Android 14 มีฟีเจอร์และ API ที่ยอดเยี่ยมสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป ความช่วยเหลือต่อไปนี้จะช่วย ให้คุณทราบเกี่ยวกับฟีเจอร์สำหรับแอปและเริ่มต้นใช้งาน API ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ดูรายการ API ที่เพิ่ม แก้ไข และนำออกโดยละเอียดได้ในรายงานความแตกต่างของ API ดูรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับ API ที่เพิ่มได้ที่เอกสารอ้างอิง Android API สำหรับ Android 14 ให้มองหา API ที่เพิ่มใน API ระดับ 34 หากต้องการดูข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับส่วนที่การเปลี่ยนแปลงของแพลตฟอร์มอาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ โปรดดูการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานของ Android 14 สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 14 และสำหรับแอปทั้งหมด
การทำให้เป็นสากล
ค่ากำหนดภาษาที่ใช้ในแอป
Android 14 ขยายฟีเจอร์ภาษาต่อแอปที่เปิดตัวใน Android 13 (API ระดับ 33) ด้วยความสามารถเพิ่มเติมต่อไปนี้
สร้าง
localeConfigของแอปโดยอัตโนมัติ: ตั้งแต่ Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 และ AGP 8.1.0-alpha07 เป็นต้นไป คุณสามารถกําหนดค่าแอปให้รองรับค่ากําหนดภาษาของแต่ละแอปโดยอัตโนมัติ ปลั๊กอิน Android Gradle จะสร้างไฟล์LocaleConfigและเพิ่มการอ้างอิงไฟล์ดังกล่าวในไฟล์ Manifest สุดท้ายโดยอิงตามทรัพยากรของโปรเจ็กต์ คุณจึงไม่ต้องสร้างหรืออัปเดตไฟล์ด้วยตนเองอีกต่อไป AGP ใช้ทรัพยากรในโฟลเดอร์resของโมดูลแอปและทรัพยากร Dependency ของโมดูลไลบรารีเพื่อระบุภาษาที่จะรวมไว้ในไฟล์LocaleConfigการอัปเดตแบบไดนามิกสำหรับ
localeConfigของแอป: ใช้วิธีในsetOverrideLocaleConfig()และgetOverrideLocaleConfig()ในLocaleManagerเพื่ออัปเดตรายการภาษาที่รองรับของแอปแบบไดนามิกในการตั้งค่าระบบของอุปกรณ์ ใช้ความยืดหยุ่นนี้เพื่อปรับแต่งรายการภาษาที่รองรับตามภูมิภาค ทำการทดสอบ A/B หรือระบุรายการภาษาที่อัปเดตแล้วหากแอปใช้การพุชฝั่งเซิร์ฟเวอร์สำหรับการแปลระดับการเข้าถึงภาษาของแอปสําหรับตัวแก้ไขวิธีการป้อนข้อมูล (IME): IME สามารถใช้วิธี
getApplicationLocales()เพื่อตรวจสอบภาษาของแอปปัจจุบันและจับคู่ภาษา IME กับภาษานั้น
Grammatical Inflection API
ผู้คนกว่า 3 พันล้านคนพูดภาษาที่มีเพศ ซึ่งเป็นภาษาที่คำในหมวดหมู่ทางไวยากรณ์ เช่น คำนาม คำกริยา คำคุณศัพท์ และคำบุพบท จะผันตามเพศของบุคคลและวัตถุที่คุณพูดด้วยหรือพูดถึง โดยทั่วไปแล้ว ภาษาที่มีเพศหลายเพศหลายภาษาใช้เพศทางไวยากรณ์เพศชายเป็นเพศเริ่มต้นหรือเพศทั่วไป
การเรียกผู้ใช้ด้วยเพศทางไวยากรณ์ที่ไม่ถูกต้อง เช่น การเรียกผู้หญิงด้วยเพศทางไวยากรณ์ของผู้ชาย อาจส่งผลเสียต่อประสิทธิภาพและทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ ในทางตรงกันข้าม UI ที่มีภาษาที่แสดงเพศตามไวยากรณ์ของผู้ใช้อย่างถูกต้องจะช่วยเพิ่มการมีส่วนร่วมของผู้ใช้ และมอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับผู้ใช้แต่ละคนและฟังดูเป็นธรรมชาติมากขึ้น
Android 14 เปิดตัว Grammatical Inflection API เพื่อช่วยคุณสร้าง UI ที่เน้นผู้ใช้สำหรับภาษาที่มีเพศแบบกำหนดเพศทางไวยากรณ์ ซึ่งจะช่วยให้คุณเพิ่มการรองรับเพศทางไวยากรณ์ได้โดยไม่ต้องรีแฟกทอริงแอป
ค่ากำหนดตามพื้นที่
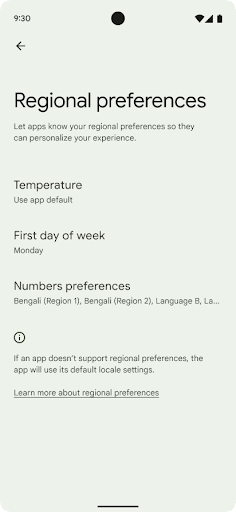
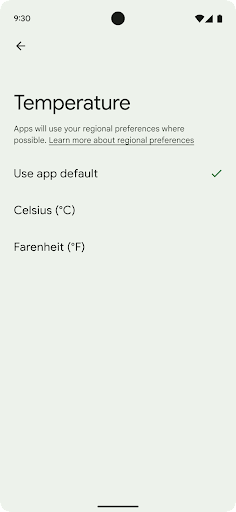
ค่ากำหนดระดับภูมิภาคช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ปรับเปลี่ยนหน่วยอุณหภูมิในแบบของคุณได้ วันของสัปดาห์ และระบบลำดับตัวเลข ชาวยุโรปที่อาศัยอยู่ในสหรัฐอเมริกา คุณอาจต้องการให้หน่วยอุณหภูมิเป็นเซลเซียสมากกว่าฟาเรนไฮต์ และสำหรับ แอปที่กำหนดให้วันจันทร์เป็นวันเริ่มต้นของสัปดาห์แทนที่จะเป็นค่าเริ่มต้นของสหรัฐอเมริกา วันอาทิตย์
