Android 14 มีฟีเจอร์และ API ที่ยอดเยี่ยมสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป ความช่วยเหลือต่อไปนี้จะช่วย ให้คุณทราบเกี่ยวกับฟีเจอร์สำหรับแอปและเริ่มต้นใช้งาน API ที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ดูรายการ API ที่เพิ่ม แก้ไข และนำออกโดยละเอียดได้ในรายงานความแตกต่างของ API ดูรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับ API ที่เพิ่มได้ที่เอกสารอ้างอิง Android API สำหรับ Android 14 ให้มองหา API ที่เพิ่มใน API ระดับ 34 หากต้องการดูข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับส่วนที่การเปลี่ยนแปลงของแพลตฟอร์มอาจส่งผลต่อแอปของคุณ โปรดดูการเปลี่ยนแปลงลักษณะการทำงานของ Android 14 สำหรับแอปที่กำหนดเป้าหมายเป็น Android 14 และสำหรับแอปทั้งหมด
การทำให้เป็นสากล
ค่ากำหนดภาษาที่ใช้ในแอป
Android 14 expands on the per-app language features that were introduced in Android 13 (API level 33) with these additional capabilities:
Automatically generate an app's
localeConfig: Starting with Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 and AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, you can configure your app to support per-app language preferences automatically. Based on your project resources, the Android Gradle plugin generates theLocaleConfigfile and adds a reference to it in the final manifest file, so you no longer have to create or update the file manually. AGP uses the resources in theresfolders of your app modules and any library module dependencies to determine the locales to include in theLocaleConfigfile.Dynamic updates for an app's
localeConfig: Use thesetOverrideLocaleConfig()andgetOverrideLocaleConfig()methods inLocaleManagerto dynamically update your app's list of supported languages in the device's system settings. Use this flexibility to customize the list of supported languages per region, run A/B experiments, or provide an updated list of locales if your app utilizes server-side pushes for localization.App language visibility for input method editors (IMEs): IMEs can utilize the
getApplicationLocales()method to check the language of the current app and match the IME language to that language.
Grammatical Inflection API
ผู้คนกว่า 3 พันล้านคนพูดภาษาที่มีเพศ ซึ่งเป็นภาษาที่คำในหมวดหมู่ทางไวยากรณ์ เช่น คำนาม คำกริยา คำคุณศัพท์ และคำบุพบท จะผันตามเพศของบุคคลและวัตถุที่คุณพูดด้วยหรือพูดถึง โดยทั่วไปแล้ว ภาษาที่มีเพศหลายเพศหลายภาษาใช้เพศทางไวยากรณ์เพศชายเป็นเพศเริ่มต้นหรือเพศทั่วไป
การเรียกผู้ใช้ด้วยเพศทางไวยากรณ์ที่ไม่ถูกต้อง เช่น การเรียกผู้หญิงด้วยเพศทางไวยากรณ์ของผู้ชาย อาจส่งผลเสียต่อประสิทธิภาพและทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ ในทางตรงกันข้าม UI ที่มีภาษาที่แสดงเพศตามไวยากรณ์ของผู้ใช้อย่างถูกต้องจะช่วยเพิ่มการมีส่วนร่วมของผู้ใช้ และมอบประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับผู้ใช้แต่ละคนและฟังดูเป็นธรรมชาติมากขึ้น
To help you build a user-centric UI for gendered languages, Android 14 introduces the Grammatical Inflection API, which lets you add support for grammatical gender without refactoring your app.
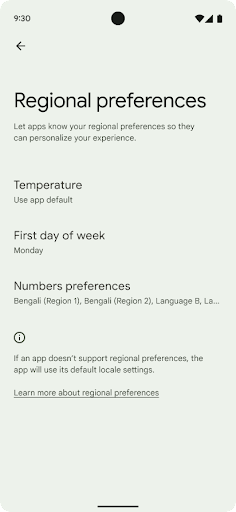
ค่ากำหนดตามพื้นที่
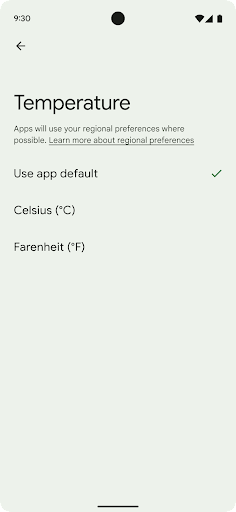
ค่ากำหนดระดับภูมิภาคช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ปรับเปลี่ยนหน่วยอุณหภูมิในแบบของคุณได้ วันของสัปดาห์ และระบบลำดับตัวเลข ชาวยุโรปที่อาศัยอยู่ในสหรัฐอเมริกา คุณอาจต้องการให้หน่วยอุณหภูมิเป็นเซลเซียสมากกว่าฟาเรนไฮต์ และสำหรับ แอปที่กำหนดให้วันจันทร์เป็นวันเริ่มต้นของสัปดาห์แทนที่จะเป็นค่าเริ่มต้นของสหรัฐอเมริกา วันอาทิตย์
เมนูใหม่ในการตั้งค่า Android สำหรับค่ากำหนดเหล่านี้ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้สามารถ
ตำแหน่งส่วนกลางที่ค้นพบได้เพื่อเปลี่ยนค่ากำหนดของแอป การตั้งค่าเหล่านี้จะยังคงอยู่ผ่านการสํารองและคืนค่าด้วย API และ Intent หลายรายการ เช่น getTemperatureUnit และ getFirstDayOfWeek จะให้สิทธิ์แอปของคุณอ่านค่ากําหนดของผู้ใช้ เพื่อให้แอปปรับวิธีแสดงข้อมูลได้ นอกจากนี้ คุณยังจดทะเบียน
BroadcastReceiver ใน
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
เพื่อจัดการการเปลี่ยนแปลงการกำหนดค่าภาษาเมื่อค่ากำหนดระดับภูมิภาคมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงได้
หากต้องการค้นหาการตั้งค่าเหล่านี้ ให้เปิดแอปการตั้งค่าแล้วไปที่ระบบ >ภาษาและการป้อนข้อมูล > ค่ากําหนดระดับภูมิภาค
การช่วยเหลือพิเศษ
การปรับขนาดแบบอักษรที่ไม่ใช่แบบเชิงเส้นเป็น 200%
Starting in Android 14, the system supports font scaling up to 200%, providing users with additional accessibility options.
