В Android 14 представлены отличные функции и API для разработчиков. Информация ниже поможет вам узнать о функциях ваших приложений и начать работу с соответствующими API.
Подробный список добавленных, измененных и удаленных API см. в отчете о различиях в API . Подробнее о добавленных API см. в справочнике по API Android . Для Android 14 найдите API, добавленные на уровне API 34. Чтобы узнать об областях, где изменения платформы могут повлиять на ваши приложения, ознакомьтесь с изменениями в поведении приложений, ориентированных на Android 14 , и для всех приложений .
Интернационализация
Настройки языка для каждого приложения
В Android 14 языковые функции каждого приложения , которые были представлены в Android 13 (уровень API 33), расширены следующими дополнительными возможностями:
Автоматически генерировать
localeConfigприложения . Начиная с Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 и AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, вы можете настроить свое приложение для автоматической поддержки языковых настроек для каждого приложения . На основе ресурсов вашего проекта плагин Android Gradle создает файлLocaleConfigи добавляет ссылку на него в окончательный файл манифеста, поэтому вам больше не придется создавать или обновлять файл вручную. AGP использует ресурсы в папкахresмодулей вашего приложения и любых зависимостях модулей библиотеки, чтобы определить локали, которые необходимо включить в файлLocaleConfig.Динамические обновления для
localeConfigприложения . Используйте методыsetOverrideLocaleConfig()иgetOverrideLocaleConfig()вLocaleManagerчтобы динамически обновлять список поддерживаемых языков вашего приложения в системных настройках устройства . Используйте эту гибкость, чтобы настроить список поддерживаемых языков для каждого региона, проводить эксперименты A/B или предоставлять обновленный список языков, если ваше приложение использует отправку на стороне сервера для локализации.Видимость языка приложения для редакторов методов ввода (IME) . IME могут использовать метод
getApplicationLocales()для проверки языка текущего приложения и сопоставления языка IME с этим языком.
API грамматического склонения
3 миллиарда человек говорят на гендерных языках : языках, в которых грамматические категории, такие как существительные, глаголы, прилагательные и предлоги, изменяются в зависимости от пола людей и предметов, с которыми вы разговариваете или о которых вы говорите. Традиционно во многих гендерных языках мужской грамматический род используется в качестве родового или общего рода по умолчанию.
Обращение к пользователям неправильного грамматического рода, например обращение к женщинам мужского грамматического рода, может негативно повлиять на их работу и отношение. Напротив, пользовательский интерфейс с языком, который правильно отражает грамматический пол пользователя, может улучшить взаимодействие с пользователем и обеспечить более персонализированный и естественный пользовательский интерфейс.
Чтобы помочь вам создать ориентированный на пользователя пользовательский интерфейс для языков с гендерной принадлежностью, в Android 14 представлен API Grammatical Inflection , который позволяет добавить поддержку грамматического рода без рефакторинга приложения.
,Чтобы помочь вам создать ориентированный на пользователя пользовательский интерфейс для языков с гендерной принадлежностью, в Android 14 представлен API Grammatical Inflection , который позволяет добавить поддержку грамматического рода без рефакторинга приложения.
,Чтобы помочь вам создать ориентированный на пользователя пользовательский интерфейс для языков с гендерной принадлежностью, в Android 14 представлен API Grammatical Inflection , который позволяет добавить поддержку грамматического рода без рефакторинга приложения.
,Чтобы помочь вам создать ориентированный на пользователя пользовательский интерфейс для языков с гендерной принадлежностью, в Android 14 представлен API Grammatical Inflection , который позволяет добавить поддержку грамматического рода без рефакторинга приложения.
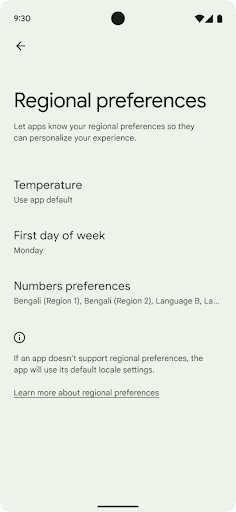
Региональные предпочтения
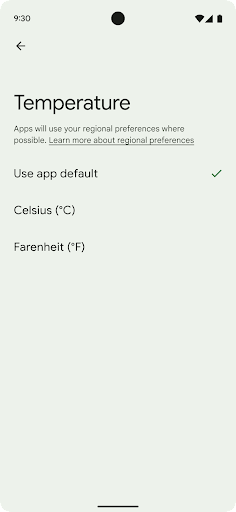
Региональные настройки позволяют пользователям персонализировать единицы измерения температуры, первый день недели и системы нумерации. Европеец, живущий в Соединенных Штатах, может предпочесть, чтобы единицы температуры были в градусах Цельсия, а не в Фаренгейте, и чтобы приложения считали понедельник началом недели, а не воскресенье по умолчанию в США.
