يقدّم الإصدار Android 14 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات رائعة للمطوّرين. تساعدك المعلومات التالية في التعرّف على ميزات تطبيقاتك والبدء في استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات ذات الصلة.
للحصول على قائمة مفصّلة بواجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تمت إضافتها وتعديلها وإزالتها، يُرجى الاطّلاع على تقرير الاختلافات في واجهات برمجة التطبيقات. للحصول على تفاصيل حول واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المضافة، يُرجى الانتقال إلى مرجع واجهات برمجة تطبيقات Android. بالنسبة إلى نظام التشغيل Android 14، ابحث عن واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تمت إضافتها في المستوى 34 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات. للتعرّف على المجالات التي قد تؤثّر فيها تغييرات النظام الأساسي في تطبيقاتك، احرص على الاطّلاع على تغييرات السلوك في الإصدار 14 من نظام التشغيل Android للتطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 14 من نظام التشغيل Android ولجميع التطبيقات.
التوافق مع أسواق عالمية
إعدادات اللغة المخصصة حسب التطبيقات
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 14 ميزات إضافية لكل تطبيق باللغة تم تقديمها في Android 13 (المستوى 33 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، وهي:
إنشاء
localeConfigللتطبيق تلقائيًا: بدءًا من الإصدار Android Studio Giraffe Canary 7 والإصدار AGP 8.1.0-alpha07، يمكنك ضبط تطبيقك ليعمل تلقائيًا على إتاحة الإعدادات المفضّلة للغة لكل تطبيق. استنادًا إلى موارد مشروعك، ينشئ المكوّن الإضافي لنظام Gradle المتوافق مع Android ملفLocaleConfigويضيف إليه إشارة في ملف البيان النهائي، ما يغنيك عن إنشاء الملف أو تعديله يدويًا. يستخدم AGP الموارد في مجلداتresالخاصة بوحدات تطبيقك وأي ملحقات لوحدات المكتبة لتحديد اللغات المطلوب تضمينها فيملفLocaleConfig.التحديثات الديناميكية لقائمة
localeConfigللتطبيق: استخدِم الطريقتَينsetOverrideLocaleConfig()وgetOverrideLocaleConfig()فيLocaleManagerلتعديل قائمة اللغات المتاحة في تطبيقك ديناميكيًا في إعدادات نظام الجهاز. يمكنك الاستفادة من هذه المرونة لتخصيص قائمة اللغات المتاحة لكل منطقة، أو إجراء تجارب أ/ب، أو تقديم قائمة محدّثة للغات إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم عمليات الإرسال من جهة الخادم لعملية التعريب.إظهار لغة التطبيق لمحرّري أساليب الإدخال (IME): يمكن لمحرّري أساليب الإدخال استخدام الأسلوب
getApplicationLocales()للتحقّق من لغة التطبيق الحالي ومطابقة لغة محرّر أسلوب الإدخال مع هذه اللغة.
Grammatical Inflection API
3 billion people speak gendered languages: languages where grammatical categories—such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and prepositions—inflect according to the gender of people and objects you talk to or about. Traditionally, many gendered languages use masculine grammatical gender as the default or generic gender.
Addressing users in the wrong grammatical gender, such as addressing women in masculine grammatical gender, can negatively impact their performance and attitude. In contrast, a UI with language that correctly reflects the user's grammatical gender can improve user engagement and provide a more personalized and natural-sounding user experience.
لمساعدتك في إنشاء واجهة مستخدم تركّز على المستخدم للغات التي تراعي الجنس، يوفّر الإصدار 14 من Android واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Grammatical Inflection API، التي تتيح لك إضافة ميزة مراعاة الجنس النحوي بدون إعادة صياغة تطبيقك.
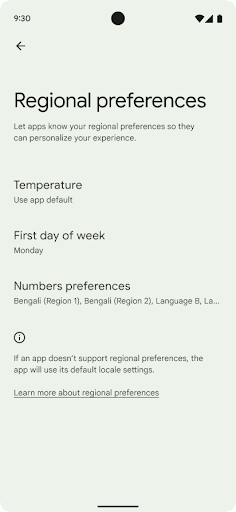
الإعدادات المفضّلة للمنطقة
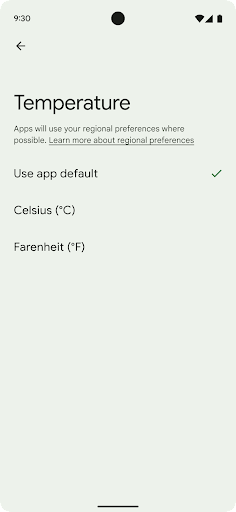
Regional preferences enable users to personalize temperature units, the first day of the week, and numbering systems. A European living in the United States might prefer temperature units to be in Celsius rather than Fahrenheit and for apps to treat Monday as the beginning of the week instead of the US default of Sunday.
