يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 15 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات رائعة للمطوّرين. توضّح الأقسام التالية هذه الميزات لمساعدتك على البدء في استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات ذات الصلة.
للحصول على قائمة مفصّلة بواجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تمت إضافتها وتعديلها وإزالتها، يُرجى قراءة تقرير الاختلافات في واجهات برمجة التطبيقات. للحصول على تفاصيل حول واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المضافة، يُرجى الانتقال إلى مرجع واجهة برمجة تطبيقات Android. بالنسبة إلى Android 15، ابحث عن واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تمت إضافتها في المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات. للتعرّف على المجالات التي قد تؤثّر فيها تغييرات النظام الأساسي في تطبيقاتك، احرص على الاطّلاع على التغييرات في سلوك Android 15 للتطبيقات التي تستهدف Android 15 ولجميع التطبيقات.
الكاميرا والوسائط
يتضمّن Android 15 مجموعة متنوعة من الميزات التي تحسّن تجربة استخدام الكاميرا والوسائط، وتتيح لك الوصول إلى الأدوات والأجهزة التي تساعد صنّاع المحتوى في تنفيذ أفكارهم الإبداعية على Android.
لمزيد من المعلومات حول أحدث الميزات والحلول المتاحة للمطوّرين في ما يخص الوسائط والكاميرا على Android، يمكنك مشاهدة جلسة إنشاء تجارب حديثة في ما يخص الوسائط والكاميرا على Android من مؤتمر Google I/O.
تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 15 ميزة تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة، وهو وضع للتعرّض التلقائي للضوء متاح في كلاً من الكاميرا 2 وإضافة "الوضع الليلي" في الكاميرا. تعمل ميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة" على تعديل مستوى تعريض المعاينة المباشرة للشاشة في ظروف الإضاءة المنخفضة. يختلف ذلك عن طريقة إنشاء الصور الثابتة من خلال إضافة الكاميرا في "الوضع الليلي"، لأنّ "الوضع الليلي" يجمع سلسلة من الصور لإنشاء صورة واحدة محسّنة. على الرغم من أنّ وضع "الإضاءة المنخفضة" يعمل بشكلٍ جيد جدًا لإنشاء صورة ثابتة، إلا أنّه لا يمكنه إنشاء بثٍ متواصلٍ من اللقطات، ولكن يمكن لميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة" فعل ذلك. وبالتالي، توفّر ميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة" ميزات كاميرا ، مثل:
- توفير معاينة محسّنة للصور، ما يتيح للمستخدمين ضبط عناصر الصور المنخفضة الإضاءة بشكلٍ أفضل
- مسح رموز الاستجابة السريعة ضوئيًا في الإضاءة المنخفضة
في حال تفعيل ميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة"، يتم تفعيلها تلقائيًا عند انخفاض مستوى الإضاءة، ويتم إيقافها عند زيادة الإضاءة.
يمكن للتطبيقات تسجيل فيديو من المعاينة المباشرة على الشاشة في ظروف الإضاءة المنخفضة لحفظه بدرجة سطوع أفضل.
لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة.
عناصر التحكّم في الكاميرا داخل التطبيق
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 15 إضافة تتيح التحكّم بشكل أكبر في أجهزة الكاميرا و algoritms على الأجهزة المتوافقة:
- تعديلات متقدّمة لقوة الفلاش تتيح التحكّم بدقة في كثافة الفلاش في كلا الوضعَين
SINGLEوTORCHأثناء التقاط الصور
التحكّم في مساحة HDR
يختار نظام التشغيل Android 15 الحد الأقصى لمستوى HDR المناسب لقدرات الجهاز الأساسي
وعمق البت في اللوحة. بالنسبة إلى الصفحات التي تتضمّن الكثير من محتوى SDR، مثل تطبيق مراسلة يعرض صورة مصغّرة واحدة بنطاق عالي الديناميكية، يمكن أن يؤدي هذا السلوك إلى التأثير سلبًا في السطوع المُلاحظ لمحتوى SDR. يتيح لك نظام التشغيل Android 15 التحكّم في الحد الأقصى لمستوى الإضاءة في تقنية HDR باستخدام رمز
setDesiredHdrHeadroom لتحقيق التوازن بين المحتوى المعروض بتقنية SDR
وتقنية HDR.
التحكّم في مستوى الصوت

يتيح نظام التشغيل Android 15 معيار CTA-2075 لمساعدتك في معرفة تجنب تناقضات ارتفاع الصوت والتأكد من عدم اضطرار المستخدمين إلى ضبط مستوى الصوت عند التبديل بين المحتوى. يستفيد النظام من البيانات خصائص أجهزة الإخراج (سماعات الرأس ومكبرات الصوت) إلى جانب البيانات الوصفية لارتفاع الصوت المتوفرة في محتوى الصوت بتنسيق AAC لضبط ارتفاع الصوت ومستويات ضغط النطاق الديناميكي
لتفعيل هذه الميزة، عليك التأكّد من توفّر البيانات الوصفية لمستوى الصوت في
محتوى AAC وتفعيل ميزة النظام الأساسي في تطبيقك. ولإجراء ذلك، عليك
إنشاء عنصر LoudnessCodecController من خلال
استدعاء طريقة المصنع create مع معرّف جلسة المحتوى الصوتي من AudioTrack المرتبط، ما يؤدي بدوره إلى
بدء تطبيق تعديلات الصوت تلقائيًا. يمكنك تمرير
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener لتعديله أو فلترته
معاملات ارتفاع الصوت قبل تطبيقها
MediaCodec
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
سيتم أيضًا تحديث AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer لاستخدام
واجهات برمجة تطبيقات LoudnessCodecController من أجل دمج سلس للتطبيقات
أجهزة MIDI 2.0 الافتراضية
أضاف نظام Android 13 إمكانية الاتصال ب أجهزة MIDI 2.0 باستخدام USB، والتي تتواصل باستخدام حِزم MIDI العالمية (UMP). يوفّر نظام التشغيل Android 15 دعمًا لبروتوكول UMP في تطبيقات MIDI الافتراضية، ما يتيح لتطبيقات إنشاء المحتوى التحكّم في تطبيقات المزج كجهاز MIDI 2.0 افتراضي تمامًا كما لو كانت تستخدم جهاز USB MIDI 2.0.
فك ترميز برامج AV1 بشكل أكثر فعالية

dav1d هو برنامج فك ترميز AV1 الرائج من VideoLAN، وهو متاح لأجهزة Android التي لا تتيح فك ترميز AV1 في الأجهزة. ويحقّق برنامج dav1d أداءً أفضل بثلاث مرات مقارنةً ببرنامج فك ترميز AV1 القديم، ما يتيح تشغيل محتوى AV1 بدقة عالية لعدد أكبر من المستخدمين، بما في ذلك بعض الأجهزة المنخفضة ومتوسطة المستوى.
يجب أن يوافق تطبيقك على استخدام dav1d من خلال استدعائه بالاسم
"c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". سيتم استخدام dav1d كبرنامج الترميز والترميز التلقائي لبرنامج AV1 في تحديث لاحق. وتمّت إتاحة هذه الميزة بشكل موحّد ونشرها على
أجهزة Android 11 التي تتلقّى تحديثات نظام Google Play.
إنتاجية المطوّرين وأدواتهم
مع أنّ معظم جهودنا لتحسين إنتاجيتك تركّز على أدوات مثل استوديو Android وJetpack Compose ومكتبات Android Jetpack، نسعى دائمًا إلى إيجاد طرق في المنصة لمساعدتك في تحقيق أهدافك بسهولة أكبر.
تعديلات OpenJDK 17
يواصل نظام التشغيل Android 15 العمل على إعادة تحميل المكتبات الأساسية لنظام التشغيل Android لمواءمتها مع الميزات في أحدث إصدارات OpenJDK LTS.
في ما يلي الميزات والتحسينات الرئيسية:
- تحسينات على مستوى الأداء في ما يتعلّق بمخازن NIO
- البث المباشر
- طرق
mathوstrictmathالإضافية - تحديثات حِزم
util، بما في ذلك الحِزم التي تتضمّن تسلسلاًcollectionوmapوset - إتاحة
ByteBufferفيDeflater - تحديثات الأمان، مثل
X500PrivateCredentialو تحديثات مفتاح الأمان
يتم تحديث واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه على أكثر من مليار جهاز يعمل بالإصدار 12 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 31 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأحدث من خلال تحديثات نظام Google Play، ما يتيح لك استخدام أحدث الميزات البرمجية.