เมนูใหม่ในการตั้งค่า Android สำหรับค่ากำหนดเหล่านี้ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้สามารถ
ตำแหน่งส่วนกลางที่ค้นพบได้เพื่อเปลี่ยนค่ากำหนดของแอป การตั้งค่าเหล่านี้จะยังคงอยู่ผ่านการสํารองและคืนค่าด้วย API และ Intent หลายรายการ เช่น getTemperatureUnit และ getFirstDayOfWeek จะให้สิทธิ์แอปของคุณอ่านค่ากําหนดของผู้ใช้ เพื่อให้แอปปรับวิธีแสดงข้อมูลได้ นอกจากนี้ คุณยังจดทะเบียน
BroadcastReceiver ใน
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
เพื่อจัดการการเปลี่ยนแปลงการกำหนดค่าภาษาเมื่อค่ากำหนดระดับภูมิภาคมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงได้
หากต้องการค้นหาการตั้งค่าเหล่านี้ ให้เปิดแอปการตั้งค่าแล้วไปที่ระบบ >ภาษาและการป้อนข้อมูล > ค่ากําหนดระดับภูมิภาค
การช่วยเหลือพิเศษ
การปรับขนาดแบบอักษรที่ไม่ใช่แบบเชิงเส้นเป็น 200%
ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป ระบบจะรองรับการปรับขนาดแบบอักษรได้สูงสุด 200% เพื่อให้ผู้ใช้มีตัวเลือกการช่วยเหลือพิเศษเพิ่มเติม
ระบบจะใช้เส้นโค้งการปรับขนาดแบบไม่เชิงเส้นเพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้องค์ประกอบข้อความขนาดใหญ่บนหน้าจอมีขนาดใหญ่เกินไป กลยุทธ์การปรับขนาดนี้หมายความว่าข้อความขนาดใหญ่ จะไม่ปรับขนาดในอัตราเดียวกับข้อความขนาดเล็ก การปรับขนาดแบบอักษรที่ไม่ใช่แบบเชิงเส้นช่วย รักษาลำดับชั้นตามสัดส่วนระหว่างองค์ประกอบที่มีขนาดต่างกัน ขณะเดียวกันก็ ลดปัญหาเกี่ยวกับการปรับขนาดข้อความเชิงเส้นในระดับสูง (เช่น ข้อความถูก ตัดออกหรือข้อความที่อ่านยากขึ้นเนื่องจากขนาดจอแสดงผลที่ใหญ่มาก)
ทดสอบแอปด้วยการปรับขนาดแบบอักษรที่ไม่ใช่แบบเชิงเส้น
หากคุณใช้หน่วยพิกเซลที่รองรับการปรับขนาด (sp) เพื่อกำหนดขนาดข้อความอยู่แล้ว ระบบจะใช้ตัวเลือกเพิ่มเติมและการปรับปรุงการปรับขนาดเหล่านี้กับข้อความในแอปโดยอัตโนมัติ อย่างไรก็ตาม คุณยังคงควรทำการทดสอบ UI โดยเปิดใช้ขนาดแบบอักษรสูงสุด (200%) เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าแอปใช้ขนาดแบบอักษรอย่างถูกต้องและรองรับขนาดแบบอักษรที่ใหญ่ขึ้นได้โดยไม่ส่งผลต่อความสามารถในการใช้งาน
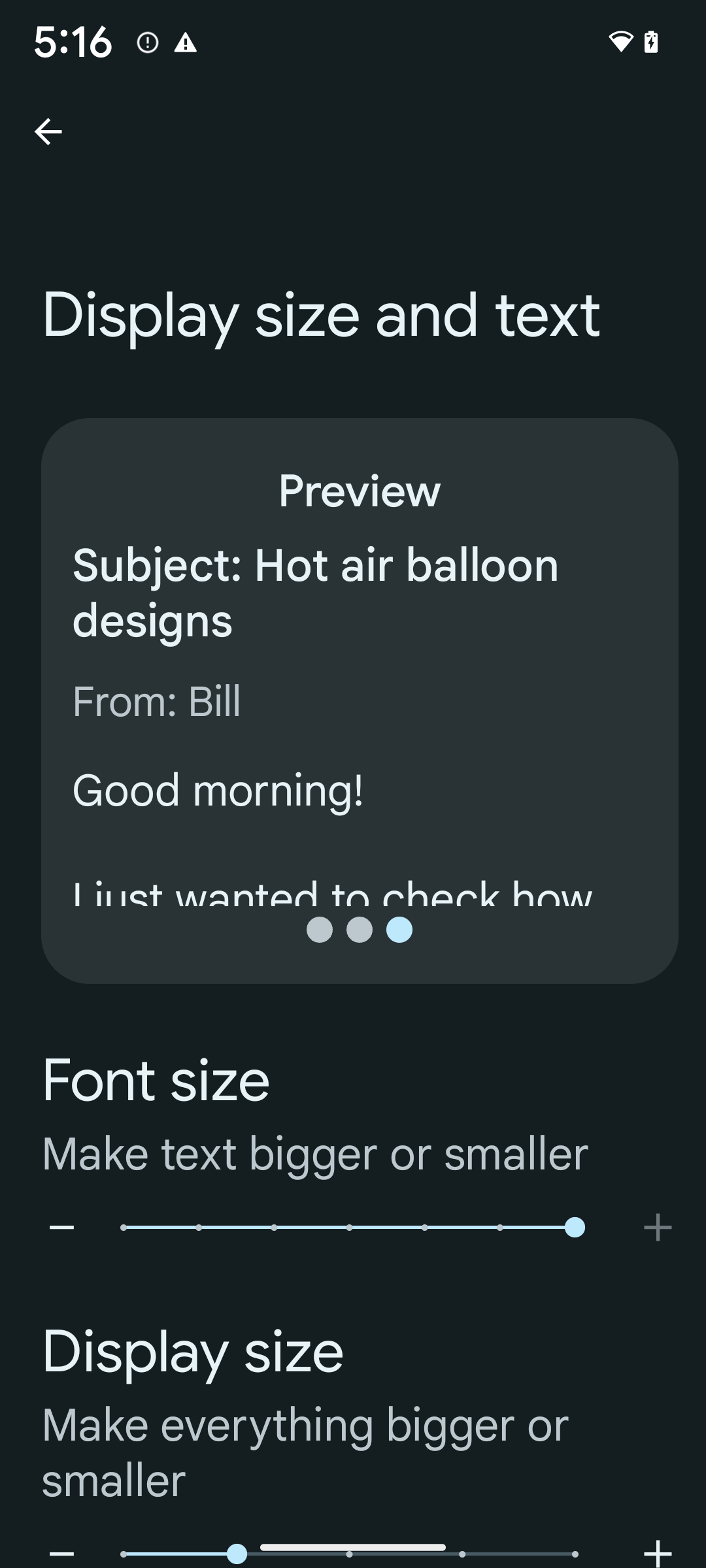
หากต้องการเปิดใช้ขนาดแบบอักษร 200% ให้ทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้
- เปิดแอปการตั้งค่า แล้วไปที่การช่วยเหลือพิเศษ > ขนาดการแสดงผลและข้อความ
- สำหรับตัวเลือกขนาดแบบอักษร ให้แตะไอคอนบวก (+) จนกว่าจะเปิดใช้การตั้งค่าขนาดแบบอักษรสูงสุด ดังที่แสดงในรูปภาพที่มาพร้อมกับส่วนนี้
ใช้หน่วยพิกเซลที่ปรับขนาดแล้ว (sp) สำหรับขนาดข้อความ
โปรดอย่าลืมระบุขนาดข้อความในหน่วย sp เสมอ เมื่อ แอปใช้หน่วย sp ระบบ Android จะใช้ขนาดข้อความที่ผู้ใช้ต้องการและ ปรับขนาดอย่างเหมาะสมได้
อย่าใช้หน่วย sp สำหรับระยะห่างจากขอบหรือกำหนดความสูงของมุมมองโดยสมมติว่ามีระยะห่างจากขอบโดยนัย เมื่อใช้การปรับขนาดแบบไม่เชิงเส้นแบบอักษร ขนาด sp อาจไม่เป็นสัดส่วน ดังนั้น 4sp + 20sp อาจไม่เท่ากับ 24sp
แปลงหน่วยพิกเซลที่ปรับขนาด (sp)
ใช้ TypedValue.applyDimension() เพื่อแปลงจากหน่วย sp เป็นพิกเซล และใช้ TypedValue.deriveDimension() เพื่อแปลงพิกเซลเป็น sp วิธีการเหล่านี้จะใช้เส้นโค้งการปรับขนาดแบบไม่เชิงเส้นที่เหมาะสมโดยอัตโนมัติ
หลีกเลี่ยงการฮาร์ดโค้ดสมการโดยใช้
Configuration.fontScale หรือ
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity เนื่องจากการปรับขนาดแบบอักษรเป็นแบบไม่เชิงเส้น scaledDensity จึงไม่ถูกต้องอีกต่อไป ควรใช้ฟิลด์ fontScale
เพื่อวัตถุประสงค์ในการให้ข้อมูลเท่านั้น เนื่องจากระบบจะไม่
ปรับขนาดแบบอักษรด้วยค่าสเกลาร์ค่าเดียวอีกต่อไป
ใช้หน่วย sp สำหรับ lineHeight
กำหนด android:lineHeight โดยใช้หน่วย sp แทน
หน่วย dp เสมอ เพื่อให้ความสูงของบรรทัดปรับขนาดไปพร้อมกับข้อความ มิฉะนั้น หากข้อความ
