Android 15 memperkenalkan fitur dan API baru yang hebat untuk para developer. Bagian berikut merangkum fitur ini untuk membantu Anda mulai menggunakan API terkait.
Untuk melihat daftar mendetail tentang API yang ditambahkan, diubah, dan dihapus, baca laporan perbedaan API. Untuk mengetahui detail tentang API yang ditambahkan, buka referensi API Android — untuk Android 15, cari API yang ditambahkan di level API 35. Untuk mempelajari area tempat perubahan platform dapat memengaruhi aplikasi Anda, pastikan untuk memeriksa perubahan perilaku Android 15 untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 15 dan untuk semua aplikasi.
Kamera dan media
Android 15 menyertakan berbagai fitur yang meningkatkan pengalaman kamera dan media, serta memberi Anda akses ke alat dan hardware untuk mendukung kreator dalam mewujudkan visi mereka di Android.
Untuk mengetahui informasi selengkapnya tentang fitur dan solusi developer terbaru untuk media dan kamera Android, lihat materi Membangun pengalaman media dan kamera Android modern dari Google I/O.
Peningkatan Cahaya Rendah
Android 15 memperkenalkan Low Light Boost, mode eksposur otomatis yang tersedia untuk Camera 2 dan ekstensi kamera mode malam. Peningkatan Cahaya Redup menyesuaikan eksposur streaming Pratinjau dalam kondisi cahaya redup. Hal ini berbeda dengan cara ekstensi kamera mode malam membuat gambar diam, karena mode malam menggabungkan serangkaian foto untuk membuat satu gambar yang ditingkatkan. Meskipun mode malam berfungsi sangat baik untuk membuat gambar diam, mode ini tidak dapat membuat streaming frame yang berkelanjutan, tetapi Low Light Boost dapat melakukannya. Dengan demikian, Pengoptimalan Cahaya Rendah memungkinkan kemampuan kamera, seperti:
- Memberikan pratinjau gambar yang ditingkatkan, sehingga pengguna dapat lebih baik membingkai gambar dalam kondisi cahaya redup
- Memindai kode QR dalam kondisi cahaya redup
Jika Anda mengaktifkan Peningkatan Cahaya Redup, fitur ini akan otomatis aktif saat ada tingkat cahaya yang rendah, dan nonaktif saat ada lebih banyak cahaya.
Aplikasi dapat merekam dari streaming Pratinjau dalam kondisi cahaya redup untuk menyimpan video yang lebih terang.
Untuk informasi selengkapnya, lihat Penguatan Cahaya Redup.
Kontrol kamera dalam aplikasi
Android 15 menambahkan ekstensi untuk lebih mengontrol hardware kamera dan algoritmanya di perangkat yang didukung:
- Penyesuaian kekuatan flash lanjutan yang memungkinkan kontrol intensitas flash
yang presisi dalam mode
SINGLEdanTORCHsaat mengambil gambar.
Kontrol ruang kosong HDR
Android 15 memilih headroom HDR yang sesuai dengan kemampuan perangkat
yang mendasari dan kedalaman bit panel. Untuk halaman yang memiliki banyak konten
SDR, seperti aplikasi pesan yang menampilkan satu thumbnail HDR, perilaku
ini dapat memengaruhi kecerahan konten
SDR yang dirasakan. Android 15 memungkinkan Anda mengontrol headroom HDR dengan
setDesiredHdrHeadroom untuk mencapai keseimbangan antara konten
SDR dan HDR.
Kontrol kerasan suara

Android 15 memperkenalkan dukungan untuk standar kenyaringan CTA-2075 guna membantu Anda menghindari inkonsistensi kenyaringan audio dan memastikan pengguna tidak perlu terus-menerus menyesuaikan volume saat beralih antarkonten. Sistem ini memanfaatkan informasi karakteristik perangkat output (headphone dan speaker) beserta metadata kenyaringan yang tersedia dalam konten audio AAC untuk menyesuaikan secara cerdas tingkat kenyaringan audio dan rentang dinamis.
Untuk mengaktifkan fitur ini, pastikan metadata kenyaringan tersedia di
konten AAC dan mengaktifkan fitur platform di aplikasi Anda. Untuk itu, Anda dapat
Buat instance objek LoudnessCodecController dengan
memanggil metode factory create-nya dengan audio
ID sesi dari AudioTrack terkait; ingin
otomatis mulai menerapkan pembaruan audio. Anda dapat meneruskan
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener untuk mengubah atau memfilter
parameter volume sebelum diterapkan di
MediaCodec.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer juga akan diupdate untuk menggunakan
LoudnessCodecController API untuk integrasi aplikasi yang lancar.
Perangkat MIDI 2.0 virtual
Android 13 menambahkan dukungan untuk terhubung ke perangkat MIDI 2.0 menggunakan USB, yang berkomunikasi menggunakan Universal MIDI Packets (UMP). Android 15 memperluas dukungan UMP ke aplikasi MIDI virtual, yang memungkinkan aplikasi komposisi mengontrol aplikasi synthesizer sebagai perangkat MIDI 2.0 virtual seperti yang dilakukan dengan perangkat USB MIDI 2.0.
Decoding software AV1 yang lebih efisien

dav1d, decoder software AV1 populer dari VideoLAN tersedia untuk perangkat Android yang tidak mendukung dekode AV1 dalam hardware. dav1d memiliki performa hingga 3x lebih baik daripada decoder software AV1 lama, sehingga memungkinkan pemutaran AV1 HD untuk lebih banyak pengguna, termasuk beberapa perangkat tingkat rendah dan menengah.
Aplikasi Anda harus memilih untuk menggunakan dav1d dengan memanggilnya berdasarkan nama
"c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". dav1d akan dijadikan decoder software
AV1 default dalam update berikutnya. Dukungan ini distandarisasi dan di-backport ke
perangkat Android 11 yang menerima update sistem Google Play.
Alat dan produktivitas developer
Meskipun sebagian besar upaya kami untuk meningkatkan produktivitas Anda berpusat pada alat seperti Android Studio, Jetpack Compose, dan library Android Jetpack, kami selalu mencari cara di platform untuk membantu Anda mewujudkan visi dengan lebih mudah.
Update OpenJDK 17
Android 15 melanjutkan pekerjaan memuat ulang library inti Android agar selaras dengan fitur dalam rilis OpenJDK LTS terbaru.
Fitur dan peningkatan utama berikut disertakan:
- Peningkatan kualitas hidup di sekitar buffer NIO
- Streaming
- Metode
mathdanstrictmathtambahan - Update paket
utiltermasukcollection,map, dansetyang diurutkan - Dukungan
ByteBufferdiDeflater - Update keamanan seperti
X500PrivateCredentialdan update kunci keamanan
API ini diupdate di lebih dari satu miliar perangkat yang menjalankan Android 12 (API level 31) dan yang lebih tinggi melalui update Sistem Google Play, sehingga Anda dapat menargetkan fitur pemrograman terbaru.