To prevent large text elements on screen from scaling too large, the system applies a nonlinear scaling curve. This scaling strategy means that large text doesn't scale at the same rate as smaller text. Nonlinear font scaling helps preserve the proportional hierarchy between elements of different sizes while mitigating issues with linear text scaling at high degrees (such as text being cut off or text that becomes harder to read due to an extremely large display sizes).
Test your app with nonlinear font scaling
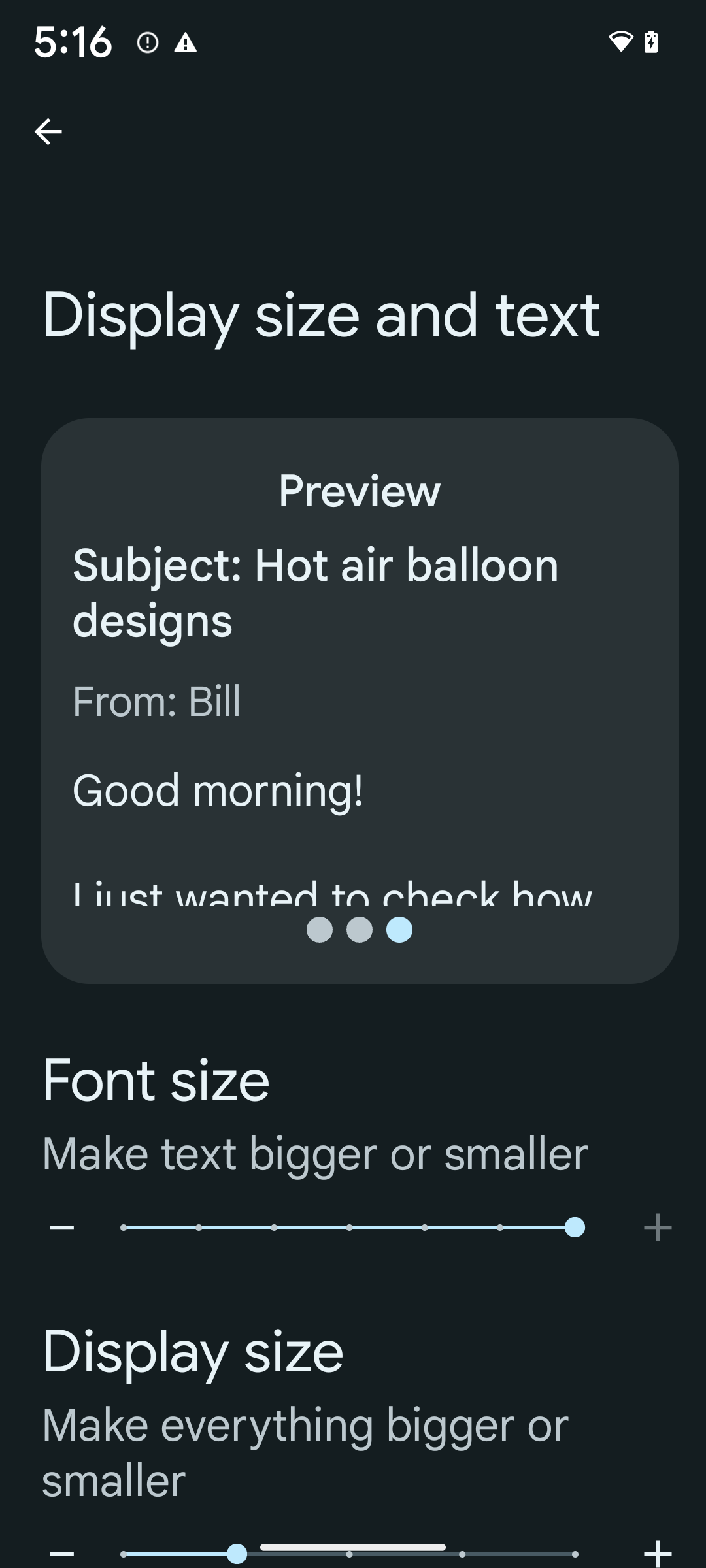
If you already use scaled pixels (sp) units to define text sizing, then these additional options and scaling improvements are applied automatically to the text in your app. However, you should still perform UI testing with the maximum font size enabled (200%) to ensure that your app applies the font sizes correctly and can accommodate larger font sizes without impacting usability.
