Android 14 כולל תכונות וממשקי API מעולים למפתחים. המאמרים הבאים יעזרו לכם להבין את התכונות של האפליקציות ולהתחיל להשתמש בממשקי ה-API שקשורים אליהן.
רשימה מפורטת של ממשקי API שנוספו, שונו או הוסרו מופיעה בדוח ההבדלים בין ממשקי ה-API. פרטים על ממשקי API שנוספו זמינים בהפניה ל-Android API. ב-Android 14, מחפשים ממשקי API שנוספו ברמת API 34. כדי לקבל מידע על תחומים שבהם שינויים בפלטפורמה עשויים להשפיע על האפליקציות שלכם, מומלץ לעיין בשינויים בהתנהגות של Android 14 באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 14 ובכל האפליקציות.
אינטרנציונליזציה
העדפות שפה לכל אפליקציה
ב-Android 14 נוספו לתכונות של שפה לכל אפליקציה, שהוצגו ב-Android 13 (רמת API 33), היכולות הבאות:
יצירה אוטומטית של
localeConfigשל אפליקציה: החל מ-Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 ו-AGP 8.1.0-alpha07, אפשר להגדיר את האפליקציה כך שתתמוך באופן אוטומטי בהעדפות שפה לכל אפליקציה. על סמך המשאבים של הפרויקט, הפלאגין של Android Gradle יוצר את הקובץLocaleConfigומוסיף לו הפניה בקובץ המניפסט הסופי, כך שאין יותר צורך ליצור או לעדכן את הקובץ באופן ידני. מערכת AGP משתמשת במשאבים בתיקיותresשל מודולי האפליקציה ובכל יחסי התלות של מודולי הספריות כדי לקבוע את האזורים הגיאוגרפיים שצריך לכלול בקובץLocaleConfig.עדכונים דינמיים של
localeConfigבאפליקציה: משתמשים בשיטותsetOverrideLocaleConfig()ו-getOverrideLocaleConfig()שמפורטות ב-LocaleManagerכדי לעדכן באופן דינמי את רשימת השפות הנתמכות באפליקציה בהגדרות המערכת של המכשיר. הגמישות הזו מאפשרת לכם להתאים אישית את רשימת השפות הנתמכות לפי אזור, להריץ ניסויים מסוג A/B או לספק רשימה מעודכנת של אזורי זמן אם האפליקציה שלכם משתמשת בהעברות (push) בצד השרת לצורך לוקליזציה.הצגת שפת האפליקציה לעורכי שיטות קלט (IME): עורכי שיטות קלט יכולים להשתמש ב-method
getApplicationLocales()כדי לבדוק את שפת האפליקציה הנוכחית ולהתאים את שפת ה-IME לשפה הזו.
Grammatical Inflection API
3 מיליארד אנשים דוברים שפות עם מגדר: שפות שבהן קטגוריות דקדוקיות – כמו שמות עצם, פעלים, שמות תואר ומילות יחס – משתנות בהתאם למגדר של האנשים והאובייקטים שאתם מדברים אליהם או עליהם. באופן מסורתי, בשפות רבות עם מגדר נעשה שימוש במגדר grammatcal masculine כמגדר ברירת המחדל או כמגדר כללי.
שימוש במגדר הדקדוקי הלא נכון למשתמשים, למשל שימוש במגדר הדקדוקי הזכרי לנשים, עלול להשפיע לרעה על הביצועים והגישה שלהם. לעומת זאת, ממשק משתמש עם שפה שמשקפת בצורה נכונה את המגדר הדקדוקי של המשתמש יכול לשפר את המעורבות של המשתמש ולספק חוויית משתמש מותאמת אישית יותר וטבעית יותר.
כדי לעזור לכם ליצור ממשק משתמש שמתמקד במשתמשים בשפות עם הבחנה בין מינים, ב-Android 14 מופיע Grammatical Inflection API, שמאפשר לכם להוסיף תמיכה בלשון מגדרית בלי לבצע רפאקציה לאפליקציה.