Peningkatan PDF
Android 15 menyertakan peningkatan substansial pada PdfRenderer
Google Cloud Platform. Aplikasi dapat menggabungkan fitur lanjutan seperti rendering
file yang dilindungi sandi, anotasi, pengeditan formulir,
penelusuran, dan pemilihan dengan salinan. PDF yang dilinierkan
pengoptimalan didukung untuk mempercepat penayangan PDF lokal dan mengurangi penggunaan resource.
Library Jetpack PDF menggunakan API ini untuk menyederhanakan penambahan PDF
menampilkan aplikasi Anda.
PdfRenderer telah dipindahkan ke modul yang dapat diupdate menggunakan update sistem
Google Play, terlepas dari rilis platform, dan kami mendukung
perubahan ini kembali ke Android 11 (API level 30) dengan membuat platform API
versi pra-Android 15 yang kompatibel, yang disebut
PdfRendererPreV.
Penyempurnaan pengalihan bahasa otomatis
Android 14 menambahkan pengenalan multibahasa di perangkat dalam audio dengan peralihan
otomatis antarbahasa, tetapi hal ini dapat menyebabkan kata dihapus,
terutama saat bahasa beralih dengan sedikit jeda di antara dua
ucapan. Android 15 menambahkan kontrol tambahan untuk membantu aplikasi menyesuaikan pengalihan ini
ke kasus penggunaannya.
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS
membatasi pengalihan otomatis ke awal sesi audio, sedangkan
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES menonaktifkan
pengalihan bahasa setelah sejumlah pengalihan yang ditentukan. Opsi ini
sangat berguna jika Anda memperkirakan bahwa akan ada satu bahasa yang diucapkan
selama sesi yang akan dideteksi secara otomatis.
Peningkatan OpenType Variable Font API
Android 15 meningkatkan kegunaan font variabel OpenType. Anda dapat membuat
instance FontFamily dari font variabel tanpa menentukan sumbu bobot
dengan buildVariableFamily API. Perender teks mengganti nilai
dari sumbu wght agar cocok dengan teks yang menampilkan.
Menggunakan API ini sangat menyederhanakan kode untuk membuat Typeface:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
Sebelumnya, untuk membuat Typeface yang sama, Anda memerlukan lebih banyak kode:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Berikut ini contoh cara Typeface dibuat dengan API lama dan baru
merender:
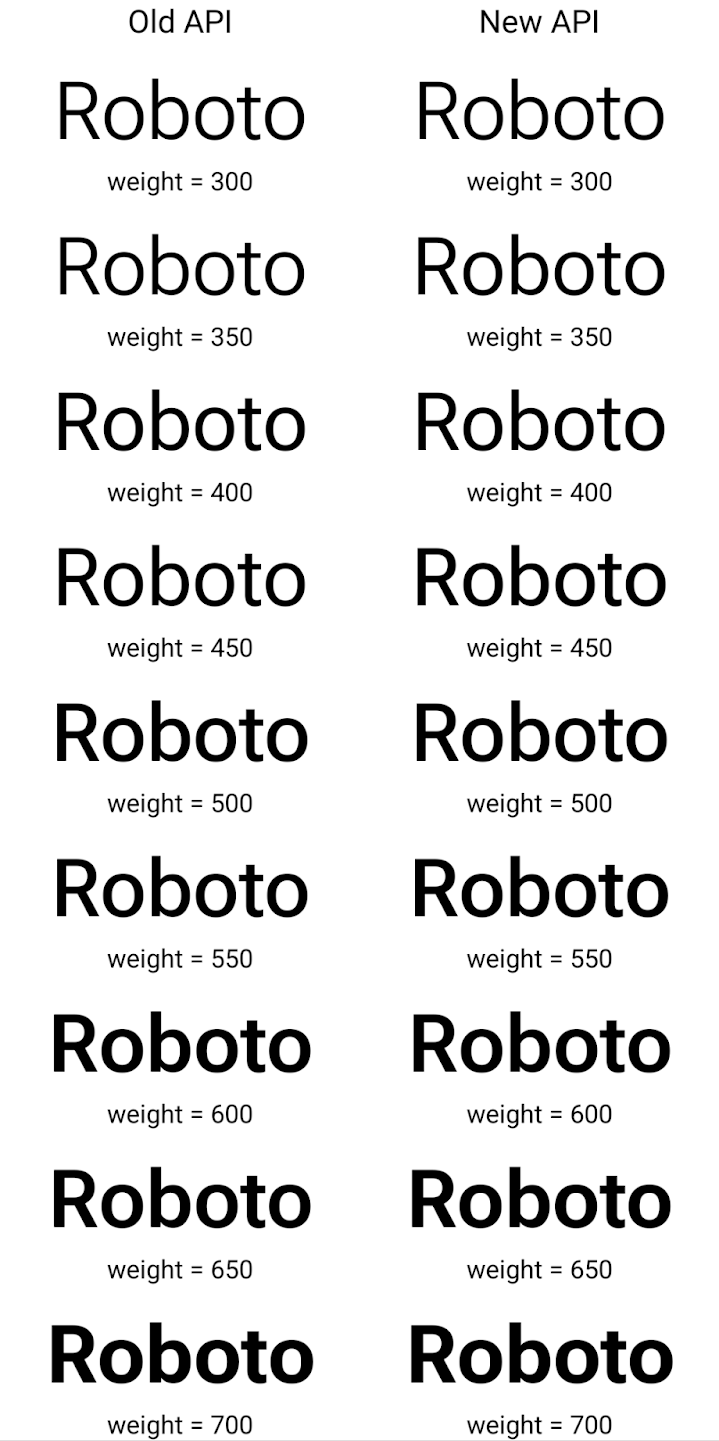
Dalam contoh ini, Typeface yang dibuat dengan API lama tidak memiliki
menciptakan bobot font yang akurat untuk 350, 450, 550 dan 650
Font, sehingga perender akan kembali ke bobot terdekat. Jadi ketika
dalam hal ini, 300 dirender, bukan 350, 400 dirender, bukan 450, dan
dan seterusnya. Sebaliknya, Typeface yang dibuat dengan API baru akan secara dinamis membuat
instance Font untuk bobot tertentu, jadi bobot yang akurat dirender untuk 350,
450, 550, dan 650.
Kontrol pemisah baris terperinci
Mulai Android 15, TextView dan pemisah
baris yang mendasarinya dapat mempertahankan bagian teks tertentu di baris yang sama untuk meningkatkan
keterbacaan. Anda dapat memanfaatkan penyesuaian akhir baris ini dengan menggunakan
tag <nobreak> dalam resource string atau
createNoBreakSpan. Demikian pula, Anda dapat mempertahankan kata dari
pemisahan kata dengan menggunakan tag <nohyphen> atau
createNoHyphenationSpan.
Misalnya, resource string berikut tidak menyertakan baris baru, dan dirender dengan teks "Pixel 8 Pro" yang terputus di tempat yang tidak diinginkan:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
Sebaliknya, resource string ini menyertakan tag <nobreak>, yang menggabungkan
frasa "Pixel 8 Pro" dan mencegah pemisahan baris:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
Perbedaan cara string ini dirender ditunjukkan dalam gambar berikut:

<nobreak>.