Новые меню настроек Android для этих настроек предоставляют пользователям доступное и централизованное место для изменения настроек приложений. Эти настройки также сохраняются при резервном копировании и восстановлении. Некоторые API и намерения, такие как getTemperatureUnit и getFirstDayOfWeek , предоставляют вашему приложению доступ для чтения к пользовательским настройкам, поэтому ваше приложение может настроить способ отображения информации. Вы также можете зарегистрировать BroadcastReceiver в ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED для обработки изменений конфигурации локали при изменении региональных предпочтений.
Чтобы найти эти настройки, откройте приложение «Настройки» и выберите «Система» > «Языки и ввод» > «Региональные настройки» .
Доступность
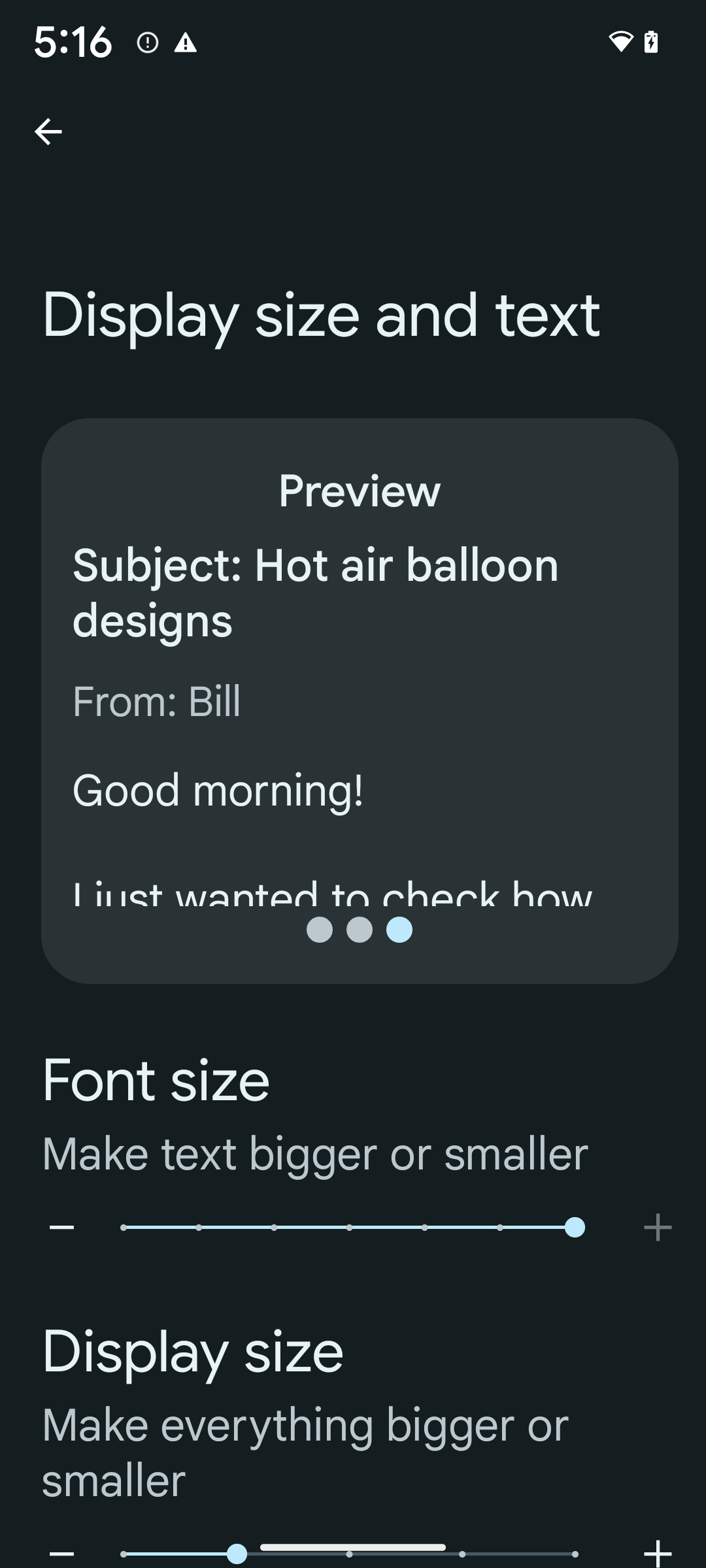
Нелинейное масштабирование шрифта до 200%
Начиная с Android 14, система поддерживает масштабирование шрифтов до 200%, предоставляя пользователям дополнительные возможности доступа.