New Android Settings menus for these preferences provide users with a
discoverable and centralized location to change app preferences. These
preferences also persist through backup and restore. Several APIs and
intents—such as
getTemperatureUnit
and
getFirstDayOfWeek—
grant your app read access to user preferences, so your app can adjust how it
displays information. You can also register a
BroadcastReceiver on
ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED
to handle locale configuration changes when regional preferences change.
To find these settings, open the Settings app and navigate to System > Languages & input > Regional preferences.
تسهيل الاستخدام
الضبط غير الخطي لحجم الخط بما يصل إلى 200%
Starting in Android 14, the system supports font scaling up to 200%, providing users with additional accessibility options.
To prevent large text elements on screen from scaling too large, the system applies a nonlinear scaling curve. This scaling strategy means that large text doesn't scale at the same rate as smaller text. Nonlinear font scaling helps preserve the proportional hierarchy between elements of different sizes while mitigating issues with linear text scaling at high degrees (such as text being cut off or text that becomes harder to read due to an extremely large display sizes).
Test your app with nonlinear font scaling
If you already use scaled pixels (sp) units to define text sizing, then these additional options and scaling improvements are applied automatically to the text in your app. However, you should still perform UI testing with the maximum font size enabled (200%) to ensure that your app applies the font sizes correctly and can accommodate larger font sizes without impacting usability.
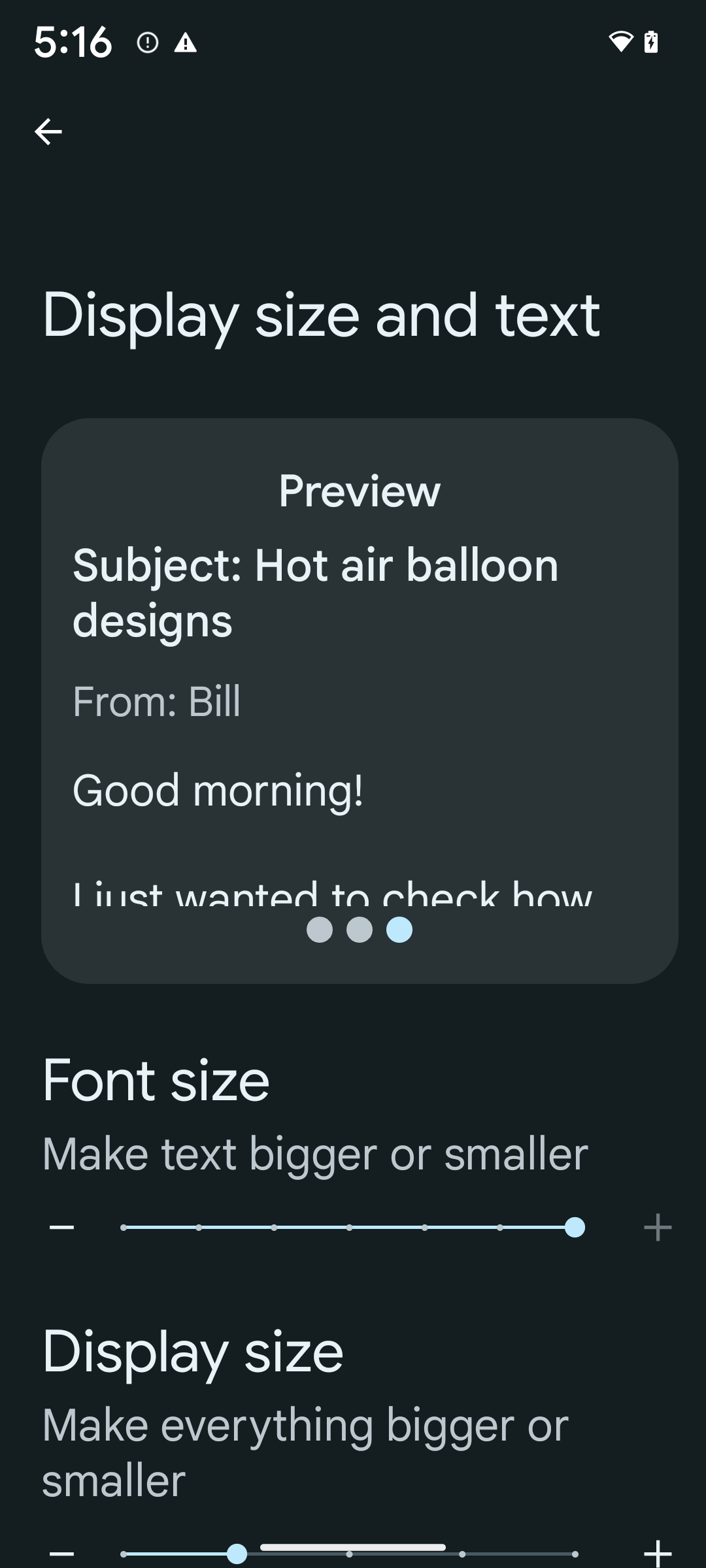
To enable 200% font size, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app and navigate to Accessibility > Display size and text.
