يقدّم Android 15 ميزات وواجهات برمجة تطبيقات رائعة للمطوّرين. توضّح الأقسام التالية هذه الميزات لمساعدتك على البدء في استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات ذات الصلة.
للحصول على قائمة مفصّلة بواجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تمت إضافتها وتعديلها وإزالتها، يُرجى قراءة تقرير الاختلافات في واجهات برمجة التطبيقات. للحصول على تفاصيل حول واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المضافة، يُرجى الانتقال إلى مرجع واجهة برمجة تطبيقات Android. بالنسبة إلى Android 15، ابحث عن واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تمت إضافتها في المستوى 35 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات. للتعرّف على المجالات التي قد تؤثّر فيها تغييرات النظام الأساسي في تطبيقاتك، احرص على الاطّلاع على التغييرات في سلوك Android 15 للتطبيقات التي تستهدف Android 15 ولجميع التطبيقات.
الكاميرا والوسائط
يتضمّن Android 15 مجموعة متنوعة من الميزات التي تحسّن تجربة استخدام الكاميرا والوسائط، وتتيح لك الوصول إلى الأدوات والأجهزة التي تساعد صنّاع المحتوى في تنفيذ أفكارهم الإبداعية على Android.
لمزيد من المعلومات حول أحدث الميزات والحلول المتاحة للمطوّرين في ما يخص الوسائط والكاميرا على Android، يمكنك مشاهدة جلسة إنشاء تجارب حديثة في ما يخص الوسائط والكاميرا على Android من مؤتمر Google I/O.
تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة
يقدّم نظام التشغيل Android 15 ميزة تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة، وهو وضع للتعرّض التلقائي للضوء متاح في كلاً من الكاميرا 2 وإضافة "الوضع الليلي" في الكاميرا. تعمل ميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة" على تعديل مستوى تعريض المعاينة المباشرة للشاشة في ظروف الإضاءة المنخفضة. يختلف ذلك عن طريقة إنشاء الصور الثابتة من خلال إضافة الكاميرا في "الوضع الليلي"، لأنّ "الوضع الليلي" يجمع سلسلة من الصور لإنشاء صورة واحدة محسّنة. على الرغم من أنّ وضع "الإضاءة المنخفضة" يعمل بشكلٍ جيد جدًا لإنشاء صورة ثابتة، إلا أنّه لا يمكنه إنشاء بثٍ متواصلٍ من اللقطات، ولكن يمكن لميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة" فعل ذلك. وبالتالي، توفّر ميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة" ميزات كاميرا ، مثل:
- توفير معاينة محسّنة للصور، ما يتيح للمستخدمين ضبط عناصر الصور المنخفضة الإضاءة بشكلٍ أفضل
- مسح رموز الاستجابة السريعة ضوئيًا في الإضاءة المنخفضة
في حال تفعيل ميزة "تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة"، يتم تفعيلها تلقائيًا عند انخفاض مستوى الإضاءة، ويتم إيقافها عند زيادة الإضاءة.
يمكن للتطبيقات تسجيل فيديو من المعاينة المباشرة على الشاشة في ظروف الإضاءة المنخفضة لحفظه بدرجة سطوع أفضل.
لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى الاطّلاع على تحسين الإضاءة المنخفضة.
عناصر التحكّم في الكاميرا داخل التطبيق
Android 15 adds an extension for more control over the camera hardware and its algorithms on supported devices:
- Advanced flash strength adjustments enabling precise control of flash
intensity in both
SINGLEandTORCHmodes while capturing images.
التحكّم في مساحة HDR
Android 15 chooses HDR headroom that is appropriate for the underlying device
capabilities and bit-depth of the panel. For pages that have lots of SDR
content, such as a messaging app displaying a single HDR thumbnail, this
behavior can end up adversely influencing the perceived brightness of the SDR
content. Android 15 lets you control the HDR headroom with
setDesiredHdrHeadroom to strike a balance between SDR
and HDR content.

التحكّم في مستوى الصوت

Android 15 introduces support for the CTA-2075 loudness standard to help you avoid audio loudness inconsistencies and ensure users don't have to constantly adjust volume when switching between content. The system leverages known characteristics of the output devices (headphones and speaker) along with loudness metadata available in AAC audio content to intelligently adjust the audio loudness and dynamic range compression levels.
To enable this feature, you need to ensure loudness metadata is available in
your AAC content and enable the platform feature in your app. For this, you
instantiate a LoudnessCodecController object by
calling its create factory method with the audio
session ID from the associated AudioTrack; this
automatically starts applying audio updates. You can pass an
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener to modify or filter
loudness parameters before they are applied on the
MediaCodec.
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer will also be updated to use the
LoudnessCodecController APIs for a seamless app integration.
أجهزة MIDI 2.0 الافتراضية
Android 13 added support for connecting to MIDI 2.0 devices using USB, which communicate using Universal MIDI Packets (UMP). Android 15 extends UMP support to virtual MIDI apps, enabling composition apps to control synthesizer apps as a virtual MIDI 2.0 device just like they would with an USB MIDI 2.0 device.
فك ترميز برامج AV1 بشكل أكثر فعالية

dav1d, the popular AV1 software decoder from VideoLAN is available for Android devices that don't support AV1 decode in hardware. dav1d is up to 3x more performant than the legacy AV1 software decoder, enabling HD AV1 playback for more users, including some low and mid tier devices.
Your app needs to opt-in to using dav1d by invoking it by name
"c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". dav1d will be made the default AV1 software
decoder in a subsequent update. This support is standardized and backported to
Android 11 devices that receive Google Play system updates.
إنتاجية المطوّرين وأدواتهم
مع أنّ معظم جهودنا لتحسين إنتاجيتك تركّز على أدوات مثل استوديو Android وJetpack Compose ومكتبات Android Jetpack، نسعى دائمًا إلى إيجاد طرق في المنصة لمساعدتك في تحقيق أهدافك بسهولة أكبر.
تعديلات OpenJDK 17
يواصل نظام التشغيل Android 15 العمل على إعادة تحميل المكتبات الأساسية لنظام التشغيل Android لمواءمتها مع الميزات في أحدث إصدارات OpenJDK LTS.
في ما يلي الميزات والتحسينات الرئيسية:
- تحسينات على مستوى الأداء في ما يتعلّق بمخازن NIO
- البث المباشر
- طرق
mathوstrictmathالإضافية - تحديثات حِزم
util، بما في ذلك الحِزم التي تتضمّن تسلسلاًcollectionوmapوset - إتاحة
ByteBufferفيDeflater - تحديثات الأمان، مثل
X500PrivateCredentialو تحديثات مفتاح الأمان
يتم تحديث واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه على أكثر من مليار جهاز يعمل بالإصدار 12 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 31 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأحدث من خلال تحديثات نظام Google Play، ما يتيح لك استخدام أحدث الميزات البرمجية.
