Comme les versions précédentes, Android 16 apporte des modifications de comportement pouvant affecter votre application. Les modifications de comportement suivantes s'appliquent exclusivement aux applications qui ciblent Android 16 ou version ultérieure. Si votre application cible Android 16 ou version ultérieure, vous devez la modifier pour qu'elle prenne en charge ces comportements, le cas échéant.
Veillez également à consulter la liste des modifications de comportement qui affectent toutes les applications exécutées sur Android 16, quel que soit le targetSdkVersion de votre application.
Expérience utilisateur et UI du système
Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) inclut les modifications suivantes, qui visent à créer une expérience utilisateur plus cohérente et intuitive.
Suppression de l'option de désactivation du mode bord à bord
Android 15 a imposé le mode bord à bord pour les applications ciblant Android 15 (niveau d'API 35), mais votre application pouvait le désactiver en définissant R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement sur true. Pour les applications ciblant Android 16 (niveau d'API 36), R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement est obsolète et désactivé. Votre application ne peut pas désactiver le mode bord à bord.
- Si votre application cible Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) et s'exécute sur un appareil Android 15,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementcontinue de fonctionner. - Si votre application cible Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) et s'exécute sur un appareil Android 16,
R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcementest désactivé.
Pour effectuer des tests dans Android 16, assurez-vous que votre application est compatible avec le mode bord à bord et supprimez toute utilisation de R.attr#windowOptOutEdgeToEdgeEnforcement afin que votre application soit également compatible avec le mode bord à bord sur un appareil Android 15. Pour prendre en charge le mode bord à bord, consultez les conseils concernant Compose et Views.
Migration ou désactivation requises pour la prévisualisation du geste Retour
Pour les applications ciblant Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) ou version ultérieure et s'exécutant sur un appareil Android 16 ou version ultérieure, les animations système de prévisualisation du retour (retour à l'écran d'accueil, multi-activités et multitâches) sont activées par défaut.
De plus, onBackPressed n'est pas appelé et KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK n'est plus distribué.
Si votre application intercepte l'événement Retour et que vous n'avez pas encore migré vers la prévisualisation du geste Retour, mettez à jour votre application pour qu'elle utilise les API de navigation Retour compatibles ou désactivez temporairement la prévisualisation en définissant l'attribut android:enableOnBackInvokedCallback sur false dans la balise <application> ou <activity> du fichier AndroidManifest.xml de votre application.
API de police élégante obsolètes et désactivées
Les applications ciblant Android 15 (niveau d'API 35) ont l'attribut elegantTextHeight
TextView défini sur true par défaut, ce qui remplace la police compacte par une police beaucoup plus lisible. Vous pouvez remplacer ce comportement en définissant l'attribut elegantTextHeight sur false.
Android 16 abandonne l'attribut elegantTextHeight, qui sera ignoré une fois que votre application ciblera Android 16. Les "UI fonts" contrôlées par ces API sont abandonnées. Vous devez donc adapter toutes les mises en page pour assurer un rendu de texte cohérent et pérenne en arabe, en lao, en birman, en tamoul, en gujarati, en kannada, en malayalam, en odia, en télougou ou en thaï.
elegantTextHeight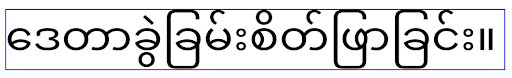
elegantTextHeight sur false.

elegantTextHeight pour les applications ciblant Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) ou pour les applications ciblant Android 15 (niveau d'API 35) qui n'ont pas remplacé la valeur par défaut en définissant l'attribut elegantTextHeight sur false.Fonctionnalité de base
Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) inclut les modifications suivantes qui modifient ou étendent diverses fonctionnalités de base du système Android.
Optimisation de la planification du travail à taux fixe
Avant de cibler Android 16, lorsque scheduleAtFixedRate manquait une exécution de tâche en raison de l'absence d'un cycle de vie de processus valide, toutes les exécutions manquées s'exécutaient immédiatement lorsque l'application revenait à un cycle de vie valide.
Lorsque vous ciblez Android 16, une seule exécution manquée de scheduleAtFixedRate est immédiatement exécutée lorsque l'application revient à un cycle de vie valide. Ce changement de comportement devrait améliorer les performances de l'application. Testez ce comportement dans votre application pour vérifier si elle est concernée.
