ב-Android 14 נוספו תכונות וממשקי API מעולים למפתחים. המאמרים הבאים יעזרו לכם להבין את התכונות של האפליקציות ולהתחיל להשתמש בממשקי ה-API שקשורים אליהן.
רשימה מפורטת של ממשקי API שנוספו, שונו או הוסרו מופיעה בדוח ההבדלים בין ממשקי ה-API. פרטים על ממשקי API שנוספו זמינים בהפניה ל-Android API. ב-Android 14, מחפשים ממשקי API שנוספו ברמת API 34. כדי לקבל מידע על תחומים שבהם שינויים בפלטפורמה עשויים להשפיע על האפליקציות שלכם, כדאי לעיין בשינויים בהתנהגות ב-Android 14 באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 14 ובכל האפליקציות.
אינטרנציונליזציה
העדפות שפה לכל אפליקציה
ב-Android 14 נוספו לתכונות של שפה לכל אפליקציה, שהוצגו ב-Android 13 (רמת API 33), היכולות הבאות:
יצירה אוטומטית של
localeConfigשל אפליקציה: החל מ-Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 ו-AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, אפשר להגדיר את האפליקציה כך שתתמוך באופן אוטומטי בהעדפות שפה לכל אפליקציה. על סמך המשאבים של הפרויקט, הפלאגין של Android Gradle יוצר את הקובץLocaleConfigומוסיף לו הפניה בקובץ המניפסט הסופי, כך שאין יותר צורך ליצור או לעדכן את הקובץ באופן ידני. מערכת AGP משתמשת במשאבים בתיקיותresשל מודולי האפליקציה ובכל יחסי התלות של מודולי הספריות כדי לקבוע את האזורים הגיאוגרפיים שצריך לכלול בקובץLocaleConfig.עדכונים דינמיים של
localeConfigבאפליקציה: משתמשים בשיטותsetOverrideLocaleConfig()ו-getOverrideLocaleConfig()שמפורטות ב-LocaleManagerכדי לעדכן באופן דינמי את רשימת השפות הנתמכות באפליקציה בהגדרות המערכת של המכשיר. הגמישות הזו מאפשרת לכם להתאים אישית את רשימת השפות הנתמכות לפי אזור, להריץ ניסויים מסוג A/B או לספק רשימה מעודכנת של אזורי זמן אם האפליקציה שלכם משתמשת בהעברות (push) בצד השרת לצורך לוקליזציה.הצגת שפת האפליקציה לעורכי שיטות קלט (IME): עורכי שיטות קלט יכולים להשתמש ב-method
getApplicationLocales()כדי לבדוק את שפת האפליקציה הנוכחית ולהתאים את שפת ה-IME לשפה הזו.
Grammatical Inflection API
3 מיליארד אנשים דוברים שפות עם מגדר: שפות שבהן קטגוריות דקדוקיות – כמו שמות עצם, פעלים, שמות תואר ומילות יחס – משתנות בהתאם למגדר של האנשים והאובייקטים שאתם מדברים אליהם או עליהם. באופן מסורתי, בשפות רבות עם מגדר נעשה שימוש במגדר grammatcal masculine כמגדר ברירת המחדל או כמגדר כללי.
שימוש במגדר הדקדוקי הלא נכון למשתמשים, למשל שימוש במגדר הדקדוקי הזכרי לנשים, עלול להשפיע לרעה על הביצועים והגישה שלהם. לעומת זאת, ממשק משתמש עם שפה שמשקפת בצורה נכונה את המגדר הדקדוקי של המשתמש יכול לשפר את המעורבות של המשתמש ולספק חוויית משתמש מותאמת אישית יותר וטבעית יותר.
כדי לעזור לכם ליצור ממשק משתמש שמתמקד במשתמשים בשפות עם הבחנה בין מינים, ב-Android 14 מופיע Grammatical Inflection API, שמאפשר לכם להוסיף תמיכה בלשון מגדרית בלי לבצע רפאקציה לאפליקציה.
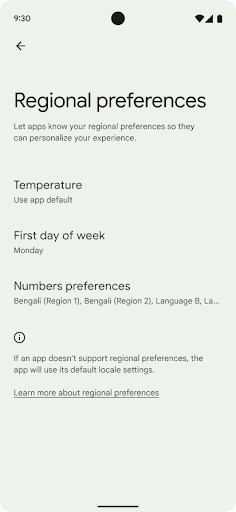
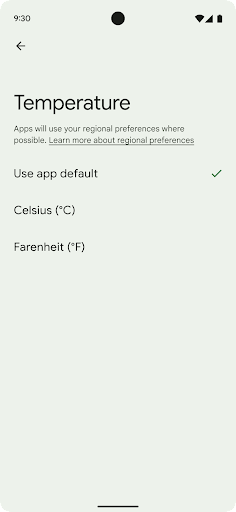
העדפות הפורמט והמידות
העדפות אזוריות מאפשרות למשתמשים להתאים אישית את יחידות הטמפרטורה, את היום הראשון בשבוע ואת מערכות המספור. אירופאי שגר בארצות הברית עשוי להעדיף יחידות טמפרטורה בצלזיוס ולא בפרנהייט אפליקציות להתייחס ליום שני כתחילת השבוע במקום כברירת המחדל בארה"ב יום ראשון.