<nobreak>.Pengarsipan aplikasi
Android dan Google Play mengumumkan dukungan untuk pengarsipan aplikasi tahun lalu, yang memungkinkan pengguna mengosongkan ruang dengan menghapus sebagian aplikasi yang jarang digunakan dari perangkat yang dipublikasikan menggunakan Android App Bundle di Google Play. Android 15 menyertakan dukungan tingkat OS untuk pengarsipan dan pembatalan pengarsipan aplikasi, sehingga mempermudah semua app store untuk menerapkannya.
Aplikasi dengan izin REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES dapat memanggil
metode PackageInstaller requestArchive untuk meminta pengarsipan
paket aplikasi yang diinstal, yang akan menghapus APK dan file dalam cache, tetapi mempertahankan
data pengguna. Aplikasi yang diarsipkan akan ditampilkan sebagai aplikasi yang dapat ditampilkan melalui
LauncherApps API; pengguna akan melihat tampilan UI
untuk menyoroti bahwa mereka
aplikasi akan diarsipkan. Jika pengguna mengetuk aplikasi yang diarsipkan, penginstal yang bertanggung jawab
akan mendapatkan permintaan untuk membatalkan pengarsipan file, dan proses pemulihan dapat
dipantau oleh siaran ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED.
Mengaktifkan mode 16 KB di perangkat menggunakan opsi developer
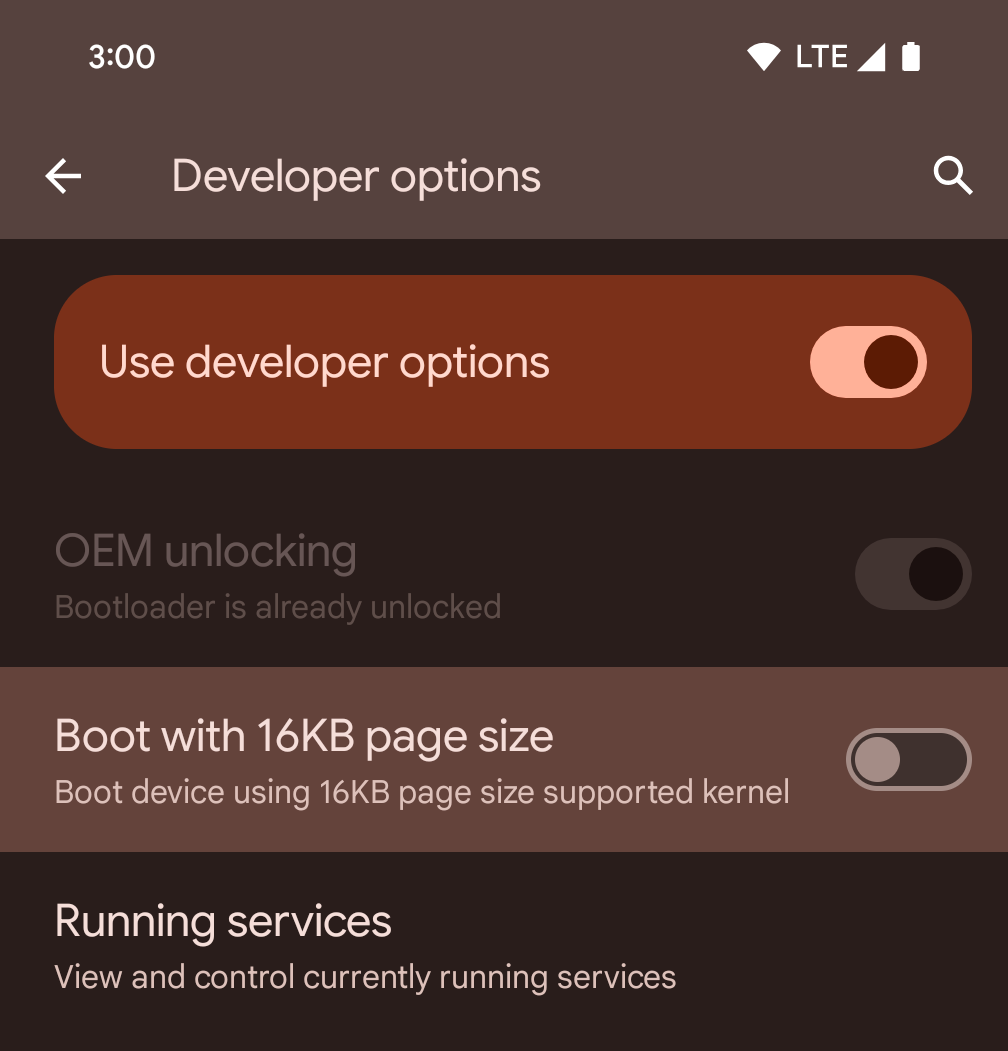
Aktifkan opsi developer Boot dengan ukuran halaman 16 KB untuk mem-boot perangkat dalam mode 16 KB.
Dalam versi QPR Android 15, Anda dapat menggunakan opsi developer yang tersedia di perangkat tertentu untuk mem-boot perangkat dalam mode 16 KB dan melakukan pengujian di perangkat. Sebelum menggunakan opsi developer, buka Setelan > Sistem > Update software dan terapkan update yang tersedia.
Opsi developer ini tersedia di perangkat berikut:
Pixel 8 dan 8 Pro (dengan Android 15 QPR1 atau yang lebih tinggi)
Pixel 8a (dengan Android 15 QPR1 atau yang lebih baru)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro, dan 9 Pro XL (dengan Android 15 QPR2 atau yang lebih baru)
Pixel 9a (dengan Android 16 atau yang lebih baru)
Grafik
Android 15 menghadirkan peningkatan grafis terbaru, termasuk ANGLE dan penambahan pada sistem grafis Canvas.
Memodernisasi akses GPU Android

Hardware Android telah berkembang cukup banyak sejak awal ketika OS inti akan berjalan di satu CPU dan GPU diakses menggunakan API berdasarkan pipeline fungsi tetap. API grafis Vulkan® telah tersedia di NDK sejak Android 7.0 (API level 24) dengan abstraksi tingkat rendah yang lebih mencerminkan hardware GPU modern, diskalakan dengan lebih baik untuk mendukung beberapa core CPU, dan menawarkan overhead driver CPU yang lebih rendah — sehingga meningkatkan performa aplikasi. Vulkan didukung oleh semua game engine modern.
Vulkan adalah antarmuka pilihan Android untuk GPU. Oleh karena itu, Android 15 menyertakan ANGLE sebagai lapisan opsional untuk menjalankan OpenGL® ES di atas Vulkan. Beralih ke ANGLE akan menstandarkan implementasi OpenGL Android untuk meningkatkan kompatibilitas, dan, dalam beberapa kasus, meningkatkan performa. Anda dapat menguji stabilitas dan performa aplikasi OpenGL ES dengan ANGLE dengan mengaktifkan opsi developer di Setelan -> Sistem -> Opsi Developer -> Eksperimental: Aktifkan ANGLE di Android 15.
