Android 14 memperkenalkan fitur dan API baru yang hebat untuk para developer. Bagian berikut membantu Anda mempelajari fitur-fitur yang tersedia untuk aplikasi Anda, serta mulai menggunakan API yang terkait.
Untuk melihat daftar mendetail tentang API yang ditambahkan, diubah, dan dihapus, baca laporan perbedaan API. Untuk mengetahui detail tentang API yang ditambahkan, buka referensi API Android — untuk Android 14, cari API yang ditambahkan di level API 34. Untuk mempelajari area tempat perubahan platform dapat memengaruhi aplikasi Anda, pastikan untuk memeriksa perubahan perilaku Android 14 untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 14 dan untuk semua aplikasi.
Internasionalisasi
Preferensi bahasa per aplikasi
Android 14 memperluas fitur bahasa per aplikasi yang diperkenalkan di Android 13 (API level 33) dengan kemampuan tambahan berikut:
Otomatis membuat
localeConfigaplikasi: Mulai dari Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 dan AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, Anda dapat mengonfigurasi aplikasi untuk mendukung preferensi bahasa per aplikasi secara otomatis. Berdasarkan resource project, plugin Android Gradle menghasilkan fileLocaleConfigdan menambahkan referensi ke file tersebut dalam file manifes akhir, sehingga Anda tidak perlu lagi membuat atau memperbarui file secara manual. AGP menggunakan resource dalam folderresmodul aplikasi Anda dan dependensi modul library apa pun untuk menentukan lokalitas yang akan disertakan dalam fileLocaleConfig.Update dinamis untuk
localeConfigaplikasi: Gunakan metodesetOverrideLocaleConfig()dangetOverrideLocaleConfig()diLocaleManageruntuk memperbarui secara dinamis daftar bahasa yang didukung aplikasi Anda di setelan sistem perangkat. Gunakan fleksibilitas ini untuk menyesuaikan daftar bahasa yang didukung per region, menjalankan eksperimen A/B, atau memberikan daftar lokalitas yang diupdate jika aplikasi Anda menggunakan push sisi server untuk pelokalan.Visibilitas bahasa aplikasi untuk editor metode input (IME): IME dapat menggunakan metode
getApplicationLocales()untuk memeriksa bahasa aplikasi saat ini dan mencocokkan bahasa IME dengan bahasa tersebut.
Grammatical Inflection API
Tiga miliar orang menggunakan bahasa bergender: bahasa yang kategori gramatikalnya—seperti kata benda, kata kerja, kata sifat, dan preposisi—diterapkan dengan gender orang dan objek yang Anda ajak bicara atau Anda bicarakan. Secara tradisional, banyak bahasa bergender menggunakan gender gramatikal maskulin sebagai gender default atau generik.
Menjangkau pengguna dalam gender gramatikal yang salah, seperti menyapa perempuan dengan gender gramatikal yang maskulin, dapat memberi dampak negatif pada performa dan sikap mereka. Sebaliknya, UI dengan bahasa yang mencerminkan gender gramatikal pengguna dengan benar dapat meningkatkan interaksi pengguna dan memberikan pengalaman pengguna yang lebih personal dan terdengar alami.
Guna membantu Anda mem-build UI yang berorientasi pengguna untuk bahasa-bahasa bergender, Android 14 memperkenalkan Grammatical Inflection API, yang memungkinkan Anda menambahkan dukungan untuk gender gramatikal tanpa perlu memfaktorkan ulang aplikasi.
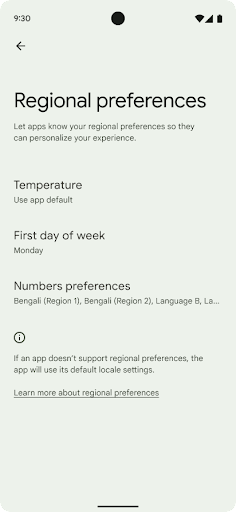
Preferensi regional
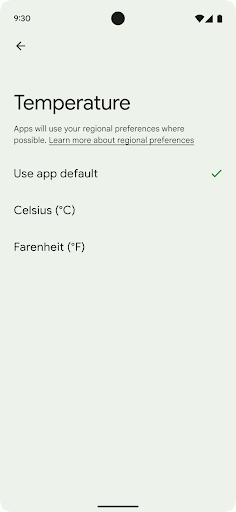
Preferensi regional memungkinkan pengguna mempersonalisasi satuan suhu, hari pertama dalam seminggu, dan sistem penomoran. Orang Eropa yang tinggal di Amerika Serikat mungkin lebih memilih satuan suhu dalam Celsius, bukan Fahrenheit, dan menginginkan aplikasi memperlakukan Senin sebagai awal minggu, bukan default Minggu seperti di Amerika.
