Android 15 incluye excelentes funciones y APIs para desarrolladores. En las siguientes secciones, se resumen estas funciones para ayudarte a comenzar a usar las APIs relacionadas.
Para obtener una lista detallada de las APIs agregadas, modificadas y quitadas, consulta el informe de diferencias de la API. Para obtener detalles sobre las APIs agregadas, consulta la referencia de la API de Android. En Android 15, busca las APIs que se agregaron en el nivel de API 35. Para conocer las áreas en las que los cambios de la plataforma podrían afectar tus apps, asegúrate de revisar los cambios en el comportamiento de Android 15 para apps orientadas a Android 15 y para todas las apps.
Cámara y contenido multimedia
Android 15 incluye una variedad de funciones que mejoran la experiencia de la cámara y los medios, y que te brindan acceso a herramientas y hardware para ayudar a los creadores a hacer realidad su visión en Android.
Para obtener más información sobre las funciones y soluciones para desarrolladores más recientes de la cámara y el contenido multimedia de Android, consulta la charla Building modern Android media and camera experiences de Google I/O.
Mejora con poca luz
Android 15 presenta Mejora de poca luz, un modo de exposición automática disponible para Camera 2 y la extensión de cámara del modo nocturno. La mejora con poca luz ajusta la exposición de la transmisión de vista previa en condiciones de poca luz. Esto es diferente de la forma en que la extensión de cámara del modo nocturno crea imágenes fijas, ya que el modo nocturno combina una ráfaga de fotos para crear una sola imagen mejorada. Si bien el modo nocturno funciona muy bien para crear una imagen fija, no puede crear una transmisión continua de fotogramas, pero el modo de mejora con poca luz sí puede hacerlo. Por lo tanto, el modo de poca luz habilita las siguientes funciones de la cámara:
- Proporciona una vista previa de imagen mejorada para que los usuarios puedan encuadrar mejor sus fotos con poca luz.
- Cómo escanear códigos QR con poca luz
Si habilitas la función de mejora de poca luz, esta se activa automáticamente cuando hay un nivel de luz bajo y se desactiva cuando hay más luz.
Las apps pueden grabar desde la transmisión de vista previa en condiciones de poca luz para guardar un video más brillante.
Para obtener más información, consulta Aumento de poca luz.
Controles de cámara en la app
Android 15 adds an extension for more control over the camera hardware and its algorithms on supported devices:
- Advanced flash strength adjustments enabling precise control of flash
intensity in both
SINGLEandTORCHmodes while capturing images.
Control de espacio libre de HDR
Android 15 chooses HDR headroom that is appropriate for the underlying device
capabilities and bit-depth of the panel. For pages that have lots of SDR
content, such as a messaging app displaying a single HDR thumbnail, this
behavior can end up adversely influencing the perceived brightness of the SDR
content. Android 15 lets you control the HDR headroom with
setDesiredHdrHeadroom to strike a balance between SDR
and HDR content.
Control de volumen

Android 15 introduces support for the CTA-2075 loudness standard to help you avoid audio loudness inconsistencies and ensure users don't have to constantly adjust volume when switching between content. The system leverages known characteristics of the output devices (headphones and speaker) along with loudness metadata available in AAC audio content to intelligently adjust the audio loudness and dynamic range compression levels.
To enable this feature, you need to ensure loudness metadata is available in
your AAC content and enable the platform feature in your app. For this, you
instantiate a LoudnessCodecController object by
calling its create factory method with the audio
session ID from the associated AudioTrack; this
automatically starts applying audio updates. You can pass an
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener to modify or filter
loudness parameters before they are applied on the
MediaCodec.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer will also be updated to use the
LoudnessCodecController APIs for a seamless app integration.
Dispositivos MIDI 2.0 virtuales
Android 13 added support for connecting to MIDI 2.0 devices using USB, which communicate using Universal MIDI Packets (UMP). Android 15 extends UMP support to virtual MIDI apps, enabling composition apps to control synthesizer apps as a virtual MIDI 2.0 device just like they would with an USB MIDI 2.0 device.
Decodificación de software AV1 más eficiente

dav1d, the popular AV1 software decoder from VideoLAN is available for Android devices that don't support AV1 decode in hardware. dav1d is up to 3x more performant than the legacy AV1 software decoder, enabling HD AV1 playback for more users, including some low and mid tier devices.
Your app needs to opt-in to using dav1d by invoking it by name
"c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". dav1d will be made the default AV1 software
decoder in a subsequent update. This support is standardized and backported to
Android 11 devices that receive Google Play system updates.
Productividad y herramientas para desarrolladores
Si bien la mayor parte de nuestro trabajo para mejorar tu productividad se centra en herramientas como Android Studio, Jetpack Compose y las bibliotecas de Android Jetpack, siempre buscamos formas de ayudarte a hacer realidad tu visión con mayor facilidad en la plataforma.
Actualizaciones de OpenJDK 17
Android 15 continues the work of refreshing Android's core libraries to align with the features in the latest OpenJDK LTS releases.
The following key features and improvements are included:
- Quality-of-life improvements around NIO buffers
- Streams
- Additional
mathandstrictmathmethods utilpackage updates including sequencedcollection,map, andsetByteBuffersupport inDeflater- Security updates such as
X500PrivateCredentialand security key updates
These APIs are updated on over a billion devices running Android 12 (API level 31) and higher through Google Play System updates, so you can target the latest programming features.