Vous pouvez également effectuer des tests à l'aide du framework de compatibilité des applications et en activant l'indicateur de compatibilité STPE_SKIP_MULTIPLE_MISSED_PERIODIC_TASKS.
Facteurs de forme des appareils
Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) inclut les modifications suivantes pour les applications lorsqu'elles sont affichées sur des appareils à grand écran.
Mises en page adaptatives
Les applications Android fonctionnant désormais sur une multitude d'appareils (téléphones, tablettes, appareils pliables, ordinateurs de bureau, voitures et téléviseurs, par exemple) et de modes de fenêtrage sur les grands écrans (comme l'écran partagé et le fenêtrage de bureau), les développeurs doivent créer des applications Android qui s'adaptent à toutes les tailles d'écran et de fenêtre, quelle que soit l'orientation de l'appareil. Les approches qui limitent l'orientation et le redimensionnement sont trop contraignantes dans le monde multi-appareils d'aujourd'hui.
Ignorer les restrictions d'orientation, de redimensionnement et de format
Pour les applications ciblant Android 16 (niveau d'API 36), les restrictions d'orientation, de redimensionnement et de format ne s'appliquent plus sur les écrans dont la plus petite largeur est supérieure ou égale à 600 dp. Les applications remplissent toute la fenêtre d'affichage, quels que soient le format ou l'orientation préférés de l'utilisateur, et le format pillarbox n'est pas utilisé.
Cette modification introduit un nouveau comportement standard de la plate-forme. Android évolue vers un modèle où les applications doivent s'adapter à des orientations, tailles d'écran et formats différents. Les restrictions telles que l'orientation fixe ou la taille non modifiable limitent l'adaptabilité des applications. Rendez votre application adaptative pour offrir la meilleure expérience utilisateur possible.
Vous pouvez également tester ce comportement à l'aide du framework de compatibilité des applications et en activant l'indicateur de compatibilité UNIVERSAL_RESIZABLE_BY_DEFAULT.
Modifications destructives courantes
Ignorer les restrictions d'orientation, de redimensionnement et de format peut avoir un impact sur l'interface utilisateur de votre application sur certains appareils, en particulier sur les éléments conçus pour de petites mises en page verrouillées en mode portrait. Par exemple, cela peut entraîner des problèmes tels que des mises en page étirées, ou des animations et des composants apparaissant hors écran. Toute hypothèse concernant le format ou l'orientation peut entraîner des problèmes visuels dans votre application. Découvrez comment les éviter et améliorer le comportement adaptatif de votre application.
Autoriser la rotation de l'appareil entraîne une recréation plus fréquente de l'activité, ce qui peut entraîner une perte de l'état de l'utilisateur s'il n'est pas correctement conservé. Découvrez comment enregistrer correctement l'état de l'UI dans Enregistrer les états de l'interface utilisateur.
Détails de l'implémentation
Les attributs de fichier manifeste et les API d'exécution suivants sont ignorés sur les appareils à grand écran en mode plein écran et multifenêtre :
screenOrientationresizableActivityminAspectRatiomaxAspectRatiosetRequestedOrientation()getRequestedOrientation()
Les valeurs suivantes pour screenOrientation, setRequestedOrientation() et getRequestedOrientation() sont ignorées :
portraitreversePortraitsensorPortraituserPortraitlandscapereverseLandscapesensorLandscapeuserLandscape
Concernant la possibilité de redimensionner l'écran, android:resizeableActivity="false", android:minAspectRatio et android:maxAspectRatio n'ont aucun effet.
Pour les applications ciblant Android 16 (niveau d'API 36), les contraintes d'orientation, de redimensionnement et de format sont ignorées par défaut sur les grands écrans. Cependant, toute application qui n'est pas entièrement prête peut temporairement annuler ce comportement en le désactivant (ce qui rétablit le comportement précédent, à savoir le placement en mode de compatibilité).
Exceptions
Les restrictions d'orientation, de redimensionnement et de format d'Android 16 ne s'appliquent pas dans les situations suivantes :
- Jeux (basés sur l'indicateur
android:appCategory) - Si les utilisateurs activent explicitement le comportement par défaut de l'application dans les paramètres de format de l'appareil
- Écrans dont la taille est inférieure à
sw600dp
Désactiver temporairement
Pour désactiver une activité spécifique, déclarez la propriété de fichier manifeste PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY :
<activity ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
...