تحسينات على ملفات PDF
يتضمن Android 15 تحسينات مهمة على PdfRenderer
واجهات برمجة التطبيقات. يمكن للتطبيقات دمج ميزات متقدّمة، مثل عرض
الملفات المحمية بكلمة مرور والتعليقات التوضيحية وتعديل النماذج
والبحث والاختيار مع النسخ. ملف PDF بتنسيق المساواة بين نقاط الاتصال
يتم دعم التحسينات لتسريع عرض ملفات PDF المحلية وتقليل استخدام الموارد.
تستخدم مكتبة ملفات PDF في Jetpack واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه لتسهيل عملية إضافة ملفات PDF.
إمكانيات العرض لتطبيقك.

تم نقل PdfRenderer إلى وحدة يمكن تحديثها باستخدام تحديثات نظام
Google Play بغض النظر عن إصدار النظام الأساسي، وسنوفّر
هذه التغييرات مرة أخرى لنظام التشغيل Android 11 (المستوى 30 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات) من خلال إنشاء إصدار متوافق
قبل Android 15 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات، والذي يُعرف باسم
PdfRendererPreV.
تحسينات على التبديل التلقائي للغات
أضاف نظام التشغيل Android 14 ميزة التعرّف على محتوى الصوت بعدّة لغات على الجهاز مع التبديل التلقائي بين اللغات، ولكن قد يؤدي ذلك إلى حذف كلمات، خاصةً عند التبديل بين اللغات بدون فترة راحة بين العبارة والعبارة الأخرى. يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 15 عناصر تحكّم إضافية لمساعدة التطبيقات في ضبط عملية التبديل هذه
حسب حالة الاستخدام.
يحدّد الخيار EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS
التبديل التلقائي ببداية جلسة الصوت، بينما يؤدي الخيار
EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES إلى إيقاف
تبديل اللغة بعد عدد محدّد من عمليات التبديل. تكون هذه الخيارات مفيدة بشكلٍ خاص إذا كنت تتوقّع أن يتم التحدّث بلغة واحدة
أثناء الجلسة التي من المفترض أن يتم رصدها تلقائيًا.
تحسين واجهة برمجة التطبيقات للخطوط المتغيّرة OpenType
Android 15 improves the usability of the OpenType variable font. You can create
a FontFamily instance from a variable font without specifying weight axes
with the buildVariableFamily API. The text renderer overrides the value
of wght axis to match the displaying text.
Using the API simplifies the code for creating a Typeface considerably:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
Previously, to create the same Typeface, you would need much more code:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
Here's an example of how a Typeface created with both the old and new APIs
renders:
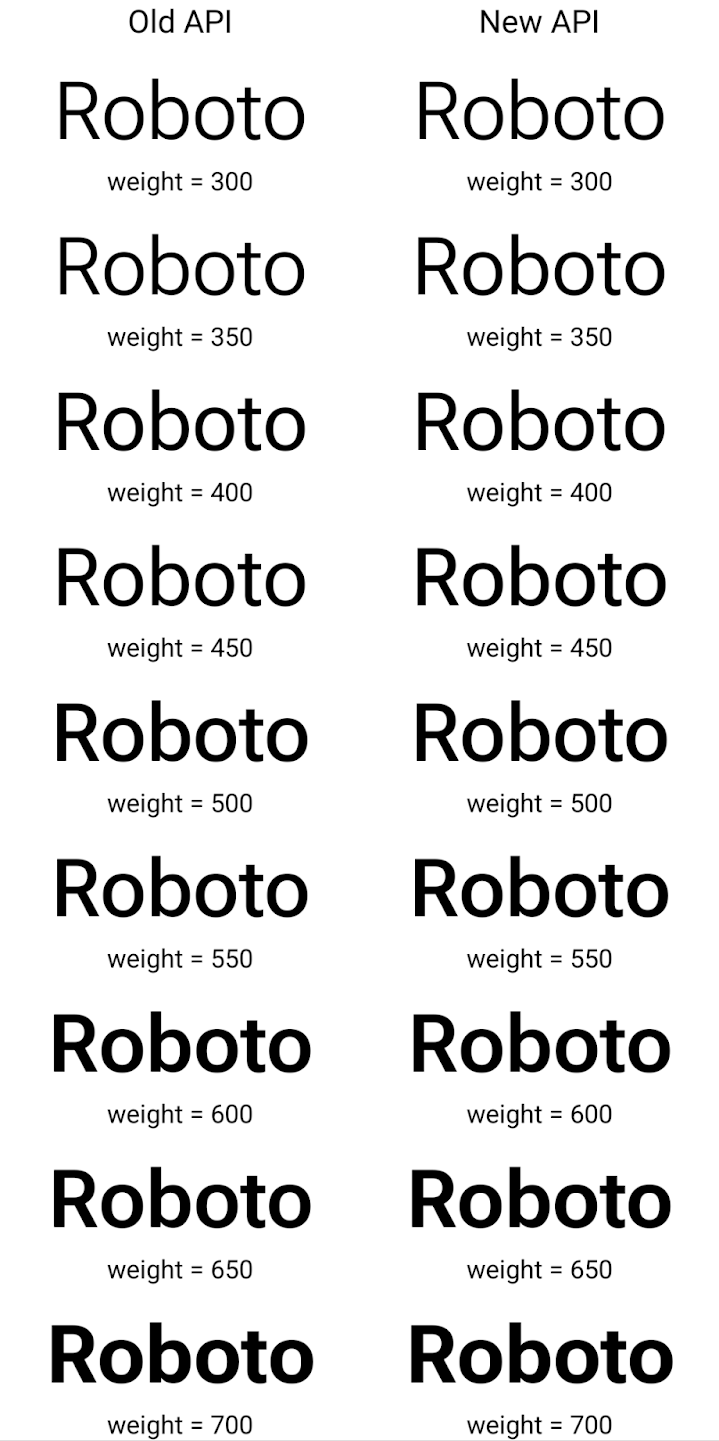
In this example, the Typeface created with the old API doesn't have the
capability to create accurate font weights for the 350, 450, 550 and 650
Font instances, so the renderer falls back to the closest weight. So in
this case, 300 is rendered instead of 350, 400 is rendered instead of 450, and
so on. By contrast, the Typeface created with the new APIs dynamically creates
a Font instance for a given weight, so accurate weights are rendered for 350,
450, 550, and 650 as well.
