Android 14 mang đến cho nhà phát triển các tính năng và API mới hữu ích. Nội dung dưới đây giúp bạn tìm hiểu các tính năng cho ứng dụng cũng như làm quen với các API liên quan.
Để biết danh sách chi tiết về các API đã thêm, sửa đổi và xoá, hãy đọc báo cáo điểm khác biệt về API. Để biết thông tin chi tiết về các API đã thêm, hãy truy cập vào tài liệu tham khảo về API cho Android. Đối với Android 14, hãy tìm các API đã được thêm vào API cấp 34. Để tìm hiểu những thay đổi của nền tảng có thể tác động đến ứng dụng của bạn, hãy nhớ tham khảo các thay đổi về hành vi của Android 14 đối với ứng dụng nhắm đến Android 14 và tất cả ứng dụng.
Quốc tế hoá
Lựa chọn ưu tiên về ngôn ngữ cho mỗi ứng dụng
Android 14 mở rộng các tính năng về ngôn ngữ cho mỗi ứng dụng từng ra mắt trong Android 13 (API cấp 33), cũng như bổ sung thêm những tính năng sau:
Tự động tạo
localeConfigcủa ứng dụng: Bắt đầu từ Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 và AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, bạn có thể định cấu hình ứng dụng của mình để tự động hỗ trợ lựa chọn ưu tiên về ngôn ngữ cho mỗi ứng dụng. Dựa trên các tài nguyên của dự án, trình bổ trợ Android cho Gradle sẽ tạo tệpLocaleConfigvà thêm mục tham chiếu đến tệp đó trong tệp kê khai cuối cùng, do đó, bạn không còn phải tạo hoặc cập nhật tệp theo cách thủ công nữa. AGP sẽ sử dụng các tài nguyên trong thư mụcrescủa mô-đun ứng dụng và mọi phần phụ thuộc của mô-đun thư viện để xác định ngôn ngữ cần đưa vào tệpLocaleConfig.Bản cập nhật động cho
localeConfigcủa ứng dụng: Sử dụng các phương thứcsetOverrideLocaleConfig()vàgetOverrideLocaleConfig()trongLocaleManagerđể tự động cập nhật danh sách ngôn ngữ được hỗ trợ của ứng dụng trong phần cài đặt hệ thống của thiết bị. Hãy sử dụng khả năng hoạt này để tuỳ chỉnh danh sách ngôn ngữ được hỗ trợ cho mỗi khu vực, chạy kiểm thử A/B hoặc cung cấp danh sách ngôn ngữ được cập nhật nếu ứng dụng sử dụng tính năng thông báo đẩy phía máy chủ để bản địa hoá.Chế độ hiển thị ngôn ngữ ứng dụng cho trình chỉnh sửa phương thức nhập (IME): IME có thể sử dụng phương thức
getApplicationLocales()để kiểm tra ngôn ngữ của ứng dụng và so khớp ngôn ngữ IME với ngôn ngữ đó.
API Biến tố ngữ pháp
Có đến 3 tỷ người sử dụng ngôn ngữ có phân biệt giống ngữ pháp: ngôn ngữ mà các danh mục ngữ pháp (chẳng hạn như danh từ, động từ, tính từ và giới từ) sẽ phản ánh theo giống của người và đối tượng mà bạn nói đến hoặc nói về. Theo truyền thống, nhiều ngôn ngữ có phân biệt giống ngữ pháp sử dụng giống đực làm giống mặc định hoặc chung.
Việc xưng hô sai ngữ pháp với người dùng, chẳng hạn như xưng hô với phụ nữ theo ngữ pháp giống đực, có thể ảnh hưởng tiêu cực đến hiệu suất và thái độ của họ. Ngược lại, giao diện người dùng có ngôn ngữ phản ánh chính xác giống ngữ pháp của người dùng có thể cải thiện mức độ tương tác, cũng như mang lại trải nghiệm tự nhiên và phù hợp hơn cho người dùng.
Để xây dựng giao diện người dùng cho các ngôn ngữ có giống ngữ pháp, Android 14 ra mắt API Biến tố ngữ pháp, cho phép bạn hỗ trợ giống ngữ pháp mà không cần tái cấu trúc ứng dụng.
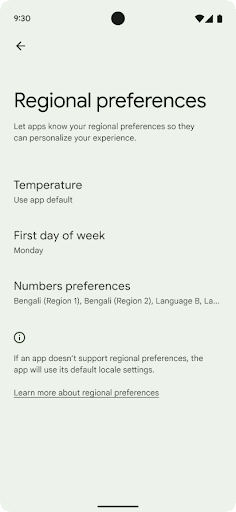
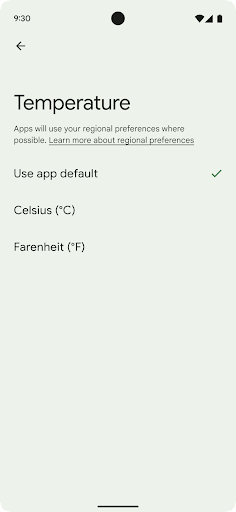
Lựa chọn ưu tiên theo khu vực
Các lựa chọn ưu tiên theo khu vực cho phép người dùng cá nhân hoá đơn vị nhiệt độ, ngày đầu tiên trong tuần và hệ thống đánh số. Có thể người Châu Âu sinh sống ở Hoa Kỳ sẽ thích dùng đơn vị nhiệt độ bằng độ C thay vì độ F và muốn ứng dụng coi thứ Hai là đầu tuần thay vì mặc định ở Hoa Kỳ là Chủ nhật.