To enable 200% font size, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Accessibility > Display size and text.
- For the Font size option, tap the plus (+) icon until the maximum font size setting is enabled, as shown in the image that accompanies this section.
Use scaled pixel (sp) units for text-sizes
Remember to always specify text sizes in sp units. When your app uses sp units, Android can apply the user's preferred text size and scale it appropriately.
Don't use sp units for padding or define view heights assuming implicit padding: with nonlinear font scaling sp dimensions might not be proportional, so 4sp + 20sp might not equal 24sp.
Convert scaled pixel (sp) units
Use TypedValue.applyDimension() to convert from sp units
to pixels, and use TypedValue.deriveDimension() to
convert pixels to sp. These methods apply the appropriate nonlinear scaling
curve automatically.
Avoid hardcoding equations using
Configuration.fontScale or
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Because font scaling is
nonlinear, the scaledDensity field is no longer accurate. The fontScale
field should be used for informational purposes only because fonts are no longer
scaled with a single scalar value.
Use sp units for lineHeight
Always define android:lineHeight using sp units instead
of dp, so the line height scales along with your text. Otherwise, if your text
is sp but your lineHeight is in dp or px, it doesn't scale and looks cramped.
TextView automatically corrects the lineHeight so that your intended
proportions are preserved, but only if both textSize and lineHeight are
defined in sp units.
กล้องและสื่อ
Ultra HDR สำหรับรูปภาพ

Android 14 เพิ่มการรองรับรูปภาพ High Dynamic Range (HDR) ที่จะเก็บข้อมูลจากเซ็นเซอร์ได้มากขึ้นเมื่อถ่ายภาพ ซึ่งช่วยให้สีสันสดใสและคอนทราสต์มากขึ้น Android ใช้รูปแบบ Ultra HDR ซึ่งเข้ากันได้กับรูปภาพ JPEG อย่างสมบูรณ์ ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปทำงานร่วมกับรูปภาพ HDR ได้อย่างราบรื่น โดยแสดงรูปภาพในรูปแบบมาตรฐานไดนามิกเรนจ์ (SDR) ตามต้องการ
เฟรมเวิร์กจะแสดงผลรูปภาพเหล่านี้ใน UI เป็น HDR โดยอัตโนมัติเมื่อแอปเลือกใช้ UI HDR สำหรับกรอบเวลากิจกรรม ไม่ว่าจะผ่านรายการไฟล์ Manifest หรือที่รันไทม์โดยการเรียกใช้ Window.setColorMode() นอกจากนี้ คุณยังจับภาพภาพนิ่ง HDR แบบ Ultra ที่บีบอัดในอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับได้ด้วย การกู้คืนสีจากเซ็นเซอร์ได้มากขึ้นช่วยให้การแก้ไขในขั้นตอนหลังมีความยืดหยุ่นมากขึ้น คุณสามารถใช้ Gainmap ที่เชื่อมโยงกับภาพ Ultra HDR เพื่อแสดงผลภาพโดยใช้ OpenGL หรือ Vulkan
ซูม โฟกัส ดูตัวอย่างหลังถ่าย และอื่นๆ ในส่วนขยายกล้อง
Android 14 อัปเกรดและปรับปรุงส่วนขยายกล้อง ซึ่งช่วยให้แอปประมวลผลได้นานขึ้น จึงให้รูปภาพที่ดีขึ้นโดยใช้อัลกอริทึมที่ต้องใช้การประมวลผลอย่างหนัก เช่น การถ่ายภาพในที่แสงน้อยในอุปกรณ์ที่รองรับ ฟีเจอร์เหล่านี้ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ได้รับประสบการณ์การใช้งานที่มีประสิทธิภาพยิ่งขึ้นเมื่อใช้ความสามารถของส่วนขยายกล้อง ตัวอย่างการปรับปรุงเหล่านี้ ได้แก่
- การประมาณเวลาในการตอบสนองของการประมวลผลภาพนิ่งแบบไดนามิกจะให้ค่าประมาณเวลาในการตอบสนองของภาพนิ่งที่แม่นยำกว่ามากโดยอิงตามฉากปัจจุบันและสภาพสภาพแวดล้อม โทรไปที่
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()เพื่อรับออบเจ็กต์StillCaptureLatencyที่มีวิธีการประมาณเวลาในการตอบสนอง 2 วิธี เมธอดgetCaptureLatency()จะแสดงผลเวลาในการตอบสนองโดยประมาณระหว่างonCaptureStartedกับonCaptureProcessStarted()และเมธอดgetProcessingLatency()จะแสดงผลเวลาในการตอบสนองโดยประมาณระหว่างonCaptureProcessStarted()กับเวลาที่เฟรมที่ประมวลผลแล้วเฟรมสุดท้ายพร้อมใช้งาน - รองรับการเรียกกลับความคืบหน้าในการจับภาพเพื่อให้แอปแสดงความคืบหน้าปัจจุบันของการดำเนินการประมวลผลภาพนิ่งที่ทำงานต่อเนื่องเป็นเวลานาน คุณสามารถตรวจสอบว่าฟีเจอร์นี้พร้อมใช้งานใน