תפריטי ההגדרות החדשים של Android עבור ההעדפות האלה מספקים למשתמשים מיקום מרכזי ונגיש לשינוי העדפות האפליקציות. האלה
גם בגיבוי ובשחזור. כמה ממשקי API וכוונות (intents) – כמו getTemperatureUnit ו-getFirstDayOfWeek – מעניקים לאפליקציה הרשאת קריאה להעדפות המשתמש, כדי שהיא תוכל לשנות את אופן הצגת המידע. אפשר גם לרשום
BroadcastReceiver במצב פעיל
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
כדי לטפל בשינויים בתצורת הלוקאל כשיש שינוי בהעדפות הפורמט והמידות.
כדי למצוא את ההגדרות האלה, צריך לפתוח את אפליקציית ההגדרות ולעבור אל מערכת > שפות קלט > העדפות אזוריות.
נגישות
הגדלה לא לינארית של הגופן עד 200%
החל מ-Android 14, המערכת תומכת בהגדלת הגופן עד 200%, וכך מספקת למשתמשים אפשרויות נגישות נוספות.
כדי למנוע מצביעה של אלמנטים גדולים של טקסט במסך להיות גדולה מדי, אפליקציית המערכת משתמשת בעקומת שינוי גודל לא לינארית. משמעות אסטרטגיית ההתאמה הזו היא שטקסט גדול לא מותאם באותו קצב כמו טקסט קטן יותר. שינוי גודל גופן לא לינארי עוזר לשמור על ההיררכיה הפרופורציונלית בין רכיבים בגדלים שונים, וגם לצמצם בעיות שקשורות לשינוי גודל טקסט לינארי במידות גבוהות (למשל, טקסט שנחתך או טקסט שקשה יותר לקרוא בגלל גדלים גדולים במיוחד של המסך).
בדיקת האפליקציה באמצעות שינוי גודל גופן לא לינארי
אם כבר השתמשתם ביחידות של פיקסלים שניתן לשנות (sp) כדי להגדיר את גודל הטקסט, האפשרויות הנוספות האלה והשיפורים בהתאמת הגודל יחולו באופן אוטומטי על הטקסט באפליקציה. עם זאת, עדיין מומלץ לבצע בדיקות של ממשק המשתמש עם גודל הגופן המקסימלי (200%) כדי לוודא שהאפליקציה מגדירה את גדלי הגופן בצורה נכונה, ושהיא יכולה להכיל גדלים גדולים יותר של גופן בלי לפגוע בשימושיות.
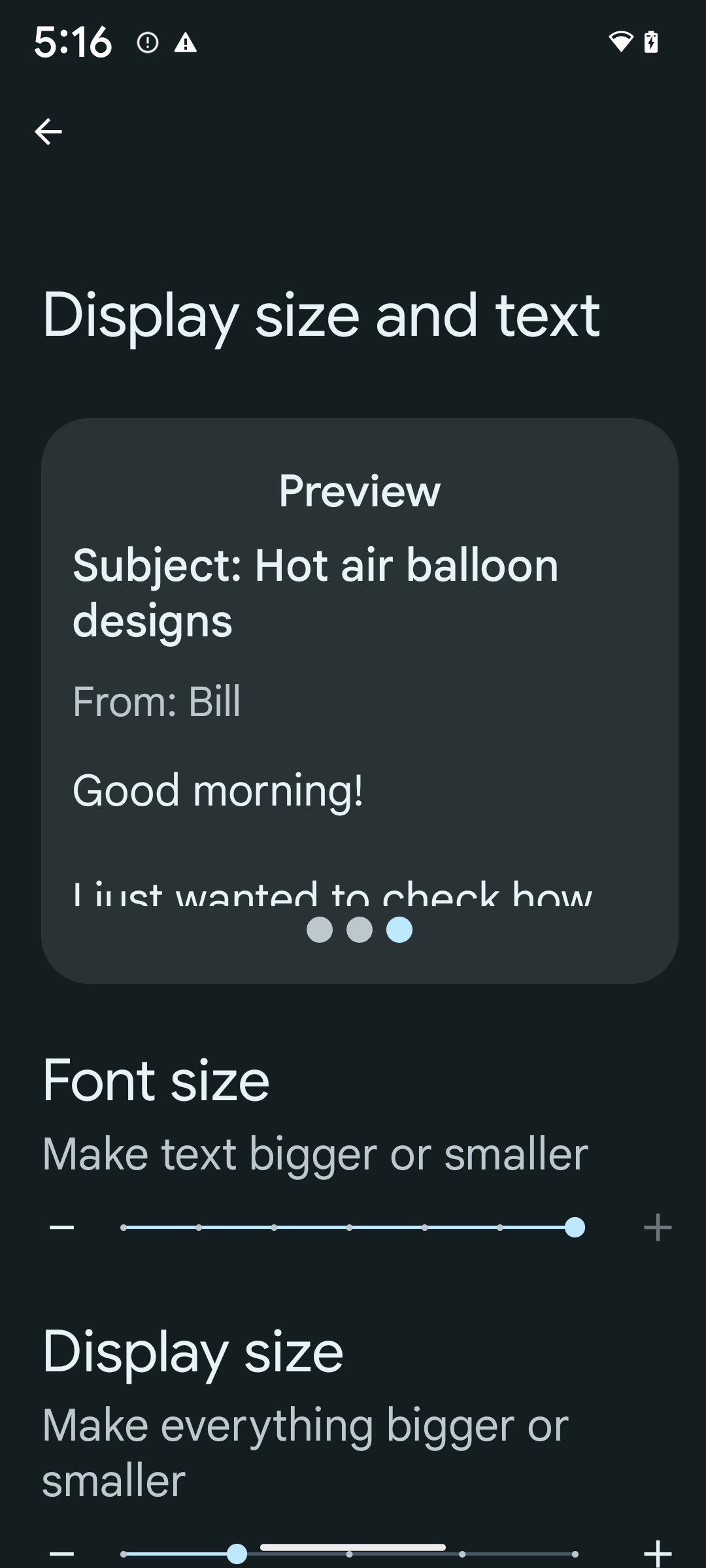
כדי להגדיר את גודל הגופן ל-200%, פועלים לפי השלבים הבאים:
- פותחים את אפליקציית ההגדרות ועוברים אל נגישות > גודל התצוגה והטקסט.
- באפשרות גודל גופן, מקישים על סמל הפלוס (+) עד שמפעילים את הגדרת גודל הגופן המקסימלי, כמו שמוצג בתמונה שמצורפת לקטע הזה.
שימוש ביחידות של פיקסלים משוקללים (sp) לגדלים של טקסט
חשוב לזכור להגדיר תמיד את גודל הטקסט ביחידות sp. כשהאפליקציה משתמשת ביחידות sp, מערכת Android יכולה להחיל את גודל הטקסט המועדף על המשתמש ולשנות את קנה המידה שלו בהתאם.