Các trình đơn Cài đặt Android mới cho những lựa chọn ưu tiên này là một nơi tập trung và dễ thấy để người dùng thay đổi các lựa chọn ưu tiên cho ứng dụng. Các lựa chọn ưu tiên này cũng được duy trì thông qua tính năng sao lưu và khôi phục. Một số API và ý định (ví dụ: getTemperatureUnit và getFirstDayOfWeek) cấp cho ứng dụng quyền đọc các lựa chọn ưu tiên của người dùng, nhờ đó, ứng dụng của bạn có thể điều chỉnh cách trình bày thông tin. Bạn cũng có thể đăng ký BroadcastReceiver trên ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED để xử lý các thay đổi về cấu hình ngôn ngữ khi các lựa chọn ưu tiên theo khu vực được thay đổi.
Để tìm các chế độ cài đặt này, hãy mở ứng dụng Cài đặt rồi chuyển đến Hệ thống > Ngôn ngữ và phương thức nhập > Lựa chọn ưu tiên theo khu vực.
Hỗ trợ tiếp cận
Điều chỉnh tỷ lệ phông chữ phi tuyến tính lên đến 200%
Kể từ Android 14, hệ thống sẽ hỗ trợ việc chuyển tỷ lệ phông chữ lên đến 200%, mang đến cho người dùng thêm một số chế độ hỗ trợ tiếp cận.
Để ngăn các thành phần văn bản cỡ lớn trên màn hình bị chuyển tỷ lệ quá lớn, hệ thống sẽ áp dụng một đường cong tỷ lệ phi tuyến tính. Chiến lược điều chỉnh tỷ lệ này có nghĩa là văn bản lớn không chuyển tỷ lệ theo cùng mức độ với văn bản nhỏ hơn. Việc chuyển tỷ lệ phông chữ phi tuyến tính giúp bảo toàn thứ bậc tỷ lệ giữa các phần tử có kích thước khác nhau, trong khi giảm thiểu vấn đề với việc chuyển tỷ lệ văn bản tuyến tính ở mức cao (chẳng hạn như văn bản bị cắt hoặc văn bản trở nên khó đọc hơn do kích thước trên màn hình cực kỳ lớn).
Kiểm thử ứng dụng bằng tỷ lệ phông chữ phi tuyến tính
Nếu đã sử dụng đơn vị pixel có thể mở rộng (sp) để xác định kích thước văn bản, thì các lựa chọn bổ sung và điểm cải tiến về tỷ lệ này sẽ tự động được áp dụng cho văn bản trong ứng dụng của bạn. Tuy nhiên, bạn vẫn nên tiến hành kiểm thử giao diện người dùng khi bật kích thước phông chữ tối đa (200%) để đảm bảo rằng ứng dụng của bạn áp dụng kích thước phông chữ một cách chính xác và có thể sử dụng phông chữ có kích thước lớn hơn mà không ảnh hưởng đến khả năng hữu dụng.
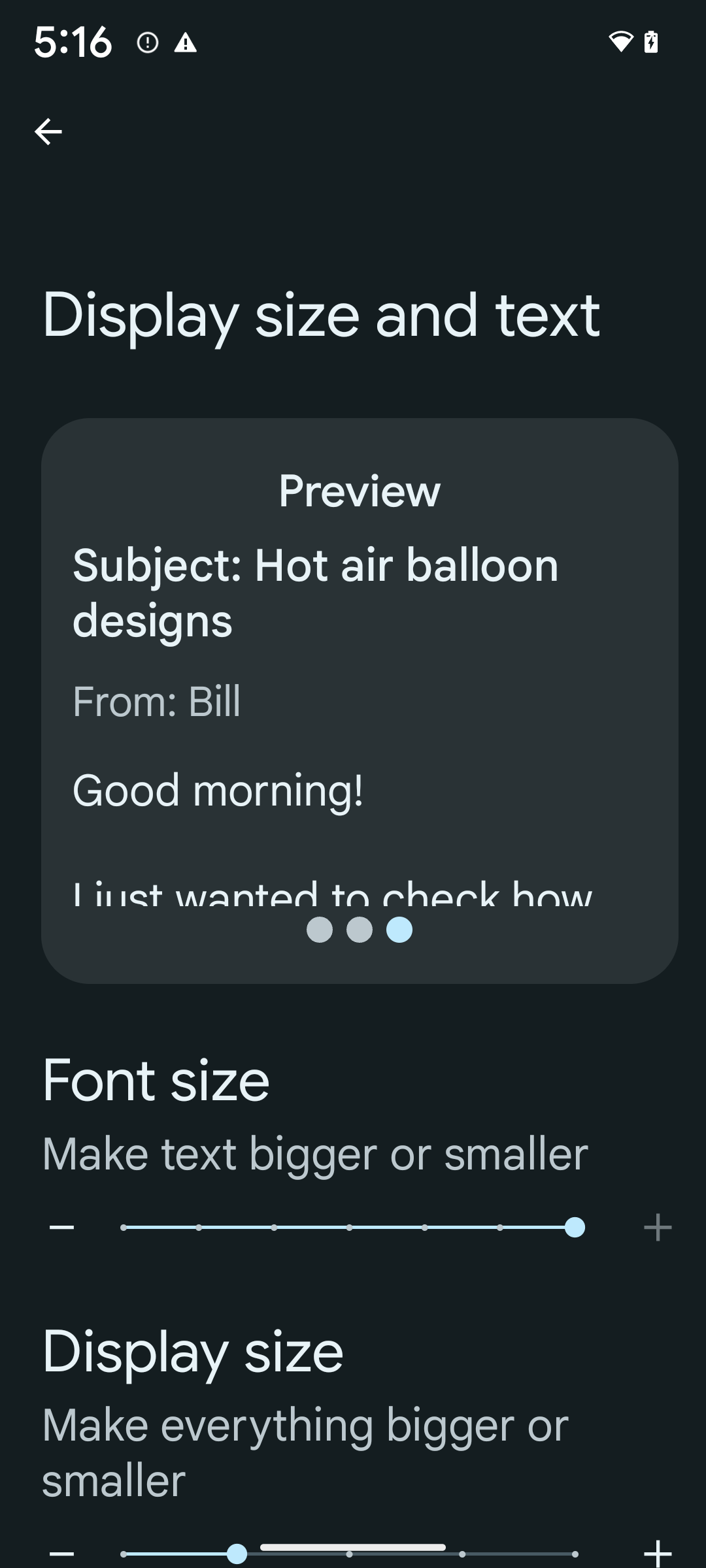
Để bật kích thước phông chữ 200%, hãy làm theo các bước sau:
- Mở ứng dụng Cài đặt rồi chuyển đến phần Hỗ trợ tiếp cận > Văn bản và kích thước hiển thị.