Menu Setelan Android yang baru untuk preferensi ini memberi pengguna
lokasi yang dapat ditemukan dan terpusat untuk mengubah preferensi aplikasi. Preferensi
ini juga tetap ada melalui pencadangan dan pemulihan. Beberapa API dan
intent—seperti
getTemperatureUnit
dan
getFirstDayOfWeek—
memberikan pembacaan aplikasi Anda akses ke preferensi pengguna, sehingga aplikasi dapat menyesuaikan cara
menampilkan informasi. Anda juga dapat mendaftarkan
BroadcastReceiver di
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
untuk menangani perubahan konfigurasi lokalitas saat preferensi regional berubah.
Untuk menemukan setelan ini, buka aplikasi Settings, lalu buka System > Languages & input > Regional preferences.
Aksesibilitas
Penskalaan font non-linear ke 200%
Mulai Android 14, sistem mendukung penskalaan font hingga 200%, yang memberikan opsi aksesibilitas tambahan kepada pengguna.
Agar elemen teks besar di layar tidak diskalakan terlalu besar, sistem akan menerapkan kurva penskalaan non-linear. Strategi penskalaan ini berarti teks besar tidak diskalakan pada kecepatan yang sama dengan teks yang lebih kecil. Penskalaan font non-linear membantu mempertahankan hierarki proporsional antara elemen dengan ukuran yang berbeda, sekaligus memitigasi masalah dengan penskalaan teks linear pada derajat yang tinggi (seperti teks terpotong atau teks yang menjadi lebih sulit dibaca karena ukuran layar yang sangat besar).
Menguji aplikasi Anda dengan penskalaan font nonlinear
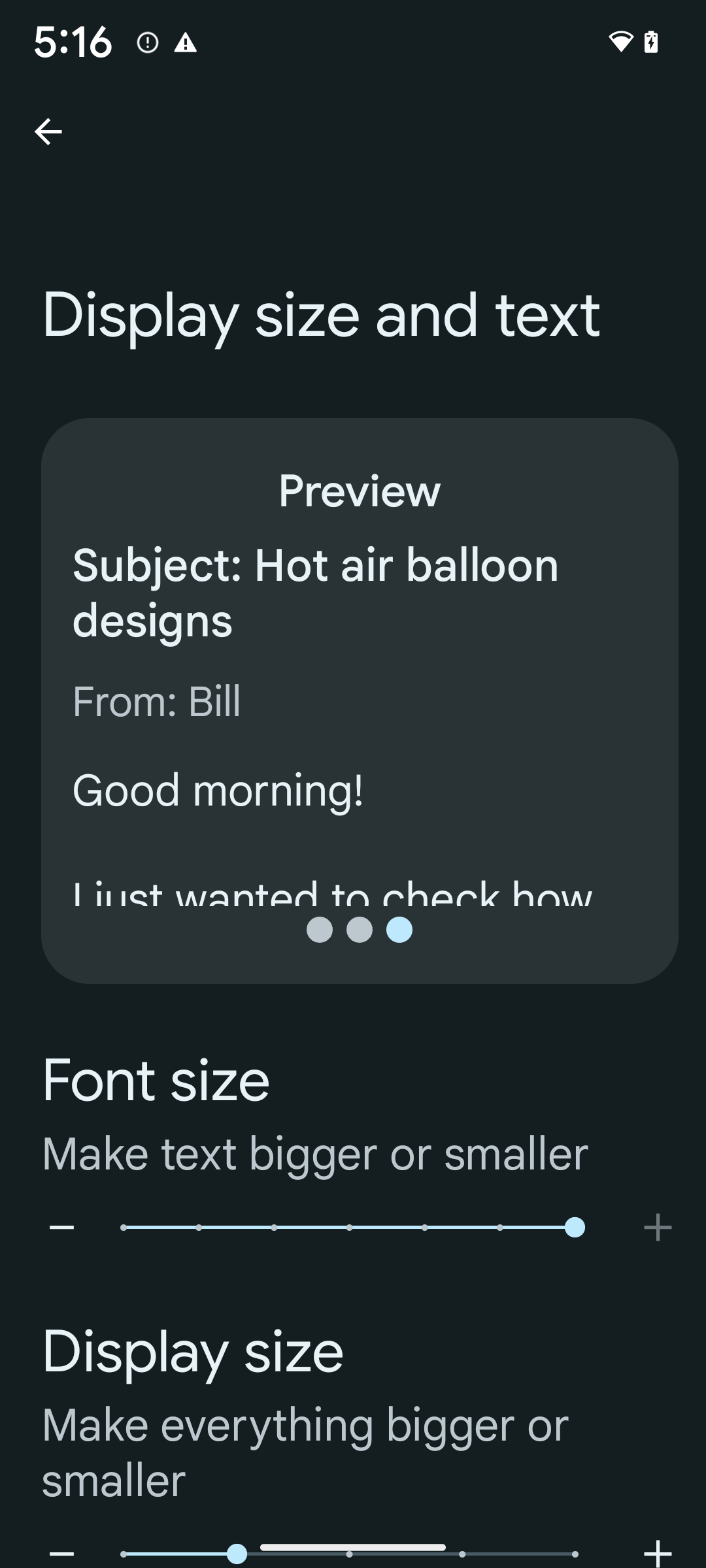
Jika Anda sudah menggunakan unit piksel skalabel (sp) untuk menentukan ukuran teks, opsi tambahan dan peningkatan penskalaan ini akan diterapkan secara otomatis ke teks di aplikasi Anda. Namun, Anda tetap harus melakukan pengujian UI dengan ukuran font maksimum diaktifkan (200%) untuk memastikan aplikasi Anda menerapkan ukuran font dengan benar dan dapat mengakomodasi ukuran font yang lebih besar tanpa memengaruhi kegunaan.
Untuk mengaktifkan ukuran font 200%, ikuti langkah-langkah berikut:
- Buka aplikasi Settings dan buka Accessibility > Display size and text.
