlı olarak dizine eklenebilen özel ağlar için destek ekler. Bu ağlar, özel özellikler, köşe adımları, değişken ve AGSL'de yazılmış köşe ve parçacık gölgelendiricileriyle belirtilir.
Köşe noktası gölgelendirici, konum ve renk gibi değişkenleri tanımlar. Öte yandan, parçacık gölgelendirici, isteğe bağlı olarak pikselin rengini tanımlayabilir. Bu işlem genellikle köşe noktası gölgelendirici tarafından oluşturulan değişkenleri kullanarak yapılır. Renk, parçacık gölgelendirici tarafından sağlanırsa örgeyi çizerken seçilen karışım modu kullanılarak mevcut Paint rengiyle karıştırılır. Üniformalar, ek esneklik için parça ve köşe üstü gölgelendiricilere iletilebilir.
Canvas için donanım arabelleği oluşturucu
Çizim yapmak için Android'in Canvas API'sini kullanma konusunda yardımcı olmak
HardwareBuffer, Android 14 için donanım hızlandırma
HardwareBufferRenderer tanıtılıyor. Bu API
kullanım alanınız sistemle iletişimi içeriyorsa özellikle yararlıdır.
düşük gecikme için SurfaceControl aracılığıyla birleştirici
çizim.