אל תשתמשו ביחידות sp למרווחים פנימיים או להגדרת גובה התצוגה בהנחה של מרווחים פנימיים מרומזים: בשינוי גודל לא לינארי של גופן, מימדי sp לא בהכרח יהיו פרופורציונליים, ולכן 4sp + 20sp לא בהכרח יהיו שווים ל-24sp.
המרת יחידות של פיקסלים שניתן לשנות (sp)
אפשר להשתמש ב-TypedValue.applyDimension() כדי להמיר יחידות sp לפיקסלים, וב-TypedValue.deriveDimension() כדי להמיר פיקסלים ליחידות sp. השיטות האלה מחילות באופן אוטומטי את עקומת ההתאמה הלא לינארית המתאימה.
אין להשתמש בקידוד קשיח של משוואות באמצעות התגים
Configuration.fontScale או
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. ההתאמה של גודל הגופן היא לא ליניארית, ולכן השדה scaledDensity כבר לא מדויק. השדה fontScale
מיועד לצורכי מידע בלבד, כי הגופנים כבר לא מותאמים באמצעות ערך סקלרי יחיד.
שימוש ביחידות sp בשביל lineHeight
תמיד צריך להגדיר את android:lineHeight באמצעות יחידות sp במקום יחידות dp, כדי שגובה השורה יותאם לגודל הטקסט. אחרת, אם הטקסט הוא sp אבל lineHeight הוא dp או px, הוא לא משתנה בהתאם לגודל המסך ונראה צפוף.
TextView מתקן אוטומטית את lineHeight כדי לשמור על הפרופורציות הרצויות, אבל רק אם גם textSize וגם lineHeight מוגדרים ביחידות sp.
מצלמה ומדיה
Ultra HDR לתמונות

ב-Android 14 נוספה תמיכה בתמונות באיכות HDR (טווח דינמי גבוה), שמאפשרות לשמור יותר מידע מהחיישן בזמן הצילום, וכך לייצר צבעים עזים וניגודיות גבוהה יותר. ב-Android נעשה שימוש בפורמט Ultra HDR, שהוא תואם לאחור לתמונות JPEG. כך האפליקציות יכולות לפעול בצורה חלקה עם תמונות HDR ולהציג אותן בטווח דינמי סטנדרטי (SDR) לפי הצורך.
המערכת מבצעת את העיבוד של התמונות האלה בממשק המשתמש ב-HDR באופן אוטומטי כשהאפליקציה בוחרת להשתמש בממשק משתמש ב-HDR בחלון הפעילות שלה, דרך רשומה במניפסט או במהלך זמן הריצה על ידי קריאה ל-Window.setColorMode(). אפשר גם לצלם תמונות סטילס דחוסות ב-Ultra HDR במכשירים נתמכים. כשהחיישן משחזר יותר צבעים, אפשר לערוך את התמונות בצורה גמישה יותר. אפשר להשתמש ב-Gainmap שמשויך לתמונות Ultra HDR כדי ליצור רינדור שלהן באמצעות OpenGL או Vulkan.