Roadmap Android ANGLE di Vulkan
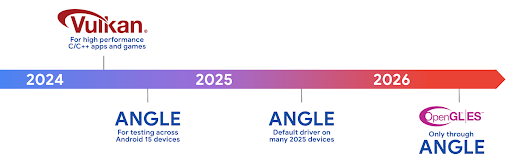
Sebagai bagian dari penyederhanaan stack GPU, ke depannya kami akan mengirimkan ANGLE sebagai driver sistem GL di lebih banyak perangkat baru, dengan ekspektasi di masa mendatang bahwa OpenGL/ES hanya akan tersedia melalui ANGLE. Meskipun demikian, kami berencana untuk melanjutkan dukungan untuk OpenGL ES di semua perangkat.
Rekomendasi langkah selanjutnya
Gunakan opsi developer untuk memilih driver ANGLE untuk OpenGL ES dan menguji aplikasi Anda. Untuk project baru, sebaiknya gunakan Vulkan untuk C/C++.
Peningkatan untuk Canvas
Android 15 melanjutkan modernisasi sistem grafis Canvas Android dengan kemampuan tambahan:
Matrix44menyediakan matriks 4x4 untuk mengubah koordinat yang harus digunakan saat Anda ingin memanipulasi kanvas dalam 3D.clipShadermemotong klip saat ini dengan shader yang ditentukan, sedangkanclipOutShadermenetapkan klip ke perbedaan klip saat ini dan shader, yang masing-masing memperlakukan shader sebagai mask alfa. Hal ini mendukung gambar bentuk kompleks secara efisien.
Performa dan baterai
Android terus berfokus untuk membantu Anda meningkatkan performa dan kualitas aplikasi Anda. Android 15 memperkenalkan API yang membantu membuat tugas di aplikasi Anda dieksekusi secara lebih efisien, mengoptimalkan performa aplikasi, dan mengumpulkan insight tentang aplikasi Anda.
Untuk mengetahui praktik terbaik yang hemat baterai, cara men-debug penggunaan jaringan dan daya, serta detail tentang cara kami meningkatkan efisiensi baterai untuk tugas latar belakang di Android 15 dan Android versi terbaru, lihat materi Meningkatkan efisiensi baterai untuk tugas latar belakang di Android dari Google I/O.
ApplicationStartInfo API
Pada versi Android sebelumnya, startup aplikasi agak misterius. Sulit
untuk menentukan dalam aplikasi Anda apakah aplikasi dimulai dari status cold, warm,
atau hot. Sulit juga untuk mengetahui berapa lama aplikasi Anda menghabiskan waktu selama
berbagai fase peluncuran: melakukan fork pada proses, memanggil onCreate, menggambar
frame pertama, dan lainnya. Saat class Application dibuat instance-nya, Anda tidak
memiliki cara untuk mengetahui apakah aplikasi dimulai dari siaran, penyedia konten, tugas, pencadangan, booting selesai, alarm, atau Activity.
ApplicationStartInfo API di Android 15 menyediakan
semua hal ini dan lainnya. Anda bahkan dapat memilih untuk menambahkan stempel waktu Anda sendiri ke dalam
alur untuk membantu mengumpulkan data pengaturan waktu di satu tempat. Selain mengumpulkan
metrik, Anda dapat menggunakan ApplicationStartInfo untuk membantu mengoptimalkan langsung
startup aplikasi; misalnya, Anda dapat menghilangkan pembuatan instance library terkait
UI yang mahal dalam class Application saat aplikasi dimulai karena
siaran.
Informasi mendetail tentang ukuran aplikasi
Sejak Android 8.0 (API level 26), Android telah menyertakan
StorageStats.getAppBytes API yang merangkum ukuran
aplikasi yang diinstal sebagai satu angka byte, yang merupakan jumlah ukuran APK, ukuran file yang diekstrak dari APK, dan file yang dihasilkan di
perangkat seperti kode yang dikompilasi ahead-of-time (AOT). Jumlah ini tidak terlalu
mendalam dalam hal cara aplikasi Anda menggunakan penyimpanan.
Android 15 menambahkan
StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API, yang memungkinkan
Anda mendapatkan insight tentang cara aplikasi menggunakan semua ruang tersebut, termasuk pemisahan file
APK, AOT, dan kode terkait percepatan, metadata dex, library, dan profil
yang dipandu.
Pembuatan profil yang dikelola aplikasi
Android 15 menyertakan class ProfilingManager,
yang memungkinkan Anda mengumpulkan informasi pembuatan profil dari dalam aplikasi seperti heap
dump, profil heap, sampling stack, dan lainnya. Fitur ini memberikan callback ke aplikasi Anda dengan tag yang disediakan untuk mengidentifikasi file output, yang dikirim ke direktori file aplikasi Anda. API melakukan pembatasan kapasitas untuk meminimalkan dampak
performa.
Untuk menyederhanakan pembuatan permintaan pembuatan profil di aplikasi Anda, sebaiknya gunakan
AndroidX API Profiling yang sesuai, yang tersedia
di Core 1.15.0-rc01 atau yang lebih tinggi.
Peningkatan database SQLite
Android 15 memperkenalkan SQLite API yang mengekspos fitur lanjutan dari mesin SQLite dasar yang menargetkan masalah performa tertentu manifes dalam aplikasi. API ini disertakan dengan update SQLite ke versi 3.44.3.
Developer harus membaca praktik terbaik untuk performa SQLite untuk mendapatkan hasil maksimal dari database SQLite, terutama saat menangani {i>database <i}atau saat menjalankan kueri yang sensitif terhadap latensi.
- Transaksi yang ditangguhkan (hanya baca): saat menerbitkan transaksi yang
hanya-baca (tidak sertakan pernyataan tulis), gunakan
beginTransactionReadOnly()danbeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)untuk melakukan transaksiDEFERREDhanya baca. Transaksi tersebut dapat berjalan secara bersamaan satu sama lain, dan jika {i>database<i} berada dalam mode WAL, mereka bisa berjalan serentak dengan transaksiIMMEDIATEatauEXCLUSIVE. - Jumlah dan ID baris: API ditambahkan untuk mengambil jumlah baris yang berubah
atau ID baris terakhir yang disisipkan tanpa mengeluarkan kueri tambahan.
getLastChangedRowCount()menampilkan jumlah baris yang dimasukkan, diperbarui, atau dihapus oleh pernyataan SQL terbaru dalam transaksi saat ini, sedangkangetTotalChangedRowCount()mengembalikan jumlah koneksi saat ini.getLastInsertRowId()menampilkanrowidbaris terakhir yang akan disisipkan pada koneksi saat ini. - Pernyataan mentah: mengeluarkan pernyataan SQlite mentah, mengabaikan wrapper kemudahan dan overhead pemrosesan tambahan yang mungkin terjadi.
