Android 15 כולל תכונות וממשקי API מעולים למפתחים. בקטעים הבאים מופיע סיכום של התכונות האלה שיעזור לכם להתחיל להשתמש בממשקי ה-API שקשורים אליהן.
רשימה מפורטת של ממשקי API שנוספו, שונו או הוסרו מופיעה בדוח ההבדלים בין ממשקי ה-API. פרטים על ממשקי API שנוספו זמינים בהפניה ל-Android API. ב-Android 15, אפשר לחפש ממשקי API שנוספו ברמת API 35. כדי לקבל מידע על תחומים שבהם שינויים בפלטפורמה עשויים להשפיע על האפליקציות שלכם, כדאי לעיין בשינויים בהתנהגות ב-Android 15 באפליקציות שמיועדות ל-Android 15 ובכל האפליקציות.
מצלמה ומדיה
Android 15 כולל מגוון תכונות שמשפרות את חוויית השימוש במצלמה ובמדיה, ומעניקות לכם גישה לכלים ולחומרה שתומכים ביוצרים בהגשמת החזון שלהם ב-Android.
מידע נוסף על התכונות והפתרונות העדכניים למפתחים בנושא מדיה ומצלמה ב-Android זמין בשיחה Building modern Android media and camera experiences מ-Google I/O.
שיפור תנאי תאורה ירודים
ב-Android 15 נוספה התכונה שיפור התמונה בתאורה חלשה, מצב חשיפה אוטומטי שזמין גם ב-Camera 2 וגם בתוסף המצלמה של מצב לילה. התכונה 'הגברת התאורה החלשה' מכווננת את החשיפת הסטרימינג של התצוגה המקדימה בתנאים של תאורה חלשה. זה שונה מהאופן שבו התוסף של מצב הלילה במצלמה יוצר תמונות סטילס, כי במצב הלילה נעשה שימוש ברצף של תמונות כדי ליצור תמונה אחת משופרת. מצב לילה מתאים מאוד ליצירת תמונה סטילס, אבל אי אפשר ליצור בו שידור רציף של פריימים. לעומת זאת, התכונה 'שיפור תמונה בתאורה חלשה' מאפשרת לעשות זאת. לכן, התכונה 'שיפור איכות בתנאי תאורה חלשה' מאפשרת למצלמה לבצע פעולות כמו:
- הצגת תצוגה מקדימה משופרת של התמונות, כדי שהמשתמשים יוכלו לבחור מסגרת טובה יותר לתמונות שצולמו בתאורה חלשה
- סריקת קודי QR בתאורה חלשה
אם מפעילים את התכונה'הגברת התאורה החלשה', היא מופעלת באופן אוטומטי כשרמת התאורה נמוכה, ומושבתת כשיש יותר אור.
אפליקציות יכולות לצלם את מקור הווידאו של התצוגה המקדימה בתנאים של תאורה חלשה כדי לשמור סרטון בהיר יותר.
מידע נוסף זמין במאמר שיפור התמונה בתאורה נמוכה.
אמצעי בקרה למצלמה באפליקציה
ב-Android 15 נוספה תוספת שמאפשרת יותר שליטה בחומרה של המצלמה ובאלגוריתמים שלה במכשירים נתמכים:
- כוונונים מתקדמים של עוצמת הפלאש שמאפשרים לשלוט בצורה מדויקת בעוצמת הפלאש במצבים
SINGLEו-TORCHבזמן הצילום.
שליטה במרווח העליון של HDR
מערכת Android 15 בוחרת את מרווח ה-HDR שמתאים ליכולות המכשיר ולעומק הביטים של המסך. בדפים שיש בהם הרבה תוכן SDR, כמו אפליקציית הודעות שמציגה תמונה ממוזערת אחת ב-HDR, ההתנהגות הזו עלולה להשפיע לרעה על הבהירות של תוכן ה-SDR. ב-Android 15 אפשר לשלוט במרווח העליון של HDR באמצעות setDesiredHdrHeadroom כדי לשמור על איזון בין תוכן SDR לתוכן HDR.
בקרת עוצמת הקול

ב-Android 15 יש תמיכה בתקן עוצמת הקול CTA-2075, כדי למנוע אי-עקביות בעוצמת האודיו ולוודא שהמשתמשים לא יצטרכו לשנות את עוצמת הקול כל הזמן כשהם עוברים בין תכנים. המערכת משתמשת במאפיינים ידועים של התקני הפלט (אוזניות ורמקול) יחד עם מטא-נתונים של עוצמת קול שזמינים בתוכן אודיו בפורמט AAC, כדי לשנות בצורה חכמה את עוצמת הקול ואת רמות הדחיסה של טווח הדינמיקה של האודיו.
כדי להפעיל את התכונה הזו, צריך לוודא שהמטא-נתונים של עוצמת הקול זמינים
את תוכן ה-AAC ולהפעיל את תכונת הפלטפורמה באפליקציה. כדי לעשות את זה,
ליצור אובייקט LoudnessCodecController באמצעות
קוראים לו ליצור שיטת יצרן עם האודיו
מזהה סשן מ-AudioTrack המשויך. הזה
החלת עדכוני אודיו תופעל באופן אוטומטי. אפשר להעביר
OnLoudnessCodecUpdateListener כדי לשנות או לסנן
את הפרמטרים של עוצמת הקול לפני שהם מוחלים
MediaCodec
// Media contains metadata of type MPEG_4 OR MPEG_D
val mediaCodec = …
val audioTrack = AudioTrack.Builder()
.setSessionId(sessionId)
.build()
...
// Create new loudness controller that applies the parameters to the MediaCodec
try {
val lcController = LoudnessCodecController.create(mSessionId)
// Starts applying audio updates for each added MediaCodec
}
גם AndroidX media3 ExoPlayer יתעדכן כך שישתמש בממשקי ה-API של LoudnessCodecController לשילוב חלק של האפליקציות.
מכשירי MIDI וירטואליים 2.0
ב-Android 13 נוספה תמיכה בחיבור למכשירי MIDI 2.0 באמצעות USB, שמתקשרים באמצעות חבילות MIDI אוניברסליות (UMP). ב-Android 15 הורחבה התמיכה ב-UMP לאפליקציות MIDI וירטואליות, כך שאפליקציות ליצירת מוזיקה יכולות לשלוט באפליקציות סינתיסייזר כמכשיר MIDI 2.0 וירטואלי, בדיוק כמו שהן יכולות לשלוט במכשיר USB MIDI 2.0.
פענוח קוד יעיל יותר של תוכנת AV1

dav1d, מקודד התוכנה הפופולרי של AV1 מ-VideoLAN, זמין למכשירי Android שלא תומכים בפענוח AV1 בחומרה. הביצועים של dav1d טובים פי 3 מאלה של מקודד התוכנה הקודם של AV1, ומאפשרים להפעיל פורמט AV1 באיכות HD למשתמשים רבים יותר, כולל במכשירים מסוימים ברמה נמוכה ובינונית.
כדי להשתמש ב-dav1d, האפליקציה צריכה להביע הסכמה להפעלה שלו בשם "c2.android.av1-dav1d.decoder". בעדכון עתידי, dav1d יהפוך למפענח התוכנה המוגדר כברירת מחדל של AV1. התמיכה הזו סטנדרטית ומועברת לאחור למכשירי Android 11 שמקבלים עדכוני מערכת של Google Play.
פרודוקטיביות וכלים למפתחים
רוב העבודה שלנו לשיפור הפרודוקטיביות מתמקדת בכלים כמו Android Studio, Jetpack Compose וספריות Android Jetpack, אבל אנחנו תמיד מחפשים דרכים בפלטפורמה שיעזרו לכם להגשים את החזון שלכם בקלות רבה יותר.
עדכונים ל-OpenJDK 17
ב-Android 15 ממשיכים בתהליך הרענון של ספריות הליבה של Android, כדי להתאים אותן לתכונות בגרסאות ה-LTS האחרונות של OpenJDK.