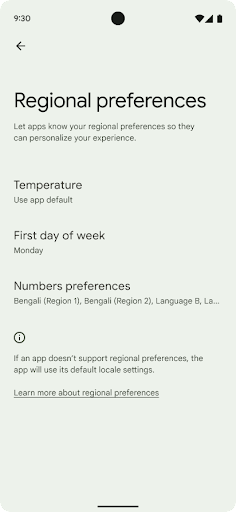
העדפות הפורמט והמידות
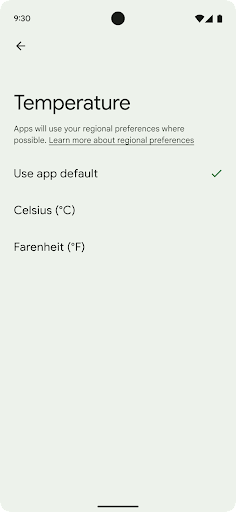
Regional preferences enable users to personalize temperature units, the first day of the week, and numbering systems. A European living in the United States might prefer temperature units to be in Celsius rather than Fahrenheit and for apps to treat Monday as the beginning of the week instead of the US default of Sunday.
New Android Settings menus for these preferences provide users with a
discoverable and centralized location to change app preferences. These
preferences also persist through backup and restore. Several APIs and
intents—such as
getTemperatureUnit
and
getFirstDayOfWeek—
grant your app read access to user preferences, so your app can adjust how it
displays information. You can also register a
BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
to handle locale configuration changes when regional preferences change.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & input > Regional preferences.
נגישות
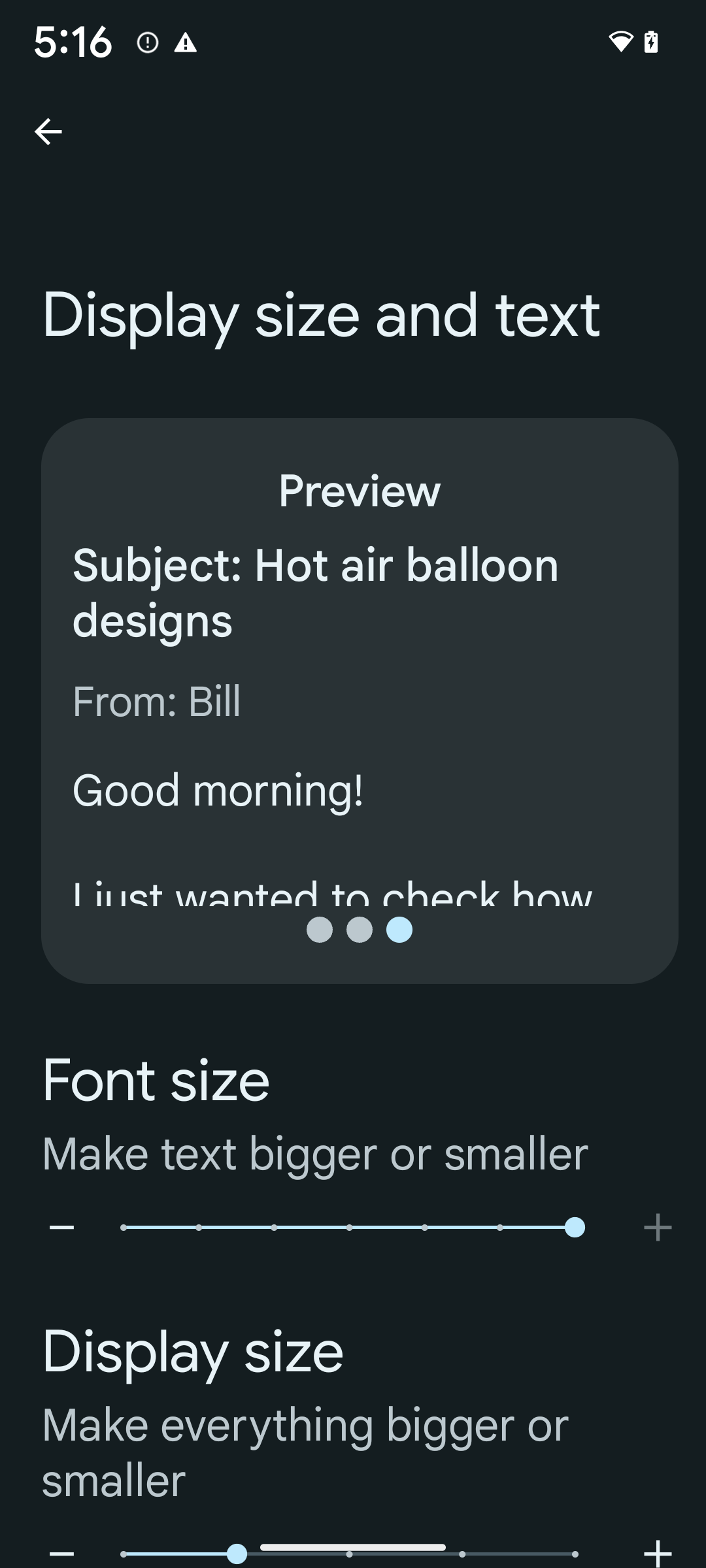
הגדלת הגופן עד 200% באופן לא לינארי
Starting in Android 14, the system supports font scaling up to 200%, providing low-vision users with additional accessibility options that align with Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG).