Update Android Dynamic Performance Framework
Android 15 melanjutkan investasi kami dalam Android Dynamic Performance Framework (ADPF), sekumpulan API yang memungkinkan game dan aplikasi yang membutuhkan performa tinggi untuk berinteraksi lebih langsung dengan sistem daya dan termal perangkat Android. Di perangkat yang didukung, Android 15 menambahkan kemampuan ADPF:
- Mode hemat daya untuk sesi petunjuk guna menunjukkan bahwa thread terkait harus lebih memilih penghematan daya daripada performa, sangat cocok untuk beban kerja latar belakang yang berjalan lama.
- Durasi kerja GPU dan CPU dapat dilaporkan dalam sesi petunjuk, sehingga sistem dapat menyesuaikan frekuensi CPU dan GPU secara bersamaan untuk memenuhi permintaan beban kerja dengan sebaik mungkin.
- Batas headroom termal untuk menafsirkan kemungkinan status throttling termal berdasarkan prediksi headroom.
Untuk mempelajari lebih lanjut cara menggunakan ADPF di aplikasi dan game Anda, buka dokumentasi.
Privasi
Android 15 menyertakan berbagai fitur yang membantu developer aplikasi melindungi privasi pengguna.
Deteksi perekaman layar
Android 15 menambahkan dukungan untuk aplikasi guna mendeteksi bahwa aplikasi sedang direkam. Callback dipanggil setiap kali aplikasi melakukan transisi antara terlihat atau tidak terlihat dalam perekaman layar. Aplikasi dianggap terlihat jika aktivitas yang dimiliki oleh UID proses pendaftaran direkam. Dengan cara ini, jika aplikasi melakukan operasi yang sensitif, Anda dapat memberi tahu pengguna bahwa mereka sedang direkam.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
Kemampuan IntentFilter yang diperluas
Android 15 di-build dengan dukungan untuk resolusi Intent yang lebih presisi melalui
UriRelativeFilterGroup, yang berisi kumpulan
objek UriRelativeFilter yang membentuk kumpulan aturan pencocokan
Intent yang harus dipenuhi, termasuk parameter kueri URL, fragmen
URL, dan aturan pemblokiran atau pengecualian.
Aturan ini dapat ditentukan dalam file XML AndroidManifest dengan
tag <uri-relative-filter-group>, yang secara opsional dapat menyertakan
tag android:allow. Tag tersebut dapat berisi tag <data> yang menggunakan atribut tag data yang ada serta atribut android:query dan android:fragment.
Berikut adalah contoh sintaksis AndroidManifest:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
Ruang privasi
Ruang privasi memungkinkan pengguna membuat ruang terpisah di perangkat mereka tempat mereka dapat menyembunyikan aplikasi sensitif dari orang lain, dengan lapisan autentikasi tambahan. Ruang privasi menggunakan profil pengguna terpisah. Pengguna dapat memilih untuk menggunakan kunci perangkat atau faktor kunci terpisah untuk ruang pribadi.
Aplikasi di ruang pribadi muncul di penampung terpisah di peluncur, dan disembunyikan dari tampilan terbaru, notifikasi, setelan, dan dari aplikasi lain saat ruang pribadi dikunci. Konten yang dibuat dan didownload pengguna (seperti media atau file) dan akun dipisahkan antara ruang pribadi dan ruang utama. Sharesheet sistem dan pemilih foto dapat digunakan untuk memberi aplikasi akses ke konten di seluruh ruang saat ruang pribadi tidak dikunci.
Pengguna tidak dapat memindahkan aplikasi yang sudah ada dan datanya ke ruang pribadi. Sebagai gantinya, pengguna memilih opsi penginstalan di ruang pribadi untuk menginstal aplikasi menggunakan app store mana pun yang mereka inginkan. Aplikasi di ruang pribadi diinstal sebagai salinan terpisah dari aplikasi apa pun di ruang utama (salinan baru dari aplikasi yang sama).
Saat pengguna mengunci ruang pribadi, profil akan dihentikan. Saat profil dihentikan, aplikasi di ruang pribadi tidak lagi aktif dan tidak dapat melakukan aktivitas latar depan atau latar belakang, termasuk menampilkan notifikasi.
Sebaiknya uji aplikasi Anda dengan ruang pribadi untuk memastikan aplikasi berfungsi seperti yang diharapkan, terutama jika aplikasi Anda termasuk dalam salah satu kategori berikut:
- Aplikasi dengan logika untuk profil kerja yang mengasumsikan bahwa salinan aplikasi yang diinstal yang tidak ada di profil utama berada di profil kerja.
- Aplikasi medis
- Aplikasi peluncur
- Aplikasi app store
Membuat kueri pilihan pengguna terbaru untuk Akses Foto yang Dipilih
Aplikasi kini hanya dapat menyoroti foto dan video yang baru saja dipilih saat
akses sebagian ke izin media diberikan. Fitur ini dapat meningkatkan
pengalaman pengguna untuk aplikasi yang sering meminta akses ke foto dan
video. Untuk menggunakan fitur ini di aplikasi Anda, aktifkan argumen
QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY saat membuat kueri MediaStore
melalui ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Privacy Sandbox di Android
Android 15 menyertakan ekstensi Layanan Iklan Android terbaru, yang menggabungkan versi terbaru Privacy Sandbox di Android. Penambahan ini adalah bagian dari upaya kami untuk mengembangkan teknologi yang meningkatkan privasi pengguna dan memungkinkan pengalaman iklan yang dipersonalisasi secara efektif untuk aplikasi seluler. Halaman sandbox privasi kami memiliki informasi selengkapnya tentang Privacy Sandbox di program pratinjau developer dan beta Android untuk membantu Anda memulai.
Health Connect
Android 15 mengintegrasikan ekstensi terbaru di seputar Health Connect dari Android, platform terpusat dan aman untuk mengelola serta membagikan data kesehatan dan kebugaran yang dikumpulkan aplikasi. Update ini menambahkan dukungan untuk jenis data tambahan di seluruh kebugaran, gizi, suhu kulit, rencana latihan, dan lainnya.
Pelacakan suhu kulit memungkinkan pengguna menyimpan dan membagikan data suhu yang lebih akurat dari perangkat wearable atau perangkat pelacakan lainnya.
Rencana latihan adalah rencana olahraga terstruktur untuk membantu pengguna mencapai kebugaran mereka tujuan tersebut. Dukungan paket pelatihan mencakup berbagai penyelesaian dan performa tujuan:
- Sasaran penyelesaian seputar kalori yang terbakar, jarak, durasi, repetisi, dan langkah.
- Sasaran performa sekitar pengulangan sebanyak mungkin (AMRAP), irama, detak jantung, daya, tingkat pengerahan tenaga yang dirasakan, dan kecepatan.
Pelajari lebih lanjut update terbaru untuk Health Connect di Android dalam presentasi Membuat pengalaman yang dapat disesuaikan dengan Android Health dari Google I/O.