تحسينات على ملفات PDF
يتضمن Android 15 تحسينات مهمة على PdfRenderer
واجهات برمجة التطبيقات. يمكن للتطبيقات دمج ميزات متقدّمة، مثل عرض
الملفات المحمية بكلمة مرور والتعليقات التوضيحية وتعديل النماذج
والبحث والاختيار مع النسخ. ملف PDF بتنسيق المساواة بين نقاط الاتصال
يتم دعم التحسينات لتسريع عرض ملفات PDF المحلية وتقليل استخدام الموارد.
تستخدم مكتبة ملفات PDF في Jetpack واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه لتسهيل عملية إضافة ملفات PDF.
إمكانيات العرض لتطبيقك.
تم نقل PdfRenderer إلى وحدة يمكن تحديثها باستخدام تحديثات نظام
Google Play بغض النظر عن إصدار النظام الأساسي، وسنوفّر
هذه التغييرات مرة أخرى لنظام التشغيل Android 11 (المستوى 30 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) من خلال إنشاء إصدار متوافق
قبل Android 15 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات، والذي يُعرف باسم
PdfRendererPreV.
تحسينات على التبديل التلقائي للغات
أضاف نظام التشغيل Android 14 ميزة التعرّف على محتوى الصوت بعدّة لغات على الجهاز مع التبديل التلقائي بين اللغات، ولكن قد يؤدي ذلك إلى حذف كلمات، خاصةً عند التبديل بين اللغات بدون فترة راحة بين العبارة والعبارة الأخرى. يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 15 عناصر تحكّم إضافية لمساعدة التطبيقات في ضبط عملية التبديل هذه
حسب حالة الاستخدام.
يحدّد الخيار EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS
التبديل التلقائي ببداية جلسة الصوت، بينما يؤدي الخيار
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES إلى إيقاف
تبديل اللغة بعد عدد محدّد من عمليات التبديل. تكون هذه الخيارات مفيدة بشكلٍ خاص إذا كنت تتوقّع أن يتم التحدّث بلغة واحدة
أثناء الجلسة التي من المفترض أن يتم رصدها تلقائيًا.
تحسين واجهة برمجة التطبيقات للخطوط المتغيّرة OpenType
يحسّن Android 15 من سهولة استخدام خط متغيّر OpenType. يمكنك الآن
إنشاء مثيل FontFamily من خط متغيّر بدون تحديد
محاور الوزن من خلال واجهة برمجة التطبيقات buildVariableFamily. يلغي عارض النص
قيمة المحور wght لمطابقة النص المعروض.
باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة، يؤدّي ذلك إلى تبسيط الرمز لإنشاء Typeface.
إلى حد كبير:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder(
FontFamily.Builder(
Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build())
.buildVariableFamily())
.build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder(
new FontFamily.Builder(
new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build())
.buildVariableFamily())
.build();
في السابق، لكي تتمكّن من إنشاء Typeface نفسها، كنت تحتاج إلى مزيد من الرموز البرمجية:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder(
FontFamily.Builder(
Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400")
.setWeight(400)
.build())
.addFont(
Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100")
.setWeight(100)
.build()
)
.addFont(
Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200")
.setWeight(200)
.build()
)
.addFont(
Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300")
.setWeight(300)
.build()
)
.addFont(
Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500")
.setWeight(500)
.build()
)
.addFont(
Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600")
.setWeight(600)
.build()
)
.addFont(
Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700")
.setWeight(700)
.build()
)
.addFont(
Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800")
.setWeight(800)
.build()
)
.addFont(
Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900")
.setWeight(900)
.build()
).build()
).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder(
new FontFamily.Builder(
new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400")
.setWeight(400)
.build()
)
.addFont(
new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100")
.setWeight(100)
.build()
)
.addFont(
new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200")
.setWeight(200)
.build()
)
.addFont(
new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300")
.setWeight(300)
.build()
)
.addFont(
new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500")
.setWeight(500)
.build()
)
.addFont(
new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600")
.setWeight(600)
.build()
)
.addFont(
new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700")
.setWeight(700)
.build()
)
.addFont(
new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800")
.setWeight(800)
.build()
)
.addFont(
new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf")
.setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900")
.setWeight(900)
.build()
)
.build()
).build();
في ما يلي مثال على طريقة إنشاء Typeface باستخدام واجهتَي برمجة التطبيقات القديمة والجديدة
العرض:
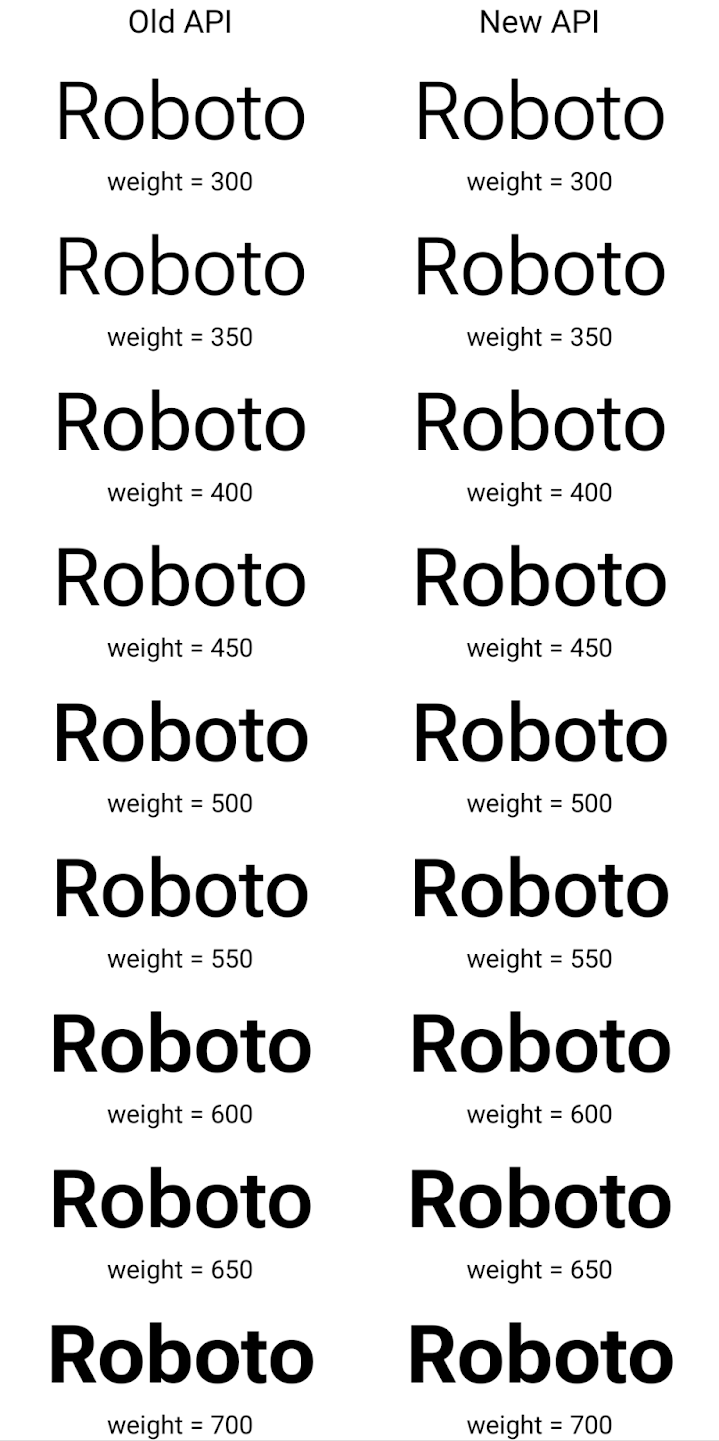
في هذا المثال، لا يحتوي Typeface الذي تم إنشاؤه باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات القديمة على
القدرة على إنشاء سُمك خط دقيقة للأحجام 350 و450 و550 و650.
مثيل Font، لذلك يعود العارض إلى أقرب وزن. ففي
في هذه الحالة، يتم عرض 300 بدلاً من 350، ويتم عرض 400 بدلاً من 450،
وهكذا. على النقيض من ذلك، فإنّ Typeface الذي تم إنشاؤه باستخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة ينشئ ديناميكيًا
مثيل Font لوزن معين، لذا يتم عرض الترجيحات الدقيقة بقيمة 350،
450 و550 و650 أيضًا.
عناصر التحكّم الدقيقة في فواصل الأسطر
بدءًا من Android 15، يمكن لرمز TextView وفاصل السطر الأساسي
الحفاظ على الجزء المحدّد من النص في السطر نفسه لتحسين قراءة النص. يمكنك الاستفادة من هذا التخصيص لفاصل السطر باستخدام علامة
<nobreak> في موارد السلاسل أو
createNoBreakSpan. بالمثل، يمكنك منع الواصلة بين الكلمات باستخدام العلامة <nohyphen> أو العلامة createNoHyphenationSpan.