- Đối với tuỳ chọn Kích thước phông chữ, hãy nhấn vào biểu tượng dấu cộng (+) cho đến khi bật chế độ cài đặt kích thước phông chữ tối đa, như trong hình ảnh kèm theo phần này.
Sử dụng đơn vị pixel được điều chỉnh theo tỷ lệ (sp) đối với kích thước văn bản
Hãy nhớ luôn chỉ định kích thước văn bản theo đơn vị sp. Khi ứng dụng của bạn sử dụng đơn vị sp, Android có thể áp dụng kích thước văn bản mà người dùng ưu tiên và chuyển tỷ lệ văn bản một cách thích hợp.
Đừng sử dụng đơn vị sp cho khoảng đệm hoặc xác định chiều cao của khung hiển thị giả định khoảng đệm ngầm ẩn: với việc chuyển tỷ lệ phông chữ phi tuyến tính theo đơn vị sp thì kích thước có thể sẽ không tỷ lệ thuận, vì vậy, 4sp + 20sp có thể không bằng 24sp.
Chuyển đổi đơn vị pixel được điều chỉnh theo tỷ lệ (sp)
Sử dụng TypedValue.applyDimension() để chuyển đổi từ đơn vị sp sang pixel và sử dụng TypedValue.deriveDimension() để chuyển đổi pixel thành sp. Các phương thức này tự động áp dụng đường cong tỷ lệ phi tuyến tính thích hợp.
Tránh phương trình mã hoá cứng bằng Configuration.fontScale hoặc DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Vì việc chuyển tỷ lệ phông chữ là phi tuyến tính, nên trường scaledDensity không còn chính xác nữa. Bạn chỉ nên sử dụng trường fontScale cho mục đích cung cấp thông tin vì phông chữ không còn được điều chỉnh tỷ lệ bằng một giá trị vô hướng duy nhất nữa.
Sử dụng đơn vị sp cho lineHeight
Luôn xác định android:lineHeight bằng đơn vị sp thay vì dp, để chiều cao dòng có thể điều chỉnh theo văn bản của bạn. Nếu không, nếu văn bản của bạn là sp nhưng lineHeight ở dp hoặc px, thì văn bản đó sẽ không được điều chỉnh tỷ lệ và trông có vẻ chật hẹp.
TextView tự động điều chỉnh lineHeight để giữ nguyên tỷ lệ mà bạn muốn, nhưng chỉ khi cả textSize và lineHeight đều được xác định bằng đơn vị sp.
Camera và nội dung nghe nhìn
Ultra HDR cho hình ảnh

Android 14 hỗ trợ thêm hình ảnh Dải động cao (HDR) giúp giữ lại nhiều thông tin hơn từ cảm biến khi chụp ảnh, nhờ đó mang lại màu sắc sống động và độ tương phản cao hơn. Android sử dụng định dạng Ultra HDR, tương thích hoàn toàn ngược với hình ảnh JPEG, cho phép các ứng dụng tương tác liền mạch với hình ảnh HDR, hiển thị hình ảnh đó ở Dải động tiêu chuẩn (SDR) nếu cần.
Khung sẽ tự động kết xuất các hình ảnh này trong giao diện người dùng ở chế độ HDR khi ứng dụng của bạn chọn sử dụng giao diện người dùng HDR cho Cửa sổ hoạt động, thông qua một mục nhập tệp kê khai hoặc trong thời gian chạy bằng cách gọi Window.setColorMode(). Bạn cũng có thể chụp hình ảnh tĩnh HDR siêu độ nét được nén trên các thiết bị được hỗ trợ. Khi cảm biến khôi phục được nhiều màu hơn, bạn có thể chỉnh sửa linh hoạt hơn sau khi chụp. Bạn có thể sử dụng Gainmap liên kết với hình ảnh Ultra HDR để kết xuất hình ảnh bằng OpenGL hoặc Vulkan.