התכונות והשיפורים העיקריים שכלולים בגרסה הזו:
- שיפורים באיכות החיים של מאגרי NIO
- Streams
- שיטות נוספות של
mathו-strictmath - עדכוני חבילות של
util, כוללcollection, mapו-set - תמיכה ב-
ByteBufferב-Deflater - עדכוני אבטחה כמו
X500PrivateCredentialועדכוני מפתחות אבטחה
ממשקי ה-API האלה מתעדכנים ביותר ממיליארד מכשירים עם Android 12 (רמת API 31) ואילך דרך עדכוני המערכת של Google Play, כך שתוכלו לטרגט לתכונות התכנות העדכניות ביותר.
שיפורים ב-PDF
Android 15 כולל שיפורים משמעותיים בPdfRenderer
ממשקי API. אפליקציות יכולות לכלול תכונות מתקדמות כמו עיבוד קבצים שמוגנים באמצעות סיסמה, הערות, עריכת טפסים, חיפוש ובחירה עם העתקה. יש תמיכה באופטימיזציה של קובצי PDF ליניאריים כדי לזרז את הצפייה ב-PDF מקומי ולצמצם את השימוש במשאבים.
אנחנו משתמשים בממשקי ה-API האלה בספריית ה-PDF של Jetpack כדי להוסיף קובצי PDF בקלות רבה יותר
יכולות צפייה באפליקציה שלך.
PdfRenderer הועבר למודול שאפשר לעדכן באמצעות עדכוני המערכת של Google Play, ללא קשר למהדורת הפלטפורמה. כדי לתמוך בשינויים האלה ב-Android 11 (רמת API 30), יצרנו גרסה תואמת של ממשק ה-API שתוכננה ל-Android 15 ואילך, שנקראת PdfRendererPreV.
שיפורים בהחלפת שפה אוטומטית
ב-Android 14 נוספה יכולת זיהוי אודיו בכמה שפות במכשיר, עם מעבר אוטומטי בין השפות. עם זאת, יכול להיות שהמילה לא תזוהה אם המעבר בין השפות קצר מדי. ב-Android 15 נוספו אמצעי בקרה נוספים שיעזרו לאפליקציות להתאים את המעבר הזה לתרחיש השימוש שלהן.
הערך EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_INITIAL_ACTIVE_DURATION_TIME_MILLIS מגביל את המעבר האוטומטי לתחילת סשן האודיו, ואילו הערך EXTRA_LANGUAGE_SWITCH_MATCH_SWITCHES משבית את המעבר בין השפות אחרי מספר מוגדר של מעברים. האפשרויות האלה שימושיות במיוחד אם אתם צופים שייאמר רק שפה אחת במהלך הסשן, ושצריך לזהות אותה באופן אוטומטי.
Improved OpenType Variable Font API
ב-Android 15 שיפרנו את נוחות השימוש בגופן המשתנה OpenType. אפשר ליצור
מופע FontFamily מגופן משתנה בלי לציין צירי משקל
באמצעות ממשק ה-API של buildVariableFamily. הכלי לרינדור הטקסט מבטל את הערך
של ציר wght כדי להתאים לטקסט המוצג.
השימוש ב-API מפשט באופן משמעותי את הקוד ליצירת Typeface:
Kotlin
val newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build()
Java
Typeface newTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf").build()) .buildVariableFamily()) .build();
בעבר, כדי ליצור את אותו Typeface, היה צורך בקוד הרבה יותר ארוך:
Kotlin
val oldTypeface = Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( FontFamily.Builder( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build()) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ).build() ).build()
Java
Typeface oldTypeface = new Typeface.CustomFallbackBuilder( new FontFamily.Builder( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 400") .setWeight(400) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 100") .setWeight(100) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 200") .setWeight(200) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 300") .setWeight(300) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 500") .setWeight(500) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 600") .setWeight(600) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 700") .setWeight(700) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 800") .setWeight(800) .build() ) .addFont( new Font.Builder(assets, "RobotoFlex.ttf") .setFontVariationSettings("'wght' 900") .setWeight(900) .build() ) .build() ).build();
דוגמה לאופן שבו Typeface שנוצר באמצעות ה-API הישן והחדש מומר:
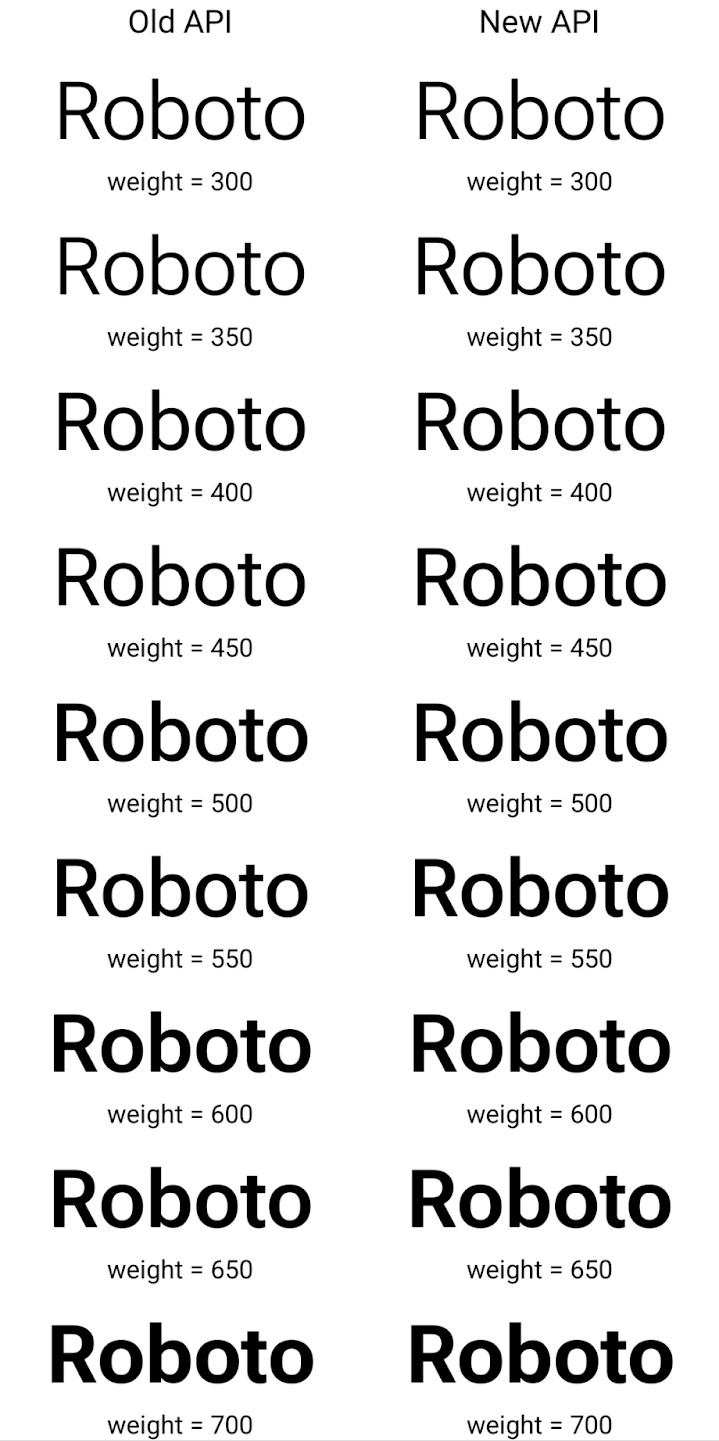
בדוגמה הזו, ה-Typeface שנוצר באמצעות ה-API הישן לא כולל את
יכולת ליצור משקלים מדויקים של גופנים עבור 350, 450, 550 ו-650
מופעים של Font, כך שהכלי לרינדור חוזר למשקל הקרוב ביותר. לכן במקרה הזה, 300 יומר במקום 350, 400 יומר במקום 450 וכן הלאה. לעומת זאת, ה-Typeface שנוצר באמצעות ממשקי ה-API החדשים יוצר באופן דינמי.
את המכונה Font למשקל נתון, כך שהתוצאה המדויקת של משקולות היא 350,
450, 550 ו-650.