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailableหรือไม่ หากพร้อมใช้งาน คุณก็สามารถใช้การเรียกกลับonCaptureProcessProgressed()ซึ่งจะส่งความคืบหน้า (จาก 0 ถึง 100) เป็นพารามิเตอร์ ข้อมูลเมตาเฉพาะของชิ้นงาน เช่น
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHสำหรับปรับระดับเอฟเฟกต์ของชิ้นงาน เช่น ระดับการเบลอพื้นหลังEXTENSION_BOKEHฟีเจอร์ดูภาพหลังถ่ายสําหรับการจับภาพนิ่งในส่วนขยายกล้อง ซึ่งจะแสดงภาพที่ประมวลผลน้อยลงได้เร็วกว่าภาพสุดท้าย หากชิ้นงานมีความล่าช้าในการประมวลผลเพิ่มขึ้น คุณอาจระบุรูปภาพหลังดูเป็นตัวยึดตําแหน่งเพื่อปรับปรุง UX และเปลี่ยนเป็นรูปภาพสุดท้ายในภายหลัง คุณสามารถตรวจสอบว่าฟีเจอร์นี้พร้อมใช้งานใน
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailableหรือไม่ จากนั้นคุณสามารถส่งOutputConfigurationไปยังExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfigurationได้การรองรับ
SurfaceViewซึ่งช่วยให้เส้นทางการแสดงผลตัวอย่างได้รับการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพและประหยัดพลังงานมากขึ้นรองรับการแตะเพื่อโฟกัสและซูมระหว่างการใช้ส่วนขยาย
การซูมในเซ็นเซอร์
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
เสียง USB แบบไม่สูญเสียข้อมูล
Android 14 gains support for lossless audio formats for audiophile-level
experiences over USB wired headsets. You can query a USB device for its
preferred mixer attributes, register a listener for changes in preferred mixer
attributes, and configure mixer attributes using the
AudioMixerAttributes class. This class represents the
format, such as channel mask, sample rate, and behavior of the audio mixer. The
class allows for audio to be sent directly, without mixing,
volume adjustment, or processing effects.
ประสิทธิภาพการทำงานและเครื่องมือสำหรับนักพัฒนาซอฟต์แวร์
Credential Manager
Android 14 เพิ่ม Credential Manager เป็น API ของแพลตฟอร์ม โดยรองรับอุปกรณ์ Android 4.4 (API ระดับ 19) เพิ่มเติมผ่านคลัง Jetpack โดยใช้บริการ Google Play Credential Manager มีเป้าหมายเพื่อช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ลงชื่อเข้าใช้ได้ง่ายขึ้นด้วย API ที่ดึงข้อมูลและจัดเก็บข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบด้วยผู้ให้บริการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบที่ผู้ใช้กําหนดค่าไว้ Credential Manager รองรับวิธีการลงชื่อเข้าใช้หลายวิธี รวมถึงชื่อผู้ใช้และรหัสผ่าน พาสคีย์ และโซลูชันการลงชื่อเข้าใช้แบบรวมศูนย์ (เช่น ฟีเจอร์ลงชื่อเข้าใช้ด้วย Google) ใน API เดียว
พาสคีย์มีข้อดีหลายประการ เช่น พาสคีย์สร้างขึ้นตามมาตรฐานอุตสาหกรรม ทำงานได้กับระบบปฏิบัติการและระบบนิเวศของเบราว์เซอร์ต่างๆ รวมถึงใช้ได้กับทั้งเว็บไซต์และแอป
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่เอกสารประกอบเกี่ยวกับเครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบและพาสคีย์และบล็อกโพสต์เกี่ยวกับเครื่องมือจัดการข้อมูลเข้าสู่ระบบและพาสคีย์
Health Connect
Health Connect เป็นพื้นที่เก็บข้อมูลในอุปกรณ์สำหรับข้อมูลสุขภาพและการออกกำลังกายของผู้ใช้ ซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้แชร์ข้อมูลระหว่างแอปโปรดได้โดยมีที่เดียวในการควบคุมข้อมูลที่ต้องการแชร์กับแอปเหล่านี้
ในอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android เวอร์ชันก่อน Android 14 คุณจะดาวน์โหลด Health Connect ในรูปแบบแอปได้ใน Google Play Store ตั้งแต่ Android 14 เป็นต้นไป Health Connect จะเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของแพลตฟอร์มและได้รับการอัปเดตผ่านการอัปเดตระบบ Google Play โดยไม่ต้องดาวน์โหลดแยกต่างหาก ซึ่งจะช่วยให้ Health Connect ได้รับการอัปเดตบ่อยครั้ง และแอปของคุณจะใช้ Health Connect ได้บนอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้ Android 14 ขึ้นไป ผู้ใช้สามารถเข้าถึง Health Connect ได้จากการตั้งค่าในอุปกรณ์ โดยจะมีการควบคุมความเป็นส่วนตัวที่ผสานรวมอยู่ในการตั้งค่าระบบ