Mejoras en PDF
Android 15 incluye mejoras sustanciales en las APIs de PdfRenderer. Las apps pueden incorporar funciones avanzadas, como la renderización de archivos protegidos por contraseña, las anotaciones, la edición de formularios, la búsqueda y la selección con copia. Se admiten optimizaciones de PDF linealizados para acelerar la visualización de PDF local y reducir el uso de recursos.
La biblioteca de PDF de Jetpack usa estas APIs para simplificar la adición de funciones de visualización de PDF a tu app.
Se trasladó PdfRenderer a un módulo que se puede actualizar con Google.
Las actualizaciones del sistema de Play son independientes
de la versión de la plataforma,
estos cambios a Android 11 (nivel de API 30) mediante la creación de una versión
versión de la plataforma de API anterior a Android 15, llamada
PdfRendererPreV
Mejoras en el cambio automático de idioma
Android 14 added on-device, multi-language recognition in audio with automatic
switching between languages, but this can cause words to get dropped,
especially when languages switch with less of a pause between the two
utterances. Android 15 adds additional controls to help apps tune this switching
to their use case.
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS
confines the automatic switching to the beginning of the audio session, while
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES deactivates the
language switching after a defined number of switches. These options are
particularly useful if you expect that there will be a single language spoken
during the session that should be autodetected.
Se mejoró la API de fuentes variables de OpenType
Android 15 mejora la usabilidad de la fuente variable OpenType. Puedes crear
una instancia de FontFamily a partir de una fuente variable sin especificar los ejes de grosor
con la API de buildVariableFamily. El renderizador de texto anula el valor del eje wght para que coincida con el texto que se muestra.
El uso de la API simplifica considerablemente el código para crear un Typeface:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
Anteriormente, para crear el mismo Typeface, necesitabas mucho más código:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Este es un ejemplo de cómo se creó un objeto Typeface con la API anterior y la nueva.
renderiza:
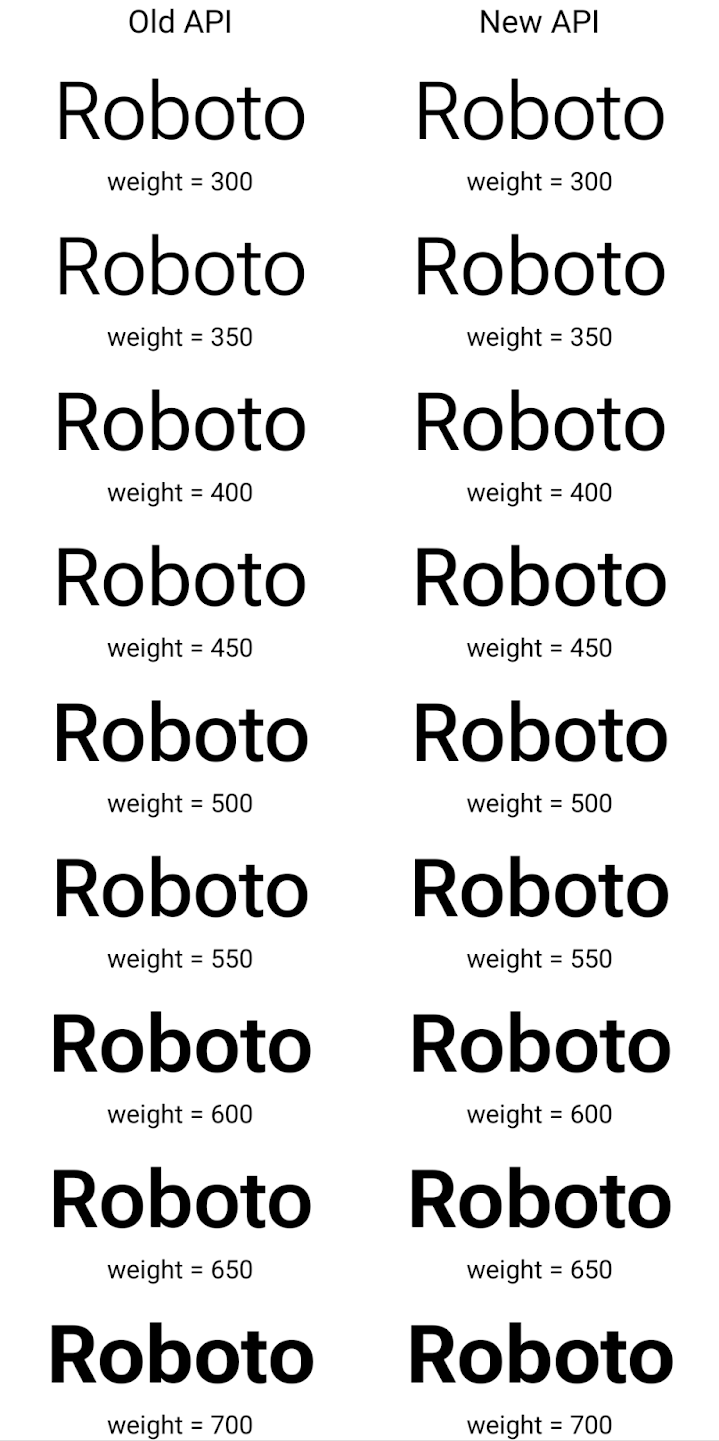
En este ejemplo, el Typeface creado con la API anterior no tiene la capacidad de crear grosores de fuente precisos para las instancias de Font de 350, 450, 550 y 650, por lo que el renderizador recurre al grosor más cercano. Por lo tanto, en este caso, se renderiza 300 en lugar de 350, 400 en lugar de 450, etcétera. Por el contrario, el Typeface creado con las APIs nuevas crea de forma dinámica
una instancia de Font para una ponderación determinada, por lo que se procesan las ponderaciones precisas de 350
450, 550 y 650.