אמצעי בקרה מפורטים למעברי שורה
החל מגרסה 15 של Android, האפשרות TextView והתכונה הבסיסית של הפסקת שורה יכולות לשמור על החלק הנתון של הטקסט באותה שורה כדי לשפר את הקריאוּת. כדי לנצל את ההתאמה האישית של הפסקות השורות, אפשר להשתמש בתג <nobreak> במשאבי מחרוזות או ב-createNoBreakSpan. באופן דומה, אפשר למנוע הוספת מקפים במילים באמצעות התג <nohyphen> או createNoHyphenationSpan.
לדוגמה, משאב המחרוזת הבא לא כולל מעבר שורה, והוא מוצג עם הטקסט "Pixel 8 Pro" במקום לא רצוי:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind Pixel 8 Pro.</string>
</resources>
לעומת זאת, משאב המחרוזת הזה כולל את התג <nobreak>, שמקיף את הביטוי 'Pixel 8 Pro' ומונע הפסקות שורה:
<resources>
<string name="pixel8pro">The power and brains behind <nobreak>Pixel 8 Pro.</nobreak></string>
</resources>
ההבדל באופן שבו מעיינים את המחרוזות האלה מוצג בתמונות הבאות:

<nobreak>.
<nobreak>.העברת אפליקציות לארכיון
השנה הודענו על תמיכה ב-Android וב-Google Play בהעברת אפליקציות לארכיון, כדי לאפשר למשתמשים לפנות מקום במכשיר על ידי הסרה חלקית של אפליקציות שהם משתמשים בהן לעיתים רחוקות, ופורסמו באמצעות Android App Bundle ב-Google Play. Android 15 כולל תמיכה ברמת מערכת ההפעלה בהעברה של אפליקציות לארכיון ובביטול ההעברה שלהן לארכיון, כך שקל יותר לכל חנויות האפליקציות להטמיע את התכונה הזו.
אפליקציות עם ההרשאה REQUEST_DELETE_PACKAGES יכולות לקרוא ל
השיטה PackageInstaller requestArchive כדי לבקש העברה לארכיון
חבילת אפליקציה מותקנת, שמסירה את ה-APK וכל הקבצים שנשמרו במטמון, אבל ממשיכה
נתוני משתמש. אפליקציות שהועברו לארכיון מוחזרות כאפליקציות שניתנות להצגה דרך ממשקי ה-API של LauncherApps. המשתמשים יראו שינוי בממשק המשתמש כדי להדגיש שהאפליקציות האלה הועברו לארכיון. אם משתמש מקיש על אפליקציה שהועברה לארכיון, מנהל ההתקנה האחראי הוא זה
יקבל בקשה לאחזר אותו מהארכיון, ותהליך השחזור יכול
נמצאים במעקב של ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED.
הפעלת מצב 16 KB במכשיר באמצעות אפשרויות למפתחים

כדי להפעיל מכשיר במצב 16KB, מחליפים את המצב של אפשרות המפתח הפעלה בגודל דף של 16KB.
החל מ-Android 15 QPR1, אפשר להשתמש באפשרות למפתחים שזמינה במכשירים מסוימים כדי להפעיל את המכשיר במצב 16KB ולבצע בדיקות במכשיר. לפני שמשתמשים באפשרות למפתחים, עוברים אל הגדרות > מערכת > עדכוני תוכנה ומחילים את כל העדכונים שזמינים.
אפשרות המפתחים הזו זמינה במכשירים הבאים:
Pixel 8 ו-Pixel 8 Pro (עם Android 15 QPR1 ומעלה)
Pixel 8a (עם Android 15 QPR1 ואילך)
Pixel 9, Pixel 9 Pro ו-Pixel 9 Pro XL (עם Android 15 QPR2 Beta 2 ומעלה)
גרפיקה
Android 15 כולל את השיפורים הגרפיים האחרונים, כולל ANGLE ותוספות למערכת הגרפיקה של Canvas.
מודרניזציה של הגישה ל-GPU ב-Android

חומרת Android התפתחה משמעותית מאז הימים הראשונים שבהם הליבה של מערכת ההפעלה רצה על מעבד יחיד, והגישה ל-GPU התבצעה באמצעות ממשקי API שמבוססים על צינורות עיבוד נתונים עם פונקציות קבועות. Vulkan® graphics API זמין ב-NDK מאז Android 7.0 (רמת API 24) עם הפשטה ברמה נמוכה יותר שמשקפת טוב יותר את החומרה המודרנית של המעבד הגרפי, מתאימה טוב יותר לתמיכה בכמה ליבות של מעבדים ומציעה עלות ריבית נמוכה יותר של מנהל ה-CPU – וכך משפרת את ביצועי האפליקציה. כל מנועי המשחקים המודרניים תומכים ב-Vulkan.
Vulkan הוא הממשק המועדף של Android ל-GPU. לכן, Android 15 כולל את ANGLE כשכבה אופציונלית להרצת OpenGL® ES מעל Vulkan. המעבר ל-ANGLE יעזור לסטנדרטיזציה של הטמעת OpenGL ב-Android, כדי לשפר את התאימות ובמקרים מסוימים גם את הביצועים. כדי לבדוק את היציבות והביצועים של אפליקציות OpenGL ES באמצעות ANGLE, מפעילים את האפשרות למפתחים ב-Android 15: הגדרות -> מערכת -> אפשרויות למפתחים -> ניסיוני: הפעלת ANGLE.
מפת הדרכים של Android ANGLE ב-Vulkan
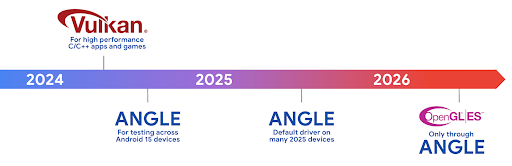
כחלק מהיעילות של סטאק ה-GPU שלנו, מעכשיו נתחיל לשלוח את ANGLE בתור מנהל המערכת GL במכשירים חדשים נוספים, ומצפים שבעתיד OpenGL/ES תהיה זמינה רק דרך ANGLE. עם זאת, אנחנו מתכננים להמשיך את התמיכה ב-OpenGL ES בכל המכשירים.
השלבים המומלצים הבאים
אפשר להשתמש באפשרויות למפתחים כדי לבחור את הנהג ANGLE ל-OpenGL ES ולבדוק את האפליקציה. בפרויקטים חדשים, מומלץ מאוד להשתמש ב-Vulkan ל-C/C++.
שיפורים ב-Canvas
ב-Android 15 אנחנו ממשיכים בתהליך המודרניזציה של מערכת הגרפיקה של Android ב-Canvas, עם יכולות נוספות:
Matrix44מספק מטריקס 4x4 לטרנספורמציה של קואורדינטות, שצריך להשתמש בו כשרוצים לבצע פעולות על הלוח ב-3D.- הפונקציה
clipShaderיוצרת חפיפה בין הקליפ הנוכחי לבין ה-shader שצוין, ואילו הפונקציהclipOutShaderמגדירה את הקליפ כהפרש בין הקליפ הנוכחי לבין ה-shader, כאשר כל אחת מהן מתייחסת ל-shader כלמסיכת אלפא. כך אפשר לצייר בצורה יעילה צורות מורכבות.
ביצועים וסוללה
אנחנו ממשיכים להתמקד בשיפור הביצועים והאיכות של האפליקציות שלכם ב-Android. ב-Android 15 מוצגים ממשקי API שעוזרים לבצע משימות באפליקציה בצורה יעילה יותר, לבצע אופטימיזציה של ביצועי האפליקציה ולאסוף תובנות לגבי האפליקציות.
כדי לקבל מידע על שיטות מומלצות לשימוש יעיל בסוללה, על ניפוי באגים בשימוש ברשת ובצריכת החשמל ועל שיפור היעילות של הסוללה בעבודה ברקע ב-Android 15 ובגרסאות האחרונות של Android, אפשר לצפות בהרצאה Improving battery efficiency of background work on Android מ-Google I/O.