זום, מיקוד, תצוגה מקדימה ועוד בתוספים למצלמה
ב-Android 14 יש שיפורים בתוספים למצלמה, שמאפשרים לאפליקציות להתמודד עם זמני עיבוד ארוכים יותר. כך אפשר לצלם תמונות טובות יותר באמצעות אלגוריתמים שמבוססים על חישובים כבדים, כמו צילום בתאורה חלשה במכשירים נתמכים. התכונות האלה מספקות למשתמשים חוויה חזקה עוד יותר כשהם משתמשים ביכולות של התוספים למצלמה. דוגמאות לשיפורים האלה:
- אומדן זמן האחזור הדינמי של עיבוד התמונות הסטטיות מספק אומדנים מדויקים הרבה יותר של זמן האחזור של התמונות הסטטיות, על סמך תנאי הסביבה והסצנה הנוכחיים. קוראים ל-
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()כדי לקבל אובייקטStillCaptureLatencyעם שתי שיטות להערכת זמן האחזור. השיטהgetCaptureLatency()מחזירה את זמן האחזור המשוער ביןonCaptureStartedל-onCaptureProcessStarted(), והשיטהgetProcessingLatency()מחזירה את זמן האחזור המשוער ביןonCaptureProcessStarted()לבין זמינות המסגרת הסופית שעברה עיבוד. - תמיכה בקריאות חזרה (callbacks) של התקדמות הצילום, כדי שאפליקציות יוכלו להציג את ההתקדמות הנוכחית של פעולות עיבוד ממושכות של צילומי סטילס. אפשר לבדוק אם התכונה הזו זמינה באמצעות
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable. אם כן, מטמיעים את פונקציית הקריאה החוזרתonCaptureProcessProgressed(), שבה מועבר הפרמטר של ההתקדמות (מ-0 עד 100). מטא-נתונים ספציפיים לתוסף, כמו
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHכדי להזין את מידת האפקט של התוסף, למשל מידת הטשטוש של הרקע באמצעותEXTENSION_BOKEH.התכונה 'תצוגה לאחר הצילום' לצילום סטילס בתוספים למצלמה, שמספקת תמונה שעברה עיבוד פחות מאשר התמונה הסופית, במהירות גבוהה יותר. אם תוסף מאריך את זמן האחזור לעיבוד, אפשר לספק תמונה שלאחר הצפייה כתמונה זמנית כדי לשפר את חוויית המשתמש, ולאחר מכן להחליף אותה בתמונה הסופית. אפשר לבדוק אם התכונה הזו זמינה באמצעות
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. לאחר מכן תוכלו להעבירOutputConfigurationאלExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.תמיכה ב-
SurfaceViewשמאפשרת נתיב עיבוד נתונים יעיל יותר וחסכוני יותר באנרגיה לתצוגה מקדימה.תמיכה בהקשה כדי להתמקד ובשינוי מרחק התצוגה במהלך השימוש בתוסף.
זום בחיישן
כשהערך של REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE ב-CameraCharacteristics מכיל את הערך SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, האפליקציה יכולה להשתמש ביכולות המתקדמות של החיישן כדי לספק לזרם RAW חתוך את אותם הפיקסלים כמו שדה הראייה המלא, באמצעות CaptureRequest עם יעד RAW שבו מוגדרת תרחיש לדוגמה של שידור כ-CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
הטמעת אמצעי הבקרה של ביטול הבקשה מאפשרת למשתמשי המצלמה המעודכנת לשלוט בהגדרת הזום עוד לפני שפקדי המצלמה האחרים מוכנים.
אודיו ב-USB ללא אובדן נתונים
ב-Android 14 יש תמיכה בפורמטים של אודיו ללא אובדן נתונים, כדי שתוכלו ליהנות מחוויית אודיו ברמה גבוהה באמצעות אוזניות קוויות עם חיבור USB. אפשר לשלוח שאילתה למכשיר USB כדי לקבל את מאפייני המיקסר המועדפים שלו, לרשום מאזין לשינויים במאפייני המיקסר המועדפים ולהגדיר את מאפייני המיקסר באמצעות הכיתה AudioMixerAttributes. המחלקה הזו מייצגת את הפורמט, כמו מסכת הערוץ, קצב הדגימה וההתנהגות של מיקסר האודיו. הסוג הזה מאפשר לשלוח אודיו ישירות, בלי ערבוב, שינוי עוצמת קול או עיבוד אפקטים.
פרודוקטיביות וכלים למפתחים
מנהל פרטי הכניסה
ב-Android 14 נוספה התמיכה ב-Credential Manager כ-API בפלטפורמה, עם תמיכה נוספת במכשירי Android 4.4 (רמת API 19) דרך ספריית Jetpack באמצעות Google Play Services. המטרה של Credential Manager היא להקל על המשתמשים להיכנס באמצעות ממשקי API שמאחזרים ומאחסנים את פרטי הכניסה באמצעות ספקי פרטי כניסה שהמשתמשים מגדירים. Credential Manager תומך במספר שיטות כניסה, כולל שם משתמש וסיסמה, מפתחות גישה ופתרונות כניסה מאוחדת (כמו 'כניסה באמצעות חשבון Google') בממשק API אחד.