Berbagi layar aplikasi
Android 15 mendukung berbagi layar aplikasi sehingga pengguna dapat berbagi atau merekam
jendela aplikasi, bukan seluruh layar perangkat. Fitur ini, yang pertama kali diaktifkan di
Android 14 QPR2, mencakup
callback MediaProjection yang memungkinkan aplikasi Anda
menyesuaikan pengalaman berbagi layar aplikasi. Perhatikan bahwa untuk aplikasi yang menargetkan
Android 14 (level API 34) atau yang lebih tinggi,
izin pengguna diperlukan untuk setiap
sesi pengambilan MediaProjection.
Pengalaman pengguna dan UI sistem
Android 15 memberi developer dan pengguna aplikasi kontrol dan fleksibilitas yang lebih besar untuk mengonfigurasi perangkat agar sesuai dengan kebutuhan mereka.
Untuk mempelajari lebih lanjut cara menggunakan peningkatan terbaru di Android 15 untuk meningkatkan pengalaman pengguna aplikasi Anda, tonton sesi Meningkatkan pengalaman pengguna aplikasi Android Anda dari Google I/O.
Pratinjau widget yang lebih kaya dengan Generated Previews API
Sebelum Android 15, satu-satunya cara untuk menyediakan pratinjau pemilih widget adalah dengan menentukan resource gambar atau tata letak statis. Pratinjau ini sering kali berbeda secara signifikan dengan tampilan widget sebenarnya saat ditempatkan di layar utama. Selain itu, resource statis tidak dapat dibuat dengan Jetpack Glance, sehingga developer Glance harus mengambil screenshot widget atau membuat tata letak XML untuk memiliki pratinjau widget.
Android 15 menambahkan dukungan untuk pratinjau yang dihasilkan. Artinya, widget aplikasi
penyedia dapat membuat RemoteViews untuk digunakan sebagai pratinjau pemilih,
resource statis.
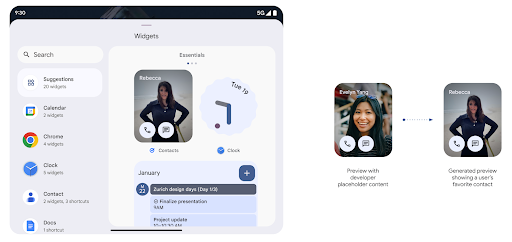
Push API
Aplikasi dapat menyediakan pratinjau yang dihasilkan melalui API push. Aplikasi dapat memberikan
melihat pratinjau di titik mana pun dalam siklus prosesnya, dan tidak menerima permintaan eksplisit
dari {i>host<i} untuk
menyediakan pratinjau. Pratinjau disimpan di AppWidgetService,
dan host dapat memintanya secara on-demand. Contoh berikut memuat widget XML
dan menyetelnya sebagai pratinjau:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
Alur yang diharapkan adalah:
- Penyedia widget akan memanggil
setWidgetPreviewkapan saja. Pratinjau yang disediakan dipertahankan diAppWidgetServicedengan info penyedia lainnya. setWidgetPreviewmemberi tahu host tentang pratinjau yang diperbarui melalui callbackAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged. Sebagai respons, widget {i>host<i} memuat ulang semua informasi penyedianya.- Saat menampilkan pratinjau widget, host akan memeriksa
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories, dan jika kategori yang dipilih tersedia, panggilAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewuntuk menampilkan pratinjau tersimpan untuk penyedia ini.
Waktu untuk menelepon setWidgetPreview
Karena tidak ada callback untuk menyediakan pratinjau, aplikasi dapat memilih untuk mengirim melihat pratinjau kapan saja saat dijalankan. Frekuensi update pratinjau bergantung pada kasus penggunaan widget.
Daftar berikut menjelaskan dua kategori utama kasus penggunaan pratinjau:
- Penyedia yang menampilkan data sebenarnya dalam pratinjau widget mereka, misalnya data yang dipersonalisasi atau informasi terbaru. Penyedia ini dapat menetapkan pratinjau setelah pengguna login atau telah melakukan konfigurasi awal di aplikasi mereka. Setelah itu, mereka dapat menyiapkan tugas berkala untuk memperbarui pratinjau pada ritme yang dipilih. Contoh widget jenis ini dapat berupa foto, kalender, cuaca, atau berita .
- Penyedia yang menampilkan informasi statis di pratinjau atau widget tindakan cepat yang tidak menampilkan data apa pun. Penyedia ini dapat menetapkan pratinjau satu kali, saat aplikasi pertama kali diluncurkan. Contoh jenis widget ini mencakup perjalanan cepat tindakan atau widget pintasan Chrome.
Beberapa penyedia mungkin menampilkan pratinjau statis pada pemilih mode hub, tetapi informasi di pemilih layar utama. Penyedia ini harus mengikuti panduan untuk kedua kasus penggunaan ini guna menetapkan pratinjau.
Picture-in-Picture
Android 15 memperkenalkan perubahan pada Picture-in-Picture (PiP) yang memastikan transisi yang lebih lancar saat memasuki mode PiP. Hal ini akan bermanfaat bagi aplikasi dengan elemen UI yang ditempatkan di atas UI utamanya, yang akan masuk ke PiP.
Developer menggunakan callback onPictureInPictureModeChanged untuk menentukan logika
yang mengubah visibilitas elemen UI overlay. Callback ini
dipicu saat animasi masuk atau keluar PiP selesai. Dimulai dalam
Android 15, class PictureInPictureUiState menyertakan status lain.
Dengan status UI ini, aplikasi yang menargetkan Android 15 (API level 35) akan mengamati
Callback Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged dipanggil dengan
isTransitioningToPip() segera setelah animasi PiP dimulai. Ada
banyak elemen UI yang tidak relevan untuk aplikasi saat dalam mode PiP, untuk
contoh tampilan atau tata letak yang menyertakan informasi seperti saran, teks mendatang
video, rating, dan judul. Saat aplikasi masuk ke mode PiP, gunakan
Callback onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged untuk menyembunyikan elemen UI ini. Jika
aplikasi masuk ke mode layar penuh dari jendela PiP, gunakan
Callback onPictureInPictureModeChanged untuk memperlihatkan elemen ini, seperti yang ditunjukkan pada
contoh berikut:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
Tombol visibilitas cepat dari elemen UI yang tidak relevan (untuk jendela PiP) membantu memastikan animasi masuk PiP yang lebih halus dan bebas kedipan.
Aturan Jangan Ganggu yang ditingkatkan
AutomaticZenRule memungkinkan aplikasi menyesuaikan aturan Pengelolaan
Perhatian (Jangan Ganggu) dan memutuskan kapan harus mengaktifkan atau menonaktifkannya. Android 15 menyempurnakan aturan ini secara signifikan dengan tujuan meningkatkan
{i>user experience<i}. Peningkatan berikut disertakan:
- Menambahkan jenis ke
AutomaticZenRule, sehingga sistem dapat menerapkan perlakuan terhadap beberapa aturan. - Menambahkan ikon ke
AutomaticZenRule, membantu membuat mode lebih menarik dikenali. - Menambahkan string
triggerDescriptionkeAutomaticZenRuleyang mendeskripsikan kondisi tempat aturan harus diaktifkan bagi pengguna. - Ditambahkan
ZenDeviceEffectskeAutomaticZenRule, yang memungkinkan aturan memicu hal-hal seperti hitam putih layar, mode malam, atau meredupkan wallpaper.