เป็น sp แต่lineHeightเป็น dp หรือ px ข้อความจะไม่ปรับขนาดและดูอึดอัด
TextView จะแก้ไข lineHeight โดยอัตโนมัติเพื่อให้สัดส่วนที่คุณต้องการยังคงอยู่ แต่จะทำเช่นนี้ได้ก็ต่อเมื่อมีการกำหนดทั้ง textSize และ lineHeight ในหน่วย sp
กล้องและสื่อ
Ultra HDR สำหรับรูปภาพ

Android 14 เพิ่มการรองรับรูปภาพ High Dynamic Range (HDR) ที่จะเก็บข้อมูลจากเซ็นเซอร์ได้มากขึ้นเมื่อถ่ายภาพ ซึ่งช่วยให้สีสันสดใสและคอนทราสต์มากขึ้น Android ใช้รูปแบบ Ultra HDR ซึ่งเข้ากันได้กับรูปภาพ JPEG อย่างสมบูรณ์ ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปทำงานร่วมกับรูปภาพ HDR ได้อย่างราบรื่น โดยแสดงรูปภาพในรูปแบบมาตรฐานไดนามิกเรนจ์ (SDR) ตามต้องการ
เฟรมเวิร์กจะแสดงผลรูปภาพเหล่านี้ใน UI เป็น HDR โดยอัตโนมัติเมื่อแอปเลือกใช้ UI HDR สำหรับกรอบเวลากิจกรรม ไม่ว่าจะผ่านรายการไฟล์ Manifest หรือที่รันไทม์โดยการเรียกใช้ Window.setColorMode() นอกจากนี้ คุณยังจับภาพภาพนิ่ง HDR แบบ Ultra ที่บีบอัดในอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับได้ด้วย การกู้คืนสีจากเซ็นเซอร์ได้มากขึ้นช่วยให้การแก้ไขในขั้นตอนหลังมีความยืดหยุ่นมากขึ้น คุณสามารถใช้ Gainmap ที่เชื่อมโยงกับภาพ Ultra HDR เพื่อแสดงผลภาพโดยใช้ OpenGL หรือ Vulkan
ซูม โฟกัส ดูตัวอย่างหลังถ่าย และอื่นๆ ในส่วนขยายกล้อง
Android 14 อัปเกรดและปรับปรุงส่วนขยายกล้อง ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปประมวลผลได้นานขึ้น จึงให้รูปภาพที่ดีขึ้นโดยใช้อัลกอริทึมที่ต้องใช้การประมวลผลอย่างหนัก เช่น การถ่ายภาพในที่แสงน้อยในอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับ ฟีเจอร์เหล่านี้ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ได้รับประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่มีประสิทธิภาพยิ่งขึ้นเมื่อใช้ความสามารถของส่วนขยายกล้อง ตัวอย่างการปรับปรุงเหล่านี้ ได้แก่
- การประมาณเวลาในการตอบสนองของการประมวลผลภาพนิ่งแบบไดนามิกจะให้ค่าประมาณเวลาในการตอบสนองของภาพนิ่งที่แม่นยำกว่ามากโดยอิงตามฉากปัจจุบันและสภาพสภาพแวดล้อม โทรไปที่
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()เพื่อรับออบเจ็กต์StillCaptureLatencyที่มีวิธีการประมาณเวลาในการตอบสนอง 2 วิธี เมธอดgetCaptureLatency()จะแสดงผลเวลาในการตอบสนองโดยประมาณระหว่างonCaptureStartedกับonCaptureProcessStarted()และเมธอดgetProcessingLatency()จะแสดงผลเวลาในการตอบสนองโดยประมาณระหว่างonCaptureProcessStarted()กับเวลาที่เฟรมที่ประมวลผลแล้วเฟรมสุดท้ายพร้อมใช้งาน - รองรับการเรียกกลับความคืบหน้าในการจับภาพเพื่อให้แอปแสดงความคืบหน้าปัจจุบันของการดำเนินการประมวลผลภาพนิ่งที่ทำงานต่อเนื่องเป็นเวลานาน คุณสามารถตรวจสอบว่าฟีเจอร์นี้พร้อมใช้งานใน
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailableหรือไม่ หากพร้อมใช้งาน คุณก็สามารถใช้การเรียกกลับonCaptureProcessProgressed()ซึ่งจะส่งความคืบหน้า (จาก 0 ถึง 100) เป็นพารามิเตอร์ ข้อมูลเมตาเฉพาะของชิ้นงาน เช่น
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHสำหรับปรับระดับเอฟเฟกต์ของชิ้นงาน เช่น ระดับการเบลอพื้นหลังEXTENSION_BOKEHฟีเจอร์ดูภาพหลังถ่ายสําหรับการจับภาพนิ่งในส่วนขยายกล้อง ซึ่งจะแสดงภาพที่ประมวลผลน้อยลงได้เร็วกว่าภาพสุดท้าย หากชิ้นงานมีความล่าช้าในการประมวลผลเพิ่มขึ้น คุณอาจระบุรูปภาพหลังดูเป็นตัวยึดตําแหน่งเพื่อปรับปรุง UX และเปลี่ยนเป็นรูปภาพสุดท้ายในภายหลัง คุณสามารถตรวจสอบว่าฟีเจอร์นี้พร้อมใช้งานใน
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailableหรือไม่ จากนั้นคุณสามารถส่งOutputConfigurationไปยังExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfigurationได้การรองรับ