- For the Font size option, tap the plus (+) icon until the maximum font size setting is enabled, as shown in the image that accompanies this section.
Use scaled pixel (sp) units for text-sizes
Remember to always specify text sizes in sp units. When your app uses sp units, Android can apply the user's preferred text size and scale it appropriately.
Don't use sp units for padding or define view heights assuming implicit padding: with nonlinear font scaling sp dimensions might not be proportional, so 4sp + 20sp might not equal 24sp.
Convert scaled pixel (sp) units
Use TypedValue.applyDimension() to convert from sp units
to pixels, and use TypedValue.deriveDimension() to
convert pixels to sp. These methods apply the appropriate nonlinear scaling
curve automatically.
Avoid hardcoding equations using
Configuration.fontScale or
DisplayMetrics.scaledDensity. Because font scaling is
nonlinear, the scaledDensity field is no longer accurate. The fontScale
field should be used for informational purposes only because fonts are no longer
scaled with a single scalar value.
Use sp units for lineHeight
Always define android:lineHeight using sp units instead
of dp, so the line height scales along with your text. Otherwise, if your text
is sp but your lineHeight is in dp or px, it doesn't scale and looks cramped.
TextView automatically corrects the lineHeight so that your intended
proportions are preserved, but only if both textSize and lineHeight are
defined in sp units.
الكاميرا والوسائط
دقة HDR فائقة للصور

يتيح نظام التشغيل Android 14 استخدام صور النطاق العالي الديناميكية (HDR) التي تحتفظ بمزيد من المعلومات الواردة من أداة الاستشعار عند التقاط صورة، ما يتيح الحصول على ألوان زاهية ودرجة تباين أكبر. يستخدم نظام Android تنسيق Ultra HDR، وهو متوافق تمامًا مع صور JPEG القديمة، ما يسمح للتطبيقات بالعمل بسلاسة مع صور HDR وعرضها بنطاق ديناميكي عادي (SDR) عند الحاجة.
ويتم عرض هذه الصور في واجهة المستخدم بتنسيق HDR تلقائيًا من خلال إطار العمل
عندما يختار تطبيقك استخدام واجهة مستخدم بتنسيق HDR لـ "نافذة النشاط"، إما من خلال أحد إدخالات ملف البيان أو أثناء التشغيل من خلال استدعاء Window.setColorMode(). يمكنك أيضًا التقاط صور ثابتة فائقة
التباين الديناميكي (HDR) المضغوطة على الأجهزة المتوافقة. من خلال استرداد المزيد من الألوان
من أداة الاستشعار، يمكن أن يكون التعديل في مرحلة ما بعد الإنتاج أكثر مرونة. يمكن استخدام رمز الترميز
Gainmap المرتبط بالصور ذات النطاق العالي الديناميكية الفائق لعرضها
باستخدام OpenGL أو Vulkan.