Menetapkan VibrationEffect untuk saluran notifikasi
Android 15 mendukung setelan getaran yang kaya untuk notifikasi masuk dengan
saluran menggunakan NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect, sehingga
pengguna dapat membedakan berbagai jenis notifikasi tanpa
hanya dengan melihat
perangkat mereka.
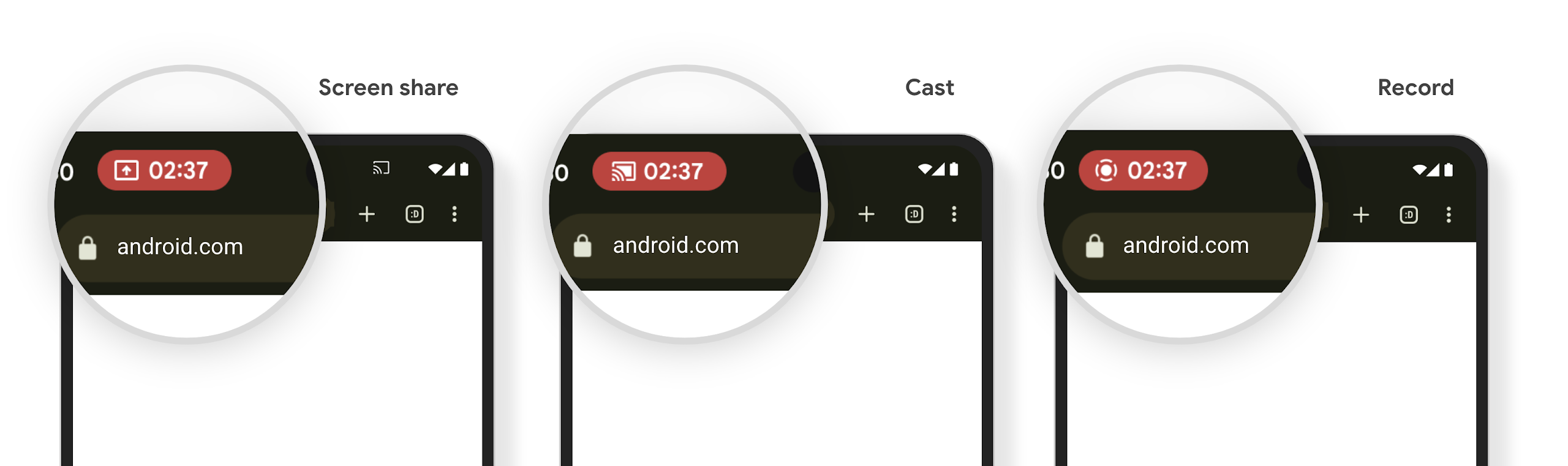
Chip status proyeksi media dan penghentian otomatis
Proyeksi media dapat mengekspos informasi pengguna pribadi. Chip status bar baru yang jelas membuat pengguna mengetahui proyeksi layar yang sedang berlangsung. Pengguna dapat mengetuk chip untuk menghentikan transmisi layar, berbagi, atau perekaman. Selain itu, untuk pengalaman pengguna yang lebih intuitif, setiap proyeksi layar yang sedang berlangsung kini otomatis berhenti saat layar perangkat dikunci.
Layar besar dan faktor bentuk
Android 15 memberi aplikasi Anda dukungan untuk mendapatkan hasil maksimal dari faktor bentuk Android, termasuk layar besar, perangkat flippable, dan perangkat foldable.
Multitasking layar besar yang ditingkatkan
Android 15 memberi pengguna cara yang lebih baik untuk melakukan multitasking di perangkat layar besar. Sebagai misalnya, pengguna dapat menyimpan kombinasi aplikasi layar terpisah favorit mereka dengan cepat mengakses dan menyematkan taskbar di layar untuk beralih antar-aplikasi dengan cepat. Artinya bahwa memastikan aplikasi Anda bersifat adaptif kini menjadi semakin penting.
Google I/O memiliki sesi tentang Membangun Android adaptif aplikasi dan Membangun UI dengan Material 3 library adaptif yang dapat membantu, dan dokumentasi kami memiliki lebih banyak hal untuk membantu Anda Mendesain untuk layar.
Dukungan layar luar
Aplikasi Anda dapat mendeklarasikan properti yang digunakan Android 15 untuk
memungkinkan Application atau Activity ditampilkan di layar penutup
kecil perangkat yang dapat dibalik yang didukung. Layar ini terlalu kecil untuk
dianggap sebagai target yang kompatibel untuk menjalankan aplikasi Android, tetapi aplikasi Anda dapat
memilih untuk mendukungnya, sehingga aplikasi Anda tersedia di lebih banyak tempat.
Konektivitas
Android 15 mengupdate platform untuk memberi aplikasi Anda akses ke kemajuan terbaru dalam teknologi nirkabel dan komunikasi.
Dukungan satelit
Android 15 terus memperluas dukungan platform untuk konektivitas satelit dan menyertakan beberapa elemen UI untuk memastikan pengalaman pengguna yang konsisten di seluruh lanskap konektivitas satelit.
Aplikasi dapat menggunakan ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() untuk
mendeteksi saat perangkat terhubung ke satelit, sehingga memberi mereka
mengapa layanan jaringan
penuh mungkin tidak tersedia. Selain itu, Android 15
menyediakan dukungan untuk aplikasi SMS dan MMS serta aplikasi RCS bawaan untuk digunakan
konektivitas satelit untuk mengirim
dan menerima pesan.
Pengalaman NFC yang lebih lancar
Android 15 berupaya membuat pengalaman pembayaran nirsentuh menjadi lebih lancar dan
andal sekaligus terus mendukung ekosistem aplikasi NFC Android yang andal. Di
perangkat yang didukung, aplikasi dapat meminta NfcAdapter untuk memasuki
mode pengamatan, tempat perangkat memproses tetapi tidak merespons pembaca
NFC, yang mengirim PollingFrame
objek layanan NFC aplikasi untuk diproses. Objek PollingFrame dapat digunakan untuk melakukan autentikasi
sebelum komunikasi pertama ke pembaca NFC, sehingga memungkinkan transaksi
sekali ketuk dalam banyak kasus.
Selain itu, aplikasi dapat mendaftarkan filter di perangkat yang didukung sehingga aplikasi dapat diberi tahu tentang aktivitas loop polling, yang memungkinkan operasi yang lancar dengan beberapa aplikasi yang mendukung NFC.
Peran Wallet
Android 15 memperkenalkan peran Wallet yang memungkinkan integrasi yang lebih erat dengan aplikasi dompet pilihan pengguna. Peran ini menggantikan setelan pembayaran nirsentuh default NFC. Pengguna dapat mengelola pemegang peran Wallet dengan membuka Setelan > Aplikasi > Aplikasi Default.