Thu phóng, Lấy nét, Xem nhanh và nhiều tính năng khác trong các tiện ích camera
Android 14 nâng cấp và cải thiện tiện ích máy ảnh, cho phép các ứng dụng xử lý trong thời gian dài hơn, nhờ đó hình ảnh được cải thiện bằng cách sử dụng các thuật toán chuyên sâu về điện toán như chụp ảnh ở điều kiện ánh sáng yếu trên các thiết bị được hỗ trợ. Các tính năng này mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm mạnh mẽ hơn nữa khi sử dụng các tính năng của tiện ích máy ảnh. Sau đây là một số ví dụ về những điểm cải tiến này:
- Tính năng ước tính độ trễ xử lý ảnh tĩnh động cung cấp thông tin ước tính độ trễ chụp ảnh tĩnh chính xác hơn nhiều dựa trên điều kiện môi trường và cảnh hiện tại. Gọi
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()để lấy đối tượngStillCaptureLatencycó hai phương thức ước tính độ trễ. Phương thứcgetCaptureLatency()trả về độ trễ ước tính giữaonCaptureStartedvàonCaptureProcessStarted(), còn phương thứcgetProcessingLatency()trả về độ trễ ước tính giữaonCaptureProcessStarted()và khung hình đã xử lý cuối cùng. - Hỗ trợ các lệnh gọi lại tiến trình chụp để ứng dụng có thể hiển thị tiến trình hiện tại của các thao tác xử lý ảnh chụp tĩnh, chạy trong thời gian dài. Bạn có thể kiểm tra xem tính năng này có dùng được với
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailablehay không. Nếu có, bạn sẽ triển khai lệnh gọi lạionCaptureProcessProgressed(), trong đó tiến trình (từ 0 đến 100) được truyền vào dưới dạng tham số. Siêu dữ liệu dành riêng cho tiện ích, chẳng hạn như
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHđể điều chỉnh mức độ của một hiệu ứng tiện ích, chẳng hạn như mức độ làm mờ nền bằngEXTENSION_BOKEH.Tính năng Xem sau cho tính năng Chụp ảnh tĩnh trong các tiện ích máy ảnh, cung cấp hình ảnh được xử lý ít hơn và nhanh hơn so với hình ảnh cuối cùng. Nếu một tiện ích tăng độ trễ xử lý, thì bạn có thể cung cấp hình ảnh sau khi xem làm phần giữ chỗ để cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng và sau đó chuyển sang hình ảnh cuối cùng. Bạn có thể kiểm tra xem tính năng này có dùng được với
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailablehay không. Sau đó, bạn có thể truyềnOutputConfigurationđếnExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Hỗ trợ
SurfaceViewcho phép đường dẫn kết xuất bản xem trước được tối ưu hoá và tiết kiệm điện năng hơn.Hỗ trợ tính năng nhấn để lấy nét và thu phóng trong quá trình sử dụng tiện ích.
Thu phóng trong cảm biến
Khi REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE trong CameraCharacteristics chứa SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, ứng dụng của bạn có thể sử dụng các tính năng cảm biến nâng cao để cung cấp luồng RAW đã cắt có cùng số pixel với trường nhìn đầy đủ bằng cách sử dụng CaptureRequest với mục tiêu RAW có trường hợp sử dụng luồng được đặt thành CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
Bằng cách triển khai các chế độ điều khiển ghi đè yêu cầu, máy ảnh đã cập nhật sẽ cho phép người dùng điều khiển tính năng thu phóng ngay cả trước khi các chế độ điều khiển khác của máy ảnh sẵn sàng.
Âm thanh qua cổng USB không bị suy hao
Android 14 hỗ trợ các định dạng âm thanh không suy hao để mang lại trải nghiệm âm thanh chất lượng cao qua tai nghe có dây USB. Bạn có thể truy vấn một thiết bị USB để biết các thuộc tính bộ trộn ưu tiên, đăng ký trình nghe cho các thay đổi trong các thuộc tính bộ trộn ưu tiên và định cấu hình các thuộc tính bộ trộn bằng cách sử dụng lớp AudioMixerAttributes. Lớp này đại diện cho định dạng, chẳng hạn như mặt nạ kênh, tốc độ lấy mẫu và hành vi của bộ trộn âm thanh. Lớp này cho phép gửi trực tiếp âm thanh mà không cần trộn, điều chỉnh âm lượng hoặc xử lý hiệu ứng.
Năng suất và công cụ dành cho nhà phát triển
Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực
Android 14 thêm Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực làm API nền tảng, với khả năng hỗ trợ bổ sung cho các thiết bị Android 4.4 (API cấp 19) thông qua Thư viện Jetpack bằng Dịch vụ Google Play. Mục đích của Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực là giúp người dùng đăng nhập dễ dàng hơn bằng các API truy xuất và lưu trữ thông tin xác thực thông qua các trình cung cấp thông tin xác thực do người dùng định cấu hình. Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức đăng nhập, bao gồm tên người dùng và mật khẩu, khoá truy cập và các giải pháp đăng nhập liên kết (chẳng hạn như Đăng nhập bằng Google) trong một API duy nhất.
Khẩu khoá truy cập mang lại nhiều lợi thế. Ví dụ: khoá truy cập được xây dựng dựa trên các tiêu chuẩn của ngành, có thể hoạt động trên nhiều hệ điều hành và hệ sinh thái trình duyệt, cũng như có thể được sử dụng với cả trang web và ứng dụng.
Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem tài liệu về Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực và khoá truy cập cũng như bài đăng trên blog về Trình quản lý thông tin xác thực và khoá truy cập.
Health Connect
Health Connect là một kho lưu trữ trên thiết bị dành cho dữ liệu sức khoẻ và thể chất của người dùng. Tính năng này cho phép người dùng chia sẻ dữ liệu giữa các ứng dụng mà họ yêu thích, với một nơi duy nhất để kiểm soát dữ liệu họ muốn chia sẻ với các ứng dụng này.
Trên các thiết bị chạy phiên bản Android trước Android 14, bạn có thể tải Health Connect xuống dưới dạng ứng dụng trên Cửa hàng Google Play. Kể từ Android 14, Health Connect là một phần của nền tảng và nhận được bản cập nhật thông qua bản cập nhật hệ thống của Google Play mà không cần tải xuống riêng. Nhờ đó, Health Connect có thể được cập nhật thường xuyên và các ứng dụng của bạn có thể dựa vào Health Connect có sẵn trên các thiết bị chạy Android 14 trở lên. Người dùng có thể truy cập vào Health Connect từ phần Cài đặt trong thiết bị của họ, với các chế độ kiểm soát quyền riêng tư được tích hợp vào phần cài đặt hệ thống.
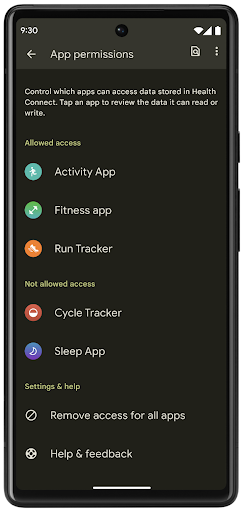
Health Connect có một số tính năng mới trong Android 14, chẳng hạn như tuyến đường tập thể dục, cho phép người dùng chia sẻ tuyến đường tập thể dục của họ và có thể được trực quan hoá trên bản đồ. Tuyến đường được xác định là danh sách các vị trí được lưu trong một khoảng thời gian và ứng dụng của bạn có thể chèn các tuyến đường vào các phiên tập thể dục, liên kết các tuyến đường đó với nhau. Để đảm bảo người dùng có toàn quyền kiểm soát dữ liệu nhạy cảm này, người dùng phải cho phép chia sẻ từng tuyến đường với các ứng dụng khác.
Để biết thêm thông tin, hãy xem tài liệu về Health Connect và bài đăng trên blog về Tính năng mới trong Android Health.
Nội dung cập nhật OpenJDK 17
Android 14 tiếp tục công cuộc làm mới các thư viện cốt lõi của Android để phù hợp với các tính năng trong bản phát hành OpenJDK LTS mới nhất, bao gồm cả bản cập nhật thư viện và tính năng hỗ trợ ngôn ngữ Java 17 cho các nhà phát triển ứng dụng và nền tảng.
Bao gồm các tính năng và điểm cải tiến sau đây:
- Cập nhật tính năng hỗ trợ Java 17 cho khoảng 300 lớp
java.base. - Khối văn bản (Text Blocks) ra mắt các giá trị cố định dạng chuỗi nhiều dòng bằng ngôn ngữ lập trình Java.
- So khớp mẫu cho instanceof, cho phép một đối tượng được xem là có một kiểu cụ thể trong
instanceofmà không cần thêm bất cứ biến nào. - Lớp kín (sealed classes) cho phép bạn hạn chế các lớp và giao diện có thể mở rộng hoặc triển khai các lớp đó.
Nhờ các bản cập nhật hệ thống Google Play (Project Mainline), hơn 600 triệu thiết bị được phép nhận các bản cập nhật Android Runtime (ART) mới nhất có các thay đổi này. Đây là một phần trong cam kết của chúng tôi nhằm cung cấp cho các ứng dụng một môi trường nhất quán, bảo mật hơn trên các thiết bị, đồng thời cung cấp các tính năng và chức năng mới cho người dùng độc lập với các bản phát hành nền tảng.
Java và OpenJDK là các nhãn hiệu hoặc nhãn hiệu đã đăng ký của Oracle và/hoặc các đơn vị liên kết với Oracle.
Những điểm cải tiến cho các cửa hàng ứng dụng
Android 14 giới thiệu một số API PackageInstaller cho phép cửa hàng ứng dụng cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng.
Yêu cầu phê duyệt lượt cài đặt trước khi tải xuống
Có thể bạn phải yêu cầu người dùng phê duyệt việc cài đặt hoặc cập nhật ứng dụng.
Ví dụ: khi trình cài đặt sử dụng quyền REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES cố gắng cài đặt một ứng dụng mới. Trong các phiên bản Android trước, cửa hàng ứng dụng chỉ có thể yêu cầu người dùng phê duyệt sau khi các tệp APK được ghi vào phiên cài đặt còn phiên hoạt động thì được cam kết.
Kể từ Android 14, phương thức requestUserPreapproval() sẽ cho phép trình cài đặt yêu cầu người dùng phê duyệt trước khi xác nhận phiên cài đặt. Điểm cải tiến này cho phép cửa hàng ứng dụng trì hoãn việc tải mọi tệp APK xuống cho đến khi người dùng phê duyệt quá trình cài đặt. Hơn nữa, sau khi người dùng phê duyệt việc cài đặt, cửa hàng ứng dụng có thể tải và cài đặt ứng dụng ở chế độ nền mà không làm gián đoạn người dùng.