SurfaceViewซึ่งช่วยให้เส้นทางการแสดงผลตัวอย่างได้รับการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพและประหยัดพลังงานมากขึ้นรองรับการแตะเพื่อโฟกัสและซูมระหว่างการใช้ส่วนขยาย
การซูมในเซ็นเซอร์
เมื่อ REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE ใน
CameraCharacteristics มี
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW แอปของคุณจะใช้ความสามารถขั้นสูงของเซ็นเซอร์เพื่อให้สตรีม RAW ที่ครอบตัดมีจำนวนพิกเซลเท่ากับมุมมองแบบเต็มได้โดยใช้ CaptureRequest ที่มีเป้าหมาย RAW ซึ่งตั้งค่า Use Case ของสตรีมเป็น CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW
การใช้การควบคุมการลบล้างคําขอช่วยให้กล้องที่อัปเดตแล้วให้ผู้ใช้ควบคุมการซูมได้ก่อนที่ตัวควบคุมกล้องอื่นๆ จะพร้อมใช้งาน
เสียง USB แบบไม่สูญเสียข้อมูล
Android 14 รองรับรูปแบบเสียงแบบไม่สูญเสียคุณภาพเพื่อให้คุณได้รับประสบการณ์ระดับออดิโอไฟล์ผ่านชุดหูฟังแบบใช้สาย USB คุณสามารถค้นหาอุปกรณ์ USB เพื่อดูแอตทริบิวต์ของมิกเซอร์ที่ต้องการ ลงทะเบียนโปรแกรมรับฟังการเปลี่ยนแปลงแอตทริบิวต์ของมิกเซอร์ที่ต้องการ และกำหนดค่าแอตทริบิวต์ของมิกเซอร์โดยใช้คลาส AudioMixerAttributes คลาสนี้แสดงรูปแบบ เช่น มาสก์ช่อง อัตราตัวอย่าง และลักษณะการทำงานของมิกเซอร์เสียง คลาสนี้ช่วยให้ส่งเสียงได้โดยตรงโดยไม่ต้องผสม ปรับระดับเสียง หรือประมวลผลเอฟเฟกต์
ประสิทธิภาพการทำงานและเครื่องมือสำหรับนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์
Credential Manager
Android 14 เพิ่ม Credential Manager เป็น API ของแพลตฟอร์ม โดยรองรับอุปกรณ์ Android 4.4 (API ระดับ 19) เพิ่มเติมผ่านคลัง Jetpack โดยใช้บริการ Google Play Credential Manager มีเป้าหมายเพื่อช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ลงชื่อเข้าใช้ได้ง่ายขึ้นด้วย API ที่ดึงข้อมูลและจัดเก็บข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบด้วยผู้ให้บริการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบที่ผู้ใช้กําหนดค่าไว้ Credential Manager รองรับวิธีการลงชื่อเข้าใช้หลายวิธี รวมถึงชื่อผู้ใช้และรหัสผ่าน พาสคีย์ และโซลูชันการลงชื่อเข้าใช้แบบรวมศูนย์ (เช่น ฟีเจอร์ลงชื่อเข้าใช้ด้วย Google) ใน API เดียว
พาสคีย์มีข้อดีหลายประการ เช่น พาสคีย์สร้างขึ้นตามมาตรฐานอุตสาหกรรม ทำงานได้กับระบบปฏิบัติการและระบบนิเวศของเบราว์เซอร์ต่างๆ รวมถึงใช้ได้กับทั้งเว็บไซต์และแอป
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่เอกสารประกอบเกี่ยวกับเครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบและพาสคีย์และบล็อกโพสต์เกี่ยวกับเครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบและพาสคีย์
Health Connect
Health Connect เป็นพื้นที่เก็บข้อมูลในอุปกรณ์สำหรับข้อมูลสุขภาพและการออกกำลังกายของผู้ใช้ ซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้แชร์ข้อมูลระหว่างแอปโปรดได้โดยมีที่เดียวในการควบคุมข้อมูลที่ต้องการแชร์กับแอปเหล่านี้
ในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android เวอร์ชันก่อน Android 14 คุณจะดาวน์โหลด Health Connect ในรูปแบบแอปได้ใน Google Play Store ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป Health Connect จะเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแพลตฟอร์มและได้รับการอัปเดตผ่านการอัปเดตระบบ Google Play โดยไม่ต้องดาวน์โหลดแยกต่างหาก ซึ่งจะช่วยให้ Health Connect ได้รับการอัปเดตบ่อยครั้ง และแอปของคุณจะใช้ Health Connect ได้บนอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 14 ขึ้นไป ผู้ใช้สามารถเข้าถึง Health Connect ได้จากการตั้งค่าในอุปกรณ์ โดยจะมีการควบคุมความเป็นส่วนตัวที่ผสานรวมอยู่ในการตั้งค่าระบบ
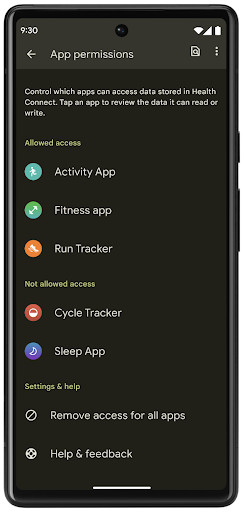