على سبيل المثال، لا يتضمّن مورد السلسلة التالي فاصل سطر، ويؤدي إلى عرض النص "Pixel 8 Pro" مقطوعًا في مكان غير مرغوب فيه:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
في المقابل، يتضمّن مورد السلسلة هذا العلامة <nobreak> التي تلتف حول العبارة "Pixel 8 Pro" وتمنع استخدام فواصل الأسطر:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
يظهر الفرق في طريقة عرض هذه السلاسل في الصور التالية:

<nobreak>
<nobreak>أرشفة التطبيقات
تم الإعلان عن إتاحة أرشفة التطبيقات في Android وGoogle Play أخيرًا عام، ما يتيح للمستخدمين إخلاء بعض المساحة من خلال إزالة التطبيقات المستخدمة بشكل غير متكرر من الجهاز الذي تم نشره باستخدام تطبيق Android حزمة على Google Play. يتضمّن نظام التشغيل Android 15 ميزة أرشفة التطبيقات وإلغاء أرشفتها على مستوى نظام التشغيل، ما يسهّل على جميع متاجر التطبيقات تنفيذ هذه الميزة.
يمكن للتطبيقات التي لديها إذن REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES طلب البيانات من
PackageInstaller requestArchive لطلب أرشفة
حزمة تطبيق مثبَّتة تؤدي إلى إزالة حزمة APK وأي ملفات مخزَّنة مؤقتًا ولكنها تظل قائمة
بيانات المستخدمين. يتم عرض التطبيقات المؤرشفة كتطبيقات قابلة للعرض من خلال واجهات برمجة التطبيقات
LauncherApps، وسيظهر للمستخدمين تنسيق واجهة مستخدم يُبرز أنّه تم أرشفة
هذه التطبيقات. إذا نقر أحد المستخدمين على تطبيق مؤرشَف، يكون أداة التثبيت المسؤولة
طلبًا لـ إخراجه من الأرشيف، ويمكن إكمال عملية استعادته
المراقبة بواسطة بث ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED.
تفعيل الوضع 16 كيلوبايت على جهاز باستخدام خيارات المطوّرين
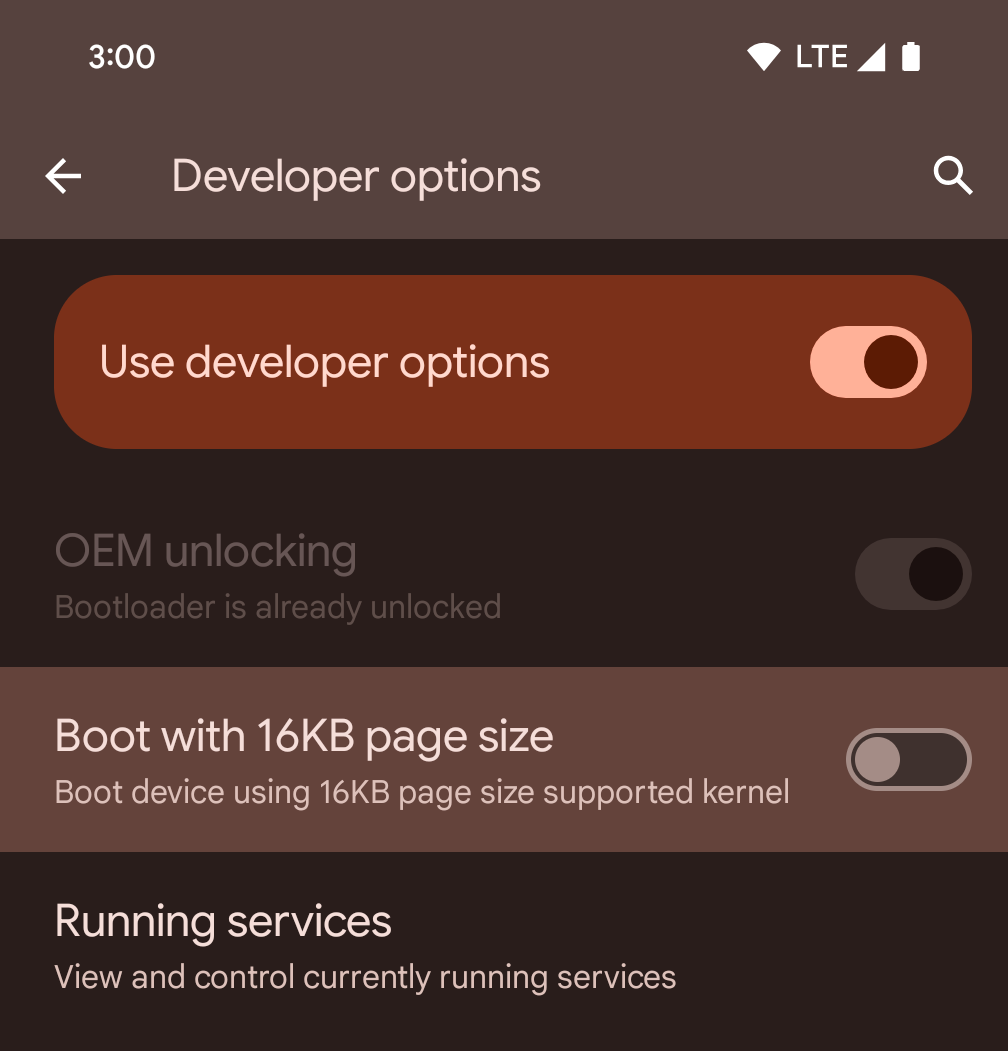
فعِّل خيار المطوّر التشغيل مع صفحات حجمها 16 كيلوبايت لتشغيل الجهاز في الوضع الذي يستخدم صفحات بحجم 16 كيلوبايت.
بدءًا من الإصدار 1 من حزمة الإصدارات التجريبية العامة (QPR1) لنظام التشغيل Android 15، يمكنك استخدام خيار المطوّرين المتاح على أجهزة معيّنة لتشغيل الجهاز في وضع 16 كيلوبايت وإجراء اختبار على الجهاز. قبل استخدام خيار المطوّرين، انتقِل إلى الإعدادات > النظام > تحديثات البرامج وطبِّق أي تحديثات متوفّرة.
يتوفّر خيار المطوّر هذا على الأجهزة التالية:
Pixel 8 وPixel 8 Pro (مع الإصدار 1 من حزمة إصلاح الأخطاء QPR لنظام التشغيل Android 15 أو إصدار أحدث)
تحذير: بسبب مشكلة معروفة في الإصدار التجريبي 3 من Android 15 QPR2، لا تعمل شاشة اللمس على أجهزة Pixel 8 بعد تثبيت الإصدار التجريبي 3 من Android 15 QPR2 وتشغيل الجهاز في وضع 16 كيلوبايت. لا تؤثّر هذه المشكلة في أجهزة Pixel 8 Pro.
Pixel 8a (مع الإصدار 1 من حزمة الإصدارات ربع السنوية لنظام Android 15 أو إصدار أحدث)
تحذير: بسبب مشكلة معروفة في الإصدار التجريبي الثالث من Android 15 QPR2، لا تعمل شاشة اللمس على أجهزة Pixel 8a بعد تثبيت الإصدار التجريبي الثالث من Android 15 QPR2 وتشغيل الجهاز في وضع 16 كيلوبايت.
Pixel 9 وPixel 9 Pro وPixel 9 Pro XL (مع الإصدار التجريبي 2 من حزمة QPR2 لنظام التشغيل Android 15 أو إصدار أحدث)
الرسومات
يوفّر Android 15 أحدث التحسينات على الرسومات، بما في ذلك ANGLE وإضافات إلى نظام رسومات Canvas.
تحديث طريقة وصول Android إلى وحدة معالجة الرسومات

لقد تطورت أجهزة Android كثيرًا منذ الأيام الأولى التي كان فيها تشغيل نظام التشغيل الأساسي على وحدة معالجة مركزية واحدة والوصول إلى وحدات معالجة الرسومات باستخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المستندة إلى قنوات معالجة الوظائف الثابتة. أصبحت واجهة برمجة تطبيقات الرسومات Vulkan® متاحة في حزمة تطوير البرامج (NDK) منذ الإصدار 7.0 من نظام Android (المستوى 24 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) مع توفير مستوى أدنى من التجريد الذي يعكس بشكل أفضل الأجهزة الحديثة لوحدة معالجة الرسومات، ويتوافق بشكل أفضل مع وحدات المعالجة المركزية المتعدّدة، ويقلّل من وقت استجابة برنامج تشغيل وحدة المعالجة المركزية، ما يؤدي إلى تحسين أداء التطبيق. يتوافق Vulkan مع جميع محرّكات الألعاب الحديثة.