Tuyên bố trách nhiệm đối với các bản cập nhật trong tương lai
Phương thức setRequestUpdateOwnership() cho phép trình cài đặt cho hệ thống biết rằng sau này trình cài đặt dự định sẽ chịu trách nhiệm về các bản cập nhật của ứng dụng đang cài đặt. Tính năng này cho phép thực thi theo quyền sở hữu bản cập nhật, nghĩa là chỉ chủ sở hữu bản cập nhật mới được phép tự động cài đặt bản cập nhật cho ứng dụng. Việc thực thi theo quyền sở hữu bản cập nhật giúp đảm bảo rằng người dùng chỉ nhận được bản cập nhật từ cửa hàng ứng dụng theo đúng mong đợi.
Mọi trình cài đặt khác (bao gồm cả những trình cài đặt sử dụng quyền INSTALL_PACKAGES) phải nhận được sự chấp thuận rõ ràng của người dùng để có thể cài đặt bản cập nhật. Nếu người dùng quyết định tiếp tục cập nhật từ một nguồn khác, thì quyền sở hữu bản cập nhật sẽ bị mất.
Cập nhật ứng dụng vào những thời điểm ít gây gián đoạn hơn
Các cửa hàng ứng dụng thường muốn tránh cập nhật một ứng dụng đang được sử dụng, vì việc này dẫn đến việc các quy trình đang chạy của ứng dụng bị dừng, có khả năng làm gián đoạn công việc mà người dùng đang thực hiện.
Kể từ Android 14, InstallConstraints API sẽ giúp trình cài đặt có thể đảm bảo quá trình cập nhật ứng dụng diễn ra đúng lúc. Ví dụ: một cửa hàng ứng dụng có thể gọi phương thức commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() để đảm bảo rằng bản cập nhật chỉ được cam kết khi người dùng không còn tương tác với ứng dụng có liên quan.
Cài đặt các phần phân tách không bắt buộc sao cho liền mạch
Nhờ tệp APK phân tách, nhiều tính năng của một ứng dụng có thể được phân phối trong các tệp APK riêng biệt, thay vì dưới dạng tệp APK nguyên khối. Tệp APK phân tách cho phép cửa hàng ứng dụng tối ưu hoá việc phân phối nhiều thành phần của ứng dụng. Ví dụ: có thể các cửa hàng ứng dụng sẽ tối ưu hoá dựa trên thuộc tính của thiết bị mục tiêu. PackageInstaller API đã hỗ trợ các phần phân tách kể từ khi ra mắt trong API cấp 22.
Trong Android 14, phương thức setDontKillApp() sẽ cho phép trình cài đặt cho biết rằng các quy trình đang chạy của ứng dụng sẽ không bị tắt khi các phần phân tách mới được cài đặt. Các cửa hàng ứng dụng có thể sử dụng tính năng này để cài đặt liền mạch những tính năng mới của một ứng dụng trong khi người dùng đang sử dụng ứng dụng đó.
Gói siêu dữ liệu ứng dụng
Kể từ Android 14, trình cài đặt gói Android cho phép bạn chỉ định siêu dữ liệu ứng dụng (ví dụ: các biện pháp đảm bảo an toàn dữ liệu) để đưa vào các trang trên cửa hàng ứng dụng như Google Play.
Phát hiện thời điểm người dùng chụp ảnh màn hình thiết bị
Để tạo ra trải nghiệm chuẩn hơn đối với việc phát hiện ảnh chụp màn hình, Android 14 ra mắt API phát hiện ảnh chụp màn hình nhằm bảo vệ quyền riêng tư. API này cho phép ứng dụng đăng ký lệnh gọi lại dựa trên từng hoạt động. Khi người dùng chụp ảnh màn hình trong khi hoạt động đó đang hiển thị, những lệnh gọi lại này sẽ được gọi và người dùng sẽ nhận được thông báo.
Trải nghiệm người dùng
Các thao tác tuỳ chỉnh trên Trang chia sẻ nội dung và cách cải thiện thứ hạng
Android 14 cập nhật trang chia sẻ nội dung của hệ thống để hỗ trợ các thao tác tuỳ chỉnh trong ứng dụng và các kết quả xem trước giàu thông tin hơn cho người dùng.
Thêm thao tác tuỳ chỉnh
Với Android 14, ứng dụng của bạn có thể thêm thao tác tuỳ chỉnh vào trang chia sẻ nội dung hệ thống mà ứng dụng đó gọi.
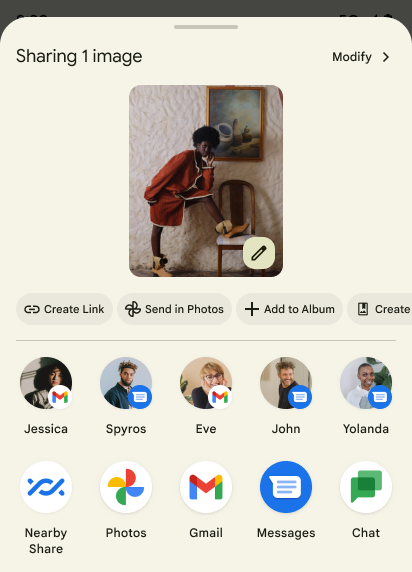
Cải thiện thứ hạng của mục tiêu Chia sẻ trực tiếp
Android 14 sử dụng thêm nhiều tín hiệu từ các ứng dụng để xác định thứ hạng của mục tiêu chia sẻ trực tiếp nhằm đưa ra kết quả hữu ích hơn cho người dùng. Để cung cấp tín hiệu hữu ích nhất cho việc xếp hạng, hãy làm theo hướng dẫn để cải thiện thứ hạng của mục tiêu Chia sẻ trực tiếp. Ứng dụng liên lạc cũng có thể báo cáo mức sử dụng phím tắt cho tin nhắn đến và đi.