Health Connect มีฟีเจอร์ใหม่ๆ หลายอย่างใน Android 14 เช่น เส้นทางออกกำลังกาย ซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้แชร์เส้นทางการออกกําลังกายที่แสดงเป็นภาพบนแผนที่ได้ เส้นทางหมายถึงรายการสถานที่ที่บันทึกไว้ภายในกรอบเวลาหนึ่งๆ และแอปของคุณสามารถแทรกเส้นทางลงในเซสชันการออกกำลังกายเพื่อเชื่อมโยงเข้าด้วยกัน ผู้ใช้ต้องอนุญาตให้แชร์เส้นทางแต่ละเส้นทางกับแอปอื่นๆ เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าผู้ใช้มีสิทธิ์ควบคุมข้อมูลที่ละเอียดอ่อนนี้อย่างสมบูรณ์
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่เอกสารประกอบเกี่ยวกับการเชื่อมต่อ Health และบล็อกโพสต์เกี่ยวกับมีอะไรใหม่ใน Android Health
การอัปเดต OpenJDK 17
Android 14 ยังคงปรับปรุงไลบรารีหลักของ Android ให้สอดคล้องกับฟีเจอร์ใน OpenJDK LTS เวอร์ชันล่าสุด ซึ่งรวมถึงทั้งการอัปเดตไลบรารีและการรองรับภาษา Java 17 สําหรับนักพัฒนาแอปและแพลตฟอร์ม
ฟีเจอร์และการปรับปรุงต่อไปนี้จะรวมอยู่ด้วย
- อัปเดตคลาส
java.baseประมาณ 300 คลาสให้รองรับ Java 17 - บล็อกข้อความ ซึ่งจะนําสตริงตัวอักษรหลายบรรทัดมาสู่ภาษาโปรแกรม Java
- การจับคู่รูปแบบสำหรับ instanceof ซึ่งช่วยให้ระบบถือว่าออบเจ็กต์มีประเภทที่เฉพาะเจาะจงใน
instanceofโดยไม่ต้องมีตัวแปรเพิ่มเติม - คลาสที่ปิด ซึ่งช่วยให้คุณจำกัดคลาสและอินเทอร์เฟซที่ขยายหรือนำไปใช้ได้
การอัปเดตระบบ Google Play (Project Mainline) ช่วยให้อุปกรณ์กว่า 600 ล้านเครื่องสามารถรับการอัปเดต Android Runtime (ART) ล่าสุดที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ ซึ่งเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของความมุ่งมั่นของเราที่จะมอบสภาพแวดล้อมที่ปลอดภัยและสอดคล้องกันมากขึ้นให้แก่แอปในอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ รวมถึงมอบฟีเจอร์และความสามารถใหม่ๆ ให้แก่ผู้ใช้โดยไม่ขึ้นอยู่กับรุ่นของแพลตฟอร์ม
Java และ OpenJDK เป็นเครื่องหมายการค้าหรือเครื่องหมายการค้าจดทะเบียนของ Oracle และ/หรือบริษัทในเครือ
การปรับปรุงสำหรับ App Store
Android 14 เปิดตัว PackageInstaller API หลายรายการที่ช่วยปรับปรุงประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้สำหรับ App Store
ขอการอนุมัติการติดตั้งก่อนดาวน์โหลด
การติดตั้งหรืออัปเดตแอปอาจต้องการอนุมัติของผู้ใช้
เช่น เมื่อผู้ติดตั้งที่ใช้สิทธิ์ REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES พยายามติดตั้งแอปใหม่ ใน Android เวอร์ชันก่อนๆ แอปสโตร์จะขอการอนุมัติจากผู้ใช้ได้หลังจากมีการเขียน APK ลงในเซสชันการติดตั้งและบันทึกเซสชันแล้วเท่านั้น
ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป เมธอด requestUserPreapproval() จะอนุญาตให้ผู้ติดตั้งขอการอนุมัติจากผู้ใช้ก่อนยืนยันเซสชันการติดตั้ง การปรับปรุงนี้ช่วยให้ App Store เลื่อนการดาวน์โหลด APK ไว้ได้จนกว่าจะได้รับการอนุมัติการติดตั้งจากผู้ใช้ นอกจากนี้ เมื่อผู้ใช้อนุมัติการติดตั้งแล้ว แอปสโตร์จะดาวน์โหลดและติดตั้งแอปในเบื้องหลังได้โดยไม่รบกวนผู้ใช้
อ้างความรับผิดชอบสำหรับการอัปเดตในอนาคต
วิธีการ setRequestUpdateOwnership() ช่วยให้ผู้ติดตั้งระบุต่อระบบว่าตนตั้งใจที่จะรับผิดชอบต่อการอัปเดตแอปที่ติดตั้งในอนาคต ความสามารถนี้ช่วยให้สามารถบังคับใช้การเป็นเจ้าของการอัปเดตได้ ซึ่งหมายความว่ามีเพียงเจ้าของการอัปเดตเท่านั้นที่ได้รับอนุญาตให้ติดตั้งการอัปเดตอัตโนมัติในแอป การบังคับใช้การเป็นเจ้าของการอัปเดตช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ว่าผู้ใช้จะได้รับอัปเดตจาก App Store ที่คาดไว้เท่านั้น
โปรแกรมติดตั้งอื่นๆ รวมถึงโปรแกรมที่ใช้สิทธิ์ INSTALL_PACKAGES จะต้องได้รับอนุมัติจากผู้ใช้อย่างชัดเจนจึงจะติดตั้งการอัปเดตได้ หากผู้ใช้ตัดสินใจที่จะอัปเดตจากแหล่งที่มาอื่น ความเป็นเจ้าของการอัปเดตจะหายไป
อัปเดตแอปในเวลาที่รบกวนน้อยลง