Vulkan هي واجهة Android المفضّلة لوحدة معالجة الرسومات. لذلك، يتضمّن الإصدار 15 من Android ANGLE كطبقة اختيارية لتشغيل OpenGL® ES على Vulkan. سيؤدي الانتقال إلى ANGLE إلى توحيد تنفيذ OpenGL في Android لتحسين التوافق، وفي بعض الحالات، تحسين الأداء. يمكنك اختبار ثبات تطبيق OpenGL ES وأدائه باستخدام ANGLE من خلال تفعيل خيار المطوّر في الإعدادات -> النظام -> خيارات المطوّرين -> ميزة تجريبية: تفعيل ANGLE على Android 15.
خارطة طريق Android ANGLE على Vulkan
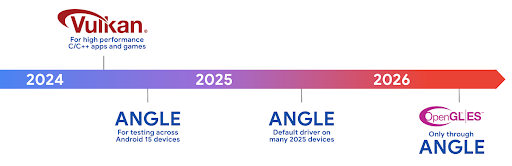
كجزء من عملية تبسيط حِزم وحدة معالجة الرسومات، سنطرح من الآن فصاعدًا ANGLE كبرنامج تشغيل نظام GL على المزيد من الأجهزة الجديدة، مع توقّع أن يكون OpenGL/ES متاحًا في المستقبل من خلال ANGLE فقط. ومع ذلك، نخطّط ل مواصلة توفير OpenGL ES على جميع الأجهزة.
الخطوات التالية المقترحة
استخدِم خيارات المطوّر لاختيار برنامج تشغيل ANGLE لـ OpenGL ES واختبار تطبيقك. بالنسبة إلى المشاريع الجديدة، ننصحك بشدة باستخدام Vulkan لـ C/C++.
تحسينات على Canvas
يواصل نظام Android 15 جهودنا لتطوير نظام الرسومات Canvas في Android من خلال إضافة ميزات إضافية:
- يوفّر
Matrix44مصفوفة 4×4 لتحويل الإحداثيات التي يجب استخدامها عندما تريد التحكّم في اللوحة في المساحات الثلاثية الأبعاد. - يقاطع
clipShaderالمقطع الحالي بالshader المحدّد، في حين يضبطclipOutShaderالمقطع على اختلاف المقطع الحالي والshader، مع اعتبار كل منهما shader على أنّه قناع شفافية. يتيح ذلك رسم أشكال معقّدة بكفاءة.
الأداء والبطارية
يواصل نظام التشغيل Android التركيز على مساعدتك في تحسين أداء تطبيقاتك وجودتها. يقدِّم نظام التشغيل Android 15 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تساعد في تنفيذ المهام في تطبيقك بكفاءة أكبر، وتحسين أداء التطبيق، وجمع إحصاءات حول تطبيقاتك.
للاطّلاع على أفضل الممارسات التي تساهم في الحفاظ على عمر البطارية، وتصحيح أخطاء استخدام الشبكة والطاقة، والتفاصيل حول كيفية تحسين كفاءة البطارية عند تنفيذ العمليات في الخلفية في Android 15 والإصدارات الحديثة من Android، يمكنك مشاهدة جلسة تحسين كفاءة البطارية عند تنفيذ العمليات في الخلفية على Android من مؤتمر Google I/O.
ApplicationStartInfo API
في الإصدارات السابقة من Android، كان تشغيل التطبيقات عملية غير معروفة إلى حدٍ ما. كان من الصعوبة تحديد ما إذا كان تطبيقك قد بدأ من حالة التشغيل على البارد أو إعادة التشغيل البطيء
أو إعادة التشغيل السريع. كان من الصعب أيضًا معرفة المدة التي استغرقها تطبيقك أثناء
مراحل الإطلاق المختلفة: إنشاء نسخة من العملية، واستدعاء onCreate، ورسم
الإطار الأول، وغير ذلك. عند إنشاء مثيل لفئة Application، لم يكن لديك
طريقة لمعرفة ما إذا كان التطبيق قد بدأ من بث أو مقدّم محتوى أو
عملية أو خدمة احتياطية أو اكتمال عملية التمهيد أو منبّه أو Activity.
توفّر واجهة برمجة التطبيقات ApplicationStartInfo على Android 15 كل هذه الميزات والمزيد. يمكنك أيضًا اختيار إضافة الطوابع الزمنية الخاصة بك إلى السلسلة للمساعدة في جمع بيانات التوقيت في مكان واحد. بالإضافة إلى جمع القياسات، يمكنك استخدام ApplicationStartInfo للمساعدة في تحسين بدء تشغيل التطبيق مباشرةً. على سبيل المثال، يمكنك إزالة عمليات إنشاء المثيلات المكلّفة للمكتبات ذات الصلة بواجهة المستخدم ضمن فئة Application عند بدء تشغيل تطبيقك بسبب بث.
معلومات مفصّلة عن حجم التطبيق
منذ الإصدار 8.0 من Android (المستوى 26 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، يتضمّن Android واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
StorageStats.getAppBytes التي تلخّص حجم التطبيق المثبَّت كعدد واحد من البايتات، وهو مجموع حجم حزمة APK وحجم الملفات المستخرَجة من حزمة APK والملفات التي تم إنشاؤها على
الجهاز، مثل الرموز البرمجية المجمَّعة مسبقًا (AOT). لا يقدّم هذا الرقم معلومات مفيدة بشأن كيفية استخدام تطبيقك لمساحة التخزين.
يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 15 واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type])، التي تتيح
لك الحصول على إحصاءات عن كيفية استخدام تطبيقك لكل هذه المساحة، بما في ذلك عمليات تقسيم ملف APK، والرموز البرمجية ذات الصلة بميزة AOT والتسريع، والبيانات الوصفية لملف dex، والمكتبات، والملفات الشخصية الإرشادية.
تحديد المواصفات الشخصية لصاحب البيانات من خلال التطبيق
يتضمّن Android 15 فئة ProfilingManager،
التي تتيح لك جمع معلومات الأداء من داخل تطبيقك، مثل ملف تفريغ ذاكرة heap
وملفات تعريف ذاكرة heap وتحليل تسلسل استدعاء الدوال البرمجية وغير ذلك. ويقدّم هذا الإجراء استدعاءً إلى
تطبيقك باستخدام علامة مقدَّمة لتحديد ملف الإخراج الذي يتم إرساله إلى دليل ملفات
تطبيقك. تفرض واجهة برمجة التطبيقات حدودًا على معدّل الإرسال لتقليل تأثير
الأداء.
لتبسيط إنشاء طلبات إنشاء ملفات شخصية في تطبيقك، ننصحك باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات المتوافقة مع Profiling AndroidX API، والمتوفّرة في الإصدار Core 1.15.0-rc01 أو الإصدارات الأحدث.
تحسينات على قاعدة بيانات SQLite
يوفّر Android 15 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات SQLite تتيح الميزات المتقدّمة من خلال أو محرك SQLite الأساسي الذي يستهدف مشكلات معينة في الأداء يمكن أن البيانات في التطبيقات. يتم تضمين واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه مع تحديث SQLite إلى الإصدار 3.44.3
على المطوّرين الرجوع إلى أفضل الممارسات لتحسين أداء SQLite للاستفادة إلى أقصى حد من قاعدة بيانات SQLite، خاصةً عند العمل مع قواعد بيانات كبيرة أو عند تنفيذ طلبات بحث حسّاسة للوقت المستغرَق في الاستجابة.
- المعاملات المؤجلة للقراءة فقط: عند إصدار معاملات
للقراءة فقط (لا تتضمّن عبارات كتابة)، استخدِم
beginTransactionReadOnly()وbeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)لإصدار معاملاتDEFERREDللقراءة فقط. يمكن تنفيذ هذه المعاملات بالتزامن مع بعضها، وإذا كانت قاعدة البيانات في وضع WAL، يمكن تنفيذها بالتزامن مع معاملاتIMMEDIATEأوEXCLUSIVE. - أعداد الصفوف وأرقام التعريف: تمت إضافة واجهات برمجة التطبيقات لاسترداد عدد الصفوف التي تم تغييرها
أو رقم تعريف الصف الذي تم إدراجه مؤخرًا بدون إصدار طلب بحث إضافي.
تعرض
getLastChangedRowCount()عدد الصفوف التي قد تم إدراجها أو تحديثها أو حذفها من خلال أحدث عبارة SQL في المعاملة الحالية، في حين أنّgetTotalChangedRowCount()يعرض العدد على الاتصال الحالي. تعرض دالةgetLastInsertRowId()rowidللصف الأخير لإدراجه في الربط الحالي. - الكشوف الأولية: إصدار عبارة SQlite أولية لتجاوز سهولة الاستخدام والبرامج الأخرى وأي نفقات معالجة إضافية قد تتكبدها.