عناصر التحكّم الدقيقة في فواصل الأسطر
Starting in Android 15, a TextView and the underlying
line breaker can preserve the given portion of text in the same line to improve
readability. You can take advantage of this line break customization by using
the <nobreak> tag in string resources or
createNoBreakSpan. Similarly, you can preserve words from
hyphenation by using the <nohyphen> tag or
createNoHyphenationSpan.
For example, the following string resource doesn't include a line break, and renders with the text "Pixel 8 Pro." breaking in an undesirable place:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
In contrast, this string resource includes the <nobreak> tag, which wraps the
phrase "Pixel 8 Pro." and prevents line breaks:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
The difference in how these strings are rendered is shown in the following images:

<nobreak> tag.
<nobreak> tag.أرشفة التطبيقات
Android and Google Play announced support for app archiving last year, allowing users to free up space by partially removing infrequently used apps from the device that were published using Android App Bundle on Google Play. Android 15 includes OS level support for app archiving and unarchiving, making it easier for all app stores to implement it.
Apps with the REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES permission can call the
PackageInstaller requestArchive method to request archiving an
installed app package, which removes the APK and any cached files, but persists
user data. Archived apps are returned as displayable apps through the
LauncherApps APIs; users will see a UI treatment to highlight that those
apps are archived. If a user taps on an archived app, the responsible installer
will get a request to unarchive it, and the restoration process can be
monitored by the ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED broadcast.
تفعيل الوضع 16 كيلوبايت على جهاز باستخدام خيارات المطوّرين
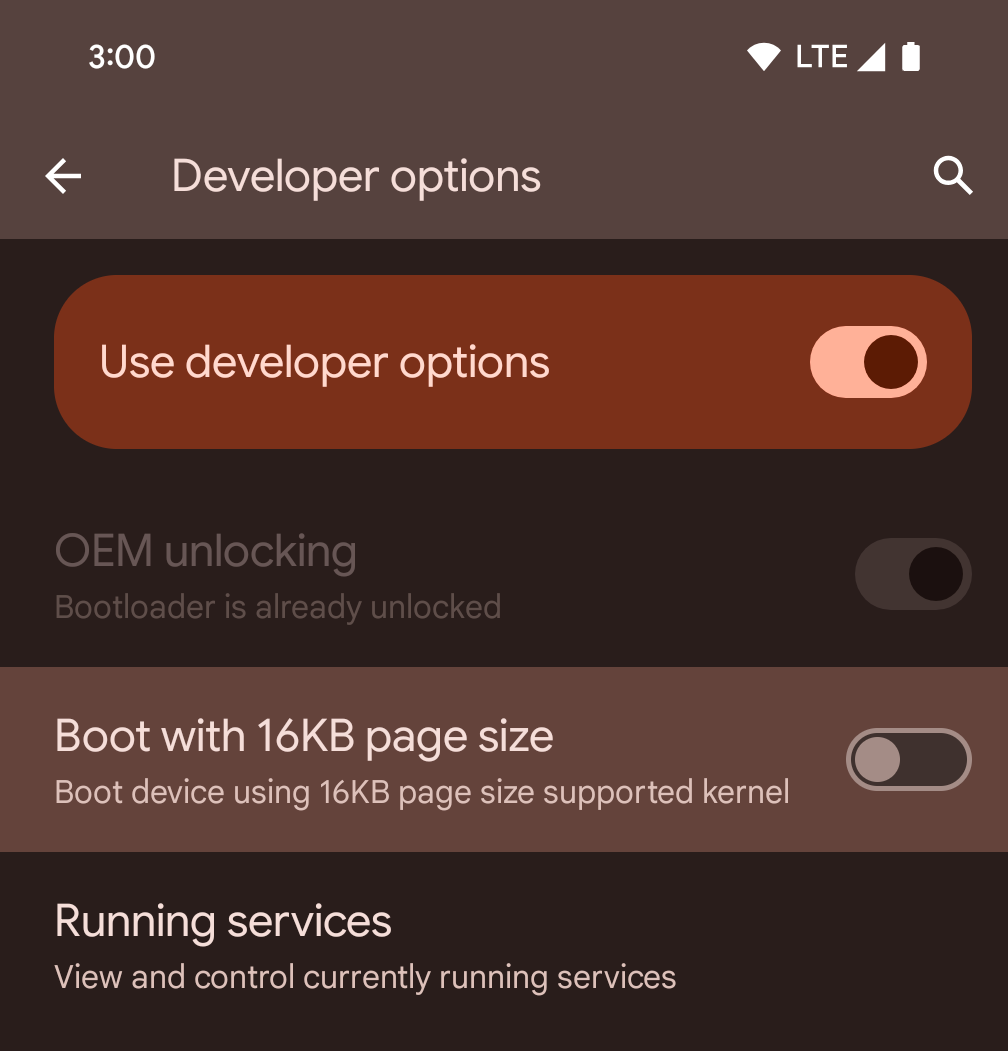
فعِّل خيار المطوّر التشغيل مع صفحات حجمها 16 كيلوبايت لتشغيل الجهاز في الوضع الذي يستخدم صفحات بحجم 16 كيلوبايت.
بدءًا من الإصدار 1 من حزمة الإصدارات التجريبية العامة (QPR1) لنظام التشغيل Android 15، يمكنك استخدام خيار المطوّرين المتاح على أجهزة معيّنة لتشغيل الجهاز في وضع 16 كيلوبايت وإجراء اختبار على الجهاز. قبل استخدام خيار المطوّرين، انتقِل إلى الإعدادات > النظام > تحديثات البرامج وطبِّق أي تحديثات متوفّرة.
يتوفّر خيار المطوّر هذا على الأجهزة التالية:
Pixel 8 وPixel 8 Pro (مع الإصدار 1 من حزمة إصلاح الأخطاء QPR لنظام التشغيل Android 15 أو إصدار أحدث)
Pixel 8a (مع الإصدار 1 من حزمة الإصدارات ربع السنوية لنظام Android 15 أو إصدار أحدث)
Pixel 9 وPixel 9 Pro وPixel 9 Pro XL (مع الإصدار التجريبي 2 من حزمة QPR2 لنظام التشغيل Android 15 أو إصدار أحدث)
الرسومات
يوفّر Android 15 أحدث التحسينات على الرسومات، بما في ذلك ANGLE وإضافات إلى نظام رسومات Canvas.
تحديث طريقة وصول Android إلى وحدة معالجة الرسومات

Android hardware has evolved quite a bit from the early days where the core OS would run on a single CPU and GPUs were accessed using APIs based on fixed-function pipelines. The Vulkan® graphics API has been available in the NDK since Android 7.0 (API level 24) with a lower-level abstraction that better reflects modern GPU hardware, scales better to support multiple CPU cores, and offers reduced CPU driver overhead — leading to improved app performance. Vulkan is supported by all modern game engines.