โดยปกติแล้ว App Store ต้องการหลีกเลี่ยงการอัปเดตแอปที่ผู้ใช้กำลังใช้งานอยู่ เนื่องจากจะส่งผลให้กระบวนการที่ทำงานอยู่ของแอปหยุดลง ซึ่งอาจขัดจังหวะสิ่งที่ผู้ใช้กำลังทำอยู่
ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป InstallConstraints API จะเปิดโอกาสให้ผู้ติดตั้งตรวจสอบว่าการอัปเดตแอปเกิดขึ้นในเวลาที่เหมาะสม ตัวอย่างเช่น แอปสโตร์สามารถเรียกใช้เมธอด commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าการอัปเดตจะดำเนินการต่อเมื่อผู้ใช้ไม่ได้โต้ตอบกับแอปที่เป็นปัญหาแล้ว
ติดตั้งส่วนแยกที่ไม่บังคับได้อย่างราบรื่น
เมื่อใช้ APK แบบแยก คุณจะส่งฟีเจอร์ของแอปเป็นไฟล์ APK แยกต่างหากได้ แทนที่จะส่งเป็น APK แบบรวม APK แบบแยกช่วยให้ App Store เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการนำส่งคอมโพเนนต์ต่างๆ ของแอปได้ เช่น แอปสโตร์อาจเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพตามพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ของอุปกรณ์เป้าหมาย PackageInstaller API รองรับการแยกตั้งแต่เปิดตัวใน API ระดับ 22
ใน Android 14 วิธีการ setDontKillApp() ช่วยให้ผู้ติดตั้งระบุได้ว่าไม่ควรหยุดกระบวนการที่ทำงานอยู่ของแอปเมื่อติดตั้งแยกใหม่ App Store สามารถใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้เพื่อติดตั้งฟีเจอร์ใหม่ของแอปได้อย่างราบรื่นขณะที่ผู้ใช้กำลังใช้แอปอยู่
App Bundle ข้อมูลเมตา
ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป เครื่องมือติดตั้งแพ็กเกจ Android จะช่วยให้คุณระบุข้อมูลเมตาของแอป เช่น แนวทางปฏิบัติด้านความปลอดภัยของข้อมูล เพื่อรวมไว้ในหน้าร้านค้าแอป เช่น Google Play
ตรวจหาเวลาที่ผู้ใช้ถ่ายภาพหน้าจอของอุปกรณ์
Android 14 ได้เปิดตัว API การตรวจหาภาพหน้าจอที่รักษาความเป็นส่วนตัวเพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ได้มาตรฐานมากขึ้นสำหรับการตรวจหาภาพหน้าจอ API นี้ช่วยให้แอปสามารถลงทะเบียนการเรียกกลับตามกิจกรรม ระบบจะเรียกใช้ การเรียกกลับเหล่านี้และแจ้งเตือนผู้ใช้เมื่อผู้ใช้ จับภาพหน้าจอขณะที่กิจกรรมนั้นแสดงอยู่
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้
การทำงานที่กำหนดเองของชีตการแชร์และการจัดอันดับที่ดียิ่งขึ้น
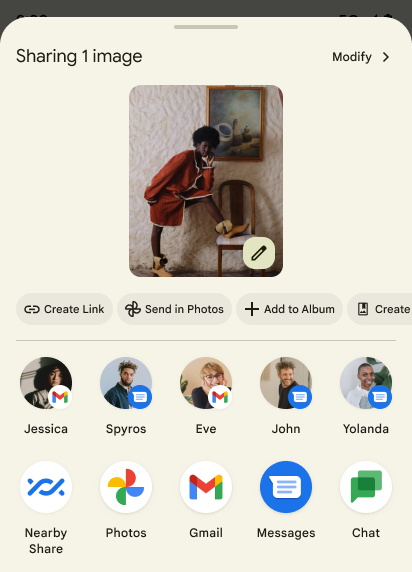
Android 14 อัปเดตชีตการแชร์ของระบบเพื่อรองรับการดำเนินการของแอปที่กำหนดเองและแสดงตัวอย่างผลลัพธ์ที่เป็นประโยชน์มากขึ้นสำหรับผู้ใช้
เพิ่มการดําเนินการที่กำหนดเอง
เมื่อใช้ Android 14 แอปของคุณจะเพิ่มการดำเนินการที่กำหนดเองลงในชีตการแชร์ของระบบที่เรียกใช้
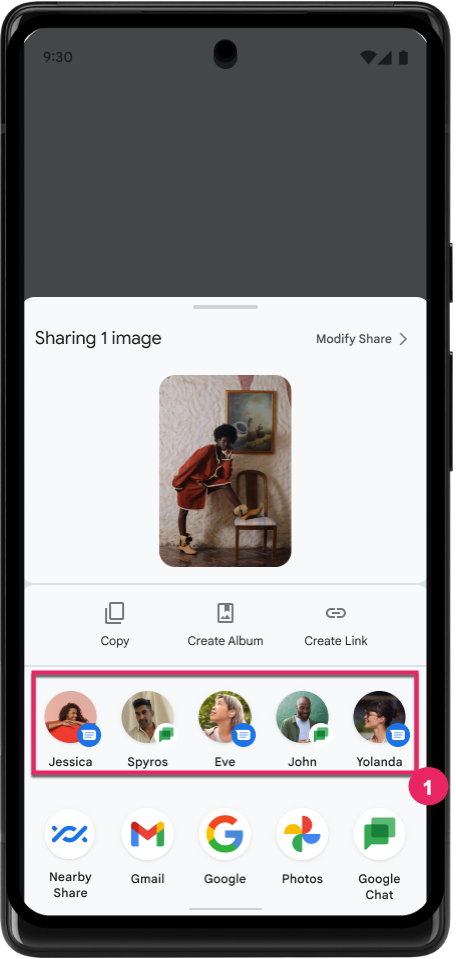
ปรับปรุงการจัดอันดับของเป้าหมายการแชร์โดยตรง
Android 14 ใช้สัญญาณจากแอปมากขึ้นเพื่อกำหนดการจัดอันดับของเป้าหมายการแชร์โดยตรงเพื่อให้ผลการค้นหาที่เป็นประโยชน์มากขึ้นแก่ผู้ใช้ โปรดปฏิบัติตามคำแนะนำสำหรับการปรับปรุงการจัดอันดับของเป้าหมายการแชร์โดยตรงเพื่อให้สัญญาณที่มีประโยชน์มากที่สุดสำหรับการจัดอันดับ นอกจากนี้ แอปการสื่อสารยังรายงานการใช้งานแป้นพิมพ์ลัดสำหรับข้อความขาออกและขาเข้าได้ด้วย
รองรับภาพเคลื่อนไหวในตัวและภาพเคลื่อนไหวที่กำหนดเองสำหรับท่าทางสัมผัสย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดา
Android 13 ได้เปิดตัวภาพเคลื่อนไหวแบบคาดเดาซึ่งนำผู้ใช้กลับไปยังหน้าจอหลักจากตัวเลือกของนักพัฒนาแอป เมื่อใช้ในแอปที่รองรับซึ่งเปิดใช้ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป การปัดย้อนกลับจะแสดงภาพเคลื่อนไหวที่ระบุว่าท่าทางสัมผัสย้อนกลับจะนำออกจากแอปกลับไปที่หน้าจอหลัก
Android 14 มีการปรับปรุงหลายอย่างและคำแนะนำใหม่สำหรับฟีเจอร์การย้อนกลับแบบคาดการณ์ ดังนี้
- คุณสามารถตั้งค่า