تحديثات "إطار عمل الأداء الديناميكي" في Android
يواصل الإصدار 15 من Android استثماراتنا في إطار عمل الأداء الديناميكي (ADPF) في Android، وهو مجموعة من واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تتيح للألعاب والتطبيقات التي تتطلب أداءً عاليًا التفاعل بشكل مباشر أكثر مع أنظمة الطاقة والحرارة في أجهزة Android. على الأجهزة المتوافقة، يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 15 ميزات ADPF التالية:
- وضع توفير الطاقة لجلسات التلميح لتحديد أنّ سلاسل المحادثات المرتبطة بها يجب أن تفضّل توفير الطاقة على الأداء، وهو أمر رائع لأحمال العمل التي تعمل في الخلفية لفترة طويلة
- يمكن تسجيل مدّة عمل كلّ من وحدة معالجة الرسومات ووحدة المعالجة المركزية في جلسات التلميح، ما يسمح للنظام بتعديل معدّلات تكرار وحدة المعالجة المركزية ووحدة معالجة الرسومات معًا لتلبية متطلبات حمولة العمل على أفضل نحو.
- حدود الحد الأقصى للطاقة الحرارية لتفسير حالة الحد الأقصى للطاقة الحرارية المحتملة استنادًا إلى توقّعات الحد الأقصى للطاقة الحرارية
للاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات عن كيفية استخدام ميزة "الإعلانات الديناميكية على شبكة البحث" في تطبيقاتك وألعابك، يمكنك الانتقال إلى مستندات المساعدة.
الخصوصية
يتضمّن Android 15 مجموعة متنوّعة من الميزات التي تساعد مطوّري التطبيقات في حماية خصوصية المستخدمين.
رصد تسجيل الشاشة
يوفّر Android 15 إمكانية استخدام التطبيقات لرصد ما يلي: يتم تسجيلها. يتم استدعاء إجراء معاودة الاتصال عند انتقال التطبيق بين أن تكون مرئية أو غير مرئية ضمن تسجيل الشاشة. التطبيق عبارة عن تُعد مرئية إذا كانت الأنشطة التي يملكها المُعرّف الفريد لعملية التسجيل يتم تسجيلها. بهذه الطريقة، إذا كان تطبيقك يُجري عملية حسّاسة، يمكنك إبلاغ المستخدم بأنّه يتم تسجيله.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
إمكانيات IntentFilter الموسّعة
يتيح Android 15 توفير دقة Intent بدرجة أكبر من خلال واجهة برمجة التطبيقات
UriRelativeFilterGroup التي تتضمّن مجموعة من عناصر
UriRelativeFilter التي تشكّل مجموعة من قواعد Intent
مطابقة يجب استيفاؤها، بما في ذلك مَعلمات طلب البحث لعناوين URL وأجزاء عناوين URL
وقواعد الحظر أو الاستبعاد.
يمكن تحديد هذه القواعد في ملف XML الخاص بـ AndroidManifest باستخدام
العلامة <uri-relative-filter-group> التي يمكن أن تتضمّن اختياريًا علامة android:allow. يمكن أن تحتوي هذه العلامات على علامات <data> تستخدِم سمات علامات بيانات
الحالية بالإضافة إلى سمتَي android:query وandroid:fragment.
في ما يلي مثال على بنية AndroidManifest:
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:domain="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
المساحة الخاصة
تتيح "المساحة الخاصة" للمستخدمين إنشاء مساحة منفصلة على أجهزتهم للحفاظ على خصوصية التطبيقات الحسّاسة من خلال طبقة مصادقة إضافية. تستخدم المساحة الخاصة ملفًا شخصيًا منفصلاً للمستخدم. يمكن للمستخدم اختيار استخدام قفل الجهاز أو وسيلة قفل منفصلة للمساحة الخاصة.
تظهر التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة في حاوية منفصلة ضِمن مشغِّل التطبيقات، وتكون مخفية من العرض بين التطبيقات المستخدَمة مؤخرًا ومن الإشعارات والإعدادات والتطبيقات الأخرى عندما تكون المساحة الخاصة مقفلة. يتم توزيع المحتوى الذي ينشئه المستخدم والذي يتم تنزيله (مثل الوسائط أو الملفات) والحسابات الخاصة به بين المساحة الخاصّة وال المساحة الرئيسية. يمكن استخدام قائمة مشاركة البيانات و أداة اختيار الصور لتمكين التطبيقات من الوصول إلى المحتوى في المساحات المختلفة عندما يتم فتح قفل المساحة الخاصة.
لا يمكن للمستخدمين نقل التطبيقات الحالية وبياناتها إلى المساحة الخاصة. بدلاً من ذلك، يختار المستخدمون خيار تثبيت في المساحة الخاصة لتثبيت تطبيق باستخدام متجر التطبيقات المفضّل لديهم. يتم تثبيت التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة كنسخ منفصلة عن أي تطبيقات في المساحة الرئيسية (نُسخ جديدة من التطبيق نفسه).
عندما يقفل المستخدم المساحة الخاصة، يتم إيقاف الملف الشخصي. عندما يتم إيقاف الملف الشخصي، تتوقف التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة عن العمل ولا يمكنها تنفيذ الأنشطة في المقدّمة أو الخلفية، بما في ذلك عرض الإشعارات.
ننصحك باختبار تطبيقك باستخدام المساحة الخاصة للتأكّد من أنّه يعمل بالشكل المتوقّع، خاصةً إذا كان تطبيقك يندرج ضمن إحدى الفئات التالية:
- التطبيقات التي تتضمّن منطقًا لملف العمل الذي يفترض أنّ أي نُسخ مثبَّتة من تطبيقه غير المضمّنة في الملف الشخصي الرئيسي تكون في ملف العمل
- التطبيقات الطبية
- تطبيقات مشغّل التطبيقات
- تطبيقات متجر التطبيقات
طلب البحث عن آخر اختيار للمستخدم في ما يخصّ "الوصول إلى الصور المحدّدة"
يمكن للتطبيقات الآن إبراز الصور والفيديوهات التي تم اختيارها مؤخرًا فقط عند منح التطبيقات
إذن وصول جزئي إلى أذونات الوسائط. يمكن أن تحسِّن هذه الميزة
تجربة المستخدم للتطبيقات التي تطلب الوصول إلى الصور
والفيديوهات بشكل متكرر. لاستخدام هذه الميزة في تطبيقك، فعِّل الوسيطة
QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY عند طلب البحث من MediaStore
من خلال ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external")
val mediaColumns = arrayOf(
FileColumns._ID,
FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME,
FileColumns.MIME_TYPE,
)
val queryArgs = bundleOf(
// Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access)
QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true,
// Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage
QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC",
QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?",
QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf(
FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(),
FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString()
)
)
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external");
String[] mediaColumns = {
FileColumns._ID,
FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME,
FileColumns.MIME_TYPE
};
Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle();
queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true);
queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC");
queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?");
queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] {
String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE),
String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO)
});
"مبادرة حماية الخصوصية" على Android
يتضمّن Android 15 أحدث إضافات "خدمات الإعلانات" من Android، بما في ذلك أحدث إصدار من مبادرة حماية الخصوصية على Android. تشكّل هذه الإضافة جزءًا من جهودنا لتطوير تقنيات تُحسِّن خصوصية المستخدمين وتتيح تجارب إعلانية مخصّصة فعّالة لتطبيقات الأجهزة الجوّالة. تتضمّن صفحة مبادرة حماية الخصوصية مزيدًا من المعلومات حول "مبادرة حماية الخصوصية" في برامج معاينة المطوّرين والإصدارات التجريبية من Android لمساعدتك في البدء.
Health Connect
يدمج نظام التشغيل Android 15 أحدث الإضافات المتعلقة بتطبيق Health Connect من Android، وهو منصّة آمنة ومتمركزة لإدارة بيانات الصحة واللياقة البدنية التي تجمعها التطبيقات ومشاركتها. يتيح هذا التعديل استخدام أنواع بيانات إضافية في ما يتعلّق باللياقة البدنية والتغذية ودرجة حرارة الجلد وخطط التدريب وغير ذلك.
تتيح ميزة تتبُّع درجة حرارة الجلد للمستخدمين تخزين بيانات دترة حرارة أكثر دقة ومشاركتها من جهاز قابل للارتداء أو جهاز تتبُّع آخر.