למפתחות הגישה יש יתרונות רבים. לדוגמה, מפתחות הגישה מבוססים על תקנים מקובלים בתחום, יכולים לפעול במגוון מערכות הפעלה וסביבות עסקיות בדפדפנים, ואפשר להשתמש בהם גם באתרים וגם באפליקציות.
למידע נוסף, עיינו במסמכי העזרה בנושא Credential Manager ומפתחות גישה ובפוסט בבלוג בנושא Credential Manager ומפתחות גישה.
Health Connect
Health Connect היא מאגר במכשיר לנתוני הבריאות והכושר של המשתמש. היא מאפשרת למשתמשים לשתף נתונים בין האפליקציות המועדפות שלהם, ובמקום אחד הם יכולים לקבוע אילו נתונים הם רוצים לשתף עם האפליקציות האלה.
במכשירים עם גרסאות Android שקדמו ל-Android 14, אפשר להוריד את Health Connect כאפליקציה מחנות Google Play. החל מגרסה Android 14, Health Connect היא חלק מהפלטפורמה ומקבלת עדכונים דרך עדכוני המערכת של Google Play, בלי צורך בהורדה נפרדת. כך אפשר לעדכן את Health Connect בתדירות גבוהה, והאפליקציות יכולות להסתמך על כך ש-Health Connect זמין במכשירים עם Android מגרסה 14 ואילך. המשתמשים יכולים לגשת ל-Health Connect מההגדרות במכשיר, עם אמצעי בקרה על הפרטיות שמוטמעים בהגדרות המערכת.
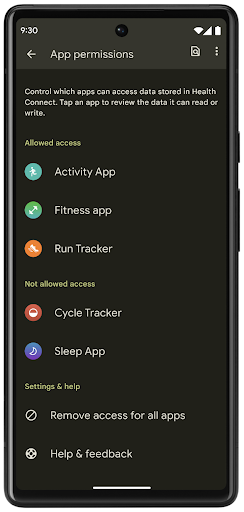
Health Connect כולל כמה תכונות חדשות ב-Android 14, כמו מסלולי אימון, שמאפשרים למשתמשים לשתף מסלול של אימון שאפשר לראות במפה. מסלול מוגדר כרשימה של מיקומים שנשמרו בחלון זמן מסוים, והאפליקציה יכולה להוסיף מסלולים לסשנים של אימונים ולקשר ביניהם. כדי להבטיח שלמשתמשים תהיה שליטה מלאה על המידע הרגיש הזה, הם צריכים לאפשר שיתוף של מסלולים ספציפיים עם אפליקציות אחרות.
מידע נוסף זמין במסמכי התיעוד של Health Connect ובפוסט בבלוג בנושא מה חדש ב-Android Health.
עדכונים ל-OpenJDK 17
ב-Android 14 אנחנו ממשיכים לעדכן את ספריות הליבה של Android כדי להתאים אותן לתכונות בגרסאות OpenJDK LTS האחרונות, כולל עדכוני ספריות ותמיכה בשפה Java 17 למפתחי אפליקציות ופלטפורמות.
התכונות והשיפורים הבאים כלולים:
- עדכנו כ-300 כיתות
java.baseלתמיכה ב-Java 17. - Text Blocks, שמאפשרים להשתמש במחרוזות מילולית של כמה שורות בשפת התכנות Java.
- התאמת דפוסים ל-instanceof, שמאפשרת להתייחס לאובייקט כאל אובייקט מסוג ספציפי ב-
instanceofבלי משתנים נוספים. - כיתות אטומות, שמאפשרות להגביל את המחלקות והממשקים שיכולים להרחיב אותם או להטמיע אותם.
בזכות עדכוני המערכת של Google Play (Project Mainline), יותר מ-600 מיליון מכשירים יכולים לקבל את עדכוני Android Runtime (ART) האחרונים שכוללים את השינויים האלה. זהו חלק מהמחויבות שלנו לספק לאפליקציות סביבה עקבית ומאובטחת יותר במכשירים שונים, ולספק למשתמשים תכונות ויכולות חדשות ללא קשר למהדורות הפלטפורמה.
Java ו-OpenJDK הם סימנים מסחריים או סימנים מסחריים רשומים של Oracle ו/או של השותפים העצמאיים שלה.
שיפורים בחנויות אפליקציות
ב-Android 14 נוספו כמה ממשקי API של PackageInstaller שמאפשרים לחנויות האפליקציות לשפר את חוויית המשתמש שלהן.
בקשה לאישור התקנה לפני ההורדה
יכול להיות שתצטרכו אישור משתמש כדי להתקין או לעדכן אפליקציה.