Чтобы предотвратить чрезмерное масштабирование крупных текстовых элементов на экране, система применяет нелинейную кривую масштабирования. Эта стратегия масштабирования означает, что крупный текст масштабируется не с той же скоростью, что и мелкий. Нелинейное масштабирование шрифтов помогает сохранить пропорциональную иерархию между элементами разных размеров, одновременно смягчая проблемы, возникающие при масштабировании линейного текста с высокой степенью масштабирования (например, обрезание текста или усложнение чтения текста из-за слишком большого размера экрана).
Протестируйте свое приложение с нелинейным масштабированием шрифтов
Если вы уже используете единицы измерения масштаба текста в пикселях (sp), то эти дополнительные параметры и улучшения масштабирования будут автоматически применены к тексту в вашем приложении. Однако вам всё равно следует провести тестирование пользовательского интерфейса с максимальным размером шрифта (200%), чтобы убедиться, что ваше приложение корректно применяет размеры шрифтов и может работать с более крупными шрифтами без ущерба для удобства использования.
Чтобы включить размер шрифта 200%, выполните следующие действия:
- Откройте приложение «Настройки» и перейдите в раздел «Специальные возможности» > «Размер дисплея и текст» .
- Для параметра «Размер шрифта» нажимайте значок плюс (+), пока не будет включена настройка максимального размера шрифта, как показано на изображении в этом разделе.
Используйте единицы измерения масштабированных пикселей (sp) для размеров текста
Не забывайте всегда указывать размеры текста в единицах измерения SP . Если ваше приложение использует единицы измерения SP, Android может применить выбранный пользователем размер текста и масштабировать его соответствующим образом.
Не используйте единицы sp для отступов и не определяйте высоту представления, предполагая неявный отступ: при нелинейном масштабировании шрифтов размеры sp могут быть не пропорциональны, поэтому 4sp + 20sp может не равняться 24sp.
Преобразовать масштабированные единицы пикселей (sp)
Используйте TypedValue.applyDimension() для преобразования единиц sp в пиксели, а метод TypedValue.deriveDimension() — для преобразования пикселей в sp. Эти методы автоматически применяют соответствующую кривую нелинейного масштабирования.
Избегайте жёсткого кодирования уравнений с помощью Configuration.fontScale или DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity . Поскольку масштабирование шрифтов нелинейно, поле scaledDensity больше не является точным. Поле fontScale следует использовать только в информационных целях, поскольку шрифты больше не масштабируются одним скалярным значением.
Используйте единицы sp для lineHeight
Всегда определяйте android:lineHeight в единицах sp, а не dp, чтобы высота строки масштабировалась вместе с текстом. В противном случае, если текст имеет значение sp, а lineHeight — в dp или px, он не масштабируется и выглядит сжатым. TextView автоматически корректирует lineHeight , сохраняя заданные пропорции, но только если textSize и lineHeight заданы в единицах sp.
Камера и медиа
Ultra HDR для изображений

В Android 14 добавлена поддержка изображений с расширенным динамическим диапазоном (HDR), которые сохраняют больше информации от датчика при съемке фотографии, что обеспечивает яркие цвета и большую контрастность. Android использует формат Ultra HDR , который полностью обратно совместим с изображениями JPEG, что позволяет приложениям беспрепятственно взаимодействовать с изображениями HDR, отображая их в стандартном динамическом диапазоне (SDR) по мере необходимости.
Рендеринг этих изображений в пользовательском интерфейсе в HDR выполняется платформой автоматически, когда ваше приложение соглашается использовать HDR пользовательский интерфейс для своего окна активности либо через запись манифеста , либо во время выполнения путем вызова Window.setColorMode() . Вы также можете захватывать сжатые неподвижные изображения Ultra HDR на поддерживаемых устройствах. Благодаря большему количеству цветов, полученных с датчика, редактирование при публикации может стать более гибким. Gainmap связанный с изображениями Ultra HDR, можно использовать для их рендеринга с помощью OpenGL или Vulkan.