ApplicationStartInfo API
בגרסאות קודמות של Android, הפעלת האפליקציות הייתה קצת מסתורית. היה קשה לקבוע באפליקציה אם היא הופעלה במצב 'התחלה קרה', 'התחלה חמה' או 'התחלה חמה מאוד'. בנוסף, היה קשה לדעת כמה זמן האפליקציה נמשכה בשלבים השונים של ההשקה: יצירת ענף בתהליך, קריאה ל-onCreate, ציור המסגרת הראשונה ועוד. כשהיווצר אובייקט של הכיתה Application, לא הייתה לכם אפשרות לדעת אם האפליקציה הופעלה על ידי שידור, ספק תוכן, משימה, גיבוי, סיום האתחול, אזעקה או Activity.
ה-API של ApplicationStartInfo ב-Android 15 מספק את כל הפונקציות האלה ועוד. אפשר גם להוסיף חותמות זמן משלכם לתהליך כדי לאסוף נתוני תזמון במקום אחד. בנוסף לאיסוף מדדים, אפשר להשתמש ב-ApplicationStartInfo כדי לבצע אופטימיזציה ישירה של הפעלת האפליקציה. לדוגמה, אפשר למנוע את היצירה היקרה של ספריות שקשורות לממשק המשתמש בכיתה Application כשהאפליקציה מופעלת בגלל שידור.
מידע מפורט על גודל האפליקציה
החל מגרסה 8.0 של Android (רמת API 26), מערכת Android כוללת את ה-API StorageStats.getAppBytes שמסכם את הגודל ההתקנה של אפליקציה כמספר יחיד של בייטים, שהוא סכום של גודל ה-APK, גודל הקבצים שחולצו מה-APK וקבצים שנוצרו במכשיר, כמו קוד שעבר הידור מראש (AOT). המספר הזה לא מספק הרבה תובנות לגבי האופן שבו האפליקציה משתמשת באחסון.
ב-Android 15 נוספה ה-API StorageStats.getAppBytesByDataType([type]), שמאפשרת לקבל תובנות לגבי האופן שבו האפליקציה משתמשת בכל האחסון הזה, כולל חלוקות של קובצי APK, קוד שקשור ל-AOT ולשיפור המהירות, מטא-נתונים של dex, ספריות ופרופילים מודרכים.
יצירת פרופילים שמנוהלת על ידי האפליקציה
מערכת Android 15 כוללת את הכיתה ProfilingManager, שמאפשרת לאסוף מידע על פרופיל האפליקציה, כמו דיווחים על אשכול, פרופילים של אשכול, דגימות מ-stack ועוד. הוא מספק קריאה חוזרת לאפליקציה עם תג שסופק כדי לזהות את קובץ הפלט, שמועבר לספריית הקבצים של האפליקציה. ממשק ה-API מגביל את קצב הבקשות כדי למזער את ההשפעה על הביצועים.
כדי לפשט את תהליך היצירה של בקשות ליצירת פרופילים באפליקציה, מומלץ להשתמש ב-Profiling AndroidX API המתאים, שזמין ב-Core 1.15.0-rc01 ואילך.
שיפורים במסד נתונים של SQLite
ב-Android 15 נוספו ממשקי API של SQLite שמציגים תכונות מתקדמות מהמנוע הבסיסי של SQLite, שמטרגטות בעיות ספציפיות בביצועים שעשויות להתרחש באפליקציות. ממשקי ה-API האלה כלולים בעדכון של SQLite לגרסה 3.44.3.
מומלץ למפתחים לעיין בשיטות מומלצות לביצועי SQLite להפיק את המרב ממסד הנתונים של SQLite, במיוחד כשעובדים עם מסדי נתונים או כשמריצים שאילתות רגישות לזמן אחזור.
- עסקאות מושהות לקריאה בלבד: כשאתם מנפיקים עסקאות לקריאה בלבד (לא כוללות הצהרות כתיבה), השתמשו ב-
beginTransactionReadOnly()וב-beginTransactionWithListenerReadOnly(SQLiteTransactionListener)כדי להנפיק עסקאותDEFERREDלקריאה בלבד. עסקאות כאלה יכולות לפעול בו-זמנית זו עם זו, ואם מסד הנתונים נמצא במצב WAL, הן יכולות לפעול בו-זמנית עם עסקאותIMMEDIATEאוEXCLUSIVE. - מספרים ומזהים של שורות: נוספו ממשקי API לאחזור מספר השורות שהשתנו או מזהה השורה האחרונה שהוכנסה, בלי להפעיל שאילתה נוספת.
הפונקציה
getLastChangedRowCount()מחזירה את מספר השורות שנוספו, עודכנו או נמחקו באמצעות הצהרת ה-SQL האחרונה בעסקה הנוכחית, בזמן ש-getTotalChangedRowCount()מחזירה את הספירה בחיבור הנוכחי. הפונקציהgetLastInsertRowId()מחזירה את הערךrowidשל השורה האחרונה. יוכנס לחיבור הנוכחי. - הצהרות גולמיות: הוצאת הצהרת SQlite גולמית, תוך עקיפת מעטפות נוחות וכל עלות עיבוד נוספת שעשויה להיגרם כתוצאה מהן.
עדכונים ב-Android Dynamic Performance Framework
ב-Android 15 אנחנו ממשיכים להשקיע ב-Android Dynamic Performance Framework (ADPF), קבוצה של ממשקי API שמאפשרים למשחקים ולאפליקציות עם ביצועים כבדים לקיים אינטראקציה ישירה יותר עם מערכות החשמל והתרמית של מכשירי Android. במכשירים נתמכים, Android 15 מוסיף יכולות ADPF:
- מצב חיסכון באנרגיה לסשנים של רמזים, כדי לציין שהשרשורים המשויכים צריכים להעדיף חיסכון באנרגיה על פני ביצועים. המצב הזה מתאים מאוד לעומסי עבודה ארוכים ברקע.
- אפשר לדווח על משכי העבודה של ה-GPU ושל המעבד במהלך סשנים של הנחיות, וכך לאפשר למערכת לשנות את התדרים של המעבד ושל ה-GPU יחד כדי לעמוד בצורה הטובה ביותר בדרישות של עומס העבודה.
- סף מרווח תרמי כדי לפרש את סטטוס הצמצום התרמי האפשרי על סמך תחזית של מרווח.
במסמכי העזרה תוכלו לקרוא מידע נוסף על השימוש ב-ADPF באפליקציות ובמשחקים.
פרטיות
Android 15 כולל מגוון תכונות שעוזרות למפתחי אפליקציות להגן על פרטיות המשתמשים.
זיהוי של הקלטת מסך
במערכת Android 15 נוספה תמיכה באפליקציות כדי לזהות הן מתועדות. קריאה חוזרת (callback) מופעלת בכל פעם שהאפליקציה עוברת ממצב גלוי למצב מוסתר במהלך הקלטת מסך. אפליקציה היא נחשב כגלוי אם פעילויות שנמצאות בבעלות ה-UID של תהליך הרישום מוקלטת. כך, אם האפליקציה מבצעת פעולה רגישה, יכול ליידע את המשתמש על כך שהוא מוקלט.
val mCallback = Consumer<Int> { state ->
if (state == SCREEN_RECORDING_STATE_VISIBLE) {
// We're being recorded
} else {
// We're not being recorded
}
}
override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
val initialState =
windowManager.addScreenRecordingCallback(mainExecutor, mCallback)
mCallback.accept(initialState)
}
override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
windowManager.removeScreenRecordingCallback(mCallback)
}
יכולות מורחבות של IntentFilter
ב-Android 15 יש תמיכה בפתרון מדויק יותר של Intent באמצעות UriRelativeFilterGroup, שמכיל קבוצה של אובייקטים מסוג UriRelativeFilter שמרכיבים קבוצה של כללי התאמה ל-Intent, שכל אחד מהם חייב להתקיים, כולל פרמטרים של שאילתה לגבי כתובת URL, קטעי כתובת URL וכללי חסימה או החרגה.