التكبير/التصغير والتركيز والمعاينة بعد الالتقاط والمزيد في إضافات الكاميرا
يُجري نظام Android 14 ترقيات وتحسينات على إضافات الكاميرا، ويسمح للتطبيقات بمعالجة الصور لفترات أطول، ما يؤدي إلى تحسين الصور باستخدام خوارزميات كثيفة الاستخدام للمعالجة، مثل التصوير في الإضاءة المنخفضة على الأجهزة المتوافقة. وتوفّر هذه الميزات للمستخدمين تجربة أكثر فعالية عند استخدام إمكانات توسيع نطاق الكاميرا. تشمل أمثلة هذه التحسينات ما يلي:
- يقدّم تقدير وقت الاستجابة لمعالجة الصور الثابتة الديناميكية مزيدًا من الدقة في تقدير وقت الاستجابة لالتقاط الصور الثابتة استنادًا إلى المشهد الحالي وظروف التصوير. استخدِم دالة
CameraExtensionSession.getRealtimeStillCaptureLatency()للحصول على عنصرStillCaptureLatencyيتضمّن طريقتَين لتقدير وقت الاستجابة. تُرجع الطريقةgetCaptureLatency()وقت الاستجابة المقدَّر بينonCaptureStartedوonCaptureProcessStarted()، وتُرجع الطريقةgetProcessingLatency()وقت الاستجابة المقدَّر بينonCaptureProcessStarted()ووقت توفُّر الإطار النهائي الذي تمت معالجته. - إتاحة عمليات استدعاء لعرض مستوى التقدّم في الالتقاط كي تتمكّن التطبيقات من عرض المستوى الحالي
للتقدّم في عمليات معالجة الصور الثابتة التي تستغرق وقتًا طويلاً يمكنك التحقّق مما إذا كانت هذه الميزة متاحة مع
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isCaptureProcessProgressAvailable، وإذا كانت متاحة، يمكنك تنفيذ دالة callback الخاصة بتسجيل التقدّمonCaptureProcessProgressed()، والتي تم تمرير التقدّم (من 0 إلى 100) إليها كمَعلمة. البيانات الوصفية الخاصة بالإضافة، مثل
CaptureRequest.EXTENSION_STRENGTHللاتصال برقم هاتفي مقدار تأثير الإضافة، مثل مقدار التمويه في الخلفية باستخدامEXTENSION_BOKEHميزة "العرض اللاحق" لالتقاط الصور في إضافات الكاميرا، والتي تقدّم صورة تمّت معالجتها بشكل أقلّ بسرعة أكبر من الصورة النهائية إذا كانت إضافة الصور تزيد من وقت الاستجابة في المعالجة، يمكن تقديم صورة ما بعد المشاهدة كعنصر بدلٍ لتحسين تجربة المستخدم واستبدالها لاحقًا بالصورة النهائية. يمكنك معرفة ما إذا كانت هذه الميزة متاحة باستخدام
CameraExtensionCharacteristics.isPostviewAvailable. بعد ذلك، يمكنك تمريرOutputConfigurationإلىExtensionSessionConfiguration.setPostviewOutputConfiguration.إتاحة استخدام
SurfaceViewللاستفادة من مسار عرض معاينة أكثر فعالية من حيث الطاقةإتاحة ميزة "النقر للتركيز" والتكبير/التصغير أثناء استخدام الإضافة
التكبير داخل المستشعر
When REQUEST_AVAILABLE_CAPABILITIES_STREAM_USE_CASE in
CameraCharacteristics contains
SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW, your app
can use advanced sensor capabilities to give a cropped RAW stream the same
pixels as the full field of view by using a CaptureRequest
with a RAW target that has stream use case set to
CameraMetadata.SCALER_AVAILABLE_STREAM_USE_CASES_CROPPED_RAW.
By implementing the request override controls, the updated camera gives users
zoom control even before other camera controls are ready.
صوت عالي الدقة عبر USB
Android 14 gains support for lossless audio formats for audiophile-level
experiences over USB wired headsets. You can query a USB device for its
preferred mixer attributes, register a listener for changes in preferred mixer
attributes, and configure mixer attributes using the
AudioMixerAttributes class. This class represents the
format, such as channel mask, sample rate, and behavior of the audio mixer. The
class allows for audio to be sent directly, without mixing,
volume adjustment, or processing effects.
إنتاجية المطوّرين وأدواتهم
مدير بيانات الاعتماد
Android 14 adds Credential Manager as a platform API, with additional support back to Android 4.4 (API level 19) devices through a Jetpack Library using Google Play services. Credential Manager aims to make sign-in easier for users with APIs that retrieve and store credentials with user-configured credential providers. Credential Manager supports multiple sign-in methods, including username and password, passkeys, and federated sign-in solutions (such as Sign-in with Google) in a single API.
Passkeys provide many advantages. For example, passkeys are built on industry standards, can work across different operating systems and browser ecosystems, and can be used with both websites and apps.
For more information, see the Credential Manager and passkeys documentation and the blogpost about Credential Manager and passkeys.
Health Connect
Health Connect is an on-device repository for user health and fitness data. It allows users to share data between their favorite apps, with a single place to control what data they want to share with these apps.
On devices running Android versions prior to Android 14, Health Connect is available to download as an app on the Google Play store. Starting with Android 14, Health Connect is part of the platform and receives updates through Google Play system updates without requiring a separate download. With this, Health Connect can be updated frequently, and your apps can rely on Health Connect being available on devices running Android 14 or higher. Users can access Health Connect from the Settings in their device, with privacy controls integrated into the system settings.