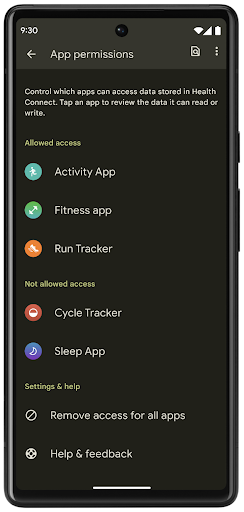
Health Connect มีฟีเจอร์ใหม่ๆ หลายอย่างใน Android 14 เช่น เส้นทางออกกำลังกาย ซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้แชร์เส้นทางการออกกําลังกายที่แสดงเป็นภาพบนแผนที่ได้ เส้นทางหมายถึงรายการสถานที่ที่บันทึกไว้ภายในกรอบเวลาหนึ่งๆ และแอปของคุณสามารถแทรกเส้นทางลงในเซสชันการออกกำลังกายเพื่อเชื่อมโยงเข้าด้วยกัน ผู้ใช้ต้องอนุญาตให้แชร์เส้นทางแต่ละเส้นทางกับแอปอื่นๆ เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าผู้ใช้มีสิทธิ์ควบคุมข้อมูลที่ละเอียดอ่อนนี้อย่างสมบูรณ์
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมได้ที่เอกสารประกอบเกี่ยวกับการเชื่อมต่อ Health และบล็อกโพสต์เกี่ยวกับมีอะไรใหม่ใน Android Health
การอัปเดต OpenJDK 17
Android 14 ยังคงปรับปรุงไลบรารีหลักของ Android ให้สอดคล้องกับฟีเจอร์ใน OpenJDK LTS เวอร์ชันล่าสุด ซึ่งรวมถึงทั้งการอัปเดตไลบรารีและการรองรับภาษา Java 17 สําหรับนักพัฒนาแอปและแพลตฟอร์ม
ฟีเจอร์และการปรับปรุงต่อไปนี้จะรวมอยู่ด้วย
- อัปเดตคลาส
java.baseประมาณ 300 คลาสให้รองรับ Java 17 - บล็อกข้อความ ซึ่งจะนําสตริงตัวอักษรหลายบรรทัดมาสู่ภาษาโปรแกรม Java
- การจับคู่รูปแบบสำหรับ instanceof ซึ่งช่วยให้ระบบถือว่าออบเจ็กต์มีประเภทที่เฉพาะเจาะจงใน
instanceofโดยไม่ต้องมีตัวแปรเพิ่มเติม - คลาสที่ปิด ซึ่งช่วยให้คุณจำกัดคลาสและอินเทอร์เฟซที่ขยายหรือนำไปใช้ได้
การอัปเดตระบบ Google Play (Project Mainline) ช่วยให้อุปกรณ์กว่า 600 ล้านเครื่องสามารถรับการอัปเดต Android Runtime (ART) ล่าสุดที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ ซึ่งเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของความมุ่งมั่นของเราที่จะมอบสภาพแวดล้อมที่ปลอดภัยและสอดคล้องกันมากขึ้นให้แก่แอปในอุปกรณ์ต่างๆ รวมถึงมอบฟีเจอร์และความสามารถใหม่ๆ ให้แก่ผู้ใช้โดยไม่ขึ้นอยู่กับรุ่นของแพลตฟอร์ม
Java และ OpenJDK เป็นเครื่องหมายการค้าหรือเครื่องหมายการค้าจดทะเบียนของ Oracle และ/หรือบริษัทในเครือ
การปรับปรุงสำหรับ App Store
Android 14 introduces several PackageInstaller APIs that
allow app stores to improve their user experience.
Request install approval before downloading
Installing or updating an app might require user approval.
For example, when an installer making use of the
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES permission attempts to install a
new app. In prior Android versions, app stores can only request user approval
after APKs are written to the install session and the
session is committed.
Starting with Android 14, the requestUserPreapproval()
method lets installers request user approval before committing the install
session. This improvement lets an app store defer downloading any APKs until
after the installation has been approved by the user. Furthermore, once a user
has approved installation, the app store can download and install the app in the
background without interrupting the user.
Claim responsibility for future updates
The setRequestUpdateOwnership() method allows an installer
to indicate to the system that it intends to be responsible for future updates
to an app it is installing. This capability enables update ownership
enforcement, meaning that only the update owner is permitted
to install automatic updates to the app. Update ownership enforcement helps to
ensure that users receive updates only from the expected app store.