אפשר להגדיר את הכללים האלה בקובץ ה-XML AndroidManifest באמצעות התג <uri-relative-filter-group>, שיכול לכלול גם תג android:allow. התגים האלה יכולים להכיל תגי <data> שמשתמשים במאפיינים של תגי נתונים קיימים, וגם במאפיינים android:query ו-android:fragment.
דוגמה לסינטקס של AndroidManifest:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
<data android:scheme="https" />
<data android:host="astore.com" />
<uri-relative-filter-group>
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="region=na" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:query="mobileoptout=true" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
<uri-relative-filter-group android:allow="false">
<data android:pathPrefix="/auth" />
<data android:fragmentPrefix="faq" />
</uri-relative-filter-group>
</intent-filter>
המרחב הפרטי
המרחב הפרטי מאפשר למשתמשים ליצור מרחב נפרד במכשיר שבו הם יכולים לשמור אפליקציות עם מידע אישי רגיש מפני עיניים זרות, באמצעות שכבת אימות נוספת. במרחב הפרטי נעשה שימוש בפרופיל משתמש נפרד. המשתמש יכול לבחור אם להשתמש בנעילת המכשיר או בשיטת ביטול נעילה נפרדת למרחב הפרטי.
האפליקציות במרחב הפרטי מופיעות במאגר נפרד במרכז האפליקציות, והן מוסתרות מהתצוגה של האפליקציות האחרונות, מההתראות, מההגדרות ומאפליקציות אחרות כשהמרחב הפרטי נעול. תוכן שנוצר על ידי משתמשים והורדתם (כמו מדיה או קבצים) וחשבונות מופרדים בין המרחב הפרטי למרחב הראשי. אתם יכולים להשתמש בלוח השיתוף של המערכת ובכלי לבחירת תמונות כדי לתת לאפליקציות גישה לתוכן במרחבים השונים כשהמרחב הפרטי לא נעול.
המשתמשים לא יכולים להעביר אפליקציות קיימות ואת הנתונים שלהן למרחב הפרטי. במקום זאת, המשתמשים בוחרים אפשרות התקנה במרחב הפרטי כדי להתקין אפליקציה באמצעות חנות האפליקציות המועדפת עליהם. אפליקציות במרחב הפרטי מותקנות כעותקים נפרדים מאפליקציות במרחב הראשי (עותקים חדשים של אותה אפליקציה).
כשמשתמש נועל את המרחב הפרטי, הפרופיל מושבת. כשהפרופיל מושבת, האפליקציות במרחב הפרטי כבר לא פעילות ולא יכולות לבצע פעילויות בחזית או ברקע, כולל הצגת התראות.
מומלץ לבדוק את האפליקציה במרחב הפרטי כדי לוודא שהיא פועלת כצפוי, במיוחד אם האפליקציה שייכת לאחת מהקטגוריות הבאות:
- אפליקציות עם לוגיקה לפרופילי עבודה שמניחות שכל העותק המותקנים של האפליקציה שלא נמצאים בפרופיל הראשי נמצאים בפרופיל העבודה.
- אפליקציות רפואיות
- אפליקציות מרכז האפליקציות
- אפליקציות בחנות האפליקציות
שאילתה לגבי הבחירה האחרונה של המשתמשים בנושא גישה לתמונות נבחרות
אפליקציות יכולות להדגיש עכשיו רק את התמונות והסרטונים שנבחרו לאחרונה
ניתנה גישה חלקית להרשאות המדיה. התכונה הזו יכולה לשפר
את חוויית המשתמש של אפליקציות שמבקשות לעיתים קרובות גישה לתמונות
סרטונים. כדי להשתמש בתכונה הזו באפליקציה, מפעילים את הארגומנט QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY כששולחים שאילתה אל MediaStore דרך ContentResolver.
Kotlin
val externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external") val mediaColumns = arrayOf( FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE, ) val queryArgs = bundleOf( // Return only items from the last selection (selected photos access) QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY to true, // Sort returned items chronologically based on when they were added to the device's storage QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER to "${FileColumns.DATE_ADDED} DESC", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION to "${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ? OR ${FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE} = ?", QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS to arrayOf( FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE.toString(), FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO.toString() ) )
Java
Uri externalContentUri = MediaStore.Files.getContentUri("external"); String[] mediaColumns = { FileColumns._ID, FileColumns.DISPLAY_NAME, FileColumns.MIME_TYPE }; Bundle queryArgs = new Bundle(); queryArgs.putBoolean(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_LATEST_SELECTION_ONLY, true); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SORT_ORDER, FileColumns.DATE_ADDED + " DESC"); queryArgs.putString(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION, FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ? OR " + FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE + " = ?"); queryArgs.putStringArray(MediaStore.QUERY_ARG_SQL_SELECTION_ARGS, new String[] { String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_IMAGE), String.valueOf(FileColumns.MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) });
ארגז החול לפרטיות ב-Android
Android 15 כולל את התוספים העדכניים ביותר של Android Ad Services, שמשלבים את הגרסה העדכנית ביותר של ארגז החול לפרטיות ב-Android. ההוספה הזו היא חלק מהמאמצים שלנו לפתח טכנולוגיות שישפרו את פרטיות המשתמשים ויאפשרו חוויית פרסום יעילה ומותאמת אישית באפליקציות לנייד. בדף של ארגז החול לפרטיות מפורט מידע נוסף על ארגז החול לפרטיות בתוכניות הבטא ובגרסת ה-Preview למפתחים של Android, שיעזרו לכם להתחיל.
Health Connect
ב-Android 15 משולבים התוספים העדכניים ביותר של Health Connect by Android, פלטפורמה מאובטחת ומרכזית לניהול ולשיתוף של נתוני בריאות וכושר שנאספים באפליקציות. העדכון הזה מוסיף תמיכה בסוגי נתונים נוספים בנושאי כושר, תזונה, טמפרטורת העור, תוכניות אימון ועוד.
מעקב אחרי טמפרטורת העור מאפשר למשתמשים לאחסן ולשתף נתוני טמפרטורה מדויקים יותר ממכשיר לבישה או ממכשיר מעקב אחר פעילות אחר.
תוכניות אימונים הן תוכניות אימונים מובנות שיעזרו למשתמש להשיג את יעדי הכושר שלו. תוכניות האימונים כוללות תמיכה במגוון מטרות להשגה וביעדי ביצועים:
- יעדי השלמה לגבי קלוריות שנשרפו, מרחק, משך זמן, חזרה וצעדים.
- יעדי ביצועים כ- חזרות רבות ככל האפשר (AMRAP), קצב הלב, קצב הלב, חשמל, שיעור תפיסת הפעילות הגופנית, וגם מהירות.
מידע נוסף על העדכונים האחרונים של Health Connect ב-Android זמין יצירת חוויות שניתנות להתאמה עם Android שיחות בתחום הבריאות מ-Google I/O.
שיתוף מסך של אפליקציה
Android 15 תומך בשיתוף מסך של אפליקציה, כך שמשתמשים יכולים לשתף או להקליט רק חלון של אפליקציה במקום את כל מסך המכשיר. התכונה הזו, שהופעל לראשונה ב-Android 14 QPR2, כוללת קריאות חזרה מסוג MediaProjection שמאפשרות לאפליקציה להתאים אישית את חוויית שיתוף המסך שלה. חשוב לזכור שבאפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 14 (רמת API 34) ואילך, נדרשת הסכמה מהמשתמשים לכל סשן צילום של MediaProjection.
חוויית המשתמש וממשק המשתמש של המערכת
ב-Android 15, מפתחי אפליקציות והמשתמשים מקבלים יותר שליטה וגמישות בהגדרת המכשיר כך שיתאים לצרכים שלהם.
כדי לקבל מידע נוסף על השימוש בשיפורים האחרונים ב-Android 15 כדי לשפר את חוויית המשתמש באפליקציה, אפשר לצפות בשיחה שיפור חוויית המשתמש באפליקציית Android מ-Google I/O.