To prevent large text elements on screen from scaling too large, the system applies a nonlinear scaling curve. This scaling strategy means that large text doesn't scale at the same rate as smaller text. Nonlinear font scaling helps preserve the proportional hierarchy between elements of different sizes while mitigating issues with linear text scaling at high degrees (such as text being cut off or text that becomes harder to read due to an extremely large display sizes).
Test your app with nonlinear font scaling
If you already use scaled pixels (sp) units to define text sizing, then these additional options and scaling improvements are applied automatically to the text in your app. However, you should still perform UI testing with the maximum font size enabled (200%) to ensure that your app applies the font sizes correctly and can accommodate larger font sizes without impacting usability.
To enable 200% font size, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Accessibility > Display size and text.
- For the Font size option, tap the plus (+) icon until the maximum font size setting is enabled, as shown in the image that accompanies this section.
Use scaled pixel (sp) units for text-sizes
Remember to always specify text sizes in sp units. When your app uses sp units, Android can apply the user's preferred text size and scale it appropriately.
Don't use sp units for padding or define view heights assuming implicit padding: with nonlinear font scaling sp dimensions might not be proportional, so 4sp + 20sp might not equal 24sp.
Convert scaled pixel (sp) units
Use TypedValue.applyDimension() to convert from sp units
to pixels, and use TypedValue.deriveDimension() to
convert pixels to sp. These methods apply the appropriate nonlinear scaling
curve automatically.
Avoid hardcoding equations using
Configuration.fontScale or
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Because font scaling is
nonlinear, the scaledDensity field is no longer accurate. The fontScale
field should be used for informational purposes only because fonts are no longer
scaled with a single scalar value.
Use sp units for lineHeight
Always define android:lineHeight using sp units instead
of dp, so the line height scales along with your text. Otherwise, if your text
is sp but your lineHeight is in dp or px, it doesn't scale and looks cramped.
TextView automatically corrects the lineHeight so that your intended
proportions are preserved, but only if both textSize and lineHeight are
defined in sp units.
מצלמה ומדיה
תמונות ב-Ultra HDR

Android 14 adds support for High Dynamic Range (HDR) images that retain more of the information from the sensor when taking a photo, which enables vibrant colors and greater contrast. Android uses the Ultra HDR format, which is fully backward compatible with JPEG images, allowing apps to seamlessly interoperate with HDR images, displaying them in Standard Dynamic Range (SDR) as needed.
Rendering these images in the UI in HDR is done automatically by the framework
when your app opts in to using HDR UI for its Activity Window, either through a
manifest entry or at runtime by calling
Window.setColorMode(). You can also capture compressed Ultra
HDR still images on supported devices. With more colors recovered
from the sensor, editing in post can be more flexible. The
Gainmap associated with Ultra HDR images can be used to render
them using OpenGL or Vulkan.
זום, פוקוס, תצוגה מקדימה ועוד בתוספים למצלמה
Android 14 upgrades and improves camera extensions, allowing apps to handle longer processing times, which enables improved images using compute-intensive algorithms like low-light photography on supported devices. These features give users an even more robust experience when using camera extension capabilities. Examples of these improvements include:
- Dynamic still capture processing latency estimation provides much more
accurate still capture latency estimates based on the current scene and
environment conditions. Call
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()to get aStillCaptureLatencyobject that has two latency estimation methods. ThegetCaptureLatency()method returns the estimated latency betweenonCaptureStartedandonCaptureProcessStarted(), and thegetProcessingLatency()method returns the estimated latency betweenonCaptureProcessStarted()and the final processed frame being available. - Support for capture progress callbacks so that apps can display the current
progress of long-running, still-capture processing operations. You can check
if this feature is available with
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable, and if it is, you implement theonCaptureProcessProgressed()callback, which has the progress (from 0 to 100) passed in as a parameter. Extension specific metadata, such as
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHfor dialing in the amount of an extension effect, such as the amount of background blur withEXTENSION_BOKEH.Postview Feature for Still Capture in camera extensions, which provides a less-processed image more quickly than the final image. If an extension has increased processing latency, a postview image could be provided as a placeholder to improve UX and switched out later for the final image. You can check if this feature is available with
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. Then you can pass anOutputConfigurationtoExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.Support for
SurfaceViewallowing for a more optimized and power-efficient preview render path.Support for tap to focus and zoom during extension usage.