- Untuk opsi Font size, ketuk ikon plus (+) hingga setelan ukuran font maksimum diaktifkan, seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam gambar yang menyertai bagian ini.
Menggunakan satuan piksel yang diskalakan (sp) untuk ukuran teks
Ingatlah untuk selalu menentukan ukuran teks dalam unit sp. Saat aplikasi Anda menggunakan unit sp, Android dapat menerapkan ukuran teks pilihan pengguna dan menskalakannya dengan benar.
Jangan gunakan unit sp untuk padding atau tentukan tinggi tampilan dengan asumsi padding implisit: dengan penskalaan font non-linear, dimensi sp mungkin tidak proporsional, sehingga 4sp + 20sp mungkin tidak sama dengan 24sp.
Mengonversi satuan piksel yang diskalakan (sp)
Gunakan TypedValue.applyDimension() untuk mengonversi dari unit sp
ke piksel, dan gunakan TypedValue.deriveDimension() untuk
mengonversi piksel ke sp. Metode ini menerapkan kurva penskalaan
non-linear yang benar secara otomatis.
Hindari persamaan hardcode menggunakan
Configuration.fontScale atau
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Karena penskalaan font bersifat non-linear, kolom scaledDensity tidak lagi akurat. Kolom fontScale
hanya boleh digunakan untuk tujuan informasi karena font tidak lagi
disesuaikan dengan satu nilai skalar.
Menggunakan satuan sp untuk lineHeight
Selalu tentukan android:lineHeight menggunakan unit sp, bukan dp, sehingga tinggi baris diskalakan bersama dengan teks Anda. Jika tidak, jika teks Anda
adalah sp, tetapi lineHeight Anda dalam dp atau px, teks tidak akan diskalakan dan terlihat sempit.
TextView otomatis mengoreksi lineHeight sehingga proporsi yang Anda inginkan tetap dipertahankan, tetapi hanya jika textSize dan lineHeight ditentukan dalam unit sp.
Kamera dan media
Ultra HDR untuk gambar

Android 14 menambahkan dukungan untuk gambar Rentang Dinamis Tinggi (HDR) yang mempertahankan lebih banyak informasi dari sensor saat mengambil foto, yang memungkinkan warna yang cerah dan kontras yang lebih besar. Android menggunakan format Ultra HDR, yang sepenuhnya kompatibel dengan gambar JPEG, sehingga aplikasi dapat berinteraksi dengan lancar dengan gambar HDR, menampilkannya dalam Rentang Dinamis Standar (SDR) sesuai kebutuhan.