В Android 14 добавлена поддержка изображений с расширенным динамическим диапазоном (HDR), которые сохраняют больше информации от датчика при съемке фотографии, что обеспечивает яркие цвета и большую контрастность. Android использует формат Ultra HDR , который полностью обратно совместим с изображениями JPEG, что позволяет приложениям беспрепятственно взаимодействовать с изображениями HDR, отображая их в стандартном динамическом диапазоне (SDR) по мере необходимости.
Рендеринг этих изображений в пользовательском интерфейсе в HDR выполняется платформой автоматически, когда ваше приложение соглашается использовать HDR пользовательский интерфейс для своего окна активности либо через запись манифеста , либо во время выполнения путем вызова Window.setColorMode() . Вы также можете захватывать сжатые неподвижные изображения Ultra HDR на поддерживаемых устройствах. Благодаря большему количеству цветов, полученных с датчика, редактирование при публикации может стать более гибким. Gainmap связанный с изображениями Ultra HDR, можно использовать для их рендеринга с помощью OpenGL или Vulkan.
Масштабирование, фокусировка, постпросмотр и другие функции в расширениях камеры
В Android 14 обновляются и совершенствуются расширения камеры , что позволяет приложениям обрабатывать больше времени, что позволяет улучшать изображения с помощью алгоритмов с интенсивными вычислениями, таких как фотография при слабом освещении, на поддерживаемых устройствах. Эти функции дают пользователям еще больше возможностей при использовании дополнительных возможностей камеры. Примеры таких улучшений включают в себя:
- Динамическая оценка задержки обработки кадров обеспечивает гораздо более точную оценку задержки захвата фотографий на основе текущей сцены и условий окружающей среды. Вызовите
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()чтобы получить объектStillCaptureLatency, имеющий два метода оценки задержки. МетодgetCaptureLatency()возвращает расчетную задержку междуonCaptureStartedиonCaptureProcessStarted(), а методgetProcessingLatency()возвращает расчетную задержку междуonCaptureProcessStarted()и доступным окончательным обработанным кадром. - Поддержка обратных вызовов процесса захвата, чтобы приложения могли отображать текущий ход длительных операций обработки неподвижного захвата. Вы можете проверить, доступна ли эта функция, с помощью
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable, и если да, вы реализуете обратный вызовonCaptureProcessProgressed(), в котором в качестве параметра передается прогресс (от 0 до 100). Метаданные, специфичные для расширения, такие как
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHдля набора величины эффекта расширения, например степени размытия фона с помощьюEXTENSION_BOKEH.Функция Postview для захвата фотографий в расширениях камеры, которая обеспечивает менее обработанное изображение быстрее, чем окончательное изображение. Если расширение имеет увеличенную задержку обработки, изображение после просмотра может быть предоставлено в качестве заполнителя для улучшения UX и позже отключено для окончательного изображения. Вы можете проверить, доступна ли эта функция, с помощью
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. Затем вы можете передатьOutputConfigurationвExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Поддержка
SurfaceViewобеспечивающая более оптимизированный и энергоэффективный путь предварительного просмотра.Поддержка касания для фокусировки и масштабирования во время использования расширения.
Зум в датчике
Если REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE в CameraCharacteristics содержит SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW , ваше приложение может использовать расширенные возможности датчика, чтобы предоставить обрезанному потоку RAW те же пиксели, что и полное поле зрения, используя CaptureRequest с целевым объектом RAW, для которого установлен вариант использования потока CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW _CASES_CROPPED_RAW . Благодаря реализации элементов управления переопределением запроса обновленная камера дает пользователям возможность управлять масштабированием даже до того, как будут готовы другие элементы управления камерой.
USB-аудио без потерь
В Android 14 появилась поддержка аудиоформатов без потерь для аудиофильского уровня через проводные USB-гарнитуры. Вы можете запросить у USB-устройства предпочтительные атрибуты микшера, зарегистрировать прослушиватель изменений в предпочтительных атрибутах микшера и настроить атрибуты микшера с помощью класса AudioMixerAttributes . Этот класс представляет формат, такой как маска канала, частота дискретизации и поведение аудиомикшера. Класс позволяет отправлять аудио напрямую , без микширования, регулировки громкости или обработки эффектов.