תצוגות מקדימות עשירות יותר של ווידג'טים באמצעות Generated Previews API
לפני Android 15, הדרך היחידה לספק תצוגות מקדימות של בורר הווידג'טים הייתה לציין משאב תמונה או פריסה סטטי. לרוב, התצוגות המקדימות האלה שונות באופן משמעותי מהמראה של הווידג'ט בפועל כשממקמים אותו במסך הבית. בנוסף, אי אפשר ליצור משאבים סטטיים באמצעות Jetpack Glance, ולכן מפתחי Glance נאלצו לצלם את הווידג'ט שלהם או ליצור פריסה של XML כדי להציג תצוגה מקדימה של הווידג'ט.
ב-Android 15 נוספה תמיכה בתצוגות מקדימות שנוצרו. המשמעות היא שספקי ווידג'טים של אפליקציות יכולים ליצור את RemoteViews כדי להשתמש בו בתצוגה המקדימה של הבורר, במקום משאב סטטי.
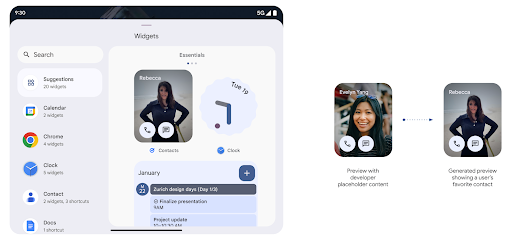
Push API
אפליקציות יכולות לספק תצוגות מקדימות שנוצרו באמצעות API לדחיפה. אפליקציות יכולות לספק תצוגות מקדימות בכל שלב במחזור החיים שלהן, והן לא מקבלות בקשה מפורשת מהמארח לספק תצוגות מקדימות. התצוגות המקדימות נשמרות ב-AppWidgetService, והמארחים יכולים לבקש אותן על פי דרישה. בדוגמה הבאה נטען משאב של פריסה של ווידג'ט בפורמט XML, והוא מוגדר כקטע המקדים:
AppWidgetManager.getInstance(appContext).setWidgetPreview(
ComponentName(
appContext,
SociaLiteAppWidgetReceiver::class.java
),
AppWidgetProviderInfo.WIDGET_CATEGORY_HOME_SCREEN,
RemoteViews("com.example", R.layout.widget_preview)
)
התהליך הצפוי הוא:
- ספק הווידג'ט יכול לבצע קריאה ל-
setWidgetPreviewבכל שלב. התצוגות המקדימות שסיפקתם נשמרות ב-AppWidgetServiceעם פרטי ספק אחרים. setWidgetPreviewתודיע למארחים על תצוגה מקדימה מעודכנת באמצעות קריאה חוזרת (callback) שלAppWidgetHost.onProvidersChanged. בתגובה, מארח הווידג'ט טוען מחדש את כל פרטי הספק שלו.- כשמציגים תצוגה מקדימה של ווידג'ט, המארח בודק את
AppWidgetProviderInfo.generatedPreviewCategories. אם הקטגוריה שנבחרה זמינה, הוא קורא ל-AppWidgetManager.getWidgetPreviewכדי להציג את התצוגה המקדימה השמורה של הספק הזה.
מתי כדאי להתקשר אל setWidgetPreview
מכיוון שאין קריאה חוזרת (callback) כדי לספק תצוגות מקדימות, האפליקציות יכולות לבחור לשלוח תצוגות מקדימות בכל שלב שבו הן פועלות. תדירות העדכון של התצוגה המקדימה תלויה בתרחיש לדוגמה שבו משתמשים בווידג'ט.
ברשימה הבאה מתוארות שתי הקטגוריות העיקריות של תרחישים לדוגמה לשימוש בתצוגה המקדימה:
- ספקים שמציגים נתונים אמיתיים בתצוגות המקדימות של הווידג'טים שלהם, כמו מידע מותאם אישית או מידע עדכני. הספקים האלה יכולים להגדיר את התצוגה המקדימה אחרי שהמשתמש נכנס לחשבון או ביצע הגדרה ראשונית באפליקציה. לאחר מכן, הם יכולים להגדיר משימה תקופתית לעדכון התצוגות המקדימה בקצב שהם בוחרים. דוגמאות לווידג'טים מהסוג הזה הן ווידג'ט של תמונות, ווידג'ט של יומן, ווידג'ט של מזג אוויר או ווידג'ט של חדשות.
- ספקים שמציגים מידע סטטי בתצוגות מקדימות או בווידג'טים של פעולות מהירות שלא מציגים נתונים. הספקים האלה יכולים להגדיר קטעי מקדים פעם אחת, כשהאפליקציה מופעלת בפעם הראשונה. דוגמאות לווידג'טים מהסוג הזה כוללות ווידג'ט של פעולות מהירות ב-Drive או ווידג'ט של קיצורי דרך ב-Chrome.
יכול להיות שחלק מהספקים יציג תצוגות מקדימות סטטיות בבורר של מצב Hub, אבל מידע אמיתי בבורר של מסך הבית. הספקים האלה צריכים לפעול בהתאם להנחיות בשני התרחישים לדוגמה האלה כדי להגדיר קטעי מקדים.
תמונה בתוך תמונה
ב-Android 15 יש שינויים בתכונה 'תמונה בתוך תמונה' (PiP) שמבטיחים מעבר חלק יותר כשנכנסים למצב PiP. זה יהיה שימושי עבור אפליקציות עם רכיבים בממשק המשתמש שמופיעים כשכבת-על מעל ממשק המשתמש הראשי שלהן, שעובר אל 'תמונה בתוך תמונה'.
מפתחים משתמשים בקריאה החוזרת (callback) onPictureInPictureModeChanged כדי להגדיר לוגיקה שמחליפה את החשיפה של רכיבי ממשק המשתמש שמופיעים בשכבה העליונה. הקריאה החוזרת הזו מופעלת כשהאנימציה של הכניסה או היציאה מ-PiP מסתיימת. החל מגרסה Android 15, הכיתה PictureInPictureUiState כוללת מצב נוסף.
כשממשק המשתמש במצב הזה, באפליקציות שמטרגטות ל-Android 15 (רמת API 35) יבחינו
מתבצעת קריאה חוזרת של Activity#onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged באמצעות
isTransitioningToPip() ברגע שהאנימציה של 'תמונה בתוך תמונה' מתחילה. יש
רכיבים רבים בממשק המשתמש שאינם רלוונטיים לאפליקציה כשהיא במצב 'תמונה בתוך תמונה',
תצוגות או פריסה לדוגמה שכוללות מידע כמו הצעות,
סרטונים, דירוגים ושמות. כשהאפליקציה עוברת למצב 'תמונה בתוך תמונה', משתמשים
קריאה חוזרת (callback) מסוג onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged כדי להסתיר את הרכיבים האלה בממשק המשתמש. כאשר
שבה האפליקציה תעבור למצב מסך מלא מהחלון של 'תמונה בתוך תמונה',
קריאה חוזרת של onPictureInPictureModeChanged כדי לבטל את ההסתרה של הרכיבים האלה, כפי שמוצג ב-
דוגמאות:
override fun onPictureInPictureUiStateChanged(pipState: PictureInPictureUiState) {
if (pipState.isTransitioningToPip()) {
// Hide UI elements
}
}
override fun onPictureInPictureModeChanged(isInPictureInPictureMode: Boolean) {
if (isInPictureInPictureMode) {
// Unhide UI elements
}
}
מתג החשיפה המהיר הזה של רכיבים לא רלוונטיים בממשק המשתמש (בחלון 'תמונה בתוך תמונה') עוזר להבטיח אנימציה חלקה יותר של 'תמונה בתוך תמונה' וללא הבהובים.
שיפורים בכללים של 'נא לא להפריע'
AutomaticZenRule מאפשר לאפליקציות להתאים אישית את תשומת הלב
כללי ניהול (נא לא להפריע) ומחליטים מתי להפעיל או להשבית
אותם. ב-Android 15 יש שיפור משמעותי בכללים האלה, במטרה לשפר את חוויית המשתמש. השיפורים הבאים כלולים:
- הוספת סוגים ל-
AutomaticZenRuleמאפשרת למערכת להחיל סוגים מיוחדים לטיפול בכללים מסוימים. - הוספת סמל אל
AutomaticZenRuleעוזרת לשפר את המצבים מה אפשר לזהות. - הוספת מחרוזת
triggerDescriptionל-AutomaticZenRuleשמתארת התנאים שבהם הכלל צריך להיות פעיל עבור המשתמש. - תאריך ההוספה
ZenDeviceEffectsעדAutomaticZenRule, כך שהכללים יכולים להפעיל פעולות כמו גווני אפור תצוגה, מצב לילה או עמעום הטפט.