Hỗ trợ ảnh động tích hợp sẵn và ảnh động tuỳ chỉnh cho tính năng Xem trước thao tác quay lại
Android 13 đã giới thiệu ảnh động xem trước thao tác quay lại màn hình chính dưới hình thức tuỳ chọn dành cho nhà phát triển. Khi vuốt ngược lại, trong một ứng dụng được hỗ trợ và tuỳ chọn dành cho nhà phát triển được bật, sẽ xuất hiện ảnh động chỉ ra rằng cử chỉ vuốt ngược là để thoát khỏi ứng dụng và quay lại màn hình chính.
Android 14 có nhiều điểm cải tiến và hướng dẫn mới về tính năng Xem trước thao tác quay lại:
- Bạn có thể thiết lập
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueđể chọn sử dụng ảnh động xem trước quay lại hệ thống cho mỗi Hoạt động thay vì cho toàn bộ ứng dụng. - Chúng tôi đã thêm ảnh động hệ thống mới để tăng cường cho ảnh động quay lại màn hình chính từ Android 13. Sau khi di chuyển sang tính năng Xem trước thao tác quay lại, bạn sẽ tự động nhận được các ảnh động hệ thống mới trên nhiều hoạt động và nhiều tác vụ.
- Chúng tôi đã thêm ảnh động mới trong Thành phần Material cho Bảng dưới cùng, Bảng bên và Tìm kiếm.
- Chúng tôi đã tạo hướng dẫn thiết kế để tạo ảnh động và hiệu ứng chuyển đổi tuỳ chỉnh trong ứng dụng.
- Chúng tôi đã thêm nhiều API mới để hỗ trợ ảnh động chuyển đổi tuỳ chỉnh trong ứng dụng:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Sử dụng
overrideActivityTransitionthay vìoverridePendingTransitionđối với các hiệu ứng chuyển đổi phản hồi khi người dùng vuốt ngược lại.
Đối với bản thử nghiệm Android 14 này, tất cả tính năng Xem trước thao tác quay lại vẫn là tuỳ chọn dành cho nhà phát triển. Xem hướng dẫn dành cho nhà phát triển để di chuyển ứng dụng sang tính năng Xem trước thao tác quay lại, cũng như hướng dẫn dành cho nhà phát triển để tạo các hiệu ứng chuyển đổi tuỳ chỉnh trong ứng dụng.
Chế độ ghi đè cho mỗi ứng dụng của nhà sản xuất thiết bị có màn hình lớn
Chế độ ghi đè cho mỗi ứng dụng cho phép nhà sản xuất thiết bị thay đổi hành vi của các ứng dụng trên thiết bị có màn hình lớn. Ví dụ: chế độ ghi đè FORCE_RESIZE_APP sẽ hướng dẫn hệ thống đổi kích thước ứng dụng cho vừa với kích thước màn hình (tránh chế độ tương thích với kích thước) ngay cả khi resizeableActivity="false" được thiết lập trong tệp kê khai ứng dụng.
Tính năng ghi đè nhằm cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng trên màn hình lớn.
Các thuộc tính tệp kê khai mới cho phép bạn tắt một số chế độ ghi đè của nhà sản xuất thiết bị cho ứng dụng của mình.
Chế độ ghi đè cho mỗi ứng dụng của người dùng trên màn hình lớn
Tính năng ghi đè cho mỗi ứng dụng thay đổi hành vi của ứng dụng trên thiết bị có màn hình lớn. Ví dụ: chế độ ghi đè của nhà sản xuất thiết bị OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE đặt tỷ lệ khung hình của ứng dụng thành 16:9 bất kể cấu hình của ứng dụng.
Android 14 QPR1 cho phép người dùng áp dụng chế độ ghi đè cho mỗi ứng dụng thông qua trình đơn cài đặt mới trên các thiết bị có màn hình lớn.
Chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng
Tính năng chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng cho phép người dùng chia sẻ một cửa sổ ứng dụng thay vì toàn bộ màn hình thiết bị trong khi ghi nội dung trên màn hình.
Khi chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng, thanh trạng thái, thanh điều hướng, thông báo và các thành phần khác trên giao diện người dùng của hệ thống sẽ bị loại trừ khỏi màn hình được chia sẻ. Chỉ nội dung của ứng dụng đã chọn mới được chia sẻ.
Tính năng chia sẻ màn hình ứng dụng giúp cải thiện năng suất và quyền riêng tư bằng cách cho phép người dùng chạy nhiều ứng dụng nhưng chỉ giới hạn việc chia sẻ nội dung ở một ứng dụng.
