Dialog bileşeni, ana uygulama içeriğinin üstündeki bir katmanda pop-up mesajlar gösterir veya kullanıcıdan giriş ister. Kullanıcıların dikkatini çekmek için kesintiye uğratan bir kullanıcı arayüzü deneyimi oluşturur.
İletişim kutularının kullanım alanları arasında şunlar yer alır:
- Kullanıcının işlemini onaylama (ör. dosya silme)
- Kullanıcıdan giriş isteğinde bulunma (ör. yapılacaklar listesi uygulamasında)
- Profil kurulumunda ülke seçme gibi kullanıcı seçimi için seçeneklerin listesini sunma
Bu konuda aşağıdaki uygulamalar sağlanmaktadır:
Sürüm uyumluluğu
Bu uygulama için projenizin minSDK değerinin API düzeyi 21 veya üstü olarak ayarlanması gerekir.
Bağımlılıklar
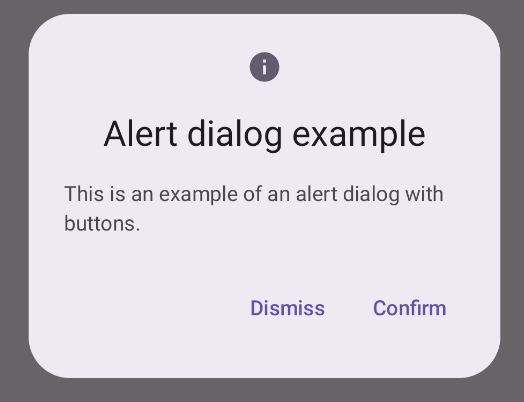
Uyarı iletişim kutusu oluşturma
AlertDialog bileşeni, Material Design temalı bir iletişim kutusu oluşturmak için kullanışlı bir API sağlar. Aşağıdaki örnekte, uyarı iletişim kutusunda biri iletişim kutusunu kapatan, diğeri ise isteği onaylayan iki düğme uygulanmaktadır:
Bu uygulama, alt composable'a şu şekilde bağımsız değişkenler aktaran bir üst composable içerir:
Sonuçlar
Önemli noktalar
AlertDialog, iletişim kutusunun belirli öğelerini işlemek için özel parametrelere sahiptir. Bunlardan bazıları şunlardır:
title: İletişim kutusunun üst kısmında görünen metin.text: İletişim kutusunun ortasında görünen metin.icon: İletişim kutusunun üst kısmında görünen grafik.onDismissRequest: Kullanıcı iletişim kutusunu kapattığında (ör. iletişim kutusunun dışına dokunarak) çağrılan işlev.dismissButton: Kapatma düğmesi işlevi gören bir kompozisyon.confirmButton: Onay düğmesi olarak kullanılan bir bileşen.Kullanıcı düğmelerden birini tıkladığında iletişim kutusu kapanır. Kullanıcı onay'ı tıkladığında, onayı da işleyen bir işlev çağrılır. Bu örnekte bu işlevler
onDismissRequest()veonConfirmRequest()'tir.İletişim kutunuz için daha karmaşık bir düğme grubu gerekiyorsa
Dialogbileşenini kullanarak ve daha serbest bir şekilde doldurarak fayda sağlayabilirsiniz.
İletişim kutusu oluşturma
Dialog, içerik için herhangi bir stil veya önceden tanımlanmış yuva sağlamayan temel bir bileşendir. Card gibi bir kapsayıcıyla doldurmanız gereken basit bir kapsayıcıdır. Aşağıda, bir iletişim kutusunun temel parametrelerinden bazıları verilmiştir:
onDismissRequest: Kullanıcı iletişim kutusunu kapattığında çağrılan lambda.properties: Özelleştirme için ek kapsam sağlayan birDialogPropertiesörneği.
Temel bir iletişim kutusu oluşturma
Aşağıdaki örnek, Dialog bileşeninin temel bir uygulamasıdır. İkincil kapsayıcı olarak Card kullanıldığını unutmayın. Card olmadan Text bileşeni, ana uygulama içeriğinin üstünde tek başına görünür.
Sonuç
İletişim kutusu açıkken altındaki ana uygulama içeriğinin karartılmış ve devre dışı göründüğünü unutmayın:

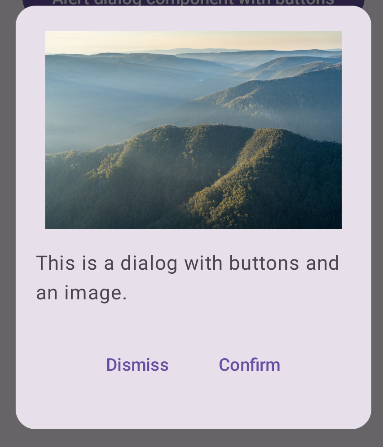
Gelişmiş iletişim kutusu oluşturma
Aşağıda, Dialog bileşeninin daha gelişmiş bir uygulaması verilmiştir. Bu durumda bileşen, önceki AlertDialog örneğine benzer bir arayüzü manuel olarak uygular.
Sonuç
Bu kılavuzu içeren koleksiyonlar
Bu kılavuz, daha geniş Android geliştirme hedeflerini kapsayan, özel olarak seçilmiş Hızlı Kılavuz koleksiyonlarından biridir:
Görünen metin

Kullanıcıdan giriş iste