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueเพื่อเลือกใช้การเคลื่อนไหวของระบบสำหรับการย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดาต่อกิจกรรมแทนทั้งแอป - เราได้เพิ่มภาพเคลื่อนไหวใหม่ของระบบเพื่อใช้ควบคู่ไปกับภาพเคลื่อนไหวของการเปลี่ยนกลับไปที่หน้าแรกจาก Android 13 ภาพเคลื่อนไหวของระบบแบบใหม่จะทำงานข้ามกิจกรรมและข้ามงาน ซึ่งคุณจะได้รับโดยอัตโนมัติหลังจากย้ายข้อมูลไปยังท่าทางสัมผัสย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดา
- เราได้เพิ่มภาพเคลื่อนไหวใหม่สำหรับคอมโพเนนต์ Material สำหรับชีตด้านล่าง ชีตด้านข้าง และการค้นหา
- เราได้จัดทำคำแนะนำด้านการออกแบบสำหรับการสร้างภาพเคลื่อนไหวและทรานซิชันในแอปที่กำหนดเอง
- เราได้เพิ่ม API ใหม่เพื่อรองรับภาพเคลื่อนไหวการเปลี่ยนภาพในแอปที่กําหนดเอง ดังนี้
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- ใช้
overrideActivityTransitionแทนoverridePendingTransitionสำหรับทรานซิชันที่ตอบสนองเมื่อผู้ใช้ปัดกลับ
ในรุ่นตัวอย่างของ Android 14 นี้ ฟีเจอร์ทั้งหมดของฟีเจอร์การกดย้อนกลับแบบคาดคะเนจะยังคงอยู่ในตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป ดูคู่มือนักพัฒนาแอปเพื่อย้ายข้อมูลแอปไปใช้แบ็กเอนด์แบบคาดการณ์ รวมถึงคู่มือนักพัฒนาแอปในการสร้างทรานซิชันในแอปที่กําหนดเอง
การลบล้างต่อแอปของผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์ที่มีหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
การลบล้างค่าแอปต่อแอปช่วยให้ผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์เปลี่ยนลักษณะการทำงานของแอปในอุปกรณ์ที่มีหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น การลบล้าง FORCE_RESIZE_APP จะสั่งให้ระบบปรับขนาดแอปให้พอดีกับขนาดการแสดงผล (หลีกเลี่ยงโหมดความเข้ากันได้ของขนาด) แม้ว่าจะมีการตั้งค่า resizeableActivity="false" ในไฟล์ Manifest ของแอปก็ตาม
การลบล้างมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อปรับปรุงประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้บนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
พร็อพเพอร์ตี้ไฟล์ Manifest ใหม่ช่วยให้คุณปิดใช้การลบล้างผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์บางรายสำหรับแอปของคุณได้
การลบล้างต่อแอปสำหรับผู้ใช้หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
การลบล้างในแต่ละแอปจะเปลี่ยนลักษณะการทำงานของแอปในอุปกรณ์หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ ตัวอย่างเช่น ผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์ OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE ลบล้างการตั้งค่าสัดส่วนภาพของแอปเป็น 16:9 โดยไม่คำนึงถึงการกำหนดค่าของแอป
Android 14 QPR1 ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ใช้การลบล้างระดับแอปได้ผ่านเมนูการตั้งค่าใหม่ในอุปกรณ์หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
การแชร์หน้าจอแอป
การแชร์หน้าจอแอปช่วยให้ผู้ใช้แชร์หน้าต่างแอปแทนหน้าจออุปกรณ์ทั้งหน้าจอได้ในระหว่างการบันทึกเนื้อหาหน้าจอ
เมื่อแชร์หน้าจอแอป ระบบจะไม่รวมแถบสถานะ แถบนําทาง การแจ้งเตือน และองค์ประกอบ UI อื่นๆ ของระบบไว้ในหน้าจอที่แชร์ ระบบจะแชร์เฉพาะเนื้อหาของแอปที่เลือกเท่านั้น
การแชร์หน้าจอแอปช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำงานและความเป็นส่วนตัวโดยอนุญาตให้ผู้ใช้เรียกใช้แอปหลายแอป แต่จำกัดการแชร์เนื้อหาไว้เพียงแอปเดียว
ฟีเจอร์ช่วยตอบที่ทำงานด้วย LLM ใน Gboard บน Pixel 8 Pro
ในอุปกรณ์ Pixel 8 Pro ที่มีฟีเจอร์ใหม่ประจำเดือนธันวาคม นักพัฒนาแอปสามารถลองใช้ฟีเจอร์ช่วยตอบที่มีคุณภาพสูงขึ้นใน Gboard ซึ่งขับเคลื่อนโดยโมเดลภาษาขนาดใหญ่ (LLM) ในอุปกรณ์ที่ทำงานบน Google Tensor
ฟีเจอร์นี้มีให้บริการเป็นเวอร์ชันตัวอย่างแบบจำกัดสำหรับภาษาอังกฤษแบบสหรัฐอเมริกาใน WhatsApp, Line และ KakaoTalk โดยต้องใช้อุปกรณ์ Pixel 8 Pro ที่มี Gboard เป็นแป้นพิมพ์