הגדרת VibrationEffect לערוצי התראות
ב-Android 15 יש תמיכה בהגדרת רטט עשירים להתראות נכנסות באמצעות
הערוץ באמצעות NotificationChannel.setVibrationEffect, כך
המשתמשים יכולים להבחין בין סוגים שונים של התראות,
שצריך לבדוק את המכשיר שלהם.
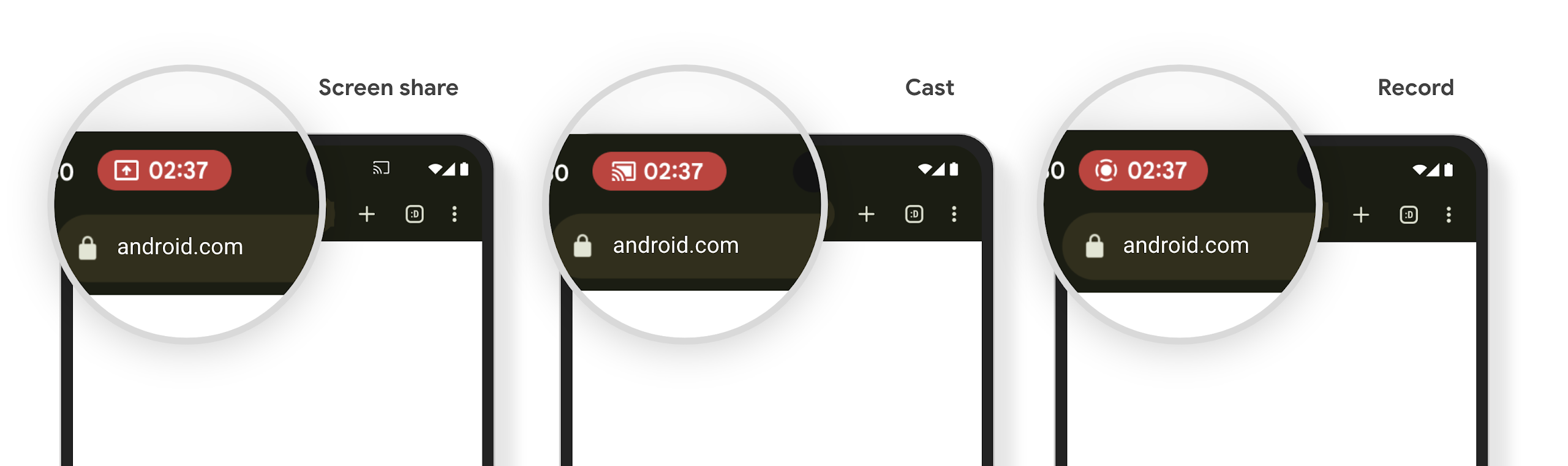
צ'יפ בשורת הסטטוס של הקרנת מדיה ועצירה אוטומטית
הקרנת מדיה עלולה לחשוף מידע פרטי של משתמשים. צ'יפ חדש ובולט בסרגל הסטטוס מאפשר למשתמשים לדעת אם המסך שלהם מוקרן. המשתמשים יכולים להקיש על הצ'יפ כדי להפסיק את ההעברה (cast), השיתוף או ההקלטה של המסך. בנוסף, כדי לשפר את חוויית המשתמש, הקרנת המסך תיפסק באופן אוטומטי כשמסך המכשיר יינעל.
מסכים גדולים וגורמי צורה
Android 15 מאפשר לאפליקציות שלכם לתמוך במגוון גורמי צורה של Android, כולל מסכים גדולים, מכשירים מתהפכים ומתקפלים.
שיפור בריבוי משימות במסך גדול
ב-Android 15 יש למשתמשים דרכים טובות יותר לבצע משימות מרובות במכשירים עם מסכים גדולים. עבור לדוגמה, משתמשים יכולים לשמור את השילובים המועדפים שלהם של אפליקציות במסך מפוצל לגשת לשורת המשימות במסך ולהצמיד אותה כדי לעבור במהירות בין אפליקציות. כלומר ולכן חשוב יותר מתמיד לוודא שהאפליקציה שלכם יכולה להיות מותאמת.
ב-Google I/O יש מפגשים בנושא יצירת Android דינמי אפליקציות ובניית ממשק משתמש באמצעות Material 3 ספרייה מותאמת שיכול לעזור, והתיעוד שלנו כולל מידע נוסף שיעזור לכם לעצב מודלים גדולים מסכים.
תמיכה במסך החיצוני
האפליקציה יכולה להצהיר על מאפיין שמערכת Android 15 משתמשת בו כדי לאפשר להציג את Application או את Activity במסכי הכיסוי הקטנים של מכשירים נפתחים נתמכים. המסכים האלה קטנים מדי כדי להיחשב כיעדים תואמים להרצה של אפליקציות ל-Android, אבל אפשר להביע הסכמה לכך שהאפליקציה תתמוך בהם, וכך להפוך אותה לזמינה במקומות נוספים.
קישוריות
ב-Android 15, הפלטפורמה מתעדכנת כדי לתת לאפליקציה שלכם גישה לחידושים האחרונים בטכנולוגיות תקשורת וטכנולוגיות אלחוטיות.
תמיכה בלוויין
ב-Android 15 אנחנו ממשיכים להרחיב את תמיכת הפלטפורמה בקישוריות לווינית, ומוסיפים כמה רכיבי ממשק משתמש כדי להבטיח חוויית משתמש עקבית בכל סביבות הקישוריות הלווינית.
אפליקציות יכולות להשתמש ב-ServiceState.isUsingNonTerrestrialNetwork() כדי
לזהות מכשירים שמחוברים ללוויין, וכך להגביר את המוּדעוּת
מדוע שירותי רשת מלאים אינם זמינים. בנוסף, ב-Android 15 יש תמיכה באפליקציות SMS ו-MMS, וגם באפליקציות RCS שהוגדרו מראש, כדי להשתמש בחיבור לווין לשליחה ולקבלה של הודעות.
חוויות NFC חלקות יותר
ב-Android 15 אנחנו פועלים כדי לשפר את חוויית התשלום בנגיעה ולהפוך אותה לחלקה ואמינה יותר, תוך המשך תמיכה בסביבת האפליקציות החזקה של NFC ב-Android. במכשירים נתמכים, אפליקציות יכולות לבקש מ-NfcAdapter להיכנס למצב תצפית, שבו המכשיר מקשיב אבל לא מגיב לקוראי NFC, ושולח לשירות ה-NFC של האפליקציה אובייקטים לעיבוד.PollingFrame אפשר להשתמש באובייקטים PollingFrame כדי לבצע אימות לפני האינטראקציה הראשונה עם קורא ה-NFC, וכך לאפשר ביצוע עסקאות בהקשה אחת במקרים רבים.
בנוסף, אפליקציות יכולות לרשום מסנן במכשירים נתמכים כדי לקבל התראות על פעילות של לולאת הסקרים. כך אפשר להפעיל כמה אפליקציות שתומכות ב-NFC בצורה חלקה.
תפקיד בארנק
ב-Android 15 נוסף תפקיד Wallet שמאפשר שילוב הדוק יותר עם אפליקציית הארנק המועדפת של המשתמש. התפקיד הזה מחליף את הגדרת ברירת המחדל של תשלומים ללא מגע ב-NFC. משתמשים יכולים לנהל את הבעלים של התפקיד Wallet דרך הגדרות > אפליקציות > אפליקציות ברירת מחדל.
התפקיד Wallet משמש לניתוב של נגיעה ב-NFC עבור מזהי AID שרשומים בקטגוריית התשלומים. הקשות תמיד מועברות לבעלים של התפקיד ב-Wallet, אלא אם אפליקציה אחרת שרשומה לאותו מזהה AID פועלת בחזית.