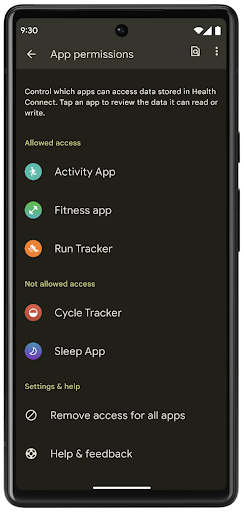
Health Connect includes several new features in Android 14, such as exercise routes, allowing users to share a route of their workout which can be visualized on a map. A route is defined as a list of locations saved within a window of time, and your app can insert routes into exercise sessions, tying them together. To ensure that users have complete control over this sensitive data, users must allow sharing individual routes with other apps.
For more information, see the Health Connection documentation and the blogpost on What's new in Android Health.
تعديلات OpenJDK 17
Android 14 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases, including both library updates and Java 17 language support for app and platform developers.
The following features and improvements are included:
- Updated approximately 300
java.baseclasses to Java 17 support. - Text Blocks, which introduce multi-line string literals to the Java programming language.
- Pattern Matching for instanceof, which allows an object to
be treated as having a specific type in an
instanceofwithout any additional variables. - Sealed classes, which allow you restrict which classes and interfaces can extend or implement them.
Thanks to Google Play system updates (Project Mainline), over 600 million devices are enabled to receive the latest Android Runtime (ART) updates that include these changes. This is part of our commitment to give apps a more consistent, secure environment across devices, and to deliver new features and capabilities to users independent of platform releases.
Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
تحسينات على متاجر التطبيقات
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 14 العديد من واجهات برمجة تطبيقات PackageInstaller التي تسمح لمتاجر التطبيقات بتحسين تجربة المستخدمين.
طلب الموافقة على التثبيت قبل التنزيل
قد يتطلّب تثبيت تطبيق أو تحديثه موافقة المستخدم.
على سبيل المثال، عندما يحاول أحد تطبيقات التثبيت التي تستخدم إذن
REQUEST_INSTALL_PACKAGES تثبيت
تطبيق جديد، لا يمكن لمتاجر التطبيقات طلب موافقة المستخدم إلا بعد كتابة حِزم APK في جلسة التثبيت وإتمام الجلسة.
اعتبارًا من Android 14، تتيح طريقة requestUserPreapproval()
للمُثبّتين طلب موافقة المستخدم قبل إكمال جلسة التثبيت. يتيح هذا التحسين لمتجر التطبيقات تأجيل تنزيل أي حِزم APK إلى
بعد أن يوافق المستخدم على التثبيت. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، بعد أن يمنح أحد المستخدمين موافقته على التثبيت، يمكن لمتجر التطبيقات تنزيل التطبيق وتثبيته في
الخلفية بدون مقاطعة المستخدم.
تأكيد مسؤولية التعديلات المستقبلية
تسمح طريقة setRequestUpdateOwnership() للمثبّت
بإعلام النظام بأنّه سيتحمّل مسؤولية التحديثات المستقبلية
للتطبيق الذي يتم تثبيته. تتيح هذه الميزة فرض ملكية التحديث، ما يعني أنّه لا يُسمح إلا لمالك التحديث
بتثبيت التحديثات التلقائية للتطبيق. ويساعد فرض ملكية التحديث في
ضمان تلقّي المستخدمين للتحديثات من متجر التطبيقات المتوقّع فقط.
يجب أن يحصل أي مُثبِّت آخر، بما في ذلك مُثبِّتي التطبيقات الذين يستخدمون إذن
INSTALL_PACKAGES، على موافقة صريحة من المستخدمين لتثبيت التحديث. إذا قرّر أحد المستخدِمين مواصلة تعديل
من مصدر آخر، ستتم فقدان ملكية التعديل.
تحديث التطبيقات في أوقات أقل إزعاجًا
تحاول متاجر التطبيقات عادةً تجنُّب تحديث تطبيق قيد الاستخدام بشكل نشط، لأنّ ذلك يؤدي إلى إيقاف العمليات الجارية للتطبيق، ما قد يؤدي بدوره إلى إيقاف ما كان يفعله المستخدم.
بدءًا من Android 14، تقدّم واجهة برمجة التطبيقات InstallConstraints
للمُثبّتين طريقة لضمان إجراء تحديثات التطبيقات في الوقت المناسب. على سبيل المثال، يمكن لمتجر تطبيقات استدعاء الأسلوب
commitSessionAfterInstallConstraintsAreMet() لمحاولة التأكد من عدم التزام المستخدم بالتغييرات إلا عندما يتوقف عن التفاعل مع التطبيق المعني.