זום בחיישן
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
אודיו ב-USB ללא אובדן נתונים
Android 14 gains support for lossless audio formats for audiophile-level
experiences over USB wired headsets. You can query a USB device for its
preferred mixer attributes, register a listener for changes in preferred mixer
attributes, and configure mixer attributes using the
AudioMixerAttributes class. This class represents the
format, such as channel mask, sample rate, and behavior of the audio mixer. The
class allows for audio to be sent directly, without mixing,
volume adjustment, or processing effects.
פרודוקטיביות וכלים למפתחים
מנהל פרטי הכניסה
ב-Android 14 נוספה התמיכה ב-Credential Manager כ-API בפלטפורמה, עם תמיכה נוספת במכשירי Android 4.4 (רמת API 19) דרך ספריית Jetpack באמצעות Google Play Services. המטרה של Credential Manager היא להקל על המשתמשים להיכנס באמצעות ממשקי API שמאחזרים ומאחסנים את פרטי הכניסה באמצעות ספקי פרטי כניסה שהמשתמשים מגדירים. Credential Manager תומך במספר שיטות כניסה, כולל שם משתמש וסיסמה, מפתחות גישה ופתרונות כניסה מאוחדת (כמו 'כניסה באמצעות חשבון Google') בממשק API אחד.
למפתחות הגישה יש יתרונות רבים. לדוגמה, מפתחות הגישה מבוססים על תקנים מקובלים בתחום, יכולים לפעול במגוון מערכות הפעלה וסביבות עסקיות בדפדפנים, ואפשר להשתמש בהם גם באתרים וגם באפליקציות.
למידע נוסף, עיינו במסמכי העזרה בנושא Credential Manager ומפתחות גישה ובפוסט בבלוג בנושא Credential Manager ומפתחות גישה.
Health Connect
Health Connect היא מאגר במכשיר לנתוני הבריאות והכושר של המשתמש. היא מאפשרת למשתמשים לשתף נתונים בין האפליקציות המועדפות שלהם, ובמקום אחד הם יכולים לקבוע אילו נתונים הם רוצים לשתף עם האפליקציות האלה.
במכשירים עם גרסאות Android שקדמו ל-Android 14, אפשר להוריד את Health Connect כאפליקציה מחנות Google Play. החל מגרסה Android 14, Health Connect היא חלק מהפלטפורמה ומקבלת עדכונים דרך עדכוני המערכת של Google Play, בלי צורך בהורדה נפרדת. כך אפשר לעדכן את Health Connect בתדירות גבוהה, והאפליקציות יכולות להסתמך על כך ש-Health Connect זמין במכשירים עם Android מגרסה 14 ואילך. המשתמשים יכולים לגשת ל-Health Connect מההגדרות במכשיר, עם אמצעי בקרה על הפרטיות שמוטמעים בהגדרות המערכת.
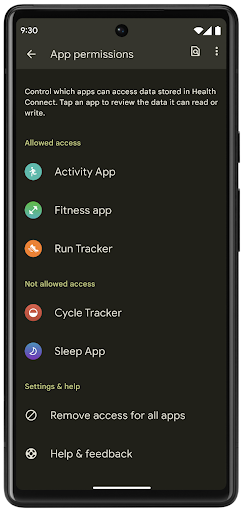
Health Connect כולל כמה תכונות חדשות ב-Android 14, כמו מסלולי אימון, שמאפשרים למשתמשים לשתף מסלול של אימון שאפשר לראות במפה. מסלול מוגדר כרשימה של מיקומים שנשמרו בחלון זמן מסוים, והאפליקציה יכולה להוסיף מסלולים לסשנים של אימונים ולקשר ביניהם. כדי להבטיח שלמשתמשים תהיה שליטה מלאה על המידע הרגיש הזה, הם צריכים לאפשר שיתוף של מסלולים ספציפיים עם אפליקציות אחרות.