לדוגמה, כשתוכנית התקנה שמשתמשת בהרשאה REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES מנסה להתקין אפליקציה חדשה. בגרסאות קודמות של Android, חנויות אפליקציות יכולות לבקש אישור מהמשתמש רק אחרי שקבצי ה-APK נכתבים בסשן ההתקנה והסשן מוגדר.
החל מ-Android 14, השיטה requestUserPreapproval() מאפשרת למתקינים לבקש אישור מהמשתמשים לפני ביצוע סשן ההתקנה. השיפור הזה מאפשר לחנות אפליקציות לדחות את הורדת חבילות ה-APK עד שהמשתמש יאשר את ההתקנה. בנוסף, אחרי שהמשתמש מאשר את ההתקנה, חנות האפליקציות יכולה להוריד ולהתקין את האפליקציה ברקע בלי להפריע למשתמש.
לטעון לבעלות על עדכונים עתידיים
השיטה setRequestUpdateOwnership() מאפשרת למתקין להציין למערכת שהוא מתכוון להיות אחראי על עדכונים עתידיים לאפליקציה שהוא מתקין. היכולת הזו מאפשרת לאכוף את הבעלות על העדכון, כלומר רק בעל העדכון רשאי להתקין עדכונים אוטומטיים לאפליקציה. אכיפת הבעלות על העדכון עוזרת לוודא שהמשתמשים מקבלים עדכונים רק מחנות האפליקציות הצפויה.
כל מתקין אחר, כולל אלה שמשתמשים בהרשאה INSTALL_PACKAGES, צריך לקבל אישור מפורש מהמשתמש כדי להתקין עדכון. אם משתמש מחליט להמשיך עם עדכון ממקור אחר, הבעלות על העדכון אבודה.
עדכון אפליקציות בזמנים פחות מפריעים
בדרך כלל, בחנויות האפליקציות לא רוצים לעדכן אפליקציה שבשימוש פעיל, כי זה מוביל לסגירת התהליכים שפועלים באפליקציה, ויכול להפריע למה שהמשתמש עושה.
החל מ-Android 14, ממשק ה-API של InstallConstraints מאפשר למתקינים לוודא שהעדכונים של האפליקציות שלהם מתבצעים בזמן המתאים. לדוגמה, חנות אפליקציות יכולה להפעיל את השיטה commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() כדי לוודא שהעדכון יאושר רק כשהמשתמש כבר לא יוצר אינטראקציה עם האפליקציה הרלוונטית.
התקנה חלקה של חלוקות אופציונליות
כשמשתמשים ב-APKs מפוצלים, אפשר לספק את התכונות של האפליקציה בקובצי APK נפרדים, במקום כ-APK מונוליתי. קובצי APK מפוצלים מאפשרים לחנויות אפליקציות לבצע אופטימיזציה של העברת הרכיבים השונים של האפליקציה. לדוגמה, חנויות אפליקציות עשויות לבצע אופטימיזציה על סמך המאפיינים של מכשיר היעד. ה-API של PackageInstaller תומך בחלוקות מאז ההשקה שלו ברמת API 22.
ב-Android 14, השיטה setDontKillApp() מאפשרת למנהל ההתקנה לציין שלא צריך להרוג את התהליכים שפועלים באפליקציה כשמתקינים פלחים חדשים. חנויות האפליקציות יכולות להשתמש בתכונה הזו כדי להתקין בצורה חלקה תכונות חדשות של אפליקציה בזמן שהמשתמש משתמש באפליקציה.
חבילות של מטא-נתונים של אפליקציות
החל מ-Android 14, מנהל החבילות של Android מאפשר לציין מטא-נתונים של אפליקציות, כמו שיטות לאבטחת נתונים, כדי לכלול אותם בדפי החנות של האפליקציות, כמו Google Play.
זיהוי מתי משתמשים מצלמים מסך במכשיר
כדי ליצור חוויה סטנדרטית יותר לזיהוי צילומי מסך, ב-Android 14 מוצג API לזיהוי צילומי מסך ששומר על הפרטיות. ה-API הזה מאפשר לאפליקציות לרשום פונקציות קריאה חוזרת על בסיס כל פעילות. הקריאות החוזרות האלה מופעלות, והמשתמש מקבל הודעה, כשהמשתמש מצלם צילום מסך בזמן שהפעילות הזו גלויה.
חוויית משתמש
פעולות מותאמות אישית ודירוג משופר של קובץ לשיתוף
ב-Android 14 מתבצע עדכון של גיליון השיתוף של המערכת כדי לתמוך בפעולות מותאמות אישית באפליקציות ובתצוגות מקדימות מפורטות יותר של תוצאות למשתמשים.
הוספת פעולות בהתאמה אישית
ב-Android 14, האפליקציה יכולה להוסיף פעולות בהתאמה אישית לגיליון השיתוף של המערכת שהיא מפעילה.