تثبيت الفواصل الاختيارية بسلاسة
باستخدام حِزم APK المجزّأة، يمكن توفير ميزات التطبيق في حِزم APK منفصلة، بدلاً من حزمة APK واحدة. تسمح ملفات APK المجزّأة لمتاجر التطبيقات بتحسين
عرض مكوّنات التطبيق المختلفة. على سبيل المثال، قد تعمل متاجر التطبيقات على تحسين
التطبيقات استنادًا إلى خصائص الجهاز المستهدَف. كانت واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
PackageInstaller متوافقة مع عمليات التقسيم منذ
إدخالها في المستوى 22 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات.
في نظام التشغيل Android 14، تسمح طريقة setDontKillApp() لتطبيق
التثبيت بتحديد أنّه يجب عدم إنهاء عمليات التطبيق الجارية عند
تثبيت أقسام جديدة. يمكن لمتاجر التطبيقات استخدام هذه الميزة لتثبيت
ميزات جديدة للتطبيق بسلاسة أثناء استخدام المستخدم للتطبيق.
حِزم البيانات الوصفية للتطبيق
اعتبارًا من الإصدار Android 14، يتيح لك أداة تثبيت حِزم Android تحديد البيانات الوصفية للتطبيق، مثل ممارسات أمان البيانات، لتضمينها في صفحات متجر التطبيقات، مثل Google Play.
رصد وقت أخذ المستخدمين لقطات شاشة للجهاز
لإنشاء تجربة أكثر توحيدًا في ما يتعلّق برصد لقطات الشاشة، يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 14 واجهة برمجة تطبيقات لرصد لقطات الشاشة تحافظ على الخصوصية. تتيح واجهة برمجة التطبيقات هذه للتطبيقات تسجيل عمليات ردّ على مستوى كل نشاط. يتم استدعاء عمليات الرجوع هذه وإرسال إشعار إلى المستخدم عندما يلتقط لقطة شاشة أثناء ظهور هذا النشاط.
تجربة المستخدم
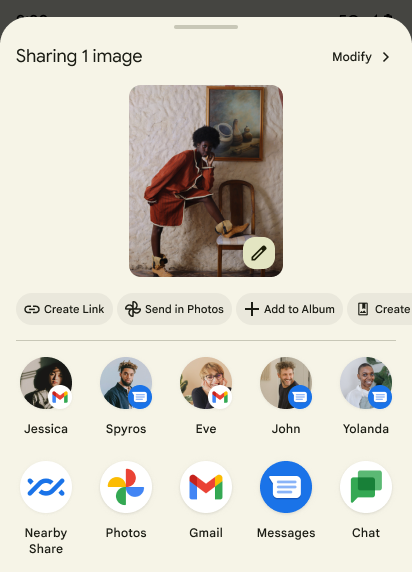
الإجراءات المخصّصة في ورقة المشاركة والترتيب المحسّن
Android 14 updates the system sharesheet to support custom app actions and more informative preview results for users.
Add custom actions
With Android 14, your app can add custom actions to the system sharesheet it invokes.
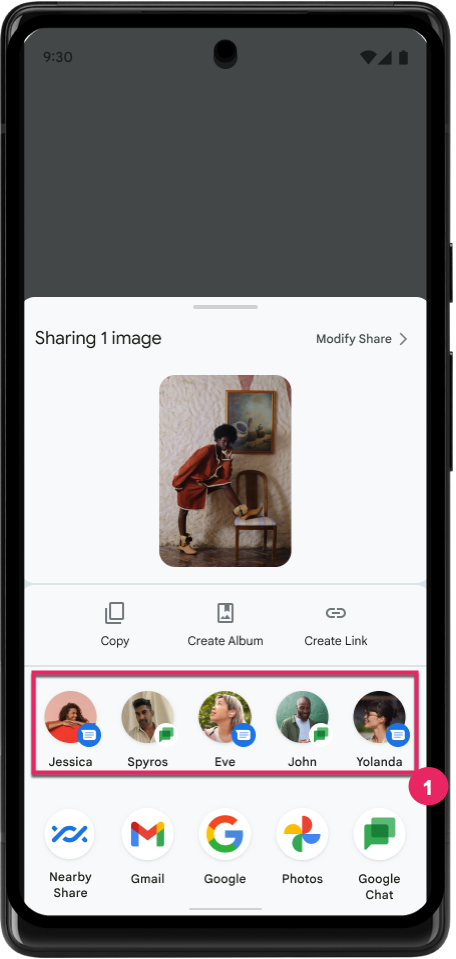
Improve ranking of Direct Share targets
Android 14 uses more signals from apps to determine the ranking of the direct share targets to provide more helpful results for the user. To provide the most useful signal for ranking, follow the guidance for improving rankings of your Direct Share targets. Communication apps can also report shortcut usage for outgoing and incoming messages.