Tính năng Trả lời thông minh dựa trên LLM trong Gboard trên Pixel 8 Pro
Trên các thiết bị Pixel 8 Pro có Bản phát hành tính năng tháng 12, nhà phát triển có thể dùng thử tính năng trả lời thông minh chất lượng cao hơn trong Gboard nhờ các Mô hình ngôn ngữ lớn (LLM) trên thiết bị chạy trên Google Tensor.
Tính năng này được cung cấp dưới dạng bản dùng thử có giới hạn cho tiếng Anh (Hoa Kỳ) trong WhatsApp, Line và KakaoTalk. Bạn cần sử dụng thiết bị Pixel 8 Pro có Gboard làm bàn phím.
Để dùng thử, trước tiên, hãy bật tính năng này trong phần Settings > Developer Options > AiCore Settings > Enable Aicore Persistent (Cài đặt > Tuỳ chọn cho nhà phát triển > Cài đặt AICore > Bật Aicore Persistent).
Tiếp theo, hãy mở một cuộc trò chuyện trong một ứng dụng được hỗ trợ để xem tính năng Trả lời thông minh dựa trên LLM trong dải đề xuất của Gboard để phản hồi tin nhắn đến.
Đồ hoạ
Các đường dẫn nay truy vấn được và nội suy được
API Path của Android là một cơ chế mạnh mẽ và linh hoạt để tạo và kết xuất đồ hoạ vectơ, với khả năng vẽ hoặc tô màu đường dẫn, tạo đường dẫn từ các đoạn thẳng hoặc đường cong bậc hai hoặc lập phương, thực hiện các thao tác boolean để có được hình dạng phức tạp hơn nữa hoặc đồng thời tất cả những hình dạng này. Một hạn chế là khả năng tìm hiểu nội dung thực sự trong đối tượng Đường dẫn; nội dung bên trong của đối tượng này được che đi trước các phương thức gọi sau khi tạo.
Để tạo Path, hãy gọi các phương thức như moveTo(), lineTo() và cubicTo() để thêm các phân đoạn đường dẫn. Nhưng không có cách nào để truy vấn đường dẫn về các phân đoạn, vì vậy bạn phải giữ lại thông tin đó tại thời điểm tạo.
Kể từ Android 14, bạn có thể truy vấn các đường dẫn để tìm hiểu nội dung bên trong đó.
Trước tiên, bạn cần sử dụng Path.getPathIterator API để lấy đối tượng PathIterator:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Tiếp theo, bạn có thể gọi PathIterator để lặp lại từng phân đoạn, truy xuất tất cả dữ liệu cần thiết cho từng phân đoạn. Ví dụ này sử dụng các đối tượng PathIterator.Segment để đóng gói dữ liệu cho bạn:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator cũng có phiên bản next() không phân bổ, trong đó bạn có thể truyền một bộ đệm để lưu giữ dữ liệu điểm.
Một trong những trường hợp sử dụng quan trọng của việc truy vấn dữ liệu Path là nội suy. Ví dụ: bạn có thể tạo hiệu ứng động (animate) hoặc biến đổi (morph) giữa hai đường dẫn riêng biệt. Để đơn giản hoá trường hợp sử dụng đó hơn nữa, Android 14 cũng bao gồm phương thức interpolate() trên Path. Giả sử hai đường dẫn này có cùng cấu trúc nội bộ, thì phương thức interpolate() sẽ tạo một Path mới với kết quả nội suy đó. Ví dụ này trả về một đường dẫn có hình dạng bằng một nửa (nội suy tuyến tính .5) giữa path và otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Thư viện Jetpack graphics-path cũng kích hoạt các API tương tự cho các phiên bản Android trước đó.
Lưới tuỳ chỉnh có chương trình đổ bóng đỉnh và mảnh
Android từ lâu đã hỗ trợ vẽ lưới tam giác bằng tính năng tô bóng tuỳ chỉnh, nhưng định dạng lưới đầu vào bị giới hạn ở một số tổ hợp thuộc tính được xác định trước. Android 14 hỗ trợ thêm lưới tuỳ chỉnh. Lưới này có thể được xác định là tam giác hoặc dải tam giác và có thể được lập chỉ mục (không bắt buộc). Các lưới này được chỉ định bằng các thuộc tính tuỳ chỉnh, bước đỉnh, thay đổi, chương trình đổ bóng đỉnh và mảnh được viết bằng AGSL.
Chương trình đổ bóng đỉnh xác định các biến thể, chẳng hạn như vị trí và màu sắc, trong khi chương trình đổ bóng mảnh có thể tuỳ ý xác định màu cho pixel, thường là bằng cách sử dụng các biến thể do chương trình đổ bóng đỉnh tạo ra. Nếu màu được cung cấp bởi chương trình đổ bóng mảnh, thì màu đó sẽ được kết hợp với màu Paint hiện tại bằng cách sử dụng chế độ kết hợp được chọn khi vẽ lưới. Bạn có thể truyền Bộ đồng nhất vào chương trình đổ bóng mảnh và đỉnh để tăng tính linh hoạt.
Trình kết xuất vùng đệm phần cứng cho Canvas
Để hỗ trợ việc sử dụng API Canvas của Android nhằm vẽ bằng tính năng tăng tốc phần cứng vào HardwareBuffer, Android 14 sẽ ra mắt HardwareBufferRenderer. API này là
đặc biệt hữu ích khi trường hợp sử dụng của bạn liên quan đến hoạt động giao tiếp với hệ thống
trình tổng hợp thông qua SurfaceControl để có độ trễ thấp
bản vẽ.