Controles detallados de saltos de línea
Starting in Android 15, a TextView and the underlying
line breaker can preserve the given portion of text in the same line to improve
readability. You can take advantage of this line break customization by using
the <nobreak> tag in string resources or
createNoBreakSpan. Similarly, you can preserve words from
hyphenation by using the <nohyphen> tag or
createNoHyphenationSpan.
For example, the following string resource doesn't include a line break, and renders with the text "Pixel 8 Pro." breaking in an undesirable place:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
In contrast, this string resource includes the <nobreak> tag, which wraps the
phrase "Pixel 8 Pro." and prevents line breaks:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
The difference in how these strings are rendered is shown in the following images:

<nobreak> tag.
<nobreak> tag.Archivado de apps
Android and Google Play announced support for app archiving last year, allowing users to free up space by partially removing infrequently used apps from the device that were published using Android App Bundle on Google Play. Android 15 includes OS level support for app archiving and unarchiving, making it easier for all app stores to implement it.
Apps with the REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES permission can call the
PackageInstaller requestArchive method to request archiving an
installed app package, which removes the APK and any cached files, but persists
user data. Archived apps are returned as displayable apps through the
LauncherApps APIs; users will see a UI treatment to highlight that those
apps are archived. If a user taps on an archived app, the responsible installer
will get a request to unarchive it, and the restoration process can be
monitored by the ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED broadcast.
Habilita el modo de 16 KB en un dispositivo con las opciones para desarrolladores
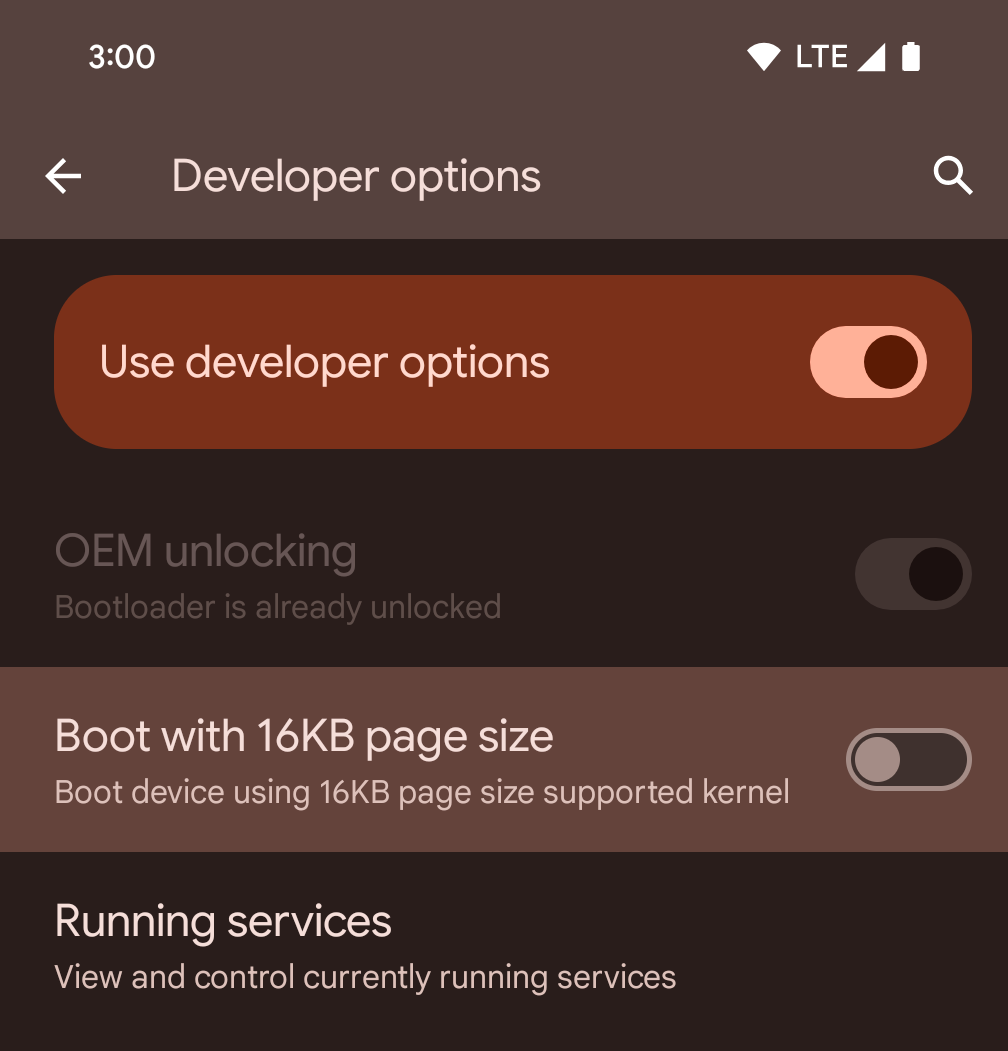
Activa la opción para desarrolladores Iniciar con tamaño de página de 16 KB para iniciar un dispositivo en el modo de 16 KB.
En las versiones de QPR de Android 15, puedes usar la opción para desarrolladores disponible en ciertos dispositivos para iniciar el dispositivo en modo de 16 KB y realizar pruebas en el dispositivo. Antes de usar la opción para desarrolladores, ve a Configuración > Sistema > Actualizaciones de software y aplica las actualizaciones disponibles.