Merender gambar ini di UI dalam HDR dilakukan secara otomatis oleh framework
saat aplikasi Anda memilih untuk menggunakan UI HDR untuk Jendela Aktivitasnya, baik melalui entri manifes atau saat runtime dengan memanggil
Window.setColorMode(). Anda juga dapat mengambil gambar diam Ultra HDR
yang dikompresi di perangkat yang didukung. Dengan lebih banyak warna yang dipulihkan
dari sensor, pengeditan pasca-produksi dapat lebih fleksibel. Gainmap
yang terkait dengan gambar Ultra HDR dapat digunakan untuk merendernya
menggunakan OpenGL atau Vulkan.
Zoom, Fokus, Postview, dan lainnya di ekstensi kamera
Android 14 mengupgrade dan meningkatkan ekstensi kamera, sehingga aplikasi dapat menangani waktu pemrosesan yang lebih lama, yang memungkinkan gambar yang lebih baik menggunakan algoritma yang intensif komputasi seperti fotografi cahaya rendah di perangkat yang didukung. Fitur ini memberi pengguna pengalaman yang lebih andal saat menggunakan kemampuan ekstensi kamera. Contoh peningkatan ini mencakup:
- Estimasi latensi pemrosesan pengambilan gambar diam dinamis memberikan estimasi latensi pengambilan gambar diam yang jauh lebih akurat berdasarkan kondisi lingkungan dan situasi saat ini. Panggil
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()untuk mendapatkan objekStillCaptureLatencyyang memiliki dua metode estimasi latensi. MetodegetCaptureLatency()menampilkan estimasi latensi antaraonCaptureStarteddanonCaptureProcessStarted(), dan metodegetProcessingLatency()menampilkan estimasi latensi antaraonCaptureProcessStarted()dan frame akhir yang diproses yang tersedia. - Dukungan untuk callback progres pengambilan sehingga aplikasi dapat menampilkan
progres saat ini dari operasi pemrosesan pengambilan gambar diam yang berjalan lama. Anda dapat memeriksa
apakah fitur ini tersedia dengan
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable, dan jika tersedia, Anda akan mengimplementasikan callbackonCaptureProcessProgressed(), yang memiliki progres (dari 0 hingga 100) yang diteruskan sebagai parameter. Metadata khusus ekstensi, seperti
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHuntuk menelepon jumlah efek ekstensi, seperti jumlah pemburaman latar belakang denganEXTENSION_BOKEH.Fitur Postview untuk Still Capture di ekstensi kamera, yang memberikan gambar yang kurang diproses dengan lebih cepat daripada gambar akhir. Jika ekstensi telah meningkatkan latensi pemrosesan, gambar pasca-tampilan dapat diberikan sebagai placeholder untuk meningkatkan UX dan diganti nanti dengan gambar akhir. Anda dapat memeriksa apakah fitur ini tersedia dengan
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. Kemudian, Anda dapat meneruskanOutputConfigurationkeExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Dukungan untuk
SurfaceViewyang memungkinkan jalur rendering pratinjau yang lebih dioptimalkan dan hemat daya.Dukungan untuk ketuk untuk memfokuskan dan melakukan zoom selama penggunaan ekstensi.
Zoom dalam sensor
Jika REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE di
CameraCharacteristics berisi
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, aplikasi Anda
dapat menggunakan kemampuan sensor lanjutan untuk memberikan streaming RAW yang dipangkas dengan piksel
yang sama dengan bidang pandang penuh menggunakan CaptureRequest
dengan target RAW yang memiliki kasus penggunaan streaming yang disetel ke
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
Dengan menerapkan kontrol penggantian permintaan, kamera yang diperbarui memberi pengguna kontrol zoom bahkan sebelum kontrol kamera lainnya siap.
Audio USB lossless
Android 14 mendapatkan dukungan untuk format audio lossless untuk pengalaman
level audiophile melalui headset berkabel USB. Anda dapat membuat kueri perangkat USB untuk
atribut mixer pilihannya, mendaftarkan pemroses untuk perubahan pada atribut
mixer pilihan, dan mengonfigurasi atribut mixer menggunakan
class AudioMixerAttributes. Class ini mewakili
format, seperti mask saluran, frekuensi sampel, dan perilaku mixer audio. Class
ini memungkinkan audio dikirim langsung, tanpa pencampuran,
penyesuaian volume, atau efek pemrosesan.