מידע נוסף זמין במסמכי התיעוד של Health Connect ובפוסט בבלוג בנושא מה חדש ב-Android Health.
עדכונים ל-OpenJDK 17
ב-Android 14 אנחנו ממשיכים לעדכן את ספריות הליבה של Android כדי להתאים אותן לתכונות בגרסאות OpenJDK LTS האחרונות, כולל עדכוני ספריות ותמיכה בשפה Java 17 למפתחי אפליקציות ופלטפורמות.
התכונות והשיפורים הבאים כלולים:
- עדכנו כ-300 כיתות
java.baseלתמיכה ב-Java 17. - Text Blocks, שמאפשרים להשתמש במחרוזות מילולית של כמה שורות בשפת התכנות Java.
- התאמת דפוסים ל-instanceof, שמאפשרת להתייחס לאובייקט כאל אובייקט מסוג ספציפי ב-
instanceofבלי משתנים נוספים. - כיתות אטומות, שמאפשרות להגביל את המחלקות והממשקים שיכולים להרחיב אותם או להטמיע אותם.
בזכות עדכוני המערכת של Google Play (Project Mainline), יותר מ-600 מיליון מכשירים יכולים לקבל את עדכוני Android Runtime (ART) האחרונים שכוללים את השינויים האלה. זהו חלק מהמחויבות שלנו לספק לאפליקציות סביבה עקבית ומאובטחת יותר במכשירים שונים, ולספק למשתמשים תכונות ויכולות חדשות ללא קשר למהדורות הפלטפורמה.
Java ו-OpenJDK הם סימנים מסחריים או סימנים מסחריים רשומים של Oracle ו/או של השותפים העצמאיים שלה.
שיפורים בחנויות אפליקציות
Android 14 introduces several PackageInstaller APIs that
allow app stores to improve their user experience.
Request install approval before downloading
Installing or updating an app might require user approval.
For example, when an installer making use of the
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES permission attempts to install a
new app. In prior Android versions, app stores can only request user approval
after APKs are written to the install session and the
session is committed.
Starting with Android 14, the requestUserPreapproval()
method lets installers request user approval before committing the install
session. This improvement lets an app store defer downloading any APKs until
after the installation has been approved by the user. Furthermore, once a user
has approved installation, the app store can download and install the app in the
background without interrupting the user.
Claim responsibility for future updates
The setRequestUpdateOwnership() method allows an installer
to indicate to the system that it intends to be responsible for future updates
to an app it is installing. This capability enables update ownership
enforcement, meaning that only the update owner is permitted
to install automatic updates to the app. Update ownership enforcement helps to
ensure that users receive updates only from the expected app store.
Any other installer, including those making use of the
INSTALL_PACKAGES permission, must receive explicit user
approval in order to install an update. If a user decides to proceed with an
update from another source, update ownership is lost.
Update apps at less-disruptive times
App stores typically want to avoid updating an app that is actively in use because this leads to the app's running processes being killed, which potentially interrupts what the user was doing.
Starting with Android 14, the InstallConstraints API
gives installers a way to ensure that their app updates happen at an opportune
moment. For example, an app store can call the
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() method to
make sure that an update is only committed when the user is no longer
interacting with the app in question.
Seamlessly install optional splits
With split APKs, features of an app can be delivered in separate APK files,
rather than as a monolithic APK. Split APKs allow app stores to optimize the
delivery of different app components. For example, app stores might optimize
based on the properties of the target device. The
PackageInstaller API has supported splits since its
introduction in API level 22.
In Android 14, the setDontKillApp() method allows an
installer to indicate that the app's running processes shouldn't be killed when
new splits are installed. App stores can use this feature to seamlessly install
new features of an app while the user is using the app.
חבילות של מטא-נתונים של אפליקציות
Starting in Android 14, the Android package installer lets you specify app metadata, such as data safety practices, to include on app store pages such as Google Play.
זיהוי מתי משתמשים מצלמים צילומי מסך במכשיר
כדי ליצור חוויה סטנדרטית יותר לזיהוי צילומי מסך, ב-Android 14 מוצג API לזיהוי צילומי מסך ששומר על הפרטיות. ה-API הזה מאפשר לאפליקציות לרשום קריאות חוזרות (callback) על בסיס כל פעילות. הקריאות החוזרות האלה מופעלות, והמשתמש מקבל הודעה, כשהמשתמש מצלם צילום מסך בזמן שהפעילות הזו גלויה.