Vulkan is Android's preferred interface to the GPU. Therefore, Android 15 includes ANGLE as an optional layer for running OpenGL® ES on top of Vulkan. Moving to ANGLE will standardize the Android OpenGL implementation for improved compatibility, and, in some cases, improved performance. You can test out your OpenGL ES app stability and performance with ANGLE by enabling the developer option in Settings -> System -> Developer Options -> Experimental: Enable ANGLE on Android 15.
The Android ANGLE on Vulkan roadmap
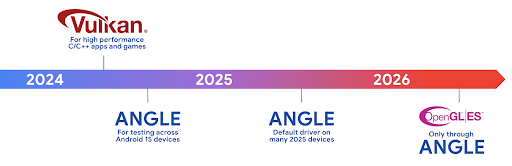
As part of streamlining our GPU stack, going forward we will be shipping ANGLE as the GL system driver on more new devices, with the future expectation that OpenGL/ES will be only available through ANGLE. That being said, we plan to continue support for OpenGL ES on all devices.
Recommended next steps
Use the developer options to select the ANGLE driver for OpenGL ES and test your app. For new projects, we strongly encourage using Vulkan for C/C++.
تحسينات على Canvas
يواصل نظام Android 15 جهودنا لتطوير نظام الرسومات Canvas في Android من خلال إضافة ميزات إضافية:
- يوفّر
Matrix44مصفوفة 4×4 لتحويل الإحداثيات التي يجب استخدامها عندما تريد التحكّم في اللوحة في المساحات الثلاثية الأبعاد. - يقاطع
clipShaderالمقطع الحالي بالshader المحدّد، في حين يضبطclipOutShaderالمقطع على اختلاف المقطع الحالي والshader، مع اعتبار كل منهما shader على أنّه قناع شفافية. يتيح ذلك رسم أشكال معقّدة بكفاءة.
الأداء والبطارية
يواصل نظام التشغيل Android التركيز على مساعدتك في تحسين أداء تطبيقاتك وجودتها. يقدِّم نظام التشغيل Android 15 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات تساعد في تنفيذ المهام في تطبيقك بكفاءة أكبر، وتحسين أداء التطبيق، وجمع إحصاءات حول تطبيقاتك.
للاطّلاع على أفضل الممارسات التي تساهم في الحفاظ على البطارية وتصحيح أخطاء استخدام الشبكة والطاقة والحصول على تفاصيل حول كيفية تحسين كفاءة البطارية عند تنفيذ العمل في الخلفية في نظام التشغيل Android 15 والإصدارات الحديثة من Android، يمكنك مشاهدة جلسة تحسين كفاءة البطارية عند تنفيذ العمل في الخلفية على Android من مؤتمر Google I/O.
ApplicationStartInfo API
In previous versions of Android, app startup has been a bit of a mystery. It was
challenging to determine within your app whether it started from a cold, warm,
or hot state. It was also difficult to know how long your app spent during the
various launch phases: forking the process, calling onCreate, drawing the
first frame, and more. When your Application class was instantiated, you had no
way of knowing whether the app started from a broadcast, a content provider, a
job, a backup, boot complete, an alarm, or an Activity.
The ApplicationStartInfo API on Android 15 provides
all of this and more. You can even choose to add your own timestamps into the
flow to help collect timing data in one place. In addition to collecting
metrics, you can use ApplicationStartInfo to help directly optimize app
startup; for example, you can eliminate the costly instantiation of UI-related
libraries within your Application class when your app is starting up due to a
broadcast.
معلومات مفصّلة عن حجم التطبيق
Since Android 8.0 (API level 26), Android has included the
StorageStats.getAppBytes API that summarizes the installed
size of an app as a single number of bytes, which is a sum of the APK size, the
size of files extracted from the APK, and files that were generated on the
device such as ahead-of-time (AOT) compiled code. This number is not very
insightful in terms of how your app is using storage.
Android 15 adds the
StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]) API, which lets
you get insight into how your app is using up all that space, including APK file
splits, AOT and speedup related code, dex metadata, libraries, and guided
profiles.
تحديد المواصفات الشخصية لصاحب البيانات من خلال التطبيق
يتضمّن Android 15 فئة ProfilingManager،
التي تتيح لك جمع معلومات الأداء من داخل تطبيقك، مثل ملف تفريغ ذاكرة heap
وملفات تعريف ذاكرة heap وتحليل تسلسل استدعاء الدوال البرمجية وغير ذلك. ويقدّم هذا الإجراء استدعاءً إلى
تطبيقك باستخدام علامة مقدَّمة لتحديد ملف الإخراج الذي يتم إرساله إلى دليل ملفات
تطبيقك. تفرض واجهة برمجة التطبيقات حدودًا على معدّل الإرسال لتقليل تأثير
الأداء.
لتبسيط إنشاء طلبات إنشاء ملفات شخصية في تطبيقك، ننصحك باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات المتوافقة مع Profiling AndroidX API، والمتوفّرة في الإصدار Core 1.15.0-rc01 أو الإصدارات الأحدث.
تحسينات على قاعدة بيانات SQLite
يوفّر Android 15 واجهات برمجة تطبيقات SQLite تتيح الميزات المتقدّمة من خلال أو محرك SQLite الأساسي الذي يستهدف مشكلات معينة في الأداء يمكن أن البيانات في التطبيقات. يتم تضمين واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه مع تحديث SQLite إلى الإصدار 3.44.3
على المطوّرين الرجوع إلى أفضل الممارسات لتحسين أداء SQLite للاستفادة إلى أقصى حد من قاعدة بيانات SQLite، خاصةً عند العمل مع قواعد بيانات كبيرة أو عند تنفيذ طلبات بحث حسّاسة للوقت المستغرَق في الاستجابة.
- المعاملات المؤجلة للقراءة فقط: عند إصدار معاملات
للقراءة فقط (لا تتضمّن عبارات كتابة)، استخدِم
beginTransactionReadOnly()وbeginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)لإصدار معاملاتDEFERREDللقراءة فقط. يمكن تنفيذ هذه المعاملات بالتزامن مع بعضها، وإذا كانت قاعدة البيانات في وضع WAL، يمكن تنفيذها بالتزامن مع معاملاتIMMEDIATEأوEXCLUSIVE. - أعداد الصفوف وأرقام التعريف: تمت إضافة واجهات برمجة التطبيقات لاسترداد عدد الصفوف التي تم تغييرها
أو رقم تعريف الصف الذي تم إدراجه مؤخرًا بدون إصدار طلب بحث إضافي.