Any other installer, including those making use of the
INSTALL_PACKAGES permission, must receive explicit user
approval in order to install an update. If a user decides to proceed with an
update from another source, update ownership is lost.
Update apps at less-disruptive times
App stores typically want to avoid updating an app that is actively in use because this leads to the app's running processes being killed, which potentially interrupts what the user was doing.
Starting with Android 14, the InstallConstraints API
gives installers a way to ensure that their app updates happen at an opportune
moment. For example, an app store can call the
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() method to
make sure that an update is only committed when the user is no longer
interacting with the app in question.
Seamlessly install optional splits
With split APKs, features of an app can be delivered in separate APK files,
rather than as a monolithic APK. Split APKs allow app stores to optimize the
delivery of different app components. For example, app stores might optimize
based on the properties of the target device. The
PackageInstaller API has supported splits since its
introduction in API level 22.
In Android 14, the setDontKillApp() method allows an
installer to indicate that the app's running processes shouldn't be killed when
new splits are installed. App stores can use this feature to seamlessly install
new features of an app while the user is using the app.
App Bundle ข้อมูลเมตา
Starting in Android 14, the Android package installer lets you specify app metadata, such as data safety practices, to include on app store pages such as Google Play.
ตรวจหาเวลาที่ผู้ใช้ถ่ายภาพหน้าจอของอุปกรณ์
To create a more standardized experience for detecting screenshots, Android 14 introduces a privacy-preserving screenshot detection API. This API lets apps register callbacks on a per-activity basis. These callbacks are invoked, and the user is notified, when the user takes a screenshot while that activity is visible.
ประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้
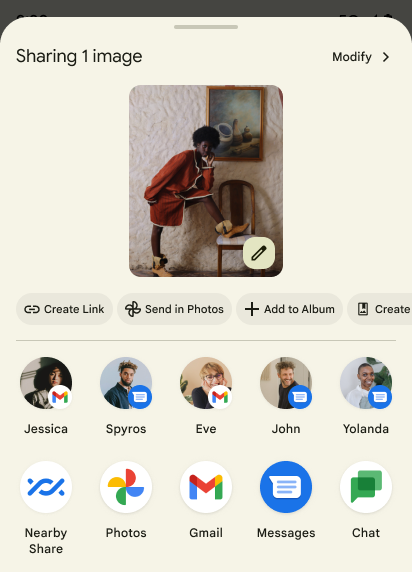
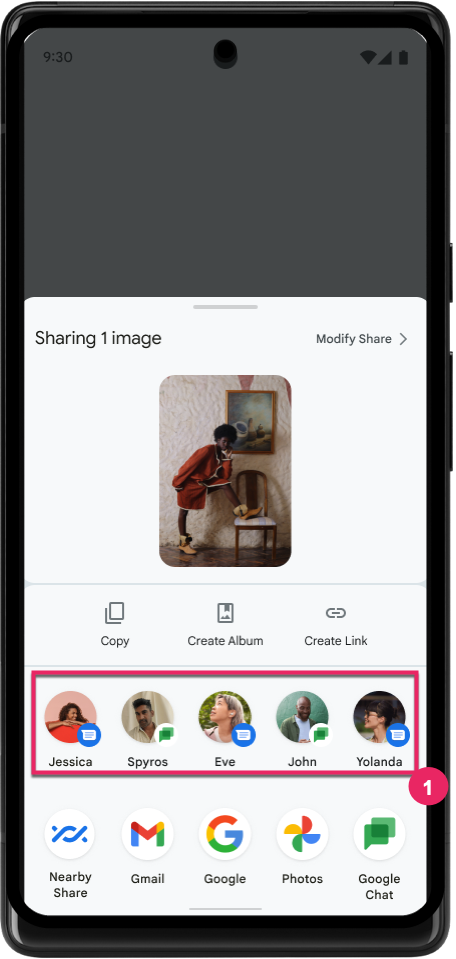
การทำงานที่กำหนดเองของชีตการแชร์และการจัดอันดับที่ดียิ่งขึ้น
Android 14 อัปเดตชีตการแชร์ของระบบเพื่อรองรับการดำเนินการของแอปที่กำหนดเองและแสดงตัวอย่างผลลัพธ์ที่เป็นประโยชน์มากขึ้นสำหรับผู้ใช้
เพิ่มการดําเนินการที่กำหนดเอง
เมื่อใช้ Android 14 แอปของคุณจะเพิ่มการดำเนินการที่กำหนดเองลงในชีตการแชร์ของระบบที่เรียกใช้
ปรับปรุงการจัดอันดับของเป้าหมายการแชร์โดยตรง
Android 14 ใช้สัญญาณจากแอปมากขึ้นเพื่อกำหนดการจัดอันดับของเป้าหมายการแชร์โดยตรงเพื่อให้ผลการค้นหาที่เป็นประโยชน์มากขึ้นแก่ผู้ใช้ โปรดปฏิบัติตามคำแนะนำสำหรับการปรับปรุงการจัดอันดับของเป้าหมายการแชร์โดยตรงเพื่อให้สัญญาณที่มีประโยชน์มากที่สุดสำหรับการจัดอันดับ นอกจากนี้ แอปการสื่อสารยังรายงานการใช้งานแป้นพิมพ์ลัดสำหรับข้อความขาออกและขาเข้าได้ด้วย
รองรับภาพเคลื่อนไหวในตัวและภาพเคลื่อนไหวที่กำหนดเองสำหรับท่าทางสัมผัสย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดา
Android 13 ได้เปิดตัวภาพเคลื่อนไหวแบบคาดเดาซึ่งนำผู้ใช้กลับไปยังหน้าจอหลักจากตัวเลือกของนักพัฒนาแอป เมื่อใช้ในแอปที่รองรับซึ่งเปิดใช้ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป การปัดย้อนกลับจะแสดงภาพเคลื่อนไหวที่ระบุว่าท่าทางสัมผัสย้อนกลับจะนำออกจากแอปกลับไปที่หน้าจอหลัก
Android 14 มีการปรับปรุงหลายอย่างและคำแนะนำใหม่สำหรับฟีเจอร์การย้อนกลับแบบคาดการณ์ ดังนี้
- คุณสามารถตั้งค่า
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueเพื่อเลือกใช้การเคลื่อนไหวของระบบสำหรับการย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดาต่อกิจกรรมแทนทั้งแอป - เราได้เพิ่มภาพเคลื่อนไหวใหม่ของระบบเพื่อใช้ควบคู่ไปกับภาพเคลื่อนไหวของการเปลี่ยนกลับไปที่หน้าแรกจาก Android 13 ภาพเคลื่อนไหวของระบบแบบใหม่จะทำงานข้ามกิจกรรมและข้ามงาน ซึ่งคุณจะได้รับโดยอัตโนมัติหลังจากย้ายข้อมูลไปยังท่าทางสัมผัสย้อนกลับแบบคาดเดา
- เราได้เพิ่มภาพเคลื่อนไหวใหม่สำหรับคอมโพเนนต์ Material สำหรับชีตด้านล่าง ชีตด้านข้าง และการค้นหา
- เราได้จัดทำคำแนะนำด้านการออกแบบสำหรับการสร้างภาพเคลื่อนไหวและทรานซิชันในแอปที่กำหนดเอง
- เราได้เพิ่ม API ใหม่เพื่อรองรับภาพเคลื่อนไหวการเปลี่ยนภาพในแอปที่กําหนดเอง ดังนี้
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- ใช้
overrideActivityTransitionแทนoverridePendingTransitionสำหรับทรานซิชันที่ตอบสนองเมื่อผู้ใช้ปัดกลับ
ในรุ่นตัวอย่างของ Android 14 นี้ ฟีเจอร์ทั้งหมดของฟีเจอร์การกดย้อนกลับแบบคาดคะเนจะยังคงอยู่ในตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป ดูคู่มือนักพัฒนาแอปเพื่อย้ายข้อมูลแอปไปใช้แบ็กเอนด์แบบคาดการณ์ รวมถึงคู่มือนักพัฒนาแอปในการสร้างทรานซิชันในแอปที่กําหนดเอง
การลบล้างต่อแอปของผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์ที่มีหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
การลบล้างค่าแอปต่อแอปช่วยให้ผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์เปลี่ยนลักษณะการทำงานของแอปในอุปกรณ์ที่มีหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น การลบล้าง FORCE_RESIZE_APP จะสั่งให้ระบบปรับขนาดแอปให้พอดีกับขนาดการแสดงผล (หลีกเลี่ยงโหมดความเข้ากันได้ของขนาด) แม้ว่าจะมีการตั้งค่า resizeableActivity="false" ในไฟล์ Manifest ของแอปก็ตาม
การลบล้างมีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อปรับปรุงประสบการณ์ของผู้ใช้บนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
พร็อพเพอร์ตี้ไฟล์ Manifest ใหม่ช่วยให้คุณปิดใช้การลบล้างผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์บางรายสำหรับแอปของคุณได้
การลบล้างต่อแอปสำหรับผู้ใช้หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
การลบล้างในแต่ละแอปจะเปลี่ยนลักษณะการทำงานของแอปในอุปกรณ์หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ ตัวอย่างเช่น ผู้ผลิตอุปกรณ์ OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE ลบล้างการตั้งค่าสัดส่วนภาพของแอปเป็น 16:9 โดยไม่คำนึงถึงการกำหนดค่าของแอป
Android 14 QPR1 ช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ใช้การลบล้างระดับแอปได้ผ่านเมนูการตั้งค่าใหม่ในอุปกรณ์หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
การแชร์หน้าจอแอป
App screen sharing enables users to share an app window instead of the entire device screen during screen content recording.
With app screen sharing, the status bar, navigation bar, notifications, and other system UI elements are excluded from the shared display. Only the content of the selected app is shared.
App screen sharing improves productivity and privacy by enabling users to run multiple apps but limit content sharing to a single app.