Esta opción para desarrolladores está disponible en los siguientes dispositivos:
Pixel 8 y 8 Pro (con Android 15 QPR1 o versiones posteriores)
Pixel 8a (con Android 15 QPR1 o versiones posteriores)
Pixel 9, 9 Pro y 9 Pro XL (con Android 15 QPR2 o versiones posteriores)
Pixel 9a (con Android 16 o versiones posteriores)
Gráficos
Android 15 incluye las mejoras gráficas más recientes, como ANGLE y adiciones al sistema de gráficos de Canvas.
Modernización del acceso a la GPU de Android

Android hardware has evolved quite a bit from the early days where the core OS would run on a single CPU and GPUs were accessed using APIs based on fixed-function pipelines. The Vulkan® graphics API has been available in the NDK since Android 7.0 (API level 24) with a lower-level abstraction that better reflects modern GPU hardware, scales better to support multiple CPU cores, and offers reduced CPU driver overhead — leading to improved app performance. Vulkan is supported by all modern game engines.
Vulkan is Android's preferred interface to the GPU. Therefore, Android 15 includes ANGLE as an optional layer for running OpenGL® ES on top of Vulkan. Moving to ANGLE will standardize the Android OpenGL implementation for improved compatibility, and, in some cases, improved performance. You can test out your OpenGL ES app stability and performance with ANGLE by enabling the developer option in Settings -> System -> Developer Options -> Experimental: Enable ANGLE on Android 15.
The Android ANGLE on Vulkan roadmap
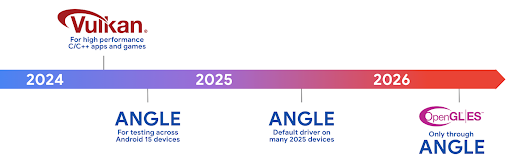
As part of streamlining our GPU stack, going forward we will be shipping ANGLE as the GL system driver on more new devices, with the future expectation that OpenGL/ES will be only available through ANGLE. That being said, we plan to continue support for OpenGL ES on all devices.
Recommended next steps
Use the developer options to select the ANGLE driver for OpenGL ES and test your app. For new projects, we strongly encourage using Vulkan for C/C++.
Mejoras en Canvas
Android 15 continúa con la modernización del sistema de gráficos Canvas de Android con las siguientes capacidades adicionales:
Matrix44proporciona una matriz 4x4 para transformar las coordenadas que se deben usar cuando deseas manipular el lienzo en 3D.clipShaderinterseca el clip actual con el sombreador especificado, mientras queclipOutShaderestablece el clip en la diferencia entre el clip actual y el sombreador, cada uno de los cuales trata el sombreador como una máscara alfa. Esto admite el dibujo de formas complejas de manera eficiente.
Rendimiento y batería
Android sigue enfocándose en ayudarte a mejorar el rendimiento y la calidad de tus apps. Android 15 introduce APIs que ayudan a que las tareas de tu app se ejecuten de manera más eficiente, optimizan el rendimiento de la app y recopilan estadísticas sobre tus apps.
Para conocer las prácticas recomendadas que permiten ahorrar batería, depurar el uso de la red y la energía, y obtener detalles sobre cómo mejoramos la eficiencia de la batería del trabajo en segundo plano en Android 15 y versiones recientes de Android, consulta la charla Improving battery efficiency of background work on Android (Cómo mejorar la eficiencia de la batería del trabajo en segundo plano en Android) de Google I/O.
API de ApplicationStartInfo
In previous versions of Android, app startup has been a bit of a mystery. It was
challenging to determine within your app whether it started from a cold, warm,
or hot state. It was also difficult to know how long your app spent during the
various launch phases: forking the process, calling onCreate, drawing the
first frame, and more. When your Application class was instantiated, you had no
way of knowing whether the app started from a broadcast, a content provider, a
job, a backup, boot complete, an alarm, or an Activity.
The ApplicationStartInfo API on Android 15 provides
all of this and more. You can even choose to add your own timestamps into the
flow to help collect timing data in one place. In addition to collecting
metrics, you can use ApplicationStartInfo to help directly optimize app
startup; for example, you can eliminate the costly instantiation of UI-related
libraries within your Application class when your app is starting up due to a
broadcast.
Información detallada sobre el tamaño de la app
Desde Android 8.0 (nivel de API 26), Android incluye la API de StorageStats.getAppBytes que resume el tamaño instalado de una app como un solo número de bytes, que es la suma del tamaño del APK, el tamaño de los archivos extraídos del APK y los archivos que se generaron en el dispositivo, como el código compilado por adelantado (AOT). Este número no es muy útil en términos de cómo tu app usa el almacenamiento.
Android 15 agrega la API de StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]), que te permite obtener estadísticas sobre cómo tu app usa todo ese espacio, incluidas las divisiones de archivos APK, el código relacionado con AOT y la aceleración, los metadatos de DEX, las bibliotecas y los perfiles guiados.
Creación de perfiles administrada por la app
Android 15 includes the ProfilingManager class,
which lets you collect profiling information from within your app such as heap
dumps, heap profiles, stack sampling, and more. It provides a callback to your
app with a supplied tag to identify the output file, which is delivered to your
app's files directory. The API does rate limiting to minimize the performance
impact.
To simplify constructing profiling requests in your app, we recommend using the
corresponding Profiling AndroidX API, available
in Core 1.15.0-rc01 or higher.