חוויית משתמש
פעולות מותאמות אישית בגיליון השיתוף ודירוג משופר
ב-Android 14 מתבצע עדכון של גיליון השיתוף של המערכת כדי לתמוך בפעולות מותאמות אישית באפליקציות ובתצוגות מקדימות מפורטות יותר של תוצאות למשתמשים.
הוספת פעולות בהתאמה אישית
ב-Android 14, האפליקציה יכולה להוסיף פעולות בהתאמה אישית לגיליון השיתוף של המערכת שהיא מפעילה.
שיפור הדירוג של יעדים לשיתוף ישיר
ב-Android 14 נעשה שימוש באותות רבים יותר מאפליקציות כדי לקבוע את הדירוג של יעדי השיתוף הישיר, וכך לספק תוצאות מועילות יותר למשתמש. כדי לספק את האות הכי שימושי לדירוג, פועלים לפי ההנחיות לשיפור הדירוג של היעדים של שיתוף ישיר. אפליקציות תקשורת יכולות גם לדווח על שימוש במקשי קיצור להודעות יוצאות ונכנסות.
תמיכה באנימציות מובנות ומותאמות אישית לחיזוי של תנועת החזרה
ב-Android 13 הוספנו את האפשרות להפעיל אנימציה חזרה למסך הבית באופן יזום, כאפשרות לפיתוח. כשמשתמשים בתנועת החלקה לאחור באפליקציה נתמכת עם אפשרות הפיתוח מופעלת, מוצגת אנימציה שמציינת שתנועת ההחלקה לאחור יוצאת מהאפליקציה ומחזירה למסך הבית.
Android 14 כולל כמה שיפורים והנחיות חדשות לגבי 'חזרה חזותית':
- אפשר להגדיר את
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueכדי להביע הסכמה לשימוש באנימציות מערכת לחיזוי תנועת החזרה לכל פעילות בנפרד, במקום לכל האפליקציה. - הוספנו אנימציות מערכת חדשות שיתלוו לאנימציה של החזרה למסך הבית מ-Android 13. אנימציות המערכת החדשות הן פעילות בכל פעילות ומשימות שונות, והן מופיעות באופן אוטומטי אחרי העברה ל'חזרה חזוי'.
- הוספנו אנימציות חדשות של רכיבי Material לגיליונות בתחתית המסך, לגיליונות צדדיים ולחיפוש.
- יצרנו הנחיות לעיצוב ליצירת אנימציות ומעברים מותאמים אישית באפליקציה.
- הוספנו ממשקי API חדשים שתומכים באנימציות מעבר בהתאמה אישית באפליקציה:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- משתמשים ב-
overrideActivityTransitionבמקום ב-overridePendingTransitionכדי ליצור מעברים שתגובה כשהמשתמש מחליק חזרה.
בגרסה הזו של Android 14 בתצוגה מקדימה, כל התכונות של 'חזרה חזותית חזרה' נותרו מאחורי אפשרות למפתחים. כדאי לעיין במדריך למפתחים בנושא העברת האפליקציה לחזרה חזותית חזוי, וגם במדריך למפתחים בנושא יצירת מעברים מותאמים אישית באפליקציה.
שינויים שמוגדרים על ידי יצרן מכשיר עם מסך גדול לכל אפליקציה
שינוי הגדרות ברמת האפליקציה מאפשר ליצרני המכשירים לשנות את ההתנהגות של האפליקציות במכשירים עם מסך גדול. לדוגמה, ההחרגה FORCE_RESIZE_APP מורה למערכת לשנות את גודל האפליקציה כך שיתאים למימדי המסך (מבלי להשתמש במצב תאימות לגודל) גם אם הערך resizeableActivity="false" מוגדר בקובץ המניפסט של האפליקציה.
השינויים מברירת המחדל נועדו לשפר את חוויית המשתמש במסכים גדולים.
מאפייני מניפסט חדשים מאפשרים להשבית חלק מהשינויים של יצרן המכשירים באפליקציה שלכם.