إتاحة صور متحركة مضمّنة ومخصّصة لإيماءة "الرجوع التنبؤي"
Android 13 introduced the predictive back-to-home animation behind a developer option. When used in a supported app with the developer option enabled, swiping back shows an animation indicating that the back gesture exits the app back to the home screen.
Android 14 includes multiple improvements and new guidance for Predictive Back:
- You can set
android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback=trueto opt in to predictive back system animations per-Activity instead of for the entire app. - We've added new system animations to accompany the back-to-home animation from Android 13. The new system animations are cross-activity and cross-task, which you get automatically after migrating to Predictive Back.
- We've added new Material Component animations for Bottom sheets, Side sheets, and Search.
- We've created design guidance for creating custom in-app animations and transitions.
- We've added new APIs to support custom in-app transition animations:
handleOnBackStarted,handleOnBackProgressed,handleOnBackCancelledinOnBackPressedCallbackonBackStarted,onBackProgressed,onBackCancelledinOnBackAnimationCallback- Use
overrideActivityTransitioninstead ofoverridePendingTransitionfor transitions that respond as the user swipes back.
With this Android 14 preview release, all features of Predictive Back remain behind a developer option. See the developer guide to migrate your app to predictive back, as well as the developer guide to creating custom in-app transitions.
عمليات الإلغاء على مستوى التطبيق من قِبل مصنّع الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة
تتيح عمليات إلغاء الإعدادات على مستوى التطبيق لصنّاع الأجهزة تغيير سلوك التطبيقات على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة. على سبيل المثال، عند إلغاء FORCE_RESIZE_APP، يتم توجيه النظام لتغيير حجم التطبيق ليلائم أبعاد العرض (وتجنُّب وضع توافق الحجم) حتى في حال ضبط resizeableActivity="false" في بيان التطبيق.
تهدف عمليات الإلغاء إلى تحسين تجربة المستخدم على الشاشات الكبيرة.
تتيح لك سمات البيان الجديدة إيقاف بعض عمليات إلغاء الشركة المصنّعة للجهاز لتطبيقك.
عمليات إلغاء على مستوى التطبيق لمستخدمي الشاشات الكبيرة
تؤدي عمليات التجاوز لكل تطبيق إلى تغيير سلوك التطبيقات على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة. على سبيل المثال، يمكن للشركة المصنّعة للجهاز OVERRIDE_MIN_ASPECT_RATIO_LARGE إلغاء الإعدادات وضبط نسبة عرض إلى ارتفاع التطبيق على 16:9 بغض النظر عن إعدادات التطبيق.
يتيح الإصدار 1 من الربع الثاني من العام 2021 من نظام التشغيل Android 14 للمستخدمين تطبيق عمليات إلغاء على مستوى كل تطبيق من خلال قائمة إعدادات جديدة على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة.
مشاركة شاشة التطبيق
App screen sharing enables users to share an app window instead of the entire device screen during screen content recording.
With app screen sharing, the status bar, navigation bar, notifications, and other system UI elements are excluded from the shared display. Only the content of the selected app is shared.
App screen sharing improves productivity and privacy by enabling users to run multiple apps but limit content sharing to a single app.
ميزة "الرد السريع" المستندة إلى نماذج اللغات الكبيرة في Gboard على هاتف Pixel 8 Pro
على أجهزة Pixel 8 Pro التي تم تثبيت حزمة ميزات شهر كانون الأول (ديسمبر) عليها، يمكن للمطوّرين تجربة ردود سريعة بجودة أعلى في Gboard، وذلك باستخدام نماذج لغوية كبيرة (LLM) على الجهاز تعمل على معالج Google Tensor.
تتوفّر هذه الميزة في إصدار تجريبي محدود باللغة الإنجليزية (الولايات المتحدة) في WhatsApp وLine وKakaoTalk. تتطلّب الميزة استخدام جهاز Pixel 8 Pro مع Gboard ك keyboard.
لتجربة هذه الميزة، عليك أولاً تفعيلها من خلال الانتقال إلى الإعدادات > خيارات المطوّرين > إعدادات AICore > تفعيل ميزة Aicore Persistent.
بعد ذلك، افتح محادثة في تطبيق متوافق للاطّلاع على ميزة "الرد السريع" المستندة إلى نموذج اللغة الكبيرة في شريط اقتراحات Gboard استجابةً للرسائل الواردة.
الرسومات
يمكن البحث عن المسارات وتعديلها.