Mejoras en la base de datos SQLite
Android 15 presenta las APIs de SQLite que exponen funciones avanzadas del un motor SQLite subyacente que se dirija a problemas de rendimiento específicos que pueden en las apps. Estas APIs se incluyen con la actualización de SQLite a la versión 3.44.3
Los desarrolladores deben consultar las prácticas recomendadas para el rendimiento de SQLite para aprovechar al máximo su base de datos, en especial cuando trabajan con bases de datos grandes o cuando ejecutan consultas sensibles a la latencia.
- Transacciones diferidas de solo lectura: Cuando emitas transacciones de solo lectura (no incluyas instrucciones de escritura), usa
beginTransactionReadOnly()ybeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)para emitir transaccionesDEFERREDde solo lectura. Estas transacciones se pueden ejecutar de forma simultánea entre sí y, si la base de datos está en modo WAL, se pueden ejecutar de forma simultánea con transaccionesIMMEDIATEoEXCLUSIVE. - Recuento y IDs de filas: Se agregaron APIs para recuperar el recuento de filas modificadas o el ID de la última fila insertada sin emitir una consulta adicional.
getLastChangedRowCount()muestra la cantidad de filas que se insertaron, actualizaron o borraron mediante la instrucción de SQL más reciente en la transacción actual, mientras quegetTotalChangedRowCount()devuelve el recuento de la conexión actual.getLastInsertRowId()muestra elrowidde la última fila que se insertará en la conexión actual. - Sentencias sin procesar: Emite una sentencia SQlite sin procesar, omitiendo los wrappers de conveniencia y cualquier sobrecarga de procesamiento adicional que puedan generar.
Actualizaciones del framework de rendimiento dinámico de Android
Android 15 continúa nuestra inversión en el framework de rendimiento dinámico de Android (ADPF), un conjunto de APIs que permiten que los juegos y las apps de alto rendimiento interactúen de forma más directa con los sistemas térmicos y de alimentación de los dispositivos Android. En dispositivos compatibles, Android 15 agrega las siguientes funciones de ADPF:
- Un modo de eficiencia energética para las sesiones de sugerencias que indique que sus subprocesos asociados deben preferir el ahorro de energía en lugar del rendimiento, lo que es ideal para cargas de trabajo en segundo plano de larga duración.
- Las duraciones de trabajo de la GPU y la CPU se pueden informar en sesiones de sugerencias, lo que permite que el sistema ajuste las frecuencias de la CPU y la GPU en conjunto para satisfacer mejor las demandas de la carga de trabajo.
- Umbrales de margen térmico para interpretar posibles estados de limitación térmica en función de la predicción del margen.
Para obtener más información sobre cómo usar ADPF en tus apps y juegos, consulta la documentación.
Privacidad
Android 15 incluye una variedad de funciones que ayudan a los desarrolladores de apps a proteger la privacidad del usuario.
Detección de grabación de pantalla
Android 15 adds support for apps to detect that they are being recorded. A callback is invoked whenever the app transitions between being visible or invisible within a screen recording. An app is considered visible if activities owned by the registering process's UID are being recorded. This way, if your app is performing a sensitive operation, you can inform the user that they're being recorded.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
Capacidades ampliadas de IntentFilter
Android 15 builds in support for more precise Intent resolution through
UriRelativeFilterGroup, which contains a set of
UriRelativeFilter objects that form a set of Intent
matching rules that must each be satisfied, including URL query parameters, URL
fragments, and blocking or exclusion rules.
These rules can be defined in the AndroidManifest XML file with the
<uri-relative-filter-group> tag, which can optionally include an
android:allow tag. These tags can contain <data> tags that use existing data
tag attributes as well as the android:query and android:fragment
attributes.
Here's an example of the AndroidManifest syntax:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
Espacio privado
Private space lets users create a separate space on their device where they can keep sensitive apps away from prying eyes, under an additional layer of authentication. The private space uses a separate user profile. The user can choose to use the device lock or a separate lock factor for the private space.
Apps in the private space show up in a separate container in the launcher, and are hidden from the recents view, notifications, settings, and from other apps when the private space is locked. User-generated and downloaded content (such as media or files) and accounts are separated between the private space and the main space. The system sharesheet and the photo picker can be used to give apps access to content across spaces when the private space is unlocked.
Users can't move existing apps and their data into the private space. Instead, users select an install option in the private space to install an app using whichever app store they prefer. Apps in the private space are installed as separate copies from any apps in the main space (new copies of the same app).
When a user locks the private space, the profile is stopped. While the profile is stopped, apps in the private space are no longer active and can't perform foreground or background activities, including showing notifications.
We recommend that you test your app with private space to make sure your app works as expected, especially if your app falls into one of the following categories:
- Apps with logic for work profiles that assumes that any installed copies of their app that aren't in the main profile are in the work profile.
- Medical apps
- Launcher apps
- App store apps
Consultar la selección de usuario más reciente para el acceso a las fotos seleccionadas
Apps can now highlight only the most-recently-selected photos and videos when
partial access to media permissions is granted. This feature can improve
the user experience for apps that frequently request access to photos and
videos. To use this feature in your app, enable the
QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY argument when querying MediaStore
through ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
Privacy Sandbox en Android
Android 15 includes the latest Android Ad Services extensions, incorporating the latest version of the Privacy Sandbox on Android. This addition is part of our work to develop technologies that improve user privacy and enable effective, personalized advertising experiences for mobile apps. Our privacy sandbox page has more information about the Privacy Sandbox on Android developer preview and beta programs to help you get started.
Health Connect
Android 15 integra las extensiones más recientes de Health Connect de Android, una plataforma segura y centralizada para administrar y compartir datos de salud y fitness recopilados por la app. Esta actualización agrega compatibilidad con tipos de datos adicionales en estado físico, nutrición, temperatura cutánea, planes de entrenamiento y mucho más.