หากต้องการลองใช้ ให้เปิดใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้ในการตั้งค่า > ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป > การตั้งค่า AiCore > เปิดใช้ AiCore Persistent ก่อน
จากนั้นเปิดการสนทนาในแอปที่รองรับเพื่อดูการช่วยตอบที่ทำงานด้วย LLM ในแถบคำแนะนำของ Gboard เพื่อตอบกลับข้อความที่เข้ามา
กราฟิก
เส้นทางสามารถค้นหาและประมาณค่าได้
Path API ของ Android เป็นกลไกที่มีประสิทธิภาพและยืดหยุ่นในการสร้างและการแสดงผลกราฟิกเวกเตอร์ โดยมีความสามารถในการขีดทับหรือเติมเส้นทาง สร้างเส้นทางจากส่วนของเส้นหรือเส้นโค้งหรือสี่เหลี่ยมลูกบาศก์ ดำเนินการบูลีนเพื่อให้ได้รูปร่างที่ซับซ้อนมากขึ้น หรือทั้งหมดนี้พร้อมกัน ข้อจำกัดอย่างหนึ่งคือความสามารถในการหาสิ่งที่อยู่ในออบเจ็กต์เส้นทาง ภายในของออบเจ็กต์จะทึบแสงสำหรับผู้เรียกหลังจากการสร้าง
หากต้องการสร้าง Path ให้ใช้เมธอด เช่น
moveTo(), lineTo() และ
cubicTo() เพื่อเพิ่มกลุ่มเส้นทาง แต่ไม่มีวิธีใดที่จะถามถึงเส้นทางว่ากลุ่มเป้าหมายคืออะไร คุณจึงต้องเก็บข้อมูลไว้ ณ เวลาที่สร้าง
ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป คุณจะค้นหาเส้นทางเพื่อดูสิ่งที่อยู่ข้างในได้
ก่อนอื่น คุณต้องรับออบเจ็กต์ PathIterator โดยใช้ Path.getPathIterator API โดยทำดังนี้
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
ถัดไป คุณสามารถเรียกใช้ PathIterator เพื่อทำซ้ำผ่านกลุ่มทีละกลุ่มโดยดึงข้อมูลที่จำเป็นทั้งหมดสำหรับแต่ละกลุ่ม ตัวอย่างนี้ใช้ออบเจ็กต์ PathIterator.Segment ซึ่งจัดแพ็กเกจข้อมูลให้คุณ
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator ยังมี next() เวอร์ชันที่ไม่จัดสรร ซึ่งคุณสามารถส่งบัฟเฟอร์เพื่อเก็บข้อมูลจุดได้
กรณีการใช้งานที่สําคัญอย่างหนึ่งของการค้นหาข้อมูล Path คือการประมาณ เช่น คุณอาจต้องการสร้างภาพเคลื่อนไหว (หรือเปลี่ยนรูปแบบ) ระหว่าง 2 เส้นทางที่แตกต่างกัน Android 14 ยังมีเมธอด interpolate() ใน Path ด้วย เพื่อลดความซับซ้อนของกรณีการใช้งานดังกล่าว สมมติว่าทั้ง 2 เส้นทางมีโครงสร้างภายในเหมือนกัน เมธอด interpolate() จะสร้าง Path ใหม่ด้วยผลลัพธ์ที่ประมาณค่านั้น ตัวอย่างนี้แสดงเส้นทางที่มีรูปร่างครึ่งหนึ่ง (การประมาณค่าในช่วงเชิงเส้นเป็น .5) ระหว่าง path ถึง otherPath
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
ไลบรารี graphics-path ของ Jetpack เปิดใช้ API ที่คล้ายกันสำหรับ Android เวอร์ชันก่อนหน้านี้ด้วย
Custom meshes with vertex and fragment shaders
Android รองรับการวาดเมชรูปสามเหลี่ยมด้วยการแรเงาที่กำหนดเองมานานแล้ว แต่รูปแบบเมชอินพุตถูกจำกัดไว้ที่การผสมผสานแอตทริบิวต์ที่กำหนดไว้ล่วงหน้าเพียงไม่กี่รายการ Android 14 เพิ่มการรองรับเมชที่กำหนดเอง ซึ่งสามารถกำหนดเป็นสามเหลี่ยมหรือแถบสามเหลี่ยม และสามารถจัดทำดัชนีได้ (ไม่บังคับ) ตาข่ายเหล่านี้ระบุด้วยแอตทริบิวต์ที่กำหนดเอง ระยะห่างของจุดยอด ตัวแปร และเชนเดอร์จุดยอดและเศษส่วนที่เขียนใน AGSL
เวิร์กเชดเดอร์กำหนดตัวแปรต่างๆ เช่น ตำแหน่งและสี ส่วนฟร็กเมนทัลเชดเดอร์จะกำหนดสีของพิกเซลได้ (ไม่บังคับ) โดยปกติจะใช้ตัวแปรต่างๆ ที่เวิร์กเชดเดอร์สร้างขึ้น หากฟร็กเมชันเชเดอร์ระบุสี ระบบจะผสมสีนั้นเข้ากับสี Paint ที่ใช้อยู่โดยใช้โหมดการผสมที่เลือกไว้เมื่อวาดเมช คุณสามารถส่งยูนิฟอร์มไปยังเชดเดอร์เศษและเชดเดอร์เวิร์กเท็กซ์เพื่อเพิ่มความยืดหยุ่นได้
เครื่องมือแสดงผลบัฟเฟอร์ฮาร์ดแวร์สำหรับ Canvas
Android 14 เปิดตัว HardwareBufferRenderer เพื่อช่วยในการใช้ Canvas API ของ Android เพื่อวาดด้วย GPU ลงใน HardwareBuffer API นี้
ซึ่งจะเป็นประโยชน์อย่างยิ่งเมื่อกรณีการใช้งานของคุณเกี่ยวข้องกับการสื่อสารกับระบบ
Compositor ผ่าน SurfaceControl สำหรับเวลาในการตอบสนองต่ำ
ภาพวาด