</activity>
Si trop de parties de votre application ne sont pas prêtes pour Android 16, vous pouvez désactiver complètement la fonctionnalité en appliquant la même propriété au niveau de l'application :
<application ...>
<property android:name="android.window.PROPERTY_COMPAT_ALLOW_RESTRICTED_RESIZABILITY" android:value="true" />
</application>
Santé et remise en forme
Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) inclut les modifications suivantes concernant les données de santé et de remise en forme.
Autorisations de santé et de remise en forme
Pour les applications ciblant Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) ou version ultérieure, les autorisations BODY_SENSORS utilisent des autorisations plus précises sous android.permissions.health, que Santé Connect utilise également. Depuis Android 16, toute API qui nécessitait auparavant BODY_SENSORS ou BODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND requiert à la place l'autorisation android.permissions.health correspondante. Cela concerne les types de données, les API et les types de services de premier plan suivants :
HEART_RATE_BPMdepuis les Services Santé sur Wear OSSensor.TYPE_HEART_RATEdepuis Android Sensor ManagerheartRateAccuracyetheartRateBpmdeProtoLayoutsur Wear OSFOREGROUND_SERVICE_TYPE_HEALTHoù l'autorisationandroid.permission.healthcorrespondante est requise à la place deBODY_SENSORS
Si votre application utilise ces API, elle doit demander les autorisations précises correspondantes :
- Pour la surveillance en cours d'utilisation de la fréquence cardiaque, de la SpO2 ou de la température cutanée :
demandez l'autorisation précise sous
android.permissions.health, par exempleREAD_HEART_RATEau lieu deBODY_SENSORS. - Pour l'accès aux capteurs en arrière-plan, demandez
READ_HEALTH_DATA_IN_BACKGROUNDau lieu deBODY_SENSORS_BACKGROUND.
Ces autorisations sont les mêmes que celles qui protègent l'accès à la lecture des données de Santé Connect, le dépôt de données Android pour les données de santé, de forme physique et de bien-être.
Dans les applications mobiles
Les applications mobiles qui migrent vers l'utilisation de READ_HEART_RATE et d'autres autorisations précises doivent également déclarer une activité pour afficher les règles de confidentialité de l'application. Cette exigence est la même que pour Santé Connect.
Connectivité
Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) inclut les modifications suivantes dans la pile Bluetooth pour améliorer la connectivité avec les appareils périphériques.
Nouvelles intentions pour gérer la perte de liaison et les modifications du chiffrement
Dans le cadre de la gestion améliorée de la perte de liaison, Android 16 introduit également deux nouveaux intents pour mieux informer les applications de la perte de liaison et des modifications de chiffrement.
Les applications ciblant Android 16 peuvent désormais:
- Recevoir un intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGlorsqu'une perte de liaison à distance est détectée, ce qui leur permet de fournir des commentaires plus informatifs sur l'utilisateur et de prendre les mesures appropriées. - Recevoir un intent
ACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEchaque fois que l'état du chiffrement du lien change. Cela inclut la modification de l'état du chiffrement, de l'algorithme de chiffrement et de la taille de la clé de chiffrement. Les applications doivent considérer que l'association est restaurée si le lien est correctement chiffré lors de la réception de l'intentACTION_ENCRYPTION_CHANGEultérieurement.
S'adapter aux implémentations OEM variées
Bien qu'Android 16 introduise ces nouveaux intents, leur implémentation et leur diffusion peuvent varier selon les fabricants d'appareils (OEM). Pour que votre application offre une expérience cohérente et fiable sur tous les appareils, les développeurs doivent concevoir leur gestion des pertes de liaison pour s'adapter de manière appropriée à ces variations potentielles.
Nous vous recommandons les comportements d'application suivants:
Si l'intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGest diffusé:Le lien ACL (Asynchronous Connection-Less) sera déconnecté par le système, mais les informations de liaison de l'appareil seront conservées (comme décrit ici).
Votre application doit utiliser cet intent comme signal principal pour la détection de la perte de liaison et guider l'utilisateur pour qu'il confirme que l'appareil distant est à portée avant de lancer l'oubli de l'appareil ou le réassociation.