El seguimiento de la temperatura de la piel permite a los usuarios almacenar y compartir datos de temperatura más precisos desde un dispositivo wearable o algún otro dispositivo de seguimiento.
Los planes de entrenamiento son planes de entrenamiento estructurados para ayudar a un usuario a alcanzar sus objetivos de fitness. La compatibilidad con los planes de entrenamiento incluye una variedad de objetivos de finalización y rendimiento:
- Objetivos de finalización relacionados con las calorías quemadas, la distancia, la duración, la repetición y los pasos.
- Los objetivos de rendimiento muchas repeticiones como sea posible (AMRAP), cadencia, frecuencia cardíaca, alimentación, tasa percibida del esfuerzo y Velocidad.
Obtén más información sobre las actualizaciones más recientes de Health Connect en Android en la charla Cómo crear experiencias adaptables con Android Health de Google I/O.
Compartir pantalla de una app
Android 15 supports app screen sharing so users can share or record just an
app window rather than the entire device screen. This feature, first enabled in
Android 14 QPR2, includes
MediaProjection callbacks that allow your app
to customize the app screen sharing experience. Note that for apps targeting
Android 14 (API level 34) or higher,
user consent is required for each
MediaProjection capture session.
Experiencia del usuario y la IU del sistema
Android 15 brinda a los desarrolladores de apps y a los usuarios más control y flexibilidad para configurar sus dispositivos según sus necesidades.
Para obtener más información sobre cómo usar las mejoras más recientes de Android 15 para mejorar la experiencia del usuario de tu app, consulta la charla Mejora la experiencia del usuario de tu app para Android de Google I/O.
Vistas previas de widgets más completas con la API de Generated Previews
Before Android 15, the only way to provide widget picker previews was to specify a static image or layout resource. These previews often differ significantly from the look of the actual widget when it is placed on the home screen. Also, static resources can't be created with Jetpack Glance, so a Glance developer had to screenshot their widget or create an XML layout to have a widget preview.
Android 15 adds support for generated previews. This means that app widget
providers can generate RemoteViews to use as the picker preview, instead
of a static resource.
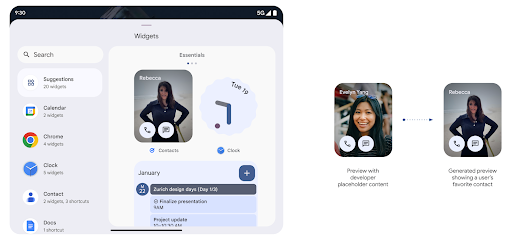
Push API
Apps can provide generated previews through a push API. Apps can provide
previews at any point in their lifecycle, and don't receive an explicit request
from the host to provide previews. Previews are persisted in AppWidgetService,
and hosts can request them on-demand. The following example loads an XML widget
layout resource and sets it as the preview:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
The expected flow is:
- At any time, the widget provider calls
setWidgetPreview. The provided previews are persisted inAppWidgetServicewith other provider info. setWidgetPreviewnotifies hosts of an updated preview through theAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChangedcallback. In response, the widget host reloads all of its provider information.- When displaying a widget preview, the host checks
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories, and if the chosen category is available, callsAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewto return the saved preview for this provider.
When to call setWidgetPreview
Because there is no callback to provide previews, apps can choose to send previews at any point when they are running. How often to update the preview depends on the widget's use case.
The following list describes the two main categories of preview use cases:
- Providers that show real data in their widget previews, such as personalized or recent information. These providers can set the preview once the user has signed in or has done initial configuration in their app. After this, they can set up a periodic task to update the previews at their chosen cadence. Examples of this type of widget could be a photo, calendar, weather or news widget.
- Providers that show static information in previews or quick-action widgets that don't display any data. These providers can set previews once, when the app first launches. Examples of this type of widget include a drive quick actions widget or chrome shortcuts widget.
Some providers might show static previews on the hub mode picker, but real information on the homescreen picker. These providers should follow the guidance for both of these use cases to set previews.
Pantalla en pantalla
Android 15 introduces changes in Picture-in-Picture (PiP) ensuring an even smoother transition when entering into PiP mode. This will be beneficial for apps having UI elements overlaid on top of their main UI, which goes into PiP.
Developers use the onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to define logic
that toggles the visibility of the overlaid UI elements. This callback is
triggered when the PiP enter or exit animation is completed. Beginning in
Android 15, the PictureInPictureUiState class includes another state.
With this UI state, apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) will observe the
Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback being invoked with
isTransitioningToPip() as soon as the PiP animation starts. There are
many UI elements that are not relevant for the app when it is in PiP mode, for
example views or layout that include information such as suggestions, upcoming
video, ratings, and titles. When the app goes to PiP mode, use the
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback to hide these UI elements. When the
app goes to full screen mode from the PiP window, use
onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to unhide these elements, as shown in
the following examples:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
This quick visibility toggle of irrelevant UI elements (for a PiP window) helps ensure a smoother and flicker-free PiP enter animation.
Reglas de No interrumpir mejoradas
AutomaticZenRule lets apps customize Attention
Management (Do Not Disturb) rules and decide when to activate or deactivate
them. Android 15 greatly enhances these rules with the goal of improving the
user experience. The following enhancements are included:
- Adding types to
AutomaticZenRule, allowing the system to apply special treatment to some rules. - Adding an icon to
AutomaticZenRule, helping to make the modes be more recognizable. - Adding a
triggerDescriptionstring toAutomaticZenRulethat describes the conditions on which the rule should become active for the user. - Added
ZenDeviceEffectstoAutomaticZenRule, allowing rules to trigger things like grayscale display, night mode, or dimming the wallpaper.