הגדרות שונות לכל אפליקציה למשתמשים במסכים גדולים
שינוי ההגדרות של כל אפליקציה בנפרד משנה את התנהגות האפליקציות במכשירים עם מסך גדול. לדוגמה, שינוי ברירת המחדל של יצרן המכשיר OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE מגדיר את יחס הגובה-רוחב של האפליקציה ל-16:9, ללא קשר להגדרות האפליקציה.
ב-Android 14 QPR1, משתמשים יכולים להחיל שינויים ספציפיים לאפליקציות באמצעות תפריט הגדרות חדש במכשירים עם מסך גדול.
שיתוף מסך של אפליקציה
App screen sharing enables users to share an app window instead of the entire device screen during screen content recording.
With app screen sharing, the status bar, navigation bar, notifications, and other system UI elements are excluded from the shared display. Only the content of the selected app is shared.
App screen sharing improves productivity and privacy by enabling users to run multiple apps but limit content sharing to a single app.
תשובה מהירה מבוססת-LLM ב-Gboard ב-Pixel 8 Pro
במכשירי Pixel 8 Pro עם גרסת Feature Drop מדצמבר, מפתחים יכולים לנסות תשובות חכמות באיכות גבוהה יותר ב-Gboard שמבוססות על מודלים גדולים של שפה (LLM) במכשיר שפועלים על Google Tensor.
התכונה הזו זמינה בתור תצוגה מקדימה מוגבלת באנגלית (ארה"ב) ב-WhatsApp, ב-Line וב-KakaoTalk. כדי להשתמש בתכונה הזו, צריך מכשיר Pixel 8 Pro עם Gboard כמקלדת.
כדי לנסות את התכונה, קודם צריך להפעיל אותה בקטע הגדרות > אפשרויות למפתחים > הגדרות AICore > הפעלת AICore Persistent.
לאחר מכן, פותחים שיחה באפליקציה נתמכת כדי לראות את התשובות המהירות שמבוססות על LLM בשורת ההצעות של Gboard בתגובה להודעות נכנסות.
גרפיקה
אפשר להריץ שאילתות על נתיבים ולבצע אינטרפולציה שלהם
Android's Path API is a powerful and flexible mechanism for
creating and rendering vector graphics, with the ability to stroke or fill a
path, construct a path from line segments or quadratic or cubic curves, perform
boolean operations to get even more complex shapes, or all of these
simultaneously. One limitation is the ability to find out what is actually in a
Path object; the internals of the object are opaque to callers after creation.
To create a Path, you call methods such as
moveTo(), lineTo(), and
cubicTo() to add path segments. But there has been no way to
ask that path what the segments are, so you must retain that information at
creation time.
Starting in Android 14, you can query paths to find out what's inside of them.
First, you need to get a PathIterator object using the
Path.getPathIterator API:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
Next, you can call PathIterator to iterate through the segments
one by one, retrieving all of the necessary data for each segment. This example
uses PathIterator.Segment objects, which packages up the data
for you:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
PathIterator also has a non-allocating version of next() where you can pass
in a buffer to hold the point data.
One of the important use cases of querying Path data is interpolation. For
example, you might want to animate (or morph) between two different paths. To
further simplify that use case, Android 14 also includes the
interpolate() method on Path. Assuming the two paths have
the same internal structure, the interpolate() method creates a new Path
with that interpolated result. This example returns a path whose shape is
halfway (a linear interpolation of .5) between path and otherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
The Jetpack graphics-path library enables similar APIs for earlier versions of Android as well.
רשתות מותאמות אישית עם הצללות של קודקודים ושל שברים
Android has long supported drawing triangle meshes with custom shading, but the input mesh format has been limited to a few predefined attribute combinations. Android 14 adds support for custom meshes, which can be defined as triangles or triangle strips, and can, optionally, be indexed. These meshes are specified with custom attributes, vertex strides, varying, and vertex and fragment shaders written in AGSL.
The vertex shader defines the varyings, such as position and color, while the
fragment shader can optionally define the color for the pixel, typically by
using the varyings created by the vertex shader. If color is provided by the
fragment shader, it is then blended with the current Paint
color using the blend mode selected when
drawing the mesh. Uniforms can be passed
into the fragment and vertex shaders for additional flexibility.
מעבד מאגר נתונים זמני של חומרה ל-Canvas
To assist in using Android's Canvas API to draw with
hardware acceleration into a HardwareBuffer, Android 14
introduces HardwareBufferRenderer. This API is
particularly useful when your use case involves communication with the system
compositor through SurfaceControl for low-latency
drawing.