الخطط التدريبية هي خطط تمارين منظمة لمساعدة المستخدم في تحقيق أهدافه المتعلّقة باللياقة البدنية. يتضمّن دعم الخطط التدريبية مجموعة متنوعة من أهداف الإنجاز والأداء:
- أهداف الإنجاز المتعلّقة بعدد السعرات الحرارية المحروقة، المسافة، والمدة، عدد التكرارات، والخطوات
- أهداف الأداء حول أكبر عدد ممكن من التكرارات (AMRAP)، الوتيرة، معدل ضربات القلب، القوة، معدل الجهد المبذول، السرعة
يمكنك الاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات حول آخر التحديثات التي أُجريت على Health Connect في Android من خلال إنشاء تجارب استخدام قابلة للتكيّف باستخدام Android معلومات حول الصحة من مؤتمر Google I/O
مشاركة شاشة التطبيق
يتيح نظام التشغيل Android 15 مشاركة شاشة التطبيق كي يتمكّن المستخدمون من مشاركة أو تسجيل
نافذة التطبيق فقط بدلاً من شاشة الجهاز بالكامل. تم تفعيل هذه الميزة لأول مرة في ملف APK لنظام التشغيل
Android 14 QPR2، وتشمل MediaProjection طلبات إعادة الاتصال التي تسمح لتطبيقك
بتخصيص تجربة مشاركة شاشة التطبيق. يُرجى العلم أنّه بالنسبة إلى التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 14 من Android (المستوى 34 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأحدث، يجب الحصول على موافقة المستخدم لكل جلسة رصد MediaProjection.
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يمنح نظام التشغيل Android 15 مطوّري التطبيقات والمستخدمين المزيد من التحكّم والمرونة في إعداد أجهزتهم بما يتناسب مع احتياجاتهم.
لمزيد من المعلومات حول كيفية استخدام أحدث التحسينات في Android 15 لتحسين تجربة المستخدم في تطبيقك، يمكنك الاطّلاع على جلسة تحسين تجربة المستخدم في تطبيق Android من مؤتمر Google I/O.
معاينات تطبيقات مصغّرة أكثر تفصيلاً باستخدام Generated Previews API
قبل الإصدار 15 من Android، كانت الطريقة الوحيدة لتقديم معاينات لأداة اختيار التطبيقات المصغّرة هي تحديد مصدر صورة أو تنسيق ثابت. غالبًا ما تختلف هذه المعاينات عن شكل التطبيق المصغّر الفعلي عند وضعه على الشاشة الرئيسية. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، لا يمكن إنشاء موارد ثابتة باستخدام Jetpack Glance، لذا كان على مطوّر Glance التقاط لقطة شاشة لأداة العرض أو إنشاء تنسيق XML للحصول على معاينة لأداة العرض.
يتيح نظام Android 15 استخدام معاينات تم إنشاؤها. وهذا يعني أنّه يمكن لموفّري التطبيقات المصغرة
إنشاء RemoteViews لاستخدامها كمعاينة لأداة الاختيار، بدلاً من
مورد ثابت.
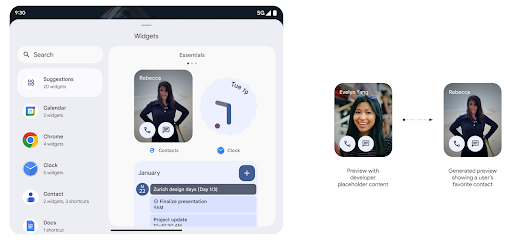
واجهة برمجة تطبيقات Push
يمكن للتطبيقات تقديم معاينات تم إنشاؤها من خلال واجهة برمجة تطبيقات Push. يمكن للتطبيقات تقديم
معاينات في أي مرحلة من مراحل نشاطها، وعدم تلقّي طلب صريح
من المضيف لتقديم معاينات. يتم الاحتفاظ بالمعاينات في AppWidgetService،
ويمكن للمضيفين طلبها عند الطلب. المثال التالي يحمّل تطبيق مصغّر بتنسيق XML
تنسيق موارد التنسيق وتعيينه كمعاينة:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
التدفق المتوقع هو:
- في أي وقت، يستدعي موفّر التطبيق المصغّر
setWidgetPreview. يتم الاحتفاظ بالمعاينات التي تم تقديمها فيAppWidgetServiceمع معلومات مقدّم الخدمة الأخرى. - يرسل "
setWidgetPreview" إشعارًا إلى المضيفين بمعاينة محدَّثة من خلالAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChangedمعاودة الاتصال. استجابةً لذلك، يُعيد مضيف التطبيقات المصغّرة تحميل جميع معلومات مقدّم الخدمة. - عند عرض معاينة التطبيق المصغّر، يتحقق المضيف من العنصر
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories، وإذا كانت الفئة التي تم اختيارها متوفرة، يتصل بالعنصرAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewلعرض المعاينة المحفوظة لهذا الموفِّر.
حالات الاتصال بـ setWidgetPreview
وبما أنّه لا تتوفّر طلبات إعادة اتصال لتقديم المعاينات، يمكن للتطبيقات اختيار إرسال المعاينات في أي وقت أثناء تشغيلها. عدد مرات تعديل المعاينة على حالة استخدام الأداة.
توضِّح القائمة التالية الفئتَين الرئيسيتَين لحالات استخدام المعاينة:
- مقدمو الخدمات الذين يعرضون بيانات فعلية في معاينات الأدوات، مثل أو معلومات حديثة. يمكن لموفّري المحتوى هؤلاء ضبط المعاينة بعد تسجيل دخول المستخدم أو إجراء الإعدادات الأولية في تطبيقه. وبعد ذلك، يمكنهم إعداد مهمة دورية لتعديل المعاينات بالوتيرة التي يختارونها. ومن الأمثلة على هذا النوع من التطبيقات المصغّرة أداة مصوّرة أو أداة تقويم أو أداة طقس أو أداة أخبار.
- مقدّمو الخدمات الذين يعرضون معلومات ثابتة في معاينات التطبيقات المصغّرة أو التطبيقات المصغّرة للإجراءات السريعة ولا يعرضون أي بيانات يمكن لموفّري المحتوى هؤلاء ضبط المعاينات مرة واحدة عند بدء تشغيل التطبيق لأول مرة. تتضمن أمثلة هذا النوع من التطبيقات المصغّرة محرك أقراص تطبيق "الإجراءات" المصغّر أو تطبيق "اختصارات Chrome" المصغّر.
قد يعرض بعض مزوّدي الخدمة معاينات ثابتة في منتقي وضع الإرساء، ولكنّها في الواقع المعلومات الموجودة في منتقي الشاشة الرئيسية. على مقدّمي هذه الخدمات اتّباع الإرشادات لكلتا حالتَي الاستخدام هاتين لضبط المعاينات.
نافذة ضمن النافذة
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 15 تغييرات في ميزة "نافذة ضمن النافذة" لضمان عملية انتقال أكثر سلاسة عند الدخول إلى هذا الوضع. سيكون هذا مفيدًا لتطبيقك إذا كان يتضمّن عناصر واجهة مستخدم متراكبة على واجهة المستخدم الرئيسية، والتي يتم عرضها في وضع "صورة في صورة".
يستخدم المطوّرون دالة الاستدعاء onPictureInPictureModeChanged لتحديد المنطق الذي يبدِّل مستوى ظهور عناصر واجهة المستخدم التي تمّت تغطيتها. يتم بدء ردّ الاتصال هذا عند اكتمال الصورة المتحركة لدخول وضع "صورة في صورة" أو الخروج منه. بدءًا من
Android 15، تتضمن فئة PictureInPictureUiState حالة أخرى.
في هذه الحالة، ستلاحظ التطبيقات التي تستهدف الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أنّه يتمّ استدعاء callback
Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged باستخدام رمز دالة
isTransitioningToPip() فور بدء عرض الصورة في صورة. هناك
العديد من عناصر واجهة المستخدم التي لا تكون ملائمة للتطبيق عندما يكون في وضع "صورة في صورة"، مثل
طرق العرض أو التنسيقات التي تتضمّن معلومات مثل الاقتراحات والفيديوهات القادمة
والتقييمات والعناوين. عندما ينتقل التطبيق إلى وضع "نافذة ضمن النافذة"، استخدِم دالة callback الخاصة بالعنصر
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged لإخفاء عناصر واجهة المستخدم هذه. عندما ينتقل
التطبيق إلى وضع ملء الشاشة من نافذة PiP، استخدِم callback
onPictureInPictureModeChanged لإلغاء إخفاء هذه العناصر، كما هو موضّح في المثالين التاليين:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
يساعد هذا التبديل السريع لعناصر واجهة المستخدم غير ذات الصلة (لتشغيل نافذة PiP) في ضمان ظهور رسوم متحركة سلسة وبدون وميض عند تشغيل وضع PiP.