تعرض
getLastChangedRowCount()عدد الصفوف التي قد تم إدراجها أو تحديثها أو حذفها من خلال أحدث عبارة SQL في المعاملة الحالية، في حين أنّgetTotalChangedRowCount()يعرض العدد على الاتصال الحالي. تعرض دالةgetLastInsertRowId()rowidللصف الأخير لإدراجه في الربط الحالي. - الكشوف الأولية: إصدار عبارة SQlite أولية لتجاوز سهولة الاستخدام والبرامج الأخرى وأي نفقات معالجة إضافية قد تتكبدها.
تحديثات "إطار عمل الأداء الديناميكي" في Android
يواصل الإصدار 15 من Android استثماراتنا في إطار عمل الأداء الديناميكي (ADPF) في Android، وهو مجموعة من واجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تتيح للألعاب والتطبيقات التي تتطلب أداءً عاليًا التفاعل بشكل مباشر أكثر مع أنظمة الطاقة والحرارة في أجهزة Android. على الأجهزة المتوافقة، يضيف نظام التشغيل Android 15 ميزات ADPF التالية:
- وضع توفير الطاقة لجلسات التلميح لتحديد أنّ سلاسل المحادثات المرتبطة بها يجب أن تفضّل توفير الطاقة على الأداء، وهو أمر رائع لأحمال العمل التي تعمل في الخلفية لفترة طويلة
- يمكن تسجيل مدّة عمل كلّ من وحدة معالجة الرسومات ووحدة المعالجة المركزية في جلسات التلميح، ما يسمح للنظام بتعديل معدّلات تكرار وحدة المعالجة المركزية ووحدة معالجة الرسومات معًا لتلبية متطلبات حمولة العمل على أفضل نحو.
- حدود الحد الأقصى للطاقة الحرارية لتفسير حالة الحد الأقصى للطاقة الحرارية المحتملة استنادًا إلى توقّعات الحد الأقصى للطاقة الحرارية
للاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات عن كيفية استخدام ميزة "الإعلانات الديناميكية على شبكة البحث" في تطبيقاتك وألعابك، يمكنك الانتقال إلى مستندات المساعدة.
الخصوصية
يتضمّن Android 15 مجموعة متنوّعة من الميزات التي تساعد مطوّري التطبيقات في حماية خصوصية المستخدمين.
رصد تسجيل الشاشة
يوفّر Android 15 إمكانية استخدام التطبيقات لرصد ما يلي: يتم تسجيلها. يتم استدعاء إجراء معاودة الاتصال عند انتقال التطبيق بين أن تكون مرئية أو غير مرئية ضمن تسجيل الشاشة. التطبيق عبارة عن تُعد مرئية إذا كانت الأنشطة التي يملكها المُعرّف الفريد لعملية التسجيل يتم تسجيلها. بهذه الطريقة، إذا كان تطبيقك يُجري عملية حسّاسة، يمكنك إبلاغ المستخدم بأنّه يتم تسجيله.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
إمكانيات IntentFilter الموسّعة
Android 15 builds in support for more precise Intent resolution through
UriRelativeFilterGroup, which contains a set of
UriRelativeFilter objects that form a set of Intent
matching rules that must each be satisfied, including URL query parameters, URL
fragments, and blocking or exclusion rules.
These rules can be defined in the AndroidManifest XML file with the
<uri-relative-filter-group> tag, which can optionally include an
android:allow tag. These tags can contain <data> tags that use existing data
tag attributes as well as the android:query and android:fragment
attributes.
Here's an example of the AndroidManifest syntax:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
المساحة الخاصة
تتيح "المساحة الخاصة" للمستخدمين إنشاء مساحة منفصلة على أجهزتهم للحفاظ على خصوصية التطبيقات الحسّاسة من خلال طبقة مصادقة إضافية. تستخدم المساحة الخاصة ملفًا شخصيًا منفصلاً للمستخدم. يمكن للمستخدم اختيار استخدام قفل الجهاز أو وسيلة قفل منفصلة للمساحة الخاصة.
تظهر التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة في حاوية منفصلة ضِمن مشغِّل التطبيقات، وتكون مخفية من العرض بين التطبيقات المستخدَمة مؤخرًا ومن الإشعارات والإعدادات والتطبيقات الأخرى عندما تكون المساحة الخاصة مقفلة. يتم توزيع المحتوى الذي ينشئه المستخدم والذي يتم تنزيله (مثل الوسائط أو الملفات) والحسابات الخاصة به بين المساحة الخاصّة وال المساحة الرئيسية. يمكن استخدام قائمة مشاركة البيانات و أداة اختيار الصور لتمكين التطبيقات من الوصول إلى المحتوى في المساحات المختلفة عندما يتم فتح قفل المساحة الخاصة.
لا يمكن للمستخدمين نقل التطبيقات الحالية وبياناتها إلى المساحة الخاصة. بدلاً من ذلك، يختار المستخدمون خيار تثبيت في المساحة الخاصة لتثبيت تطبيق باستخدام متجر التطبيقات المفضّل لديهم. يتم تثبيت التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة كنسخ منفصلة عن أي تطبيقات في المساحة الرئيسية (نُسخ جديدة من التطبيق نفسه).
عندما يقفل المستخدم المساحة الخاصة، يتم إيقاف الملف الشخصي. عندما يتم إيقاف الملف الشخصي، تتوقف التطبيقات في المساحة الخاصة عن العمل ولا يمكنها تنفيذ الأنشطة في المقدّمة أو الخلفية، بما في ذلك عرض الإشعارات.
ننصحك باختبار تطبيقك باستخدام المساحة الخاصة للتأكّد من أنّه يعمل بالشكل المتوقّع، خاصةً إذا كان تطبيقك يندرج ضمن إحدى الفئات التالية:
- التطبيقات التي تتضمّن منطقًا لملف العمل الذي يفترض أنّ أي نُسخ مثبَّتة من تطبيقه غير المضمّنة في الملف الشخصي الرئيسي تكون في ملف العمل
- التطبيقات الطبية
- تطبيقات مشغّل التطبيقات
- تطبيقات متجر التطبيقات
طلب آخر اختيار للمستخدم في ما يخصّ إذن الوصول إلى "الصور المحدّدة"
يمكن للتطبيقات الآن إبراز الصور والفيديوهات التي تم اختيارها مؤخرًا فقط عند منح التطبيقات
إذن وصول جزئي إلى أذونات الوصول إلى الوسائط. يمكن أن تحسِّن هذه الميزة
تجربة المستخدم للتطبيقات التي تطلب الوصول إلى الصور
والفيديوهات بشكل متكرر. لاستخدام هذه الميزة في تطبيقك، فعِّل الوسيطة
QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY عند طلب MediaStore
من خلال ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
"مبادرة حماية الخصوصية" على Android
Android 15 includes the latest Android Ad Services extensions, incorporating the latest version of the Privacy Sandbox on Android. This addition is part of our work to develop technologies that improve user privacy and enable effective, personalized advertising experiences for mobile apps. Our privacy sandbox page has more information about the Privacy Sandbox on Android developer preview and beta programs to help you get started.