שיפור הדירוג של יעדים לשיתוף ישיר
ב-Android 14 נעשה שימוש באותות רבים יותר מאפליקציות כדי לקבוע את הדירוג של יעדי השיתוף הישיר, וכך לספק תוצאות מועילות יותר למשתמש. כדי לספק את האות הכי שימושי לדירוג, פועלים לפי ההנחיות לשיפור הדירוג של היעדים של שיתוף ישיר. אפליקציות תקשורת יכולות גם לדווח על שימוש במקשי קיצור להודעות יוצאות ונכנסות.
תמיכה באנימציות מובנות ומותאמות אישית לחיזוי של תנועת החזרה
ב-Android 13 הוספנו את האפשרות להפעיל אנימציה חזרה למסך הבית באופן יזום, כאפשרות לפיתוח. כשמשתמשים בתנועת החלקה לאחור באפליקציה נתמכת עם אפשרות הפיתוח מופעלת, מוצגת אנימציה שמציינת שתנועת ההחלקה לאחור יוצאת מהאפליקציה ומחזירה למסך הבית.
Android 14 כולל כמה שיפורים והנחיות חדשות לגבי 'חזרה חזותית':
- אפשר להגדיר את
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueכדי להביע הסכמה לשימוש באנימציות מערכת לחיזוי תנועת החזרה לכל פעילות בנפרד, במקום לכל האפליקציה. - הוספנו אנימציות מערכת חדשות שיתלוו לאנימציה של החזרה למסך הבית מ-Android 13. אנימציות המערכת החדשות הן פעילות בכל פעילות ומשימות שונות, והן מופיעות באופן אוטומטי אחרי העברה ל'חזרה חזוי'.
- הוספנו אנימציות חדשות של רכיבי Material לגיליונות בתחתית המסך, לגיליונות צדדיים ולחיפוש.
- יצרנו הנחיות לעיצוב ליצירת אנימציות ומעברים מותאמים אישית באפליקציה.
- הוספנו ממשקי API חדשים שתומכים באנימציות מעבר בהתאמה אישית באפליקציה:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- משתמשים ב-
overrideActivityTransitionבמקום ב-overridePendingTransitionכדי ליצור מעברים שתגובה כשהמשתמש מחליק חזרה.
בגרסה הזו של Android 14 בתצוגה מקדימה, כל התכונות של 'חזרה חזותית חזרה' נותרו מאחורי אפשרות למפתחים. כדאי לעיין במדריך למפתחים בנושא העברת האפליקציה לחזרה חזותית חזוי, וגם במדריך למפתחים בנושא יצירת מעברים מותאמים אישית באפליקציה.
ביטולים של הגדרות ברירת המחדל לכל אפליקציה בנפרד על ידי יצרן מכשיר עם מסך גדול
שינוי הגדרות ברמת האפליקציה מאפשר ליצרני המכשירים לשנות את ההתנהגות של האפליקציות במכשירים עם מסך גדול. לדוגמה, ההחרגה FORCE_RESIZE_APP מורה למערכת לשנות את גודל האפליקציה כך שיתאים למימדי המסך (מבלי להשתמש במצב תאימות לגודל) גם אם הערך resizeableActivity="false" מוגדר בקובץ המניפסט של האפליקציה.
השינויים מברירת המחדל נועדו לשפר את חוויית המשתמש במסכים גדולים.
מאפייני מניפסט חדשים מאפשרים להשבית חלק מהשינויים של יצרן המכשירים באפליקציה שלכם.
הגדרות ברירת מחדל שונות לכל אפליקציה למשתמשים במסכים גדולים
שינוי ההגדרות של כל אפליקציה בנפרד משנה את התנהגות האפליקציות במכשירים עם מסך גדול. לדוגמה, שינוי ברירת המחדל של יצרן המכשיר OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE מגדיר את יחס הגובה-רוחב של האפליקציה ל-16:9, ללא קשר להגדרות האפליקציה.
ב-Android 14 QPR1, משתמשים יכולים להחיל שינויים ספציפיים לאפליקציות באמצעות תפריט הגדרות חדש במכשירים עם מסך גדול.
שיתוף מסך של אפליקציה
שיתוף מסך של אפליקציה מאפשר למשתמשים לשתף חלון של אפליקציה במקום את כל מסך המכשיר במהלך הקלטת תוכן המסך.
כשמשתפים את המסך של אפליקציה, סרגל הסטטוס, סרגל הניווט, ההתראות ואלמנטים אחרים בממשק המשתמש של המערכת לא נכללים במסך המשותף. רק התוכן של האפליקציה שנבחרה ישותף.
שיתוף המסך של אפליקציות משפר את הפרודוקטיביות והפרטיות, כי הוא מאפשר למשתמשים להפעיל כמה אפליקציות אבל להגביל את שיתוף התוכן לאפליקציה אחת.
תשובה מהירה מבוססת-LLM ב-Gboard ב-Pixel 8 Pro
במכשירי Pixel 8 Pro עם גרסת Feature Drop מדצמבר, מפתחים יכולים לנסות תשובות חכמות באיכות גבוהה יותר ב-Gboard שמבוססות על מודלים גדולים של שפה (LLM) במכשיר שפועלים על Google Tensor.