Производительность и инструменты разработчика
Менеджер по учетным данным
В Android 14 добавлен диспетчер учетных данных в качестве API платформы с дополнительной поддержкой устройств Android 4.4 (уровень API 19) через библиотеку Jetpack с использованием сервисов Google Play. Диспетчер учетных данных призван упростить вход в систему для пользователей с помощью API, которые извлекают и сохраняют учетные данные с помощью поставщиков учетных данных, настраиваемых пользователем. Диспетчер учетных данных поддерживает несколько методов входа, включая имя пользователя и пароль, ключи доступа и решения для федеративного входа (например, вход с помощью Google) в одном API.
Ключи доступа дают множество преимуществ. Например, ключи доступа созданы на основе отраслевых стандартов , могут работать в различных операционных системах и экосистемах браузеров и могут использоваться как с веб-сайтами, так и с приложениями.
Дополнительные сведения см. в документации по диспетчеру учетных данных и ключам доступа, а также в записи блога о диспетчере учетных данных и ключах доступа .
Health Connect
Health Connect — это встроенное в устройство хранилище данных о здоровье и фитнесе пользователей. Это позволяет пользователям обмениваться данными между своими любимыми приложениями, используя единое место для управления тем, какими данными они хотят делиться с этими приложениями.
На устройствах под управлением версий Android до Android 14 Health Connect можно загрузить в виде приложения в магазине Google Play. Начиная с Android 14, Health Connect является частью платформы и получает обновления через обновления системы Google Play, не требуя отдельной загрузки. Благодаря этому Health Connect может часто обновляться, и ваши приложения могут рассчитывать на то, что Health Connect будет доступен на устройствах под управлением Android 14 или более поздней версии. Пользователи могут получить доступ к Health Connect из настроек своего устройства, а элементы управления конфиденциальностью интегрированы в настройки системы.
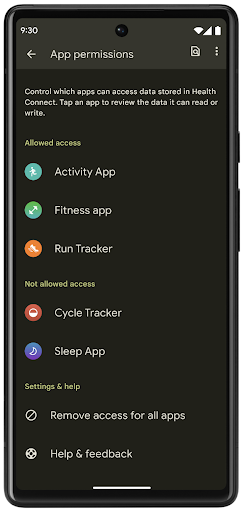
Health Connect включает в себя несколько новых функций в Android 14, таких как маршруты тренировок, позволяющие пользователям делиться маршрутом своей тренировки, который можно визуализировать на карте. Маршрут определяется как список мест, сохраненных в течение определенного периода времени, и ваше приложение может вставлять маршруты в сеансы тренировок, связывая их вместе. Чтобы обеспечить полный контроль над этими конфиденциальными данными, пользователи должны разрешить совместное использование отдельных маршрутов с другими приложениями.
Дополнительные сведения см. в документации Health Connection и в записи блога «Что нового в Android Health» .
Обновления OpenJDK 17
В Android 14 продолжается работа по обновлению основных библиотек Android, чтобы они соответствовали функциям последних выпусков OpenJDK LTS, включая обновления библиотек и поддержку языка Java 17 для разработчиков приложений и платформ.
Включены следующие функции и улучшения:
- Обновлено около 300 классов
java.baseдля поддержки Java 17. - Текстовые блоки , которые вводят многострочные строковые литералы в язык программирования Java.
- Сопоставление с образцом для экземпляра , которое позволяет рассматривать объект как имеющий определенный тип в
instanceofбез каких-либо дополнительных переменных. - Запечатанные классы , позволяющие ограничить классы и интерфейсы, которые могут их расширять или реализовывать.
Благодаря обновлениям системы Google Play (Project Mainline) более 600 миллионов устройств могут получать последние обновления среды выполнения Android (ART), включающие эти изменения. Это часть нашего обязательства предоставить приложениям более согласованную и безопасную среду на всех устройствах, а также предоставить пользователям новые функции и возможности независимо от версий платформы.
Java и OpenJDK являются товарными знаками или зарегистрированными товарными знаками Oracle и/или ее дочерних компаний.
Улучшения для магазинов приложений
В Android 14 представлено несколько API-интерфейсов PackageInstaller , которые позволяют магазинам приложений улучшить взаимодействие с пользователем.