Si un appareil se déconnecte après la réception de
ACTION_KEY_MISSING, votre application doit être prudente lors de la reconnexion, car l'appareil peut ne plus être associé au système.Si l'intent
ACTION_KEY_MISSINGn'est PAS diffusé:Le lien ACL restera connecté, et les informations d'association de l'appareil seront supprimées par le système, comme dans Android 15.
Dans ce scénario, votre application doit poursuivre ses mécanismes de gestion des pertes de liaison existants, comme dans les versions précédentes d'Android, pour détecter et gérer les événements de perte de liaison.
Nouvelle façon de supprimer l'association Bluetooth
Toutes les applications ciblant Android 16 peuvent désormais dissocier des appareils Bluetooth à l'aide d'une API publique dans CompanionDeviceManager. Si un appareil associé est géré en tant qu'association CDM, l'application peut déclencher la suppression de l'association Bluetooth à l'aide de la nouvelle API removeBond(int) sur l'appareil associé. L'application peut surveiller les changements d'état de l'association en écoutant l'événement de diffusion de l'appareil Bluetooth ACTION_BOND_STATE_CHANGED.
Sécurité
Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) inclut les modifications de sécurité suivantes.
Blocage de la version MediaStore
Pour les applications ciblant Android 16 ou version ultérieure, MediaStore#getVersion() sera désormais unique pour chaque application. Cela élimine les propriétés d'identification de la chaîne de version pour éviter les utilisations abusives et l'utilisation de techniques d'empreinte digitale. Les applications ne doivent pas faire d'hypothèses sur le format de cette version. Les applications doivent déjà gérer les modifications de version lorsqu'elles utilisent cette API et, dans la plupart des cas, elles ne doivent pas avoir besoin de modifier leur comportement actuel, sauf si le développeur a tenté d'inférer des informations supplémentaires qui dépassent le champ d'application prévu de cette API.
Intents plus sûrs
La fonctionnalité Safer Intents est une initiative de sécurité en plusieurs phases conçue pour améliorer la sécurité du mécanisme de résolution des intents d'Android. L'objectif est de protéger les applications contre les actions malveillantes en ajoutant des vérifications lors du traitement des intents et en filtrant les intents qui ne répondent pas à des critères spécifiques.
Dans Android 15, la fonctionnalité était axée sur l'application d'envoi. Désormais, avec Android 16, le contrôle est transféré à l'application de réception, ce qui permet aux développeurs d'activer la résolution stricte des intents à l'aide du fichier manifeste de leur application.
Deux modifications importantes sont mises en œuvre :
Les intents explicites doivent correspondre au filtre d'intent du composant cible : si un intent cible explicitement un composant, il doit correspondre au filtre d'intent de ce composant.
Les intents sans action ne peuvent correspondre à aucun filtre d'intent : les intents pour lesquels aucune action n'est spécifiée ne doivent être résolus en aucun filtre d'intent.
Ces modifications ne s'appliquent que lorsque plusieurs applications sont impliquées et n'affectent pas la gestion des intents dans une seule application.
Impact
Les développeurs doivent l'activer explicitement dans le fichier manifeste de leur application pour qu'elle prenne effet. Par conséquent, l'impact de la fonctionnalité sera limité aux applications dont les développeurs :
- connaissent la fonctionnalité Intentions plus sûres et ses avantages.
- choisissent activement d'intégrer des pratiques de gestion des intentions plus strictes dans leurs applications.
Cette approche d'activation minimise le risque de casser les applications existantes qui peuvent s'appuyer sur le comportement actuel de résolution des intents moins sécurisé.
Bien que l'impact initial dans Android 16 puisse être limité, l'initiative Safer Intents prévoit un impact plus large dans les futures versions d'Android. L'objectif est de faire de la résolution stricte de l'intention le comportement par défaut.
La fonctionnalité Intents plus sûrs peut améliorer considérablement la sécurité de l'écosystème Android en rendant plus difficile l'exploitation des failles du mécanisme de résolution des intents par les applications malveillantes.
Toutefois, la transition vers la désactivation et l'application obligatoire doivent être gérées avec soin pour résoudre les éventuels problèmes de compatibilité avec les applications existantes.
Implémentation
Les développeurs doivent activer explicitement la correspondance d'intent plus stricte à l'aide de l'attribut intentMatchingFlags dans le fichier manifeste de leur application.