Cómo establecer VibrationEffect para los canales de notificación
Android 15 supports setting rich vibrations for incoming notifications by
channel using NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect, so
your users can distinguish between different types of notifications without
having to look at their device.
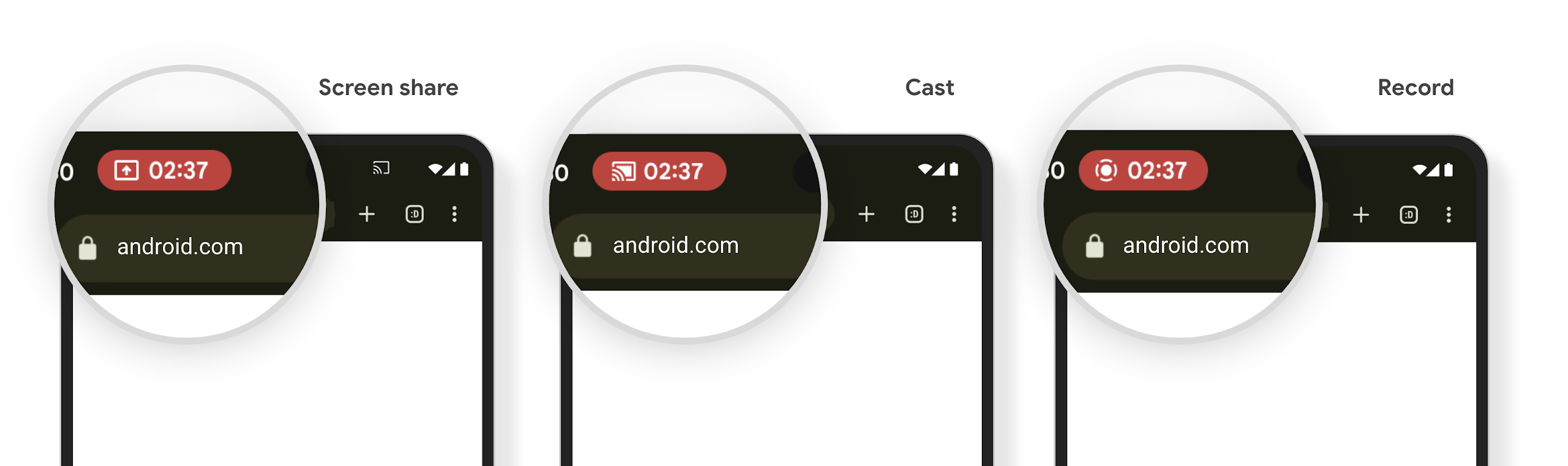
Chip de la barra de estado de proyección de contenido multimedia y detención automática
La proyección de contenido multimedia puede exponer información privada del usuario. Un nuevo chip de barra de estado prominente informa a los usuarios sobre cualquier proyección de pantalla en curso. Los usuarios pueden presionar el chip para detener la transmisión, el uso compartido o la grabación de la pantalla. Además, para brindar una experiencia del usuario más intuitiva, cualquier proyección de pantalla en curso ahora se detiene automáticamente cuando se bloquea la pantalla del dispositivo.
Pantallas grandes y factores de forma
Android 15 brinda a tus apps la compatibilidad necesaria para aprovechar al máximo los factores de forma de Android, incluidas las pantallas grandes, los dispositivos plegables y los que se pueden voltear.
Mejoras en la realización de tareas múltiples en pantallas grandes
Android 15 gives users better ways to multitask on large screen devices. For example, users can save their favorite split-screen app combinations for quick access and pin the taskbar on screen to quickly switch between apps. This means that making sure your app is adaptive is more important than ever.
Google I/O has sessions on Building adaptive Android apps and Building UI with the Material 3 adaptive library that can help, and our documentation has more to help you Design for large screens.
Compatibilidad con la pantalla de la cubierta
Your app can declare a property that Android 15 uses to
allow your Application or Activity to be presented on the small cover
screens of supported flippable devices. These screens are too small to be
considered as compatible targets for Android apps to run on, but your app can
opt in to supporting them, making your app available in more places.
Conectividad
Android 15 actualiza la plataforma para que tu app tenga acceso a los avances más recientes en tecnologías inalámbricas y de comunicación.
Compatibilidad con satélites
Android 15 continúa ampliando la compatibilidad de la plataforma con la conectividad satelital y, además, incluye algunos elementos de la IU para garantizar una experiencia del usuario coherente en todo el panorama de conectividad satelital.
Las apps pueden usar ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() para detectar cuándo un dispositivo está conectado a un satélite, lo que les permite saber por qué es posible que los servicios de red completos no estén disponibles. Además, Android 15 admite apps de SMS y MMS, así como apps de RCS precargadas para usar conectividad satelital para enviar y recibir mensajes.

Experiencias de NFC más fluidas
Android 15 is working to make the tap to pay experience more seamless and
reliable while continuing to support Android's robust NFC app ecosystem. On
supported devices, apps can request the NfcAdapter to enter
observe mode, where the device listens but doesn't respond to NFC
readers, sending the app's NFC service PollingFrame
objects to process. The PollingFrame objects can be used to auth
ahead of the first communication to the NFC reader, allowing for a one tap
transaction in many cases.
In addition, apps can register a filter on supported devices so they can be notified of polling loop activity, which allows for smooth operation with multiple NFC-aware applications.