Перед загрузкой запросите разрешение на установку
Для установки или обновления приложения может потребоваться одобрение пользователя . Например, когда установщик, использующий разрешение REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES пытается установить новое приложение. В предыдущих версиях Android магазины приложений могли запрашивать одобрение пользователя только после того, как APK-файлы были записаны в сеанс установки и сеанс был зафиксирован .
Начиная с Android 14, метод requestUserPreapproval() позволяет установщикам запрашивать одобрение пользователя перед завершением сеанса установки. Это улучшение позволяет магазину приложений отложить загрузку любых APK-файлов до тех пор, пока установка не будет одобрена пользователем. Более того, как только пользователь одобрил установку, магазин приложений сможет загрузить и установить приложение в фоновом режиме, не отвлекая пользователя.
Взять на себя ответственность за будущие обновления
Метод setRequestUpdateOwnership() позволяет установщику указать системе, что он намерен нести ответственность за будущие обновления устанавливаемого приложения. Эта возможность обеспечивает принудительное применение прав собственности на обновления. Это означает, что только владельцу обновления разрешено устанавливать автоматические обновления для приложения. Обеспечение прав собственности на обновления помогает гарантировать, что пользователи получают обновления только из ожидаемого магазина приложений.
Любой другой установщик, в том числе использующий разрешение INSTALL_PACKAGES , должен получить явное одобрение пользователя для установки обновления. Если пользователь решает продолжить обновление из другого источника, право собственности на обновление теряется.
Обновляйте приложения в удобное для вас время
Магазины приложений обычно стараются избегать обновления активно используемого приложения, поскольку это приводит к остановке запущенных процессов приложения, что потенциально может прерывать действия пользователя.
Начиная с Android 14, API InstallConstraints дает установщикам возможность гарантировать, что обновления их приложений будут выполняться в подходящий момент. Например, магазин приложений может вызвать метод commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() чтобы убедиться, что обновление фиксируется только тогда, когда пользователь больше не взаимодействует с рассматриваемым приложением.
Простая установка дополнительных сплит-систем
Благодаря разделенным APK-файлам функции приложения могут быть представлены в отдельных APK-файлах, а не в виде монолитного APK. Разделенные APK-файлы позволяют магазинам приложений оптимизировать доставку различных компонентов приложения. Например, магазины приложений могут оптимизироваться на основе свойств целевого устройства. API PackageInstaller поддерживает разделение с момента его появления на уровне API 22.
В Android 14 метод setDontKillApp() позволяет установщику указать, что запущенные процессы приложения не должны завершаться при установке новых разбиений. Магазины приложений могут использовать эту функцию для беспрепятственной установки новых функций приложения, пока пользователь его использует.
Пакеты метаданных приложения
Начиная с Android 14, установщик пакетов Android позволяет указать метаданные приложения , например правила безопасности данных, для включения на страницы магазина приложений, например Google Play.
Определите, когда пользователи делают снимки экрана устройства
Для создания более стандартизированного процесса обнаружения скриншотов в Android 14 представлен API обнаружения скриншотов, сохраняющий конфиденциальность. Этот API позволяет приложениям регистрировать обратные вызовы для каждого действия. Эти обратные вызовы вызываются, и пользователь получает уведомление, когда делает снимок экрана, пока это действие отображается.
Пользовательский опыт
Пользовательские действия в Sharesheet и улучшенный рейтинг
В Android 14 обновляется общая таблица системы для поддержки настраиваемых действий приложения и более информативных результатов предварительного просмотра для пользователей.
Добавить специальные действия
В Android 14 ваше приложение может добавлять специальные действия в общую таблицу системы, которую оно вызывает.
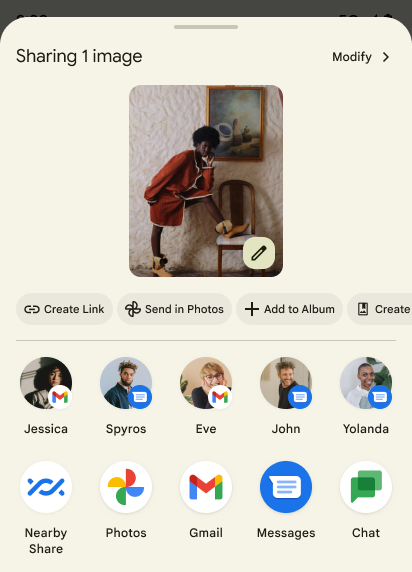
Улучшить рейтинг целей Direct Share
Android 14 использует больше сигналов от приложений для определения рейтинга целей прямого обмена и предоставления более полезных результатов для пользователя. Чтобы обеспечить наиболее полезный сигнал для ранжирования, следуйте инструкциям по улучшению рейтинга ваших целей Direct Share . Коммуникационные приложения также могут сообщать об использовании ярлыков для исходящих и входящих сообщений.