Alat dan produktivitas developer
Credential Manager
Android 14 menambahkan Pengelola Kredensial sebagai API platform, dengan dukungan tambahan kembali ke perangkat Android 4.4 (API level 19) melalui Library Jetpack menggunakan layanan Google Play. Pengelola Kredensial bertujuan untuk mempermudah login bagi pengguna dengan API yang mengambil dan menyimpan kredensial dengan penyedia kredensial yang dikonfigurasi pengguna. Pengelola Kredensial mendukung beberapa metode login, termasuk nama pengguna dan sandi, kunci sandi, dan solusi login gabungan (seperti Login dengan Google) dalam satu API.
Kunci sandi memberikan banyak manfaat. Misalnya, kunci sandi dibuat berdasarkan standar industri, dapat berfungsi di berbagai sistem operasi dan ekosistem browser, serta dapat digunakan dengan situs dan aplikasi.
Untuk informasi selengkapnya, lihat dokumentasi Credential Manager dan kunci sandi serta postingan blog tentang Credential Manager dan kunci sandi.
Health Connect
Health Connect adalah repositori di perangkat untuk data kesehatan dan kebugaran pengguna. Fitur ini memungkinkan pengguna berbagi data antar-aplikasi favorit mereka, dengan satu tempat untuk mengontrol data yang ingin dibagikan kepada aplikasi ini.
Di perangkat yang menjalankan versi Android sebelum Android 14, Health Connect tersedia untuk didownload sebagai aplikasi di Google Play Store. Mulai Android 14, Health Connect adalah bagian dari platform dan menerima update melalui update sistem Google Play tanpa memerlukan download terpisah. Dengan demikian, Health Connect dapat sering diperbarui, dan aplikasi Anda dapat mengandalkan Health Connect yang tersedia di perangkat yang menjalankan Android 14 atau yang lebih tinggi. Pengguna dapat mengakses Health Connect dari Setelan di perangkat mereka, dengan kontrol privasi yang terintegrasi ke dalam setelan sistem.
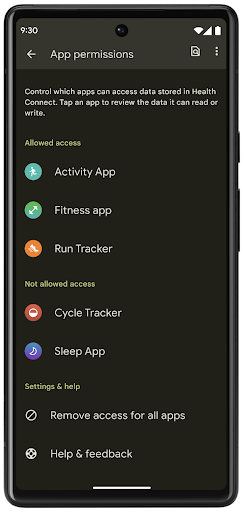
Health Connect menyertakan beberapa fitur baru di Android 14, seperti rute olahraga, yang memungkinkan pengguna membagikan rute olahraga mereka yang dapat divisualisasikan di peta. Rute ditentukan sebagai daftar lokasi yang disimpan dalam periode waktu, dan aplikasi Anda dapat menyisipkan rute ke dalam sesi olahraga, yang menggabungkannya bersama-sama. Untuk memastikan pengguna memiliki kontrol penuh atas data sensitif ini, pengguna harus mengizinkan berbagi setiap rute dengan aplikasi lain.
Untuk informasi selengkapnya, lihat dokumentasi Health Connect dan postingan blog tentang Yang baru di Android Health.
Update OpenJDK 17
Android 14 melanjutkan pekerjaan memuat ulang library inti Android agar selaras dengan fitur dalam rilis OpenJDK LTS terbaru, termasuk update library dan dukungan bahasa Java 17 untuk developer aplikasi dan platform.
Fitur dan peningkatan berikut disertakan:
- Mengupdate sekitar 300 class
java.baseke dukungan Java 17. - Pemblokiran Teks, yang memperkenalkan literal string multibaris ke bahasa pemrograman Java.
- Pencocokan Pola untuk instance, yang memungkinkan objek
diperlakukan sebagai memiliki jenis tertentu dalam
instanceoftanpa variabel tambahan. - Class tertutup, yang memungkinkan Anda membatasi class dan antarmuka yang dapat memperluas atau menerapkannya.
Berkat update sistem Google Play (Project Mainline), lebih dari 600 juta perangkat diaktifkan untuk menerima update Android Runtime (ART) terbaru yang menyertakan perubahan ini. Ini adalah bagian dari komitmen kami untuk memberi aplikasi lingkungan yang lebih konsisten dan aman di seluruh perangkat, serta memberikan fitur dan kemampuan baru kepada pengguna, terlepas dari rilis platform.