Health Connect
يدمج نظام التشغيل Android 15 أحدث الإضافات المتعلقة بتطبيق Health Connect من Android، وهو منصّة آمنة ومتمركزة لإدارة بيانات الصحة واللياقة البدنية التي تجمعها التطبيقات ومشاركتها. يتيح هذا التعديل استخدام أنواع بيانات إضافية في ما يتعلّق باللياقة البدنية والتغذية ودرجة حرارة الجلد وخطط التدريب وغير ذلك.
تتيح ميزة تتبُّع درجة حرارة الجلد للمستخدمين تخزين بيانات دترة حرارة أكثر دقة ومشاركتها من جهاز قابل للارتداء أو جهاز تتبُّع آخر.
الخطط التدريبية هي خطط تمارين منظمة لمساعدة المستخدم في تحقيق أهدافه المتعلّقة باللياقة البدنية. يتضمّن دعم الخطط التدريبية مجموعة متنوعة من أهداف الإنجاز والأداء:
- أهداف الإنجاز المتعلّقة بعدد السعرات الحرارية المحروقة، المسافة، والمدة، عدد التكرارات، والخطوات
- أهداف الأداء حول أكبر عدد ممكن من التكرارات (AMRAP)، الوتيرة، معدل ضربات القلب، القوة، معدل الجهد المبذول، السرعة
يمكنك الاطّلاع على مزيد من المعلومات حول آخر التحديثات التي أُجريت على Health Connect في Android من خلال إنشاء تجارب استخدام قابلة للتكيّف باستخدام Android معلومات حول الصحة من مؤتمر Google I/O
مشاركة شاشة التطبيق
Android 15 supports app screen sharing so users can share or record just an
app window rather than the entire device screen. This feature, first enabled in
Android 14 QPR2, includes
MediaProjection callbacks that allow your app
to customize the app screen sharing experience. Note that for apps targeting
Android 14 (API level 34) or higher,
user consent is required for each
MediaProjection capture session.
تجربة المستخدم وواجهة مستخدم النظام
يمنح نظام التشغيل Android 15 مطوّري التطبيقات والمستخدمين المزيد من التحكّم والمرونة في إعداد أجهزتهم بما يتناسب مع احتياجاتهم.
لمزيد من المعلومات حول كيفية استخدام أحدث التحسينات في Android 15 لتحسين تجربة المستخدم في تطبيقك، يمكنك الاطّلاع على جلسة تحسين تجربة المستخدم في تطبيق Android من مؤتمر Google I/O.
معاينات تطبيقات مصغّرة أكثر تفصيلاً باستخدام Generated Previews API
Before Android 15, the only way to provide widget picker previews was to specify a static image or layout resource. These previews often differ significantly from the look of the actual widget when it is placed on the home screen. Also, static resources can't be created with Jetpack Glance, so a Glance developer had to screenshot their widget or create an XML layout to have a widget preview.
Android 15 adds support for generated previews. This means that app widget
providers can generate RemoteViews to use as the picker preview, instead
of a static resource.
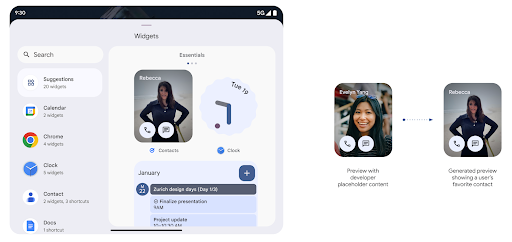
Push API
Apps can provide generated previews through a push API. Apps can provide
previews at any point in their lifecycle, and don't receive an explicit request
from the host to provide previews. Previews are persisted in AppWidgetService,
and hosts can request them on-demand. The following example loads an XML widget
layout resource and sets it as the preview:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
The expected flow is:
- At any time, the widget provider calls
setWidgetPreview. The provided previews are persisted inAppWidgetServicewith other provider info. setWidgetPreviewnotifies hosts of an updated preview through theAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChangedcallback. In response, the widget host reloads all of its provider information.- When displaying a widget preview, the host checks
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories, and if the chosen category is available, callsAppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewto return the saved preview for this provider.
When to call setWidgetPreview
Because there is no callback to provide previews, apps can choose to send previews at any point when they are running. How often to update the preview depends on the widget's use case.
The following list describes the two main categories of preview use cases:
- Providers that show real data in their widget previews, such as personalized or recent information. These providers can set the preview once the user has signed in or has done initial configuration in their app. After this, they can set up a periodic task to update the previews at their chosen cadence. Examples of this type of widget could be a photo, calendar, weather or news widget.
- Providers that show static information in previews or quick-action widgets that don't display any data. These providers can set previews once, when the app first launches. Examples of this type of widget include a drive quick actions widget or chrome shortcuts widget.
Some providers might show static previews on the hub mode picker, but real information on the homescreen picker. These providers should follow the guidance for both of these use cases to set previews.
نافذة ضمن النافذة
Android 15 introduces changes in Picture-in-Picture (PiP) ensuring an even smoother transition when entering into PiP mode. This will be beneficial for apps having UI elements overlaid on top of their main UI, which goes into PiP.
Developers use the onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to define logic
that toggles the visibility of the overlaid UI elements. This callback is
triggered when the PiP enter or exit animation is completed. Beginning in
Android 15, the PictureInPictureUiState class includes another state.
With this UI state, apps targeting Android 15 (API level 35) will observe the
Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback being invoked with
isTransitioningToPip() as soon as the PiP animation starts. There are
many UI elements that are not relevant for the app when it is in PiP mode, for
example views or layout that include information such as suggestions, upcoming
video, ratings, and titles. When the app goes to PiP mode, use the
onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged callback to hide these UI elements. When the
app goes to full screen mode from the PiP window, use
onPictureInPictureModeChanged callback to unhide these elements, as shown in
the following examples:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
This quick visibility toggle of irrelevant UI elements (for a PiP window) helps ensure a smoother and flicker-free PiP enter animation.