قواعد محسّنة لميزة "عدم الإزعاج"
AutomaticZenRule يسمح للتطبيقات بتخصيص "الانتباه"
قواعد الإدارة (عدم الإزعاج) وتحديد وقت التفعيل أو الإيقاف
معهم. ويقدم Android 15 تحسينات كبيرة على هذه القواعد بهدف تحسين
تجربة المستخدم. تم تضمين التحسينات التالية:
- إضافة أنواع إلى
AutomaticZenRule، ما يسمح للنظام بتطبيق إجراءات خاصة التعامل مع بعض القواعد. - إضافة رمز إلى
AutomaticZenRule، ما يساعد في تمييز الأوضاع بشكلٍ أفضل - إضافة سلسلة
triggerDescriptionإلىAutomaticZenRuleتصف الشروط التي يجب أن تصبح فيها القاعدة نشطة للمستخدم - تمت الإضافة
ZenDeviceEffectsعلىAutomaticZenRule، ما يسمح للقواعد بتشغيل أشياء مثل التدرج الرمادي العرض أو الوضع الليلي أو تعتيم الخلفية.
ضبط VibrationEffect لقنوات الإشعارات
يتيح Android 15 ضبط اهتزازات تفاعلية للإشعارات الواردة من خلال
قناة تستخدم NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect، لذلك
يستطيع المستخدمون التمييز بين الأنواع المختلفة من الإشعارات بدون
الاضطرار إلى النظر إلى أجهزتهم.
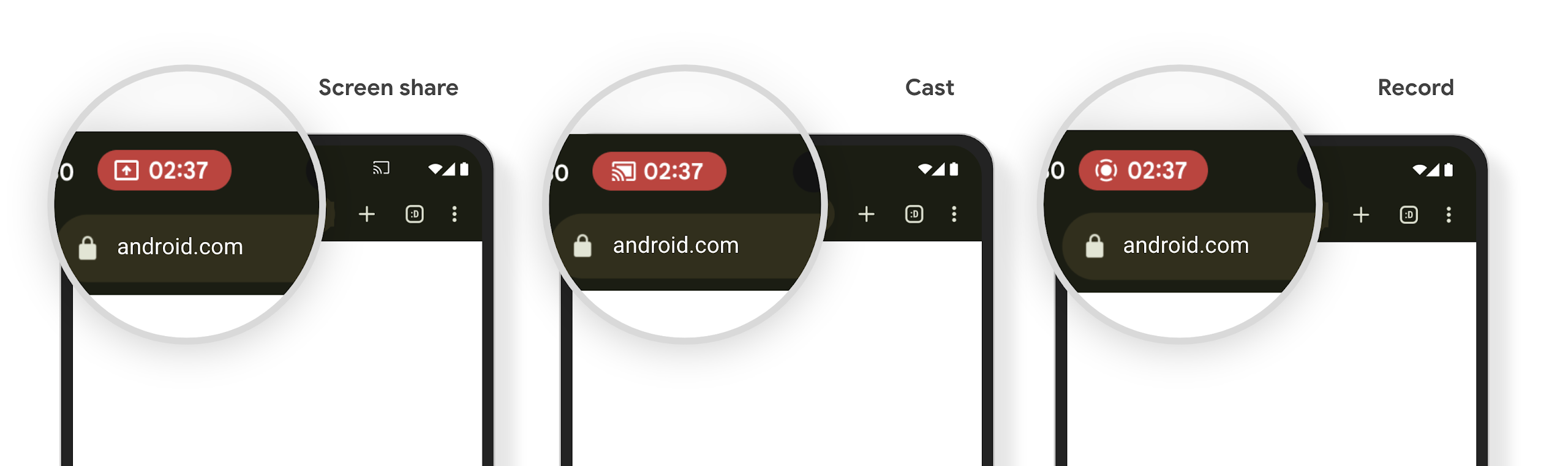
شريحة شريط حالة عرض الوسائط والإيقاف التلقائي
يمكن أن تؤدي ميزة "إلقاء الوسائط" إلى الكشف عن معلومات المستخدمين الخاصة. شريحة بارزة جديدة للحالة تُعلم المستخدمين بأي بث شاشة جارٍ. يمكن للمستخدمين النقر على الشريحة لإيقاف بث الشاشة أو مشاركتها أو تسجيلها. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، لتوفير تجربة مستخدم أكثر سهولة، يتم الآن تلقائيًا إيقاف أي عملية بث شاشة قيد التنفيذ عند قفل شاشة الجهاز.
الشاشات الكبيرة وأشكال الأجهزة
يوفّر نظام التشغيل Android 15 لتطبيقاتك إمكانية الاستفادة إلى أقصى حدّ من أشكال أجهزة Android، بما في ذلك الشاشات الكبيرة والأجهزة القابلة للطي والقلب.
تحسين تعدُّد المهام على الشاشات الكبيرة
يوفّر Android 15 للمستخدمين طرقًا أفضل لتنفيذ مهام متعددة على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة. بالنسبة يمكن للمستخدمين مثلاً حفظ مجموعات التطبيقات المفضّلة لديهم في "وضع تقسيم الشاشة" للحصول على الوصول إلى شريط التطبيقات وتثبيته على الشاشة للتبديل بسرعة بين التطبيقات. وهذا يعني أنّ التأكّد من توافق تطبيقك مع الأجهزة المختلفة بات أكثر أهمية من أي وقت مضى.
جلسات مؤتمر Google I/O حول تصميم Android التكيُّفي التطبيقات وواجهة مستخدم المبنى باستخدام Material 3 المكتبة التكيّفية التي يمكن أن تساعدك، كما توفر مستنداتنا المزيد من المساعدة لتصميم مواقع الشاشات
إمكانية استخدام الشاشة الخارجية
يمكن لتطبيقك تعريف خاصية يستخدمها نظام التشغيل Android 15 لسماحApplication أو Activity بعرض المحتوى على الشاشات الصغيرة المخصّصة للغلاف في الأجهزة القابلة للطي المتوافقة. هذه الشاشات صغيرة جدًا لكي يتم
اعتبارها استهدافات متوافقة لتشغيل تطبيقات Android عليها، ولكن يمكن لتطبيقك
تفعيل توافقها، ما يجعل تطبيقك متاحًا في المزيد من الأماكن.
إمكانية الاتصال
يعدّل Android 15 النظام الأساسي لمنح تطبيقك إمكانية الوصول إلى أحدث التطورات في تكنولوجيات الاتصال والشبكات اللاسلكية.
التوافق مع الأقمار الصناعية
يواصل نظام Android 15 توسيع نطاق توفّر المنصة للاتصال عبر الأقمار الصناعية ويضمّ بعض عناصر واجهة المستخدم لضمان تجربة مستخدم متّسقة على مستوى منظومة الاتصال عبر الأقمار الصناعية.
يمكن للتطبيقات استخدام ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() لرصد الحالات التي يكون فيها الجهاز متصلاً بأحد الأقمار الصناعية، ما يمنح التطبيقات المزيد من المعلومات عن سبب عدم توفّر خدمات الشبكة الكاملة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يقدّم الإصدار 15 من Android
توافقًا مع تطبيقات الرسائل القصيرة ورسائل الوسائط المتعددة، بالإضافة إلى تطبيقات RCS المحمَّلة مسبقًا لاستخدام
الاتصال عبر الأقمار الصناعية لإرسال الرسائل واستلامها.
تجارب أكثر سلاسة باستخدام تقنية NFC
يعمل نظام التشغيل Android 15 على تحسين تجربة الدفع بدون تلامس الأجهزة وجعلها أكثر سلاسة وموثوقية، مع مواصلة توفير منظومة التطبيقات المتكاملة لتقنية NFC القوية في Android. على
الأجهزة المتوافقة، يمكن للتطبيقات أن تطلب من NfcAdapter الدخول إلى
وضع المراقبة، حيث يستمع الجهاز إلى قراء
NFC ولكنه لا يستجيب لهم، ويرسل خدمة NFC الخاصة بالتطبيق PollingFrame
العناصر لمعالجتها. يمكن استخدام عناصر PollingFrame لمنح الإذن
قبل إجراء عملية التواصل الأولى مع قارئ NFC، ما يتيح إجراء معاملة
بنقرة واحدة في العديد من الحالات.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكن للتطبيقات تسجيل فلتر على الأجهزة المتوافقة لكي تتم إعلامها بنشاط حلقة الاستطلاع، ما يتيح التشغيل السلس مع تطبيقات متعددة متوافقة مع NFC.
دور المحفظة
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 15 دور "محفظة" يتيح دمجًا أكثر انسجامًا مع تطبيق المحفظة المفضّل لدى المستخدم. ويحلّ هذا الدور محلّ إعداد الدفع بدون تلامس الأجهزة التلقائي عبر تقنية NFC. يمكن للمستخدمين إدارة حامل دور "محفظة Google" من خلال الانتقال إلى الإعدادات > التطبيقات > التطبيقات التلقائية.