Java dan OpenJDK adalah merek dagang atau merek dagang terdaftar dari Oracle dan/atau afiliasinya.
Peningkatan untuk app store
Android 14 memperkenalkan beberapa PackageInstaller API yang
memungkinkan app store meningkatkan pengalaman pengguna mereka.
Meminta persetujuan penginstalan sebelum mendownload
Menginstal atau mengupdate aplikasi mungkin memerlukan persetujuan pengguna.
Misalnya, saat penginstal yang menggunakan izin
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES mencoba menginstal
aplikasi baru. Pada versi Android sebelumnya, app store hanya dapat meminta persetujuan pengguna
setelah APK ditulis ke sesi penginstalan dan
sesi berkomitmen.
Mulai Android 14, metode requestUserPreapproval()
memungkinkan penginstal meminta persetujuan pengguna sebelum melakukan sesi
penginstalan. Peningkatan ini memungkinkan app store menunda download APK apa pun hingga
setelah penginstalan disetujui oleh pengguna. Selain itu, setelah pengguna
menyetujui penginstalan, app store dapat mendownload dan menginstal aplikasi di
latar belakang tanpa mengganggu pengguna.
Mengklaim tanggung jawab untuk update mendatang
Metode setRequestUpdateOwnership() memungkinkan penginstal
memberi tahu sistem bahwa penginstal bermaksud bertanggung jawab atas update mendatang
untuk aplikasi yang diinstalnya. Kemampuan ini memungkinkan penerapan
kepemilikan update, yang berarti bahwa hanya pemilik update yang diizinkan
untuk menginstal update otomatis ke aplikasi. Penerapan
kepemilikan update membantu memastikan bahwa pengguna hanya menerima update dari app store
yang diharapkan.
Penginstal lainnya, termasuk yang menggunakan izin
INSTALL_PACKAGES, harus menerima persetujuan eksplisit
pengguna untuk menginstal update. Jika pengguna memutuskan untuk melanjutkan update dari sumber lain, kepemilikan update akan hilang.
Mengupdate aplikasi pada waktu yang tidak terlalu mengganggu
App store biasanya ingin menghindari update aplikasi yang aktif digunakan karena hal ini menyebabkan proses aplikasi yang sedang berjalan dihentikan, yang berpotensi mengganggu aktivitas pengguna.
Mulai Android 14, InstallConstraints API
memberi penginstal cara untuk memastikan update aplikasi mereka terjadi pada
momen yang tepat. Misalnya, app store dapat memanggil metode
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() untuk
memastikan update hanya dilakukan saat pengguna tidak lagi
berinteraksi dengan aplikasi yang dimaksud.
Menginstal pemisahan opsional dengan lancar
Dengan APK terpisah, fitur aplikasi dapat dikirimkan dalam file APK terpisah,
bukan sebagai APK monolitik. APK terpisah memungkinkan app store mengoptimalkan
pengiriman berbagai komponen aplikasi. Misalnya, app store dapat mengoptimalkan
berdasarkan properti perangkat target. PackageInstaller
API telah mendukung pemisahan sejak
diperkenalkan di API level 22.
Di Android 14, metode setDontKillApp() memungkinkan
penginstal menunjukkan bahwa proses aplikasi yang sedang berjalan tidak boleh dihentikan saat
pemisahan baru diinstal. App store dapat menggunakan fitur ini untuk menginstal
fitur baru aplikasi dengan lancar ketika pengguna sedang menggunakan aplikasi.
Paket metadata aplikasi
Mulai Android 14, penginstal paket Android memungkinkan Anda menentukan metadata aplikasi, seperti praktik keamanan data, yang akan disertakan di halaman app store seperti Google Play.
Mendeteksi kapan pengguna mengambil screenshot perangkat
Untuk menciptakan pengalaman yang lebih standar dalam mendeteksi screenshot, Android 14 memperkenalkan API deteksi screenshot yang menjaga privasi. API ini memungkinkan aplikasi mendaftarkan callback per aktivitas. Callback ini dipanggil, dan pengguna akan diberi tahu saat pengguna mengambil screenshot ketika aktivitas itu terlihat.
Pengalaman pengguna
Tindakan kustom Sharesheet dan peringkat yang ditingkatkan
Android 14 mengupdate sharesheet sistem untuk mendukung tindakan aplikasi kustom dan hasil pratinjau yang lebih informatif bagi pengguna.