ฟีเจอร์ช่วยตอบที่ทำงานด้วย LLM ใน Gboard บน Pixel 8 Pro
ในอุปกรณ์ Pixel 8 Pro ที่มีฟีเจอร์ใหม่ประจำเดือนธันวาคม นักพัฒนาแอปสามารถลองใช้ฟีเจอร์ช่วยตอบที่มีคุณภาพสูงขึ้นใน Gboard ซึ่งขับเคลื่อนโดยโมเดลภาษาขนาดใหญ่ (LLM) ในอุปกรณ์ที่ทำงานบน Google Tensor
ฟีเจอร์นี้มีให้บริการเป็นเวอร์ชันตัวอย่างแบบจำกัดสำหรับภาษาอังกฤษแบบสหรัฐอเมริกาใน WhatsApp, Line และ KakaoTalk โดยต้องใช้อุปกรณ์ Pixel 8 Pro ที่มี Gboard เป็นแป้นพิมพ์
หากต้องการลองใช้ ให้เปิดใช้ฟีเจอร์นี้ในการตั้งค่า > ตัวเลือกสำหรับนักพัฒนาแอป > การตั้งค่า AiCore > เปิดใช้ AiCore Persistent ก่อน
จากนั้นเปิดการสนทนาในแอปที่รองรับเพื่อดูการช่วยตอบที่ทำงานด้วย LLM ในแถบคำแนะนำของ Gboard เพื่อตอบกลับข้อความที่เข้ามา
กราฟิก
เส้นทางสามารถค้นหาและประมาณค่าได้
Android's Path API is a powerful and flexible mechanism for
creating and rendering vector graphics, with the ability to stroke or fill a
path, construct a path from line segments or quadratic or cubic curves, perform
boolean operations to get even more complex shapes, or all of these
simultaneously. One limitation is the ability to find out what is actually in a
Path object; the internals of the object are opaque to callers after creation.
To create a Path, you call methods such as
moveTo(), lineTo(), and
cubicTo() to add path segments. But there has been no way to
ask that path what the segments are, so you must retain that information at
creation time.
Starting in Android 14, you can query paths to find out what's inside of them.
First, you need to get a PathIterator object using the
Path.getPathIterator API:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Next, you can call PathIterator to iterate through the segments
one by one, retrieving all of the necessary data for each segment. This example
uses PathIterator.Segment objects, which packages up the data
for you:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator also has a non-allocating version of next() where you can pass
in a buffer to hold the point data.
One of the important use cases of querying Path data is interpolation. For
example, you might want to animate (or morph) between two different paths. To
further simplify that use case, Android 14 also includes the
interpolate() method on Path. Assuming the two paths have
the same internal structure, the interpolate() method creates a new Path
with that interpolated result. This example returns a path whose shape is
halfway (a linear interpolation of .5) between path and otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
The Jetpack graphics-path library enables similar APIs for earlier versions of Android as well.
Custom meshes with vertex and fragment shaders
Android รองรับการวาดเมชรูปสามเหลี่ยมด้วยการแรเงาที่กำหนดเองมานานแล้ว แต่รูปแบบเมชอินพุตถูกจำกัดไว้ที่การผสมผสานแอตทริบิวต์ที่กำหนดไว้ล่วงหน้าเพียงไม่กี่รายการ Android 14 เพิ่มการรองรับเมชที่กำหนดเอง ซึ่งสามารถกำหนดเป็นสามเหลี่ยมหรือแถบสามเหลี่ยม และสามารถจัดทำดัชนีได้ (ไม่บังคับ) ตาข่ายเหล่านี้ระบุด้วยแอตทริบิวต์ที่กำหนดเอง ระยะห่างของจุดยอด ตัวแปร และเชนเดอร์จุดยอดและเศษส่วนที่เขียนใน AGSL
เวิร์กเชดเดอร์กำหนดตัวแปรต่างๆ เช่น ตำแหน่งและสี ส่วนฟร็กเมนทัลเชดเดอร์จะกำหนดสีของพิกเซลได้ (ไม่บังคับ) โดยปกติจะใช้ตัวแปรต่างๆ ที่เวิร์กเชดเดอร์สร้างขึ้น หากฟร็กเมชันเชเดอร์ระบุสี ระบบจะผสมสีนั้นเข้ากับสี Paint ที่ใช้อยู่โดยใช้โหมดการผสมที่เลือกไว้เมื่อวาดเมช คุณสามารถส่งยูนิฟอร์มไปยังเชดเดอร์เศษและเชดเดอร์เวิร์กเท็กซ์เพื่อเพิ่มความยืดหยุ่นได้
เครื่องมือแสดงผลบัฟเฟอร์ฮาร์ดแวร์สำหรับ Canvas
Android 14 เปิดตัว HardwareBufferRenderer เพื่อช่วยในการใช้ Canvas API ของ Android เพื่อวาดด้วย GPU ลงใน HardwareBuffer API นี้
ซึ่งจะเป็นประโยชน์อย่างยิ่งเมื่อกรณีการใช้งานของคุณเกี่ยวข้องกับการสื่อสารกับระบบ
Compositor ผ่าน SurfaceControl สำหรับเวลาในการตอบสนองต่ำ
ภาพวาด