يتم استخدام دور "محفظة Google" عند توجيه عمليات النقر باستخدام تقنية NFC لأرقام تعريف العملاء المسجّلة في فئة الدفع. يتم دائمًا توجيه النقرات إلى حامل دور "محفظة Google" ما لم يكن هناك تطبيق آخر مسجَّل للمعرّف الإعلاني نفسه قيد التشغيل في المقدّمة.
ويُستخدَم هذا الدور أيضًا لتحديد مكان مربّع "الوصول السريع" في "محفظة Google" عند تفعيله. عند ضبط الدور على "بدون"، لا يكون مربّع "الوصول السريع" متاحًا ولا يتم إرسال نقرات NFC الخاصة بفئة الدفع إلا إلى التطبيق الذي يعمل في المقدّمة.
الأمان
يساعدك نظام التشغيل Android 15 في تعزيز أمان تطبيقك وحماية بياناته، كما يتيح للمستخدمين المزيد من الشفافية والتحكّم في بياناتهم. يمكنك مشاهدة جلسة الحفاظ على أمان المستخدمين على Android من مؤتمر Google I/O للتعرّف على المزيد من الإجراءات التي نتّخذها لتحسين وسائل حماية المستخدمين وحماية تطبيقك من التهديدات الجديدة.
دمج Credential Manager مع ميزة "الملء التلقائي"
بدءًا من الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android، يمكن للمطوّرين ربط طرق عرض معيّنة، مثل حقل اسم المستخدم أو حقل كلمة المرور بطلبات "مدير بيانات الاعتماد"، ما يسهّل تقديم تجربة مخصّصة للمستخدم أثناء عملية تسجيل الدخول. عندما يركز المستخدم على أحد هذه العروض، يتم إرسال طلب مقابل إلى مدير بيانات الاعتماد. يتم تجميع بيانات الاعتماد الناتجة على مستوى جميع مقدّمي الخدمات وعرضها في واجهات مستخدم النسخ الاحتياطي لملء البيانات تلقائيًا، مثل الاقتراحات المضمّنة أو الاقتراحات في القوائم المنسدلة. مكتبة Jetpack androidx.credentials هي نقطة النهاية المفضّلة للمطوّرين لاستخدامها، وستتوفّر قريبًا لتحسين هذه الميزة بشكلٍ أكبر في Android 15 والإصدارات الأحدث.
دمج ميزة "نقرة واحدة لتسجيل الدخول أو إنشاء حساب" مع طلبات المقاييس الحيوية
مدير بيانات الاعتماد يدمج طلبات المقاييس الحيوية في إنشاء بيانات الاعتماد وتسجيل الدخول، ما يغنيك عن حاجة مقدّمي الخدمات إلى إدارة طلبات المقاييس الحيوية. نتيجةً لذلك، ما على موفّري بيانات الاعتماد سوى التركيز على نتائج مسارات الإنشاء والحصول، بالإضافة إلى نتيجة مسار البيانات الحيوية. توفّر هذه العملية المبسّطة بيانات اعتماد أكثر كفاءة وسلاسة. عملية الإنشاء والاسترجاع.
إدارة المفاتيح للتشفير التام بين الأطراف
نقدّم E2eeContactKeysManager في Android 15، وهو تنسيق ملف يسهّل التشفير التام بين الأطراف (E2EE) في تطبيقات Android من خلال توفير واجهة برمجة تطبيقات على مستوى نظام التشغيل لتخزين المفاتيح العامة للتشفير.
تم تصميم E2eeContactKeysManager للدمج مع تطبيق
جهات الاتصال في النظام الأساسي لمنح المستخدمين طريقة مركزية لإدارة مفاتيحهم المفتوحة
لجهات الاتصال وإثبات ملكيتها.
عمليات التحقّق من الأذونات على معرّفات الموارد المنتظمة للمحتوى
يقدّم الإصدار 15 من Android مجموعة من واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تُجري عمليات التحقّق من الأذونات في عناوين محتوى URI:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: يؤدي هذا الإجراء إلى التحقّق من الأذونات بالكامل في معرّفات الموارد المنتظمة للمحتوى.Activityسمة البيانrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: تفرض هذه السمة أذونات محدّدة على معرّفات الموارد المنتظمة للمحتوى المقدّمة عند بدء النشاط.- فئة
ComponentCallerلمُتصليActivity: يمثّل هذا التطبيق الذي بدأ النشاط.
تسهيل الاستخدام
يضيف Android 15 ميزات تعمل على تحسين إمكانية الوصول للمستخدمين.
تحسينات على لغة برايل
في الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android، أصبح بإمكان TalkBack إتاحة استخدام شاشات برايل التي تستخدم معيار HID عبر USB وBluetooth الآمن.
سيساعد هذا المعيار، مثل المعيار المستخدَم في الفئران ولوحات المفاتيح، نظام Android على إتاحة نطاق أوسع من أجهزة العرض بلغة برايل بمرور الوقت.
التوافق مع أسواق عالمية
يضيف Android 15 ميزات وإمكانات تكمل تجربة المستخدم عند استخدام الجهاز بلغات مختلفة.
خط CJK متغيّر
اعتبارًا من الإصدار 15 من Android، أصبح ملف الخط NotoSansCJK المخصّص للغات الصينية واليابانية والكورية (CJK) خطًا متغيّرًا. توفّر الخطوط المتغيّرة إمكانيات لتصميمات الطباعة الإبداعية بلغات CJK. يمكن للمصمّمين استكشاف مجموعة أوسع من الأنماط وإنشاء تنسيقات مميّزة من الناحية المرئية كانت في السابق صعبة أو مستحيلة.

ضبط المسافات بين الأحرف
بدءًا من الإصدار 15 من Android، يمكن ضبط النص على الاتّجاه الأيمن باستخدام ميزة "محوّر المسافة بين الأحرف" من خلال
استخدام JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. كان التبرير بين الكلمات
تم تقديمه لأول مرة في Android 8.0 (المستوى 26 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، وبين الأحرف
التبرير إمكانات مماثلة للغات التي تستخدم
حرف المسافة البيضاء للتقسيم، مثل الصينية واليابانية وغيرها.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTERإعدادات فاصل الأسطر التلقائي
بدأ Android في إتاحة فواصل الأسطر المستندة إلى العبارة باللغتين اليابانية والكورية
Android 13 (المستوى 33) ومع ذلك، وبينما تعمل فواصل الأسطر المستندة إلى عبارة على تحسين
لسهولة قراءة السطور القصيرة من النص، فإنها لا تعمل بشكل جيد مع الأسطر الطويلة من النص.
في Android 15، يمكن للتطبيقات تطبيق فواصل الأسطر المستندة إلى العبارة على الأسطر القصيرة فقط.
من النص، باستخدام LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
. يحدد هذا الخيار أفضل خيار نمط كلمة للنص.
بالنسبة إلى الأسطر القصيرة من النص، يتم استخدام فواصل الأسطر المستندة إلى العبارة، وتعمل بالطريقة نفسها
كـ LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE، كما هو موضح في
الصورة التالية:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
يطبق فواصل الأسطر المستندة إلى العبارة لتحسين سهولة قراءة النص.
هذا مماثل لتطبيق
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.بالنسبة إلى أسطر النص الأطول، يستخدم LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO نمط كلمات بدون
فاصل سطر، ويعمل بالطريقة نفسها التي يعمل بها
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE، كما هو موضّح في
الصورة التالية:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
عدم تطبيق أي نمط من أنماط الكلمات بفواصل أسطر لتحسين إمكانية قراءة النص.
هذا مماثل لتطبيق
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.خط إضافي للغة اليابانية Hentaigana
في نظام التشغيل Android 15، ملف خط للهيرغانا اليابانية القديمة (المعروفة باسم Hentaigana) بشكل افتراضي. يمكن للأشكال الفريدة لأحرف الهينتيجانا إضافة طابعًا مميزًا للأعمال الفنية أو التصميم، مع المساعدة أيضًا في الحفاظ على دقة انتقال وفهم الوثائق اليابانية القديمة.

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. يمكن لأي شخص استخدام هذا الشعار أو نسخة معدَّلة منه أو تعديله للإشارة إلى مشروع VideoLAN أو أي منتج طوَّره فريق VideoLAN، ولكن لا يشير ذلك إلى موافقة المشروع.
Vulkan وشعار Vulkan علامتان تجاريتان مسجّلتان لشركة Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL هي علامة تجارية مسجّلة وشعار OpenGL ES هو علامة تجارية تابعة للشركة Hewlett Packard Enterprise وتستخدمها شركة Khronos بموجب إذن.