Voici un exemple où la fonctionnalité est activée pour l'ensemble de l'application, mais désactivée/désactivable sur un récepteur :
<application android:intentMatchingFlags="enforceIntentFilter">
<receiver android:name=".MyBroadcastReceiver" android:exported="true" android:intentMatchingFlags="none">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.MY_ANOTHER_CUSTOM_ACTION" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
En savoir plus sur les indicateurs acceptés :
| Nom de l'indicateur | Description |
|---|---|
| enforceIntentFilter | Applique une correspondance plus stricte pour les intents entrants |
| aucune | Désactive toutes les règles de correspondance spéciales pour les intents entrants. Lorsque vous spécifiez plusieurs indicateurs, les valeurs conflictuelles sont résolues en donnant la priorité à l'indicateur "none" (aucun). |
| allowNullAction | Assouplit les règles de correspondance pour autoriser la correspondance des intentions sans action. Cette option doit être utilisée conjointement avec "enforceIntentFilter" pour obtenir un comportement spécifique. |
Tester et déboguer
Lorsque l'application de la règle est active, les applications doivent fonctionner correctement si l'appelant d'intent a correctement renseigné l'intent.
Toutefois, les intents bloqués déclenchent des messages d'avertissement dans le journal, tels que "Intent does not match component's intent filter:" et "Access blocked:", avec le tag "PackageManager.". Cela indique un problème potentiel qui pourrait avoir un impact sur l'application et qui nécessite une attention particulière.
Filtre Logcat :
tag=:PackageManager & (message:"Intent does not match component's intent filter:" | message: "Access blocked:")
Filtrage des appels système du GPU
Pour renforcer la surface du GPU Mali, les IOCTL du GPU Mali qui ont été abandonnés ou qui sont destinés uniquement au développement du GPU ont été bloqués dans les versions de production. De plus, les IOCTL utilisés pour le profilage du GPU ont été limités au processus shell ou aux applications débogables. Pour en savoir plus sur la stratégie au niveau de la plate-forme, consultez la mise à jour du SAC.
Cette modification s'applique aux appareils Pixel qui utilisent le GPU Mali (Pixel 6 à 9). Arm
a fourni une catégorisation officielle de ses IOCTL dans
Documentation/ioctl-categories.rst de sa version r54p2. Cette
liste continuera d'être mise à jour dans les futures versions des pilotes.
Cette modification n'a aucune incidence sur les API graphiques compatibles (y compris Vulkan et OpenGL) et ne devrait pas avoir d'impact sur les développeurs ni sur les applications existantes. Les outils de profilage du GPU tels que Streamline Performance Analyzer et Android GPU Inspector ne seront pas affectés.
Tests
Si vous voyez un refus SELinux semblable à celui-ci, il est probable que votre application ait été affectée par cette modification :
06-30 10:47:18.617 20360 20360 W roidJUnitRunner: type=1400 audit(0.0:85): avc: denied { ioctl }
for path="/dev/mali0" dev="tmpfs" ino=1188 ioctlcmd=0x8023
scontext=u:r:untrusted_app_25:s0:c512,c768 tcontext=u:object_r:gpu_device:s0 tclass=chr_file
permissive=0 app=com.google.android.selinux.pts
Si votre application doit utiliser des IOCTL bloqués, veuillez signaler un bug et l'attribuer à android-partner-security@google.com.
Questions fréquentes
Cette modification de stratégie s'applique-t-elle à tous les OEM ? Cette modification sera facultative, mais disponible pour tous les OEM qui souhaitent utiliser cette méthode de renforcement. Vous trouverez les instructions pour implémenter la modification dans la documentation sur l'implémentation.
Est-il obligatoire d'apporter des modifications au codebase OEM pour implémenter cela, ou est-ce inclus par défaut dans une nouvelle version AOSP ? La modification au niveau de la plate-forme sera fournie par défaut avec une nouvelle version AOSP. Les fournisseurs peuvent choisir d'activer cette modification dans leur codebase s'ils le souhaitent.