התפקיד הזה משמש גם לקביעת המיקום שבו יופיע הכרטיס לגישה מהירה ל-Wallet כשהוא יופעל. כשהתפקיד מוגדר כ'ללא', המשבצת של הגישה המהירה לא זמינה והקשות על תגי NFC בקטגוריית התשלומים מועברות רק לאפליקציה שבחזית.
אבטחה
Android 15 עוזר לשפר את האבטחה של האפליקציה, להגן על הנתונים של האפליקציה ולספק למשתמשים שקיפות ושליטה רבות יותר על הנתונים שלהם. בשיחה Safeguarding user security on Android (שמירה על אבטחת המשתמשים ב-Android) מ-Google I/O מוסבר מה אנחנו עושים כדי לשפר את אמצעי ההגנה על המשתמשים ולהגן על האפליקציה שלכם מפני איומים חדשים.
שילוב של מנהל פרטי הכניסה עם מילוי אוטומטי
החל מגרסה 15 של Android, מפתחים יכולים לקשר תצוגות ספציפיות, כמו שדות של שם משתמש או סיסמה, לבקשות של מנהל פרטי הכניסה. כך קל יותר לספק חוויית משתמש מותאמת אישית במהלך תהליך הכניסה. כשהמשתמש מתמקד באחת מהתצוגות האלה, נשלחת בקשה תואמת ל-Credential Manager. פרטי הכניסה שמתקבלים נצברים אצל כל הספקים ומוצגים בממשקי המשתמש החלופיים של המילוי האוטומטי, כמו הצעות בשורה או הצעות בתפריט הנפתח. ספריית Jetpack androidx.credentials היא נקודת הקצה המועדפת למפתחים, ותהיה זמינה בקרוב כדי לשפר את התכונה הזו ב-Android מגרסה 15 ואילך.
שילוב של הרשמה וכניסה בלחיצה אחת עם הנחיות ביומטריות
מנהל פרטי הכניסה משלב הנחיות ביומטריות בתהליכי היצירה והכניסה של פרטי הכניסה, כך שהספקים לא צריכים לנהל את ההנחיות הביומטריות. כתוצאה מכך, ספקי פרטי הכניסה צריכים להתמקד רק בתוצאות של תהליכי היצירה והאחזור, עם תוספת של תוצאת התהליך הביומטרי. התהליך הפשוט הזה יוצר פרטי כניסה יעילים וקלים יותר תהליך היצירה והאחזור.
ניהול מפתחות להצפנה מקצה לקצה
אנחנו משיקים את E2eeContactKeysManager ב-Android 15, שמאפשר הצפנה מקצה לקצה (E2EE) באפליקציות ל-Android באמצעות ממשק API ברמת מערכת ההפעלה לאחסון מפתחות ציבוריים קריפטוגרפיים.
ה-E2eeContactKeysManager מיועד לשילוב עם אפליקציית אנשי הקשר של הפלטפורמה, כדי לספק למשתמשים דרך מרוכזת לניהול ולאימות של המפתחות הציבוריים של אנשי הקשר שלהם.
בדיקות הרשאות ב-URI של תוכן
ב-Android 15 נוספה קבוצה של ממשקי API שמבצעים בדיקות הרשאות על מזהי URI של תוכן:
Context.checkContentUriPermissionFull: מתבצעת בדיקת הרשאות מלאה על URI של תוכן.- מאפיין המניפסט
ActivityrequireContentUriPermissionFromCaller: המאפיין הזה אוכף הרשאות ספציפיות על מזהי ה-URI של התוכן שסופקו בזמן ההפעלה של הפעילות. - הקלאס
ComponentCallerלמפעיליActivity: הוא מייצג את האפליקציה שהפעילה את הפעילות.
נגישות
ב-Android 15 נוספו תכונות שמשפרות את הנגישות למשתמשים.
שיפורים בברייל
ב-Android 15, הוספנו ל-TalkBack תמיכה בצגי ברייל שמשתמשים בתקן HID גם דרך USB וגם דרך Bluetooth מאובטח.
התקן הזה, בדומה לזה שמשמש עכברים ומקלדות, יעזור ל-Android לתמוך במגוון רחב יותר של צגי בריל לאורך זמן.
אינטרנציונליזציה
ב-Android 15 נוספו תכונות ויכולות שמשלימות את חוויית המשתמש כשמשתמשים במכשיר בשפות שונות.
גופן משתנה של CJK
החל מגרסה 15 של Android, קובץ הגופן של השפות הסינית, היפנית והקוריאנית (CJK), NotoSansCJK, הוא עכשיו גופן משתנה. גופנים משתנים פותחים אפשרויות לטיפוגרפיה קריאייטיב בשפות CJK. מעצבים יכולים לבחור מתוך מגוון רחב יותר של סגנונות וליצור פריסות חזותיות מרהיבות שקשה או בלתי אפשרי ליצור אותן בדרכים אחרות.

הצדקה בין תווים
החל מ-Android 15, אפשר להצדיק את הטקסט עם ריווח של אותיות
באמצעות JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER. ההצדקה בין המילים הייתה
הושקה לראשונה ב-Android 8.0 (רמת API 26),
להצדקה מספק יכולות דומות לשפות שמשתמשות
לצורך פילוח, כמו סינית, יפנית ועוד.

JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_NONE.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_WORD.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.
JUSTIFICATION_MODE_INTER_CHARACTER.הגדרה אוטומטית של מעברי שורה
Android התחילה לתמוך במעברי שורה שמבוססים על ביטויים ביפנית ובקוריאנית
Android 13 (רמת API 33). עם זאת, אמנם הפסקות שורות שמבוססות על ביטויים משפרות את הקריאוּת של שורות קצרות של טקסט, אבל הן לא מתאימות לשורות ארוכות של טקסט.
ב-Android 15, אפליקציות יכולות להשתמש בהפסקות שורות שמבוססות על ביטויים רק בשורות קצרות של טקסט, באמצעות האפשרות LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO. האפשרות הזו בוחרת את סגנון המילים המתאים ביותר לטקסט.
בשורות טקסט קצרות, המערכת משתמשת במעברי שורה שמבוססים על ביטויים, ופועלים באופן זהה
בתור LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE, כמו שמוצג
התמונה הבאה:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
מחיל חלוקות שורות שמבוססות על ביטויים כדי לשפר את הקריאוּת של הטקסט.
הפעולה הזו זהה להחלת
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_PHRASE.בשורות טקסט ארוכות יותר, LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO משתמש בפונקציית "לא"
סגנון מילים של מעבר שורה, שפועל באותו אופן כמו
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE, כפי שמוצג
התמונה הבאה:

LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_AUTO
לא מחילה סגנון מילים של מעבר שורה כדי לשפר את נוחות הקריאה של הטקסט.
הפעולה הזו זהה להחלת
LINE_BREAK_WORD_STYLE_NONE.גופן נוסף של הינטאיגנה יפנית
בגרסה Android 15, קובץ גופן של היראגאנה היפנית הישנה (המכונה Hentaigana) נכלל בחבילה כברירת מחדל. הצורות הייחודיות של דמויות הנטאייגה יכולות להוסיף מראה ייחודי לגרפיקה או לעיצוב, תוך שמירה על רמת דיוק גבוהה הפצה והבנה של מסמכים יפניים עתיקים.

VideoLAN cone Copyright (c) 1996-2010 VideoLAN. כל אחד יכול להשתמש בלוגו הזה או בגרסה שונה שלו כדי להפנות לפרויקט VideoLAN או לכל מוצר שפותח על ידי צוות VideoLAN, אבל השימוש בלוגו לא מעיד על תמיכה בפרויקט.
Vulkan והלוגו של Vulkan הם סימנים מסחריים רשומים של Khronos Group Inc.
OpenGL הוא סימן מסחרי רשום והלוגו של OpenGL ES הוא סימן מסחרי של Hewlett Packard Enterprise, ש-Khronos משתמשת בו ברשות.