התכונה הזו זמינה בתור תצוגה מקדימה מוגבלת באנגלית (ארה"ב) ב-WhatsApp, ב-Line וב-KakaoTalk. כדי להשתמש בתכונה הזו, צריך מכשיר Pixel 8 Pro עם Gboard כמקלדת.
כדי לנסות את התכונה, קודם צריך להפעיל אותה בקטע הגדרות > אפשרויות למפתחים > הגדרות AICore > הפעלת AICore Persistent.
לאחר מכן, פותחים שיחה באפליקציה נתמכת כדי לראות את התשובות המהירות שמבוססות על LLM בשורת ההצעות של Gboard בתגובה להודעות נכנסות.
גרפיקה
אפשר להריץ שאילתות על נתיבים ולבצע אינטרפולציה שלהם
ה-API Path של Android הוא מנגנון עוצמתי וגמיש ליצירה ולרינדור של גרפיקה וקטורית, עם אפשרות לצייר או למלא נתיב, לבנות נתיב מקטעי קו או מעקומות ריבועיות או ממעלה שלישית, לבצע פעולות בוליאניות כדי לקבל צורות מורכבות יותר או את כל האפשרויות האלה בו-זמנית. אחת מהמגבלות היא היכולת לברר מה נמצא בפועל באובייקט Path. הרכיבים הפנימיים של האובייקט לא גלויים למבצעי הקריאה אחרי היצירה.
כדי ליצור Path, צריך לבצע קריאה ל-methods כמו moveTo(), lineTo() ו-cubicTo() כדי להוסיף קטעי נתיב. אבל לא הייתה אפשרות לשאול את הנתיב הזה מהם הפלחים, ולכן צריך לשמור את המידע הזה בזמן היצירה.
החל מ-Android 14, אפשר לשלוח שאילתות לגבי נתיבים כדי לבדוק מה נמצא בהם.
קודם כול, צריך לקבל אובייקט PathIterator באמצעות API של Path.getPathIterator:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
לאחר מכן אפשר לקרוא ל-PathIterator כדי לבצע איטרציה אחרי הפילוחים אחד אחרי השני, ולאחזר את כל הנתונים הנדרשים לכל פלח. בדוגמה הזו נעשה שימוש באובייקטים מסוג PathIterator.Segment, שמארזים את הנתונים בשבילכם:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
ב-PathIterator יש גם גרסה של next() שלא מקצה לה, שבה אפשר להעביר במאגר נתונים זמני כדי לשמור את נתוני הנקודות.
אחד מהתרחישים החשובים לדוגמה לשליחת שאילתות לגבי נתוני Path הוא אינטרפולציה. לדוגמה, יכול להיות שתרצו ליצור אנימציה (או טרנספורמציה) בין שני נתיבים שונים. כדי לפשט את התרחיש הזה, Android 14 כולל גם את השיטה interpolate() ב-Path. בהנחה שלשני הנתיבים יש מבנה פנימי זהה, ה-method interpolate() יוצרת Path חדש עם התוצאה בעלת האינטרפולציה. הדוגמה הזו מחזירה נתיב שהצורה שלו היא חצי (אינטרפולציה לינארית של 0 .5) בין path ל-otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
ספריית graphics-path של Jetpack מאפשרת להשתמש בממשקי API דומים גם בגרסאות קודמות של Android.
רשתות מותאמות אישית עם הצללות של קודקודים ושל פרגמנטים
כבר זמן רב יש ב-Android תמיכה בציור של רשתות משולשים עם הצללה בהתאמה אישית, אבל פורמט הרשת של הקלט היה מוגבל למספר שילובים מוגדרים מראש של מאפיינים. ב-Android 14 נוספה תמיכה במערכות רשת מותאמות אישית, שאפשר להגדיר כמשולשיים או כרצועות משולשים, ואפשר גם להוסיף אותן לאינדקס. המרקשים האלה מצוינים באמצעות מאפיינים מותאמים אישית, צעדים של קודקודים, משתנים ושגיאות של קודקודים וחלקיקים שנכתבו ב-AGSL.
ב-vertex shader מוגדרים המשתנים, כמו המיקום והצבע, ואילו ב-fragment shader אפשר להגדיר את הצבע של הפיקסל, בדרך כלל באמצעות המשתנים שנוצרו על ידי ה-vertex shader. אם הצבע מסופק על ידי ה-fragment shader, הוא מעורבב עם הצבע הנוכחי של Paint באמצעות מצב המיזוג שנבחר בזמן ציור המכסה. אפשר להעביר מאפיינים אחידים לשדרוגים של הפיקסלים והקודקודים כדי לקבל גמישות נוספת.
מעבד מאגר נתונים זמני של חומרה ל-Canvas
כדי לעזור לכם להשתמש ב-API של Canvas ב-Android כדי לצייר עם האצת חומרה ב-HardwareBuffer, ב-Android 14 הוספנו את HardwareBufferRenderer. ה-API הזה
שימושי במיוחד כאשר התרחיש לדוגמה כולל תקשורת עם המערכת
קומפוזיציה עד SurfaceControl עם זמן אחזור קצר
שרטוט.