Les SoC sont-ils responsables de la mise à jour de la liste IOCTL ? Par exemple, si mon appareil utilise un GPU ARM Mali, dois-je contacter ARM pour toute modification ? Les SoC individuels doivent mettre à jour leurs listes IOCTL par appareil lors de la publication des pilotes. Par exemple, ARM actualisera sa liste IOCTL publiée lors des mises à jour des pilotes. Toutefois, les OEM doivent s'assurer d'intégrer les mises à jour dans leur SEPolicy et d'ajouter les IOCTL personnalisés sélectionnés aux listes, si nécessaire.
Cette modification s'applique-t-elle automatiquement à tous les appareils Pixel disponibles sur le marché, ou une action de l'utilisateur est-elle requise pour activer une option afin d'appliquer cette modification ? Cette modification s'applique à tous les appareils Pixel disponibles sur le marché qui utilisent le GPU Mali (Pixel 6 à 9). Aucune action de l'utilisateur n'est requise pour appliquer cette modification.
L'utilisation de cette stratégie aura-t-elle un impact sur les performances du pilote du kernel ? Cette stratégie a été testée sur le GPU Mali à l'aide de GFXBench, et aucune modification mesurable des performances du GPU n'a été observée.
La liste IOCTL doit-elle correspondre aux versions actuelles de l'espace utilisateur et du pilote du kernel ? Oui, la liste des IOCTL autorisés doit être synchronisée avec les IOCTL compatibles avec les pilotes de l'espace utilisateur et du kernel. Si les IOCTL dans l'espace utilisateur ou le pilote du kernel sont mis à jour, la liste des IOCTL SEPolicy doit être mise à jour pour correspondre.
ARM a classé les IOCTL comme "restreints"/"instrumentation", mais nous souhaitons en utiliser certains en production et/ou en refuser d'autres. Il incombe à chaque OEM/SoC de décider comment catégoriser les IOCTL qu'ils utilisent, en fonction de la configuration de leurs bibliothèques Mali de l'espace utilisateur. La liste ARM peut vous aider à prendre ces décisions, mais le cas d'utilisation de chaque OEM/SoC peut être différent.
Confidentialité
Android 16 (niveau d'API 36) inclut les modifications de confidentialité suivantes.
Autorisation d'accès au réseau local
Les appareils du réseau local sont accessibles par n'importe quelle application disposant de l'autorisation INTERNET.
Cela permet aux applications de se connecter facilement aux appareils locaux, mais cela a également des implications en termes de confidentialité
, comme la création d'une empreinte de l'utilisateur et l'utilisation d'un proxy pour la
localisation.
Le projet Local Network Protections (LNP) vise à protéger la confidentialité de l'utilisateur en limitant l'accès au réseau local à l'aide d'une nouvelle autorisation d'exécution.
Plan de publication
Ce changement sera déployé entre deux versions, 25Q2 et 26Q2 respectivement. Il est impératif que les développeurs suivent ces instructions pour la version 25Q2 et partagent leurs commentaires, car ces protections seront appliquées dans une version ultérieure d'Android. De plus, ils devront mettre à jour les scénarios qui dépendent de l'accès implicite au réseau local en suivant les instructions ci-dessous et se préparer au refus et à la révocation de la nouvelle autorisation par les utilisateurs.
Impact
À l'heure actuelle, LNP est une fonctionnalité facultative, ce qui signifie que seules les applications qui l' activent seront affectées. L'objectif de la phase d'activation est de permettre aux développeurs d'applications de comprendre quelles parties de leur application dépendent de l'accès implicite au réseau local afin qu'ils puissent se préparer à les protéger pour la prochaine version.
Les applications seront affectées si elles accèdent au réseau local de l'utilisateur à l'aide des éléments suivants :
- Utilisation directe ou de bibliothèque de sockets bruts sur des adresses de réseau local (par exemple, le protocole de découverte de service mDNS ou SSDP)
- Utilisation de classes au niveau du framework qui accèdent au réseau local (par exemple, NsdManager)
Le trafic vers et depuis une adresse de réseau local nécessite une autorisation d'accès au réseau local. Le tableau suivant présente quelques cas courants :
| Opération réseau de bas niveau de l'application | Autorisation de réseau local requise |
|---|---|
| Établir une connexion TCP sortante | oui |
| Accepter les connexions TCP entrantes | oui |
| Envoyer une monodiffusion, une multidiffusion ou une diffusion UDP | oui |
| Recevoir une monodiffusion, une multidiffusion ou une diffusion UDP entrante | oui |
Ces restrictions sont implémentées en profondeur dans la pile réseau, et s'appliquent donc à toutes les API réseau. Cela inclut les sockets créés dans du code natif ou géré, les bibliothèques réseau telles que Cronet et OkHttp, ainsi que toutes les API implémentées par-dessus. Toute tentative de résolution de services sur le réseau local (c'est-à-dire ceux avec un suffixe .local) nécessitera une autorisation de réseau local permission.