قواعد محسّنة لميزة "عدم الإزعاج"
AutomaticZenRule lets apps customize Attention
Management (Do Not Disturb) rules and decide when to activate or deactivate
them. Android 15 greatly enhances these rules with the goal of improving the
user experience. The following enhancements are included:
- Adding types to
AutomaticZenRule, allowing the system to apply special treatment to some rules. - Adding an icon to
AutomaticZenRule, helping to make the modes be more recognizable. - Adding a
triggerDescriptionstring toAutomaticZenRulethat describes the conditions on which the rule should become active for the user. - Added
ZenDeviceEffectstoAutomaticZenRule, allowing rules to trigger things like grayscale display, night mode, or dimming the wallpaper.
ضبط VibrationEffect لقنوات الإشعارات
Android 15 supports setting rich vibrations for incoming notifications by
channel using NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect, so
your users can distinguish between different types of notifications without
having to look at their device.
شريحة شريط الحالة لعرض الوسائط والإيقاف التلقائي
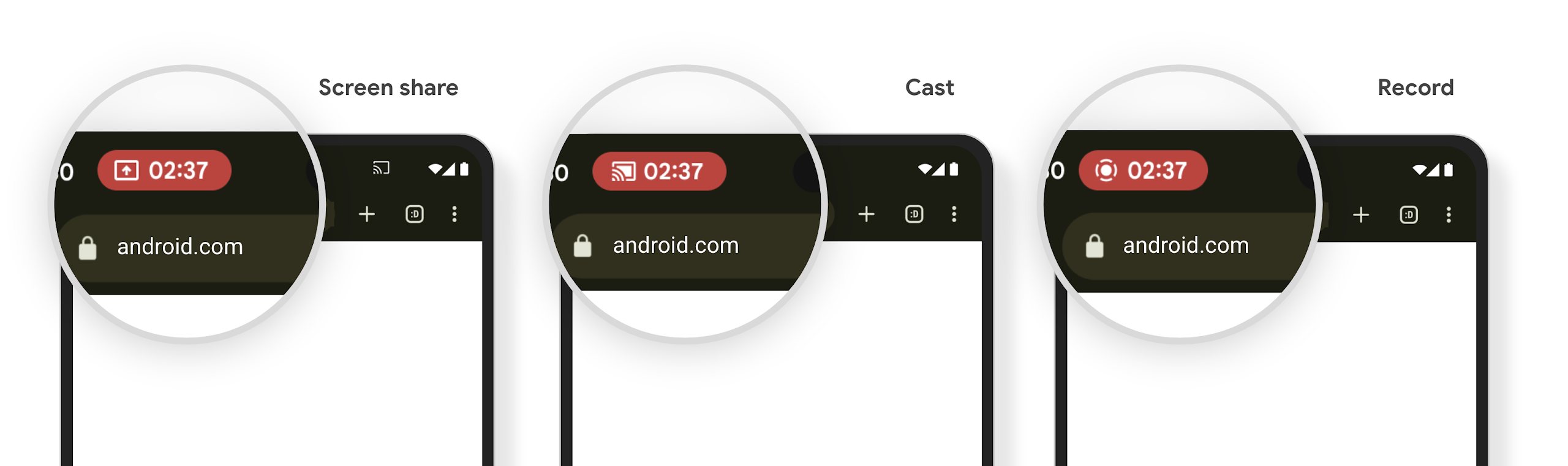
Media projection can expose private user information. A new, prominent status bar chip makes users aware of any ongoing screen projection. Users can tap the chip to stop screen casting, sharing, or recording. Also, for a more intuitive user experience, any in‑progress screen projection now automatically stops when the device screen is locked.
الشاشات الكبيرة وأشكال الأجهزة
يوفّر نظام التشغيل Android 15 لتطبيقاتك إمكانية الاستفادة إلى أقصى حدّ من أشكال أجهزة Android، بما في ذلك الشاشات الكبيرة والأجهزة القابلة للطي والقلب.
تحسين تعدُّد المهام على الشاشات الكبيرة
يوفّر Android 15 للمستخدمين طرقًا أفضل لتنفيذ مهام متعددة على الأجهزة ذات الشاشات الكبيرة. بالنسبة يمكن للمستخدمين مثلاً حفظ مجموعات التطبيقات المفضّلة لديهم في "وضع تقسيم الشاشة" للحصول على الوصول إلى شريط التطبيقات وتثبيته على الشاشة للتبديل بسرعة بين التطبيقات. وهذا يعني أنّ التأكّد من توافق تطبيقك مع الأجهزة المختلفة بات أكثر أهمية من أي وقت مضى.
جلسات مؤتمر Google I/O حول تصميم Android التكيُّفي التطبيقات وواجهة مستخدم المبنى باستخدام Material 3 المكتبة التكيّفية التي يمكن أن تساعدك، كما توفر مستنداتنا المزيد من المساعدة لتصميم مواقع الشاشات
إمكانية استخدام الشاشة الخارجية
Your app can declare a property that Android 15 uses to
allow your Application or Activity to be presented on the small cover
screens of supported flippable devices. These screens are too small to be
considered as compatible targets for Android apps to run on, but your app can
opt in to supporting them, making your app available in more places.
إمكانية الاتصال
يعدّل Android 15 النظام الأساسي لمنح تطبيقك إمكانية الوصول إلى أحدث التطورات في تكنولوجيات الاتصال والشبكات اللاسلكية.
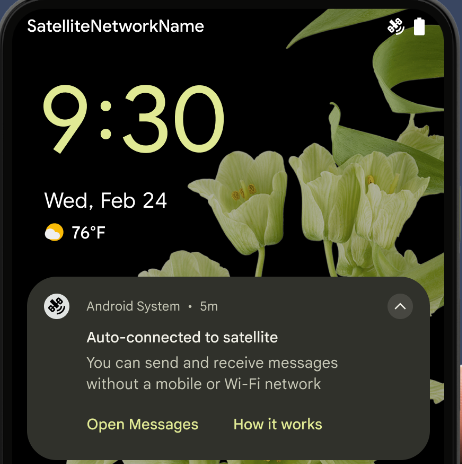
التوافق مع الأقمار الصناعية
Android 15 continues to extend platform support for satellite connectivity and includes some UI elements to ensure a consistent user experience across the satellite connectivity landscape.
Apps can use ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() to
detect when a device is connected to a satellite, giving them more awareness of
why full network services might be unavailable. Additionally, Android 15
provides support for SMS and MMS apps as well as preloaded RCS apps to use
satellite connectivity for sending and receiving messages.