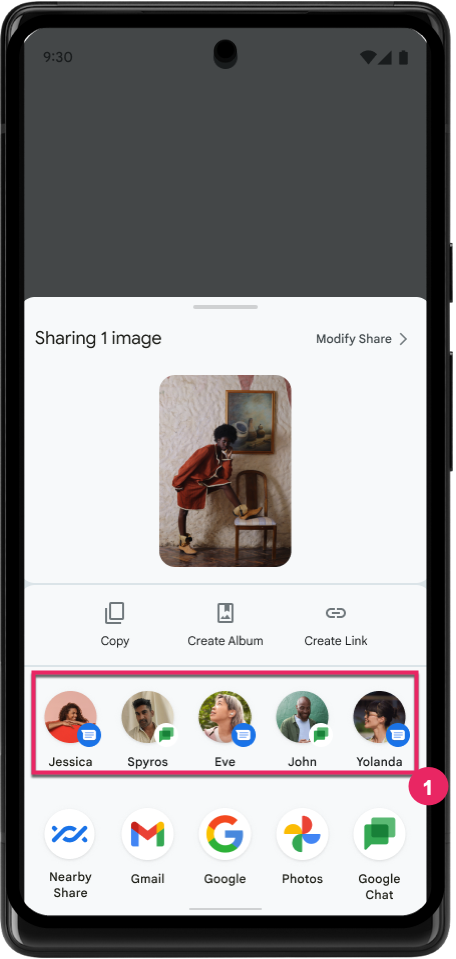
Поддержка встроенных и пользовательских анимаций для Predictive Back
В Android 13 появилась предиктивная анимация возвращения домой, доступная для разработчиков. При использовании в поддерживаемом приложении с включенной опцией разработчика при смахивании назад отображается анимация, указывающая, что жест возврата позволяет выйти из приложения обратно на главный экран.
Android 14 включает в себя множество улучшений и новые рекомендации по функции Predictive Back:
- Вы можете установить
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueчтобы включить прогнозируемую обратную системную анимацию для каждого действия, а не для всего приложения. - Мы добавили новые системные анимации, сопровождающие анимацию возвращения домой из Android 13. Новые системные анимации связаны с перекрестными действиями и задачами, которые вы получаете автоматически после перехода на Predictive Back .
- Мы добавили новые анимации компонентов материала для нижних листов , боковых листов и поиска .
- Мы создали руководство по дизайну для создания пользовательских анимаций и переходов в приложениях.
- Мы добавили новые API для поддержки пользовательских анимаций перехода в приложении:
-
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallback -
onBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback - Используйте
overrideActivityTransitionвместоoverridePendingTransitionдля переходов, которые реагируют, когда пользователь проводит пальцем назад.
-
В этой предварительной версии Android 14 все функции Predictive Back остаются за пределами возможностей разработчика. См. руководство для разработчиков, чтобы вернуть приложение на интеллектуальный режим , а также руководство для разработчиков по созданию пользовательских переходов внутри приложения .
Переопределения для каждого приложения производителем устройства с большим экраном
Переопределения для каждого приложения позволяют производителям устройств изменять поведение приложений на устройствах с большим экраном. Например, переопределение FORCE_RESIZE_APP предписывает системе изменить размер приложения в соответствии с размерами дисплея (избегая режима совместимости размеров), даже если в манифесте приложения установлено resizeableActivity="false" .
Переопределения предназначены для улучшения взаимодействия с пользователем на больших экранах.
Новые свойства манифеста позволяют отключить некоторые переопределения производителя устройства для вашего приложения.
Переопределения для каждого приложения на большом экране
Переопределения для каждого приложения меняют поведение приложений на устройствах с большим экраном. Например, переопределение производителя устройства OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE устанавливает соотношение сторон приложения на 16:9 независимо от конфигурации приложения.
Android 14 QPR1 позволяет пользователям применять переопределения для каждого приложения с помощью нового меню настроек на устройствах с большим экраном.
Совместное использование экрана приложения
Совместное использование экрана приложения позволяет пользователям делиться окном приложения, а не всем экраном устройства во время записи содержимого экрана.