Menambahkan tindakan kustom
Dengan Android 14, aplikasi Anda dapat menambahkan tindakan kustom ke sharesheet sistem yang dipanggilnya.
Meningkatkan peringkat target Berbagi Langsung
Android 14 menggunakan lebih banyak sinyal dari aplikasi untuk menentukan peringkat target langsung berbagi agar memberikan hasil yang lebih bermanfaat bagi pengguna. Untuk memberikan sinyal yang paling berguna untuk peringkat, ikuti panduan untuk meningkatkan peringkat target Berbagi Langsung. Aplikasi komunikasi juga dapat melaporkan penggunaan pintasan untuk pesan keluar dan masuk.
Dukungan untuk animasi bawaan dan kustom untuk Kembali Prediktif
Android 13 memperkenalkan animasi "kembali ke layar utama" prediktif di balik opsi developer. Saat digunakan pada aplikasi yang didukung dengan opsi developer yang diaktifkan, menggeser kembali akan menampilkan animasi yang menunjukkan bahwa gestur kembali akan menutup aplikasi untuk kembali ke layar utama.
Android 14 menyertakan beberapa peningkatan dan panduan baru untuk Kembali Prediktif:
- Anda dapat menetapkan
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueuntuk mengaktifkan animasi sistem kembali prediktif per Aktivitas, bukan untuk seluruh aplikasi. - Kami telah menambahkan animasi sistem baru untuk menyertai animasi "kembali ke layar utama" dari Android 13. Animasi sistem yang baru terdiri dari lintas aktivitas dan lintas tugas, yang Anda dapatkan secara otomatis setelah bermigrasi ke Kembali Prediktif.
- Kami telah menambahkan animasi Komponen Material baru untuk Sheet bawah, Sheet samping, dan Penelusuran.
- Kami telah membuat panduan desain untuk membuat animasi dan transisi kustom dalam aplikasi.
- Kami telah menambahkan API baru untuk mendukung animasi transisi kustom dalam aplikasi:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Gunakan
overrideActivityTransition, bukanoverridePendingTransition, untuk transisi yang merespons saat pengguna menggeser kembali.
Dengan rilis pratinjau Android 14 ini, semua fitur Kembali Prediktif tetap berada di balik opsi developer. Lihat panduan developer untuk memigrasikan aplikasi ke kembali prediktif, serta panduan developer untuk membuat transisi kustom dalam aplikasi.
Penggantian per aplikasi produsen perangkat layar besar
Penggantian per aplikasi memungkinkan produsen perangkat mengubah perilaku aplikasi di perangkat layar besar. Misalnya, penggantian FORCE_RESIZE_APP menginstruksikan sistem untuk mengubah ukuran aplikasi agar sesuai dengan dimensi tampilan (menghindari mode kompatibilitas ukuran) meskipun resizeableActivity="false" disetel dalam manifes aplikasi.
Ganti dimaksudkan untuk meningkatkan pengalaman pengguna di perangkat layar besar.
Properti manifes baru memungkinkan Anda menonaktifkan beberapa penggantian produsen perangkat untuk aplikasi Anda.
Penggantian per aplikasi pengguna perangkat layar besar
Penggantian per aplikasi mengubah perilaku aplikasi di perangkat layar besar. Misalnya, penggantian produsen perangkat OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE menetapkan rasio aspek aplikasi ke 16:9, terlepas dari konfigurasi aplikasi.
Android 14 QPR1 memungkinkan pengguna menerapkan penggantian per aplikasi melalui menu setelan baru di perangkat layar besar.
Berbagi layar aplikasi
Berbagi layar aplikasi memungkinkan pengguna berbagi jendela aplikasi, bukan seluruh layar perangkat selama perekaman konten layar.
Dengan berbagi layar aplikasi, status bar, menu navigasi, notifikasi, dan elemen UI sistem lainnya dikecualikan dari tampilan bersama. Hanya konten aplikasi yang dipilih yang dibagikan.
Berbagi layar aplikasi meningkatkan produktivitas dan privasi dengan memungkinkan pengguna menjalankan beberapa aplikasi, tetapi membatasi berbagi konten ke satu aplikasi.
Smart Reply yang didukung LLM di Gboard pada Pixel 8 Pro
Di perangkat Pixel 8 Pro dengan Feature Drop Desember, developer dapat mencoba smart reply berkualitas lebih tinggi di Gboard yang didukung oleh Model Bahasa Besar (LLM) di perangkat yang berjalan di Google Tensor.