Peran Wallet digunakan saat merutekan tempelan NFC untuk AID yang terdaftar dalam kategori pembayaran. Ketukan selalu mengarah ke pemegang peran Wallet, kecuali jika aplikasi lain yang terdaftar untuk AID yang sama sedang berjalan di latar depan.
Peran ini juga digunakan untuk menentukan tempat kartu Akses Cepat Wallet harus ditempatkan saat diaktifkan. Jika peran disetel ke "Tidak ada", kartu Akses Cepat tidak tersedia dan ketukan NFC kategori pembayaran hanya dikirim ke aplikasi latar depan.
Keamanan
Android 15 membantu Anda meningkatkan keamanan aplikasi, melindungi data aplikasi, dan memberi pengguna lebih banyak transparansi dan kontrol atas data mereka. Tonton video Menjaga keamanan pengguna di Android dari Google I/O untuk mengetahui lebih lanjut tindakan yang kami lakukan untuk meningkatkan pengamanan pengguna dan melindungi aplikasi Anda dari ancaman baru.
Mengintegrasikan Credential Manager dengan isi otomatis
Mulai Android 15, developer dapat menautkan tampilan tertentu seperti kolom nama pengguna atau sandi dengan permintaan Pengelola Kredensial, sehingga lebih mudah untuk memberikan pengalaman pengguna yang disesuaikan selama proses login. Saat pengguna berfokus pada salah satu tampilan ini, permintaan yang sesuai akan dikirim ke Pengelola Kredensial. Kredensial yang dihasilkan digabungkan di seluruh penyedia dan ditampilkan di UI penggantian isi otomatis, seperti saran inline atau saran dropdown. Library androidx.credentials Jetpack adalah endpoint pilihan yang dapat digunakan developer dan akan segera tersedia untuk lebih meningkatkan fitur ini di Android 15 dan yang lebih baru.
Mengintegrasikan pendaftaran dan login sekali ketuk dengan perintah biometrik
Pengelola Kredensial mengintegrasikan perintah biometrik ke dalam pembuatan kredensial dan proses login, sehingga penyedia tidak perlu lagi mengelola prompt biometrik. Akibatnya, penyedia kredensial hanya perlu fokus pada hasil alur create dan get, yang ditambah dengan hasil alur biometrik. Proses yang disederhanakan ini menciptakan proses pembuatan dan pengambilan kredensial yang lebih efisien dan sederhana.
Pengelolaan kunci untuk enkripsi end-to-end
Kami memperkenalkan E2eeContactKeysManager di Android 15, yang
memfasilitasi enkripsi end-to-end (E2EE) di aplikasi Android Anda dengan menyediakan
API tingkat OS untuk penyimpanan kunci publik kriptografis.
E2eeContactKeysManager dirancang untuk berintegrasi dengan aplikasi
kontak platform guna memberi pengguna cara terpusat untuk mengelola dan memverifikasi
kunci publik kontak mereka.
Pemeriksaan izin pada URI konten
Android 15 memperkenalkan serangkaian API yang melakukan pemeriksaan izin pada URI konten:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: Tindakan ini melakukan pemeriksaan izin penuh pada URI konten.- Atribut manifes
ActivityrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: Ini menerapkan izin yang ditentukan pada URI konten yang diberikan saat peluncuran aktivitas. - Class
ComponentCalleruntuk pemanggilActivity: Class ini mewakili aplikasi yang meluncurkan aktivitas.
Aksesibilitas
Android 15 menambahkan fitur yang meningkatkan aksesibilitas bagi pengguna.
Braille yang Lebih Baik
Di Android 15, kami telah memungkinkan TalkBack untuk mendukung layar Braille yang menggunakan standar HID melalui USB dan Bluetooth aman.
Standar ini, seperti yang digunakan oleh mouse dan keyboard, akan membantu Android mendukung berbagai penampil Braille yang lebih luas dari waktu ke waktu.
Internasionalisasi
Android 15 menambahkan fitur dan kemampuan yang melengkapi pengalaman pengguna saat perangkat digunakan dalam bahasa yang berbeda.
Font variabel CJK
Mulai Android 15, file font untuk bahasa China, Jepang, dan Korea (CJK), NotoSansCJK, kini menjadi font variabel. Font variabel membuka kemungkinan untuk tipografi kreatif dalam bahasa CJK. Desainer dapat menjelajahi berbagai gaya yang lebih luas dan membuat tata letak yang menarik secara visual yang sebelumnya sulit atau tidak mungkin dicapai.

Justifikasi antar-karakter
Mulai Android 15, teks dapat dibenarkan menggunakan spasi huruf dengan
menggunakan JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. Justifikasi antarkata
pertama kali diperkenalkan di Android 8.0 (API level 26), dan justifikasi antarkarakter
memberikan kemampuan serupa untuk bahasa yang menggunakan
karakter spasi kosong untuk segmentasi, seperti China, Jepang, dan lainnya.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.Konfigurasi jeda baris otomatis
Android mulai mendukung jeda baris berbasis frasa untuk bahasa Jepang dan Korea di
Android 13 (level API 33). Namun, sementara jeda baris berbasis frasa meningkatkan
keterbacaan baris pendek teks, mereka tidak bekerja dengan baik untuk baris teks yang panjang.
Di Android 15, aplikasi dapat menerapkan jeda baris berbasis frasa hanya untuk baris pendek
teks, menggunakan LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
sebelumnya. Opsi ini memilih opsi gaya kata terbaik untuk teks.
Untuk baris teks pendek, jeda baris berbasis frasa digunakan, yang berfungsi sama
seperti LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, seperti yang ditunjukkan dalam
gambar berikut:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
menerapkan pemisah baris berbasis frasa untuk meningkatkan keterbacaan teks.
Hal ini sama dengan menerapkan
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.Untuk baris teks yang lebih panjang, LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO menggunakan
gaya kata jeda baris, berfungsi sama dengan
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, seperti yang ditunjukkan di
gambar berikut:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
tidak menerapkan gaya kata pemisah baris untuk meningkatkan keterbacaan teks.
Hal ini sama dengan menerapkan
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.Font Hentaigana Jepang Tambahan
Di Android 15, file font untuk huruf Hiragana Jepang lama (yang dikenal sebagai Hentaigana) secara default dipaketkan. Bentuk unik karakter Hentaigana dapat menambahkan gaya unik pada karya seni atau desain sekaligus membantu mempertahankan transmisi dan pemahaman yang akurat tentang dokumen Jepang kuno.

Kegel VideoLAN Hak Cipta (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. Logo ini atau versi yang dimodifikasi dapat digunakan atau dimodifikasi oleh siapa saja untuk merujuk ke project VideoLAN atau produk apa pun yang dikembangkan oleh tim VideoLAN, tetapi tidak menunjukkan dukungan oleh project.
Vulkan dan logo Vulkan adalah merek dagang terdaftar dari Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL adalah merek dagang terdaftar dan logo OpenGL ES adalah merek dagang Hewlett Packard Enterprise yang digunakan dengan izin dari Khronos.