Exceptions aux règles ci-dessus :
- Si le serveur DNS d'un appareil se trouve sur un réseau local, le trafic vers ou depuis celui-ci (sur le port 53) ne nécessite pas d'autorisation d'accès au réseau local.
- Les applications qui utilisent Output Switcher comme sélecteur intégré n'auront pas besoin d'autorisations de réseau local (plus d'informations à venir au quatrième trimestre 2025).
Instructions pour les développeurs (activation)
Pour activer les restrictions de réseau local, procédez comme suit :
- Flashez l'appareil vers une version avec la bêta 3 de 25Q2 ou une version ultérieure.
- Installez l'application à tester.
Activez ou désactivez l'option Appcompat dans adb :
adb shell am compat enable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>Redémarrez l'appareil.
L'accès de votre application au réseau local est désormais limité et toute tentative de accès au réseau local entraînera des erreurs de socket. Si vous utilisez des API qui effectuent des opérations de réseau local en dehors du processus de votre application (par exemple, NsdManager), elles ne seront pas affectées pendant la phase d'activation.
Pour rétablir l'accès, vous devez accorder à votre application l'autorisation NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICES.
- Assurez-vous que l'application déclare l'autorisation
NEARBY_WIFI_DEVICESdans son fichier manifeste. - Accédez à Settings > Apps > [Nom de l'application] > Permissions > Nearby devices > Autoriser (Paramètres > Applications > [Nom de l'application] > Autorisations > Appareils à proximité > Autoriser).
L'accès de votre application au réseau local devrait maintenant être rétabli et tous vos scénarios devraient fonctionner comme avant l'activation de l'application.
Une fois l'application de la protection du réseau local lancée, voici l'impact sur le trafic réseau de l'application.
| Autorisation | Requête LAN sortante | Requête Internet sortante/entrante | Requête LAN entrante |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accordé | Works | Works | Works |
| Refusé | Gags | Works | Gags |
Utilisez la commande suivante pour désactiver l'option App-Compat :
adb shell am compat disable RESTRICT_LOCAL_NETWORK <package_name>
Erreurs
Les erreurs résultant de ces restrictions seront renvoyées au socket appelant chaque fois qu'il appelle send ou une variante d'envoi vers une adresse de réseau local.
Exemples d'erreurs :
sendto failed: EPERM (Operation not permitted)
sendto failed: ECONNABORTED (Operation not permitted)
Définition du réseau local
Dans ce projet, un réseau local fait référence à un réseau IP qui utilise une interface réseau compatible avec la diffusion, telle que le Wi-Fi ou Ethernet, mais exclut les connexions cellulaires (WWAN) ou VPN.
Les éléments suivants sont considérés comme des réseaux locaux :
IPv4:
- 169.254.0.0/16 // Liaison locale
- 100.64.0.0/10 // CGNAT
- 10.0.0.0/8 // RFC1918
- 172.16.0.0/12 // RFC1918
- 192.168.0.0/16 // RFC1918
IPv6:
- Liaison locale
- Routes directement connectées
- Réseaux stub comme Thread
- Plusieurs sous-réseaux (à déterminer)
De plus, les adresses de multidiffusion (224.0.0.0/4, ff00::/8) et l'adresse de diffusion IPv4 (255.255.255.255) sont classées comme adresses de réseau local.
Photos appartenant à l'application
Lorsqu'une application ciblant le SDK 36 ou version ultérieure sur des appareils équipés d'Android 16 ou version ultérieure demande des autorisations de photo et de vidéo, les utilisateurs qui choisissent de limiter l'accès aux contenus multimédias sélectionnés verront les photos appartenant à l'application présélectionnées dans le sélecteur de photos. Les utilisateurs peuvent désélectionner n'importe lequel de ces éléments présélectionnés, ce qui révoque l'accès de l'application à ces photos et vidéos.