Fitur ini tersedia sebagai pratinjau terbatas untuk bahasa Inggris Amerika Serikat di WhatsApp, Line, dan KakaoTalk. Fitur ini memerlukan penggunaan perangkat Pixel 8 Pro dengan Gboard sebagai keyboard Anda.
Untuk mencobanya, aktifkan fitur ini terlebih dahulu di Setelan > Opsi Developer > Setelan AICore > Aktifkan AIcore Persistent.
Selanjutnya, buka percakapan di aplikasi yang didukung untuk melihat Smart Reply yang didukung LLM di bilah saran Gboard sebagai respons terhadap pesan masuk.
Grafik
Jalur dapat dikueri dan diinterpolasi
Path API Android adalah mekanisme yang andal dan fleksibel untuk
membuat dan merender grafik vektor, dengan kemampuan untuk membuat goresan atau mengisi
jalur, membuat jalur dari segmen garis atau kurva kuadrat atau kubik, melakukan
operasi boolean untuk mendapatkan bentuk yang lebih kompleks, atau semuanya
secara bersamaan. Salah satu keterbatasannya adalah kemampuan untuk mengetahui apa yang sebenarnya ada di
objek Path; bagian dalam objek bersifat buram bagi pemanggil setelah dibuat.
Untuk membuat Path, panggil metode seperti
moveTo(), lineTo(), dan
cubicTo() untuk menambahkan segmen jalur. Namun, belum ada cara untuk menanyakan kepada jalur tersebut tentang segmennya, jadi Anda harus menyimpan informasi tersebut pada waktu pembuatan.
Mulai Android 14, Anda dapat mengkueri jalur untuk mencari tahu apa yang ada di dalamnya.
Pertama, Anda perlu mendapatkan objek PathIterator menggunakan
Path.getPathIterator API:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Selanjutnya, Anda dapat memanggil PathIterator untuk melakukan iterasi melalui segmen
satu per satu, mengambil semua data yang diperlukan untuk setiap segmen. Contoh ini
menggunakan objek PathIterator.Segment, yang mengemas data
untuk Anda:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator juga memiliki versi next() yang tidak mengalokasikan, tempat Anda dapat meneruskan
buffer untuk menyimpan data titik.
Salah satu kasus penggunaan yang penting untuk mengkueri data Path adalah interpolasi. Misalnya,
Anda mungkin ingin menganimasikan (atau mengubah) antara dua jalur berbeda. Untuk
lebih menyederhanakan kasus penggunaan tersebut, Android 14 juga menyertakan
metode interpolate() di Path. Dengan asumsi bahwa kedua jalur memiliki
struktur internal yang sama, metode interpolate() akan membuat Path baru
dengan hasil interpolasi tersebut. Contoh ini menampilkan jalur yang bentuknya
setengah (interpolasi linier 0,5) antara path dan otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
Library graphics-path Jetpack juga memungkinkan API serupa untuk versi Android yang lebih lama.
Mesh kustom dengan shader verteks dan fragmen
Android telah lama mendukung mesh segitiga gambar dengan bayangan kustom, tetapi format mesh input telah dibatasi untuk beberapa kombinasi atribut yang telah ditentukan. Android 14 menambahkan dukungan untuk mesh kustom, yang dapat didefinisikan sebagai segitiga atau strip segitiga, dan dapat, secara opsional, diindeks. Mesh ini ditentukan dengan atribut kustom, langkah vertex, beragam, serta shader vertex dan fragmen yang ditulis dalam AGSL.
Vertex shader menentukan variasi, seperti posisi dan warna, sedangkan
fragment shader secara opsional dapat menentukan warna untuk piksel, biasanya dengan
menggunakan variasi yang dibuat oleh vertex shader. Jika warna disediakan oleh shader fragmen, warna tersebut akan digabungkan dengan warna Paint saat ini menggunakan mode gabungan yang dipilih saat menggambar mesh. Seragam dapat diteruskan
ke shader fragmen dan vertex untuk fleksibilitas tambahan.
Perender buffer hardware untuk Canvas
Untuk membantu dalam penggunaan Canvas API Android untuk menggambar
akselerasi hardware ke HardwareBuffer, Android 14
memperkenalkan HardwareBufferRenderer. API ini
sangat berguna jika kasus penggunaan Anda melibatkan komunikasi dengan
komponer sistem melalui SurfaceControl untuk gambar
dengan latensi rendah.