Rol de la billetera
Android 15 presenta un rol de billetera que permite una integración más estrecha con la app de billetera preferida del usuario. Este rol reemplaza la configuración predeterminada de pago sin contacto de NFC. Los usuarios pueden administrar el titular del rol de la Billetera navegando a Configuración > Apps > Apps predeterminadas.
El rol de billetera se usa cuando se enrutan los toques NFC para los AID registrados en la categoría de pago. Los toques siempre se dirigen al titular del rol de la Billetera, a menos que otra app que esté registrada para el mismo AID se esté ejecutando en primer plano.
Este rol también se usa para determinar dónde debe ir la tarjeta de acceso rápido a la Billetera cuando se activa. Cuando el rol se establece en "Ninguno", la tarjeta de acceso rápido no está disponible y las presiones de NFC de la categoría de pago solo se entregan a la app en primer plano.
Seguridad
Android 15 te ayuda a mejorar la seguridad de tu app, proteger sus datos y brindarles a los usuarios más transparencia y control sobre sus datos. Para obtener más información sobre lo que estamos haciendo para mejorar las medidas de protección del usuario y proteger tu app contra nuevas amenazas, mira la charla Safeguarding user security on Android de Google I/O.
Cómo integrar Credential Manager con el autocompletado
Starting with Android 15, developers can link specific views like username or password fields with Credential Manager requests, making it easier to provide a tailored user experience during the sign-in process. When the user focuses on one of these views, a corresponding request is sent to Credential Manager. The resulting credentials are aggregated across providers and displayed in autofill fallback UIs, such as inline suggestions or drop-down suggestions. The Jetpack androidx.credentials library is the preferred endpoint for developers to use and will soon be available to further enhance this feature in Android 15 and higher.
Integra el acceso y el registro con un solo toque con solicitudes biométricas
Credential Manager integrates biometric prompts into the credential creation and sign-in processes, eliminating the need for providers to manage biometric prompts. As a result, credential providers only need to focus on the results of the create and get flows, augmented with the biometric flow result. This simplified process creates a more efficient and streamlined credential creation and retrieval process.
Administración de claves para la encriptación de extremo a extremo
Presentamos E2eeContactKeysManager en Android 15, que facilita la encriptación de extremo a extremo (E2EE) en tus apps para Android, ya que proporciona una API a nivel del SO para el almacenamiento de claves públicas criptográficas.
E2eeContactKeysManager está diseñado para integrarse a la app de contactos de la plataforma y brindarles a los usuarios una forma centralizada de administrar y verificar las claves públicas de sus contactos.
Verificaciones de permisos en URIs de contenido
Android 15 presenta un conjunto de APIs que realizan verificaciones de permisos en los URIs de contenido:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: Realiza una verificación de permisos completa en los URIs de contenido.- Atributo del manifiesto
ActivityrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: Aplica permisos especificados en los URIs de contenido proporcionados al iniciar la actividad. - Clase
ComponentCallerpara los llamadores deActivity: Representa la app que inició la actividad.
Accesibilidad
Android 15 agrega funciones que mejoran la accesibilidad para los usuarios.
Mejoras en el braille
En Android 15, habilitamos que TalkBack admita pantallas braille que usan el estándar HID a través de USB y Bluetooth seguro.
Este estándar, al igual que el que usan los mouses y los teclados, ayudará a que Android admita una gama más amplia de pantallas braille con el tiempo.
Internacionalización
Android 15 agrega funciones y capacidades que complementan la experiencia del usuario cuando un dispositivo se usa en diferentes idiomas.
Fuente variable CJK
Starting with Android 15, the font file for Chinese, Japanese, and Korean (CJK) languages, NotoSansCJK, is now a variable font. Variable fonts open up possibilities for creative typography in CJK languages. Designers can explore a broader range of styles and create visually striking layouts that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve.

Justificación entre caracteres
Starting with Android 15, text can be justified utilizing letter spacing by
using JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. Inter-word justification was
first introduced in Android 8.0 (API level 26), and inter-character
justification provides similar capabilities for languages that use the
whitespace character for segmentation, such as Chinese, Japanese, and others.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.Configuración automática de saltos de línea
Android started supporting phrase-based line breaks for Japanese and Korean in
Android 13 (API level 33). However, while phrase-based line breaks improve the
readability of short lines of text, they don't work well for long lines of text.
In Android 15, apps can apply phrase-based line breaks only for short lines
of text, using the LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
option. This option selects the best word style option for the text.
For short lines of text, phrase-based line breaks are used, functioning the same
as LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, as shown in the
following image:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
applies phrase-based line breaks to improve the readability of the text.
This is the same as applying
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.For longer lines of text, LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO uses a no
line-break word style, functioning the same as
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, as shown in the
following image:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
applies no line-break word style to improve the readability of the text.
This is the same as applying
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.Fuente adicional de Hentaigana japonés
En Android 15, se incluyó un archivo de fuente para el antiguo hiragana japonés (conocido como Hentaigana). se agrupa de forma predeterminada. Las formas únicas de los caracteres hentaigana pueden agregar un estilo distintivo al material gráfico o al diseño, a la vez que ayudan a preservar la transmisión y la comprensión precisas de los documentos japoneses antiguos.

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. This logo or a modified version may be used or modified by anyone to refer to the VideoLAN project or any product developed by the VideoLAN team, but does not indicate endorsement by the project.
Vulkan and the Vulkan logo are registered trademarks of the Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL is a registered trademark and the OpenGL ES logo is a trademark of Hewlett Packard Enterprise used by permission by Khronos.