При совместном использовании экрана приложения строка состояния, панель навигации, уведомления и другие элементы пользовательского интерфейса системы исключаются из общего дисплея. Доступен только контент выбранного приложения.
Совместное использование экрана приложений повышает производительность и конфиденциальность, позволяя пользователям запускать несколько приложений, но ограничивая общий доступ к контенту одним приложением.
Умный ответ на базе LLM в Gboard на Pixel 8 Pro
На устройствах Pixel 8 Pro с декабрьским выпуском функций разработчики могут опробовать более качественные интеллектуальные ответы в Gboard на основе встроенных в устройство моделей больших языков (LLM), работающих на Google Tensor.
Эта функция доступна в виде ограниченной предварительной версии для американского английского языка в WhatsApp, Line и KakaoTalk. Для этого необходимо использовать устройство Pixel 8 Pro с Gboard в качестве клавиатуры.
Чтобы опробовать эту функцию, сначала включите эту функцию в «Настройки» > «Параметры разработчика» > «Настройки AiCore» > «Включить Aicore Persistent» .
Затем откройте беседу в поддерживаемом приложении, чтобы увидеть интеллектуальный ответ на базе LLM в полосе предложений Gboard в ответ на входящие сообщения.
Графика
Пути можно запрашивать и интерполировать.
API Path Android — это мощный и гибкий механизм для создания и рендеринга векторной графики с возможностью обводки или заливки пути, построения пути из сегментов линий, квадратичных или кубических кривых, выполнения логических операций для получения еще более сложных фигур или все из них одновременно. Одним из ограничений является возможность узнать, что на самом деле находится в объекте Path; внутренности объекта непрозрачны для вызывающих сторон после создания.
Чтобы создать Path , вы вызываете такие методы, как moveTo() , lineTo() и cubicTo() , чтобы добавить сегменты пути. Но у этого пути не было возможности узнать, что представляют собой сегменты, поэтому вы должны сохранить эту информацию во время создания.
Начиная с Android 14, вы можете запрашивать пути, чтобы узнать, что внутри них. Во-первых, вам нужно получить объект PathIterator с помощью API Path.getPathIterator :
Котлин
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Ява
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Затем вы можете вызвать PathIterator для перебора сегментов один за другим, извлекая все необходимые данные для каждого сегмента. В этом примере используются объекты PathIterator.Segment , которые упаковывают данные за вас:
Котлин
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Ява
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator также имеет версию next() без выделения памяти, в которую вы можете передать буфер для хранения данных точек.
Одним из важных вариантов использования запроса данных Path является интерполяция. Например, вы можете захотеть анимировать (или трансформировать ) между двумя разными путями. Чтобы еще больше упростить этот вариант использования, Android 14 также включает метод interpolate() в Path . Предполагая, что два пути имеют одинаковую внутреннюю структуру, метод interpolate() создает новый Path с этим интерполированным результатом. В этом примере возвращается путь, форма которого находится на полпути (линейная интерполяция .5) между path otherPath :
Котлин
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Ява
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Библиотека графических путей Jetpack поддерживает аналогичные API и для более ранних версий Android.
Пользовательские сетки с вершинными и фрагментными шейдерами
Android уже давно поддерживает рисование треугольных сеток с настраиваемой заливкой, но формат входной сетки был ограничен несколькими предопределенными комбинациями атрибутов. В Android 14 добавлена поддержка пользовательских сеток , которые можно определить как треугольники или треугольные полосы и при необходимости можно индексировать. Эти сетки задаются с помощью пользовательских атрибутов , шагов вершин, переменных , а также вершинных и фрагментных шейдеров, написанных на AGSL .
Вершинный шейдер определяет такие вариации, как положение и цвет, тогда как фрагментный шейдер может дополнительно определять цвет пикселя, обычно используя вариации, созданные вершинным шейдером. Если цвет предоставляется фрагментным шейдером, он затем смешивается с текущим цветом Paint используя режим наложения , выбранный при рисовании сетки . Униформы можно передавать во фрагментные и вершинные шейдеры для дополнительной гибкости.
Аппаратный буферный рендерер для Canvas
Чтобы помочь в использовании Android Canvas API для рисования с аппаратным ускорением в HardwareBuffer , в Android 14 представлен HardwareBufferRenderer . Этот API особенно полезен, когда ваш вариант использования предполагает связь с системным наборщиком через SurfaceControl для рисования с малой задержкой.