تجارب أكثر سلاسة باستخدام تقنية NFC
يعمل نظام التشغيل Android 15 على تحسين تجربة الدفع بدون تلامس الأجهزة وجعلها أكثر سلاسة وموثوقية، مع مواصلة توفير منظومة التطبيقات المتكاملة لتقنية NFC القوية في Android. على
الأجهزة المتوافقة، يمكن للتطبيقات أن تطلب من NfcAdapter الدخول إلى
وضع المراقبة، حيث يستمع الجهاز إلى قراء
NFC ولكنه لا يستجيب لهم، ويرسل خدمة NFC الخاصة بالتطبيق PollingFrame
العناصر لمعالجتها. يمكن استخدام عناصر PollingFrame لمنح الإذن
قبل إجراء عملية التواصل الأولى مع قارئ NFC، ما يتيح إجراء معاملة
بنقرة واحدة في العديد من الحالات.
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكن للتطبيقات تسجيل فلتر على الأجهزة المتوافقة لكي تتم إعلامها بنشاط حلقة الاستطلاع، ما يتيح التشغيل السلس مع تطبيقات متعددة متوافقة مع NFC.
دور المحفظة
Android 15 introduces a Wallet role that allows tighter integration with the user's preferred wallet app. This role replaces the NFC default contactless payment setting. Users can manage the Wallet role holder by navigating to Settings > Apps > Default Apps.
The Wallet role is used when routing NFC taps for AIDs registered in the payment category. Taps always go to the Wallet role holder unless another app that is registered for the same AID is running in the foreground.
This role is also used to determine where the Wallet Quick Access tile should go when activated. When the role is set to "None", the Quick Access tile isn't available and payment category NFC taps are only delivered to the foreground app.
الأمان
يساعدك نظام التشغيل Android 15 في تعزيز أمان تطبيقك وحماية بياناته، كما يتيح للمستخدمين المزيد من الشفافية والتحكّم في بياناتهم. يمكنك مشاهدة جلسة الحفاظ على أمان المستخدمين على Android من مؤتمر Google I/O للتعرّف على المزيد من الإجراءات التي نتّخذها لتحسين وسائل حماية المستخدمين وحماية تطبيقك من التهديدات الجديدة.
دمج Credential Manager مع ميزة "الملء التلقائي"
Starting with Android 15, developers can link specific views like username or password fields with Credential Manager requests, making it easier to provide a tailored user experience during the sign-in process. When the user focuses on one of these views, a corresponding request is sent to Credential Manager. The resulting credentials are aggregated across providers and displayed in autofill fallback UIs, such as inline suggestions or drop-down suggestions. The Jetpack androidx.credentials library is the preferred endpoint for developers to use and will soon be available to further enhance this feature in Android 15 and higher.
دمج ميزة "نقرة واحدة لتسجيل الدخول أو إنشاء حساب" مع طلبات المقاييس الحيوية
Credential Manager integrates biometric prompts into the credential creation and sign-in processes, eliminating the need for providers to manage biometric prompts. As a result, credential providers only need to focus on the results of the create and get flows, augmented with the biometric flow result. This simplified process creates a more efficient and streamlined credential creation and retrieval process.
إدارة المفاتيح للتشفير التام بين الأطراف
We are introducing the E2eeContactKeysManager in Android 15, which
facilitates end-to-end encryption (E2EE) in your Android apps by providing an
OS-level API for the storage of cryptographic public keys.
The E2eeContactKeysManager is designed to integrate with the platform
contacts app to give users a centralized way to manage and verify their
contacts' public keys.
عمليات التحقّق من الأذونات على معرّفات الموارد المنتظمة للمحتوى
Android 15 introduces a set of APIs that perform permission checks on content URIs:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: This performs a full permission check on content URIs.Activitymanifest attributerequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: This enforces specified permissions on the provided content URIs at activity launch.ComponentCallerclass forActivitycallers: This represents the app that launched the activity.
تسهيل الاستخدام
يضيف Android 15 ميزات تعمل على تحسين إمكانية الوصول للمستخدمين.
تحسينات على لغة برايل
في الإصدار 15 من نظام التشغيل Android، أصبح بإمكان TalkBack إتاحة استخدام شاشات برايل التي تستخدم معيار HID عبر USB وBluetooth الآمن.
سيساعد هذا المعيار، مثل المعيار المستخدَم في الفئران ولوحات المفاتيح، نظام Android على إتاحة نطاق أوسع من أجهزة العرض بلغة برايل بمرور الوقت.
التوافق مع أسواق عالمية
يضيف Android 15 ميزات وإمكانات تكمل تجربة المستخدم عند استخدام الجهاز بلغات مختلفة.
خط CJK متغيّر
اعتبارًا من الإصدار 15 من Android، أصبح ملف الخط NotoSansCJK المخصّص للغات الصينية واليابانية والكورية (CJK) خطًا متغيّرًا. توفّر الخطوط المتغيّرة إمكانيات لتصميمات الطباعة الإبداعية بلغات CJK. يمكن للمصمّمين استكشاف مجموعة أوسع من الأنماط وإنشاء تنسيقات مميّزة من الناحية المرئية كانت في السابق صعبة أو مستحيلة.

ضبط المسافات بين الأحرف
Starting with Android 15, text can be justified utilizing letter spacing by
using JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. Inter-word justification was
first introduced in Android 8.0 (API level 26), and inter-character
justification provides similar capabilities for languages that use the
whitespace character for segmentation, such as Chinese, Japanese, and others.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.إعدادات الفواصل التلقائية بين الأسطر
Android started supporting phrase-based line breaks for Japanese and Korean in
Android 13 (API level 33). However, while phrase-based line breaks improve the
readability of short lines of text, they don't work well for long lines of text.
In Android 15, apps can apply phrase-based line breaks only for short lines
of text, using the LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
option. This option selects the best word style option for the text.
For short lines of text, phrase-based line breaks are used, functioning the same
as LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, as shown in the
following image:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
applies phrase-based line breaks to improve the readability of the text.
This is the same as applying
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.For longer lines of text, LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO uses a no
line-break word style, functioning the same as
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, as shown in the
following image:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
applies no line-break word style to improve the readability of the text.
This is the same as applying
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.خط إضافي للغة اليابانية Hentaigana
In Android 15, a font file for old Japanese Hiragana (known as Hentaigana) is bundled by default. The unique shapes of Hentaigana characters can add a distinctive flair to artwork or design while also helping to preserve accurate transmission and understanding of ancient Japanese documents.

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. يمكن لأي شخص استخدام هذا الشعار أو نسخة معدَّلة منه أو تعديله للإشارة إلى مشروع VideoLAN أو أي منتج طوَّره فريق VideoLAN، ولكن لا يشير ذلك إلى موافقة المشروع.
Vulkan وشعار Vulkan علامتان تجاريتان مسجّلتان لشركة Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL هي علامة تجارية مسجّلة وشعار OpenGL ES هو علامة تجارية تابعة للشركة Hewlett Packard Enterprise وتستخدمها شركة Khronos بموجب إذن.