Path API هي آلية فعّالة ومرنة ل
إنشاء الرسومات المتجهّة وعرضها، مع إمكانية رسم خطوط أو ملء
مسار أو إنشاء مسار من أجزاء خطية أو منحنيات ثنائية أو ثلاثية الحدود، أو تنفيذ
عمليات منطقية للحصول على أشكال أكثر تعقيدًا، أو كل ذلك
في الوقت نفسه. ويتمثل أحد القيود في القدرة على معرفة ما هو موجود بالفعل في كائن "مسار"، وتكون العناصر الداخلية للكائن معتمة للمتصلين بعد إنشائه.
لإنشاء Path، يمكنك استدعاء طرق مثل
moveTo() وlineTo() و
cubicTo() لإضافة شرائح مسار. ولكن لم تكن هناك طريقة للسؤال عن
الأجزاء في هذا المسار، لذلك يجب عليك الاحتفاظ بهذه المعلومات في وقت الإنشاء.
بدءًا من Android 14، يمكنك طلب البحث عن المسارات لمعرفة ما بداخلها.
عليك أولاً الحصول على كائن PathIterator باستخدام واجهة برمجة تطبيقات Path.getPathIterator:
Kotlin
val path = Path().apply { moveTo(1.0f, 1.0f) lineTo(2.0f, 2.0f) close() } val pathIterator = path.pathIterator
Java
Path path = new Path(); path.moveTo(1.0F, 1.0F); path.lineTo(2.0F, 2.0F); path.close(); PathIterator pathIterator = path.getPathIterator();
بعد ذلك، يمكنك استدعاء الدالة PathIterator لتكرار الشرائح الواحد تلو الآخر، واسترداد جميع البيانات اللازمة لكل شريحة. يستخدم هذا المثال
كائنات PathIterator.Segment التي تحزم البيانات
نيابةً عنك:
Kotlin
for (segment in pathIterator) { println("segment: ${segment.verb}, ${segment.points}") }
Java
while (pathIterator.hasNext()) { PathIterator.Segment segment = pathIterator.next(); Log.i(LOG_TAG, "segment: " + segment.getVerb() + ", " + segment.getPoints()); }
لدى PathIterator أيضًا إصدار غير مخصّص من next() يمكنك تمريره
في مخزن مؤقت للاحتفاظ ببيانات النقاط.
من حالات الاستخدام المهمة لطلب بيانات Path هي الاستقراء. على سبيل المثال، قد ترغب في إضافة تأثير متحرك (أو تحويل) بين مسارين مختلفين. لتبسيط حالة الاستخدام هذه بشكل أكبر، يتضمّن Android 14 أيضًا طريقة
interpolate() في Path. بافتراض أنّ المسارَين لهما البنية الداخلية نفسها، تنشئ الطريقة interpolate() Path جديدة مع تلك النتيجة المضمَّنة. يعرض هذا المثال مسارًا يكون شكله
في منتصف الطريق (تداخل خطي بنسبة 0.5) بين path وotherPath:
Kotlin
val interpolatedResult = Path() if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, .5f, interpolatedResult) }
Java
Path interpolatedResult = new Path(); if (path.isInterpolatable(otherPath)) { path.interpolate(otherPath, 0.5F, interpolatedResult); }
تتيح مكتبة graphics-path في Jetpack واجهات برمجة تطبيقات مشابهة لإصدارات Android الأقدم أيضًا.
شبكات مخصّصة مع مظلّلات الرؤوس والتقسيمات
Android has long supported drawing triangle meshes with custom shading, but the input mesh format has been limited to a few predefined attribute combinations. Android 14 adds support for custom meshes, which can be defined as triangles or triangle strips, and can, optionally, be indexed. These meshes are specified with custom attributes, vertex strides, varying, and vertex and fragment shaders written in AGSL.
The vertex shader defines the varyings, such as position and color, while the
fragment shader can optionally define the color for the pixel, typically by
using the varyings created by the vertex shader. If color is provided by the
fragment shader, it is then blended with the current Paint
color using the blend mode selected when
drawing the mesh. Uniforms can be passed
into the fragment and vertex shaders for additional flexibility.
أداة عرض المخزن المؤقت للأجهزة في Canvas
للمساعدة في استخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Canvas في Android للرسم باستخدام
التسارع في الأجهزة في HardwareBuffer، يوفّر الإصدار 14 من Android HardwareBufferRenderer. واجهة برمجة التطبيقات هذه
عندما تشتمل حالة الاستخدام على التواصل مع النظام
المكون من خلال SurfaceControl لوقت الاستجابة المنخفض
رسم.

